The Historical and Cultural Value of RC Constructions and the Main Critical Issues for Rehabilitation
Abstract
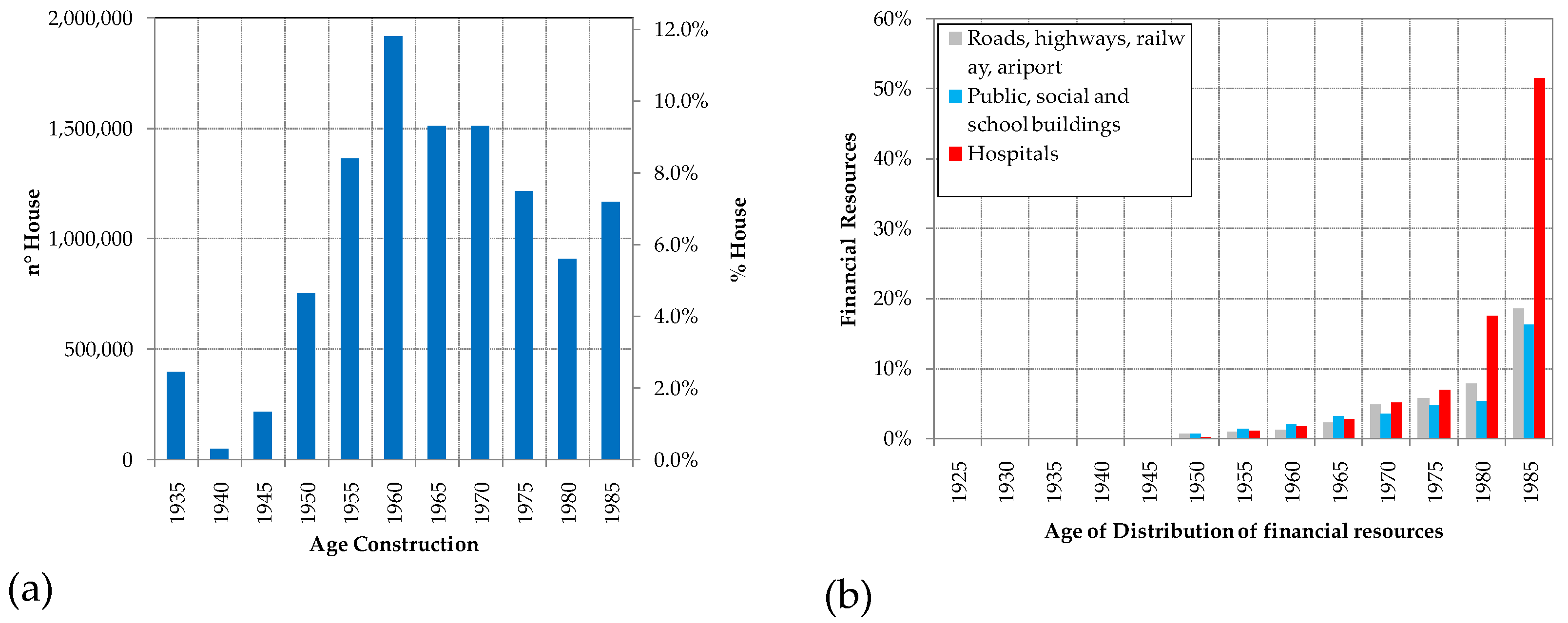
1. Introduction
2. RC Buildings and Civil Engineering Works: Cultural and Historical Value
3. Methodological Approach for Retrofitting
- −
- Social sustainability (safety of the buildings and civil engineering works).
- −
- Economic sustainability (enhancement of the buildings and civil engineering works).
- −
- Environmental sustainability (for example, the energy performance of the buildings).
- Construction technologies, design standards and methodologies, procedures, design loads, construction details, design working life and durability, materials, etc., which are noticeably different from the forecasts of current codes.
- Durability (without significant loss of utility) and maintenance programs are inconsistent with the requirements of current regulations. As a consequence, a high level of degradation is usually detectable.
- Buildings and civil engineering works without required performances for public safety.
- Lack of methods and reliable procedures for decision making.
- −
- Original procedures for design;
- −
- Reconstruction of the history, the state of use and maintenance, as well as of the seismic events and/or other events of particular importance that affected the structure;
- −
- Presence of any conditions of damage and/or degradation and their evolution, particularly for corrosion.
Statement of Objectives
- Seismic and gravity loads structural assessment;
- Comparison of different retrofit strategies;
- Selection of an optimal retrofit strategy based on the results of the assessment.
- −
- Modification of the structural system to obtain a more favorable dynamic behavior;
- −
- Addition of new structural elements;
- −
- Strengthening of some structural elements to sustain seismic actions through steel jacketing and bracing system for the seismic protection of RC structures;
- −
- Efficient and quick strengthening of RC slabs for gravity loads, for example, based on external unbounded post-tensioning;
- −
- Elimination of degradation and deterioration effects (mainly due to corrosion).
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dolce, M.; Di Bucci, D. Comparing recent Italian earthquakes. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2015, 15, 497–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Ludovico, M.; Prota, A.; Moroni, C.; Manfredi, G.; Dolce, M. Reconstruction process of damaged residential buildings outside historical centres after the L’Aquila earthquake: Part II—Heavy damage reconstruction. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2017, 15, 693–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vona, M.; Harabaglia, P.; Murgante, B. Thinking about resilience cities studying Italian earthquake. Urban Des. Plan. 2016, 169, 185–199. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorento, G.; Forte, A.; Pagano, E.; Sabetta, F.; Baggio, C.; Lavorato, D.; Nuti, C.; Santini, S. Damage patterns in the town of Amatrice after August 24th 2016 Central Italy earthquakes. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 16, 1399–1423. [Google Scholar]
- CEN. European Standard EN 1998-3-2005; Eurocode 8: Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance–Part 3: Assessment and Retrofitting of Buildings. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2005.
- Payá-Zaforteza, I.; Garlock, M. Eminent Structural Engineer: David, P. Billington (1927–2018). Inspiring Generations Through the Integration of Engineering and Art. Struct. Eng. Int. 2018, 29, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ordóñez, D. Eugène Freyssinet: “I Was Born a Builder”. Tagungsband. In 28. Dresdner Brückenbau Symposium; Institutfür Massivbau Freunde des Bauingenieurwesense. e.V. TUDIAS: Dresdner, 2018; pp. 101–129. ISSN 1613-1169. ISBN 978-3-86780-544-5. [Google Scholar]
- Espion, B. Thin concrete shells by Eugène Freyssinet. In Building Knowledge, Constructing Histories, Proceedings of the 6th International Congress on Construction History (6ICCH 2018), Brussels, Belgium, 9–13 July 2018; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 199–206, ISBN13: 978-1-138-58414-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun, E.P.G. Robert Maillart: The evolution of RC bridge forms. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Short and Medium Span Bridges, Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–18 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
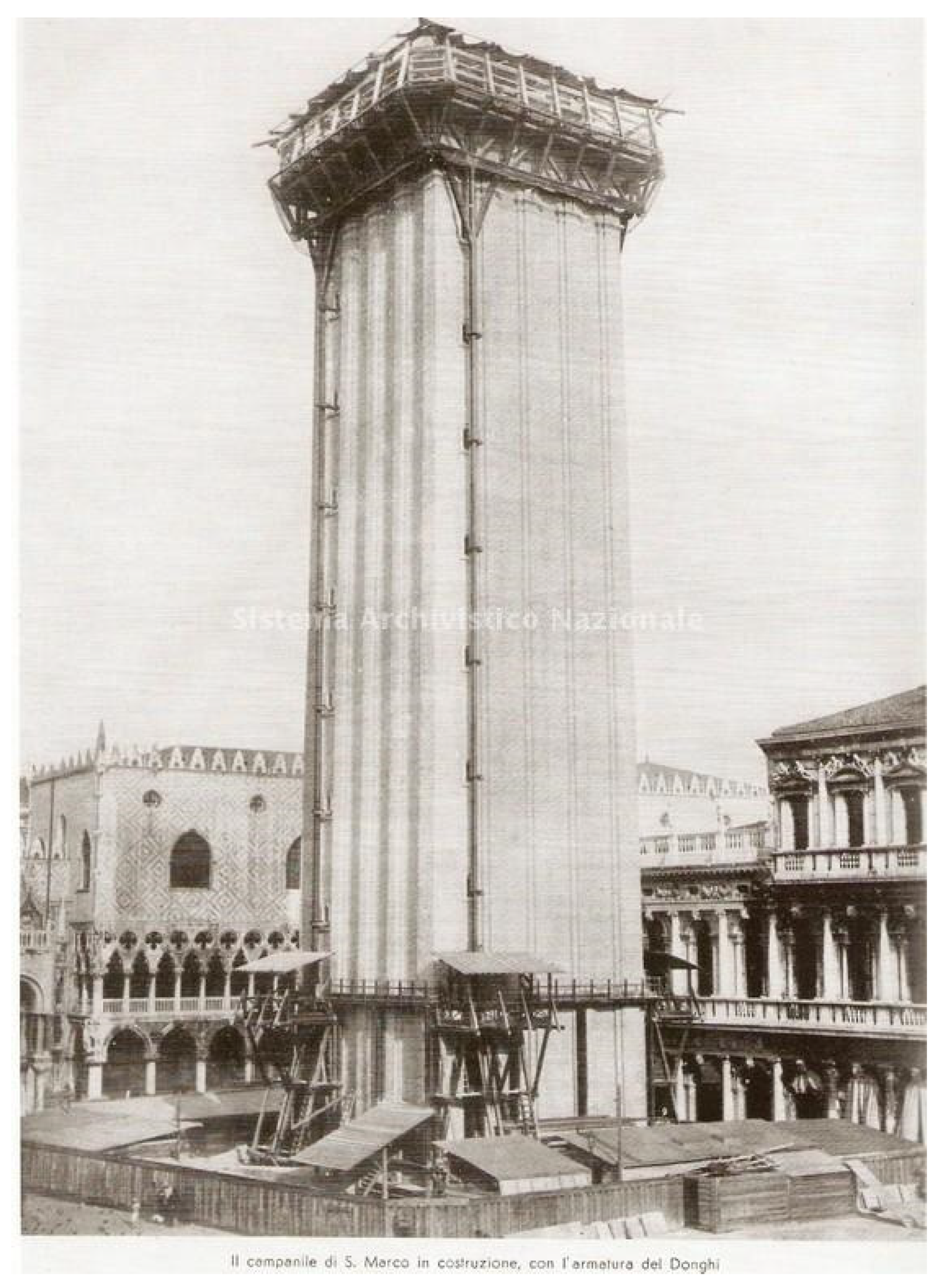
- Macchi, G.; Macchi, S.; Jamiolkowski, M.; Pastore, V.; Vanni, D. Strengthening of the San Marco Bell Tower Foundation in Venice, Geotechnics and Heritage; Bilotta, E., Flora, A., Lirer, S., Viggiani, C., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-1-138-00054-4. [Google Scholar]
- Royal Decree n. 2229. Design Code of Reinforced Concrete Structures. 1939. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Iori, T. L’ingegneria italiana del dopoguerra: Appunti per una storia. In Teoria e Saperi del Costruire: Saperi, Strumenti, Modelli; Mochi, G., Ed.; ITA–EdizioniModerna: Bologna, Italy, 2005; pp. 763–772. [Google Scholar]
- Iori, T. Engineers in Italian architecture. The role of RC in the first half of the twentieth century. In Proceedings of the Second International Congress on Construction History, Queens’ College, Cambridge University, Cambridge, UK, 29 March–2 April 2006; EXETER; Short Run Press Exeter: UK, 2006; Volume 2, pp. 1981–1995. [Google Scholar]
- Iori, T. Il boom dell’ingegneria italiana: Il ruolo di Gustavo Colonnetti e Arturo Danusso. In Storia dell’ingegneria, atti del 2° Convegno Nazionale; D’Agostino, S., Ed.; ITA–Cuzzolineditore: Napoli, Italy, 2008; pp. 1501–1510. [Google Scholar]
- Iori, T.; Poretti, S. Tra scienza e tecnica. Storia della scuola italiana di Ingegneria. L’IndustriaDelleCostr. 2014, 438, 96–107. [Google Scholar]
- Iori, T.; Poretti, S. The language of Structures. The Italian school of engineering. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Congress on Construction History, Chicago, IL, USA, 3–7 June 2015; Bowen, B., Leslie, F.T., Ochsendorf, J., Eds.; Construction History Society of America: Chicago, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 2, pp. 347–354. [Google Scholar]
- Verderame, G.M.; Manfredi, G.; Frunzio, G. Le proprietà meccaniche dei calcestruzzi impiegati nelle strutture in cemento armato realizzate negli anni ’60. X Convegno nazionale “L’Ingegneria Sismica in Italia”. Potenza and Matera, 2001. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Elfgren, L.; Thun, H.; Ohlsson, U. Concrete strength in old Swedish concrete bridges. Nord. Concr. Res. 2006, 35, 47–60. [Google Scholar]
- Marie-Victoire, E.; Cailleux, E.; Texier, V. Carbonation and historical buildings made of concrete. J. De Phys. IV (Proc.) 2006, 136, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courard, L.; Gillard, A.; Darimont, A.; Bleus, J.M.; Paquet, P. Pathologies of concrete in Saint-Vincent Neo-Byzantine Church and Pauchot reinforced artificial stone. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 34, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carsana, M.; Gastaldi, M.; Redaelli, E. A case study on corrosion conditions and guidelines for repair of a reinforced concrete chimney in industrial environment. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, S. Modern matters: Breaking the barriers to conserving modern heritage. In Conservation Perspectives 49. The GCI Newsletter; Getty Conservation Institute: Suite, LA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Havinga, L.; Colenbrander, B.; Schellen, H. Heritage significance and the identification of attributes to preserve in a sustainable refurbishment. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 43, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidelöw, S.; Örn, T.; Luciani, A.; Rizzo, A. Energy-efficiency measures for heritage buildings: A literature review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 45, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosoarca, M.; Victor, G. Structural safety of historical buildings made of reinforced concrete, from Banat region–Romania. J. Cult. Herit. 2013, 14, e29–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena-Cruz, J.; Ferreira, R.M.; Ramos, L.F.; Fernandes, F.; Miranda, T.; Castro, F. Luiz Bandeira bridge: Assessment of a historical reinforced concrete (RC) bridge. Int. J. Arch. Herit. 2013, 7, 628–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onysyk, J.; Onysyk, J.; Biliszczuk, J.; Prabucki, P.; Sadowski, K.; Toczkiewicz, R. Strengthening the 100-year-old reinforced concrete dome of the Centennial Hall in Wrocław. Struct. Concr. 2014, 15, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Marcos, J.; San-José, J.T.; Garmendia, L.; Santamaría, A.; Manso, J.M. Central lessons from the historical analysis of 24 reinforced-concrete structures in northern Spain. J. Cult. Herit. 2016, 20, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, L.G.; Rodríguez, I.-M.; Arlanzón, N.L.; Blanco, E.B. Damage assessment and conservation strategy for the largest covered market in Europe: The Ribera Market (Bilbao). Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2018, 12, 997–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriadis, K.; Aspiotis, K.; Mazur, A.; Tolstoy, P.; Badogiannis, E.; Tsivilis, S. Characterization of Old Concrete from a Heritage Structure of Inousses Cluster of Islands. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Protection of Historical Constructions PROHITECH 2021, Athens, Greece, 25–27 October 2021; pp. 80–89. [Google Scholar]
- Mitoulis, S.A.; Domaneschi, M.; Cimellaro, G.P.; Casas, J.R. Bridge and transport network resilience–A perspective. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Bridge Eng. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carsana, M.; Biondini, F.; Redaelli, E.; Valoti, D.O. On-Site Corrosion Characterization of 50-Year-Old PC Deck Beams. In Proceedings of the 1st Conference of the European Association on Quality Control of Bridges and Structures, Padova, Italy, 29 August–1 September 2021; pp. 954–961. [Google Scholar]
- Malomo, D.; Scattarreggia, N.; Orgnoni, A.; Moratti, M.; Calvi, G.M. Numerical Study on the Collapse of the Morandi Bridge. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2020, 34, 04020044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondini, F.; Manto, S.; Beltrami, C.; Panseri, L.; Quaranta, L. BRIDGE|50 research project: Residual structural performance of a 50-year-old bridge Bridge Maintenance, Safety, Management, Life-Cycle Sustainability and Innovations. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Bridge Maintenaince, Safety and Management, IABMAS, Sapporo, Japan, 28 June–2 July 2021; pp. 3337–3344. [Google Scholar]
- Cimellaro, G.P.; Arcidiacono, V.; Reinhorn, A.M. Disaster Resilience Assessment of Building and Transportation System. J. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 25, 703–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgese, M.; Ansari, F.; Domaneschi, M.; Cimellaro, G.P. Post-collapse analysis of Morandi’sPolcevera viaduct in Genoa Italy. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2020, 10, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarsiero, G.; Masi, A.; Picciano, V. Durability of Gerber saddles in RC bridges: Analyses and applications (Musmeci Bridge, Italy). Infrastructures 2021, 6, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vona, M.; Anelli, A.; Mastroberti, M.; Murgante, B.; Santa-Cruz, S. Prioritization strategies to reduce the seismic risk of the public and strategic buildings. Disaster Adv. 2017, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Santa-Cruz, S.; Palomino, J.; Liguori, N.; Vona, M.; Tamayo, R. Seismic Risk Assessment of Hospitals in Lima City Using GIS Tools. In Computational Science and Its Applications–ICCSA 2017; Springer: Cham, Switherlands, 2017; Volume 10406, pp. 354–367. [Google Scholar]
- Anelli, A.; Santa-Cruz, S.; Vona, M.; Tarque, N.; Laterza, M. A proactive and resilient seismic risk mitigation strategy for existing school buildings. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2018, 15, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decreto Legislativo 22 gennaio 2004, n. 42. Codice dei Beni Culturali e del Paesaggio, ai Sensi Dell’articolo 10 Della Legge 6 Luglio 2002, n. 137. G.U. n. 45 del 24 Febbraio 2004, s.o. n. 28(In Italian). Available online: https://www.bosettiegatti.eu/info/norme/statali/2004_0042.htm (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- Ribera, F.; Nesticò, A.; Cucco, P.; Maselli, G. A multicriteria approach to identify the Highest and Best Use for historical buildings. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 41, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anelli, A.; Vona, M.; Santa-Cruz, S. Comparison of different intervention options for massive seismic upgrading of essential facilities. Buildings 2020, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vona, M.; Flora, A.; Carlucci, E.; Foscolo, E. Seismic retrofitting resilience-based for strategic RC buildings. Buildings 2021, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, A.; Vona, M. Estimation of the In-Situ Concrete Strength: Provisions of the European and Italian Seismic Codes and Possible Improvements. In Proceedings of the Final Conference of ReLUIS-DPC 2005–2008 Project, Napoli, Italy, 1–3 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Vona, M.; Nigro, D. Evaluation of the predictive ability of the in situ concrete strength through core drilling and its effects on the capacity of the RC columns. Mater. Struct. Mater. Constr. 2015, 48, 1043–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, A.; Chiauzzi, L. An experimental study on the within-member variability of in situ concrete strength in RC building structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellebois, A.; Launoy, A.; Pierre, C.; De Lanève, M.; Espion, B. 100-year-old Hennebique concrete, from composition to performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 44, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vona, M. A review of experimental results about in situ concrete strength. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 773, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, M.; Tanganelli, M.; Viti, S. Variability in concrete mechanical properties as a source of in-plan irregularity for existing RC framed structures. Eng. Struct. 2014, 59, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quagliarini, E.; Clementi, F.; Maracchini, G.; Monni, F. Experimental assessment of concrete compressive strength in old existing RC buildings: A possible way to reduce the dispersion of DT results. J. Build. Eng. 2016, 8, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, L.; Carsana, M.; Redaelli, E. Conservation of historical reinforced concrete structures damaged by carbonation induced corrosion by means of electrochemical realkalisation. J. Cult. Herit. 2008, 9, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, L.; Carsana, M.; Gastaldi, M.; Lollini, F.; Redaelli, E. Corrosion assessment and restoration strategies of reinforced concrete buildings of the cultural heritage. Mater. Corros. 2011, 62, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronelli, D.; Gambarova, P.G. Structural Assessment of Corroded Reinforced Concrete Beams: Modeling Guidelines. ASCE J. Struct. Eng. 2004, 130, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, J.; Plizzari, G.A.; Du, Y.; Law, D.W.; Franzoni, C. Mechanical properties of corrosion-damaged reinforcement. ACI Mater. J. 2005, 102, 256–264. [Google Scholar]
- Broomfield, J.P. Corrosion of Steel in Concrete: Understanding, Investigation and Repair, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis Ltd.: London, UK, 2006; ISBN13: 978-0415334044. [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi, Z.; Valente, C.; Pardi, L. A simplified methodology for the evaluation of the residual life of corroded elements. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2008, 4, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, M.; Tanner, P.; Andrade, C. Bond Response in Structural Concrete with Corroded Steel Bars. Experimental Results, Modelling of Corroding Concrete Structures. In Proceedings of the Joint Fib-RILEM Workshop; RILEM Bookseries; Madrid, Spain, 22–23 November 2010, 2011; Volume 5, pp. 231–241. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, Y.; Tsai, L.; Chen, H. Cyclic performance of large-scale corroded reinforced concrete beams. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2012, 41, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardone, D.; Perrone, G.; Sofia, S. Experimental and numerical studies on thecyclic behavior of R/C hollow bridge piers with corroded rebars. Earthq. Struct. 2013, 4, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiu, C.Y. Building depreciation and sustainable development. J. Build. Apprais. 2007, 3, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Manganelli, B. Maintenance, building depreciation and land rent. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 357–360, 2207–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, M.N.; Rosli, M.Z.R.; Hamid, M.; Zakaria, M.A.; Deraman, R. Deferred maintenance of buildings: A review paper. In Proceedings of the 10th Asia Pacific Structural Engineering and Construction Conference, Langkawi, Malaysia, 13–15 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Knight, J.R.; Sirmans, C.F. Depreciation, Maintenance, and Housing Prices. J. Hous. Econ. 1996, 5, 369–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manganelli, B.; Vona, M.; De Paola, P. Evaluating the cost and benefits of earthquake protection of buildings. J. Eur. Real Estate Res. 2018, 11, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaccone, D.; Fanelli, P.; Santamaria, U. Influence of the geometric model on the structural analysis of architectural heritage. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 43, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vona, M.; Cascini, G.; Mastroberti, M.; Murgante, B.; Nolè, G. Characterization of URM buildings and evaluation of damages in a historical center for the seismic risk mitigation and emergency management. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2017, 24, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toni, E.; Cello, G. Spatiotemporal evolution of the Central Apennines fault system (Italy). J. Geodyn. 2003, 36, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulargia, F.; Stark, P.B.; Robert, J.; Geller, R.J. Why is Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis (PSHA) still used? Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2017, 264, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerial Decree 58/2017. Sisma Bonus—Linee Guida per la Classificazione del Rischio Sismico delle Costruzioni Nonché le Modalità per L’attestazione, da Parte di Professionisti Abilitati, Dell’efficacia Degli Interventi Effettuati; Ministero delle Infrastrutture e dei Trasporti: Rome, Italy, 2017. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vona, M.; Manganelli, B. The Historical and Cultural Value of RC Constructions and the Main Critical Issues for Rehabilitation. Infrastructures 2022, 7, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures7030035
Vona M, Manganelli B. The Historical and Cultural Value of RC Constructions and the Main Critical Issues for Rehabilitation. Infrastructures. 2022; 7(3):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures7030035
Chicago/Turabian StyleVona, Marco, and Benedetto Manganelli. 2022. "The Historical and Cultural Value of RC Constructions and the Main Critical Issues for Rehabilitation" Infrastructures 7, no. 3: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures7030035
APA StyleVona, M., & Manganelli, B. (2022). The Historical and Cultural Value of RC Constructions and the Main Critical Issues for Rehabilitation. Infrastructures, 7(3), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures7030035






