Abstract
This review article examines global initiatives in the adoption of building information modeling (BIM) for road infrastructure. It begins with an overview of the distinctions between BIM applications for buildings and infrastructure projects. This study evaluates noteworthy BIM publications (NBPs) from various countries and organizations to understand BIM’s transformative impact on roadway infrastructure projects. It analyzes the evolution of these publications, compares academic output with NBP, identifies the stages of BIM maturity, and evaluates adherence to ISO 19650 standards. Through this analysis, the article presents current global and regional scenarios, providing a comprehensive overview of the current state and future prospects of BIM implementation in the road infrastructure sector.
1. Introduction
The architecture, engineering, construction, and operation (AECO) sector is a crucial segment of modern society, responsible for the development and maintenance of infrastructure and buildings. This sector encompasses all activities and professionals involved in the design, construction, and operation phases of buildings and infrastructure. Similar to other industry sectors, AECO has undergone transformations throughout its existence, particularly during the Industrial Revolution.
Building information modeling (BIM) has been introduced to the AECO sector within the context of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, also referred to as Industry 4.0, which is characterized by the fusion of technologies that blur the lines between physical, digital, and biological domains. BIM is an information management methodology that uses a digital model to represent the physical and functional attributes of a building or infrastructure throughout its entire life cycle [1]. BIM has revolutionized collaboration and work processes, reshaping the structures and methodologies of the AECO sector in efforts to improve efficiency and achieve environmental objectives [2].
The use of BIM is becoming increasingly prevalent in the construction industry, particularly within the construction sector [3]. Its expanding adoption is attributed to the array of benefits it offers across various stages of the construction process. Key benefits include the following:
- Improved detection of design flaws [4,5,6,7,8,9];
- Automated quantity measurement [7,10];
- Optimized job site planning during construction [11,12];
- Enhanced road alignment in a virtual environment, contributing to the enhancement of the final design [5,12,13];
- Risk reduction through enabling prior safety analysis [7,14];
- Real-time flexibility for adjusting the construction process [4];
- Data collection for more precise representations of real conditions in “as-built” documentation [11]; and
- Enhanced implementation of built asset management methods [6,13,15,16].
The adoption of the BIM methodology necessitates substantial shifts in organizational culture and project management approaches [6,17]. The AECO sector is currently in a transitional phase, in which numerous procedures and practices within public and private entities require adaptation or initiation to align with the evolving landscape of BIM implementation.
Motivated by the necessity to comprehend the current state of BIM in the road infrastructure sector, this research aims to provide a global perspective on BIM implementations in this domain. Through a comprehensive analysis of research endeavors, the focus is on understanding the driving initiatives for adopting this methodology, characterizing the current state, and identifying the evolutionary movements shaping the sector today. This study seeks to offer guidelines and forecasts to advance research efforts and enhance the efficiency of using BIM in road projects.
2. BIM for Transport Infrastructure
Although many BIM dissemination strategies do not distinguish between BIM for buildings and infrastructure sectors, establishing a homogeneous adoption policy, numerous studies have highlighted the differences between BIM models for transport infrastructure and general buildings.
These differences arise from the distinct characteristics of these two types of projects. Linear infrastructure projects are characterized by their extensive dimensions and significant interactions with the ground. Consequently, these projects are often managed using geographic information system (GIS) tools. This technology allows for the visualization and exploration of information associated with each element across large areas of land [18].
However, while GIS has a territorial scope and is optimized for storing such data, it lacks the detailed granularity that is a hallmark of BIM models [6]. This makes the integration of BIM and GIS crucial for linear infrastructure projects such as roads and rail networks.
Due to these physical characteristics, there is also a difference in the complexity of the projects. Complexity is considered the number of objects present in a project and the variability of the constituent attributes of each object. The greater the quantity of objects and attributes, the higher the complexity of the model. Thus, when compared to building models, transport structure models have reduced complexity [3].
The infrastructure sector is known for its intense use of 2D-based projects and a large volume of static documentation, necessitating a more mature asset management process that allows for better handling of non-graphical data connected to the project model [19]. Non-graphical data refer to information that is not visually represented in the model but is essential for the management and execution of the project. Examples of non-graphical data include material composition specifications, physical characteristics of soils, sources of quarry materials, and environmental regulations.
The transport infrastructure plays a crucial role as the backbone of any nation, significantly contributing to its economic and social development [20]. Due to the substantial investment values and critical societal impact, public entities are the primary clients for BIM models in the realm of transport infrastructure, in contrast to building models where private clients are more prevalent [21].
Upon analyzing the availability of BIM software in the market, defined as software capable of engaging in a BIM process by interpreting, generating, or manipulating BIM models, it is apparent that a lack of software tailored to the requirements of infrastructure designers leads to the widespread practice of utilizing and adapting established software intended initially for building projects [3].
The cultural aspects of the projects also vary, as highlighted in [3]. In the building sector, projects are typically oriented toward architectural features and spatial utilization, whereas infrastructure projects often prioritize constructability and cost considerations. This distinction underscores the sector-specific priorities, with architectural design and spatial functionality taking precedence in buildings, while construction efficiency and economic management play pivotal roles in infrastructure projects.
The lack of comprehensive BIM software designed for transport infrastructure modeling underscores the need for interoperability in model development, which requires a combination of various software tools to achieve holistic modeling. Interoperability, defined as the ability of BIM applications to exchange data, enables the integration of diverse software tools for comprehensive modeling and workflow automation [22]. An assessment of key non-proprietary formats such as industrial foundation classes (IFCs) indicates that the interoperability in BIM for infrastructure trails behind that of building projects [3].
Recent studies indicate that the BIM methodology is used predominantly in building projects, with less development in the infrastructure sector [23]. This discrepancy leads to a maturity gap in the advancement of the BIM methodology for transport infrastructure.
Table 1 presents the main differences found in the literature, while Figure 1 schematically illustrates how the application of BIM differs between both sectors.

Table 1.
Differences in BIM for transport infrastructure.
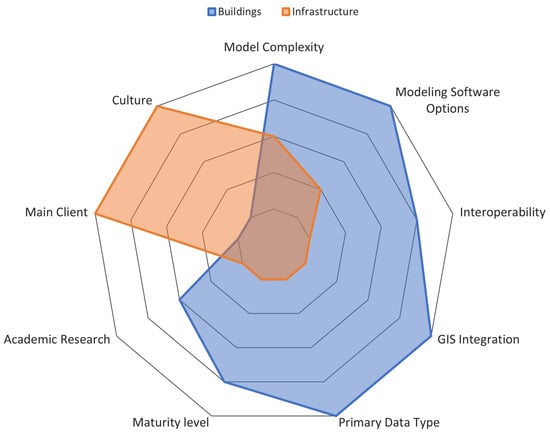
Figure 1.
Schematic difference between BIM for construction and infrastructure.
3. Materials and Methods
Figure 2 schematically presents the research method adopted. This work began with a systematic literature review, following the steps defined by Okoli [25], using the search string: (“Building Information Modelling” OR BIM OR “Building Information Modeling”) and (Infrastructure) and (Road or Highway) [19,26]. This search yielded 160 works relevant works between 2016 and 2023 [27] from repositories such as DOAJ, SciELO, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar. Subsequently, these results were meticulously selected, categorized, and evaluated, with 26 works highlighted for inclusion in the research.
To broaden the analysis, the concept of noteworthy BIM publications (NBPs) was adopted. NBPs encompass a diverse array of documents, including sector initiatives, peer-reviewed journals, published books, and other prominent sources. These publications, resulting from collaborative efforts among academic, government and industrial entities, play a vital role in knowledge dissemination, guide implementation strategies, and define requirements for BIM [28].
Subsequently, a search, selection, classification, and evaluation process for NBPs was undertaken. Given the absence of dedicated databases for this type of documentation, the search was conducted using open research sources, exploring websites of governmental and private organizations, conferences, and specialized journals. This broad approach guaranteed a more comprehensive overview of the NBP landscape within the context of BIM.
Due to the diverse nature of NBPs, Kassem et al. [28] propose criteria for accepting a publication as an NBP, as follows:
- NBPs are documents (i.e., not websites, blogs, or similar formats);
- NBPs reflect BIM knowledge (i.e., publications focused on skills, BIM tools, government adoption decrees, or roadmaps are excluded);
- NBPs are the results of BIM participants (i.e., publications delivered by participants from other industries are excluded);
- NBPs cover relevant BIM topics (i.e., publications covering pre-BIM maturity stage topics are excluded); and
- NBPs are macroscopic (i.e., documents intended for small groups of professionals or students are excluded).
For Borges et al. [29], NBPs are publicly available documents from the AECO sector that incorporate guidelines, protocols, and requirements focused on BIM products and workflows. These publications are the products of various agencies, industrial associations, communities of practice, and research institutions that aim to facilitate the adoption of BIM and realize its potential added value. Therefore, the following criteria were added to those of Kassem et al. [28]:
- NBPs originate from collaboration within the AECO sector (i.e., they are not individual contributions); and
- NBPs are not translations of other NBPs.
Following these established criteria, NBP selection was carried out, resulting in a total of 234 NBP publications chosen to form the research corpus. Subsequently, these NBPs (based on their main themes) were classified into general, infrastructure, and road transportation infrastructure categories.
The analysis stages began with the classification of NBPs within the road transportation infrastructure group. The initial stage involved conducting a qualitative analysis to evaluate the content of the NBPs, focusing on methodological approaches, innovations, integration with standards, and specific contributions to advancing BIM in infrastructure projects. This analysis provided a deeper understanding of the correlations between research, its impact, and the practical implications of the global effort to adopt BIM for road infrastructure, allowing a prognosis of the sector’s evolution in the coming years.
The second stage consolidated the data obtained in the first stage to enable quantitative analysis, aiming to
- Verify the global effort on road infrastructure;
- Identify the period of growth in the number of publications;
- Verify the countries with the largest collections of NBPs and track their evolution over the years;
- Assess the alignment of these collections with the relevance of scientific article publications;
- Evaluate the BIM maturity of the publications, as presented by Succar [1], reflecting the capability of the BIM methodology and setting critical milestones for its evolution; and
- Investigate the adherence of the publications to ISO 19650 [30], an international standard specifying requirements for information management using BIM throughout the asset lifecycle. This standard, based on the PAS 1192 series [31,32,33,34], covers concepts, principles, asset delivery and operation phases, and digital security, aiming for process standardization, increased efficiency and collaboration, ensuring information quality, risk reduction, and an integrated project lifecycle approach.
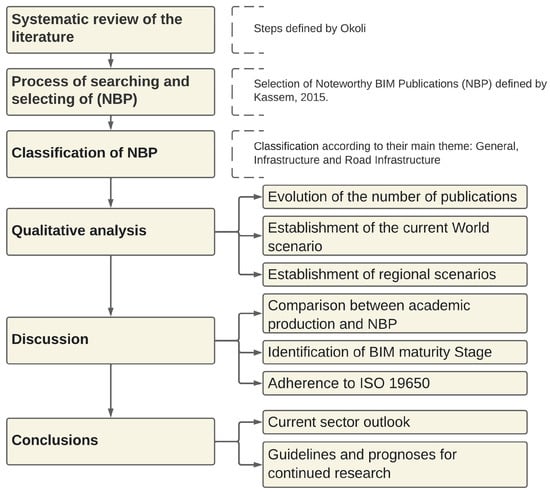
Figure 2.
Steps of the research method adopted [17,30].
4. Results
Of the 234 NBPs identified and spread across 28 countries, 45 publications from 12 different countries were classified under transportation infrastructure (railways, airways and roads). Table 2 presents the outcome of this selection of NBPs, focusing on road transportation infrastructure on a global scale. These selections cover a variety of formats, including a series of guides, mandates, protocols, standards, and standardization.

Table 2.
NBP for road infrastructure, separated by country of origin.
4.1. The Growth of Publications
The progression of publications over the years, as illustrated in Figure 3, shows consistent growth across all main themes. The uptick in NBPs centered on road infrastructure underscores the expanding global interest in BIM within the sector. This trend of rising NBP publications is in harmony with the uptrend in academic articles in the AECO sector [35], highlighting the increasing acknowledgment of the significance of BIM in the construction industry [24].
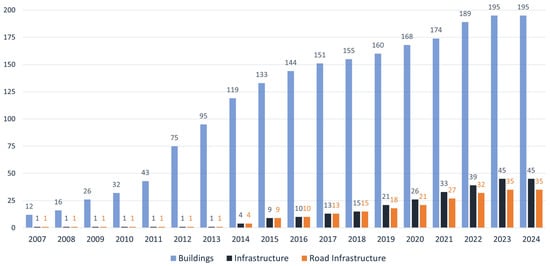
Figure 3.
The evolution of publications over the years.
In addition, the increasing number of NBP publications reflects the increasing importance accorded to BIM by governmental bodies, academic institutions, and other organizations. The proliferation of NBPs as a knowledge source in BIM is a clear indicator of the industry’s transition toward a more integrated and collaborative environment, where interoperability plays a pivotal role.
4.2. Adoption Effort
Figure 4 shows a timeline of BIM adoption in the countries emphasized in the NBP publications pertaining to the road sector. This chronological representation delineates key milestones in each country’s BIM adoption trajectory, offering a foundational framework for further in-depth analysis of their major publications.
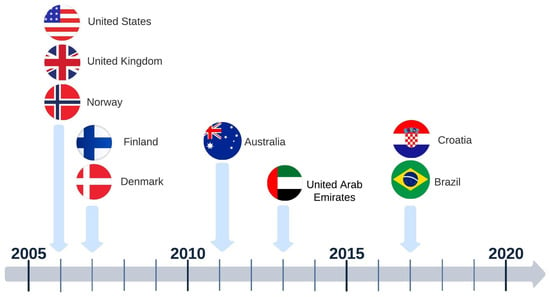
Figure 4.
BIM adoption timeline in reference countries for the road sector.
4.2.1. Australia
In 2011, Australia initiated its National BIM Strategy, laying the groundwork for the extensive adoption of BIM in government projects. This strategy defined the principles and objectives for the implementation of BIM throughout the construction supply chain, underlining the importance of collaboration and information exchange throughout the project life cycles.
In 2015, Australia introduced open BIM standards based on IFC. The infrastructure sector quickly embraced the BIM methodology, with highway and railway agencies in Australia adopting it to enhance the efficiency of planning, designing, and constructing transport infrastructure projects.
In collaboration with the National Research Centre for Sustainable Built Environment, universities, and institutions, national BIM guidelines, and case studies for infrastructure were published [36].
Austroads, the prominent organization of road transport and traffic agencies in the Australasian region, initiated the Asset Data Harmonization Stage III-BIM IFC Alignment Review, underscoring the significance of alignment in road infrastructure projects and delineating the distinctions between BIM applications for infrastructure and buildings [37]. This publication also addresses the requirements for evolving the IFC scheme to ensure the interoperability of alignment corridors for infrastructure projects.
Austroads provides a comprehensive collection of informational resources, including project manuals and follow-up reports. What is particularly noteworthy is the “Guide to Project Delivery” series, which comprises five volumes published between 2014 and 2022. Part 2 of this series focuses on project planning and control. Although not exclusively a BIM manual, it incorporates essential aspects such as risk management, project timelines, and costs. These topics are approached with BIM concepts, termed digital engineering, in this context [38]. This integration underscores the relevance of BIM in modernizing infrastructure project management processes, emphasizing a systemic and integrated approach.
Furthermore, the “Digital Enablement for Queensland Infrastructure” project, initiated in 2018, underscores the implementation strategy of the Queensland State Government. In 2021, the Department of Transportation and Main Roads launched “Building Information Modeling (BIM) “ for Transportation and Main Roads”, offering guidelines for integrating BIM into road infrastructure projects to enhance efficiency, quality, and stakeholder communication. This guide addresses modeling and documentation practices, project reviews, information management, and the benefits of BIM [39].
4.2.2. Brazil
In 2017, Brazil enacted a decree mandating the adoption of BIM without specific distinctions between building and infrastructure projects. Initially, BIM efforts and publications across the country, as in many others, focused primarily on buildings. Notably, the Brazilian Chamber of Construction Industry (CBIC) collaborated significantly, partnering with Finnish agencies such as the FTIA to develop a substantial collection of resources.
Subsequently, the Paraná Department of Roads and Highways (DER-PR), with support from the CBIC, began developing BIM applications for road works. This initiative led to the publication of the Road Infrastructure BIM Guide in 2022.
Concurrently, the National Department of Transport Infrastructure (DNIT) introduced the BIM Execution Plan Manuals [40] and the BIM Technical Requirements Guide [40]. The BIM Execution Plan Manual provides a template for developing BIM execution plans in infrastructure projects, while the technical requirements guide specifies essential criteria for BIM modeling from DNIT’s perspective.
It should be noted that while DNIT has published these crucial documents, they focus on specific aspects of BIM rather than providing comprehensive manuals like those found in other countries. Each document addresses a facet of BIM knowledge without offering an overarching, integrated view of the methodology seen in international equivalents. This segmented approach reflects a focused strategy but also indicates a need for more holistic materials that encompass all aspects of BIM to enhance its effective implementation in Brazil.
Furthermore, city-level initiatives have tackled access routes in a simplified manner, exemplified by the Federal District Secretariat’s publication of the BIM Manual for urban planning and infrastructure projects [41].
4.2.3. Croatia
Driven by the goal of enhancing project efficiency and quality, Croatia has recognized BIM as a pivotal tool, particularly in its efforts to secure project funding through European Union funds. The adoption of BIM has thus become a strategic imperative to harmonize local standards with international requirements.
The BIM journey in Croatia formally began with the establishment of official guidelines in 2017. A significant milestone in the development and standardization of BIM implementation in infrastructure projects occurred in 2021 when the Croatian Chamber of Civil Engineers launched the “Smjernice za BIM pristup u infrastrukturnim projektima” (Guidelines for the BIM Approach in Infrastructure Projects) [42].
4.2.4. Denmark
Denmark, led by the Executive Agency of the Ministry of Transport, DRD, adopted a BIM mandate in 2007, establishing itself as one of the pioneers in this initiative. Initially focused on construction, this mandate did not specifically cover the infrastructure sector. However, in 2015, Denmark released the guide titled “A Practical Guide to BIM in Construction and Infrastructure Projects” [43].
In 2018, the BIMInfra collaboration project began a five-year initiative involving two of Denmark’s main infrastructure owners: Banedanmark, the railway authority, and DRD. This project aims to accelerate the digital transformation in the infrastructure sector, leveraging international standardization efforts.
Within this context, DRD has implemented various sub-projects focused on digital project delivery. These initiatives primarily aim to broaden team expertise, foster organizational acceptance, and enhance BIM experience. Practical examples of these actions include the use of digital models for machine control, visualization, clash detection, the use of digital notes and checklists, and real-time access to data during the construction process.
To date, DRD has primarily utilized proprietary tools to achieve its BIM objectives. However, the organization is actively transitioning to open BIM processes.
4.2.5. United Arab Emirates
The Dubai municipality, a prominent government institution in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), plays a crucial role in the growth and development of the city. It is renowned for its innovative projects and smart services.
In 2013, the Dubai municipality established a significant guideline by issuing a circular outlining the implementation of BIM. An update to the mandate followed in 2015, primarily focusing on buildings. It was not until 2021 that a complementary circular was introduced explicitly directed toward infrastructure projects, underscoring the municipality’s ongoing commitment to expanding BIM applications across different sectors.
Inspired by best practices from the United Kingdom, the Department of Municipalities and Transport of Abu Dhabi City Municipality launched the first version of the BIM Documentation Guidelines for Infrastructure in 2020 [44]. This milestone reflects their commitment to excellence and international alignment in BIM implementation approaches, laying a solid foundation for improving efficiency and quality in regional infrastructure projects.
4.2.6. Finland
Infrastructure management at the national level in Finland is overseen by the Ministry of Transport and Communications, in collaboration with Väylävirasto-the Finnish Transport Infrastructure Agency (FTIA). This partnership plays a pivotal role in coordinating and implementing strategic initiatives aimed at enhancing the country’s transportation infrastructure.
In 2007, the Finnish Senate mandated the adoption of BIM processes for national public property projects to enhance project management efficiency. Within FTIA, the InfraBIM division has been a leader in integrating open BIM practices for infrastructure projects that are in line with national objectives. By 2012, Finland had set standardized BIM requirements for construction projects, establishing a uniform approach for BIM implementation. However, it was not until 2014 that FTIA expanded these initiatives to encompass infrastructure sectors such as roads, railways, and waterways.
Since 2014, FTIA has been advocating for the adoption of open or non-proprietary BIM standards. In 2014, FTIA introduced specific guidelines for bridges [45], followed by similar guidelines for roads in 2015 [46,47]. Subsequent efforts have focused on facilitating seamless information exchange among different software applications, thereby promoting the widespread implementation of open BIM practices.
The Velho Alliance project was launched in 2018 as an online repository and information hub for project and design assets related to roads, rails, and maritime routes. This initiative aims to facilitate the seamless exchange of standardized project and construction data among contractors and consultants while adhering to ISO 19.650 standards. Consequently, the technical requirement publications were updated in 2019 to align with these advancements [48,49].
In light of this project, a comprehensive set of documents, reports, and accounts can be accessed on the website, including the Väyläviraston ohjeita 32/2022. This document serves as a pivotal resource, outlining guidelines and criteria for FTIA’s information modeling practices [50]. It furnishes intricate directives for the development, structuring, and transmission of infrastructure information models, guaranteeing the precision, comprehensiveness, and applicability of data for stakeholders.
4.2.7. Norway
The incorporation of BIM for road infrastructure in Norway began in 2006 when the Norwegian Public Roads Administration (NPRA) implemented pioneering strategies to address construction cost variations. Among these initiatives were aerial terrain surveys and the shift from conventional drawings to generating 3D models, incorporating open-standard BIM formats.
In 2010, NPRA initiated the development of Manual V770 (138 Modellgrunnlag) to guide data model outputs for infrastructure projects. The first edition of this manual was launched in 2012 and established fundamental standards for BIM-based endeavors. Subsequently, in 2015, a specialized edition called Manual N400 was introduced for bridges and structural infrastructure projects, significantly bolstering adherence to BIM methodologies. Fast forward to 2023, an updated iteration of Manual V770, named R110, was released, underscoring the continuous commitment to advancing information modeling practices in road infrastructure projects [51].
In 2018, Bane Nor, entrusted with overseeing railway infrastructures, embarked on creating the “project KIM” information standard. This standard is designed to define universal specifications for information-driven modeling, extending its scope beyond roads to include railways and various structural elements. Concurrently, Nye Veier, responsible for significant road projects in Norway, integrated BIM into their contracts, mandating that all project-related data for delivery, operation, and upkeep be encapsulated within information models hosted on servers integrated with open file standards.
To guide these processes, the Håndbok for digital planlegging-veiledning STY-600239 was established as a comprehensive guide for the digital planning of road projects. This handbook addresses crucial aspects such as fundamental project data, model-based project concepts, and federated models [52]. Regularly updated, it defines the requirements for the project documentation and provides guidance on the deliverables in accordance with the project information management procedures.
Supplementing the publications above, the 2022 report “Status of LOD and Related Work at Nordic Infrastructure Clients” offers an in-depth evaluation of the level of development (LOD) landscape in Norway. This report serves to standardize the principles of LOD among public owners and relevant stakeholders involved in road infrastructure projects [53].
Notably, within NPRA, terms such as ISO 19650 and the various information requirement acronyms (OIR, AIR, PIR, PIM, AIM) are not utilized. NPRA believes that these terms introduce unnecessary complexity. Instead, the focus should be on clearly defining the data needs of the owner and the road management entities [54].
4.2.8. United Kingdom
The adoption of BIM for road infrastructure in the United Kingdom exemplifies a remarkable synergy between the public and private sectors, fostering innovation and collaboration. A notable milestone in this trajectory occurred in 2011 when the UK’s BIM Task Group, operating within the purview of the Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy (BEIS), formulated the Government Construction Strategy. This seminal directive established the target that by 2016, all construction suppliers bidding for centrally procured government projects should be operating at BIM Level 2 maturity.
This initiative was propelled by the recognition that around 40% of construction expenditure in the UK came from the government, half of which was centrally procured by governmental entities such as the Department for Transport. The overarching objective was to curtail the expenses associated with government construction projects by 15 to 20%, harnessing the government’s purchasing influence to facilitate a shift toward digital processes within the construction sector.
Industry responded strongly to this public policy and procurement strategy, leading to a notable increase in adoption and awareness of BIM in diverse public sectors involved in capital project delivery and asset management, including highways. The British Standards Institute (BSI) played a pivotal role in this transformation by issuing a series of standards—PAS 1192: Parts 1 to 6—outlining criteria for model detailing, information, definition, and exchange [55]. These standards were instrumental in driving the establishment of global BIM conventions, exemplified by the ISO 19.650 standards [56].
The UK’s BIM mandate is widely recognized as a success story, showcasing its role in driving the uptake of collaborative software and pioneering workflows in project delivery. This strategic approach transcends mere technology integration, placing a paramount emphasis on tailored information requisites and harmonization with the operational norms of fellow European countries.
The oversight and progression of the UK’s BIM initiative were delegated to the Centre for Digital Built Britain (CDBB), a partnership between BEIS and the University of Cambridge. The CDBB distinguished itself through cutting-edge research on digital construction and intelligent asset management. A notable achievement of CDBB was the formulation of UK-specific annexes for ISO 19.650 standards, tackling aspects such as asset management and cybersecurity within BIM applications.
The CDBB endeavored to advance BIM to higher maturity levels by introducing integrative and interactive concepts like ’operate and integrate’. Despite its dissolution in September 2022, the CDBB had a lasting impact through its robust international collaborations with more than 30 countries and governments across Europe, Latin America, and Asia. This collaborative effort focused on harmonizing strategies and standards, including the ISO 19.650 series [30,56,57,58,59], to promote shared advantages and global progress. The initiative facilitated the integration and customization of the UK’s strategic framework and technical standards for BIM on a global scale, leaving behind a lasting and influential legacy.
In 2021, the UK’s Department for Transport (DFT) issued the “BIM Guidance for Infrastructure Bodies” to support organizations in the transport and infrastructure sectors in grasping and implementing BIM. This comprehensive guide covers essential requirements, explores the asset lifecycle, outlines asset management processes, and discusses the challenges linked to inadequate information management. It also outlines effective information management strategies and provides a detailed roadmap for BIM implementation, spanning from initial business case development to the successful integration and adoption of BIM as a regular practice.
The release of this guide in 2021, following the 2016 BIM implementation target, underlines a crucial insight: BIM adoption is a continual evolution rather than a one-time event. This reality underscores the complexities and obstacles inherent in substantial digital transformation within the infrastructure sector. The issuance of ongoing guidance, exemplified by the 2021 guide, underscores that despite notable progress, there remain hurdles to overcome, including resistance to change, the need for technical training, and the standardization of practices. Therefore, the guide not only furnishes valuable resources for facilitating BIM integration but also acknowledges that the journey toward BIM implementation is a journey necessitating continual adjustment and learning, even post-initial implementation.
4.2.9. United States of America
In the United States, the progression of BIM implementation began in 2006, with its utilization mandated for new public building projects. While not initially obligatory, the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) initiated a study into the advantages of BIM for the road infrastructure sector in 2007, signaling the beginning of innovative endeavors in this domain.
By 2017, the FHWA significantly expanded its engagement in comprehending and implementing BIM. Its website commenced offering an array of resources, including National BIM guides (NBPs) and subsequent reports. In its initial endeavors, the agency emphasized technological facets, disseminating case studies and practical directives, as evidenced in publications such as “Utilizing 3D Digital Design Data in Highway Construction-Case Studies” [60], “Automation in Highway Construction Part II: Design Guidance and Guide Specification Manual” [61], and “Effective Use of Geospatial Tools in Highway Construction” [62].
Subsequently, in a phase dedicated to fostering a more profound comprehension of BIM, FHWA embarked on visits to prominent international agencies in countries such as Finland, Norway, Denmark, the United Kingdom, Sweden, and the Netherlands. This initiative led to the publication of a series of reports concentrating on information management, exemplified by works like “Advancing the Development and Deployment of BIM for Infrastructure” [63] and “The Dimensions of BIM for Infrastructure” [64]. These strategic efforts may help elucidate why the United States has already embraced BIM in nearly 50% of its infrastructure projects, as highlighted by Biancardo et al. [65].
The fact that “The Dimensions of BIM for Infrastructure”, a National BIM Guide (NBP), introduces concepts that some authors may find questionable underscores the importance of understanding the iterative nature of ideas that swiftly evolve, a hallmark of disruptive innovation.
A notable publication is “Building Information Modeling (BIM) Practices in Highway Infrastructure 2021”, which offers a comprehensive overview of the entire evolutionary process and presents the primary findings from benchmarking exercises conducted with similar agencies across different countries. This document evaluates the levels of awareness, leadership, readiness, and collaboration concerning BIM within other agencies, identifies the critical pillars of BIM for infrastructure, and examines the practical implementation of BIM, encompassing organizational frameworks, data modeling, information exchange, and interoperability requisites. Providing a consolidated guide, this publication enhances understanding of the present and future landscape of BIM for road infrastructure in the United States [54].
In addition to the significant contributions made by FHWA, universities also play a crucial role in advancing BIM development. One example is the publication “Lifecycle BIM for Infrastructure: A Business Case for Project Delivery and Asset Management”, which assesses BIM implementation in infrastructure projects specifically from the asset management standpoint [66].
4.2.10. Joint Initiatives
Among the collaborative efforts focused on BIM, the “Building Information Modelling (BIM) for road infrastructure: TEM requirements and recommendations” by the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) emerges as a significant initiative. This publication highlights the critical importance of process integration and the seamless dissemination of digital information across the entire lifecycle of infrastructure assets.
The UNECE document addresses the imperative of digital transformation within the sector of road infrastructure, with a particular focus on highway construction and maintenance projects. It highlights the BIM approach for its ability to enhance coordination and communication among stakeholders, offering a more precise and accurate project overview throughout all stages. Leveraging BIM enables a detailed digital representation of the construction process, facilitating informed decision-making and reducing the occurrence of errors and rework [67].
Additionally, the publication delineates BIM objectives, applications, and guidelines for the effective deployment of BIM in the construction of road infrastructure. The general objective is to improve efficiency, reduce costs, improve safety measures, and foster digitization of processes within the realm of road infrastructure, with the objective of increasing the efficiency and sustainability of the project.
5. Discussion
5.1. Global Effort on Road Infrastructure
Figure 5 provides an evolutionary representation of the principal agencies that develop NBPs for road infrastructure in key countries, aiding in the analysis of the interrelation among these publications.
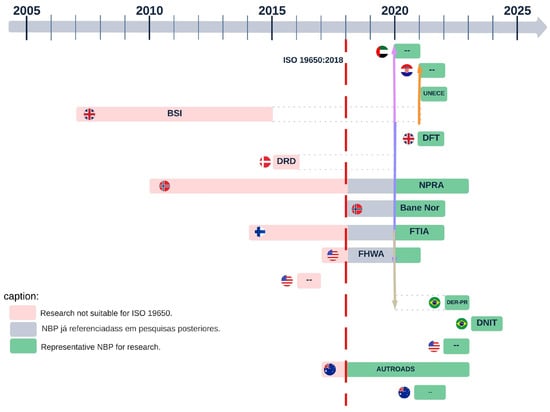
Figure 5.
Timeline of the global NBP efforts on road infrastructure.
Moreover, Table 3 showcases the abbreviations of the agencies, accompanied by their full names and countries of origin. This table aims to improve clarity and simplify comprehension of Figure 5.

Table 3.
Main agencies for road infrastructure by countries.
The United Kingdom has long been a significant leader in exporting the BIM methodology, influencing practices in numerous nations. A significant portion of this influence can be attributed to academic initiatives such as the Centre for Digital Built Britain (CDBB), a successful collaboration between BEIS and the University of Cambridge. Their extensive research underscores that BIM adoption is an ongoing and evolving process rather than a one-time event, recognizing the complexities and challenges inherent in large-scale digital transformation within the infrastructure sector.
Finland, represented by the FTIA, has shown proactive commissioning of academic research, particularly at the master’s and doctoral levels, to create public guides, standards, and guidelines. A similar commitment to academic collaboration is evident in both the United States and Australia, renowned for their BIM implementation in the sector. This pattern indicates the presence of a beneficial synergy between academia and the construction industry, forming a virtuous cycle of advancement.
Norway, a trailblazer in BIM adoption, has consistently advocated for the methodology. Its track record of reviewing NBPs from 2010 to the present reflects a resilient and adaptable approach to BIM evolution.
In the United States, the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) has played a pivotal role in driving the advancement of BIM in the context of road infrastructure. Noteworthy research focused on integrating BIM throughout the asset lifecycle utilizing the IFC schema has been particularly prominent. This underscores BIM’s crucial role as a tool shaping the future of road infrastructure.
In Australia, Autoroads has emerged as a significant benchmark, influencing neighboring regions like New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, and other islands by adapting manuals and managerial practices to incorporate BIM.
A notable advancement in the United States is the initiation of research evolution focused on integrating BIM throughout the asset lifecycle using the IFC schema. This underlines BIM’s significance as a crucial tool for the future of road infrastructure.
Countries that have more recently adopted BIM, such as Brazil, the United Arab Emirates, and Croatia, exhibit a diverse landscape in their approach. While the United Arab Emirates and Croatia introduced a single NBP each with comprehensive content, aiding in the holistic assimilation of the BIM methodology, Brazil, particularly through the DNIT initiative, lacks a comprehensive NBP that covers all aspects of BIM for a cohesive and efficient implementation, including taxonomic standardization. On the other hand, the NBP developed by DER-PR adopts a more instructive approach, providing a comprehensive overview of the BIM methodology. However, there are still opportunities for further exploration and expansion, as suggested in this research.
5.2. Comparison between Academic Production and NBP
When analyzing the NBPs related to road Infrastructure, the countries with the largest collections of publications were identified (Figure 6).
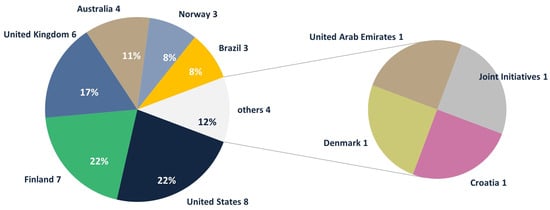
Figure 6.
The largest collections of NBP.
When comparing the listings of countries with the largest collections of NBPs with the major producers of academic articles, as highlighted by Nascimento et al. [26], Corrêa et al. [3], and Han et al. [4], a convergence is observed. It is evident that the United Kingdom and the United States hold prominent positions, followed by Australia. This convergence underscores the consistency and relevance of these countries in the context of BIM, both in terms of academic production and NBP generation. The results reinforce the leadership of these nations in contributing to the advancement and development of BIM, particularly in the realm of infrastructure and road infrastructure.
While Finland is grouped with the United Kingdom and the United States in NBP production, it is not consistently highlighted in academic article production, being mentioned only by Nascimento et al. [26]. Similarly, Brazil stands out with respect to the number of NBPs, particularly in the infrastructure theme, being cited exclusively by Salzano et al. [68] as a standout country. These indications suggest that the approach of these countries to the BIM methodology may be less integrated with the academic environment.
On the other hand, Spain, Italy, and Germany excel in academic production but do not stand out in the NBP scenario, suggesting a less oriented focus toward practical implementation. The findings of Vignali et al. support this perspective [69], which emphasizes a strong academic development of BIM in Italy. It is inferred that similar dynamics may apply to Spain and Germany. These observations underscore the importance of a comprehensive analysis that integrates academic publications and NBPs to fully grasp the influence and adoption of BIM in diverse contexts and regions.
Furthermore, it is emphasized that a deeper study of BIM for infrastructure demands a detailed analysis of publications from the United Kingdom, the United States, and Australia. This necessity arises from the notable convergence of their prominence in both NBPs and academic articles, positioning these countries prominently in the application of BIM methodology focused on infrastructure. These countries not only contribute substantial volumes of BIM research, but also demonstrate a significant commitment to various publications that guide the effective implementation of the methodology in road infrastructure projects.
5.3. The Delay Compared to the Buildings Sector
From Figure 3, the predominance of content related to the building segment is evident. This trend can be partially explained by the consistent occurrence of publications focused on buildings since 2007. In contrast, publications on transportation infrastructure began to emerge more regularly only in 2014.
The first publication related to BIM being considered for infrastructure is the BSI 1192:2007 [31]. Although originally aimed at buildings, this standard established a policy and approach for collaborative work that remains influential to this day, extending its guidance to infrastructure projects. Despite its primary focus on buildings, its application in transportation infrastructure underscores the importance of collaborative project guidelines.
However, the first material explicitly dedicated to transportation infrastructure was the BIM Guidelines for Bridges [45], a Finnish publication released in 2014. This suggests an initial delay of about 7 years between the first general BIM publication and the first sector-specific publication for infrastructure. Only after 2014 did publications focused on transportation infrastructure begin to gain consistency, reflecting the growing attention of the BIM methodology to this sector.
Thus, while the road infrastructure sector began to gain consistency in BIM publications, publications related to buildings have surpassed the mark of 100 publications. This disparity reinforces the significant differences between the sectors and suggests the need for additional efforts to promote the use of BIM in transportation infrastructure.
One possible explanation for this delay is related to the type of client. Although the main client in the construction market is the private sector, the infrastructure sector primarily serves the public sector as its centralized client [21]. Cultural differences between these sectors may justify this initial delay [3]. In addition, the public sector often bases its demands on regulations, standards, and procedures established by legal and administrative processes. These processes tend to change and evolve more slowly, being less receptive to methodological changes, which may explain the delay.
Another possible explanation for the time delay is associated with the concept of interoperability, a fundamental principle in the BIM methodology. Interoperability enables the exchange of information between different applications, allowing multiple tools to collaborate effectively on tasks [70].
The primary information exchange schema adopted is the IFC [70]. It is an open and platform-neutral standard, meaning it is not tied to any specific BIM software manufacturer. One of its key characteristics is its ability to support the representation of semantic information, which includes information with specific meaning for different disciplines.
Its first version (IFC 1.0) came into use in 1997. Since 2005, the standard has been developed and maintained by BuildingSMART International, an organization working to establish IFC as a universal industry standard. With this goal in mind, ISO 12006-3:2007 [71] and ISO 16739:2013 [72] were consolidated. To remain viable as a potential universal standard, IFC underwent several updates and revisions to keep pace with technological advances and changes in industry practices. However, it was not until 2013 (version 4.0) that IFC enabled interoperability between BIM and GIS. This advancement marked a significant step for transportation infrastructure, as interoperability is a crucial requirement for the implementation of BIM in transportation infrastructure projects [6].
This chronological coincidence between the development of IFC and the increase in publications on transportation infrastructure from 2014 offers a plausible explanation for the initially greater development of BIM in building themes.
Following the introduction of IFC for infrastructure projects, numerous updates and revisions have been made to improve compatibility with technological advances and evolving industry practices. Some of its significant milestones include the following:
- IFC 4.2-2016: This update to IFC 4 focused on bug fixes and minor improvements, reinforcing IFC’s capability to support infrastructure projects [73]; and
- IFC 4.3-2022: The latest update resulted from a multi-year international process and introduced IFCRail and IFCInfra. Alongside corrections and minor improvements, this version enhanced IFC’s capacity to accommodate bridges, ports, waterways, and elongated elements such as roads and railways [53].
5.4. BIM Maturity Stage of Publications
The maturity stage of publications was examined to gain a comprehensive understanding of the current landscape, using the maturity stage classification outlined by SUCCAR [1], as recalled below:
- Stage 1—Modeling focus: marks the beginning of the transition from traditional CAD to BIM;
- Stage 2—Collaboration focus: project team members begin to actively collaborate through multidisciplinary models; and
- Stage 3—Integration focus: characterized by the creation, sharing, and collaborative maintenance of rich data integrated or federated models, with all necessary information and data for project development extracted from a single model in a common data environment (CDE).
The publications presented over the years by maturity stage are shown in Figure 7. Overall, it is observed that publications classified at stage 1 are declining, with no records of publications at this level since 2019. This decrease can be attributed to the evolution of the BIM maturity stage, where approaches and procedures progress rapidly. Additionally, it reflects a natural trend indicating that older publications have less relevance to current sector dynamics.
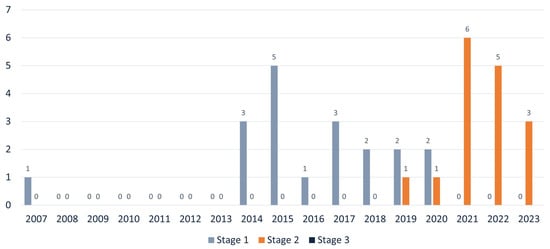
Figure 7.
BIM maturity stage of publication.
In stage 2, there has been a significant increase in publications, making it the stage with the largest quantity of current publications (last 5 years), indicating a growing emphasis on enhanced collaboration in road project development. Furthermore, the concentration of publications in this stage suggests that this represents the current maturity level of the BIM methodology worldwide for the sector. This concentration also points to 2019 as a turning point in global maturity in the adoption of BIM.
Surprisingly, no publications were identified in stage 3. This suggests that any projects or studies at this maturity stage should still be considered exceptions or experimental in nature. It reflects ample room for innovation and targeted research to advance road infrastructure toward more sophisticated maturity stages.
The temporal evolution of publications from various countries in different stages of BIM maturity was then analyzed (Figure 8 and Figure 9).
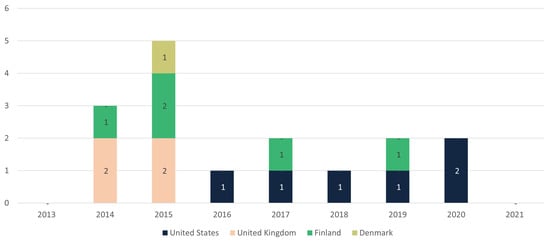
Figure 8.
Temporal evolution of NBP in stage 01.
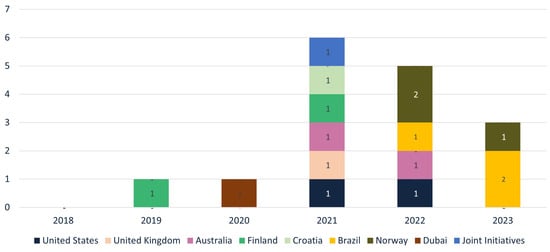
Figure 9.
Temporal evolution of NBP in stage 02.
Before 2019, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Finland led BIM publications, particularly in the infrastructure and road sectors. However, after 2019, this leadership began to extend to other countries, such as Hong Kong, Brazil, Norway, the United Arab Emirates, and others.
An interesting observation is that countries like Australia and the United Arab Emirates concentrated all their publications in the road sector from the outset. In contrast, Brazil, despite the importance of the road sector in the national transportation matrix, initially focused its publications on other infrastructure sectors, with the first publication in the road sector appearing only in 2022.
Another notable fact is that countries like Brazil, the United Arab Emirates, and Croatia, which began adopting BIM later, quickly advanced to stage 2 of maturity. This indicates that the stages of maturity do not necessarily follow a linear development sequence. It suggests a rapid acceptance of the benefits of BIM in these countries. In contrast, nations like Finland and the United States continue to publish material from stage 1, even after advancing to stage 2. This reinforces the idea that progression through maturity stages is not necessarily rigid.
The absence of publications in stage 3, even in countries with nearly a decade of BIM experience, such as the United Kingdom, Finland, and Denmark, reinforces the idea that the global BIM community still has much to explore to achieve higher levels of maturity.
This analysis of the origin of publications in the sector reveals the dynamic and evolutionary nature of BIM. Countries that started later have quickly advanced to stage 2, demonstrating a swift and effective adaptation to more advanced BIM practices. Additionally, this trend suggests a forecast of declining influence for the United Kingdom, historically a reference, due to a significant decrease in the quantity of publications in recent years.
Alongside the decline in UK publications, countries like Australia are emerging as potential future references. In contrast, Brazil, with speedy growth in publications, could also become a sectoral reference if it maintains the momentum of scientific and technical production.
5.5. Adherence to ISO 19.650
The ISO 19650 standard [30,56,57,58,59] plays a pivotal role in the BIM context by offering global guidelines for information management across asset life cycles. It establishes protocols for organizing, sharing and delivering information in construction and engineering projects that adopt the BIM methodology. This subsection presents an analysis assessing NBP’s adherence to ISO 19650 [30,56,57,58,59].
This adherence was verified through the presence of citations, concepts introduced by ISO, or explicit references. The result is presented in Figure 10.
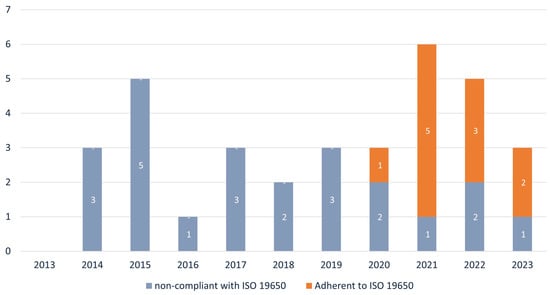
Figure 10.
Adherence to ISO 19.650 [30,56,57,58,59].
Since the standard was published in 2018, there has been a significant transition in NBP, demonstrating a rapid adoption of the principles and guidelines established in ISO. This fact emphasizes the relevance of ISO in the current scenario, where standards play a crucial role in guiding and continually improving the approaches adopted by professionals and researchers.
6. Conclusions
After conducting an SLR and studying NBPs, this research offers a comprehensive review of the initiatives aimed at implementing and advancing the BIM methodology in road infrastructure. The study begins by identifying and consolidating the distinctions between BIM applications in buildings and the transportation infrastructure sector, as succinctly outlined in Table 1.
In this study, priority was given to NBPs over the systematic review of the academic literature. These publications, resulting from collaborative efforts among academic, government and industrial entities, play a crucial role in the dissemination of knowledge, the guide to implementation and the definition of BIM requirements [28].
The continued growth in the number of publications, as depicted in Figure 3, and the expanded diversity of the origin countries signify increased awareness, acceptance, and interest in the BIM methodology within the road sector. This trend reinforces the understanding that BIM is a constantly expanding methodology [24].
Significant convergence was observed when comparing the leading countries in the publishing of academic articles and NBP in the road sector. The United States, the United Kingdom, and Australia have emerged as prominent leaders in this regard, indicating the alignment between industry practices and academia, positioning them as global references in BIM methodology for road infrastructure. In contrast, Spain, Italy, and Germany excel in academic production but do not feature prominently in the NBP landscape, implying a more experimental or research-focused development trajectory.
Finland presents an intriguing case with its pioneering adoption of BIM and substantial prominence in NBP production. However, its visibility in academic article production is not as widespread, with mention made only by Nascimento et al. [26]. It is noteworthy that many of the analyzed NBPs stem from doctoral theses and master’s dissertations, indicating alignment and synergy between the market and the academic sector, albeit with less emphasis on article production.
In terms of BIM maturity on the global scale, it was noted that the leading countries predominantly fall within stage 2 of maturity, with 2019 marking a transitional phase from the previous stage. Countries that have more recently adopted BIM, such as Brazil, the United Arab Emirates, and Croatia, have aimed to implement it at this stage, showcasing an updated understanding of the methodology. This trend signifies a positive direction for nations and institutions initiating BIM implementation to aspire directly for more advanced stages of maturity.
The concept of Open BIM is gaining traction worldwide and has become the subject of research in key countries such as Finland, Denmark, the United Kingdom, and Australia. This concept is closely related to the interoperability of data in sector projects. The adoption of the IFC schema has been highlighted in various academic publications, primarily due to its use as a basis for research and development and its alignment with sector expansions through schema updates. There is a growing trend toward adopting IFC as the standard language for file interoperability in the infrastructure sector.
The ISO 19650 standard [30,56,57,58,59] has been gaining increasing adherence globally since its publication. This trend reflects the need to align BIM protocols with international standards, a crucial step for consolidating BIM as the standard methodology in road infrastructure projects. The only notable exception to this adherence appears to be the Norwegian Public Roads Administration (NPRA), which has so far chosen not to adopt ISO 19650 [30,56,57,58,59].
This global panorama reflects the demand for standardization, collaboration, and innovation, positioning pioneering countries such as the United Kingdom, Norway, and Finland as models for others, while also highlighting emerging key countries in the sector, such as the United States and Australia. Rapid adaptation and compliance of initiatives with ISO 19650 [30,56,57,58,59], along with identification of the current stage of maturity of BIM, provides valuable guidelines for future research and policy development. Furthermore, this understanding enables the assessment of the current position of countries in the development of BIM within the sector.
The conclusions of this study have significant implications for road infrastructure professionals and policy makers. For professionals, it is essential to recognize the growing importance and acceptance of the BIM methodology, highlighting the need for familiarity and training in this area. From the policymakers’ perspective, a collaboration between academia, government, and industry is fundamental for disseminating knowledge, guiding implementation, and defining requirements for BIM.
Policymakers should also recognize the global trend of increasing interest in BIM for road infrastructure and consider policies to support and encourage the adoption of this methodology in public projects. Analyzing BIM maturity at the international level can guide the development of training policies to ensure that their countries are aligned with global best practices. Adhering to international standards, such as ISO 19650, is crucial for ensuring quality, efficiency, and collaboration in road infrastructure projects. Therefore, policymakers should promote compliance with these standards within their jurisdiction.
In summary, professionals and policymakers should be aware of the growing impact of BIM on road infrastructure, seek strategic collaborations, and adopt international best practices to enhance the efficiency and quality of projects in this critical sector.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, O.A.N.; writing—review and editing, O.A.N. and P.C.P.; Visualization, A.d.S.F.F.; Supervision, G.M.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AASHTO | American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials |
| AECO | Architecture, Engineering, Construction, and Operations |
| BEIS | Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy of United Kingdom |
| BIM | building information modeling |
| BSI | British Standards Institute |
| CDBB | Centre for Digital Built Britain |
| DER-PR | Department of Roads and Highways-Paraná |
| DFT | Department for Transport of United Kingdom |
| DNIT | National Department of Transport Infrastructure OF Brazil |
| DRD | Danish Road Directorate |
| DOAJ | Directory of open-access journals |
| FTIA | Väylävirasto or Finnish Transport Infrastructure Agency |
| FHWA | Federal Highway Administration |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| NBP | Noteworthy BIM Publications |
| RWS | Rijkswaterstaat or General Directorate of the Ministry of Infrastructure and Water Management of the Netherlands |
| UNECE | United Nations Economic Commission for Europe |
References
- Succar, B. Building Information Modelling Maturity Matrix. In Handbook of Research on Building Information Modelling and Construction Informatics: Concepts and Technologies; IGI Publishing: Hershey, PA, USA, 2010; pp. 65–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Joo, M. Building information modelling (BIM) framework for practical implementation. Autom. Constr. 2011, 20, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, S.L.M.; Siviero, L.F.; Freitas, R.D.O.; Corrêa, F.R.; Santos, E.T. BIM para infraestrutura de transportes. In Simpósio Brasileiro de Tecnologia da Informação e Comunicação na Construção; ANTAC: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Tang, F.; Ma, T.; Gu, L.; Tong, Z. Construction quality evaluation of asphalt pavement based on BIM and GIS. Autom. Constr. 2022, 141, 104398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiorno, N.; Bosurgi, G.; Carbone, F.; Pellegrino, O.; Sollazzo, G. Potentialities of a Highway Alignment Optimization Method in an I-BIM Environment. Period. Polytech. Civ. Eng. 2019, 63, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepa, J.J.; Pavôn, R.M.; Alberti, M.G.; Ciccone, A.; Asprone, D. A Review on the Implementation of the BIM Methodology in the Operation Maintenance and Transport Infrastructure. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoregie, A.; Turnbull, D.E. Highway infrastructure and Building Information Modelling in UK. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Munic. Eng. 2016, 169, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Ma, T.; Zhang, J.; Guan, Y.; Chen, L. Integrating three-dimensional road design and pavement structure analysis based on BIM. Autom. Constr. 2020, 113, 103152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; Laquidara-Carr, D.; Lorenz, A.; Buckley, B.; Barnett, S. The business value of BIM for infrastructure 2017. SmartMarket Report; Dodge Data & Analytics: Bedford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vitásek, S.; Zak, J. Cost estimating and building information modelling (BIM) in road construction. In Proceedings of the Creative Construction Conference 2018-Proceedings, Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 30 June–3 July 2018; pp. 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepa, J.J.; Pavôn, R.M.; Alberti, M.G.; Caramés, P. Towards BIM-GIS integration for road intelligent management system. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2023, 29, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, C.; Li, H.; Huijser, H.; Skitmore, M. Exploring an Interdisciplinary BIM-Based Joint Capstone Course in Highway Engineering. J. Civ. Eng. Educ. 2020, 146, 05020004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, H.Y.; Lopez, R.; Wan, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z. Comparative Analysis on the Adoption and Use of BIM in Road Infrastructure Projects. J. Manag. Eng. 2016, 32, 05016021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh, B.; Celik, T.; Karimi Ghaleh Jough, F.; Matthews, J.C. Road Map to BIM Use for Infrastructure Domains: Identifying and Contextualizing Variables of Infrastructure Projects. Sci. Iran. 2022, 29, 2803–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Lamallam, S.; Yaagoubi, R.; Sebari, I.; Doukari, O. Extending the IFC Standard to Enable Road Operation and Maintenance Management through OpenBIM. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.P.; Viana, F.; Cerqueira, A.; Souza, B. A tecnologia BIM como ferramenta de maximização de resultados. Rev. Interdiscip. Pensamento Científico 2019, 5. Available online: http://reinpec.cc/index.php/reinpec/article/view/307 (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Zheng, L.; Lu, W.; Chen, K.; Chau, K.W.; Niu, Y. Benefit sharing for BIM implementation: Tackling the moral hazard dilemma in inter-firm cooperation. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2017, 35, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, S.A.; Olusina, J.O.; Ngene, B.U.; Busari, A.A.; Adediran, J.; Eletu, A. Assessment of road infrastructure using remote sensing and GIS methodology for monitoring the condition of paved and unpaved roads. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 640, 012099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, A.; Li, H.; Lark, R.; Dunn, S. BIM for infrastructure: An overall review and constructor perspective. Autom. Constr. 2016, 71, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costin, A.; Adibfar, A.; Hu, H.; Chen, S.S. Building Information Modeling (BIM) for transportation infrastructure—Literature review, applications, challenges, and recommendations. Autom. Constr. 2018, 94, 257–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agdas, D.; Ellis, R.D. IT in transportation construction: Opportunities and barriers to implementation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering, Nottingham, UK, 30 June–2 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Eastman, C.M. (Ed.) BIM Handbook: A Guide to Building Information Modeling for Owners, Managers, Designers, Engineers and Contractors, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, D.R.D.C.; Felicetti, L.; Witiuk, R.; Gomes, S.; Miceli Junior, G.; Pellanda, P.C. Análise do nível de desenvolvimento requerido para modelagem em BIM de projetos de infraestrutura de transportes. In Proceedings of the 35° ANPET, virtual, 8–18 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, O.A.; Miceli Junior, G.; Pellanda, P.C. Estudo da expansão de pesquisas em BIM a partir de palavras-chave: Uma análise bibliométrica. In Simpósio Brasileiro de Tecnologia da Informação e Comunicação na Construção; ANTAC: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2023; Volume 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoli, C. A Guide to Conducting a Standalone Systematic Literature Review. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2015, 37, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo Simões, C.R.S.; dos Santos, G.J.R.; de Almeida-Filho, A.T.; Palha, R.P. BIM para infraestruturas rodoviárias: Uma revisão sistemática. In ImpóSio Brasileiro de Tecnologia da Informação e Comunicação na Construção; ANTAC: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2023; Volume 4, pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strieder, H.L.; Schreinert, G.G. Metodologia BIM em obras de infraestrutura: Uma revisão sistemática. In Proceedings of the 47th Reunião Anual de Pavimentação (RAPv), Bento Gonçalves, Brazil, 9–12 August 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kassem, M.; Succar, B.; Dawood, N. Building Information Modeling: Analyzing Noteworthy Publications of Eight Countries Using a Knowledge Content Taxonomy. In American Society of Civil Engineers; Teesside University: Middlesbrough, UK, 2015; pp. 329–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, M.; Melo, R.; Giesta, J.; Santos, D. Characterization of the use of BIM in the Brazilian states Rio Grande do Norte e Paraiba. In Proceedings of the 37th CIB W78 Information Technology for Construction Conference (CIB W78), São Paulo, Brazil, 2–4 June 2020; pp. 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 19650-1; 2018 Organization and Digitization of Information about Buildings and Civil Engineering Works, Including Building Information Modelling (BIM)—Information Management Using Building Information Modelling—Part 1: Concepts and Principles. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- BSI 1192:2007; Collaborative Production of Architectural, Engineering and Construction Information-Code of Practice. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2007.
- PAS 1192-3:2014; Specification for Information Management for the Operational Phase of Assets Using Building Information Modelling. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2014.
- PAS 1192-2:2015; Specification for information management for the capitaldelivery phase of construction projects using building information modelling. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2015.
- PAS 1192-5:2015; Specification for Security-Minded Building Information Modelling, Digital Built Environments and Smart Asset Management. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2015.
- Cheng, J.C.P.; Lu, Q.; Student, M.P. A review of the efforts and roles of the public sector for BIM adoption worldwide. J. Inf. Technol. Constr. 2015, 20, 442–478. [Google Scholar]
- National BIM Guidelines and Case Studies for Infrastructure. 2017. Available online: https://sbenrc.com.au/app/uploads/2013/10/National-BIM-Guidelines-FINAL.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Gelder, J. Asset Data Harmonisation Stage III: BIM IFC Alignment Review; Austroads: Sydney, Australia, 2018; Available online: https://austroads.com.au/publications/asset-management/ap-t333-18 (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Powers, N. Guide to Project Delivery Part 2: Planning and Control; Austroads: Sydney, Australia, 2018; Available online: https://austroads.com.au/publications/project-delivery/agpd02 (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Building Information Modelling (BIM) for Transport and Main Roads. Queensland Government, Australia, 2021. Available online: https://www.tmr.qld.gov.au/business-industry/Technical-standards-publications/Building-Information-Modelling (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Caderno de requisitos técnicos BIM do DNIT. Departamento nacional de Infraestrutura de Transporte, Brasil, 2023. Available online: https://www.gov.br/dnit/pt-br/assuntos/planejamento-e-pesquisa/bim-no-dnit/mosaico-de-servicos/documentos-tecnicos-bim/CRTBIM_V012022.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Manual BIM para Desenvolvimento de Projetos de Urbanismo e Infraestrutura. Secretaria de Obras e Infraestrutura do Distrito Federal, Brasil, 2023. 2020. Available online: https://www.so.df.gov.br/wp-conteudo/uploads/2023/08/MANUAL_BIM_R07_03_01_23__Versao_Final-1.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Filip, A.; Zlata, D.A.; Anton, E.; Dražen, G.; Mirko, G. Smjernice za BIM Pristup u Infrastrukturnim Projektima; Hrvatska Komora Inženjera Građevinarstva: Zagreb, Croatia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, P.B.; Breiner, O.M.; Pape, D.W. A Practical Guide to BIM in Construction and Infrastructure Projects; MTHojgaard: Søborg, Denmark, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- BIM Documentation Guidelines for Infrastructure; Department of Municipalities and Transport: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2020. Available online: https://www.dmt.gov.ae/adm/-/media/Project/DMT/ADM/E-Library/0001-Jan-2022-Doc/ADM-BIM-002Documentation-Guidelines-for-Infrastructure-projects.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Saarnikko, J. BIM Guidelines for Bridges. Finnish Transport Infrastructure Agency, Finland, 2014. Available online: https://ava.vaylapilvi.fi/ava/Julkaisut/Liikennevirasto/lo_2014-06eng_bim_guidelines_web.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Oy, S.S.D. Common InfraBIM Requirements-YIV2015; buildingSMART: Helsinki, Finland, 2015; Available online: https://wiki.buildingsmart.fi/en/04_Guidelines_and_Standards/COBIM_Infra_Requirements (accessed on 6 July 2023).
- Common InfraBIM Requirements-YIV2015-Managing Model Based Project. buildingSMART: Finland, 2015. Available online: https://wiki.buildingsmart.fi/en/04_Guidelines_and_Standards/COBIM_Infra_Requirements (accessed on 9 July 2023).
- Common InfraBIM Requirements-Data Exchange Requirements for Handover Material. buildingSMART: Finland, 2019. Available online: https://wiki.buildingsmart.fi/en/04_Guidelines_and_Standards/COBIM_Infra_Requirements (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Common InfraBIM Requirements-YIV 2019-General Inicial Data Design Construction. buildingSMART: Finland, 2019. Available online: https://wiki.buildingsmart.fi/en/04_Guidelines_and_Standards/COBIM_Infra_Requirements (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Sinikka, K. Väyläviraston ohjeita 32/2022. Finnish Transport Infrastructure Agency, Finland, 2022. Available online: https://ava.vaylapilvi.fi/ava/Julkaisut/Vaylavirasto/vo_2022-32_inframallivaatimukset.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Manual R110. Statens Vegvesen, Norway, 2023. Available online: https://store.vegnorm.vegvesen.no/r110 (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Håndbok for Digital Planlegging-Veiledning; Bane NOR: Oslo, Norway, 2022.
- Status of LOD and Related Work at Nordic Infrastructure Clients; Nordic Road & Rail BIM Colanoration: Norway, 2022; Available online: https://www.bimalliance.se/media/dgulrzt3/nbc-report-status-of-lod-and-related-work-at-nordic-infrastructure-clients.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Building Information Modeling (BIM) Practices in Highway Infrastructure; US Department of Transportation: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2021.
- BS 1192-4:2014; Collaborative Production of Information—Part 4: Fulfilling Employer’s Information Exchange Requirements Using COBie—Code of Practice. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2014.
- ISO 19650-2: 2018; Organization and Digitization of Information about Buildings and Civil Engineering Works, Including Building Information Modelling (BIM)—Information Management Using Building Information Modelling—Part 2: Delivery Phase of the Assets. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- ISO 19650-3: 2020; Organization and Digitization of Information about Buildings and Civil Engineering Works, Including Building Information Modelling (BIM)—Information Management Using Building Information Modelling—Part 3: Operational Phase of the Assets. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- ISO 19650-4: 2022; Organization and Digitization of Information about Buildings and Civil Engineering Works, Including Building Information Modelling (BIM)—Information Management Using Building Information Modelling—Part 4: Information Exchange. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- ISO 19650-5: 2020; Organization and Digitization of Information about Buildings and Civil Engineering Works, Including Building Information Modelling (BIM)—Information Management Using Building Information Modelling—Part 5: Security-Minded Approach to Information Management. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Maier, F.; Chummers, L.E.; Pulikanti, S.; Struthers, J.Q.; Mallela, J.; Morgan, R.H. Utilizing 3D Digital Design Data in Highway Construction-Case Studies; Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, F. Automation in Highway Construction Part II: Design Guidance and Guide Specification Manual; Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Effective Use of Geospatial Tools in Highway Construction; U.S. Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- Wood, N.C. Advancing the Development and Deployment of BIM Background for Infrastructure; Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, N.C. The Dimensions of BIM for Infrastructure; Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Biancardo, S.A.; Viscione, N.; Cerbone, A.; Dessì, E. BIM-Based Design for Road Infrastructure: A Critical Focus on Modeling Guardrails and Retaining Walls. Infrastructures 2020, 5, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.; Williges, C.; Messner, J. Cooperative Research Program Division; Transportation Research Board; National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. In Lifecycle Building Information Modeling for Infrastructure: A Business Case for Project Delivery and Asset Management; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimenić, D. Building Information Modelling (BIM) for Road Infrastructure: TEM Requirements and Recommendations; United Nations Economic Commission for Europe: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Salzano, A.; Intignano, M.; Mottola, C.; Biancardo, S.A.; Nicolella, M.; Dell’Acqua, G. Systematic Literature Review of Open Infrastructure BIM. Buildings 2023, 13, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignali, V.; Acerra, E.M.; Lantieri, C.; Di Vincenzo, F.; Piacentini, G.; Pancaldi, S. Building information Modelling (BIM) application for an existing road infrastructure. Autom. Constr. 2021, 128, 103752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, C.; Teicholz, P.; Sacks, R.; Liston, k. BIM Handbook: A Guide to Building Information Modeling; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 12006-3:2007; Building Construction-Organization of Information about Construction Works—Part 3: Framework for Object-Oriented Information. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- ISO 16739:2013; Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) for Data Sharing in the Construction and Facility Management Industries. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- Ribeiro, S.A.; Krauss, P.F. Análise comparativa entre versões de arquivos IFC utilizando a verificação de interferência. In Proceedings of the SBTIC, Campinas, Brazil; 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).