Deficits in Face Recognition and Consequent Quality-of-Life Factors in Individuals with Cerebral Visual Impairment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
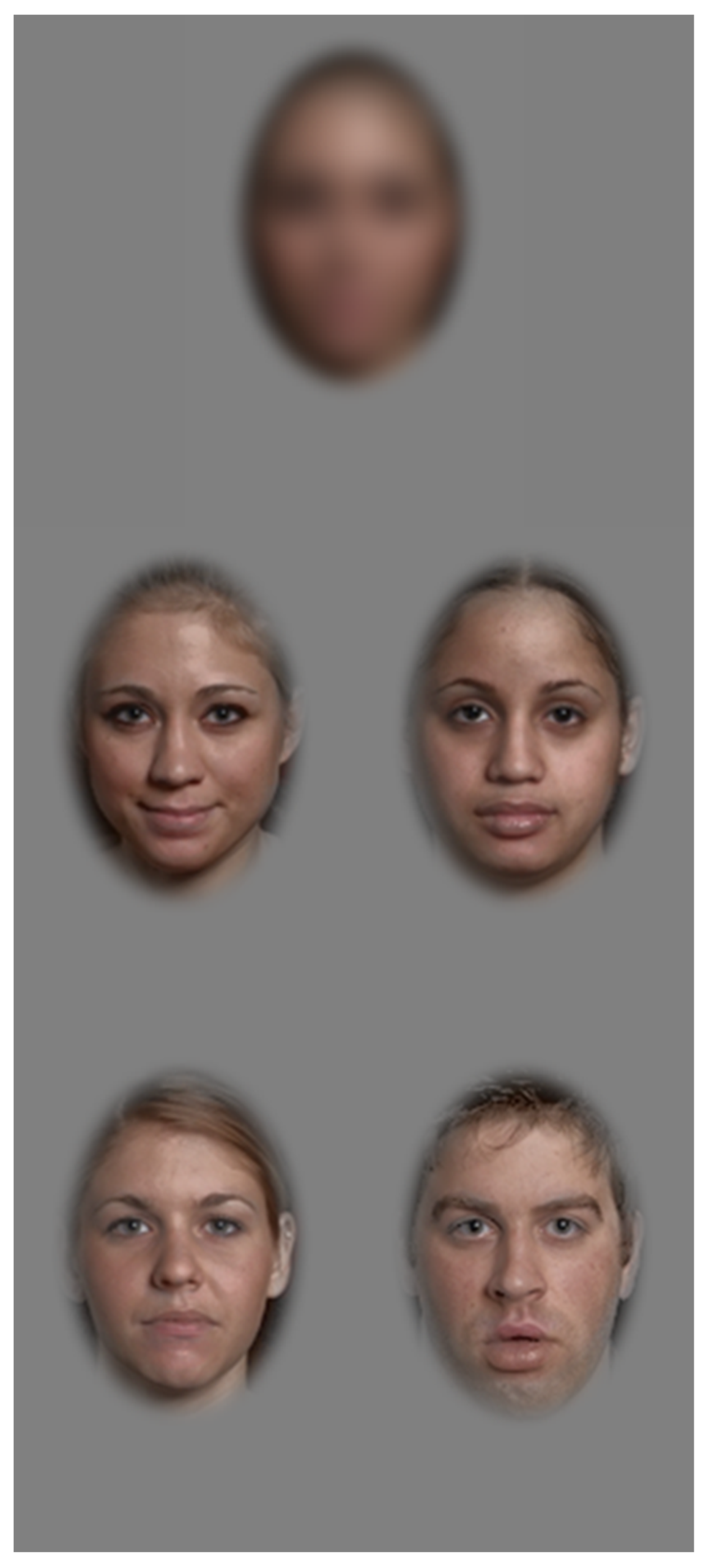
2.2. Face Recognition Task
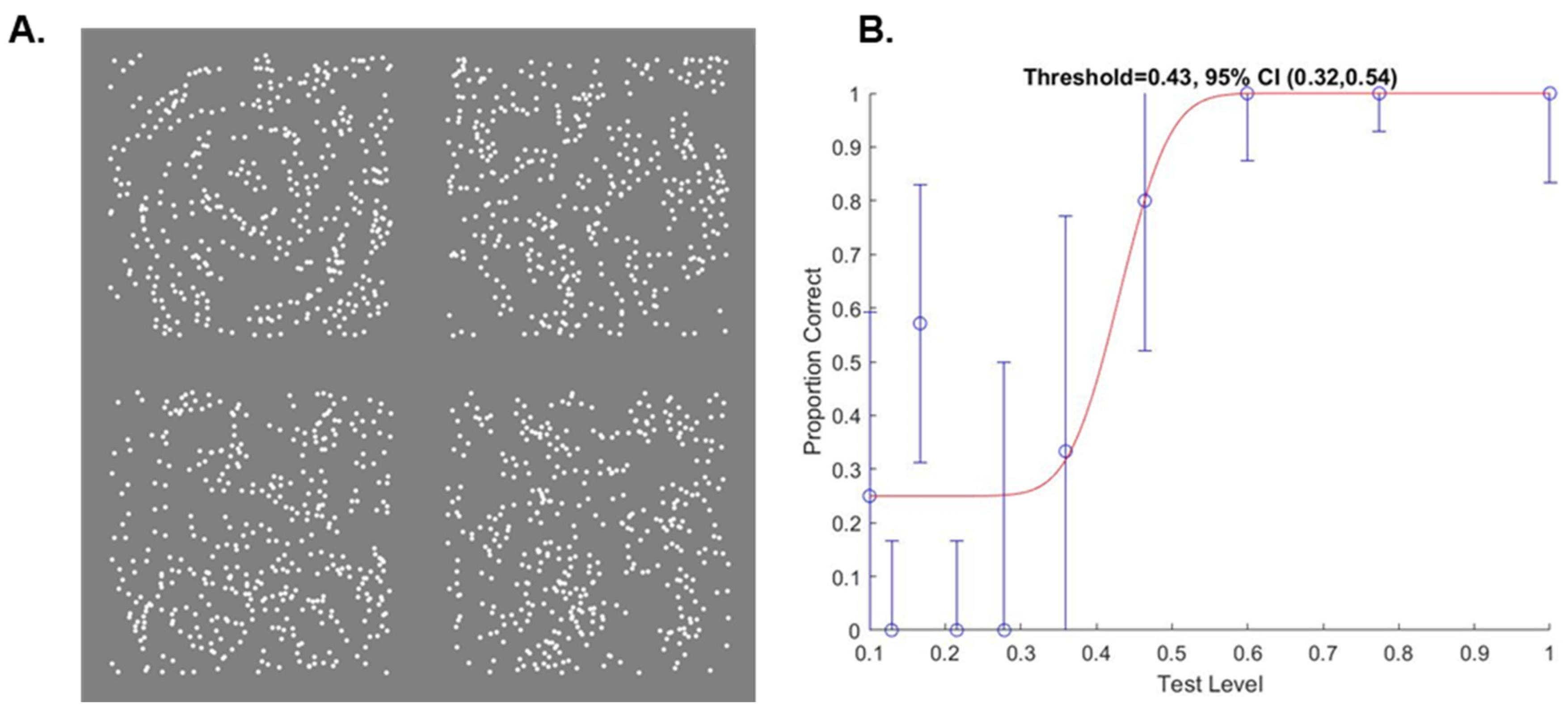
2.3. Glass Pattern Task
2.4. CVI Inventory
2.5. Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. Repeated Measures Adjusting for Age
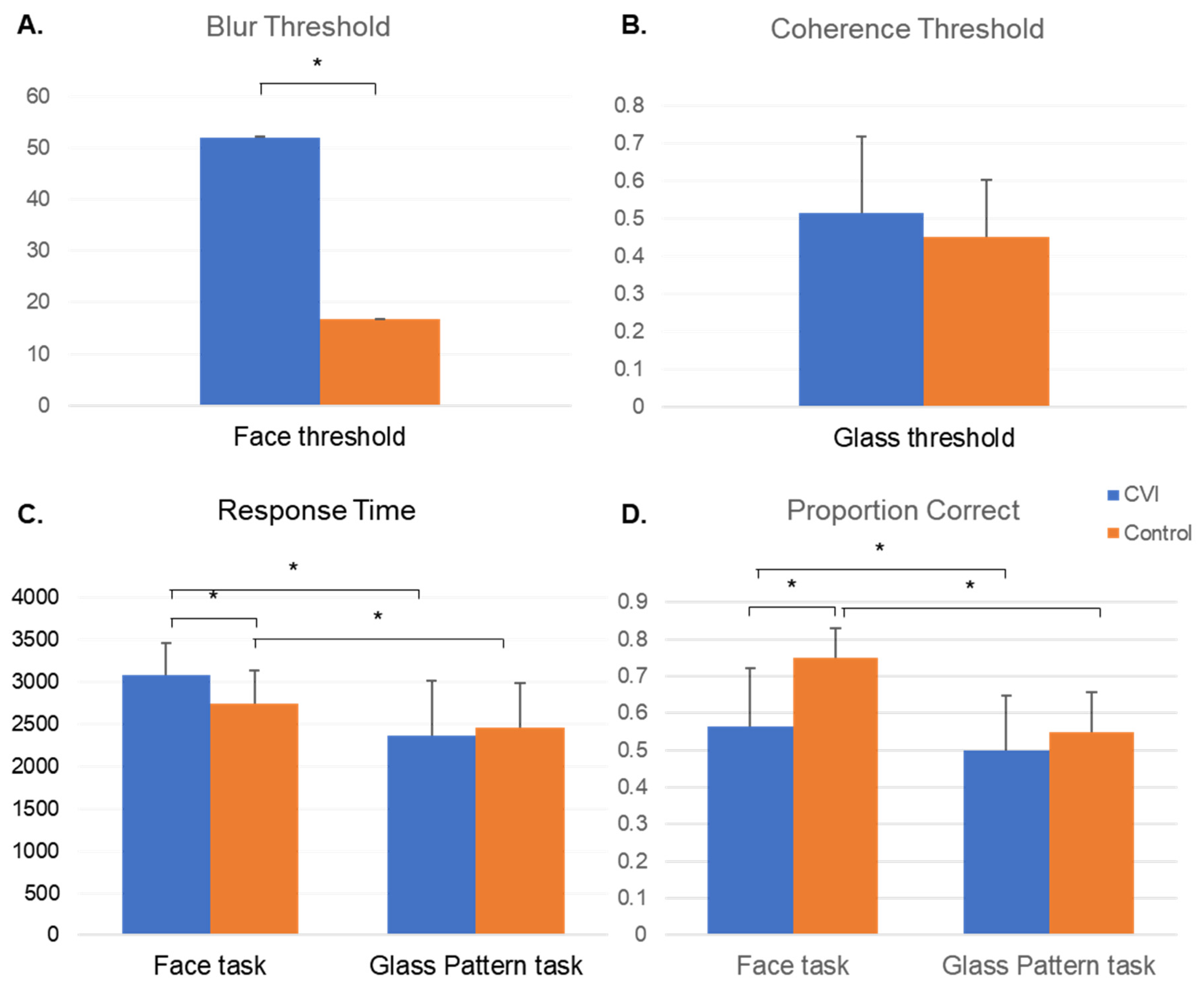
3.2.1. Threshold
3.2.2. Proportion Correct
3.2.3. Response Time
3.3. Non-Repeated Measures Covarying for Age
3.3.1. Faces
Threshold
Proportion Correct
Response Time
3.3.2. Glass Pattern
Threshold
Proportion Correct
Response Time
3.4. Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire and Dutton Inventory
Group Differences in SDQ and Dutton Outcomes Covarying for Age
3.5. Partial Correlations between Behavioral Tasks and the SDQ
4. Discussion
4.1. Face Recognition Task
4.2. Glass Pattern
4.3. Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire
4.4. Potential Impact of Age
4.5. Implications for CVI
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kanwisher, N.; Dilks, D.D. The Functional Organization of the Ventral Visual Pathway in Humans. In The New Visual Neurosciences; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 733–746. [Google Scholar]
- Peelen, M.V.; Downing, P.E. Category Selectivity in Human Visual Cortex: Beyond Visual Object Recognition. Neuropsychologia 2017, 105, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heutink, J.; Indorf, D.L.; Cordes, C. The Neuropsychological Rehabilitation of Visual Agnosia and Balint’s Syndrome. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2019, 29, 1489–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalrymple, K.A.; Fletcher, K.; Corrow, S.; das Nair, R.; Barton, J.J.S.; Yonas, A.; Duchaine, B. “A Room Full of Strangers Every Day”: The Psychosocial Impact of Developmental Prosopagnosia on Children and Their Families. J. Psychosom. Res. 2014, 77, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yardley, L.; McDermott, L.; Pisarski, S.; Duchaine, B.; Nakayama, K. Psychosocial Consequences of Developmental Prosopagnosia: A Problem of Recognition. J. Psychosom. Res. 2008, 65, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, C.; Dai, S. Cross-Sectional Study on Prevalence, Causes and Avoidable Causes of Visual Impairment in Maori Children. N. Z. Med. J. 2013, 126, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Gogate, P.; Gilbert, C.; Zin, A. Severe Visual Impairment and Blindness in Infants: Causes and Opportunities for Control. Middle East Afr. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 18, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, M.A.O.; Sei, M.; Sampaio, M.W.; Kara-Jose, N. Causes of Visual Impairment in Children: A Study of 3,210 Cases. J. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2007, 44, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijthuijsen, A.A.M.; Beunders, V.A.A.; Jiawan, D.; De Mesquita-Voigt, A.M.B.; Pawiroredjo, J.; Mourits, M.; Tanck, M.; Verhoeff, J.; Saeed, P. Causes of Severe Visual Impairment and Blindness in Children in the Republic of Suriname. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 97, 812–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Fry, M.; Al-Samarraie, M.; Gilbert, C.; Steinkuller, P.G. An Update on Progress and the Changing Epidemiology of Causes of Childhood Blindness Worldwide. J. Am. Assoc. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2012, 16, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewerenz, D.; Peter, K.; Ford, P. Prevalence of Conditions Causing Visual Impairment in Students at the Oklahoma School for the Blind. J. Vis. Impair. Blind. 2016, 110, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezer, E.; Chetrit, A.; Kalter-Leibovici, O.; Kinori, M.; Ben-Zion, I.; Wygnanski-Jaffe, T. Trends in the Incidence and Causes of Severe Visual Impairment and Blindness in Children from Israel. J. Am. Assoc. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2015, 19, 260–265.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudanko, S.-L.; Laatikainen, L. Visual Impairment in Children Born at Full Term from 1972 through 1989 in Finland. Ophthalmology 2004, 111, 2307–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Steen, I.; Bouwhuis, C.B.; Kuijlaars, J.S.; Wezenberg, D.; Vlieland, T.P.M.V. Monitoring and Prevalence of Cerebral Visual Impairment in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2017, 59, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, G.N. Cerebral Visual Impairment in Children: The Importance of Classification. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2020, 63, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilling, R.F.; Allen, L.; Bowman, R.; Ravenscroft, J.; Saunders, K.J.; Williams, C. Clinical Assessment, Investigation, Diagnosis and Initial Management of Cerebral Visual Impairment: A Consensus Practice Guide. Eye 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakki, H.E.A.; Dale, N.J.; Sargent, J.; Perez-Roche, T.; Bowman, R. Is There Consensus in Defining Childhood Cerebral Visual Impairment? A Systematic Review of Terminology and Definitions. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 102, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, G.N. ‘Dorsal Stream Dysfunction’ and ‘Dorsal Stream Dysfunction plus’: A Potential Classification for Perceptual Visual Impairment in the Context of Cerebral Visual Impairment? Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2009, 51, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macintyre-Béon, C.; Ibrahim, H.; Hay, I.; Cockburn, D.; Calvert, J.; Dutton, G.N.; Bowman, R. Dorsal Stream Dysfunction in Children. A Review and an Approach to Diagnosis and Management. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2010, 6, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamir, Z.; Bauer, C.M.; Bailin, E.S.; Bex, P.J.; Somers, D.C.; Merabet, L.B. Neural Correlates Associated with Impaired Global Motion Perception in Cerebral Visual Impairment (CVI). NeuroImage Clin. 2021, 32, 102821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houliston, M.J.; Taguri, A.H.; Dutton, G.N.; Hajivassiliou, C.; Young, D.G. Evidence of Cognitive Visual Problems in Children with Hydrocephalus: A Structured Clinical History-Taking Strategy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1999, 41, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, M. Should Individuals Who Do Not Fit the Definition of Visual Impairment Be Excluded from Visual Impairment Services? J. Vis. Impair. Blind. 2017, 111, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiers, P.; Swillen, A.; De Smedt, B.; Lagae, L.; Devriendt, K.; D’Agostino, E.; Sunaert, S.; Fryns, A.-P. Atypical Neuropsychological Profile in a Boy with 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome. Child Neuropsychol. J. Norm. Abnorm. Dev. Child. Adolesc. 2005, 11, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutton, G.; Bax, M. Visual Impairment in Children Due to Damage to the Brain; Clinics in Developmental Medicine, No. 186; Mac Keith Press: London, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-1-908316-24-0. [Google Scholar]
- Stoet, G. PsyToolkit: A Novel Web-Based Method for Running Online Questionnaires and Reaction-Time Experiments. Teach. Psychol. 2017, 44, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoet, G. PsyToolkit: A Software Package for Programming Psychological Experiments Using Linux. Behav. Res. Methods 2010, 42, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macintyre-Beon, C.; Young, D.; Calvert, J.; Ibrahim, H.; Dutton, G.N.; Bowman, R. Reliability of a Question Inventory for Structured History Taking in Children with Cerebral Visual Impairment. Eye 2012, 26, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrie, F.; Goodall, K.; Rush, R.; Ravenscroft, J. Towards Population Screening for Cerebral Visual Impairment: Validity of the Five Questions and the CVI Questionnaire. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazzi, E.; Bova, S.; Giovenzana, A.; Signorini, S.; Uggetti, C.; Bianchi, P. Cognitive Visual Dysfunctions in Preterm Children with Periventricular Leukomalacia. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2009, 51, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, D.; Nierenberg, B. Test of Memory and Learning. In Encyclopedia of Child Behavior and Development; Goldstein, S., Naglieri, J.A., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 1479–1480. ISBN 978-0-387-79061-9. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Roche, T.; Altemir, I.; Giménez, G.; Prieto, E.; González, I.; López Pisón, J.; Pueyo, V. Face Recognition Impairment in Small for Gestational Age and Preterm Children. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2017, 62, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potharst, E.S.; Van Wassenaer-Leemhuis, A.G.; Houtzager, B.A.; Livesey, D.; Kok, J.H.; Last, B.F.; Oosterlaan, J. Perinatal Risk Factors for Neurocognitive Impairments in Preschool Children Born Very Preterm. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2013, 55, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjabi, I.; Ouahabi, A.; Benzaoui, A.; Taleb-Ahmed, A. Past, Present, and Future of Face Recognition: A Review. Electronics 2020, 9, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westheimer, G. Measuring Visual Form Discrimination with Blur Thresholds. J. Vis. 2013, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balas, B.; Gable, J.; Pearson, H. The Effects of Blur and Inversion on the Recognition of Ambient Face Images. Perception 2019, 48, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandford, A.; Sarker, T.; Bernier, T. Effects of Geometric Distortions, Gaussian Blur, and Contrast Negation on Recognition of Familiar Faces. Vis. Cogn. 2018, 26, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collishaw, S.M.; Hole, G.J. Featural and Configurational Processes in the Recognition of Faces of Different Familiarity. Perception 2000, 29, 893–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Liu, R.; Chien, L. Compensation for Blur Requires Increase in Field of View and Viewing Time. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, J.V.; O’Brien, J.M.D. Visual Form-Processing Deficits in Autism. Perception 2006, 35, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsermentseli, S.; O’Brien, J.M.; Spencer, J.V. Comparison of Form and Motion Coherence Processing in Autistic Spectrum Disorders and Dyslexia. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2008, 38, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomares, M.; Shannon, M.T. Global Dot Integration in Typically Developing Children and in Williams Syndrome. Brain Cogn. 2013, 83, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Luo, Y.L.L.; Dilks, D.D.; Liu, J. Resting-State Neural Activity across Face-Selective Cortical Regions Is Behaviorally Relevant. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 10323–10330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKendrick, A.M.; Weymouth, A.E.; Battista, J. Visual Form Perception from Age 20 through 80 Years. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 1730–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.H.F.; Kourtzi, Z.; Welchman, A.E. Mechanisms for Extracting a Signal from Noise as Revealed through the Specificity and Generality of Task Training. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 10962–10971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, H.R.; Wilkinson, F. Detection of Global Structure in Glass Patterns: Implications for Form Vision. Vis. Res. 1998, 38, 2933–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortibus, E.; Verhoeven, J.; Sunaert, S.; Casteels, I.; De Cock, P.; Lagae, L. Integrity of the Inferior Longitudinal Fasciculus and Impaired Object Recognition in Children: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2012, 54, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortibus, E.; Lagae, L.; Casteels, I.; Demaerel, P.; Stiers, P. Assessment of Cerebral Visual Impairment with the L94 Visual Perceptual Battery: Clinical Value and Correlation with MRI Findings. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2009, 51, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathelt, J.; de Haan, M.; Dale, N.J. Adaptive Behaviour and Quality of Life in School-Age Children with Congenital Visual Disorders and Different Levels of Visual Impairment. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2019, 85, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brossard-Racine, M.; Waknin, J.; Shikako-Thomas, K.; Shevell, M.; Poulin, C.; Lach, L.; Law, M.; Schmitz, N.; QUALA Group; Majnemer, A. Behavioral Difficulties in Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy. J. Child Neurol. 2013, 28, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colver, A.; Rapp, M.; Eisemann, N.; Ehlinger, V.; Thyen, U.; Dickinson, H.O.; Parkes, J.; Parkinson, K.; Nystrand, M.; Fauconnier, J.; et al. Self-Reported Quality of Life of Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy: A Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Analysis. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2015, 385, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fevang, S.K.E.; Hysing, M.; Sommerfelt, K.; Elgen, I. Mental Health Assessed by the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire for Children Born Extremely Preterm without Severe Disabilities at 11 Years of Age: A Norwegian, National Population-Based Study. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2017, 26, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germine, L.T.; Duchaine, B.; Nakayama, K. Where Cognitive Development and Aging Meet: Face Learning Ability Peaks after Age 30. Cognition 2011, 118, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigelt, S.; Koldewyn, K.; Dilks, D.D.; Balas, B.; McKone, E.; Kanwisher, N. Domain-Specific Development of Face Memory but Not Face Perception. Dev. Sci. 2014, 17, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherf, K.S.; Behrmann, M.; Humphreys, K.; Luna, B. Visual Category-Selectivity for Faces, Places and Objects Emerges along Different Developmental Trajectories. Dev. Sci. 2007, 10, F15–F30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Heering, A.; Turati, C.; Rossion, B.; Bulf, H.; Goffaux, V.; Simion, F. Newborns’ Face Recognition Is Based on Spatial Frequencies below 0.5 Cycles per Degree. Cognition 2008, 106, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantz, R.L. Pattern Vision in Newborn Infants. Science 1963, 140, 296–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farroni, T.; Chiarelli, A.M.; Lloyd-Fox, S.; Massaccesi, S.; Merla, A.; Di Gangi, V.; Mattarello, T.; Faraguna, D.; Johnson, M.H. Infant Cortex Responds to Other Humans from Shortly after Birth. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascalis, O.; Scott, L.S.; Kelly, D.J.; Shannon, R.W.; Nicholson, E.; Coleman, M.; Nelson, C.A. Plasticity of Face Processing in Infancy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5297–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, T.L.; Ellemberg, D.; Maurer, D.; Dirks, M.; Wilkinson, F.; Wilson, H.R. A Window on the Normal Development of Sensitivity to Global Form in Glass Patterns. Perception 2004, 33, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deen, B.; Richardson, H.; Dilks, D.D.; Takahashi, A.; Keil, B.; Wald, L.L.; Kanwisher, N.; Saxe, R. Organization of High-Level Visual Cortex in Human Infants. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| n CVI | CVI Mean (s.d.) | CVI Min | CVI Max | n Control | Control Mean | Control Min | Control Max | T/F Stat | p-Value | adj. p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 16 | 18.78 (6.51) | 8.56 | 30.36 | 25 | 20.99 (4.82) | 9.44 | 34.6 | −1.24 | 0.2209 | |
| Sex | 15 female | 15 female | 0.026 | 0.87 | |||||||
| Face Recognition Task | |||||||||||
| Face threshold | 14 | 51.93 (45.36) | 11.02 | 148.77 | 22 | 16.70 (6.15) | 3.32 | 30.65 | 3.01 | 0.0002 | 0.0006 |
| Face response time (ms) | 3078.50 (388.88) | 2593.90 | 3658.35 | 2744.70 (385.87) | 1945.05 | 3294.28 | 12.22 | 0.011 | 0.032 | ||
| Face proportion correct | 0.56 (0.16) | 0.18 | 0.83 | 0.75 (0.08) | 0.63 | 0.88 | 38.14 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||
| Face n null | 3 (2.78) | 0 | 10 | 1.41 (1.14) | 0 | 3 | 2.1 | 0.051 | |||
| Glass Pattern Task | |||||||||||
| Glass threshold | 13 | 0.52 (0.20) | 0.29 | 1.00 | 25 | 0.45 (0.15) | 0.05 | 0.67 | 1.66 | 0.30 | 0.90 |
| Glass response time (ms) | 2368.12 (646.56) | 1646.80 | 3836.05 | 2461.20 (523.95) | 1413.05 | 3310.25 | 0.05 | 0.65 | 1 | ||
| Glass proportion correct | 0.5 (0.15) | 0.23 | 0.70 | 0.55 (0.11) | 0.38 | 0.78 | 3.06 | 0.26 | 0.79 | ||
| Glass n null | 3.87 (4.52) | 0 | 18 | 3 (2.57) | 1 | 11 | 0.68 | 0.51 | |||
| Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire | |||||||||||
| Emotional problems scale | 14 | 5.21 (2.42) | 2 | 10 | 21 | 3.14 (1.90) | 0 | 6 | 8.83 | 0.0056 | 0.045 |
| Conduct problems scale | 1.86 (1.41) | 0 | 5 | 1.43 (1.08) | 0 | 4 | 1.5 | 0.23 | 1 | ||
| Hyperactivity scale | 3.57 (2.38) | 0 | 8 | 3.24 (2.10) | 0 | 7 | 0.17 | 0.68 | 1 | ||
| Peer problems scale | 3 (1.71) | 1 | 7 | 1.86 (1.31) | 0 | 6 | 4.4 | 0.044 | 0.35 | ||
| Prosocial scale | 8 (1.96) | 5 | 10 | 8.71 (1.45) | 4 | 10 | 1.11 | 0.30 | 1 | ||
| Total difficulties score | 13.64 (4.70) | 8 | 22 | 9.67 (4.62) | 2 | 19 | 6.38 | 0.017 | 0.13 | ||
| Externalizing score | 5.43 (2.87) | 1 | 10 | 4.67 (2.74) | 1 | 11 | 0.72 | 0.40 | 1 | ||
| Internalizing score | 8.21 (3.51) | 4 | 14 | 5 (2.35) | 1 | 8 | 10.7 | 0.0026 | 0.021 | ||
| CVI Inventory | |||||||||||
| Faces positive screen | 15 | 2 (1.41) | 0 | 4 | 21 | 0.19 (0.51) | 0 | 2 | 32.07 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Objects positive screen | 1.8 (1.26) | 0 | 4 | 0 (0) | 0 | 0 | 46.67 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||
| The Five Questions positive screen | 3.73 (1.49) | 0 | 5 | 0.57 (0.87) | 0 | 3 | 65.93 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bauer, C.M.; Manley, C.E.; Ravenscroft, J.; Cabral, H.; Dilks, D.D.; Bex, P.J. Deficits in Face Recognition and Consequent Quality-of-Life Factors in Individuals with Cerebral Visual Impairment. Vision 2023, 7, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision7010009
Bauer CM, Manley CE, Ravenscroft J, Cabral H, Dilks DD, Bex PJ. Deficits in Face Recognition and Consequent Quality-of-Life Factors in Individuals with Cerebral Visual Impairment. Vision. 2023; 7(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision7010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleBauer, Corinna M., Claire E. Manley, John Ravenscroft, Howard Cabral, Daniel D. Dilks, and Peter J. Bex. 2023. "Deficits in Face Recognition and Consequent Quality-of-Life Factors in Individuals with Cerebral Visual Impairment" Vision 7, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision7010009
APA StyleBauer, C. M., Manley, C. E., Ravenscroft, J., Cabral, H., Dilks, D. D., & Bex, P. J. (2023). Deficits in Face Recognition and Consequent Quality-of-Life Factors in Individuals with Cerebral Visual Impairment. Vision, 7(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision7010009




