Long-Term Behaviour of Padded Concrete Sleepers on Reduced Ballast Bed Thickness
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Description of the Test Section
2.2. Track Quality Assessment
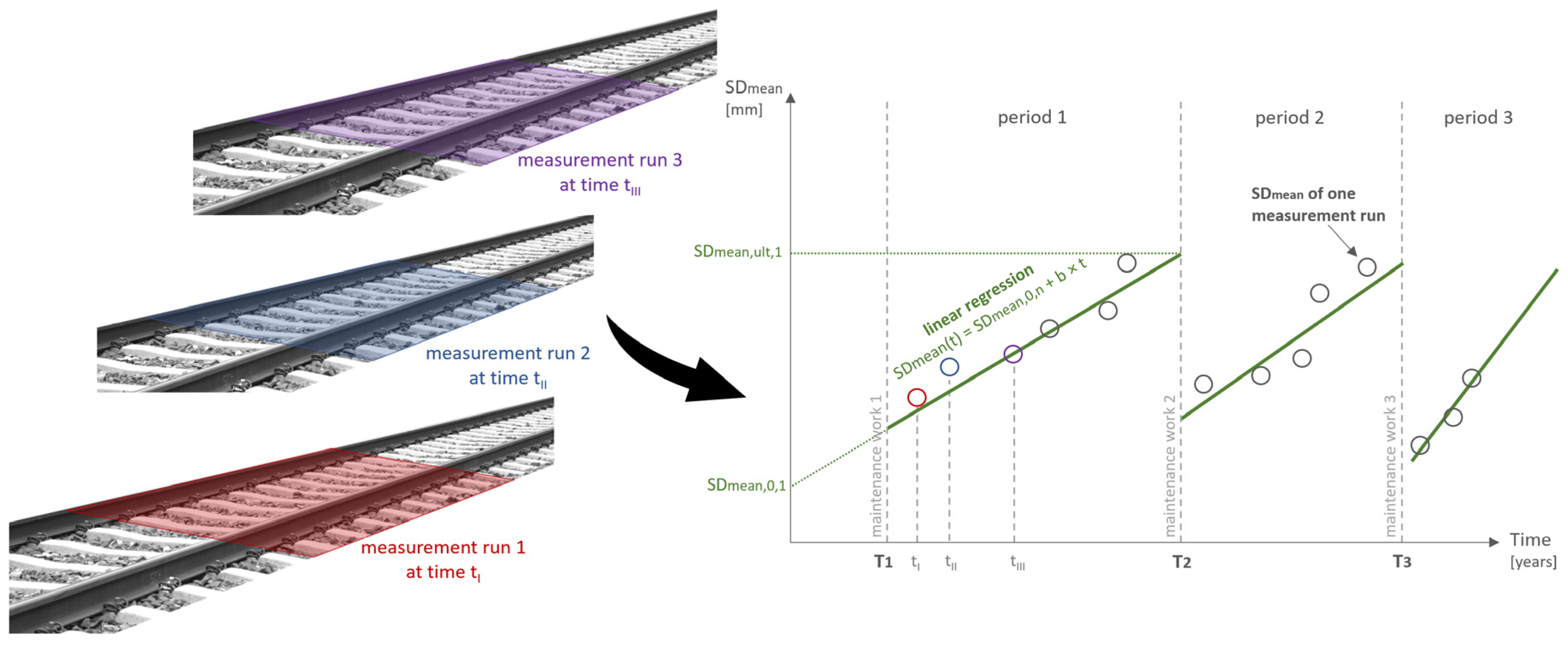
2.2.1. Standard Deviation of the Longitudinal Level
2.2.2. Time Series Analyses
2.2.3. Fractal Analysis
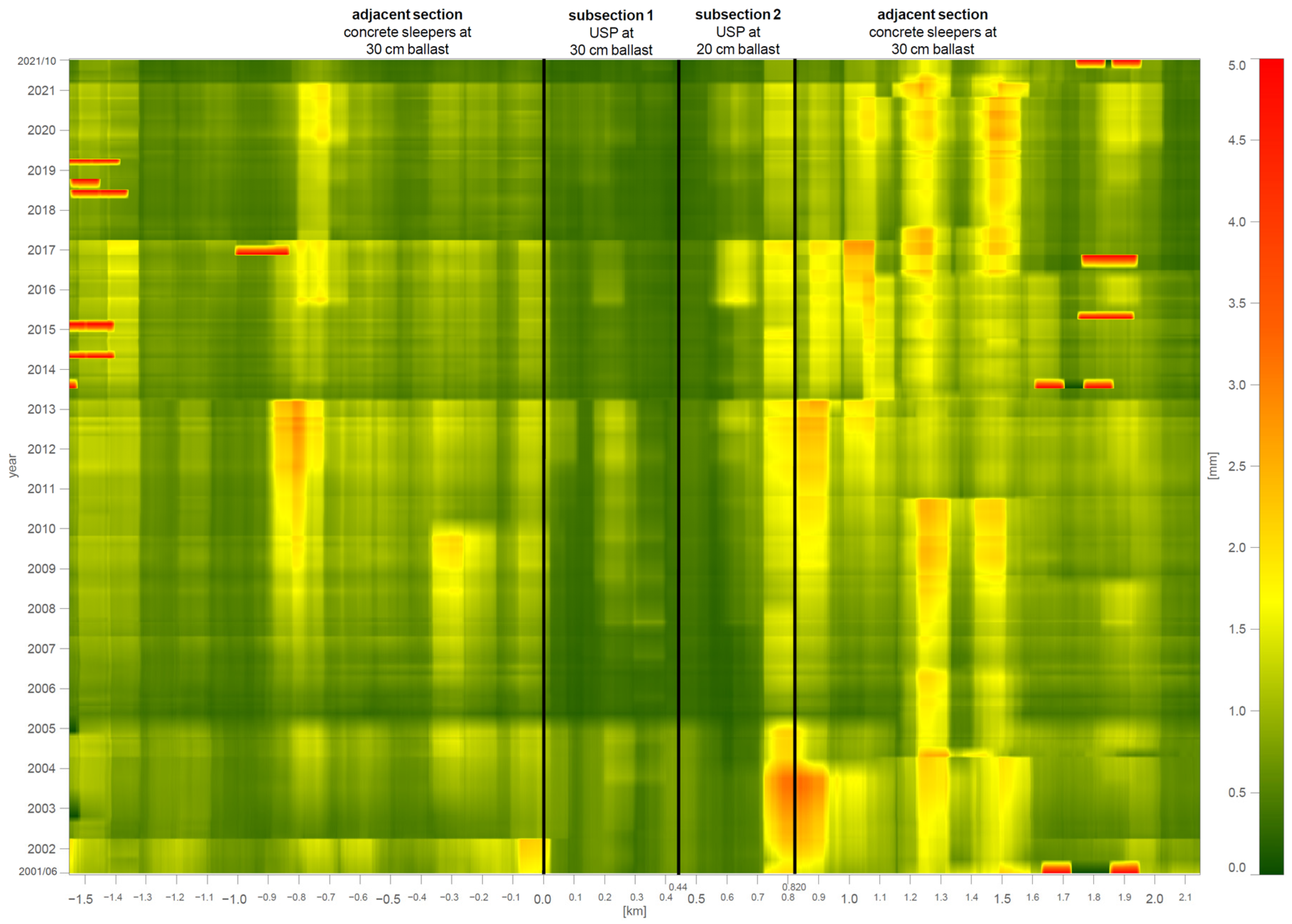
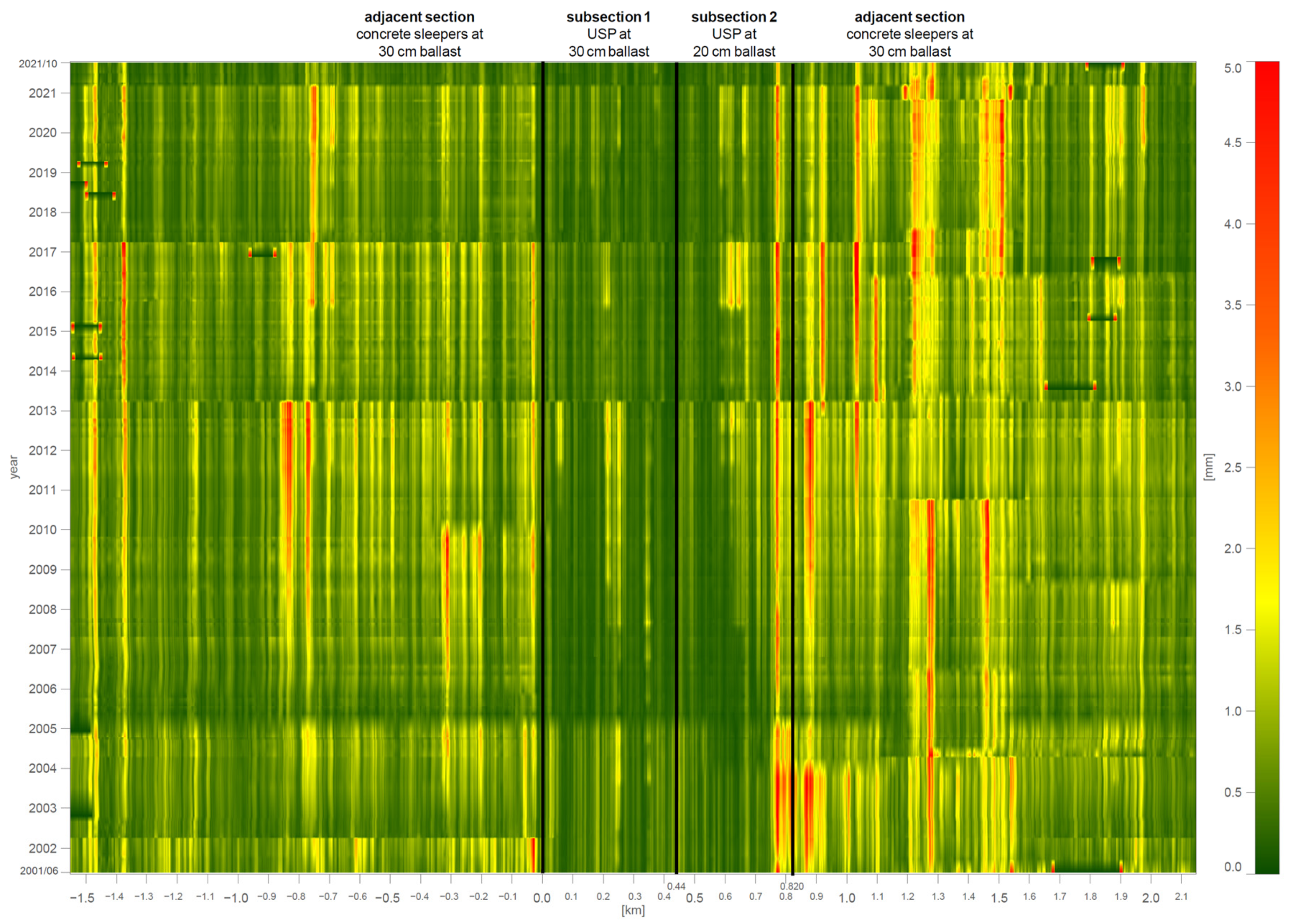
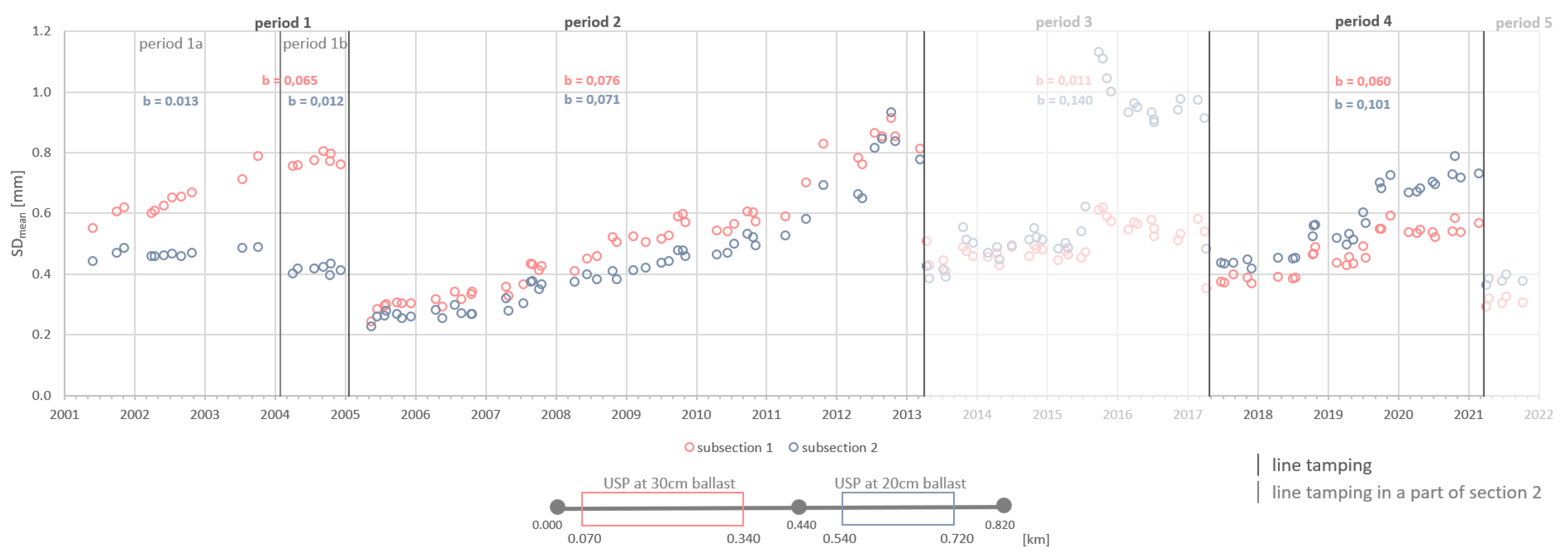
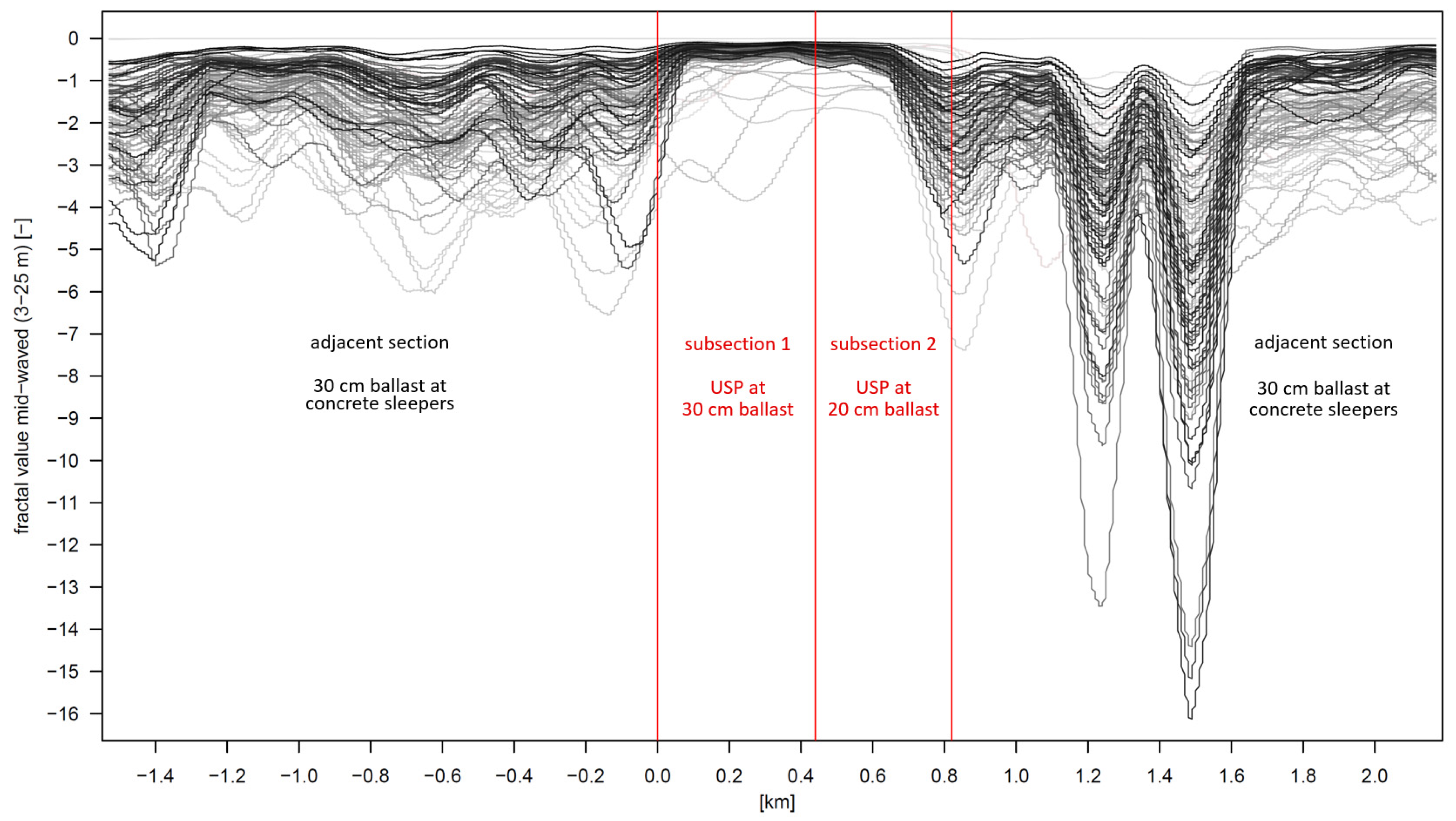
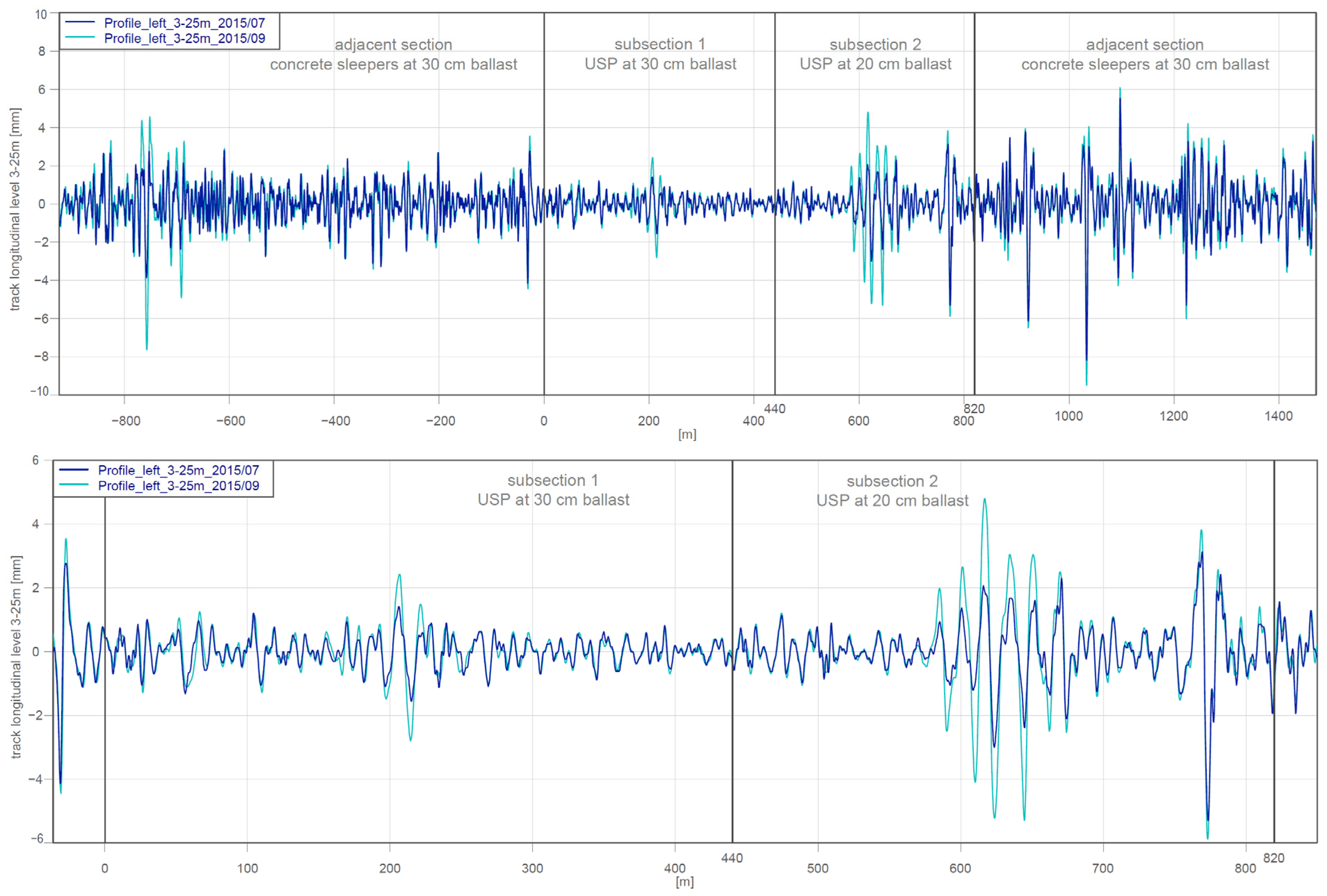
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferdous, W.; Manalo, A. Failures of mainline railway sleepers and suggested remedies—Review of current practice. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2014, 44, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-sayed, H.M.; Fayed, M.N.; Riad, H.S.; Zohny, H.N. A review of the structural performance of prestressed monoblock concrete sleepers in ballasted railway tracks. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 140, 106522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, E.; Ito, K.; Hayano, K.; Momoya, Y. A new approach for evaluating lateral resistance of railway ballast associated with extended sleeper spacing. Soils Found. 2021, 61, 1565–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, V. Untersuchungen zu Schwellenbesohlungen im Oberbau. Ph.D. Thesis, Graz University of Technology, Graz, Austria, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Berghold, A. Behaviour of different types of ballasted track with and without under sleeper pads. ZEVRail 2016, 140. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, T.; le Pen, L.; Zervos, A.; Powrie, W. Measuring the area and number of ballast particle contacts at sleeper/ballast and ballast/subgrade interfaces. IJRT 2015, 4, 45–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Suhr, B.; Marschnig, S.; Dietmaier, P.; Marte, C.; Six, K. Micro-mechanical investigation of railway ballast behavior under cyclic loading in a box test using DEM: Effects of elastic layers and ballast types. Granul. Matter 2019, 21, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, F.; Schilder, R. Technische und wirtschaftliche Aspekte zum Thema Schwellenbesohlungen—Teil 1: Langzeiterfahrungen im Netz der ÖBB (Technical and economical aspects to under sleeper pads—Part 1: Long-term experiences in the Oebb-network). ZEVRail 2009, 133, 180–193. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Marschnig; Veit, P. Technische und wirtschaftliche Aspekte zum Thema Schwellenbesohlungen – Teil 2: Wirtschaftlichkeit im Netz der ÖBB (Technical and economical aspects to Under Sleeper Pads—Part 2: Economic efficiency in the OeBB-network). ZEVRail 2009, 133, 436–443. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Jayasuriya, C.; Indraratna, B.; Ferreira, F.B. The Use of Under Sleeper Pads to Improve the Performance of Rail Tracks. Indian Geotech. J. 2020, 50, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omodaka, A.; Kumakura, T.; Konishi, T. Maintenance Reduction by the Development of Resilient Sleepers for Ballasted Track with Optimal Under-sleeper Pads. Procedia Cirp 2017, 59, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; Bolmsvik, R.; Nielsen, J. In situ performance of a ballasted railway track with under sleeper pads. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit. 2011, 225, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräbe, P.J.; Mtshotana, B.F.; Sebati, M.M.; Thünemann, E.Q. The effects of under-sleeper pads on sleeper–ballast interaction. J. S. Afr. Inst. Civ. Eng. 2016, 58, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pospischil, F.; Loy, H. Sustainable superstructure with Under Sleeper Pads. In Proceedings of the 7th Transport Research Arena TRA 2018, Vienna, Austria, 16–19 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, M.S.; Navar, F.M.; Gámez, M.C.R. The Use of Deconstructed Tires as Elastic Elements in Railway Tracks. Materials 2014, 7, 5903–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, A.; Nielsen, J.; Bolmsvik, R.; Karlström, A.; Lundén, R. Roger Under sleeper pads—Influence on dynamic train–track interaction. Wear 2008, 265, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN 45673-1:2010-08; Mechanical Vibration—Resilient Elements Used in Railway Tracks—Part1: Terms and Definitions, Classification, Test Procedures. Deutsches Institut für Normung (German Institute for Standardisation Registered Association): Berlin, Germany, 2010.
- Schilder, R. USP (Under Sleeper Pads)—A Contribution to Save Money in Track Maintenance; AusRAIL PLUS: Sydney, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- EN 16730:2016-09; Railway Applications—Track—Concrete Sleepers and Bearers with under Sleeper Pads. European Standards: Dublin, Ireland, 2016.
- Zakeri, J.A.; Esmaeili, M.; Heydari, H. A field investigation into the effect of under sleeper pads on the reduction of railway-induced ground-borne vibrations. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit 2015, 230, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraśkiewicz, C.; Zbiciak, A.; Sabouni-Zawadzka, A.A.; Piotrowski, A. Experimental Research on Fatigue Strength of Prototype under Sleeper Pads Used in the Ballasted Rail Track Systems. Arch. Civ. Eng. 2020, 67, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEN-EN 13848-1; Railway Applications—Track—Track Geometry Quality—Part 1. BSI Standards Publication: London, UK, 2019.
- Fellinger, M. Sustainable Asset Management for Turnouts: From Measurement Data Analysis to Behaviour and Maintenance Prediction; Railway Research, No. 4; Verlag der Technischen Universität Graz: Graz, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhold, J.; Vidovic, I.; Marschnig, S. Preparing Track Geometry Data for Automated Maintenance Planning. J. Transp. Eng. Part A Syst. 2020, 146, 04020032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. How long is the coast of Great Britain? Statistical self-similarity and fractional dimension. Science 1967, 156, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landgraf, M.; Hansmann, F. Fractal analysis as an innovative approach for evaluating the condition of railway tracks. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit 2019, 233, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landgraf, M. Smart Data for Sustainable Railway Asset Management; Verlag der Technischen Universität Graz: Graz, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhold, J.; Landgraf, M.; Neuper, G. Effekte von Schwellenbesohlungen auf das langfristige Qualitätsverhalten des Gleises (Effects of Under-Sleeper-Pads on long-term track quality behaviour). ZEVrail 2018, 142, 276–281. (In German) [Google Scholar]

| Subsection 1 | Subsection 2 | Adjacent Sections | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superstructure | 60E1 rails | 60E1 rails | 60E1 rails |
| concrete sleepers | concrete sleepers | unsoled concrete sleepers | |
| 8 mm USP * | 8 mm USP * | - | |
| 20 cm ballast ** | 30 cm ballast ** | 30 cm ballast ** | |
| Substructure | 8 cm bituminous asphalt layer | 8 cm bituminous asphalt layer | 8 cm bituminous asphalt layer |
| 45 cm frost protection layer | 45 cm frost protection layer | 45 cm frost protection layer | |
| 20 cm soil replacement | 20 cm soil replacement | 20 cm soil replacement | |
| Subsoil | natural ground | natural ground | natural ground |
| Short-Waved | Mid-Waved | Long-Waved | |
|---|---|---|---|
| wavelength due to EM 250 | 1–3 m | 3–25 m | 25–70 m |
| Abbreviation | Explanation |
|---|---|
| SD | standard deviation |
| le/ri | left/right rail |
| x | value of the longitudinal level |
| i | index for the ith data point (25 cm spacing) |
| N | number of considered data points (depending on the moving influence length) |
| j | number of calculated mean standard deviations SDi |
| mean | arithmetic mean |
| (10 m) | moving influence length of 10 m |
| (100 m) | moving influence length of 100 m |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marschnig, S.; Ehrhart, U.; Offenbacher, S. Long-Term Behaviour of Padded Concrete Sleepers on Reduced Ballast Bed Thickness. Infrastructures 2022, 7, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures7100132
Marschnig S, Ehrhart U, Offenbacher S. Long-Term Behaviour of Padded Concrete Sleepers on Reduced Ballast Bed Thickness. Infrastructures. 2022; 7(10):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures7100132
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarschnig, Stefan, Ursula Ehrhart, and Stefan Offenbacher. 2022. "Long-Term Behaviour of Padded Concrete Sleepers on Reduced Ballast Bed Thickness" Infrastructures 7, no. 10: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures7100132
APA StyleMarschnig, S., Ehrhart, U., & Offenbacher, S. (2022). Long-Term Behaviour of Padded Concrete Sleepers on Reduced Ballast Bed Thickness. Infrastructures, 7(10), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures7100132







