Impact Strength Properties and Failure Mode Classification of Concrete U-Shaped Specimen Retrofitted with Polyurethane Grout Using Machine Learning Algorithms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Specimen Preparation
2.3. Testing Methods
Multiple Drop-Weight Impact Tests of Composite U-Shaped Specimens
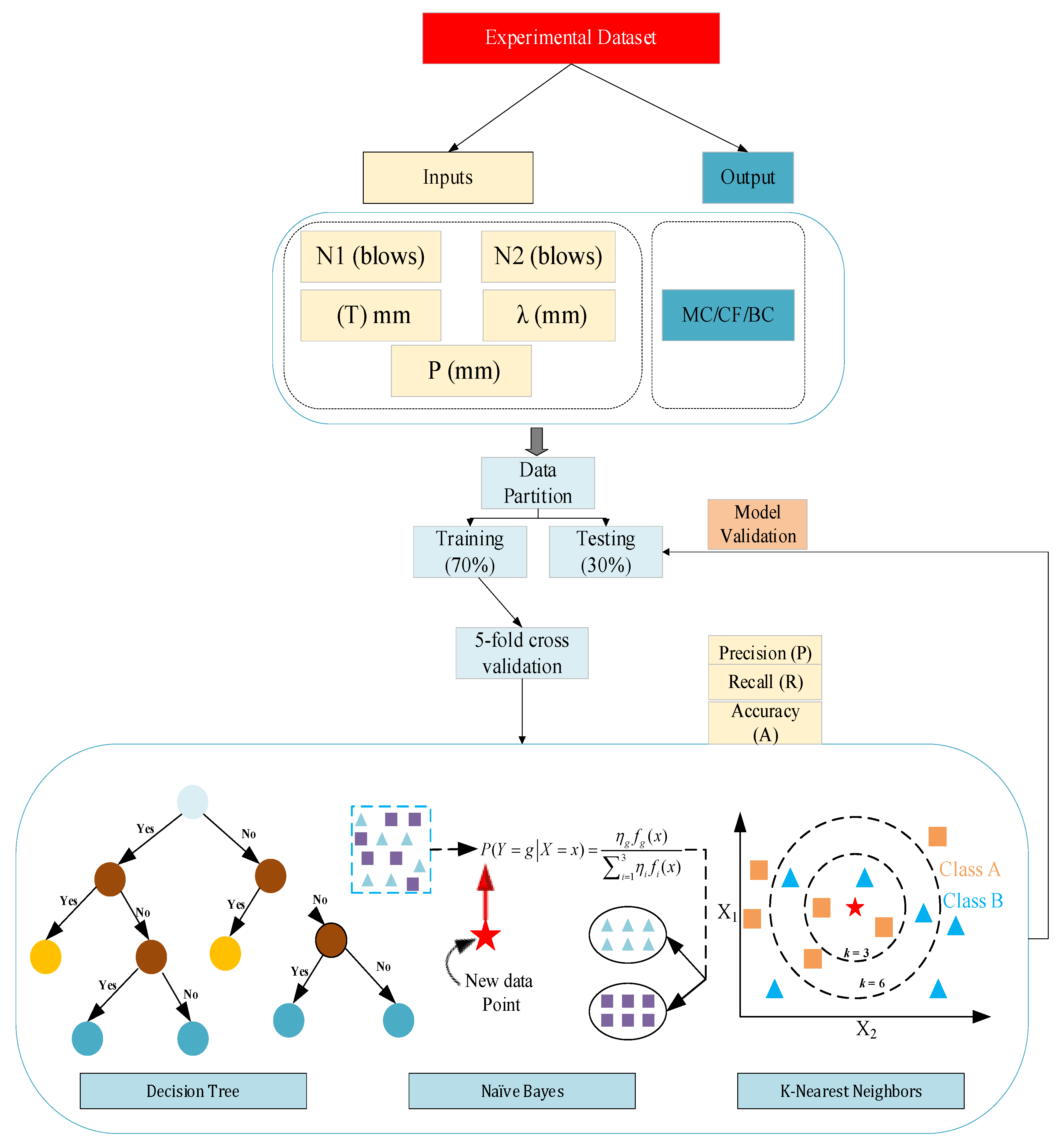
2.4. AI Modeling Procedure
2.4.1. Decision Tree
- (1)
- Split up the training dataset area t1, t2, t3, …tp into H separate and overlapping areas K1, K2, K3, …Kp. The Gini index (GI) is utilized for the region’s split binary operation [46], which specifies how the overall variance across all j classes was measured.
- (2)
- Cost-complexity pruning can be used to implement the preventative actions for overfitting or potentially complicated trees, taking into account a collection of trees groups of trees organized by nonnegative tuning index α. Given that the GI of the holdout data is decreased during the procedure, the max α-value might be obtained by the k-fold cross-validation method.
2.4.2. Naïve Bayes (NB)
2.4.3. K-Nearest Neighbors
2.4.4. Performance Evaluation
3. Discussion and Results
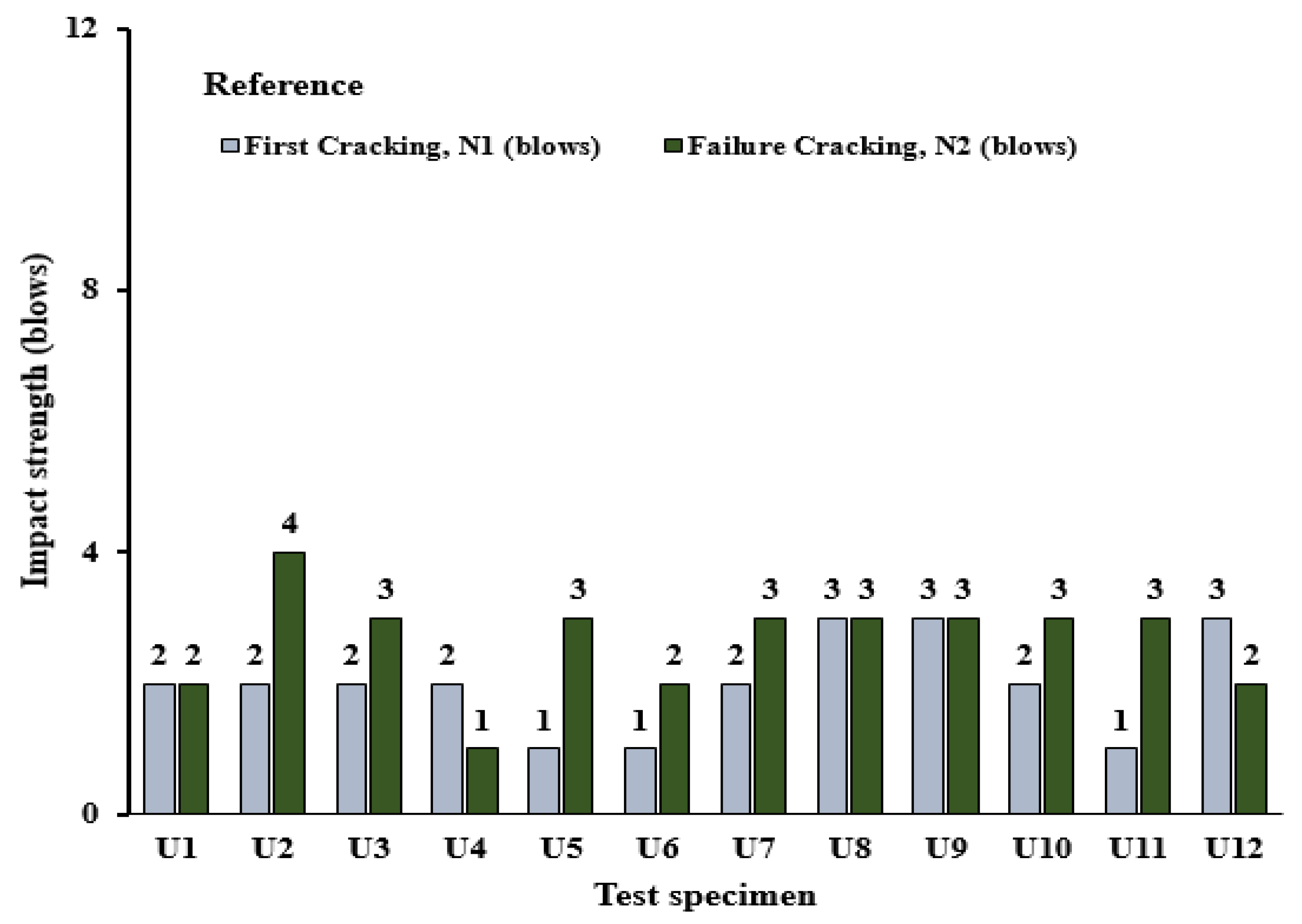
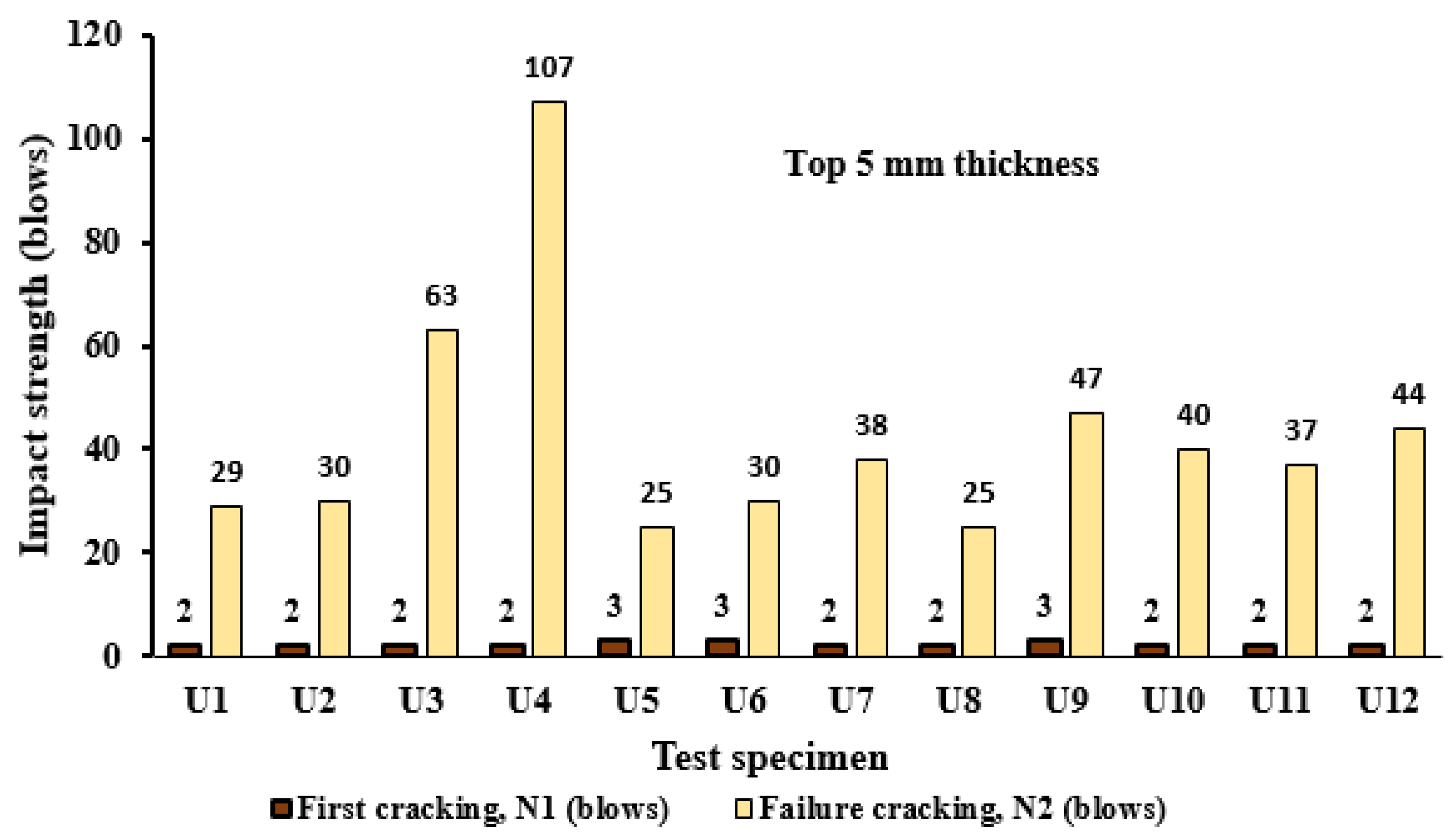
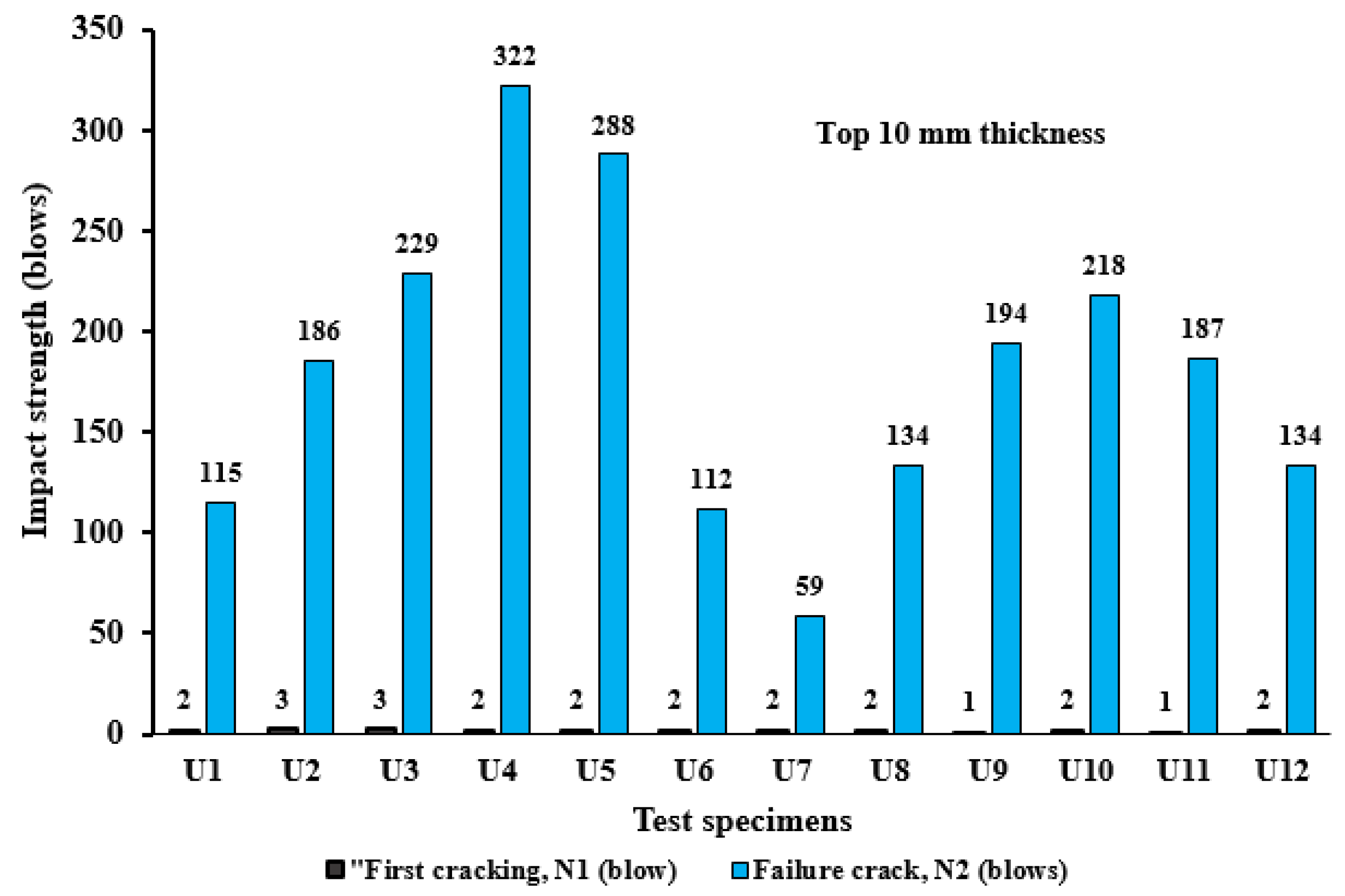
3.1. Failure Mode of Composite U-Shaped Specimens
3.2. Impact Resistance of Composite U-Shaped Specimens
4. AI-Based Model Result
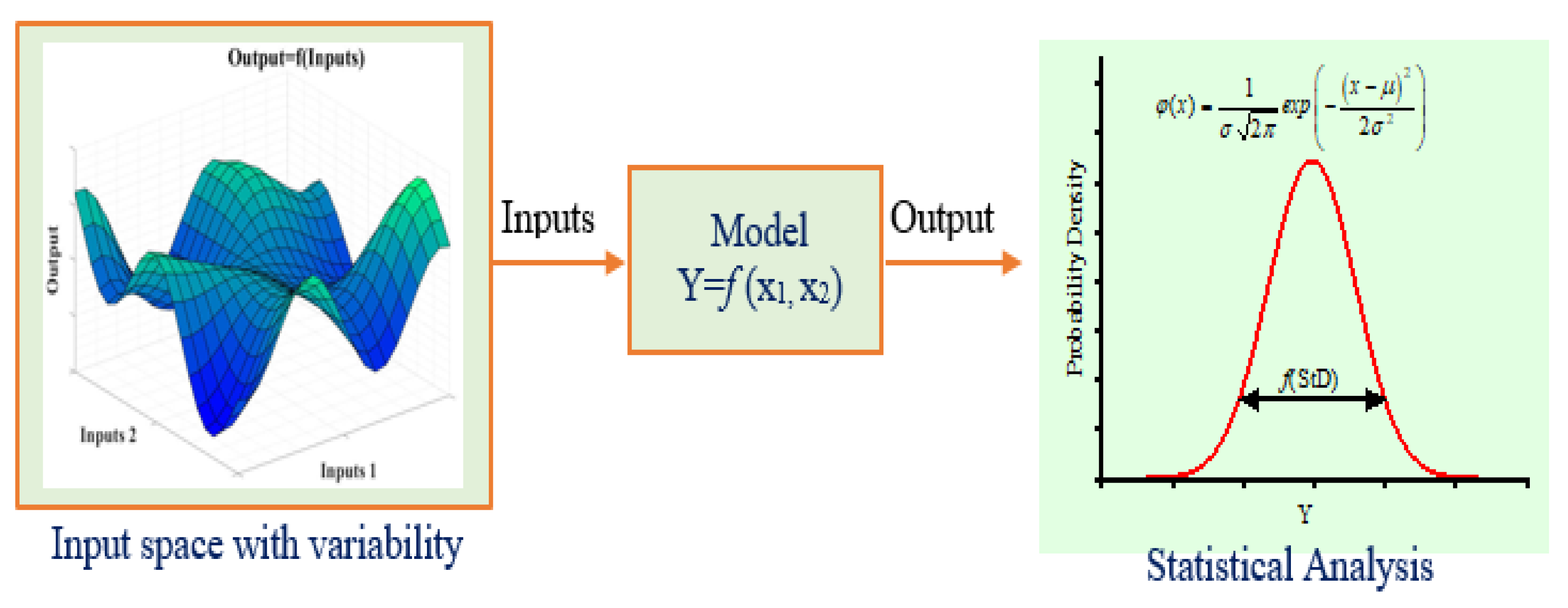
4.1. Monte Carlo Simulation (MCS)
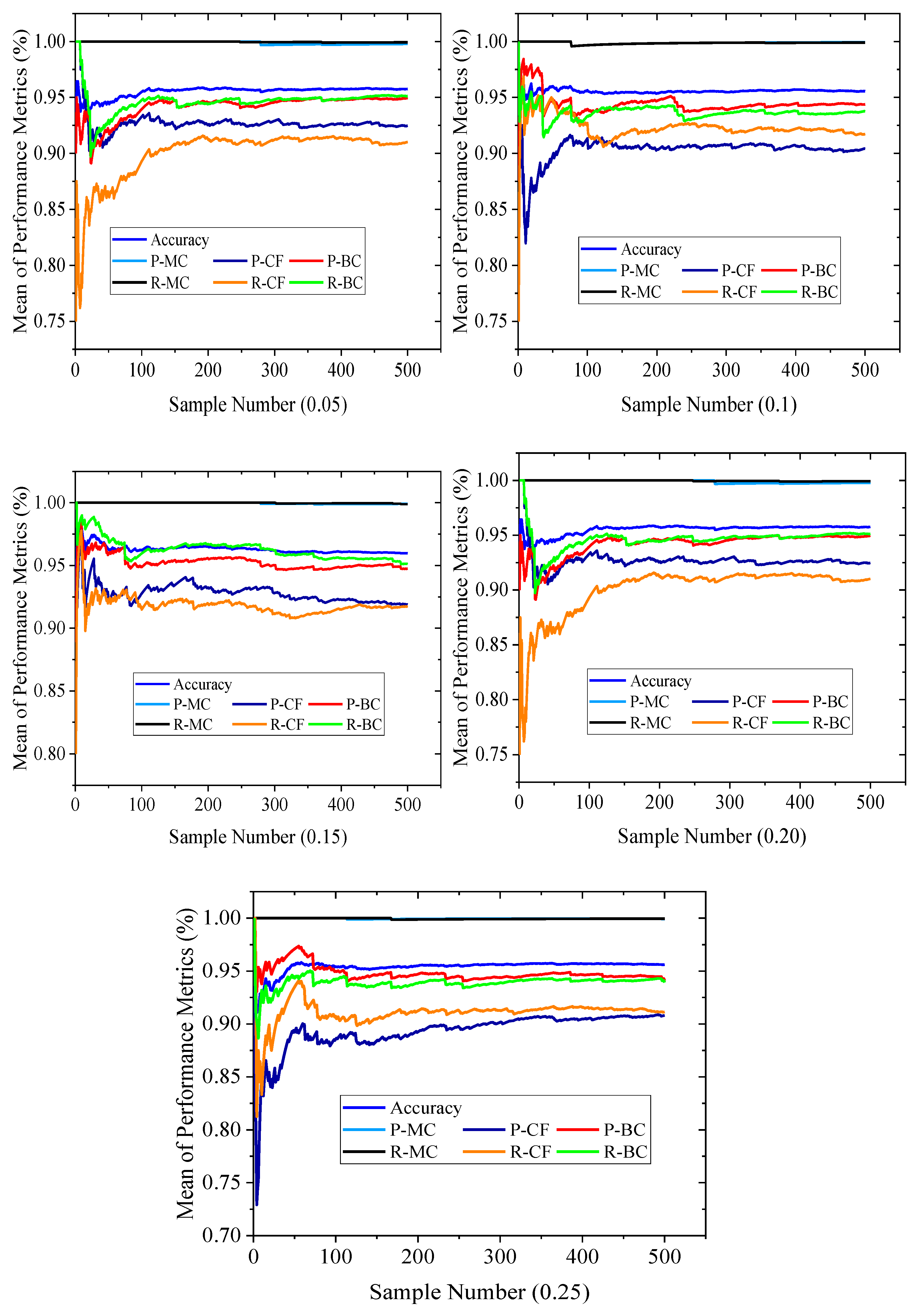
4.2. Convergence Plot
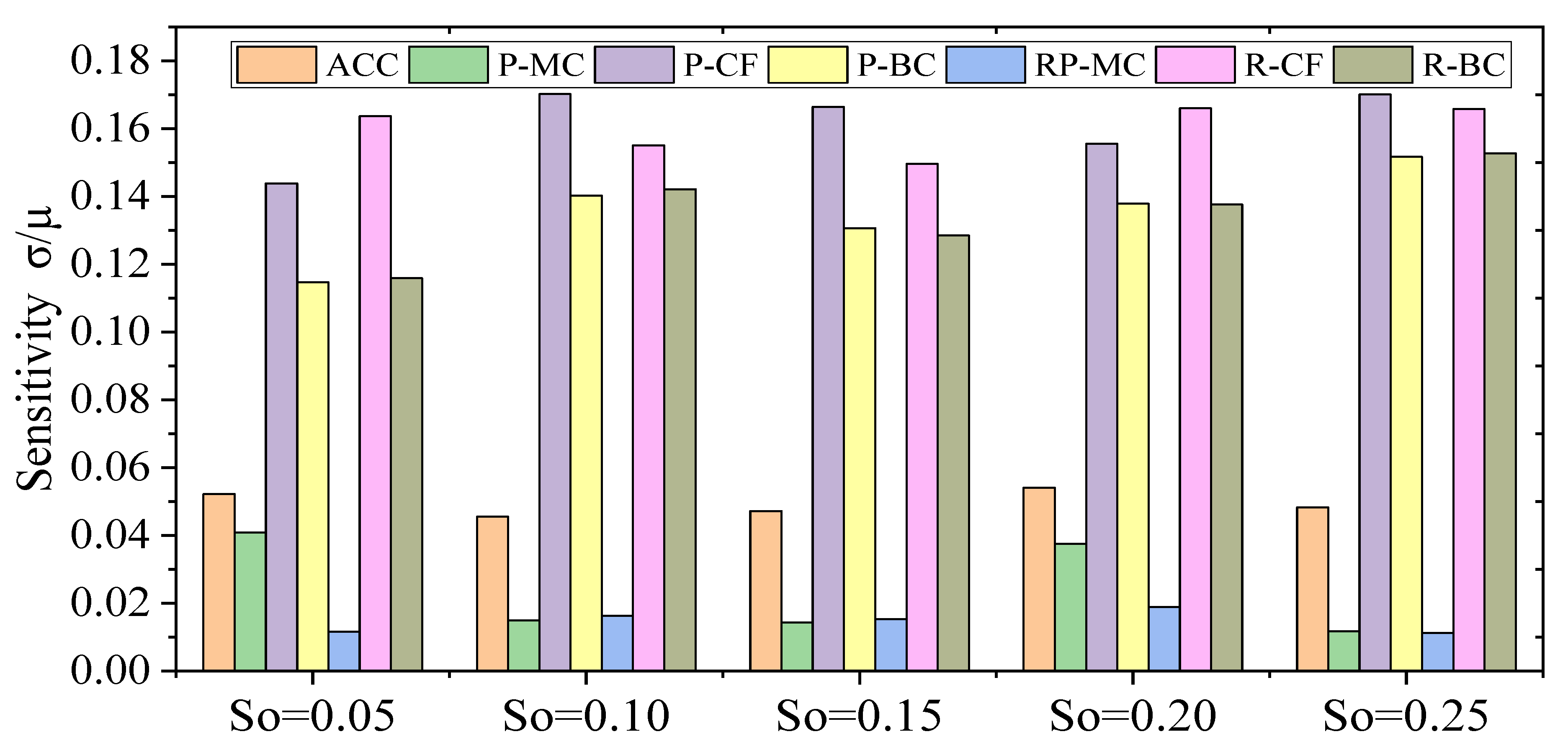
4.3. Sensitivity Analysis
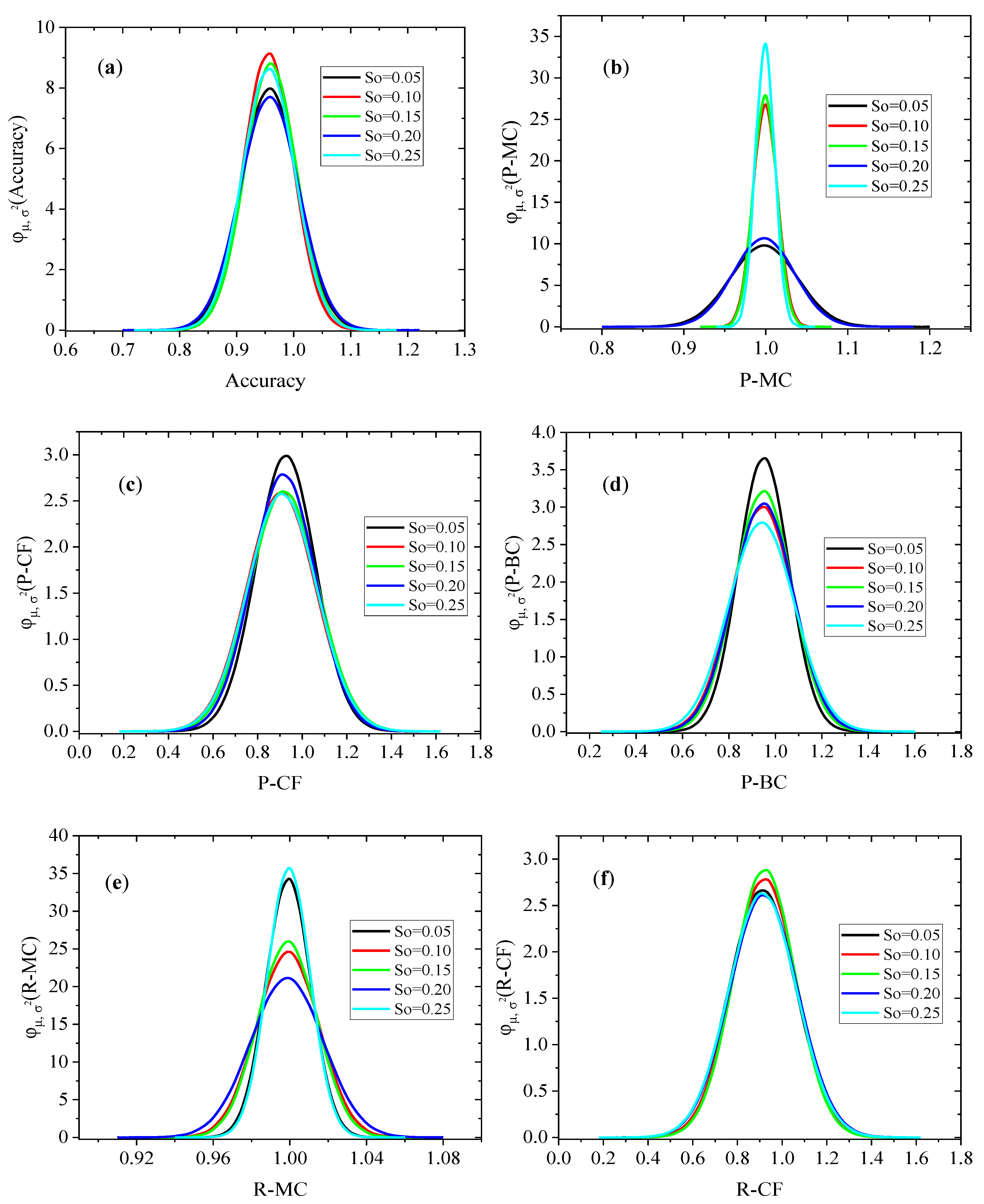
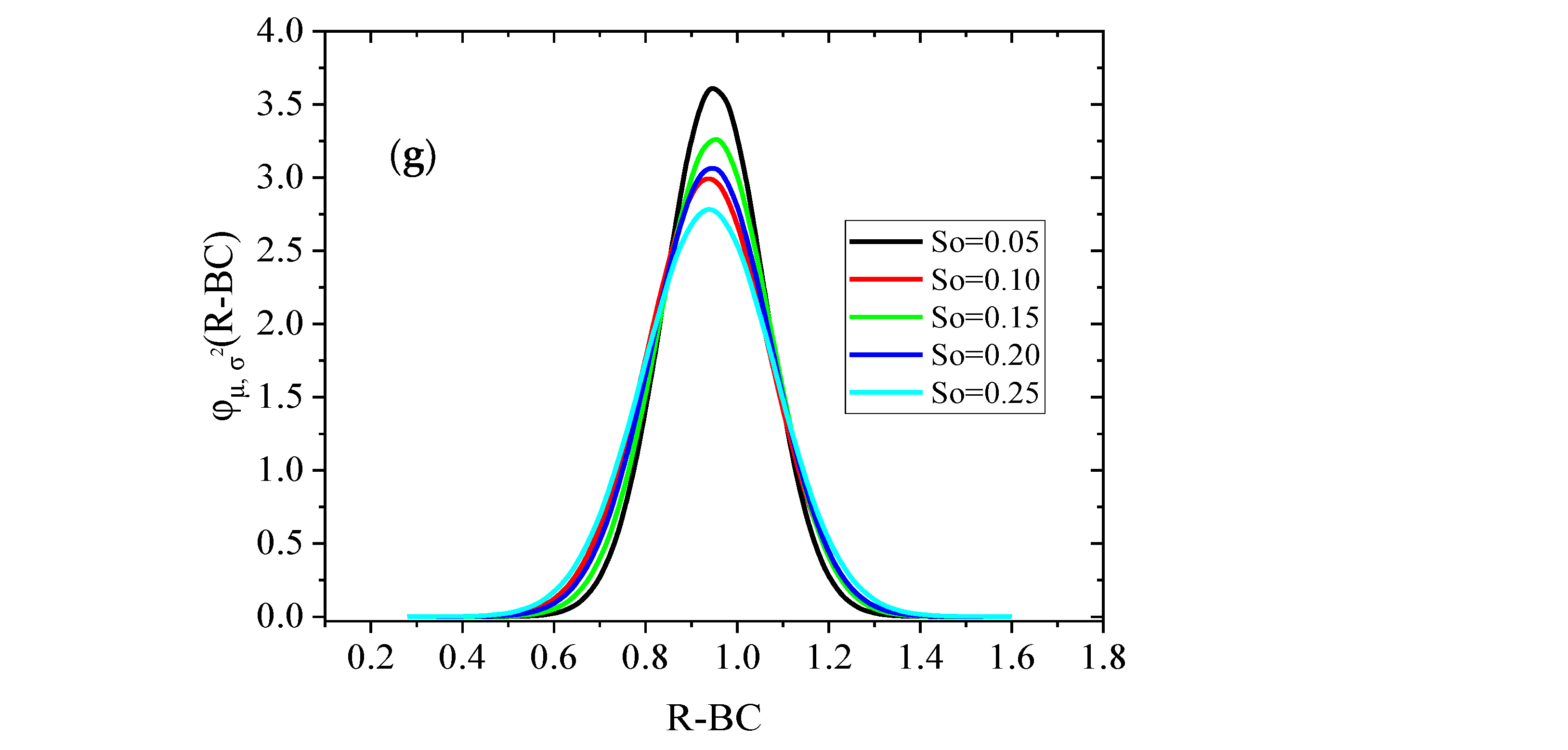
4.4. Probability Density Function
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The retrofitting effect of polyurethane grout resulted in significant improvement in the impact strength of the U-shaped specimen. The U-shaped specimen strengthened at the top surface showed little or no effect on the number of drops to originated first crack. However, the specimen strengthened at the top-to-bottom surface revealed significant improvement at both the first crack and failure crack stages.
- (2)
- Three major failure patterns, including mid-section crack (MC), crushing foot (CF), and bend section crack (BC), were observed according to the specimen’s condition. Control specimens exhibited the typical single crack at the mid-section of the specimens. On the other hand, composite specimen demonstrated failure at the bend section and crushing of footing due to the retrofitting effect of PU grout overlaid, resulting the high endurance of the composite specimen to multiple drop-weight impact load.
- (3)
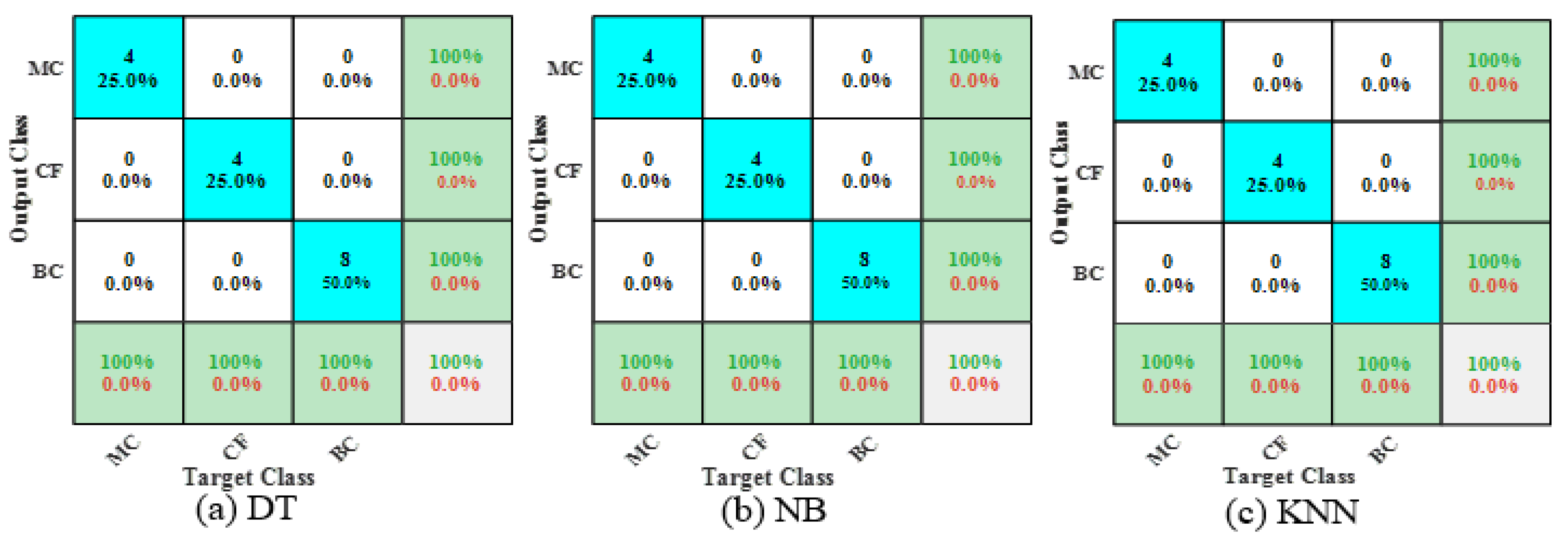
- All the trained models could predict the three types of failures with an accuracy greater than 95%. The KNN model predicted the failure modes with 3.1% higher accuracy than the DT and NB models. The excellent performance of the models was related to the performance of the developed models and the better correlation of the input variables with the target failure modes.
- (4)
- The accuracy, precision, and recall of the KNN model converged within 300 runs of Monte Carlo simulation. Similarly, the developed KNN model predicted the failure modes with 95% accuracy under different uncertainties. The maximum accuracy of the model under each uncertainty was 100%, and the average mean accuracy was 95.8%, which shows the robustness of the developed KNN model. The average mean precision of MC, CF, and BC failure modes was 99.8, 91.7, and 94.6%, respectively. The average mean of the failure mode recall was 99.9, 91.6, and 94.5%, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, X.; Xie, Y.; Long, G.; Zeng, X.; Li, J.; Yao, L.; Jiang, W.; Pan, Z. DEM analysis of the effect of interface transition zone on dynamic splitting tensile behavior of high-strength concrete based on multi-phase model. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 149, 106577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Romero, P.; Zhang, H.; Huang, M.; Lai, F. Unsaturated polyester resin concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 228, 116709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounanga, P.; Gbongbon, W.; Poullain, P.; Turcry, P. Proportioning and characterization of lightweight concrete mixtures made with rigid polyurethane foam wastes. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2008, 30, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdolotti, L.; Lavorgna, M.; Di Maio, E.; Iannace, S. Hydration-induced reinforcement of rigid polyurethane-cement foams: The effect of the co-continuous morphology on the thermal-oxidative stability. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabello, L.G.; da Conceição Ribeiro, R.C. A novel vermiculite/vegetable polyurethane resin-composite for thermal insulation eco-brick production. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 221, 109035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, A.O.; Teixeira, G.F.; Zaghete, M.A.; Longo, E.; Malmonge, J.A.; Silva, M.J.; Sakamoto, W.K. Influence of polymer insertion on the dielectric, piezoelectric and acoustic properties of 1-0-3 polyurethane/cement-based piezo composite. Mater. Res. Bull. 2019, 119, 110541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbhari, V.M.; Eckel, D.A.; Tunis, G.C., II. Strengthening of concrete column stubs through resin infused composite wraps. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 1993, 6, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, H.K.; Liu, G.W.; Yong, Y.W. Experimental study to investigate mechanical properties of new material polyurethane–cement composite (PUC). Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 50, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.M.L.; Ferreira, A.J.M. Assessment of fracture properties of epoxy polymer concrete reinforced with short carbon and glass fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2004, 18, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-T.; Liu, P.; Wang, H.; Dai, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Shiu, B.-C.; Lou, C.-W.; Lin, J.-H. Preparation and characteristics of flexible polyurethane foam filled with expanded vermiculite powder and concave-convex structural panel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 12, 1288–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.D.M.; de Souza Pádua, M.; de Carvalho, J.P.R.G.; Simonassi, N.T.; Lopez, F.P.D.; Colorado, H.A.; Vieira, C.M.F. Natural based polyurethane matrix composites reinforced with bamboo fiber waste for use as oriented strand board. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 12, 2317–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulaouche, T.; Kherroub, D.E.; Benzerafa, A.; Khimeche, K.; Belbachir, M. New synthesis of polyurethane nanocomposites based on Maghnite used both as a catalyst and as an inorganic improver of thermal, mechanical and textural properties. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 15222–15232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harith, I.K. Study on polyurethane foamed concrete for use in structural applications. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2018, 8, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruna, S.I.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, W.; Shao, J. Evaluation of impact resistance properties of polyurethane-based polymer concrete for the repair of runway subjected to repeated drop-weight impact test. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 309, 125152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Du, M.; Wang, F.; Xue, B.; Zhang, C.; Fang, H. Study on the mechanical properties of polyurethane (PU) grouting material of different geometric sizes under uniaxial compression. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 259, 119797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-kahtani, M.S.M.; Zhu, H.; Haruna, S.I.; Shao, J. Evaluation of Mechanical Properties of Polyurethane-Based Polymer Rubber Concrete Modified Ground Glass Fiber Using Response Surface Methodology. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 48, 4695–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Tong, J.; Huang, M.; Wang, F.; Pang, H. Model and experimental studies on the effects of load characteristics and polyurethane densities on fatigue damage of rigid polyurethane grouting materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 347, 128595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laqsum, S.A.; Zhu, H.; Bo, Z.; Haruna, S.I.; Al-shawafi, A.; Borito, S.M. Static properties and impact resistance performance of U-shaped PU-modified concrete under repeated drop-weight impact load. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2023, 23, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca-Romero, L.A.; Arroyo, R.; Alonso, Á.; Gutiérrez-González, S.; Calderón, V. Characterization properties and fire behaviour of cement blocks with recycled polyurethane roof wastes. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 50, 104075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamees, T.; Põldaru, M.; Ilomets, S.; Klõšeiko, P.; Kallavus, U.; Rosenberg, M.; Õiger, K. Failure analysis of a spray polyurethane foam roofing system. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 32, 101752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, C.; Zou, W.; Zhang, Y. Research on the dynamic impact performance of polyurethane cement-based composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 336, 127574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parniani, S.; Toutanji, H. Monotonic and fatigue performance of RC beams strengthened with a polyurea coating system. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 101, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-shawafi, A.; Zhu, H.; Haruna, S.I.; Bo, Z.; Laqsum, S.A.; Borito, S.M. Impact resistance of ultra-high-performance concrete retrofitted with polyurethane grout material: Experimental investigation and statistical analysis. Structures 2023, 55, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, M.; Haruna, S.I.; Malami, S.I.; Ibrahim, M.N.; Abba, S.I.; Ibrahim, Y.E. Prediction of compressive strength of concrete incorporated with jujube seed as partial replacement of coarse aggregate: A feasibility of Hammerstein–Wiener model versus support vector machine. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 8, 3435–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouk, A.I.B.; Zhu, J. Prediction of Interface Bond Strength Between Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC) and Normal Strength Concrete (NSC) Using a Machine Learning Approach. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 5337–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.L.; Maestas, D.; Emery, J.M.; Grigoriu, M.D.; Smith, M.D.; Martinez, C. Failure classification of porous additively manufactured parts using Deep Learning. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2022, 204, 111098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasoud, A.S. Enhanced Metaheuristics with Machine Learning Enabled Cyberattack Detection Model. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2023, 37, 2849–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangalathu, S.; Jeon, J.-S. Machine learning–based failure mode recognition of circular reinforced concrete bridge columns: Comparative study. J. Struct. Eng. 2019, 145, 4019104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderpour, H.; Mirrashid, M.; Parsa, P. Failure mode prediction of reinforced concrete columns using machine learning methods. Eng. Struct. 2021, 248, 113263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.; Liu, J.; Ouyang, Y. Residual-based damage evaluation of RC columns using feature classification and model optimization. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2021, 30, e1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Truong, G.T.; Shin, M. Development of extreme gradient boosting model for prediction of punching shear resistance of r/c interior slabs. Eng. Struct. 2021, 235, 112067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderpour, H.; Mirrashid, M. Classification of failure modes in ductile and non-ductile concrete joints. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 103, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.A.; Rougier, E.; O’Malley, D.; Srinivasan, G.; Hunter, A.; Viswanathan, H. Predictive modeling of dynamic fracture growth in brittle materials with machine learning. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2018, 148, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrayes, F.S.; Zakariah, M.; Driss, M.; Boulila, W. Deep Neural Decision Forest (DNDF): A Novel Approach for Enhancing Intrusion Detection Systems in Network Traffic Analysis. Sensors 2023, 23, 8362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najeeb, M.I.; Syamsir, A.; Amir, S.M.M.; Khan, T.; Sebaey, T.A. Failure Analysis of Plant Fibre-Reinforced Composite in Civil Building Materials Using Non-Destructive Testing Methods: Current and Future Trend. J. Nat. Fibers. 2023, 20, 2246654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruna, S.I.; Zhu, H.; Ibrahim, Y.E.; Shao, J.; Adamu, M.; Farouk, A.I.B. Experimental and Statistical Analysis of U-Shaped Polyurethane-Based Polymer Concrete under Static and Impact Loads as a Repair Material. Buildings 2022, 12, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somarathna, H.; Raman, S.N.; Mohotti, D.; Mutalib, A.A.; Badri, K.H. Hyper-viscoelastic constitutive models for predicting the material behavior of polyurethane under varying strain rates and uniaxial tensile loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 236, 117417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somarathna, H.M.C.C.; Raman, S.N.; Mohotti, D.; Mutalib, A.A.; Badri, K.H. Rate dependent tensile behavior of polyurethane under varying strain rates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 254, 119203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Chen, A. Studying a flexible polyurethane elastomer with improved impact-resistant performance. Polymers 2019, 11, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, S.; Tan, P.; Zhu, H. Mechanical performance and shear constitutive model study of a new high-capacity polyurethane elastomeric bearing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 232, 117227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG55-2011; Specification for Mix Proportion Design of Ordinary Concrete. Chinese National Standard: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Jiang, W.; Zhu, H.; Haruna, S.I.; Zhao, B.; Shao, J.; Yu, Y. Effect of crumb rubber powder on mechanical properties and pore structure of polyurethane-based polymer mortar for repair. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 309, 125169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACI 544-2R; Measurement of Properties of Fiber Reinforced Concrete. ACI: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 1989; pp. 433–439.
- Dietterich, T.G. Ensemble Methods in Machine Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Vandewiele, G.; Janssens, O.; Ongenae, F.; De Turck, F.; Van Hoecke, S. Genesim: Genetic extraction of a single, interpretable model. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.05722. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L.; Ihaka, R. Nonlinear Discriminant Analysis via Scaling and ACE; Department of Statistics, University of California Davis One Shields Avenue: Davis, CA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Rasjid, Z.E.; Setiawan, R. Performance Comparison and Optimization of Text Document Classification using k-NN and Naïve Bayes Classification Techniques. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 116, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, K.; Goldstein, J.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Shaft, U. When Is “Nearest Neighbor” Meaningful? BT-Database Theory—ICDT’99’; Beeri, C., Buneman, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 217–235. [Google Scholar]
- Cover, T.; Hart, P. Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory. 1967, 13, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.C.; Zhu, H.; Li, H.R. Drop-weight impact test on U-shape concrete specimens with statistical and regression analyses. Materials 2015, 80, 5877–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruna, S.I.; Zhu, H.; Shao, J. Experimental study; modeling, and reliability analysis of impact resistance of micro steel fiber-reinforced concrete modified with nano silica. Struct. Concr. 2022, 23, 1659–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskulski, R.; Wiliński, P. Probabilistic Analysis of Shear Resistance Assured by Concrete Compression. Procedia Eng. 2017, 172, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Jivkov, A.P. Monte Carlo simulations of mesoscale fracture of concrete with random aggregates and pores: A size effect study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 80, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouk, A.I.B.; Zhu, J.; Ding, J.; Haruna, S.I. Prediction and uncertainty quantification of ultimate bond strength between UHPC and reinforcing steel bar using a hybrid machine learning approach. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 345, 128360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, B.T.; Nguyen, M.D.; Van Dao, D.; Prakash, I.; Ly, H.-B.; Le, T.-T.; Ho, L.S.; Nguyen, K.T.; Ngo, T.Q.; Hoang, V.; et al. Development of artificial intelligence models for the prediction of Compression Coefficient of soil: An application of Monte Carlo sensitivity analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 679, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, H.-B.; Monteiro, E.; Le, T.-T.; Le, V.M.; Dal, M.; Regnier, G.; Pham, B.T. Prediction and Sensitivity Analysis of Bubble Dissolution Time in 3D Selective Laser Sintering Using Ensemble Decision Trees. Materials 2019, 12, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, T.T.M.; Ly, H.-B.; Pham, B.T. A possibility of AI application on mode-choice prediction of transport users in Hanoi. In CIGOS 2019, Innovation for Sustainable Infrastructure; Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 1179–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Mordechai, S. Applications of Monte Carlo Method in Science and Engineering; InTech: Houston TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]






| Specimen ID | Cement | Fine Aggregate | Median Aggregate | Water |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 425 | 718 | 966 | 170 |
| Polyurethane grouting materials | ||||
| PU: Sand | PU matrix/200 g | |||
| Castor oil (g) | PAPI (g) | diluent (g) | ||
| PU grout | 1:0.5 | 167.00 | 33.00 | 8.40 |
| PUG Overlaid (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Specimen ID | Configuration | Top Surface | Bottom Surface |
| NC-PU0 | - | - | - |
| NC-PUT5 | T | 5 | - |
| NC-PUTB5 | T&B | 5 | 5 |
| NC-PUT10 | T | 10 | - |
| Parameters | First Crack Strength | Failure Strength | Thickness | Midspan Deflection | Max. Load |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 (Blows) | N2 (Blows) | (T) mm | λ (mm) | P (kN) | |
| Max | 28 | 322 | 12.5 | 2.6 | 18.26 |
| Min | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.23 | 10.58 |
| Mean | 5.04 | 91.67 | 6.88 | 1.48 | 13.14 |
| St.D | 5.95 | 82.80 | 4.80 | 0.81 | 2.37 |
| Kurtosis | 4.56 | −0.06 | −1.45 | −1.32 | −0.49 |
| Skewness | 2.10 | 0.74 | −0.28 | −0.26 | 0.77 |
| N1 (Blows) | N2 (Blows) | (T) mm | λ (mm) | P (kN) | MC/CF/BC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 (blows) | 1 | |||||
| N2 (blows) | 0.2786 | 1 | ||||
| T (mm) | 0.5825 | 0.7884 | 1 | |||
| λ (mm) | −0.1199 | 0.4606 | 0.4634 | 1 | ||
| P (kN) | 0.0907 | −0.4625 | −0.5595 | −0.7378 | 1 | |
| MC/CF/BC | 0.4497 | 0.8257 | 0.9813 | 0.5882 | −0.6560 | 1 |
| Uncertainties | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC | CF | BC | MC | CF | BC | |||
| 0.05 | Max | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Min | 0.429 | 0.111 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.800 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| Mean | 0.958 | 0.998 | 0.927 | 0.949 | 0.999 | 0.912 | 0.951 | |
| StD | 0.050 | 0.041 | 0.133 | 0.109 | 0.012 | 0.149 | 0.110 | |
| 0.1 | Max | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Min | 0.857 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| Mean | 0.956 | 0.999 | 0.906 | 0.944 | 0.999 | 0.920 | 0.938 | |
| StD | 0.044 | 0.015 | 0.154 | 0.132 | 0.016 | 0.143 | 0.133 | |
| 0.15 | Max | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Min | 0.857 | 0.750 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.750 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| Mean | 0.960 | 0.999 | 0.919 | 0.947 | 0.999 | 0.921 | 0.951 | |
| StD | 0.045 | 0.014 | 0.153 | 0.124 | 0.015 | 0.138 | 0.122 | |
| 0.2 | Max | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Min | 0.429 | 0.200 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| Mean | 0.958 | 0.998 | 0.917 | 0.948 | 0.999 | 0.918 | 0.945 | |
| StD | 0.052 | 0.037 | 0.143 | 0.131 | 0.019 | 0.152 | 0.130 | |
| 0.25 | Max | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Min | 0.857 | 0.833 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.750 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| Mean | 0.956 | 0.999 | 0.910 | 0.941 | 1.000 | 0.913 | 0.939 | |
| StD | 0.046 | 0.012 | 0.155 | 0.143 | 0.011 | 0.151 | 0.143 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haruna, S.I.; Ibrahim, Y.E.; Ahmed, O.S.; Farouk, A.I.B. Impact Strength Properties and Failure Mode Classification of Concrete U-Shaped Specimen Retrofitted with Polyurethane Grout Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Infrastructures 2024, 9, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures9090150
Haruna SI, Ibrahim YE, Ahmed OS, Farouk AIB. Impact Strength Properties and Failure Mode Classification of Concrete U-Shaped Specimen Retrofitted with Polyurethane Grout Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Infrastructures. 2024; 9(9):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures9090150
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaruna, Sadi Ibrahim, Yasser E. Ibrahim, Omar Shabbir Ahmed, and Abdulwarith Ibrahim Bibi Farouk. 2024. "Impact Strength Properties and Failure Mode Classification of Concrete U-Shaped Specimen Retrofitted with Polyurethane Grout Using Machine Learning Algorithms" Infrastructures 9, no. 9: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures9090150
APA StyleHaruna, S. I., Ibrahim, Y. E., Ahmed, O. S., & Farouk, A. I. B. (2024). Impact Strength Properties and Failure Mode Classification of Concrete U-Shaped Specimen Retrofitted with Polyurethane Grout Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Infrastructures, 9(9), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures9090150







