A Review of the Performance of Smart Lawnmower Development: Theoretical and Practical Implications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Analysis on Smart Lawnmower Performance
2.1. Navigation and Obstacle Avoidance
2.2. Battery Life
2.3. Energy Efficiency
2.4. Mowing Quality
2.5. Weather and Terrain Performance
2.6. Human–Machine Interaction
2.7. Environmental Impact
2.8. Prototype and Design
2.9. Operational Efficiency
2.10. Engine Efficiency
2.11. Material Selection
3. Discussion
3.1. Key Performance Indicators
3.2. Theoretical Implications
3.3. Practical Implications
3.4. Cost Analysis
4. Recommendations for Future Research
4.1. Short-Term Directions
4.2. Long-Term Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HMI | Human–machine interaction |
| FCe | Effective Field Capacity |
| CAGR | Compound Annual Growth Rate |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| LiDAR | Light Detection and Ranging |
| SLAM | Simultaneous Localization and Mapping |
| ROS | Robot Operating System |
| TIS | Total Intelligent System |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| CPP | Coverage Path Planning |
| TRIZ | Theory of Inventive Problem Solving |
| RLM | Robotic lawnmower |
References
- Lehdonvirta, V.; Shi, L.P.; Hertog, E.; Nagase, N.; Ohta, Y. The Future(s) of Unpaid Work: How Susceptible Do Experts from Different Backgrounds Think the Domestic Sphere Is to Automation? PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignatieva, M.; Hughes, M.; Chaudhary, A.K.; Mofrad, F. The Lawn as a Social and Cultural Phenomenon in Perth, Western Australia. Land 2024, 13, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, A.J. Why Mow?: A Review of the Resulting Ecosystem Services and Disservices from Mowing Turfgrass. Crop Sci. 2025, 65, e21376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Economic News Release. Available online: https://www.bls.gov/news.release/atus.t01.htm (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- Koppel, T.; Tint, P.; Karajeva, G.; Reinhold, K.; Kalle, S. Vibration and Noise Caused by Lawn Maintenance Machines in Association with Risk to Health. Agron. Res. 2012, 10, 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- Deafness and Hearing Loss: Safe Listening. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/deafness-and-hearing-loss-safe-listening (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- Kang, C.Q.; Ng, P.K.; Liew, K.W. The Conceptual Synthesis and Development of a Multifunctional Lawnmower. Inventions 2021, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.; Brown, A.; Maljian, J. Lawn Buddy. Electrical Engineering Department, California Polytechnic State University: San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 2020; Available online: https://digitalcommons.calpoly.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?params=/context/eesp/article/1513/&path_info=Senior_Project_Final_Report___Lawn_Buddy.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Tahir, T.; Khalid, A.; Arshad, J.; Haider, A.; Rasheed, I.; Rehman, A.U.; Hussen, S. Implementation of an IoT-Based Solar-Powered Smart Lawn Mower. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 1971902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sportelli, M.; Luglio, S.M.; Caturegli, L.; Pirchio, M.; Magni, S.; Volterrani, M.; Frasconi, C.; Raffaelli, M.; Peruzzi, A.; Gagliardi, L.; et al. Trampling Analysis of Autonomous Mowers: Implications on Garden Designs. AgriEngineering 2022, 4, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robotic Lawn Mowers Market Size & Share Report, 2030. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/robotic-lawn-mowers-market (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Adi, S.; Abhishek, P.; Chaitanya, N.V.; Reddy, A. Autonomous Solar Based Lawn Mower. Int. J. Pure Appl. Math. 2018, 119, 13129–13132. [Google Scholar]
- Sasikumar, G.; Mujiburrahman, K.; Subhashini, R.; Begum, S.S. IoT Enabled Solar-Powered Grass Cutter Utilizing Radiant Solar Energy. J. Integr. Sci. Technol. 2024, 12, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.-S.; Lin, H.-C.; Lin, K.-C.; Kao, S.-H. Intelligent Auto-Saving Energy Robotic Lawn Mower. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Istanbul, Türkiye, 10–13 October 2010; pp. 4130–4136. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Padhan, A.; Saurabh, S.; Priyesh, K.; Rai, M.; Naveen, T. A Review and Comparative Analysis of Solar, Electric and Gasoline Lawnmowers: An Extensive Study. IJISET-Int. J. Innov. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2016, 3, 370–376. [Google Scholar]
- Robotic Lawn Mowers Market Revenue Trends and Growth Drivers. Available online: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/robotic-lawn-mowers-market-88178569.html (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- Pk, R.; Patel, N. Autonomous Lawn Mower—A Comprehensive Review. Int. Res. J. Adv. Sci. Hub 2023, 5, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivbhakta, B.; Humnabadkar, A.; Kokate, M. Solar-Powered Grass Trimmer: Advancing Lawn Care with Bluetooth Connectivity. Int. J. Nov. Res. Eng. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 9, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandababu, C.S.; Vijayakrishna, R.; Venugopal, R.; Vishnuprasad, Y. Development of an Autonomous Solar Grass Cutting Robot with a Path Memorizing Mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication and Applied Informatics (ACCAI), Chennai, India, 9–10 May 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Rahim, N.A.S.A.; Shamsudin, A.U. Laser-Based Autonomous Navigation of Lawnmower. Evol. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2022, 3, 349–356. [Google Scholar]
- Murugan, K.; Balambigai, G.; Manikandan, B.; Karthick, S.; Kishore, R.; Jagan, A. Revolutionizing Lawn Care: AI-Driven Solar-Powered Humorless Grassland Mower With IoT Integration. J. Adv. Zool. 2024, 45, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanu Sri, C.; Khaja Mohiddin, S.; Naresh Kumar, S.; Mohan Kalyan, V.; Veer Raju, A.; Nagendra Prasad, K.; Sai Mohan, U. IOT Based Solar Grass Cutting Robot. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. (IJFMR) 2024, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniyan, I.; Balogun, V.; Adeodu, A.; Oladapo, B.; Peter, J.K.; Mpofu, K. Development and Performance Evaluation of a Robot for Lawn Mowing. Procedia Manuf. 2020, 49, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, N.G.; Luciano, R.G. Design And Development Of Android-Controlled Grass Cutting Robot Using RPA Method. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2020, 9, 223–234. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, M. Design of Smart and Self-Controlled Solar Grass Cutter with Lawn Coverage. Int. J. Autom. Smart Technol. 2024, 14, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Borah, A. Design and Implementation of IoT-Integrated Wireless Solar Grass Cutting Robot. Bachelor’s Thesis, Assam University, Silchar, India, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Jin, L.; Wang, S. A Path Planning System for Orchard Mower Based on Improved A* Algorithm. Agronomy 2024, 14, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Clemens, J.; Stronzek-Pfeifer, D.; Simonelli, R.; Serov, A.; Schettino, S.; Runge, M.; Schill, K.; Buskens, C. Coverage Path Planning and Precise Localization for Autonomous Lawn Mowers. In Proceedings of the 2022 Sixth IEEE International Conference on Robotic Computing (IRC), Naples, Italy, 5–7 December 2022; pp. 238–242. [Google Scholar]
- Okwu, M.O.; Tartibu, L.K.; Enarevba, D.R.; Oyejide, O.J.; Otanocha, O.B.; Adumene, S. Development of a Light Weight Autonomous Lawn Mower and Performance Analysis Using Fuzzy Logic Technique. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, Computing and Data Communication Systems (icABCD), Durban, South Africa, 4–5 August 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, S.; Ma, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G. Development of an Automatic Lawnmower with Real-Time Computer Vision for Obstacle Avoidance. Int. J. Comput. Methods 2021, 19, 2142001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishna, K.; Rajesh, N. Design of Remote Monitored Solar Powered Grasscutter Robot with Obstacle Avoidance Using IoT. Glob. Transit. Proc. 2022, 3, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Huang, J.; Song, L.; Xiong, F. Differential Steering Control System of Lawn Mower Robot. In Proceedings of the Data and Information in Online Environments; Bisset Álvarez, E., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 354–367. [Google Scholar]
- Premarathne, U.S.; Wijesinghe, W.A.P.C. Path Finding Robot for Energy Efficient Automated Grass Cutter. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Image Processing and Robotics (ICIPRoB), Colombo, Sri Lanka, 9–10 March 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, J.H.; Min, T.S. A Review on Sensor Technologies and Control Methods for Mobile Robot with Obstacle Detection System. Int. J. Robot. Autom. Sci. 2024, 6, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, B.C.; Lim, W.S.; Lim, H.S. Lane Detection in the Absence of Lane Markings for Roadway Surveillance with Thermal Vision. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control (IJICIC) 2016, 12, 677–688. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, B.C.; Lim, H.S.; Lim, W.S. Vehicle Detection for Thermal Vision-Based Traffic Monitoring System Using Principal Component Analysis. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control (IJICIC) 2016, 12, 1467. [Google Scholar]
- Hameem, M.; Mir, F.A.; Malik, M. Autonomous Grass Cutting Rover. Ph.D. Thesis, Bachelor of Technology, Mechanical Engineering, Islamic University of Science & Technology, Pulwama, India, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Balaji, A.; Shanthini, E.R.; Rooshan, M.J.; Sivaram, V. Robust Design of Smart Lawn Cutter for Gardening Companion. IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1012, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoda, R.; Kashyap, B.; Yadav, A.; Datta, P. Solar Power Based Automatic Lawn Mower. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on IoT, Communication and Automation Technology (ICICAT), Gorakhpur, India, 23–24 November 2024; pp. 1438–1443. [Google Scholar]
- Rahim, M.S.A.A.; Johar, T.D.M.A. System Development of an Autonomous Lawnmower System Using Ardupilot Mission Planner. Res. Prog. Mech. Manuf. Eng. 2021, 2, 533–538. [Google Scholar]
- Akinyemi, A.O.; Ayobami, H.F.; Solomon, A. Design and Fabrication of a Solar Operated Lawnmower. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. Technol. 2020, 5, 1161–1197. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, M.D. Measurement and Analysis of Lawn Mower Performance and Noise. Master’s Thesis, Iowa State University, Digital Repository, Ames, The Netherlands, 1997; p. 10925154. [Google Scholar]
- Pirchio, M.; Fontanelli, M.; Frasconi, C.; Martelloni, L.; Raffaelli, M.; Peruzzi, A.; Gaetani, M.; Magni, S.; Caturegli, L.; Volterrani, M.; et al. Autonomous Mower vs. Rotary Mower: Effects on Turf Quality and Weed Control in Tall Fescue Lawn. Agronomy 2018, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaji, S.V.; Chandrakant, C.S.; Shashikant, P.S.; Raju, G.O.; Bhalchandra, G.S. Automated Mower Robo. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 5, 343–346. [Google Scholar]
- Magar, A.P.; Abuj, M.D.; Bastewad, T.B.; Adagale, P.V. Performance Evaluation of Grass Cutter. Int. J. Agric. Eng. 2010, 3, 153–155. [Google Scholar]
- Nkakini, S.; Yabefa, B. Design, Fabrication and Evaluation of a Spiral Blade Lawn Mower. Eur. Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2014, 3, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Kulhariya, S.K.; Tomer, D.A.S.; Krishan, K.; Yadav, N.K.; Mishra, R.K. Performance Evaluation of Solar Operated Bidirectional Grass Cutter. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2020, 9, 329–334. [Google Scholar]
- Rajmani, A.S.; Gaonkar, A.N.; Darak, A.; Joshi, A.; Murgod, V.M. Design and Fabrication of Hybrid Operating Grass Cutter. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. (IJERT) 2019, 8, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foong, T.; Ismail, S. Design, Fabrication, and Analysis of a Smart Mower. J. Mod. Manuf. Syst. Technol. 2019, 3, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuabuchi, E.M.; Ekeopara, J.U.; Sule, R.; Ayanbisi, O.; Akinwumi, S.A.; Olawole, O.C.; Ogunwale, E. Development and Evaluation of Efficient Smart Solar Lawn Mower. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1342, 012045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhoshini, P.; Helen Prabha, K.; Jaibalaji, S.T.; Krishna Vishwa, C.B.; Kumar, H.R.; Mano Sundar, S. Implementation of Automatic Lawn Mower System for Smart Lawn Maintenance. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Signal Processing (AISP), Vijayawada, India, 26–28 October 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Adeboye, B.S.; Kolawole, O.; Oyewusi, T.F.; Oyewo, A.T. Development and Evaluation of an Autonomous Solar Lawnmower. UNIZIK J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2025, 4, 1852–1863. [Google Scholar]
- Dada, M.; Popoola, P. Recent Advances in Solar Photovoltaic Materials and Systems for Energy Storage Applications: A Review. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2023, 12, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, R.A.; Parade, N.D.; Waghmare, S.S. Fully Automated Solar Powered Lawn Cutter Robot. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Eng. Commun. Technol. 2024, 13, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Fineas, M.; Sever-Gabriel, R. Autonomous Lawn Mowers: A Comparative Approach. Proc. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 17, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Derander, J.M.; Andersson, P.; Wennerberg, E.; Nitsche, A.; Moex, E.; Labe, F. Smart Robot Lawn Mower. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Gothenburd, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Siregar, B.; Hutagaol, B.M.; Salim Sitompul, O. Smartphone-Controllable Lawn Mower Robot. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on ICT for Smart Society (ICISS), Bandung, Indonesia, 19–20 November 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Saidani, M.; Pan, E.; Kim, H.; Greenlee, A.; Wattonville, J.; Yannou, B.; Leroy, Y.; Cluzel, F. Assessing the Environmental and Economic Sustainability of Autonomous Systems: A Case Study in the Agricultural Industry. Procedia CIRP 2020, 90, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Ng, P.K. The Design and Development of a Foldable Wheelchair Stretcher. Inventions 2021, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.K.; Jee, K. Design and Development of an Ergonomic Milling Machine Control Knob Using TRIZ Principles. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2016, 13, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Ng, P.K. Synthesisation of Design Features for Multifunctional Stretcher Concepts. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2021, 45, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrum, A.; Corteo, J.; Oppel, J.; Seth, M. An Autonomous Lawnmower ‘The ManScaper’; University of Central Florid: Orlando, FL, USA, 2013; Available online: https://www.ece.ucf.edu/seniordesign/sp2013su2013/g02/documents/Group2_ConferencePaper.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Hossain, M.Z.; Komatsuzaki, M. Weed Management and Economic Analysis of a Robotic Lawnmower: A Case Study in a Japanese Pear Orchard. Agriculture 2021, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.Q.; Ng, P.K.; Liew, K.W. A TRIZ-Integrated Conceptual Design Process of a Smart Lawnmower for Uneven Grassland. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisari, M.; Ramola, J.; Amritha, M.; Bency, B.; Ramees, N. Hybrid Automated Lawnmower. Int. J. Adv. Res. Ideas Innov. Technol. 2021, 7, 635–636. [Google Scholar]
- Aditya, Y.; Yasasri, B.; Priya, A.J.; Devi, D.N.; Madhukar, E. Bluetooth Controlled Green Sward Cutter Using IoT. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Emerging Systems and Intelligent Computing (ESIC), Bhubaneswar, India, 9–10 February 2024; pp. 411–415. [Google Scholar]
- Baluprithviraj, K.N.; Kalavathi Devi, T.; Madhan Mohan, M.; Harini, R.; Janarthanan, M.M.; Jasodhasree, C. Smart IoT Based Solar Powered Lawn Mower Robot. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kharagpur, India, 3–5 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Khillare, S.R.; Morey, D.P.; Ghoti, B.A.; Thorat, S.S.; Pimple, S.D.; Sharma, M.O. A Review of Fully Automated Grass Cutter Using Solar Power. Int. J. Res. Eng. Sci. Manag. 2020, 3, 108–111. [Google Scholar]
- Tunmise, A.D.; Mathew, O.M.; Toheeb, B. Development of an Improved Solar Powered Lawnmower. Int. J. Women Tech. Educ. Employ. 2022, 3, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Nirmal, U. Adhesive Wear and Frictional Performance of Banana Fibre Reinforced Epoxy (BaFRE) Composite. Polymers 2022, 14, 3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmal, U.; Chin, C.W.; Yuhazri, M.Y.; Husin, M.A.; Megat Ahmad, M.M.H. On the Improvement of Tribological Performance Using Treated Betelnut Fiber Reinforced Polyester (T-BFRP) and Teflon Composite for Automotive Applications. In Biocomposite and Synthetic Composites for Automotive Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2021; pp. 107–146. ISBN 978-0-12-820559-4. [Google Scholar]
- Nirmal, U.; Lau, S.; Hashim, J. Interfacial Adhesion Characteristics of Kenaf Fibres Subjected to Different Polymer Matrices and Fibre Treatments. J. Compos. 2014, 2014, 350737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajuri, F.; Mazlan, N.; Ishak, M.R. Effect of Silica Nanoparticles in Kenaf Reinforced Epoxy: Flexural and Compressive Properties. Pertanika J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 25, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Nordi, S.S.; Noor, E.E.M.; Kok, C.K.; Julkapli, N.M.; Baig, M.F. Phase, Chemical, Thermal, and Morphological Analyses of Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) Nanocomposites Reinforced with Jute Cellulose Nanofibers (CNFs). Polymers 2025, 17, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Laziz, A.; Mazlan, N.; Mohamed Yusoff, M.Z.; Ariff, A. Investigation of Alkaline Surface Treatment Effected on Flax Fibre Woven Fabric with Biodegradable Polymer Based on Mechanical Properties. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2020, 52, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajuri, F.; Mazlan, N.; Ishak, M.; Uyup, M.K.A. Effect of Impregnation on Hybrid Mesoporous Silica/Kenaf Reinforced Epoxy Composites in Term of Flexural, Compressive and Water Absorption Properties. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2020, 14, 7528–7539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmuş-Sayar, A.; Tansan, M.; Çinko-Çoban, T.; Serttan, D.; Dizman, B.; Yildiz, M.; Ünal, S. Incorporation of Graphene Nanoplatelets into Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites in the Presence of Highly Branched Waterborne Polyurethanes. Polymers 2024, 16, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, V.; Namasivayam, S.N. Carbon Nanotubes: A Reliable Additive for the Natural Fiber-Reinforced Composites. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2020, 15, 1934–1951. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, E.; Chalse, H.; Mutha, S.; Mundhe, Y.; Ambhore, N.; Kulkarni, A.; Mache, A. Review on Synthetic/Natural Fibers Polymer Composite Filled with Nanoclay and Their Mechanical Performance. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 77, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, C. BMW i Ventures Invests in High-Performance Composites Made from Natural Fibres. Available online: https://www.press.bmwgroup.com/global/article/detail/T0377293EN/bmw-i-ventures-invests-in-high-performance-composites-made-from-natural-fibres?language=en (accessed on 28 April 2025).
- Pozo Morales, A.; Güemes, A.; Fernandez-Lopez, A.; Carcelen Valero, V.; De La Rosa Llano, S. Bamboo–Polylactic Acid (PLA) Composite Material for Structural Applications. Materials 2017, 10, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raychura, A.; Jauhari, S.; Prajapati, V.; Dholakiya, B. Synthesis and Performance Evaluation of Vegetable Oil Based Wood Finish Polyurethane Coating. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2018, 3, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takpere, A.; Bansode, G.; Borle, J.; Joshi, C.; Lade, N. Automated Solar Powered Lawn Mower Using IoT. Int. Res. J. Mod. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2020, 7, 3150–3151. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, S.M.; Prajakta, B.; Snehal, K.; Dhanashri, P. Smart Solar Grass Cutter With Lawn Coverage. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. (IRJET) 2018, 5, 3476–3479. [Google Scholar]
- Akhilesh, B.B.; Daniel, A.; Divyashree, S.; Himashree, M.S.; Manu, D.K. Design and Implementation of Solar Grass Cutter. JEE 2021, 14, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.-C.; Chen, S.-H.; Zhuang, Z.-Y.; Wu, B.-W.; Chen, Y.-J. Designing and Manufacturing of Automatic Robotic Lawn Mower. Processes 2021, 9, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, B.; Siva Brahmaiah, V.; Sharma, P. Design of Smart Autonomous Remote Monitored Solar Powered Lawnmower Robot. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 28, 2338–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, T.; Chau, V.T.; Gallardo, M.A.; Lopez, D.R.; Pazmino, A.X. Autonomous Rover for Groundwork Lawn Mowing. Int. J. Interdiscip. Telecommun. Netw. 2022, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluprithviraj, K.N.; Harini, R.; Janarthanan, M.M.; Jasodhasree, C. Design and Development of Smart Lawn Mower. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Smart Electronics and Communication (ICOSEC), Trichy, India, 7–9 October 2021; pp. 1215–1219. [Google Scholar]
- Blisston Kirubha, S.; Gokhularamanan, K.; Suriya Bharathi, E.; Boopathi Rajan, P. Smart Lawn Mower. Int. J. Res. Eng. Sci. Manag. 2020, 3, 232–235. [Google Scholar]
- Septian, M.S. Design and Build an Arduino Mega-Based Automatic Lawn Mower. Instal J. Komput. 2022, 14, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugaselvam, P.; Yogaraj, J.N.R.; Ragul, P.; John, B.P. Design and Implementation of Android Based Robot for Grass Cutting. AIP Conf. Proc. 2022, 2519, 040014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganya, T.; Mangaiyarkarasi, P.; Thirugnanam, G.; Sathish Kumar, T.M. A Hybrid Approach with MPPT Controller for Weed Cutting Based on Solar Powered Lawnmower with Minimal Intervention of Human Involvement Adopting IoT Technology. Analog. Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2024, 119, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.M.; Karthik, K.; Charan, K.S.; Prakash, G.D.S. Automated Lawn Maintenance System. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Conference on Emerging Frontiers in Electrical and Electronic Technologies (ICEFEET), Patna, India, 21–23 November 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kayode, A.O.; Ishola, B.D.; Olubunmi, I.E.; John, A.A. Fuzzy Logic Track Control of an Automated Lawnmower. IAES Int. J. Robot. Autom. (IJRA) 2022, 11, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, S. Applications of Robot Swarms. Available online: https://www.azorobotics.com/Article.aspx?ArticleID=657 (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Amos, Z. How Swarm Robotics Could Transform Agriculture. Available online: https://community.robotshop.com/index.php/blog/show/how-swarm-robotics-could-transform-agriculture (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Inami, T.; Takahashi, S.; Motegi, K.; Shiraishi, Y. Rapid Control Prototyping of Random Forest Model and Its Performance Estimation by Simulation for Robotic Lawn Mower. In Proceedings of the 2024 SICE Festival with Annual Conference (SICE FES), Kochi City, Japan, 27–30 August 2024; pp. 117–120. [Google Scholar]
- Cannan, J.; Hu, H. Human-Machine Interaction (HMI): A Survey; School of Computer Science & Electronic Engineering, University of Essex: Essex, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Yao, X.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Q. Impact of Pricing and Product Information on Consumer Buying Behavior With Customer Satisfaction in a Mediating Role. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 720151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Azis, N.N.B.; Kamil, N.H.B.M.; Hamzah, M.N.M.B.A.; Kasim, N.B. MECHANICAL LAWN MOWER. 2020. Available online: http://repository.psa.edu.my/bitstream/123456789/3146/1/MECHANICAL%20LAWN%20MOWER.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Ng, P.K.; Saptari, A.; Yeow, J. Synthesising the Roles of Torque and Sensation in Pinch Force: A Framework. Theor. Issues Ergon. Sci. 2014, 15, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
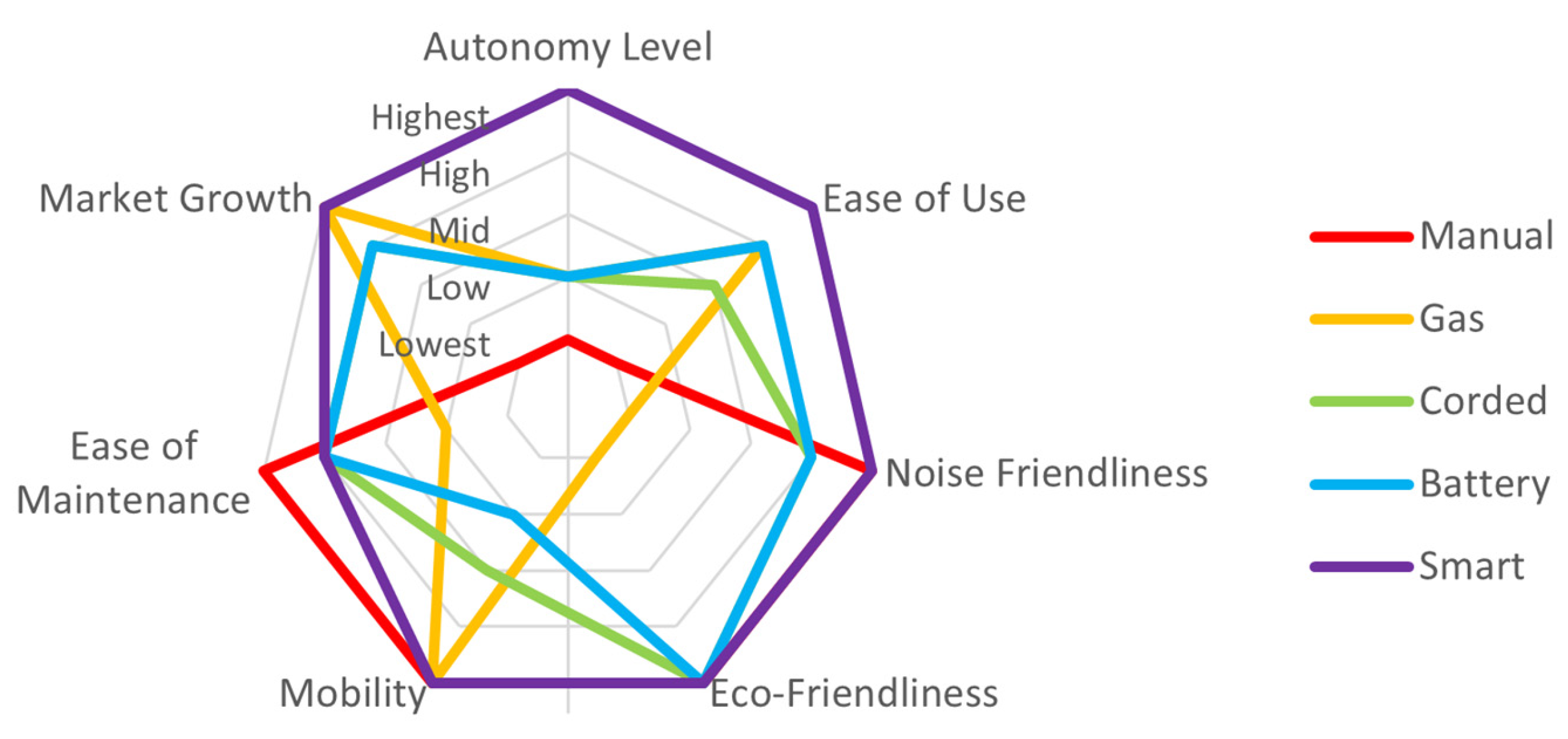
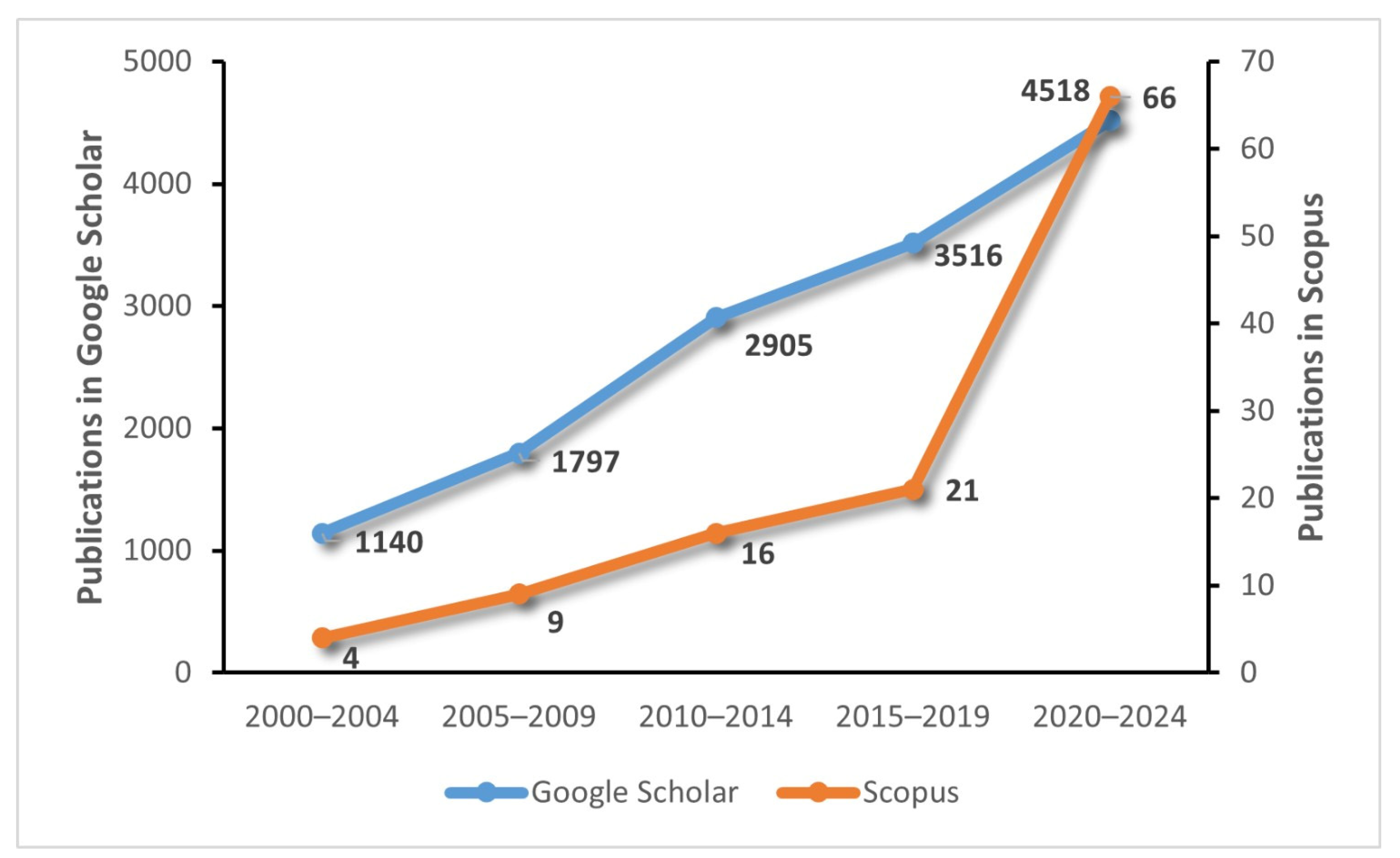
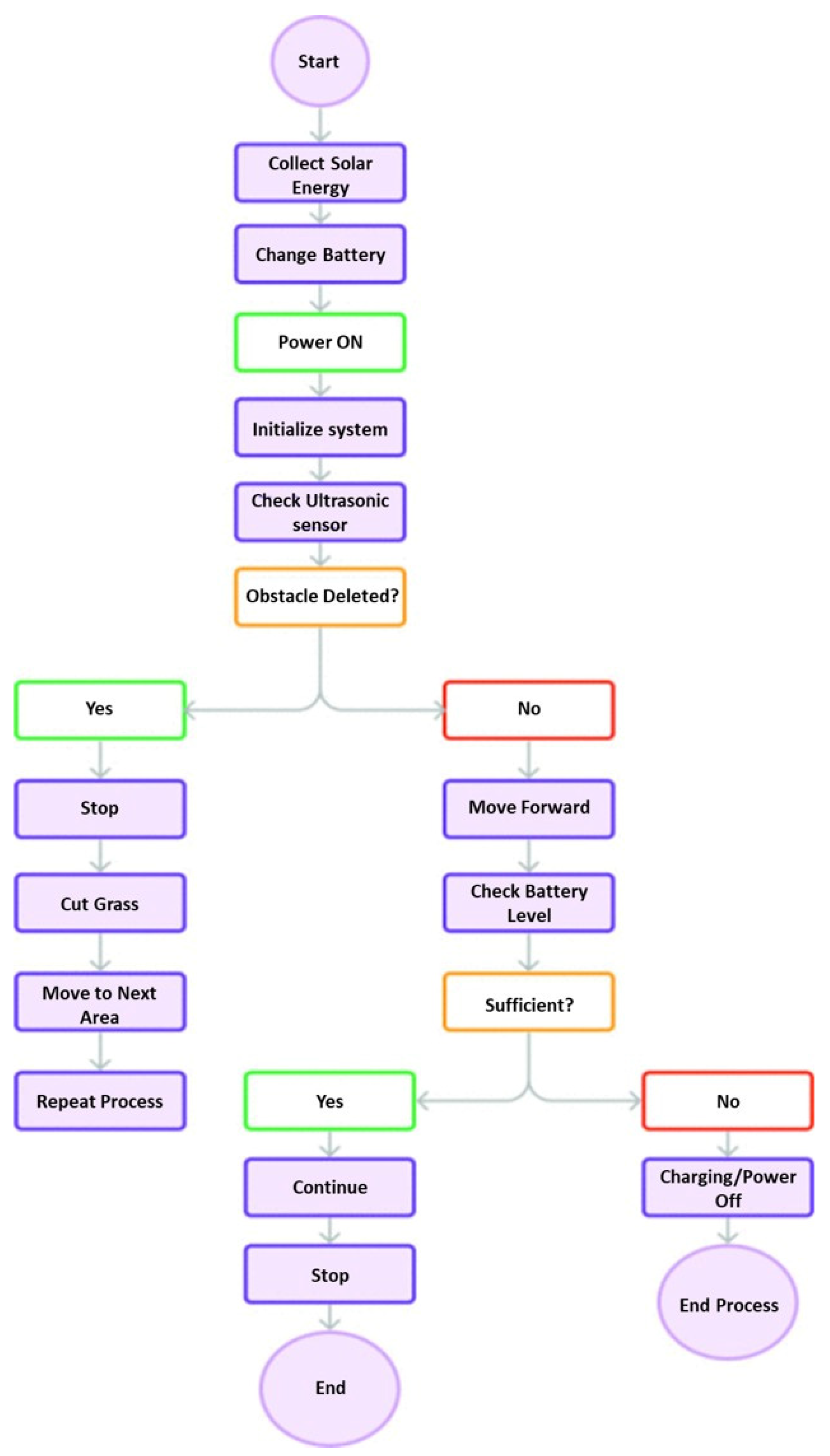
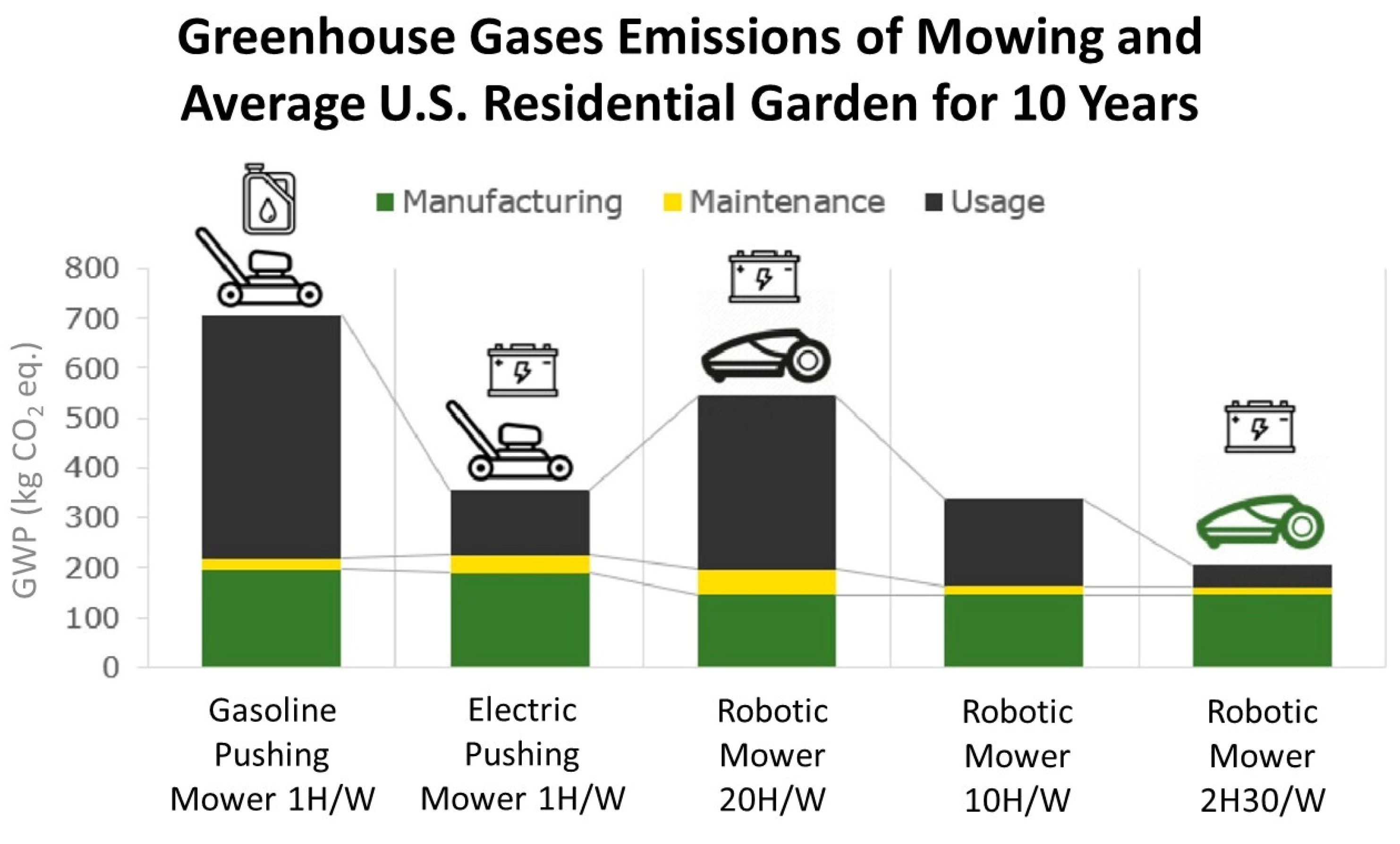
| Aspect | Manual Mower | Gas-Powered Mower | Electrical Mower | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corded | Battery Operated | Smart | |||
| Autonomy Level | Fully Manual | Partially Assisted | Partially Assisted | Partially Assisted | Fully Autonomous |
| Ease of Use | Very Demanding | Easy to Use | Moderately Easy | Easy to Use | Effortless |
| Noise Friendliness | Quiet | Very Noisy | Quiet | Quiet | Quietest |
| Eco-Friendliness | Emission-Free | Emits Pollutants | Emission-Free | Emission-Free | Emission-Free |
| Mobility | Unlimited Range | Unlimited Range | Cord-Limited | Battery-Limited | Unlimited Range |
| Ease of Maintenance | Minimal Upkeep | High Maintenance | Low Maintenance | Low Maintenance | Low Maintenance |
| Market Growth | Minimal Demand | Currently Dominant | Rapid Growth | Rapid Growth | Fastest Growing |
| Navigation and Obstacle Avoidance | Engine Efficiency | Operational Efficiency | Human–Machine Interaction | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Navigation System | Obstacle Avoidance System | Power Source | Charging Time (hours) | Operating Time (hours) | Optimization of Energy through Smart Features | Remote Control Capability | Safety System | |
| LiDAR, cameras, ultrasonic sensors, and wheel encoders | Ultrasonic sensors | Solar | 6 | Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) algorithms, which maximize solar panel energy collection. | [19] | |||
| LiDAR sensor with Robot Operating System (ROS), Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) | LiDAR sensors and Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) | Mower blade is designed to slide inside when mower is turned off. | [20] | |||||
| GPS and ultrasonic sensors | Ultrasonic sensors | Solar | Autonomously return to its self-charging station when battery levels are low, and the integration of IoT technology for real-time monitoring and decision-making. | Mobile app or Web app | [21] | |||
| GPS, cameras, IR Sensors, and ultrasonic sensors | Infrared sensors and ultrasonic sensors | Electrical and solar | Mobile app | [23] | ||||
| GPS | Heat and thermal sensors | Electric | Android App through Wi-Fi | Heat and thermal sensor, emergency stop function through app, | [24] | |||
| Ultrasonic sensors | Ultrasonic sensors | Solar | 3 | 2.8 | Arduino microcontroller and the zig-zag movement algorithm | nylon strings for cutting | [25] | |
| Ultrasonic sensors | Ultrasonic sensors | Solar | Battery Management System (BMS) | Mobile app through Bluetooth | [26] | |||
| Beidou Navigation Satellite System, inertial navigation technology, and various sensors, including laser radar and cameras | Laser radar and cameras | Electric | 1.5 | [27] | ||||
| RTK-augmented GNSS with inertial navigation system (INS) | [28] | |||||||
| Ultrasonic sensor | IR sensor and PSI | Electric | 1.45 | Atmega 328 microcontroller | Mobile app | PSI for human avoidance | [29] | |
| Cameras | Computer vision technology and simplified convolutional neural network (CNN) | [30] | ||||||
| Ultrasonic sensors | Ultrasonic sensors | Blynk app | [31] | |||||
| Coverage Path Planning (CPP) algorithm | Ultrasonic sensors | Solar supplemented by electric | Solar panels | [33] | ||||
| Proximity sensor | Electric | Mobile app through Bluetooth | [38] | |||||
| GPS (Ardupilot Mission Planner) | Sensors | [40] | ||||||
| GPS | Boundary wire | 2.7 | 5.3 | [43] | ||||
| Ultrasonic sensor | Ultrasonic Sensor | Intelligent navigation and obstacle avoidance | Mobile app | Auto shut-off when the mower is lifted | [51] | |||
| Ultrasonic sensor | Ultrasonic sensor | Electric | Mobile app through Bluetooth | [57] | ||||
| Perimeter wire and ultrasonic sensors | Ultrasonic sensors | Electric supplemented by solar | Lightweight design and solar panels | Auto shut-off when the mower is lifted | [64] | |||
| Ultrasonic sensors | Ultrasonic sensors | Solar and electric | Users can tailor operations to specific lawn conditions | Bluetooth controller | [65] | |||
| ESP32 camera module | Solar | Users can tailor operations to specific lawn conditions | Mobile app | [66] | ||||
| Cameras | Cameras | Solar and electric | Mobile app | Prevents the blades from operating when the mower is lifted | [67] | |||
| Ultrasonic sensor | App using IoT | [83] | ||||||
| Gyroscope sensor | Gyroscope sensor | The system stops when an obstacle is detected | [84] | |||||
| Ultrasonic sensor | Ultrasonic sensor | Auto shut-off when the mower is lifted or touches a hard surface | [85] | |||||
| Cameras | Cameras | Phython and Tkinter | human body infrared sensor, emergency stop button on the human–machine interface | [86] | ||||
| Ultrasonic sensors | Ultrasonic sensors and PIR sensors | 7.8 | Mobile app through Bluetooth | [87] | ||||
| Ultrasonic sensors | Ultrasonic sensors | Solar | Web app | [88] | ||||
| Camera | Ultrasonic sensor | Solar | Mobile app | [89] | ||||
| GPS and ultrasonic sensors | Ultrasonic sensors and a Pi camera | Electric | Mobile app | [90] | ||||
| Ultrasonic sensors | Ultrasonic sensors | Electric | Mobile app | Limit switch crash sensor | [91] | |||
| Ultrasonic sensors | Ultrasonic sensors | Mobile app | [92] | |||||
| A combination of sensors | IoT technology for real-time monitoring and decision-making | IoT | [93] | |||||
| Ultrasonic sensors | Ultrasonic sensors | Electric | Automatic stop feature | [94] | ||||
| Ultrasonic sensors | Three ultrasonic sensors and Two infrared (IR) proximity sensors | Fuzzy logic control | [95] | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Selvanesan, E.N.; Liew, K.W.; Tay, C.H.; Yeow, J.A.; Ng, Y.J.; Chong, P.L.; Kang, C.Q. A Review of the Performance of Smart Lawnmower Development: Theoretical and Practical Implications. Designs 2025, 9, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs9030055
Selvanesan EN, Liew KW, Tay CH, Yeow JA, Ng YJ, Chong PL, Kang CQ. A Review of the Performance of Smart Lawnmower Development: Theoretical and Practical Implications. Designs. 2025; 9(3):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs9030055
Chicago/Turabian StyleSelvanesan, Elwin Nesan, Kia Wai Liew, Chai Hua Tay, Jian Ai Yeow, Yu Jin Ng, Peng Lean Chong, and Chun Quan Kang. 2025. "A Review of the Performance of Smart Lawnmower Development: Theoretical and Practical Implications" Designs 9, no. 3: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs9030055
APA StyleSelvanesan, E. N., Liew, K. W., Tay, C. H., Yeow, J. A., Ng, Y. J., Chong, P. L., & Kang, C. Q. (2025). A Review of the Performance of Smart Lawnmower Development: Theoretical and Practical Implications. Designs, 9(3), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs9030055








