No Evidence of Cross-Orientation Suppression Differences in Migraine with Aura Compared to Healthy Controls
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Observers
2.2. Aparatus
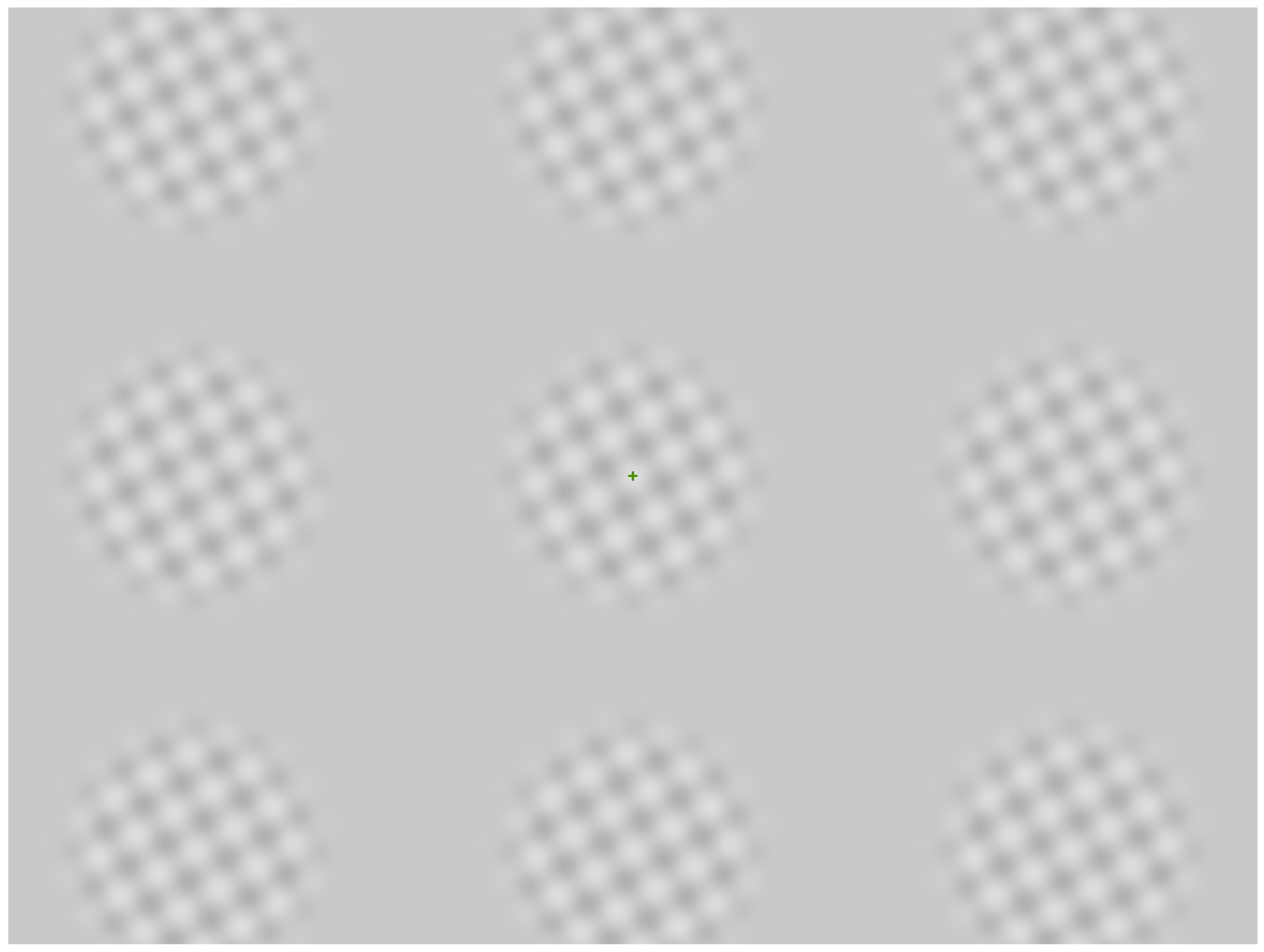
2.3. Stimuli
2.4. Procedure
2.5. Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Resting State Alpha Peak Frequency
3.2. Cross-Orientation Suppression
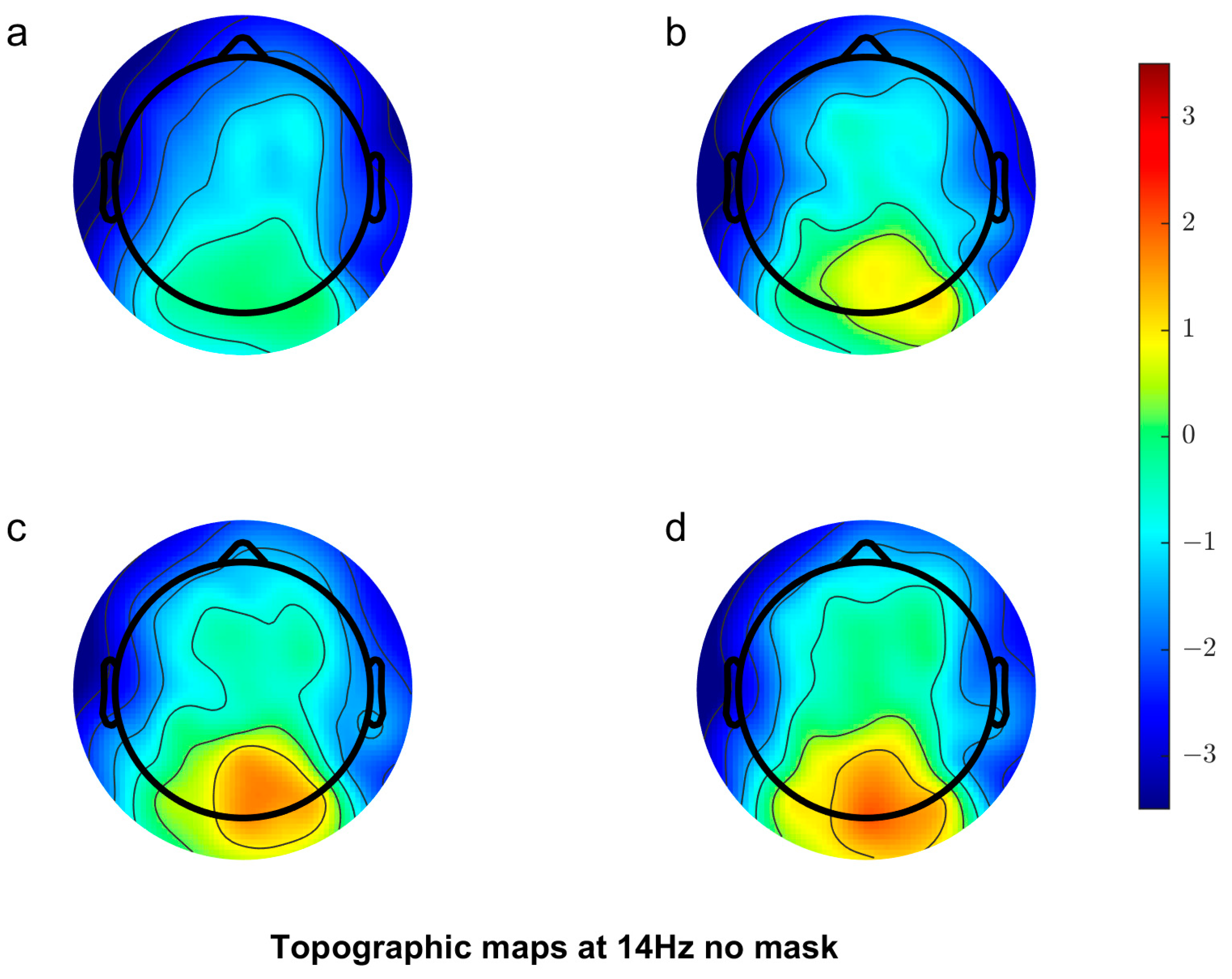
3.2.1. Scalp Topography
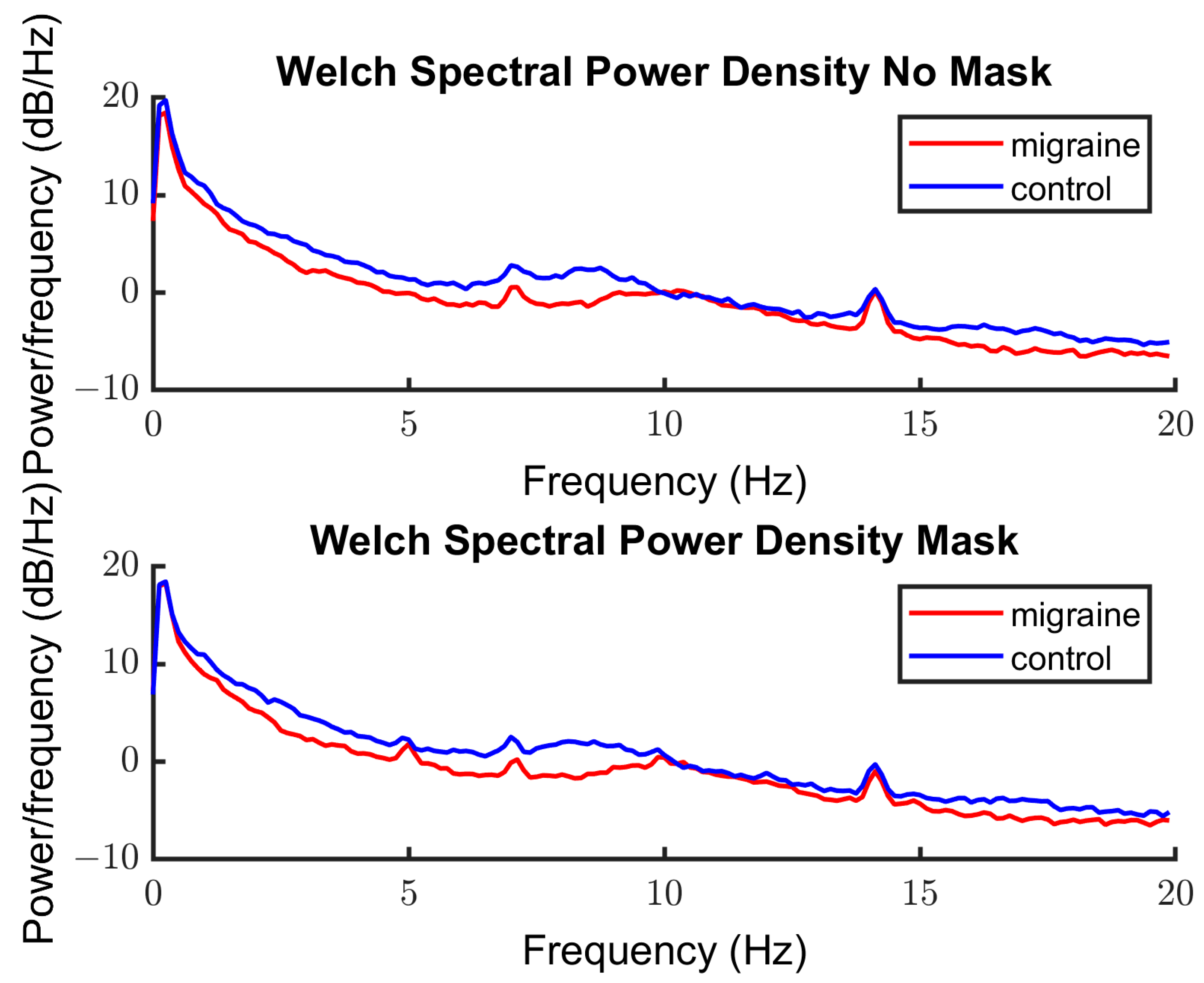
3.2.2. Spectra
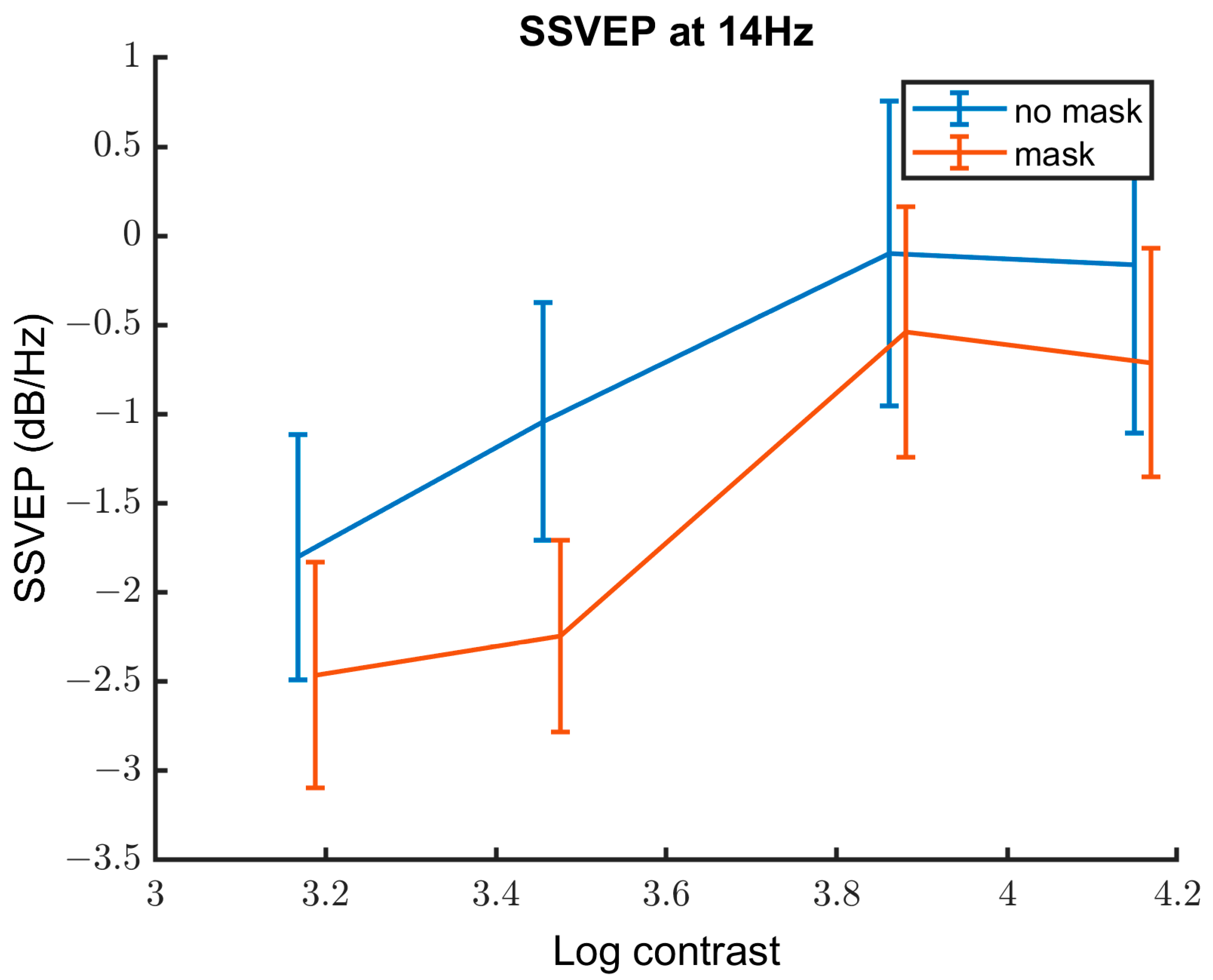
3.2.3. Contrast Response Function
3.3. Behavioural Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

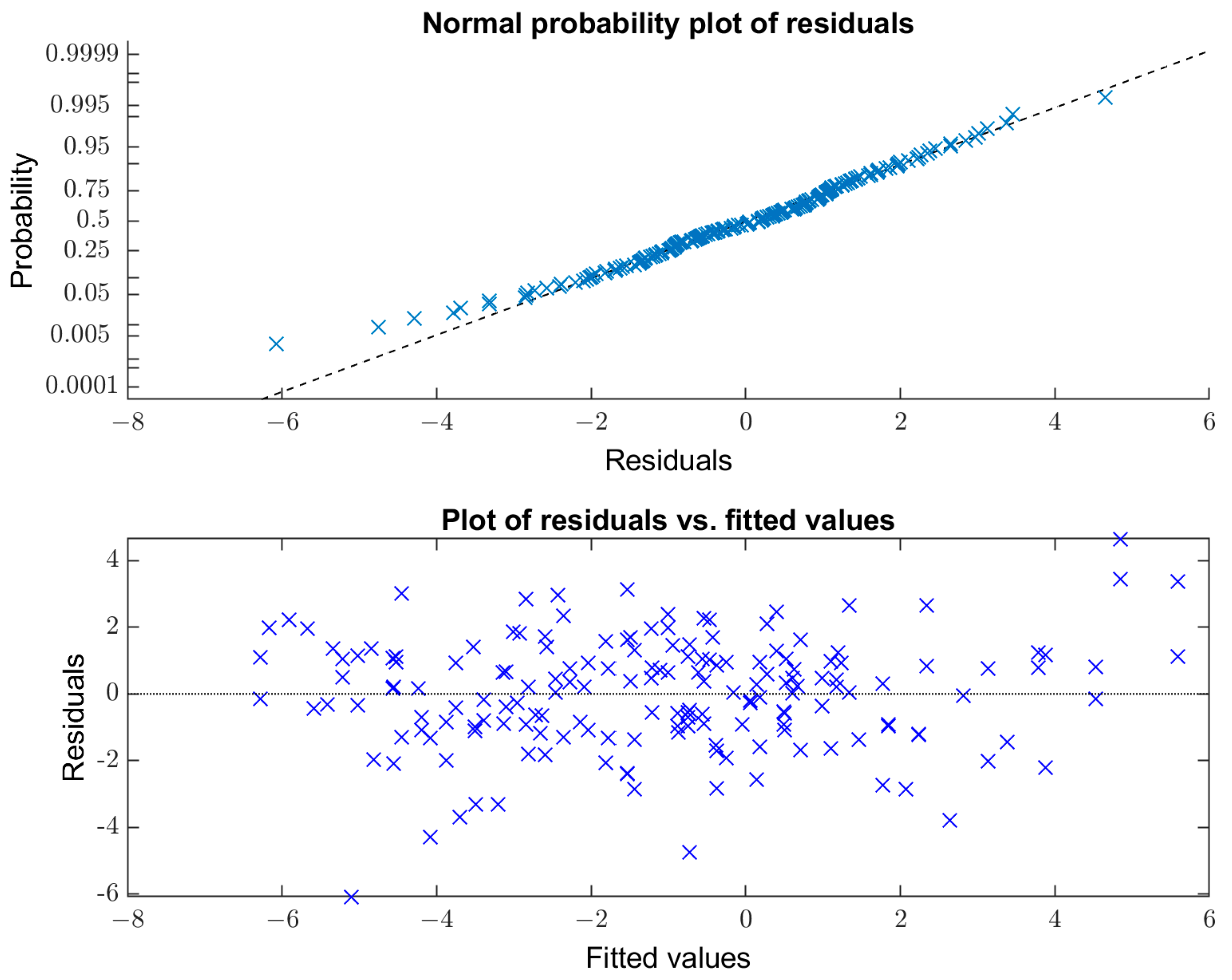
Appendix B
Appendix C
| Variable | Estimate of the Coefficient | SE | p-Value | Lower CI | Upper CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contrast | 1.42 | 0.28 | 1.05 × 10−6 | 0.87 | 1.97 |
| Group | −0.45 | 0.39 | 0.24 | −0.31 | 1.22 |
| Mask | −3.82 | 0.61 | 2.65 × 10−9 | −5.02 | −2.63 |
References
- Woldeamanuel, Y.W.; Cowan, R.P. Migraine affects 1 in 10 people worldwide featuring recent rise: A systematic review and meta-analysis of community-based studies involving 6 million participants. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 372, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, M.D. The economic burden of migraine to society. Pharmacoeconomics 1998, 13, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, R.B.; Stewart, W.F.; Diamond, S.; Diamond, M.L.; Reed, M. Prevalence and burden of migraine in the United States: Data from the American Migraine Study II. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2001, 41, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradeep, R.; Nemichandra, S.C.; Harsha, S.; Radhika, K. Migraine disability, quality of life, and its predictors. Ann. Neurosci. 2020, 27, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Headache Classification Committee (HCC) of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viana, M.; Sances, G.; Linde, M.; Ghiotto, N.; Guaschino, E.; Allena, M.; Terrazzino, S.; Nappi, G.; Goadsby, P.J.; Tassorelli, C. Clinical features of migraine aura: Results from a prospective diary-aided study. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schott, G.D. Exploring the visual hallucinations of migraine aura: The tacit contribution of illustration. Brain 2007, 130, 1690–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goadsby, P.J.; Holland, P.R.; Martins-Oliveira, M.; Hoffmann, J.; Schankin, C.; Akerman, S. Pathophysiology of migraine: A disorder of sensory processing. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 553–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hare, L.; Hibbard, P.B. Visual processing in migraine. Cephalalgia 2016, 36, 1057–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brighina, F.; Palermo, A.; Fierro, B. Cortical inhibition and habituation to evoked potentials: Relevance for pathophysiology of migraine. J. Headache Pain 2009, 10, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hare, L.; Tarasi, L.; Asher, J.M.; Hibbard, P.B.; Romei, V. Excitation-inhibition imbalance in migraine: From neurotransmitters to brain oscillations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, G.; Ambrosini, A.; Clemente, L.D.; Magis, D.; Fumal, A.; Gerard, P.; Pierelli, F.; Schoenen, J. Interictal abnormalities of gamma band activity in visual evoked responses in migraine: An indication of thalamocortical dysrhythmia? Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, G.; Di Renzo, A.; Tinelli, E.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Parisi, V.; Serrao, M.; Schoenen, J.; Pierelli, F. Thalamo-cortical network activity during spontaneous migraine attacks. Neurology 2016, 87, 2154–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugué, L.; Marque, P.; VanRullen, R. The phase of ongoing oscillations mediates the causal relation between brain excitation and visual perception. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 11889–11893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, O.; Gips, B.; Bergmann, T.O.; Bonnefond, M. Temporal coding organized by coupled alpha and gamma oscillations prioritize visual processing. Trends Neurosci. 2014, 37, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecere, R.; Rees, G.; Romei, V. Individual differences in alpha frequency drive crossmodal illusory perception. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llinás, R.R.; Ribary, U.; Jeanmonod, D.; Kronberg, E.; Mitra, P.P. Thalamocortical dysrhythmia: A neurological and neuropsychiatric syndrome characterized by magnetoencephalography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 15222–15227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørk, M.H.; Stovner, L.J.; Nilsen, B.M.; Stjern, M.; Hagen, K.; Sand, T. The occipital alpha rhythm related to the “migraine cycle” and headache burden: A blinded, controlled longitudinal study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 120, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xiang, J.; Wu, T.; Zhu, D.; Shi, J. Abnormal resting-state brain activity in headache-free migraine patients: A magnetoencephalography study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 2855–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenen, J.; Wang, W.; Albert, A.; Delwaide, P.J. Potentiation instead of habituation characterizes visual evoked potentials in migraine patients between attacks. Eur. J. Neurol. 1995, 2, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurora, S.K.; Barrodale, P.; Chronicle, E.P.; Mulleners, W.M. Cortical inhibition is reduced in chronic and episodic migraine and demonstrates a spectrum of illness. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2005, 45, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, G.; Curra, A.; Sava, S.L.; Alibardi, A.; Parisi, V.; Pierelli, F.; Schoenen, J. Changes in visual-evoked potential habituation induced by hyperventilation in migraine. J. Headache Pain 2010, 11, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisicki, M.; Ruiz-Romagnoli, E.; D’Ostilio, K.; Piedrabuena, R.; Giobellina, R.; Schoenen, J.; Magis, D. Familial history of migraine influences habituation of visual evoked potentials. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oelkers, R.; Grosser, K.; Lang, E.; Geisslinger, G.; Kobal, G.; Brune, K.; Lötsch, J. Visual evoked potentials in migraine patients: Alterations depend on pattern spatial frequency. Brain 1999, 122, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sand, T.; Zhitniy, N.; White, L.R.; Stovner, L.J. Visual evoked potential latency, amplitude and habituation in migraine: A longitudinal study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omland, P.M.; Nilsen, K.B.; Uglem, M.; Gravdahl, G.; Linde, M.; Hagen, K.; Sand, T. Visual evoked potentials in interictal migraine: No confirmation of abnormal habituation. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2013, 53, 1071–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, A.; Föcker, J.; O’Hare, L. Effect of temporal frequency on habituation in migraine. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2023, 57, 1383–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.E.; Grieve, K.L.; Wang, W.; Sillito, A.M. Surround suppression in primate V1. J. Neurophysiol. 2001, 86, 2011–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadin, D.; Lappin, J.S.; Gilroy, L.A.; Blake, R. Perceptual consequences of centre–surround antagonism in visual motion processing. Nature 2003, 424, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdev, R.N.S.; Krause, M.R.; Mazer, J.A. Surround suppression and sparse coding in visual and barrel cortices. Front. Neural Circuits 2012, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, J.; Badcock, D.R.; McKendrick, A.M. Migraine increases centre-surround suppression for drifting visual stimuli. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKendrick, A.M.; Chan, Y.M.; Vingrys, A.J.; Turpin, A.; Badcock, D.R. Daily vision testing can expose the prodromal phase of migraine. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysel, U.T.; Crook, J.M.; Machemer, H.F. GABA-induced remote inactivation reveals cross-orientation inhibition in the cat striate cortex. Exp. Brain Res. 1990, 80, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seriès, P.; Latham, P.E.; Pouget, A. Tuning curve sharpening for orientation selectivity: Coding efficiency and the impact of correlations. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, F.; Crotogino, J. Orientation discrimination thresholds in migraine: A measure of visual cortical inhibition. Cephalalgia 2000, 20, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibber, M.S.; Guedes, A.; Shepherd, A.J. Orientation discrimination and contrast detection thresholds in migraine for cardinal and oblique angles. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 5599–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asher, J.M.; O’Hare, L.; Romei, V.; Hibbard, P.B. Typical lateral interactions, but increased contrast sensitivity, in migraine-with-aura. Vision 2018, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitmeyer, B.G.; Kafalıgönül, H.; Öğmen, H.; Mardon, L.; Todd, S.; Ziegler, R. Meta- and paracontrast reveal differences between contour- and brightness-processing mechanisms. Vis. Res. 2006, 46, 2645–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.E.; Chronicle, E.P.; Rolan, P.; Mulleners, W.M. Cortical hyperexcitability is cortical under-inhibition: Evidence from a novel functional test of migraine patients. Cephalalgia 2000, 20, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; DeLano, M.; Cao, Y. Visual cortical inhibitory function in migraine is not generally impaired: Evidence from a combined psychophysical test with an fMRI study. Cephalalgia 2006, 26, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, A.J.; Wyatt, G.; Tibber, M.S. Visual metacontrast masking in migraine. Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, M.B.; Ulrich, V.; Gervil, M.; Olesen, J. Migraine without aura and migraine with aura are distinct disorders. A population-based twin survey. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2002, 42, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligthart, L.; Boomsma, D.I.; Martin, N.G.; Stubbe, J.H.; Nyholt, D.R. Migraine with aura and migraine without aura are not distinct entities: Further evidence from a large Dutch population study. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2006, 9, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengpiel, F.; Baddeley, R.J.; Freeman, T.C.; Harrad, R.; Blakemore, C. Different mechanisms underlie three inhibitory phenomena in cat area 17. Vis. Res. 1998, 38, 2067–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrone, M.C.; Burr, D.C.; Speed, H.D. Cross-orientation inhibition in cat is GABA mediated. Exp. Brain Res. 1987, 67, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, S.; Freeman, T.C.; Carandini, M. Temporal properties of surround suppression in cat primary visual cortex. Vis. Neurosci. 2007, 24, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, J.D.; Melzer, P.; Ding, Y.; Bonds, A.B.; Casagrande, V.A. Differential contributions of magnocellular and parvocellular pathways to the contrast response of neurons in bush baby primary visual cortex (V1). Vis. Neurosci. 2000, 17, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Thompson, J.K.; Duong, T.; Peterson, M.R.; Freeman, R.D. Origins of cross-orientation suppression in the visual cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 2006, 96, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapley, R.; Kaplan, E.; Soodak, R. Spatial summation and contrast sensitivity of X and Y cells in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the macaque. Nature 1981, 292, 543–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burr, D.C.; Morrone, M.C. Inhibitory interactions in the human vision system revealed in pattern-evoked potentials. J. Physiol. 1987, 389, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.K.; Wade, A.R.; Penkman, K.E.; Baker, D.H. Dietary modulation of cortical excitation and inhibition. J. Psychopharmacol. 2017, 31, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brainard, D.H. The psychophyscis toolbox. Spat. Vis. 1997, 10, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelli, D.G. The videotoolbox software for visual psychophysics: Transforming numbers into movies. Spat. Vis. 1997, 10, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiner, M.; Brainard, D.; Pelli, D. What’s new in Psychtoolbox-3? Perception 2007, 36, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratton, G.; Coles, M.G.H.; Donchin, E. A new method for off-line removal of ocular artifact. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1983, 55, 468–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adjamian, P. The application of electro-and magneto-encephalography in tinnitus research–methods and interpretations. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norcia, A.M.; Appelbaum, L.G.; Ales, J.M.; Cottereau, B.R.; Rossion, B. The steady-state visual evoked potential in vision research: A review. J. Vis. 2015, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzsaki, G. Rhythms of the Brain; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Guindani, M.; Grieco, S.F.; Chen, L.; Holmes, T.C.; Xu, X. Beyond t test and ANOVA: Applications of mixed-effects models for more rigorous statistical analysis in neuroscience research. Neuron 2022, 110, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baguley, T. Standardized or simple effect size: What should be reported? Br. J. Psychol. 2009, 100, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleston, D.M.; Chronicle, E.; Ruddock, K.H.; Kennard, C. Precortical dysfunction of spatial and temporal visual processing in migraine. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1994, 57, 1208–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKendrick, A.M.; Vingrys, A.J.; Badcock, D.R.; Heywood, J.T. Visual dysfunction between migraine events. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 626–633. [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld, M.; Treves, T.; Korczyn, A. EEG and topographic frequency analysis in common and classic migraine. Headache J. Head Face Pain 1991, 31, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.-G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattanawong, W.; Rapoport, A.; Srikiatkhachorn, A. Neurobiology of migraine progression. Neurobiol. Pain 2022, 12, 100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porciatti, V.; Bonanni, P.; Fiorentini, A.; Guerrini, R. Lack of cortical contrast gain control in human photosensitive epilepsy. Nat. Neurosci. 2000, 3, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogawski, M.A. Migraine and Epilepsy—Shared Mechanisms within the Family of Episodic Disorders. In Jasper’s Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies [Internet], 4th ed.; Noebels, J.L., Avoli, M., Rogawski, M.A., Olsen, R.W., Delgado-Escueta, A.V., Eds.; National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hauge, A.W.; Kirchmann, M.; Olesen, J. Characterization of consistent triggers of migraine with aura. Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 416–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelman, L. The triggers or precipitants of the acute migraine attack. Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, T.; White, L.; Hagen, K.; Stovner, L. Visual evoked potential and spatial frequency in migraine: A longitudinal study. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2009, 120, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judit, A.; Sandor, P.; Schoenen, J. Habituation of visual and intensity dependence of audotiry evoked cortical potentials tends ot normalize just before and during the migraine attack. Cephalalgia 2000, 20, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chronicle, E.P.; Pearson, A.J.; Mulleners, W.M. Objective assessment of cortical excitability in migraine with and without aura. Cephalalgia 2006, 26, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McColl, S.L.; Wilkinson, F. Visual contrast gain control in migraine: Measures of visual cortical excitability and inhibition. Cephalalgia 2000, 20, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, D.; Manahilov, V.; Loffler, G.; Gordon, G.E.; Dutton, G.N. Visual noise selectively degrades vision in migraine. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 2294–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, J.M.; O’Hare, L.; Hibbard, P.B. No Evidence of Reduced Contrast Sensitivity in Migraine-with-Aura for Large, Narrowband, Centrally Presented Noise-masked Stimuli. Vision 2021, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosher, B.A.; Lu, Z.L. Perceptual learning reflects external noise filtering and internal noise reduction through channel reweighting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13988–13993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibber, M.S.; Kelly, M.G.; Jansari, A.; Dakin, S.C.; Shepherd, A.J. An inability to exclude visual noise in migraine. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 2539–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hare, L.; Goodwin, P.; Sharp, A.; Contillo, A.; Pavan, A. Improvement in visual perception after high-frequency transcranial random noise stimulation (hf-tRNS) in those with migraine: An equivalent noise approach. Neuropsychologia 2021, 161, e107990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sex | Age | Attack Frequency (per Month) | Disorder Duration (Years) | Professional Diagnosis 1 | Time since Last Attack (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 20 | 1–3 | U 2 | Yes | 2 weeks ago |
| Female | 20 | <1 | 5 | Yes | 1 year ago 3 |
| Male | 33 | <1 | 5 | Yes | U 2 |
| Male | 23 | <1 | 10 | Yes | 3 years ago |
| Male | 64 | <1 | U 2 | Yes | U 2 |
| Female | 36 | U 2 | 10 | Yes | 4 months ago |
| Female | 32 | <1 | 7 | Yes | 2 months ago |
| Female | 24 | <1 | U 2 | Yes | 10 months ago |
| Male | 18 | <1 | 5 | No | 4 months ago |
| Female | 21 | <1 | 7 | Yes | 15 days ago |
| Male | 20 | <1 | 8 | Yes | 40 days ago |
| Female | 22 | 1–3 | 8 | Yes | 4 days ago |
| Variable | Estimate of the Coefficient | SE | p-Value | Lower CI | Upper CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contrast | 1.71 | 0.29 | 1.24 × 10−8 | 0.14 | 2.28 |
| Group | −0.57 | 0.38 | 0.14 | −1.32 | 0.18 |
| Mask | −3.92 | 0.60 | 5.82 × 10−10 | −5.09 | −2.74 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
O’Hare, L.; Wan, C.L. No Evidence of Cross-Orientation Suppression Differences in Migraine with Aura Compared to Healthy Controls. Vision 2024, 8, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision8010002
O’Hare L, Wan CL. No Evidence of Cross-Orientation Suppression Differences in Migraine with Aura Compared to Healthy Controls. Vision. 2024; 8(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision8010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleO’Hare, Louise, and Choi Lam Wan. 2024. "No Evidence of Cross-Orientation Suppression Differences in Migraine with Aura Compared to Healthy Controls" Vision 8, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision8010002
APA StyleO’Hare, L., & Wan, C. L. (2024). No Evidence of Cross-Orientation Suppression Differences in Migraine with Aura Compared to Healthy Controls. Vision, 8(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision8010002





