Abstract
Harmonic issues in power systems are becoming an important topic for industrial customers and power suppliers alike due to their adverse effects in both consumer appliances as well as for utility suppliers. Consumers should seek to reduce harmonic pollution, regardless of voltage or current distortion already present in the network. This article suggests a new method for suppressing distortions by using the non-linearity current index (NLCI) to determine the shunt single-tuned passive filter (STPF) compensator value in non-sinusoidal power systems, with the objective of maintaining the power factor within desired limits. The objective of the proposed method is to minimize the nonlinear current of customer’s loads in the power system at the point of common coupling (PCC). Moreover, the proposed design takes into consideration other practical constraints for the total voltage and individual harmonic distortion limits, ensuring compliance with (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) IEEE 519-2014 guidelines, maintaining distortions at an acceptable level while also abiding by the capacitor loading constraints established in IEEE 18-2012. The performance of the optimally designed compensator is assessed using well documented IEEE standards based on numerical examples of nonlinear loads taken from previous publications.
1. Introduction
In recent years, there have been serious concerns regarding the quality of available power in electrical networks, making this issue a significant focus of research interest for both suppliers and users. Power system harmonics are considered one of the most important issues because of their reduction in power quality in power systems [1,2,3]. This is due to the widespread nonlinear loads exhibited across different appliances (such as variable frequency drives and switching mode power supplies), which can result in distortion currents with a frequency greater than the fundamental frequency. These harmonics can have detrimental effects on other components of the power system across all electrical sectors. Some of these effects are immediate (i.e., noise, interference, and control circuits, etc.) while others are long-term (i.e., heating due to extra power losses, damage). Furthermore, they lead to the degradation of the load power factor and higher transmission line losses, and thus contribute to a reduction in the efficiency of the transmission network. Thus, it is clear that harmonic levels should be minimized by all participants in the electrical grid [4,5,6,7]. There are different approaches to mitigating the effects of harmonics problems, such as load conditioning, which ensures that the electrical equipment is less sensitive to power disturbances. Other approaches used involve adding filters to the line power system, either in series or shunt connections. Harmonic mitigation techniques such as the K-factor transformer and shifting transformer are also applied in order to limit the power quality problem [8,9,10]. Industrial electrical systems contain the majority of medium- to high-powered contaminant sources, often in the form of static power converters and electric arc furnaces. In such systems, single objective filter solutions are usually preferred, to attempt to comply with the relevant power quality standards while incurring the least costs [11]. Adding harmonic filters (passive and/or active) is the most frequently used approach [12,13,14,15,16]. Further, passive filters are deemed to be the most effective and viable solution for mitigating harmonics in power systems. Therefore, they are broadly used in transmission and distribution power systems due to their simple design, cost effectiveness, simplicity in maintenance, and high reliability. Passive filters are characterized by having a dual purpose, reducing current harmonics and correcting the power factor (PF). Therefore, they have been recommended for reducing nonlinear current loads, especially for existing industrial users [6,17,18]. On the other hand, employing passive filters may introduce resonance into the power system; thus, they should be designed such that they are safely located away from existing power harmonics [19,20]. Passive filters can be classified into two general categories, namely (i) tuned passive filters, (single-tuned or double-tuned filters) and (ii) high-pass passive filters. These filters typically have two types of connection, either in series, which presents a high-impedance series path, or as shunt, which presents a low-impedance path. In this context, a shunt connection is generally preferred and used more often for harmonics reduction than the series connection due to its ability to support a range of voltages while also compensating reactive power at the fundamental frequency [2,6,21]. Figure 1 presents several configurations of shunt passive harmonic filters [17].
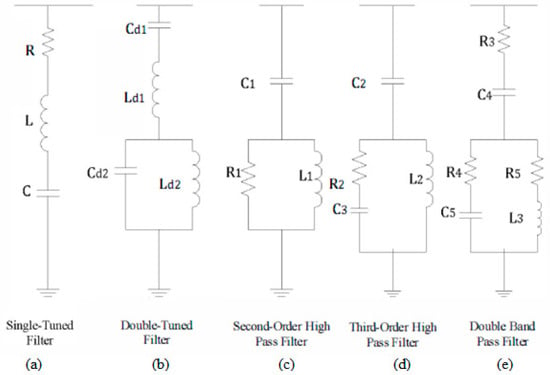
Figure 1.
Several arrangements of passive filters [17].
Several studies have already addressed the problem of optimal filter design for harmonic mitigation in power systems. A single tuned passive filter compensator has been demonstrated to be an effective method of improving the power factor, as well as reducing power losses and decreasing voltage distortion to acceptable levels [22,23]. However, the design of passive power filters should be handled with caution as it is not a straightforward problem due to the contradictory requirements in power factor specifications, voltage total harmonic distortion (VTHD), and current total harmonic distortion (ITHD) [24].
In the literature, the maximization of the PF has received the highest priority as an objective during the design of optimal passive filters [25,26,27], while maximizing the load PF with minimum transmission loss has frequently been taken as a main objective for the design of the compensation elements of passive filters in order to achieve reasonable levels of total harmonic distortion (voltage) (THDV) [28,29]. However, maximizing PF alone may not succeed in minimizing the total harmonic distortion of both voltage and current, although it may work to reduce them. In contrast, another goal, e.g., [30] has been to minimize THDV, to obtain an optimal passive filter design which takes into consideration the non-linearity of the load, in which having the load PF at an acceptable, pre-specified level is used as a constraint. A passive filter solution based on minimizing THDV and total harmonic distortion current (THDI) in a power system has also been proposed in [31]; however, both obligations for capacitor loading as given in IEEE 18-2012 and the power supply characteristics, were neglected. THDI and THDV were also used to determine compensator values for passive filters [32] but the approach failed, albeit only just, to achieve the manufacturer’s standard values for shunt capacitors. Different objectives have been used collectively in different combinations for the same goal, and these objectives include the maximization of PF and minimization of filter cost, THDV, and THDI [33]. However, in considering such objectives, the nature of the supply source in any power system should always be considered when determining the optimal parameters for the design of passive filters.
In all the above studies, passive filters were designed to mitigate harmonics and correct the PF using different objective functions under distorted current load conditions. Such conventional objective functions do not distinguish between the current due to the mains supply distortion and the nonlinear current due to the industrial customer’s loads at the PCC. However, the NLCI (non-linearity current index) [34] is an objective function which does make this important distinction. The NLCI depends on the likelihood that the supply system alone is responsible for the unbalanced and harmonic distortion at the PCC if the loads under test are linear and balanced. The NLCI has been successfully evaluated to identify just the harmonic pollution responsibility at the PCC in a power system.
In this paper, a new approach is presented for minimizing NLCI, whereby it is required to keep the PF at the desired level, while considering the non-linearity of the loads. Other considerations have been taken into account, including the frequency-dependent nature of the power supply source and the resonant problems which may result from the compensator filter values. In this way, an optimum single-tuned passive filter (STPF) compensator is designed to minimize the expected value of NLCI for a specified range of source harmonic and impedance values. Finally, examples from previous publications are discussed to illustrate and validate the contribution of the newly developed method.
The resonance phenomenon in a power system is the most critical issue when connecting an STPF to the network. Resonance issues (either series or parallel) arise at a frequency lower than the tuned frequency. Theoretically, the maximum efficiency is obtained if the STPF is tuned correctly to be equivalent to the harmonics frequency that has to be mitigated. Usually, the STPF is tuned between 3% and 10% of the series, and parallel resonance frequency to detune the effects. This provides a margin of safety in cases where high temperatures can lead to component failure or drifts in either capacitance or inductance nominal values [35,36].
2. Formulation of the NLCI Minimized STPF
In this section, an example of a non-sinusoidal power system is presented after compensation with the newly designed STPF and the mathematical expressions to define NLCI for the compensated system are presented. The major advantages of this approach are demonstrated since several relevant criteria have been taken into consideration in the proposed design when determining the STPF compensator values. The design accounts for the following:
- The effect of transmission line impedance on the load voltage at the PCC.
- Source nonlinearity is included in the problem formulation by incorporating as separate parameters the source harmonic current ISh and the source harmonic voltage VSh.
- Load nonlinearity is included in the problem formulation as separate parameters, the harmonic load current ILh and the harmonic load voltage VLh.
- The frequency dependence of the solution is taken into consideration.
- Compensator values that would generate resonance phenomena are identified and excluded from the domain of possible solutions.
A typical industrial power system, such as the one given in Figure 2, is considered to describe a novel approach based on NLCI. The configuration used is similar to that used for a single-line design of single-tuned passive filters using the response surface methodology [24], it comprises a transformer, the consumer loads (which include both linear and nonlinear loads) and the STPF filter connected to the PCC. Figure 3 describes the single-phase equivalent circuit of the industrial system under study with the novel shunt STPF providing compensation. In this circuit, the background voltage harmonic components are taken into account; these are represented by VSh. These voltage harmonic distortions affect a load bus at the PCC, which is which may be already suffering from extra current harmonic distortion due to nonlinear loads associated with the power distribution in the network.
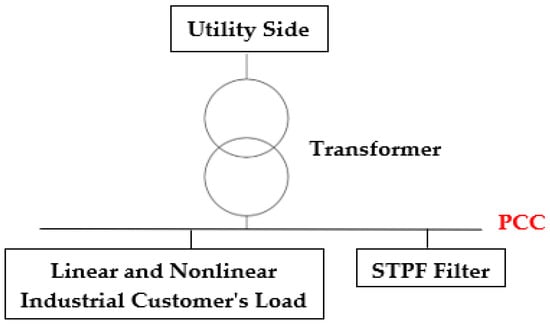
Figure 2.
Single-line diagram representation of the emulated system (after [23]).
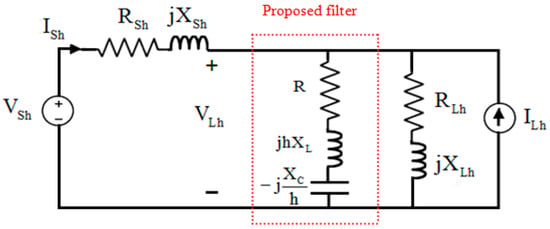
Figure 3.
Single-phase equivalent circuit of the compensated system.
The NLCI based current source model is also described by the nonlinear load currents ILh, where subscript h represents the harmonic order.
A linear load, such as a motor, will draw a non-linear current, i.e., one containing harmonics, if the voltage is distorted. However, the motor is simply drawing a current that is proportional, at each frequency, to its source voltage, based upon its impedance. Only a motor fed by a purely 60 Hz source was found to draw a current without any harmonic content [36]. Therefore, at any harmonic order h, the voltage source presented by the mains power provider, and the harmonic current source presented by the nonlinear user load, are given as
Furthermore, the source impedance (short-circuit impedance) ZSh and load impedance ZLh can be respectively expressed as
where RSh and XSh represent the Thevenin source resistance and reactance, respectively; and RLh represents the load resistance; and XLh represents the load reactance. All are given in ohms at harmonic order h.
The harmonic compensator impedance for the STPF at the hth harmonic is given as
where XL is the magnitude of the inductive reactance of the shunt filter at the fundamental frequency, XC is the magnitude of the capacitive reactance of the STPF at the fundamental frequency, R is the filter’s internal resistance and XF is the total complex filter reactance.
Following this analysis, the hth harmonic linear current (Ilinh) drawn by the ideal load and the compensated load voltage (VLh) at each harmonic number (h) are expressed as follows:
where
so that,
Then, one can define NLCI for the compensated system, as follows:
In this study, the effects of the main sources of uncertainty and disturbance were analyzed using four different case studies. The first two cases represent the system with low short-circuit capacity (80 MVA) and the second two cases represent a high short-circuit capacity (150 VA). For each short circuit capacity, the first scenario (cases 1 and 3) represents the system with no background voltage distortion but with load current harmonic distortion; the second scenario (cases 2 and 4) represents the system with both voltage and current harmonic voltage distortion.
Five different power quality indices were considered to assess and analyze the compensated system performance:
The compensated load power factor (PF) is calculated as follows:
where PL is the load active power per phase in watts (W).
The compensated displacement power factor (DPF), which is expressed as follows:
(where subscript “1” stands for the fundamental h order).
The transmission power loss (TL), which is given as follows:
The transmission efficiency (η), which is defined as follows:
where PS is the supply active power per phase in W.
Voltage total harmonic distortion (VTHD), which has been introduced to identify the harmonic component at the load bus, is expressed as
It has been assumed that the resistance of the compensator reactance was ignored because of its small size with respect to the magnitude of its fundamental reactance [37].
3. Constraints
3.1. Formulation of the Harmonic Resonance Constraint
Harmonic resonances are considered as the most significant factor that should be taken into consideration while designing a shunt STPF. Parallel resonance can be expressed as a high impedance to the flow of harmonic current, while series resonance can be expressed as a low impedance [35].
It is necessary to determine the value of the inductor and capacitors (hXL and XC/h) in order to avoid resonances in the power system under study. Consequently, the compensator parameters resulting in a resonant phenomenon have to be identified and considered in the optimization problem in order to be excluded from the available search space.
The hth equivalent impedance ZTHK as seen from the source-side, for the power system under study shown in Figure 3, is given as
Setting its imaginary part to zero and after some simplification, the resonance constraint equation is given as:
where
Solving for (hXL and XC/h),
where parameters αi (i = 1,2,3) in (22) are associated with the quadratic equation in XC and XL for any given harmonic order in the search algorithm.
3.2. Shunt Capacitor Constraints Based on the IEEE 18-2012 Standard
An algorithm with built in provisions to identify and avoid compensator parameters of the passive filter would likely produce its own resonance. Under resonance conditions, the system with a filter can, therefore, be considerably worse than a system without filters. Hence the algorithm has been designed to arrive at the optimal filter solution that satisfies the limitations of the PF constraints taking into account the source and load nonlinearities. Furthermore, the algorithm has been developed to optimally satisfy the practical constraints for the voltage total harmonic distortion at the PCC between the mains and the industrial consumer limits in compliance with IEEE 519-2014 guidelines to below the 5.0% limit of VTHD, with each individual harmonic limited to 3%.
The design of the shunt STPF requires compliance with IEEE Standard 18-2012 [38], which states that shunt capacitors will be capable of continuous operation without exceeding the following limitations:
1. Not to exceed 135% of the nominal the square of the root mean square (rms) capacitor current IC:
where the current of the capacitor (ICh) at the hth harmonic is given as:
2. Not to exceed 110 % of the nominal rms capacitor voltage (VC):
where the voltage of the capacitor (VCh) at the hth harmonic is given as:
3. Not to exceed 120 % of the peak voltage (VCP):
4. Not to exceed 135 % of the nominal kvar (QC):
3.3. Other Constraints Based on the IEEE 519-2014 Standard
Load power factor limits are taken into account due to some utilities imposing additional charges or penalties when the power factor is less than 90% or 95%, or for short periods of time up to 80% [35].
VTHD and ITHD expressed in (34) and (35), respectively, are considered the most common measurements used to represent the harmonic content waveform. Both are applied as constraints where the specifying limits are based on the IEEE 519-2014 Standard [39].
4. Optimization Technique and Search Algorithm
Minimization of the non-linearity current index (NLCI), measured at PCC, is proposed to represent the objective function for the optimal design parameter values of the filter. Maximizing PF enables the optimization of the STPF values, as it results to a passive filter design with an enhanced resonance damping ability. Both can be expressed as functions of the STPF filter parameters (XC and XL).
Thus, the objective functions of the filter design become as follows:
Minimize NLCI (XCi and XLi), subject to: 90 % ≤ PF (XCi and XLi) ≤ 100 %
XCi and XLi are excluded from the solution of Equation (27).
These nonlinear constraints limit PF within an acceptable specified range and avoid resonance. A general flow chart for the STPF search algorithm is demonstrated in Figure 4 using the feasible sequential quadratic programming (FFSQP) package. Optimal design of a filter often appears as a multi-factorial problem, because it generally contains different objectives with contradictory constraints pulling in different directions. FFSQP is ideal for this non-linear optimization design problem under conflicting design requirements [30].
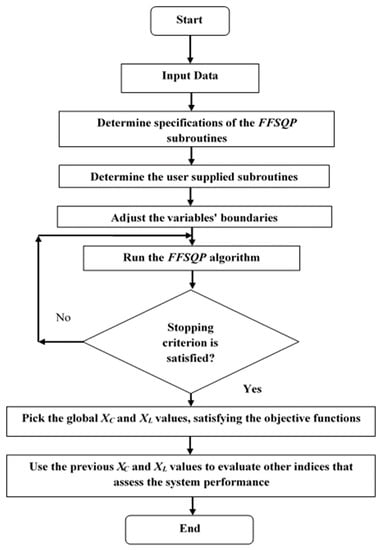
Figure 4.
Flowchart of the FFSQP search algorithm.
The FFSQP search algorithm steps in sequence, defined for the objective function under consideration, were as follows:
- Construct the needed subroutines (objective subroutine (f), constraints subroutine (g)) to develop the FFSQP search.
- Construct other subroutines that describe the mathematical modelling of the system.
- Run the search algorithm considering constraints.
- Choose the first value of the reactive power QCi rating of capacitor in kvar, so that QCi = {QC1, QC2… QCj}, where ΔQC or (QCj-QCj-1) is the kvar step. Also, j is the number of discrete values for the used voltage rating and i is a counter that has a starting value of 1.
- Calculate from
- Calculate XLi from equation (27).
- Run the search algorithm considering the filter component values to be the initial values at the beginning of each search in each region.
- Find the local solutions that achieve the best fitness of the considered objective.
- The algorithm will stop when a feasible point is reached or when the stopping criterion defined in terms of ε is met, where ε represents the relative difference in the objective function as a convergence-stopping criterion.
- After stopping, scan through local solutions to get the global one.
- Determine the filter parameters values corresponding to the global solution.
5. Case Studies and Simulated Results
Four cases of an industrial power system [40,41] were simulated by applying the above-mentioned optimization method. Table 1 and Table 2 show the numerical data and the corresponding industrial customer’s loading, respectively [40,41], these values have been subsequently adopted in other IEEE publications [42] and other publications on the subject [43]. The inductive three-phase linear and nonlinear load group is 5100 kW and 4965 kvar with a DPF of 0.7165. The 60-cycle supply bus voltage is 4.16 kV (line-to-line). Table 1 also gives the uncompensated power system performance results which are comparable with the shunt STPF compensation results.

Table 1.
Industrial plant parameters and source harmonics.

Table 2.
Detailed industrial loadings.
In Table 1, the first 2 rows show different power system parameters, subsequent 2 rows show the corresponding load parameters and all subsequent rows show the associated source and load harmonics. The first two cases (vertical columns) represent the system with low short-circuit capacity (80 MVA), while the third and fourth cases represent the system with high short-circuit capacity (150 MVA). For each short circuit capacity, the first scenario (Cases 1 and 3) represent the system with no background supply voltage distortion (VS 5 = 0 V, VS7 = 0 V, VS11 = 0 V, VS13 = 0 V) but with load current harmonic distortion (IL5 = 33 A, IL7 = 25 A, IL11 = 9 A, IL13 = 8 A); the second scenario (Cases 2 and 4) represents the system with both voltage and current harmonic distortion (VS5 = 96 V, VS7 = 72 V, VS11 = 48 V, VS13 = 24 V) and (IL5 = 33 A, IL7 = 25 A, IL11 = 9 A, IL13 = 8 A) respectively, where ILh is the hth harmonic load current in amperes and VSh is the hth harmonic source voltage in volts.
Table 3 presents the shunt STPF compensation simulated results using the proposed technique to account for the nonlinear loads. The optimal parameters of STPF (XL and XC) are subsequently found, these are dependent on the problem formulation. The system performance cases with shunt STPF installed at the load side confirms that different optimal solutions are obtained, satisfying all different criteria and constraints involved. Table 4 below, shows the levels of harmonic distortion and DPF after compensation. All resulting values appear well within the standard limits prescribed by IEEE Standard 519-2014 [39]. The objective function to minimize NLCI limited the total harmonic distortion of the voltage to 5% and the values are all well within the IEEE 519-2014 standard limits for the design of an STPF in all cases. It can be observed that all the tested orders of harmonics were reduced, including the low order harmonics (as can be seen in Figure 7 for case 2 and case 4).

Table 3.
Simulated outcomes for the presented optimization approach.

Table 4.
Harmonic distortions level and DPF after compensation for all cases under study.
The main merit of the presented approach is minimization of the NLCI, which is expected to reduce harmonics of the load voltage compared to an uncompensated system, even under the uncertainty of varying parameters. Moreover, placing more stringent requirements for voltage distortion reduction can benefit the level of harmonic current distortion. The simulation results highlight that the filter compensators can achieve the maximum PF (> 99%) in most cases. Figure 5 and Figure 6 show PF and TL values before and after being compensated for all cases, respectively.
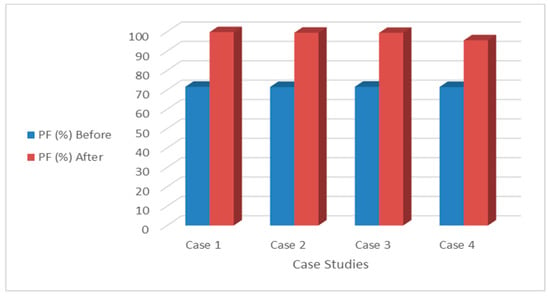
Figure 5.
PF improvement across all case studies.
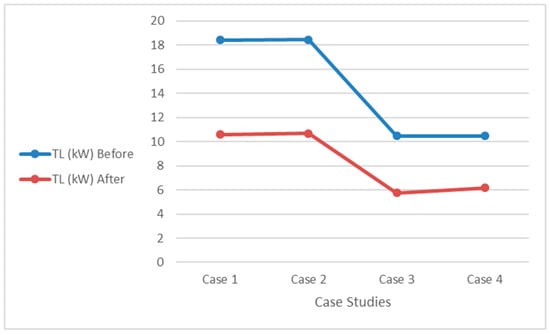
Figure 6.
Reduction in Transmission Losses (TL) across all case studies.
Transmission power losses can be reduced by correcting the power factor. Hence, the objective function of the filter design is subject to a constraint of 90 % ≤ PF ≤ 100 %. For all case studies, Figure 5 and Figure 6 show improvements in PF and reductions in transmission power losses respectively. For Figure 5 a reduction in transmission power losses for all case studies is attributed to the improvement in PF.
Figure 7 shows a comparison of the VTHD results for the four case studies before compensation and after, when incorporating the objective function of minimizing NLCI as an objective function. Lower VTHD values are achieved in all the cases studied, showing the quality of the PCC voltage is also enhanced in each case. This is explained by an increase in the fundamental harmonic value of the voltage for all the case studies and leads to the conclusion that harmonic voltage components are considerably reduced, compared to the uncompensated components in each case. Figure 7 also shows clear improvements by reductions in all the tested load harmonic voltages, in cases 2 and 4, which follow from the application of our optimization method.
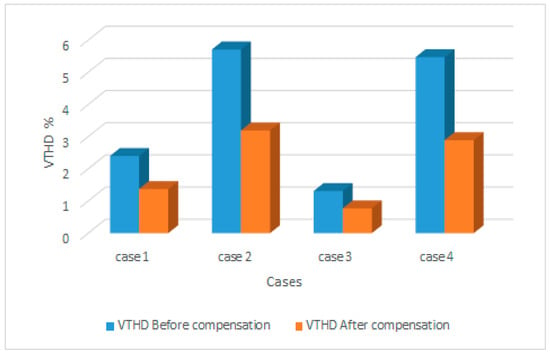
Figure 7.
Improvement shown by reduction of the voltage harmonic distortion levels (VTHD) below the IEEE 519-2014 standard limits in all case studies, using NLCI as an objective function.
The proposed design of the shunt STPF results in an improvement in both the PF and DPF values in all cases. Furthermore, a notable decrease in the transmission losses, with a commensurate increase in the transmission efficiency of the compensated system, leads to a reduction in the rms value of the line current. This indicates that the system has become more linear after compensation with the optimally designed filter based on the NLCI objective function. As a result, the differences between the rms value of the supply current and the rms value of the linear current are minimized, as calculated at the PCC.
Regarding capacitor loading constraints, Table 5 illustrates the calculated capacitor of the STPF duties for all cases under study. A comparison with the standard limits according to IEEE 18-2012 in the proposed design [38] validates the proposed approach.

Table 5.
Capacitor duties calculation for all case studies.
6. Conclusions
A mathematical model has been developed and a solution presented for minimizing the non-linearity current index at the voltage load bus; this is aimed at maintaining the power factor of distribution circuits when subjected to nonlinear loads within accepted operational levels (above 90% or 95% PF [35]), using an STPF compensator.
The main contribution of this paper is the innovative adoption of the NLCI in an STPF to distinguish between the current due to the mains supply distortion and the nonlinear current due to the industrial user’s loads. The user’s load sourced nonlinear currents produce harmonic voltages as they pass through upstream power system impedance components, such as cables etc. The IEEE Recommended Practice and Requirements for Harmonic Control in Electrical Power Systems (IEEE 519-2014 standard) [36] states that harmonic currents should be reduced in order to minimize voltage harmonics. The passive filter which we propose, as designed by the proposed NLCI minimization approach, has proven its effectiveness by reducing harmonic currents and minimizing harmonic voltage distortion in standard power system models. Our methodology takes into account the IEEE 519-2014 guidelines, the capacitor loading expectations as defined in IEEE 18-2012, and the resonance conditions in the power system. This improves the correctness of the obtained solution and enhances the capability of the search algorithm to ensure convergence to the optimal solution. STPFs have been suggested for nonlinear loads due to their characteristic features, making them suitable to act as compensators to improve the PF for such nonlinear industrial loads. Furthermore, they prevent the spread of harmonic load currents into networks.
The simplest type of shunt passive filter is the single-tuned passive filter; it forms a short-circuit across the harmonic source at the tuned frequency. In this case, the harmonic current of this order will oscillate between the harmonic source and the passive filter. If there are multiple arms in the single-tuned shunt filters, each of them will form a closed path with the harmonic source at its resonant frequency. In some cases, one single filter will be able to eliminate two or three harmonic orders simultaneously; these are called double-tuned filters or triple-tuned filters. However, they are more commonly used in HVDC systems rather than in other more common power system situations.
Standard passive filters are not suitable for varying power system conditions, since, once installed, they are fixed in place and have restricted operation as neither the tuned frequency nor the size of the filter can be changed easily. The passive elements in the filter are close-tolerance components, such that a change in the system operating conditions can lead to some detuning. Therefore, for routine operation, they require definite-purpose circuit breakers and special protective and monitoring devices. However, a well-designed, single-tuned passive filter has distinct advantages, including [2]:
- Tolerance to high levels of MVAr and almost maintenance-free service;
- They are more economical to implement than their rotating counterparts;
- A fast response time, of the order of one cycle or less, (which is particularly important in the presence of nonlinear loads).
The current paper tests a simple implementation of a newly designed single tuned passive filter, in model power systems with parameters selected to reflect IEEE standards and under typically experienced conditions. We recognize that real-world deployment would require, for example, additional filters (passive, active, or hybrid) and surge/transients protection (line reactors); however, this is beyond the scope of this paper.
Four cases of model power systems have been studied, with various configurations. Overall, all the performance indicators of the simulated results for the proposed method have been found to be satisfactory. This is illustrated by our results, which show that the newly designed filters assure that resonance is not introduced while maintaining objective functions within permissible limits for the power system, industrial customer’s loads, and passive filter. In addition, the approach and suggested methodology presented provide a reduction in power line transmission losses, a reduction of harmonic distortion levels, and power factor improvement compared with other published solutions. Future approaches that will be explored within the context of filter design include the use of fractional order identification algorithms [44] to optimize the in situ responses of the designed filters and the use of descriptor representations for designing more complex RLC filters [45] with tailored responses.
Author Contributions
M.A. designed and implemented the presented research study, analyzed the results, conducted the literature review and drafted the paper. S.H. oversaw the methodologies used. Both authors contributed to the editing of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education of Saudi Arabia through a PhD Scholarship to M.A.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sher, H.A.; Addoweesh, K.E.; Khan, K.E. Harmonics generation, propagation and purging techniques in non-linear loads. In an Update on Power Quality; Lu, D., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.C. Power System Harmonics and Passive Filter Designs; Wiley: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dugan, R.C.; McGranaghan, M.F.S.; Beaty, H.W. Electric Power Systems Quality; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, R.L.D.; de Azevedo, C.C.; de Sousa, R.M. A Robust Adaptive Control Strategy of Active Power Filters for Power Factor Correction, Harmonic Compensation, and Balancing of Nonlinear Loads. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 718–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Teng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X. Spectral correction approach based on desirable sidelobe window for harmonic analysis of industrial power system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassif, A.B.; Xu, W.; Freitas, W. An investigation on the selection of filter topologies for passive filter applications. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2009, 24, 1710–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobaa, A.F.; Vaccaro, A.; Zeineldin, H.H.; Lecci, A.; Monem, A.M.A. Sizing of passive filters in time-varying nonsinusoidal environments. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Harmonics and Quality of Power (ICHQP’10), Bergamo, Italy, 26–29 September 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Izhar, M.; Hadzer, C.M.; Syafrudin, M.; Taib, S.; Idris, S. Performance for passive and active power filter in reducing harmonics in the distribution system. In Proceedings of the PECon 2004—IEEE National Power Energy Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 29–30 November 2004; pp. 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri, P.; Xu, W. A technique to mitigate zero-sequence harmonics in power distribution systems. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2014, 29, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, A. An adaptive distance protection scheme in the presence of phase shifting transformer. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2015, 129, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, J.C.; Nascimento, M.H.R.; Júnior, J.D.A.B.; Fonseca, M.; de Freitas, C.A.O.; Carvajal, T.L.R. Optimization using NSGA II for Passive Filters in Industrial Networks. In Proceedings of the 13th IEEE International Conference on Industry Applications (INDUSCON), São Paulo, Brazil, 12–14 November 2018; pp. 339–346. [Google Scholar]
- Parkatti, P.; Tuusa, H.; Sarén, H.; Kuusela, K.; Björkman, M. Analysis and Performance of a High-Efficiency Transformerless Hybrid Active Filter. Int. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2011, 6, 537–546. [Google Scholar]
- Rozlan, M.B.M.; Zobaa, A.F.; Aleem, S.H.E.A. The Optimisation of Stand-Alone Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems Using HOMER. Int. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2011, 6, 1802–1810. [Google Scholar]
- Farhoodnea, M.; Mohamed, A.; Shareef, H.; Zayandehroodi, H. Localization of Multiple Harmonic Sources in Non-Radial Power Distribution Systems. Int. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2012, 7, 4134–4145. [Google Scholar]
- Jou, H.L.; Wu, J.C.; Wu, K.D.; Huang, M.S.; Lin, C.A. A Hybrid Compensation System Comprising Hybrid Power Filter and AC Power Capacitor. Electr. Power Energy Syst. J. 2006, 28, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwoharjono, M.A.; Penangsang, O.; Soeprijanto, A. Optimal Placement of SVC for Losses Reduction and Voltage Profile Improvement in Electrical Power System Using Improved Gravitational Search Algorithm. Int. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2013, 8, 329–339. [Google Scholar]
- Baitha, A.; Gupta, N. A comparative analysis of passive filters for power quality improvement. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Technological Advancements in Power and Energy (TAP Energy), Kollam, India, 24–26 June 2015; pp. 327–332. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, D.R.; Anuradha, K.; Saraswathi, P.; Gokaraju, R.; Ramamoorty, M. New low cost passive filter configuration for mitigating bus voltage distortions in distribution systems. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Building Efficiency and Sustainable Technologies, Singapore, 31 August–1 September 2015; pp. 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Zobaa, A.F. The Optimal Passive Filters to Minimize Voltage Harmonic Distortion at a Load Bus. IEEE Trans. Power Del. 2005, 20, 1592–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.M.; El-Zahab, E.E.A.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Zobaa, A.F. LC compensators for power factor correction of nonlinear loads. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2004, 19, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleem, S.H.E.; Zobaa, A.F.; Balci, M.E. Optimal resonance-free third-order high-pass filters based on minimization of the total cost of the filters using Crow Search Algorithm. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 151, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, G.G.; Klinkhachorn, P.; Tan, O.T.; Hartana, R.K. Optimal LC compensators for nonlinear loads with uncertain nonsinusoidal source and load characteristics. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1989, 4, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartana, R.K.; Richards, G.G. Comparing capacitive and LC compensators for power factor correction and voltage harmonic reduction. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 1989, 17, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakar, S.; Karaoglan, A.D.; Balci, M.E.; Aleem, S.H.A.; Zobaa, A.F. Optimal design of single-tuned passive filters using response surface methodology. In Proceedings of the 2015 International School on Nonsinusoidal Currents and Compensation (ISNCC), Lagow, Poland, 15–18 June 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zacharia, P.; Menti, A.; Zacharias, T. Genetic algorithm based optimal design of shunt compensators in the presence of harmonics. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2008, 78, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menti, A.; Zacharias, T.; Argitis, J.M. Optimal sizing and limitations of passive filters in the presence of background harmonic distortion. Electr. Eng. 2009, 91, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Aleem, S.H.E.; Balci, M.E.; Zobaa, A.F.; Sakar, S. Optimal passive filter design for effective utilization of cables and transformers under non-sinusoidal conditions. In Proceedings of the 2014 16th International Conference on Harmonics and Quality of Power (ICHQP’14), Bucharest, Romania, 25–28 May 2014; pp. 626–630. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.M.; El-Zahab, E.E.A.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Zobaa, A.F. Comparing capacitive and LC compensators for power factor correction. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Harmonics and Quality of Power, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 6–9 October 2002; pp. 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.M.; El-Zahab, E.E.A.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Zobaa, A.F. Practical considerations on power factor correction for nonlinear loads. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Harmonics and Quality of Power (ICHQP’02), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 6–9 October 2002; pp. 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel Aleem, S.H.E.; Zobaa, A.F.; Aziz, M.M.A. Optimal C-type passive filter based on minimization of the voltage harmonic distortion for nonlinear loads. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baici, M.E.; Karaoglan, A.D. Optimal design of C-type passive filters based on response surface methodology for typical industrial power systems. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2013, 41, 653–668. [Google Scholar]
- Zeineldin, H.H.; Zobaa, A.F. Particle swarm optimization of passive filters for industrial plants in distribution networks. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2011, 39, 1795–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.-R.; Shi, X.-C.; Peng, Y.-L.; Li, H.-M. Simulated annealing based multi-object optimal planning of passive power filters. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE/PES Transmission & Distribution Conference & Exposition: Asia and Pacific, Dalian, China, 18 August 2005; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Dell’Aquila, A.; Marinelli, M.; Monopoli, V.G.; Zanchetta, P. New power-quality assessment criteria for supply systems under unbalanced and nonsinusoidal conditions. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2004, 19, 1284–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahar, N.H.A.; Zobaa, A.F. Application of mixed integer distributed ant colony optimization to the design of undamped single-tuned passive filters based harmonics mitigation. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2019, 44, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piel, J.K.; Carnovale, D.J. Economic and Electrical Benefit of Harmonic Reduction Methods in Commercial Facilities; Eaton Electrical Inc.: Moon Township, PA, USA, 2004; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Elmathana, M.T.; Zobaa, A.F.; Hegazy, Y. Optimal Harmonic Filters Design Based Mean Value Estimation of the Source and Load Characteristics. Recent Pat. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2012, 5, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Standard 18-2012. IEEE Standard for Shunt Power Capacitors; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE Standard 519-2014. IEEE Recommended Practice and Requirements for Harmonic Control. In Electrical Power Systems; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE Standard 519-1992. IEEE Recommended Practices and Requirements for Harmonic Control. In Electrical Power Systems; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Wu, B.; Xu, D.; Zargari, N.R. A model predictive power factor control scheme with active damping function for current source rectifiers. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 2655–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, D.M.; Almelian, M.M. Optimal design of a single tuned passive filter to mitigate harmonics in power frequency. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2015, 10, 9009–9014. [Google Scholar]
- Abdollahi, R. Harmonic Mitigation using 36-Pulse AC-DC Converter for Direct Torque Controlled Induction Motor Drives. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2015, 13, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jacyntho, L.A.; Teixeira, M.C.M.; Cardim, E.A.R.; Galvão, R.K.H.; Hadjiloucas, S. Identification of fractional-order transfer functions using a step excitation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II, Express Briefs 2015, 62, 896–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, R.K.H.; Kienitz, K.H.; Hadjiloucas, S. Conversion of descriptor representations to state-space form: an extension of the shuffle algorithm. Int. J. Control 2018, 91, 2199–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).