Ocular Manifestations in Congenital Insensitivity to Pain with Anhidrosis: A Window into a Rare Syndrome
Abstract
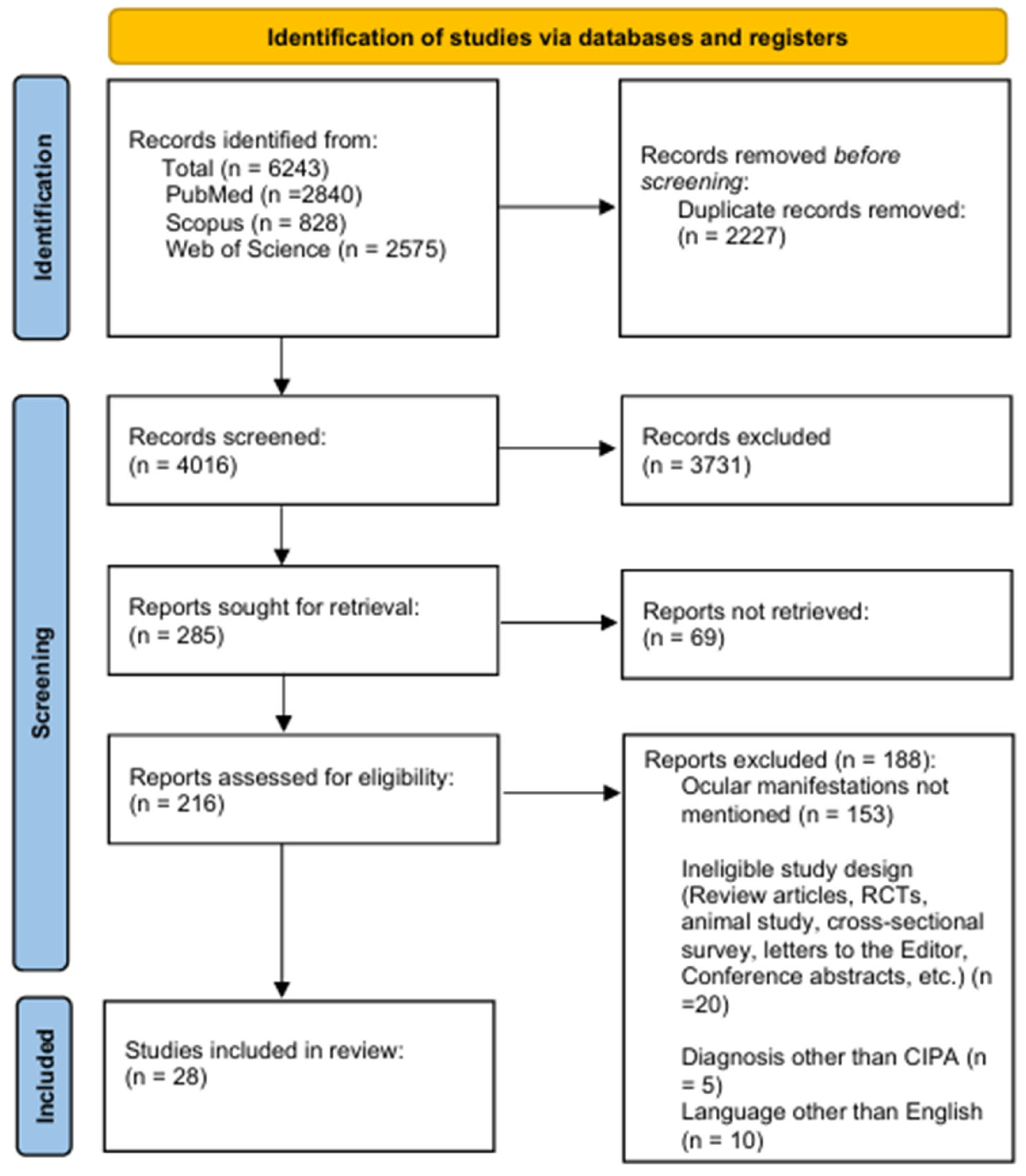
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Search Strategy and Information Sources
2.2.1. Medline/PUBMED
2.2.2. Scopus
2.2.3. Web of Science
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Study Selection and Screening
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Quality Assessment of Studies
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics and Patient Demographics
3.2. Ocular Manifestations
3.2.1. Common Ocular Manifestations
3.2.2. Rare Ocular Manifestations
3.3. Potential Medical Treatments of Ocular Abnormalities and Their Outcomes
3.4. Genetic Defects and Family History of Inherited Diseases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dyck, P.J.; Mellinger, J.F.; Reagan, T.J.; Horowitz, S.J.; Mcdonald, J.W.; Litchy, W.J.; Daube, J.R.; Fealey, R.D.; Go, V.L.; Kao, P.C.; et al. Not “indifference to pain” but varieties of hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy. Brain 1983, 106, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haga, N.; Kubota, M.; Miwa, Z. Epidemiology of hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type IV and V in Japan. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2013, 161, 871–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indo, Y.; Tsuruta, M.; Hayashida, Y.; Karim, M.A.; Ohta, K.; Kawano, T.; Mitsubuchi, H.; Matsuda, I.; Tonoki, H.; Awaya, Y. Mutations in the trka/high affinity ngf receptor gene in patients with congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis. Jpn. J. Hum. Genet. 1997, 42, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Drissi, I.; Woods, W.A.; Woods, C.G. Understanding the genetic basis of congenital insensitivity to pain. Br. Med. Bull. 2020, 133, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardy, S.; Miura, Y.; Endo, F.; Matsuda, I.; Indo, Y. Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis (CIPA): Effect of TRKA (NTRK1) missense mutations on autophosphorylation of the receptor tyrosine kinase for nerve growth factor. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudt, M.D.; Bailey, C.S.; Siddiqi, F. Charcot spinal arthropathy in patients with congenital insensitivity to pain: A report of two cases and review of the literature. Neurosurg. Rev. 2018, 41, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.J.; Reimann, F.; Nicholas, A.K.; Thornton, G.; Roberts, E.; Springell, K.; Karbani, G.; Jafri, H.; Mannan, J.; Raashid, Y.; et al. An SCN9A channelopathy causes congenital inability to experience pain. Nature 2006, 444, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.W.; Lee, M.C.H.; Harrison, E.K.; Menon, D.K.; Woods, C.G. Case Report: Neuropathic pain in a patient with congenital insensitivity to pain. F1000Research 2015, 3, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy Erez, D.; Levy, J.; Friger, M.; Aharoni-Mayer, Y.; Cohen-Iluz, M.; Goldstein, E. Assessment of cognitive and adaptive behaviour among individuals with congenital insensitivity to pain and anhidrosis. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2010, 52, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsana, B.; Gradstein, L.; Imtirat, A.; Yagev, R.; Barrett, C.; Ling, G.; Abu Tailakh, M.; Baidousi, A.; Tsumi, E. Ocular manifestations of congenital insensitivity to pain: A long-term follow-up. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 106, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchetti, M.; Lambiase, A. Diagnosis and management of neurotrophic keratitis. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2014, 8, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimura, T.; Amano, S.; Fukuoka, S.; Honda, N.; Arita, R.; Ochiai, M.; Yanagisawa, M.; Usui, T.; Ono, K.; Araki, F.; et al. In vivo confocal microscopy of hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy. Curr. Eye Res. 2008, 33, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, D.; Thomas, M.; Jacob, P. Neurotrophic keratitis and congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis—A case report with 10-year follow-up. Cornea 2011, 30, 100–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yang, Z.H.; Huang, D.; Weng, H.; Zeng, X.T. Methodological quality (risk of bias) assessment tools for primary and secondary medical studies: What are they and which is better? Mil. Med. Res. 2020, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardy, P.A.; Greenberg, L.W.; Kachel, C.; de Leon, G.F. Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhydrosis. Report of a family and review of literature with reference to immune deficiency. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1979, 133, 1153–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verity, C.M.; Dunn, H.G.; Berry, K. Children with reduced sensitivity to pain: Assessment of hereditary sensory neuropathy types II and IV. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1982, 24, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahim, J.S.; Roberts, M.W.; McDonald, H.D. Oral and maxillofacial complications associated with congenital sensory neuropathy with anhydrosis: Report of two cases. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1987, 45, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashtan, H.I.; Heyneker, T.J.; Morell, R.C. Atypical response to scopolamine in a patient with type IV hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy. Anesthesiology 1992, 76, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilz, M.J.; Stemper, B.; Axelrod, F.B. Sympathetic skin response differentiates hereditary sensory autonomic neuropathies III and IV. Neurology 1999, 52, 1652–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagev, R.; Levy, J.; Shorer, Z.; Lifshitz, T. Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis: Ocular and systemic manifestations. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1999, 127, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatzky, S.; Moses, S.; Levy, J.; Pinsk, V.; Hershkovitz, E.; Herzog, L.; Shorer, Z.; Luder, A.; Parvari, R. Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis (CIPA) in Israeli- Bedouins: Genetic heterogeneity, novel mutations in the TRKA/NGF receptor gene, clinical findings, and results of nerve conduction studies. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2000, 92, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarade, E.F.; El-Sheikh, H.F.; Tabbara, K.F. Indolent corneal ulcers in a patient with congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis: A case report and literature review. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 12, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shorer, Z.; Moses, S.W.; Hershkovitz, E.; Pinsk, V.; Levy, J. Neurophysiologic studies in congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis. Pediatr. Neurol. 2001, 25, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiura, M.; Torigoe, K.; Numata, O.; Yazaki, S.; Kuwabara, A.; Matsunaga, M.; Hasegawa, S.; Boku, N.; Ino, H.; Indo, Y.; et al. Case of congenital indifference to pain with anhidrosis using sympathetic skin response as a useful supportive diagnostic method in the early stage of infancy. Pediatr. Int. 2002, 44, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, J.; Monos, T.; Levy, J.; Shelef, I.; Nash, M.; Lifshitz, T. Intrasinus wood foreign body causing orbital cellulitis in congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis syndrome. Ophthal. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2004, 20, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalka, M.M.S.; Corrêa, M.S.N.P.; Ciamponi, A.L. Congenital insensitivity-to-pain with anhidrosis (CIPA): A case report with 4-year follow-up. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontology 2006, 101, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, S.; Fukuoka, S.; Usui, T.; Honda, N.; Ideta, R.; Ochiai, M.; Yamagami, S.; Araie, M.; Awaya, Y. Ocular manifestations of congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2006, 141, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçükdurmaz, F.; Imren, Y.; Uruc, V.; Sen, C. Congenital Insensitivity to Pain with Anhidrosis (CIPA) Manifested with Chronic Osteomyelitis; A Case Report. J. Clin. Aanalytical Med. 2015, 6, 230–232. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Guo, H.; Ye, N.; Bai, Y.; Liu, X.; Yu, P.; Xue, Y.; Ma, S.; Wei, K.; Jin, Y.; et al. Oral and Craniofacial Manifestations and Two Novel Missense Mutations of the NTRK1 Gene Identified in the Patient with Congenital Insensitivity to Pain with Anhidrosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, M.; Spiegler, J.; Härtel, C.; Gillessen-Kaesbach, G.; Kaiser, M.M. Severe complications in wound healing and fracture treatment in two brothers with congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. Part B 2013, 22, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, S.; Javed, M.A. Seeing is not always believing: Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis mimicking leprosy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, e153–e154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guven, Y.; Altunoglu, U.; Aktoren, O.; Uyguner, Z.O.; Kayserili, H.; Kaewkahya, M.; Kantaputra, P.N. Twins with hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type IV with preserved periodontal sensation. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2014, 57, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofluoğlu, D.; Altın, N.; Yaman, E.; Tuna İnce, E.B.; Aytepe, Z.; Tanyeri, H. Oral Manifestations and Prosthetic Rehabilitation in Hereditary Sensory and Autonomic Neuropathy (Hsan) Type Iv: A Case Report. J. Istanbul Univ. Fac. Dent. 2016, 50, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, S.A.; Malik, A.A. Case Report Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis in Sudanese children. Sudan. J. Paediatr. 2016, 16, 80. [Google Scholar]
- Altassan, R.; Al Saud, H.; Masoodi, T.A.; Al Dosssari, H.; Khalifa, O.; Al-Zaidan, H.; Sakati, N.; Rhabeeni, Z.; Al-Hassnan, Z.; Binamer, Y.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies novel NTRK1 mutations in patients with HSAN-IV phenotype. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2017, 173, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Liu, Y.; Ren, X.Z.; Guan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mao, B.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X. Novel NTRK1 mutations in Chinese patients with congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis. Mol. Pain 2018, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, B.; Reddy, V.; Kurth, I.; Jagadeesh, S. A Child Presenting with Recurrent Corneal Ulcers: Hereditary Sensory and Autonomic Neuropathy IV (HSAN IV). Neuro-Ophthalmol. 2019, 43, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masri, A.; Shboul, M.; Khasawneh, A.; Jadallah, R.; ALmustafa, A.; Escande-Beillard, N.; Hamamy, H.; Bakri, F.; Reversade, B. Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis syndrome: A series from Jordan. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2020, 189, 105636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Cortés, A.; Zambrano, A.K.; Guevara-Ramírez, P.; Echeverría, B.A.; Guerrero, S.; Cabascango, E.; Pérez-Villa, A.; Armendáriz-Castillo, I.; García-Cárdenas, J.M.; Yumiceba, V.; et al. Clinical, genomics and networking analyses of a high-altitude native American Ecuadorian patient with congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis: A case report. BMC Med. Genom. 2020, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, A.; Ramasubramanian, S.; Swaminathan, M. The painless eye: Neurotrophic keratitis in a child suffering from hereditary sensory autonomic neuropathy type IV. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 68, 2270–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indo, Y. NGF-dependent neurons and neurobiology of emotions and feelings: Lessons from congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 87, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederhauser, O.; Mangold, M.; Schubenel, R.; Kusznir, E.A.; Schmidt, D.; Hertel, C. NGF ligand alters NGF signaling via p75(NTR) and TrkA. J. Neurosci. Res. 2000, 61, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.; Eid, S.; Joulani, J.; Hazaimeh, E.; Jbarah, O.; Khawaldeh, M.; Bashaireh, Y.; Al-Kareem, K.A.; Bani-Amer, S. Ocular Manifestations of Congenital Insensitivity to Pain with Anhidrosis: A Systematic Review (P7-8.002). Neurology 2024, 102 (Suppl. S1), 3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Authors | Sample Size (Cases) | aAge (Years) | Sex | Country | Study Design | Ocular Manifestations | Ophthalmic Examinations/Investigations | Comorbidities | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | Male | ||||||||
| Vardy et al., 1979 [16] | 1 | 0.33 | 1 | 0 | Israel | Case report | Corneal opacities | N/A | Hypotonia, hypersalivation, osteomyelitis |
| Verity et al., 1982 [17] | 1 | 4.00 | 0 | 1 | UK | Case report | blepharoptosis, retinal arteries were unusually tortuous | N/A | Bilateral Horner’s syndrome, osteomyelitis, fractured lumbar verte bra, poor temperature control, ab normal behavior, left otitis media, rupture of the eardrum, self-mutilated fingers, diminished sensitivity to pain |
| Brahim et al., 1987 [18] | 2 | 9.00 | 0 | 2 | USA | Case report | Corneal opacities | N/A | Dry skin, shortened fingertips scarred by trauma, absence of sensation to superficial, deep, or visceral pain |
| Kashtan et al., 1992 [19] | 1 | 23.00 | 1 | 0 | USA | Case Report | Decreased lacrimation | N/A | Chronic right-hip osteomyelitis |
| Hilz et al., 1999 [20] | 1 | 10.00 | 0 | 1 | USA | Neurophysiologic study | Corneal scar | N/A | 7 patients had burns and bone fractures, 5 had joint deformities of the knees and ankles |
| Yagev et al., 1999 [21] | 15 | 3.75 | 8 | 7 | Israel | Prospective case series | Corneal opacities, corneal ulcers | Visual acuity, refraction where possible, ex amination of corneal sensation, ocular movement examination, and a biomicroscopic examination of the anterior and posterior segments, tear-film breakup time test. Examination showed clear lenses and normal fundi in all patients. | Microcephalus arthrogryposis, deafness, congenital dislocation of the hip |
| Shatzky et al., 2000 [22] | 12 | N/A | 0 | 12 | Israel | Neurophysiologic study | Neurotrophic keratitis, corneal ulcers | N/A | Amputations of fingers and limbs, septic arthritis, Charcot joints |
| Jarade et al., 2001 [23] | 1 | 6.00 | 0 | 1 | Saudi Arabia | Case report | Corneal ulcers, eye redness | Schirmer reflex test, corneal reflex test, corneal scrapings from both eyes were subjected to Giemsa and Gram stains and cultured for bacteria and fungi | N/A |
| Shorer et al., 2001 [24] | 7 | 4.90 | 0 | 7 | Israel | Neurophysiologic study | Corneal ulcers | Visual acuity, evaluation of corneal sensation, ocular movement, biomicroscopic ex amination of the anterior and posterior segments, lacrimation was assessed by a tear-film breakup time test | N/A |
| Hiura et al., 2002 [25] | 1 | 0.25 | 0 | 1 | Japan | Case report | Blepharoptosis | N/A | High fever, deciduous teeth germ |
| Levy et al., 2004 [26] | 1 | 2.00 | 0 | 1 | Israel | Case report | Corneal erosion | N/A | Orbital cellulitis |
| Schalka et al., 2006 [27] | 1 | 1.33 | 1 | 0 | Brazil | Case report | Corneal ulcer | N/A | Oral lesions, unexplained recurrent fever episodes, osteomyelitis, bites fingers, self-mutilated |
| Amano et al., 2006 [28] | 18 | 10.50 | 7 | 11 | Japan | Prospective case series | Corneal opacities, Superficial punctate keratopathy (SPK), ciliary entropion, exotropia, esotropia, keratoconus | visual acuity, refraction by skiascopy or autorefractometer, slit-lamp examination of the anterior segment, tear breakup time (TBUT), Schirmer 1 test | N/A |
| John et al., 2010 [13] | 1 | 3.00 | 1 | 0 | India | Case report | Neurotrophic keratitis (watering, epithelial defect and hypopyon, corneal scar with thinning and vascularization) | Slit-lamp examination, corneal sensation checked with the tip of cotton wool, corneal scraping for bacterial and fungal smear (culture did not show any pathogens) | Autoamputation of fingers and toes and Charcot joints |
| Kucukdurmaz et al., 2012 [29] | 1 | 10.00 | 0 | 1 | Turkey | Case report | Corneal opacities | N/A | high fever, septic arthritis, osteo myelitis |
| Gao et al., 2013 [30] | 1 | 6.00 | 0 | 1 | China | Case report | Corneal ulcer, congenital keratitis | N/A | congenital nasal defects, submucous cleft palate and alveolar bone loss of the maxilla and mandible |
| Rapp et al. 2013 [31] | 2 | 4.00 | 0 | 2 | Germany | Case report | Corneal ulcer | N/A | Osteomyelitis, avascular necrosis |
| Iftikhar et al. 2013 [32] | 1 | 30.00 | 1 | 0 | Pakistan | Case report | Corneal opacity, sluggishly reactive pupils | Schirmer’s test | N/A |
| Guven et al., 2014 [33] | 2 | 17.00 | 0 | 2 | Turkey | Case report | Corneal opacities | N/A | N/A |
| Ofluoglu et al., 2015 [34] | 1 | 11.00 | 0 | 1 | Turkey | Case report | Corneal ulcer, scleral hyperemia, neurotrophic keratitis | N/A | Tissue loss due to burn injury of the second right finger, deep oral ulcers |
| Othman et al., 2016 [35] | 1 | 2.00 | 1 | 0 | Sudan | Prospective case series | Corneal scar | N/A | Dry hot skin, lower respiratory tract infection, hypotonia, insensitivity to pain |
| Altassan et al., 2017 [36] | 2 | 4.00 | 1 | 1 | Saudi Arabia | Case report | Corneal opacities | N/A | Dextrocardia, bilateral conductive hearing loss, Charcot deformity, autonomic dysfunction |
| Geng et al., 2018 [37] | 5 | 7.92 | 0 | 0 | China | Case series | Blepharoptosis | N/A | Damaged tongue, slow wound healing, fractures, osteomyelitis |
| Suresh et al., 2018 [38] | 1 | 0.83 | 0 | 1 | India | Case report | Recurrent corneal ulcer, neurotrophic keratitis | N/A | recurrent respiratory infections, several febrile episodes |
| Masri et al., 2019 [39] | 4 | 1.00 | 1 | 3 | Jordan | Retrospective analysis | Corneal ulcers | N/A | 1 patient had hip joint dislocation and jaw fracture, 1 had bilateral hip and shoulder dislocation following a seizure, 1 had arthritis and fracture of upper limb, 1 had chronic osteomyelitis and acute transient renal failure, and all had microcephaly |
| López-Cortés et al., 2020 [40] | 1 | 9.00 | 1 | 0 | Ecuador | Case report | Corneal ulcers | N/A | Pneumonia, osteomyelitis, tibial fracture, osteochondroma, femoral fracture |
| Sethi et al., 2020 [41] | 1 | 3.00 | 1 | 0 | India | Case report | Neurotrophic keratitis, blurred vision, redness, watering, superficial punctate keratitis, nebulo-macular corneal scar | Schirmer’s test, slit-lamp, tear film, visual acuity | N/A |
| Elsana et al., 2021 [10]) | 32 | 15.13 | 13 | 19 | Israel | Retrospective analysis | Corneal ulceration, corneal opacities, Superficial punctate keratitis, esotropia, exotropia blepharoptosis, astigmatism, keratoconus with corneal hy drops, decreased lacrimation | visual acuity, cycloplegic refraction, corneal sensitivity, TBUT, Schirmer test and posterior segment findings | N/A |
| Ocular Manifestations | Sample Size (Cases) | Sample Size (Eyes) | Bilateral Involvement (Number of Cases) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absent corneal sensitivity | 56 (47.5%) | 112 | 56 (100%) | [10,13,16,17,18,21,27,28,29,31,33,34,35,36,37,38,40] |
| Corneal ulcer | 46 (38.98%) | 54 | 8 (17.08%) | [10,21,22,23,26,27,30,31,34,38,39,40] |
| Corneal opacity | 32 (27.11%) | 51 | 19 (57.57%) | [10,16,18,21,28,29,32,33,36] |
| Decreased lacrimation | 26 (22%) | 52 | N/A | [10,16,17,19,20,28,31,32,33,41] |
| Superficial punctate keratopathy | 19 (16.1%) | 27 | N/A | [10,28,41] |
| Blepharoptosis | 8 (6.7%) | 9 | 1 (12.5%) | [10,17,25,37] |
| Neurotrophic keratitis | 4 (3.3%) | 5 | 3 (75%) | [13,22,34,41] |
| Exotropia | 4 (3.3%) | 4 | N/A | [10,28] |
| Esotropia | 4 (3.3%) | 4 | 0 | [10,28] |
| Corneal scar | 4 (3.3%) | 2 (50%) | [13,20] | |
| Red eye | 3 (2.5%) | 6 | 3 (100%) | [23,34,41] |
| Ciliary entropion | 2 (1.6%) | 3 | 1 (50%) | [28] |
| Keratoconus | 2 (1.6%) | 4 | 2 (100%) | [10,28] |
| Epiphora | 2 (1.6%) | 4 | 2 (50%) | [13,41] |
| Astigmatism | 2 (1.6%) | 2 | 0 | [10] |
| Congenital keratitis | 1 (0.8%) | 1 | 0 | [30] |
| Hypopyon | 1 (0.8%) | 1 | 0 | [13] |
| Sluggishly reactive pupil | 1 (0.8%) | 1 | 0 | [32] |
| Blurred vision | 1 (0.8%) | 1 | 0 | [41] |
| Tortuous retinal arteries | 1 (0.8%) | 1 | 0 | [17] |
| Ocular Manifestation | Mutation | Reference | Number of Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corneal ulcers | rs763758904 (Arg602*) | López-Cortés 2020 [40] | 1 |
| c.1860_186 1insT; p.Pro621fs | Masri 2019 [39] | 4 | |
| c.1561T-C in exon 13 and c.2057 G-A in exon 15 | Gao 2013 [30] | 1 | |
| “TrkA: 1926-ins-T” and “TrkA: Pro-689-Leu” | Shatzky 2000 [22] | 12 | |
| TrkA: 1926-ins-T | Shorer 2001 [24] | 7 | |
| homozygous c.274dupG, pGlu92GlysfsX81 | Rapp 2013 [31] | 1 | |
| TrkA: 1926-ins-T | Elsana 2021 [10] | 8 | |
| frameshift mutation NTRK1 c.717delG and pMet239fs | Suresh 2018 [38] | 1 | |
| Corneal opacity | three missense mutations (p.Arg110Asp, p.Arg643Gln, p.Leu694- Pro) and two nonsense mutations (p.Ser146Ter, p.Lys476Ter) | Altassann 2017 [36] | 2 |
| homozygous c.2001C-T alteration in exon 15 | Guven 2014 [33] | 2 | |
| Absent corneal reflex | five missense mutations (c.1784T>G, c.1927C>T, c.2056C>T, c.2152G > A, and c.2293C>T), one nonsense mutation (c.1786C>T, R596*), two frameshift mutations (c.963delG, c.1736delT), and four intronic splicing mutations (c.851-33T>A, c.287+2dupT c.850+1G>A, c.2188-11G>A) | Geng 2018 [37] | 5 |
| rs763758904 (Arg602*) | López-Cortés 2020 [40] | 1 | |
| three missense mutations (p.Arg110Asp, p.Arg643Gln, p.Leu694- Pro) and two nonsense mutations (p.Ser146Ter, p.Lys476Ter) | Altassann 2017 [36] | 2 | |
| homozygous c.2001C-T alteration in exon 15 | Guven 2014 [33] | 2 | |
| homozygous c.274dupG, pGlu92GlysfsX81 | Rapp 2013 [31] | 2 | |
| TrkA: 1926-ins-T | Elsana 2021 [10] | 13 | |
| frameshift mutation NTRK1 c.717delG and pMet239fs | Suresh 2018 [38] | 1 | |
| Decreased Lacrimation | TrkA: 1926-ins-T | Elsana 2021 [10] | 9 |
| homozygous c.274dupG, pGlu92GlysfsX81 | Rapp 2013 [31] | 2 | |
| homozygous c.2001C-T alteration in exon 15 | Guven 2014 [33] | 2 | |
| Superficial Punctate Keratopathy | TrkA: 1926-ins-T | Elsana 2021 [10] | 6 |
| blepharoptosis | TrkA: 1726-del-C | Hiura et al. [25] | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baker, M.; Abedal-Kareem, K.; Eid, S.; Alkhawaldeh, M.; Albashaireh, Y.; Joulani, J.; Bani Amer, S.; Hazaimeh, E.; Jbarah, O.F.; Aleshawi, A.; et al. Ocular Manifestations in Congenital Insensitivity to Pain with Anhidrosis: A Window into a Rare Syndrome. Vision 2025, 9, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9030062
Baker M, Abedal-Kareem K, Eid S, Alkhawaldeh M, Albashaireh Y, Joulani J, Bani Amer S, Hazaimeh E, Jbarah OF, Aleshawi A, et al. Ocular Manifestations in Congenital Insensitivity to Pain with Anhidrosis: A Window into a Rare Syndrome. Vision. 2025; 9(3):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9030062
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaker, Mohammed, Kenda Abedal-Kareem, Sadeen Eid, Mahmoud Alkhawaldeh, Yahya Albashaireh, Jihan Joulani, Sara Bani Amer, Ethar Hazaimeh, Omar F. Jbarah, Abdelwahab Aleshawi, and et al. 2025. "Ocular Manifestations in Congenital Insensitivity to Pain with Anhidrosis: A Window into a Rare Syndrome" Vision 9, no. 3: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9030062
APA StyleBaker, M., Abedal-Kareem, K., Eid, S., Alkhawaldeh, M., Albashaireh, Y., Joulani, J., Bani Amer, S., Hazaimeh, E., Jbarah, O. F., Aleshawi, A., & Al-Dwairi, R. (2025). Ocular Manifestations in Congenital Insensitivity to Pain with Anhidrosis: A Window into a Rare Syndrome. Vision, 9(3), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9030062





