Impact of Pseudo-Random Number Generators on Dosimetric Parameters in Validation of Medical Linear Accelerator Head Simulation for 6 MV Photons Using the GATE/GEANT4 Platform
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
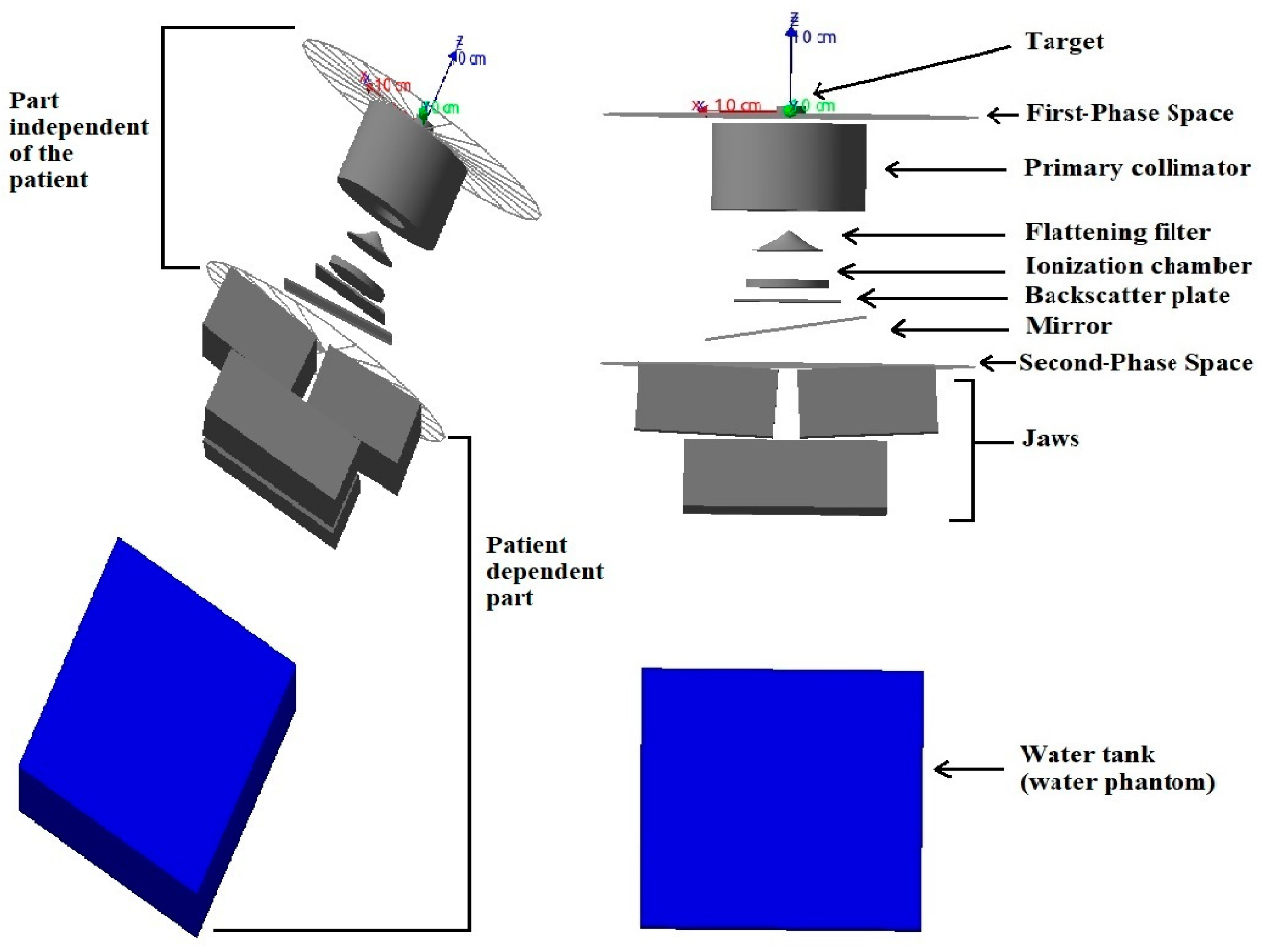
2.1. Medical Linear Accelerator, Source, and Voxel Water Phantom Simulation
2.2. Computing Time Optimization
2.3. Common Pseudo-Random Number Generators (PRNGs)
2.4. Output of Simulation
2.5. Experimental Data
2.6. Evaluation Criteria
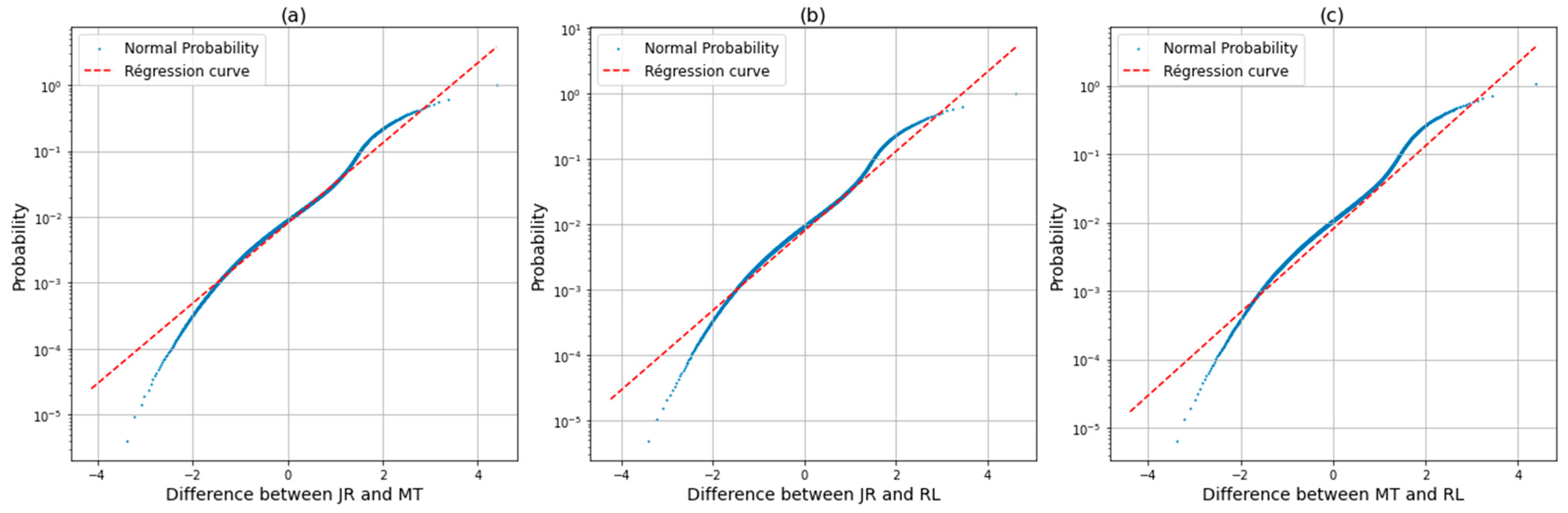
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
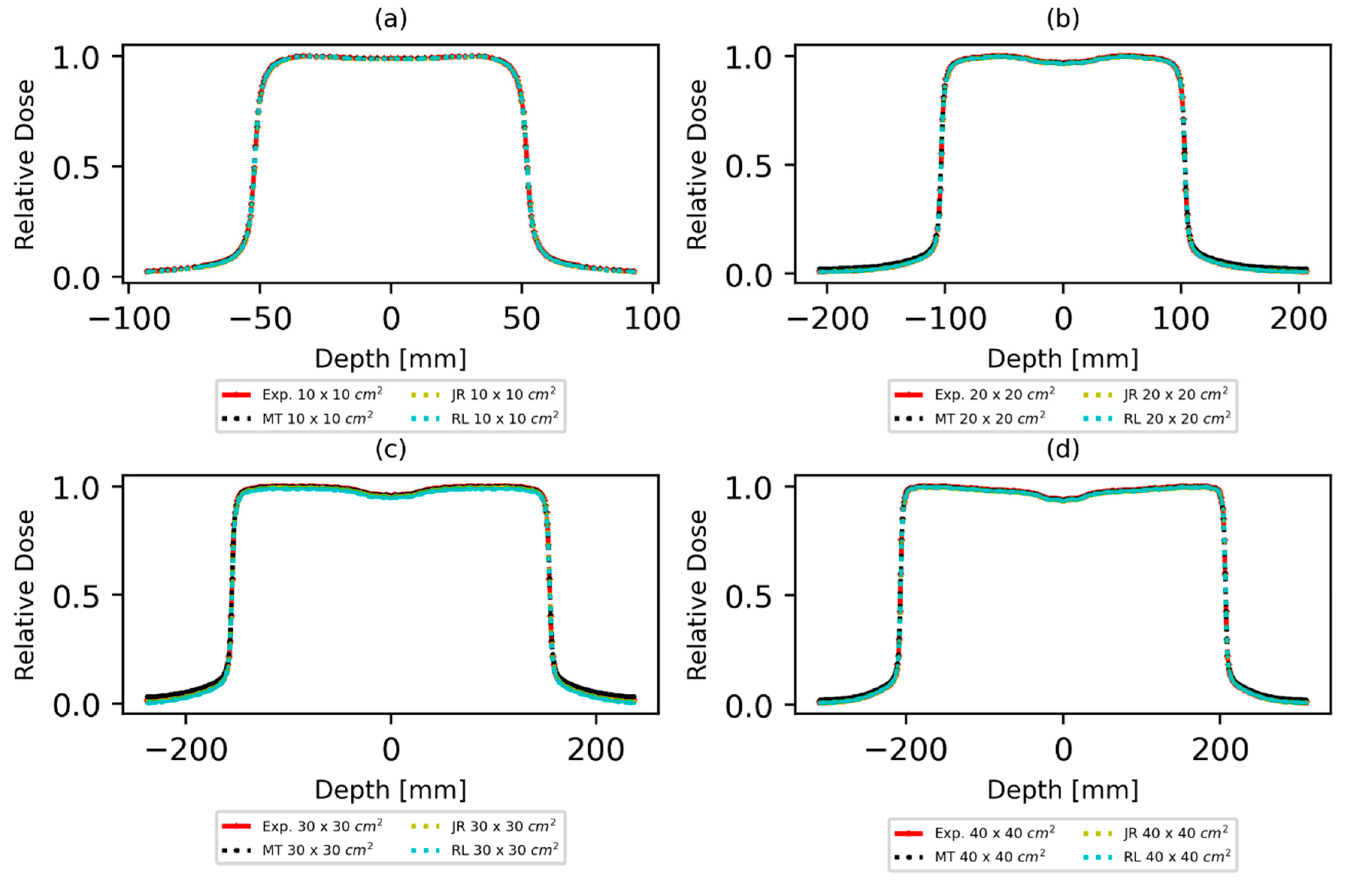
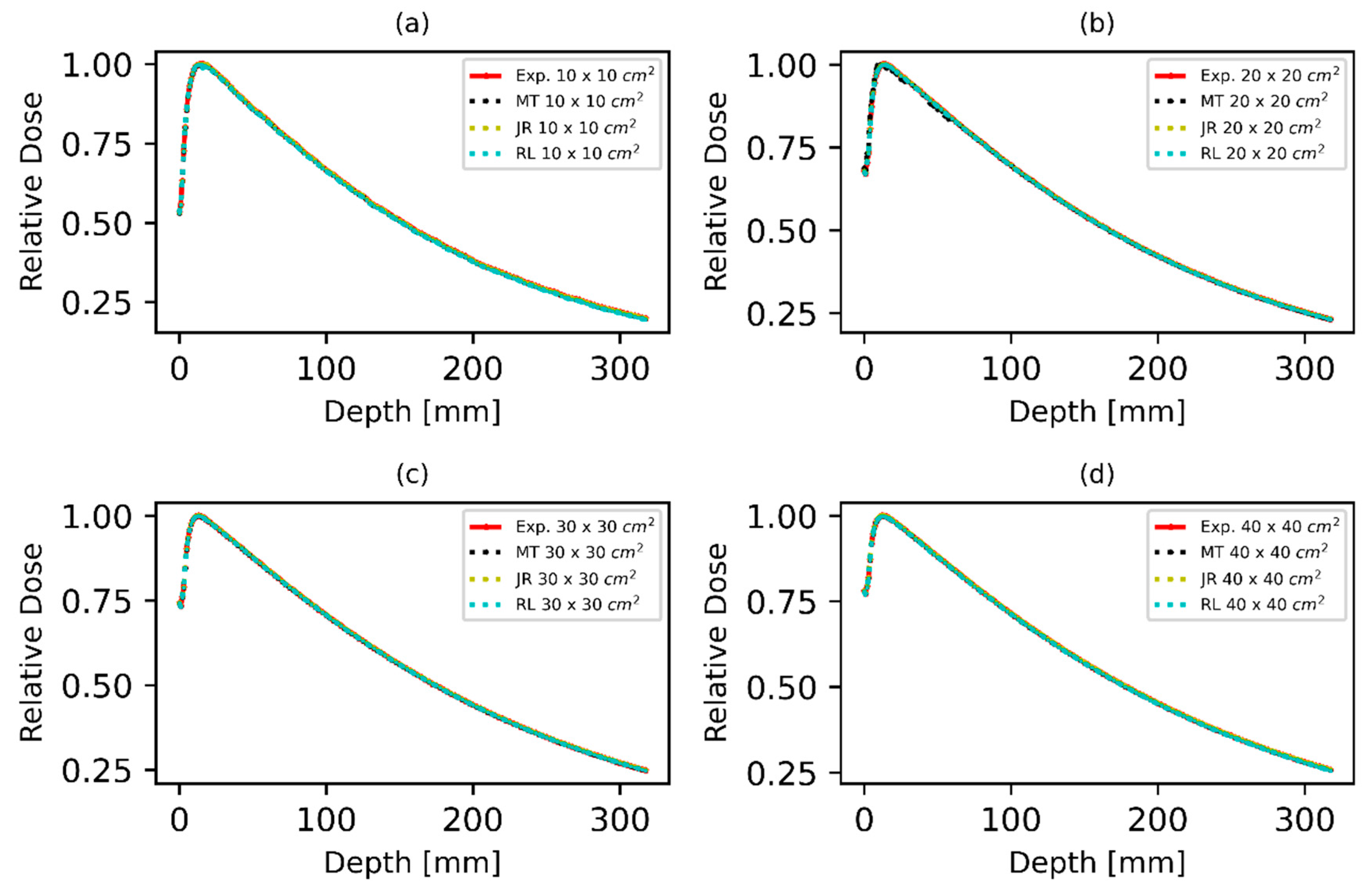
3.1. Dose Profile and Percentage Depth Dose Curve
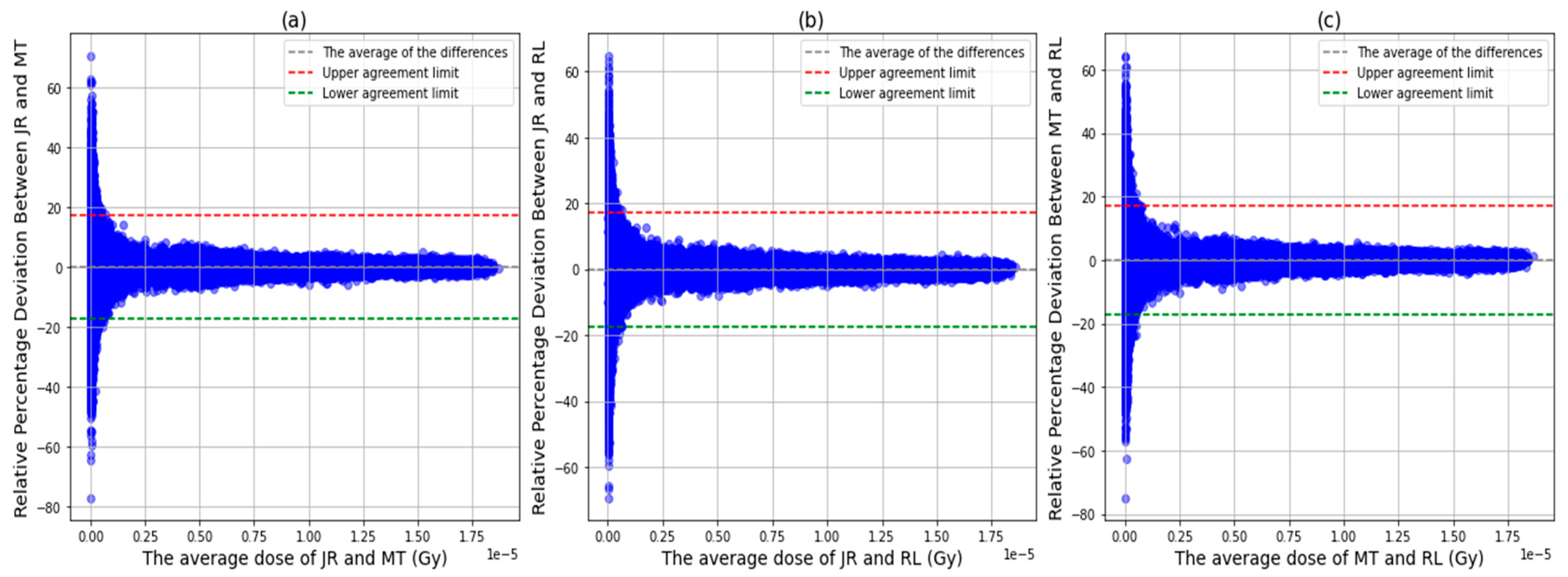
3.2. Voxel Dose Analysis
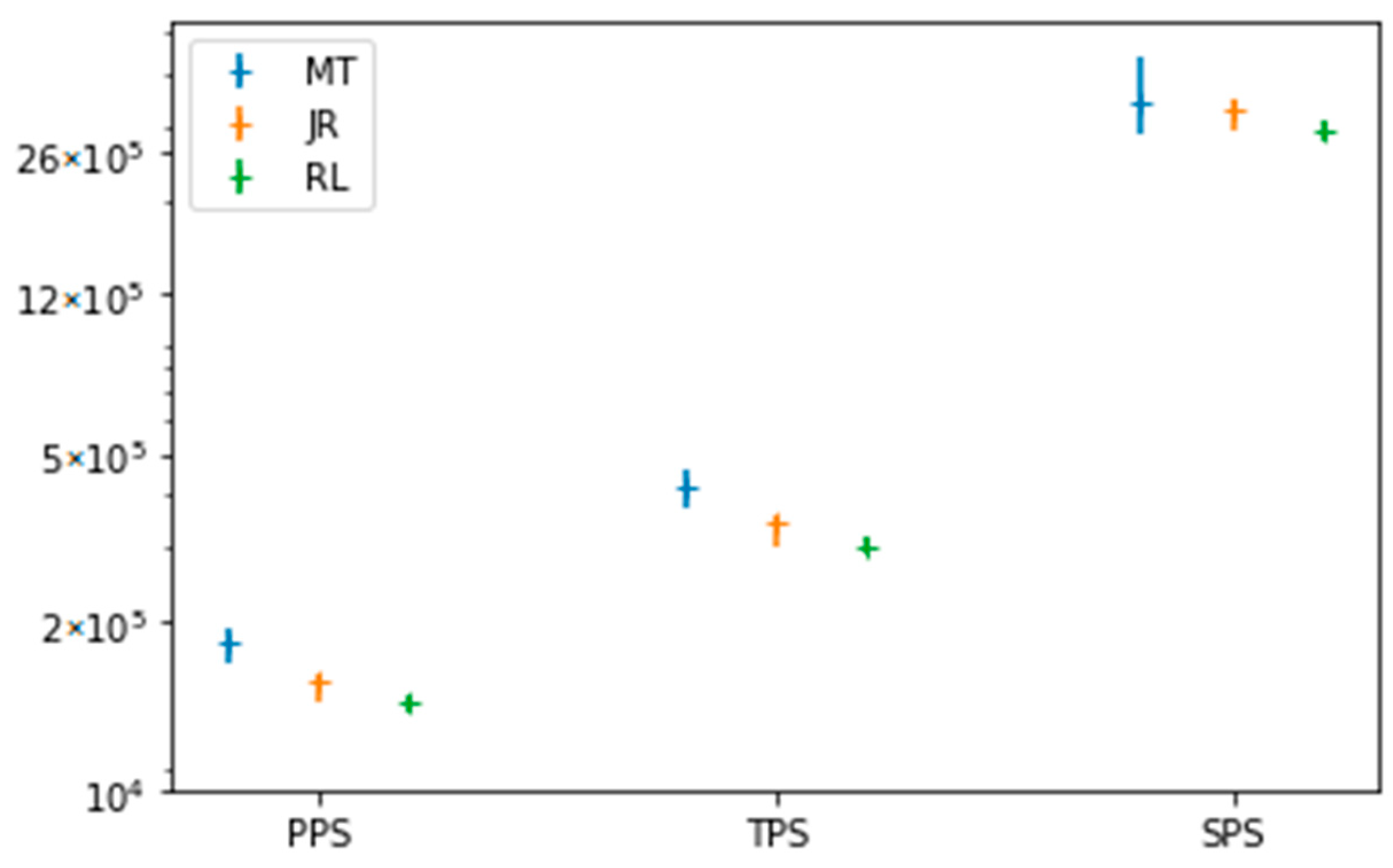
3.3. Simulation Statistic Data
3.4. The Elapsed Time
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simulation Monte Carlo: Méthodes, Évaluation et Applications—Nova Science Publishers. Consulté le: 20 Février 2024. [En ligne]. Available online: https://novapublishers.com/shop/monte-carlo-simulation-methods-assessment-and-applications/ (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Carl, G.; Denis, T. Simulation Stochastique et Methodes de Monte Carlo; Les Editions de l’Ecole Polytechnique: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sempau, J.; Acosta, E.; Baro, J.; Fernández-Varea, J.; Salvat, F. An algorithm for Monte Carlo simulation of coupled electron-photon transport. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 1997, 132, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, J. Une Revue des Méthodes de Monte Carlo et de Leur Application en Physique Médicale Pour Simuler le Transport de Rayonnements. [En ligne]. Available online: https://scholars.unh.edu/honors/657 (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Joao, S.; Frank, V.; Joao, S.; Frank, V. Monte Carlo Techniques in Radiation Therapy Applications to Dosimetry, Imaging, and Preclinical Radiotherapy, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Andreo, P. Monte Carlo simulations in radiotherapy dosimetry. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparapani, R. Random Number Generation and Monte Carlo Methods (2nd Edition). J. Stat. Softw. 2004, 11, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coddington, P.D. Analysis of Random Number Generators Using Monte Carlo Simulation. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 1994, 5, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Click, T.H.; Liu, A.; Kaminski, G.A. Quality of random number generators significantly affects results of Monte Carlo simulations for organic and biological systems. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demchik, V. Pseudo-random number generators for Monte Carlo simulations on ATI Graphics Processing Units. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2011, 182, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vattulainen, I.; Kankaala, K.; Saarinen, J.; Ala-Nissila, T. A comparative study of some pseudorandom number generators. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1995, 86, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, F. A review of pseudorandom number generators. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1990, 60, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehri, F.; Hajivaliei, M.; Rajabi, H. Selection of random number generators in GATE Monte Carlo toolkit. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2020, 973, 164172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.; Sawilowsky, S. Bias in Monte Carlo Simulations Due To Pseudo-Random Number Generator Initial Seed Selection. Theoretical and Behavioral Foundations of Education Faculty Publications, May 2011. [En ligne]. Available online: https://digitalcommons.wayne.edu/coe_tbf/3 (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Deng, L.-Y.; Guo, R.; Lin, D.K.; Bai, F. Improving Random Number Generators in the Monte Carlo simulations via twisting and combining. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2008, 178, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coddington, P.D. Tests of Random Number Generators Using Ising Model Simulations. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 1996, 7, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongo, K.; Maezono, R.; Miura, K. Random number generators tested on quantum Monte Carlo simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 2186–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantaoui, M.; Krim, M.; Ghazi, I.; Sobhy, Z.; Kaanouch, O.; Kartouni, A.; Sahraoui, S. Optimization of the calculation time in simulation using the GATE/GEANT4 Monte Carlo of radiotherapy treatment plans for small fields. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 297, 01047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grevillot, L.; Frisson, T.; Maneval, D.; Zahra, N.; Badel, J.-N.; Sarrut, D. Simulation of a 6 MV Elekta Precise Linac photon beam using GATE/GEANT4. Phys. Med. Biol. 2011, 56, 903–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawrakow, I.; Rogers, D.W.O.; Walters, B.R.B. Large efficiency improvements in BEAMnrc using directional bremsstrahlung splitting. Med. Phys. 2004, 31, 2883–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, M.; Nishimura, T. Mersenne twister: A 623-dimensionally equidistributed uniform pseudo-random number generator. ACM Trans. Model. Comput. Simul. 1998, 8, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Ecuyer, P. History of uniform random number generation. In Proceedings of the 2017 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 202–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AIEA. International Atomic Energy Agency, Absorbed Dose Determination in External Beam Radiotherapy; Technical Reports Series, no. 398; AIEA: Vienne, France, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Low, D.A.; Harms, W.B.; Mutic, S.; Purdy, J.A. A technique for the quantitative evaluation of dose distributions. Med. Phys. 1998, 25, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Validation of Monte Carlo Simulation of 6 MV Photon Beam Produced by Varian Clinac 2100 Linear Accelerator Using Beamnrc Code and Dosxyznrc Code|PDF|Gamma Ray|Radiation Therapy. [En ligne]. Available online: https://fr.scribd.com/document/549916162/s-154747711705003-x (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Toward a Better Understanding of the Gamma Index: Investigation of Parameters with a Surface-Based Distance Method—PMC. [En ligne]. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3298565/ (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Altman, D.G.; Bland, J.M. Measurement in Medicine: The Analysis of Method Comparison Studies. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. D (Stat.) 1983, 32, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetty, I.J.; Rosu, M.; Kessler, M.L.; Fraass, B.A.; Haken, R.K.T.; Kong, F.-M.; McShan, D.L. Reporting and analyzing statistical uncertainties in Monte Carlo–based treatment planning. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 65, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Radiation Fields | PRNG | 2%/2 mm | 3%/2 mm | 3%/3 mm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Profil | PDD | Profil | PDD | Profil | PDD | ||
| 10 × 10 cm2 | MT | 95.33% | 96.12% | 96.02% | 99.52% | 99.81% | 99.82% |
| JR | 94.67% | 95.75% | 95.99% | 97.35% | 96.74% | 98.35% | |
| RL | 95.98% | 95.31% | 93.67% | 95.87% | 97.32% | 97.90% | |
| 20 × 20 cm2 | MT | 92.86% | 95.93% | 93.83% | 94.71% | 94.83% | 96.71% |
| JR | 91.04% | 91.73% | 91.93% | 93.01% | 92.72% | 95.01% | |
| RL | 93.67% | 92.42% | 93.12% | 92.97% | 93.12% | 96.97% | |
| 30 × 30 cm2 | MT | 93.56% | 93.88% | 95.62% | 95.88% | 95.62% | 97.94% |
| JR | 92.78% | 94.91% | 93.85% | 94.91% | 93.50% | 96.86% | |
| RL | 93.49% | 96.30% | 93.56% | 96.30% | 94.03% | 97.36% | |
| 40 × 40 cm2 | MT | 93.11% | 94.91% | 93.73% | 96.91% | 98.87% | 97.85% |
| JR | 91.23% | 93.78% | 92.04% | 95.78% | 97.65% | 96.26% | |
| RL | 93.28% | 94.78% | 93.34% | 94.78% | 98.41% | 97.77% | |
| dS | dmax (cm) | D10 (%) | d80 (cm) | TPR10,20 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental | 53.15 | 1.40 | 66.58 | 6.52 | 0.66 |
| MT | 53.05 | 1.34 | 66.47 | 6.45 | 0.65 |
| Difference δ (%) | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.2 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| JR | 53.18 | 1.31 | 66.39 | 6.50 | 0.63 |
| Difference δ (%) | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.2 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| RL | 53.01 | 1.56 | 66.37 | 6.54 | 0.64 |
| Difference δ (%) | <0.2 | <0.2 | <0.2 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tantaoui, M.; Krim, M.; Essaidi, E.M.; Kaanouch, O.; Mesradi, M.R.; Kartouni, A.; Sahraoui, S. Impact of Pseudo-Random Number Generators on Dosimetric Parameters in Validation of Medical Linear Accelerator Head Simulation for 6 MV Photons Using the GATE/GEANT4 Platform. Quantum Beam Sci. 2025, 9, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs9020016
Tantaoui M, Krim M, Essaidi EM, Kaanouch O, Mesradi MR, Kartouni A, Sahraoui S. Impact of Pseudo-Random Number Generators on Dosimetric Parameters in Validation of Medical Linear Accelerator Head Simulation for 6 MV Photons Using the GATE/GEANT4 Platform. Quantum Beam Science. 2025; 9(2):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs9020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleTantaoui, Meriem, Mustapha Krim, El Mehdi Essaidi, Othmane Kaanouch, Mohammed Reda Mesradi, Abdelkrim Kartouni, and Souha Sahraoui. 2025. "Impact of Pseudo-Random Number Generators on Dosimetric Parameters in Validation of Medical Linear Accelerator Head Simulation for 6 MV Photons Using the GATE/GEANT4 Platform" Quantum Beam Science 9, no. 2: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs9020016
APA StyleTantaoui, M., Krim, M., Essaidi, E. M., Kaanouch, O., Mesradi, M. R., Kartouni, A., & Sahraoui, S. (2025). Impact of Pseudo-Random Number Generators on Dosimetric Parameters in Validation of Medical Linear Accelerator Head Simulation for 6 MV Photons Using the GATE/GEANT4 Platform. Quantum Beam Science, 9(2), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/qubs9020016






