The Limbal Niche and Regenerative Strategies
Abstract
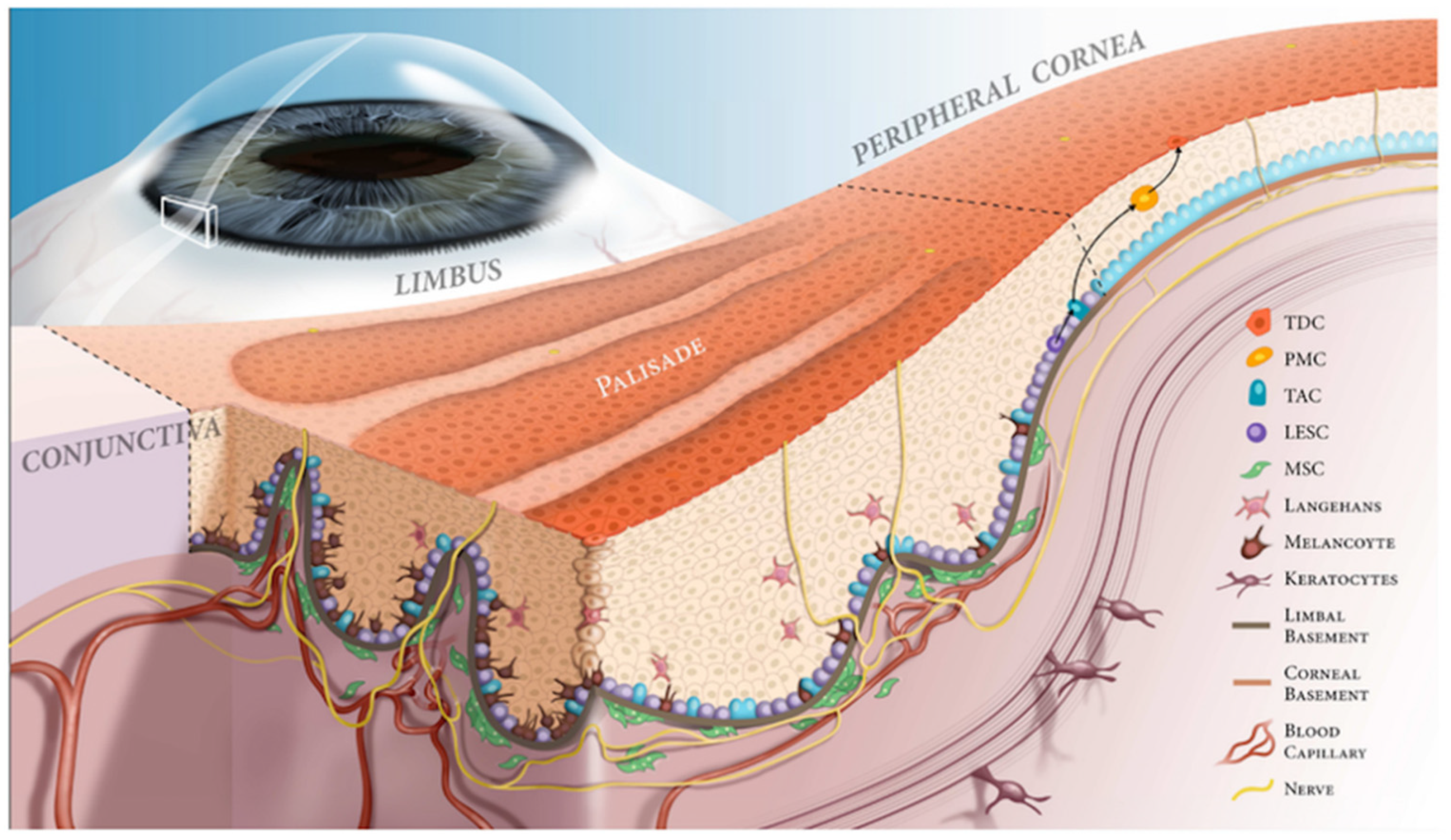
1. Corneal and Limbal Epithelium
2. Pathology of Limbal Niche
3. Therapeutic Regeneration of the Limbal Niche
3.1. Cell-Based Therapies
3.1.1. Limbal Transplantation
3.1.2. Ex-Vivo Epithelial Cell Cultivation
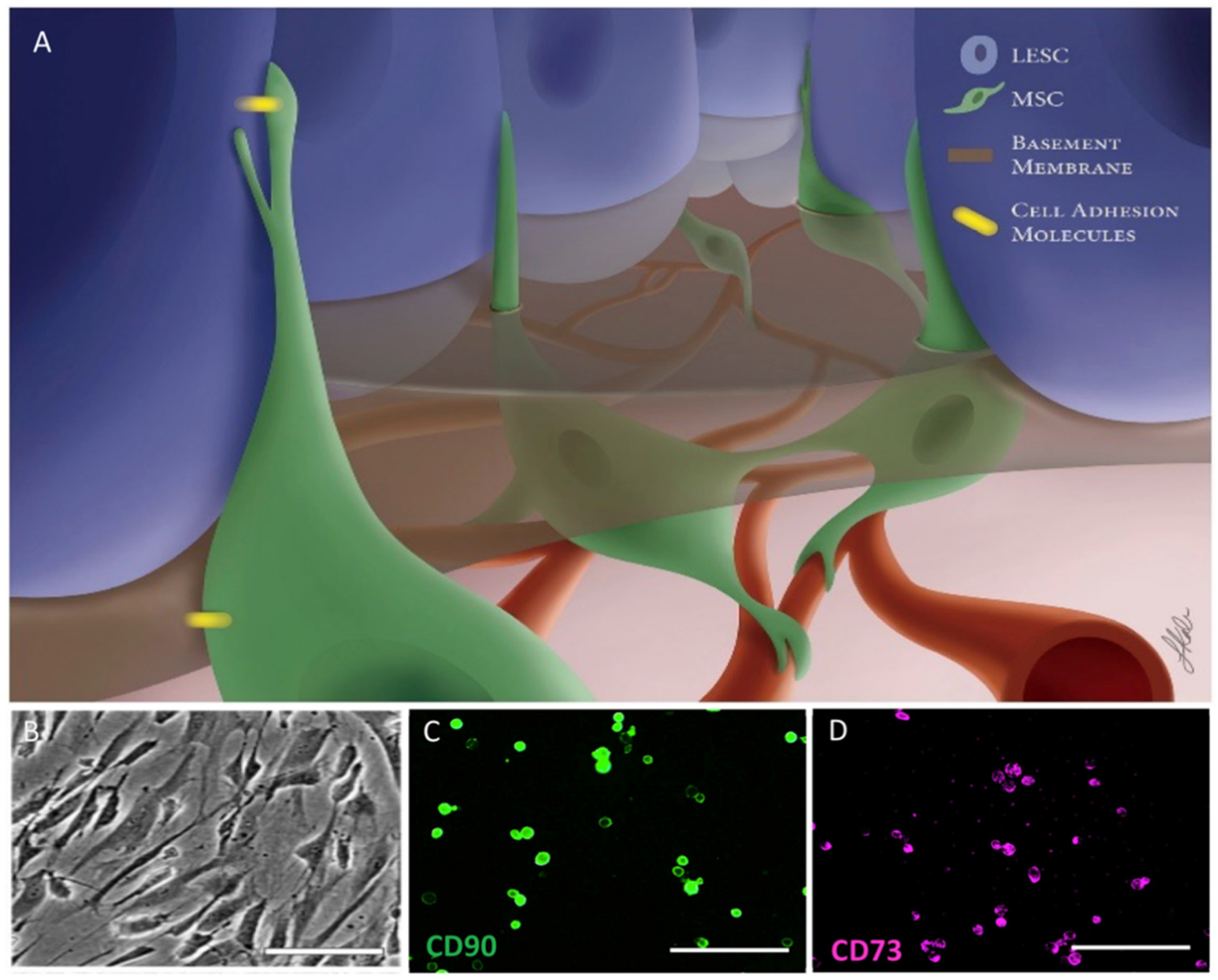
3.1.3. Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells
3.1.4. Melanocytes
3.2. Biologically Stimulating Scaffolds
3.2.1. Human Amniotic Membrane
3.2.2. Fabricated ECMs
3.2.3. Bio-Active Hydrogels
3.2.4. Biomaterials for Construction of Scaffolds
3.3. Therapeutic Factor-Derived Solutions
3.3.1. Blood Product Derivatives
3.3.2. Amniotic Membrane Derivatives
3.3.3. Growth Factor Formulations/Cell Secretions
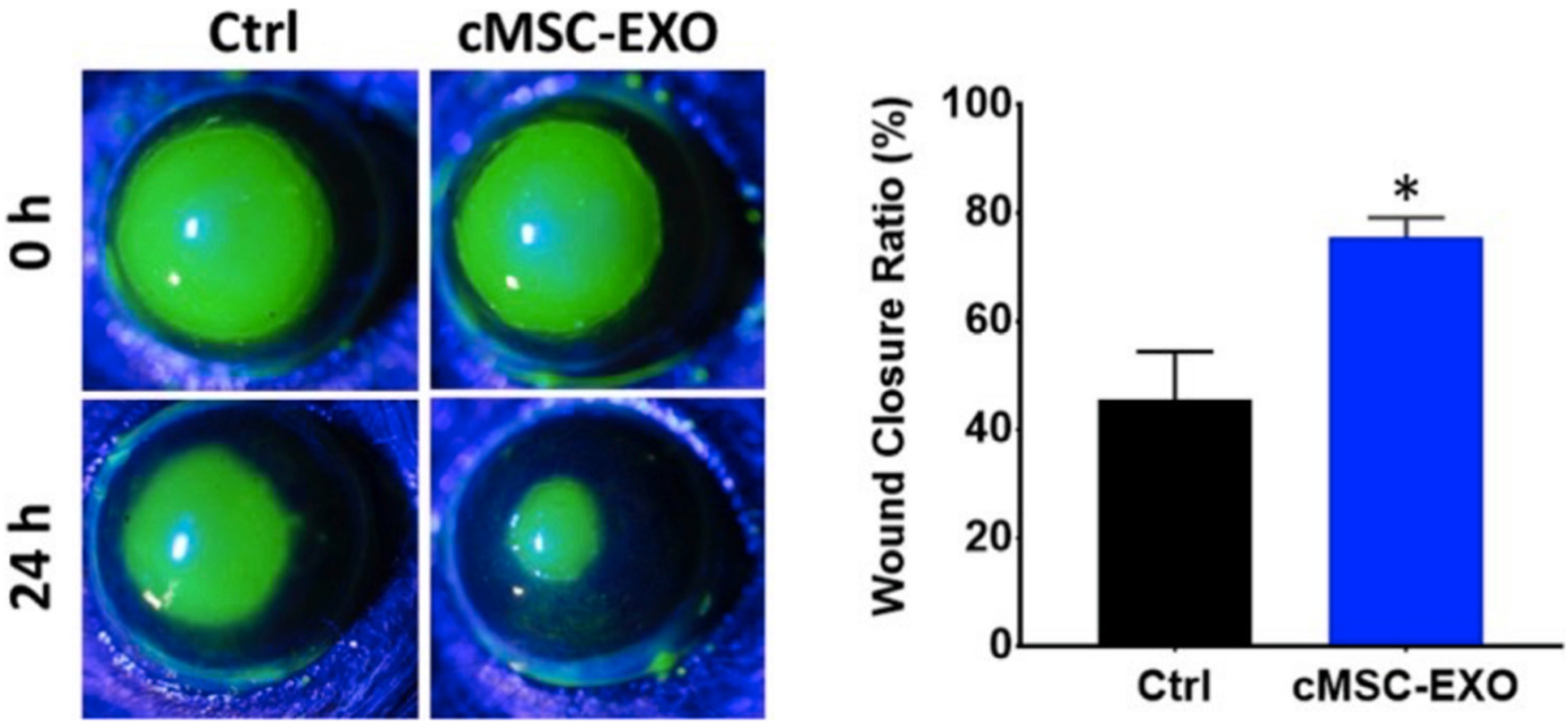
3.3.4. Exosomes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kulkarni, B.B.; Tighe, P.J.; Mohammed, I.; Yeung, A.M.; Powe, D.G.; Hopkinson, A.; Shanmuganathan, V.A.; Dua, H.S. Comparative transcriptional profiling of the limbal epithelial crypt demonstrates its putative stem cell niche characteristics. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dua, H.S.; Shanmuganathan, V.A.; Powell-Richards, A.O.; Tighe, P.; Joseph, A. Limbal epithelial crypts: A novel anatomical structure and a putative limbal stem cell niche. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 89, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Inoue, T.; Takamatsu, F.; Kobayashi, T.; Shiraishi, A.; Maeda, N.; Ohashi, Y.; Nishida, K. Differences Between Niche Cells and Limbal Stromal Cells in Maintenance of Corneal Limbal Stem Cells. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 1453–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, A.; Harris, D.L.; Blanco, T.; Lopez, M.J.; Hamrah, P. Resident plasmacytoid dendritic cells patrol vessels in the naïve limbus and conjunctiva. Ocul. Surf. 2020, 18, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdanpanah, G.; Haq, Z.; Kang, K.; Jabbehdari, S.; Rosenblatt, M.L.; Djalilian, A.R. Strategies for reconstructing the limbal stem cell niche. Ocul. Surf. 2019, 17, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meek, K.M.; Boote, C. The organization of collagen in the corneal stroma. Exp. Eye Res. 2004, 78, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meek, K.M.; Knupp, C. Corneal structure and transparency. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2015, 49, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Young, R.D.; Lewis, P.N.; Shinomiya, K.; Meek, K.M.; Kinoshita, S.; Caterson, B.; Quantock, A.J. Mesenchymal-epithelial cell interac-tions and proteoglycan matrix composition in the presumptive stem cell niche of the rabbit corneal limbus. Mol. Vision 2015, 21, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Pauklin, M.; Steuhl, K.P.; Meller, D. Characterization of the corneal surface in limbal stem cell deficiency and after trans-plantation of cultivated limbal epithelium. Ophthalmology 2009, 116, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notara, M.; Refaian, N.; Braun, G.; Steven, P.; Bock, F.; Cursiefen, C. Short-term uvb-irradiation leads to putative limbal stem cell damage and niche cell-mediated upregulation of macrophage recruiting cytokines. Stem Cell Res. 2015, 15, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massie, I.; Dziasko, M.; Kureshi, A.; Levis, H.J.; Morgan, L.; Neale, M.; Sheth, R.; Tovell, V.E.; Vernon, A.J.; Funderburgh, J.L.; et al. Advanced imaging and tissue engineering of the human limbal epithelial stem cell niche. In Stem Cell Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology (Methods and Protocols); Rich, I., Ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1235. [Google Scholar]
- Nubile, M.; Curcio, C.; Dua, H.S.; Calienno, R.; Lanzini, M.; Iezzi, M.; Mastropasqua, R.; Agnifili, L.; Mastropasqua, L. Pathological changes of the anatomical structure and markers of the limbal stem cell niche due to inflammation. Mol. Vis. 2013, 19, 516–525. [Google Scholar]
- Polisetti, N.; Zenkel, M.; Menzel-Severing, J.; Kruse, F.E.; Schlötzer-Schrehardt, U. Cell Adhesion Molecules and Stem Cell-Niche-Interactions in the Limbal Stem Cell Niche. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.Y.; Riaz, K.M.; Bakhtiari, P.; Chan, C.C.; Welder, J.D.; Holland, E.J.; Basti, S.; Djalilian, A.R. Medically reversible limbal stem cell disease: Clinical features and management strategies. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baradaran-Rafii, A.; Eslani, M.; Haq, Z.; Shirzadeh, E.; Huvard, M.J.; Djalilian, A.R. Current and Upcoming Therapies for Ocular Surface Chemical Injuries. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossen, J.; Amram, A.; Milani, B.; Park, D.; Harthan, J.; Joslin, C.; McMahon, T.; Djalilian, A. Contact Lens-induced Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency. Ocul. Surf. 2016, 14, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Jacobs, D.S. Long-term outcome of using Prosthetic Replacement of Ocular Surface Ecosystem (PROSE) as a drug delivery system for bevacizumab in the treatment of corneal neovascularization. Ocul. Surf. 2019, 17, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schornack, M.M. Limbal stem cell disease: Management with scleral lenses. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2011, 94, 592–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.X.; Kruse, F.; Gomes, J.A.P.; Chan, C.C.; Daya, S.; Dana, R.; Figueiredo, F.C.; Kinoshita, S.; Rama, P.; Sangwan, V.; et al. Global Consensus on the Management of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency. Cornea 2020, 39, 1291–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanpanah, G.; Bohm, K.J.; Hassan, O.M.; Karas, F.I.; Elhusseiny, A.M.; Nonpassopon, M.; Niparugs, M.; Tu, E.Y.; Sugar, J.; Rosenblatt, M.I.; et al. Management of Con-genital Anirid-ia-Associated Keratopathy: Long-Term Outcomes from a Tertiary Referral Center. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 210, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbehdari, S.; Starnes, T.W.; Kurji, K.H.; Eslani, M.; Cortina, M.S.; Holland, E.J.; Djalilian, A.R. Management of advanced ocular surface disease in patients with severe atopic keratoconjunctivitis. Ocul. Surf. 2019, 17, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanpanah, G.; Jabbehdari, S.; Djalilian, A.R. Limbal and corneal epithelial homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2017, 28, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daya, S.M.; Chan, C.C.; Holland, E.J. Cornea Society Nomenclature for Ocular Surface Rehabilitative Procedures. Cornea 2011, 30, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslani, M.; Cheung, A.Y.; Kurji, K.; Pierson, K.; Sarnicola, E.; Holland, E.J. Long-term outcomes of conjunctival limbal autograft in patients with unilateral total limbal stem cell deficiency. Ocul. Surf. 2019, 17, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welder, J.D.; Pandya, H.K.; Nassiri, N.; Djalilian, A.R. Conjunctival Limbal Autograft and Allograft Transplantation Using Fibrin Glue: The official journal of the International Society for Imaging in the Eye. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging Retin. 2012, 43, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangwan, V.S.; Basu, S.; MacNeil, S.; Balasubramanian, D. Simple limbal epithelial transplantation (SLET): A novel surgical technique for the treatment of unilateral limbal stem cell deficiency. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 96, 931–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazirani, J.; Ali, M.H.; Sharma, N.; Gupta, N.; Mittal, V.; Atallah, M.; Amescua, G.; Chowdhury, T.; Abdala-Figuerola, A.; Ramirez-Miranda, A.; et al. Autologous simple limbal epithelial transplanta-tion for unilateral limbal stem cell deficiency: Multicentre results. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 100, 1416–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Sureka, S.P.; Shanbhag, S.S.; Kethiri, A.R.; Singh, V.; Sangwan, V.S. Simple Limbal Epithelial Transplantation: Long-Term Clinical Outcomes in 125 Cases of Unilateral Chronic Ocular Surface Burns. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djalilian, A.R.; Mahesh, S.P.; Koch, C.; Nussenblatt, R.B.; Shen, D.; Zhuang, Z.; Holland, E.J.; Chan, C.-C. Survival of Donor Epithelial Cells after Limbal Stem Cell Transplantation. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Djalilian, A.R.; Schwartz, G.S.; Holland, E.J. Ocular surface reconstruction: Limbal stem cell transplantation. Ophthalmol. Clin. North Am. 2003, 16, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, A.Y.; Holland, E.J. Keratolimbal allograft. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2017, 28, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, G.; Lambiase, A.; Macaluso, C.; Pocobelli, A.; Deng, S.; Cavallini, G.M.; Esteki, R.; Rama, P. From discovery to approval of an advanced therapy medicinal product-containing stem cells, in the EU. Regen. Med. 2016, 11, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.M.; Fuchsluger, T.; Ahmad, S.; Katikireddy, K.R.; Armant, M.; Dana, R. Comparative analysis of hu-man-derived feeder layers with 3T3 fibroblasts for the ex vivo expansion of human limbal and oral epithelium. Stem Cell Rev. 2012, 8, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashita, H.; Shimmura, S.; Higa, K.; Yoshida, S.; Kawakita, T.; Shimazaki, J.; Tsubota, K. A novel NIH/3T3 duplex feeder system to engineer corneal epithelial sheets with enhanced cytokeratin 15-positive progenitor populations. Tissue Eng. Part A 2008, 14, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, S.; Deng, S.X. Presence of native limbal stromal cells increases the expansion efficiency of limbal stem/progenitor cells in culture. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 116, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kureshi, A.K.; Dziasko, M.; Funderburgh, J.L.; Daniels, J.T. Human corneal stromal stem cells support limbal epithelial cells cultured on RAFT tissue equivalents. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez, B.E.; Sánchez, A.; Herreras, J.M.; Fernández, I.; Garcia-Sancho, J.; Nieto-Miguel, T.; Calonge, M. Stem Cell Therapy for Corneal Epithelium Regeneration following Good Manufacturing and Clinical Procedures. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, X.-Y.; Ruan, Y.-X.; Wang, L.; Jiang, M.-M.; Wu, J.; Chen, J. Construction of corneal epithelium with human amniotic epithelial cells and repair of limbal deficiency in rabbit models. Hum. Cell 2014, 28, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Li, Y.; Zeng, G.; Yang, B.; Zhu, Y. Transplantation with cultured stem cells derived from the human amniotic membrane for corneal alkali burns: An experimental study. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2014, 44, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Ganger, A.; Vanathi, M.; Mohanty, S.; Tandon, R. Long-Term Outcomes of Cultivated Limbal Epithelial Transplantation: Evaluation and Comparison of Results in Children and Adults. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levis, H.J.; Brown, R.A.; Daniels, J.T. Plastic compressed collagen as a biomimetic substrate for human limbal epithelial cell culture. Biomater. 2010, 31, 7726–7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Sheardown, H. Dendrimer crosslinked collagen as a corneal tissue engineering scaffold: Mechanical properties and corneal epithelial cell interactions. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4608–4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama, P.; Bonini, S.; Lambiase, A.; Golisano, O.; Paterna, P.; De Luca, M.; Pellegrini, G. Autologous Fibrin-Cultured Limbal Stem Cells Permanently Restore the Corneal Surface of Patients with Total Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency. Transplantion 2001, 72, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.; Low, S.; Mariappan, I.; Abberton, K.M.; Short, R.; Zhang, H.; Maddileti, S.; Sangwan, V.; Steele, D.; Daniell, M. Plasma Polymer-Coated Contact Lenses for the Culture and Transfer of Corneal Epithelial Cells in the Treatment of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency. Tissue Eng. Part A 2014, 20, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silber, P.C.; Ricardo, J.R.; Cristovam, P.C.; Hazarbassanov, R.; Dreyfuss, J.L.; Gomes, J.A. Conjunctival Epithelial Cells Cultivated Ex Vivo from Patients with Total Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 25, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Choi, S.H.; Wolosin, J.M.; Chung, S.-H.; Joo, C.-K. Regeneration of the corneal epithelium with conjunctival epithelial equivalents generated in serum- and feeder-cell–free media. Mol. Vis. 2013, 19, 2542–2550. [Google Scholar]
- Ricardo, J.R.S.; Cristovam, P.C.; Filho, P.A.N.; Farias, C.C.; de Araujo, A.L.; Loureiro, R.R.; Covre, J.L.; de Barros, J.N.; Barreiro, T.P.; dos Santos, M.S.; et al. Transplantation of Conjunctival Epithelial Cells Cultivated Ex Vivo in Patients with Total Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency. Cornea 2013, 32, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolli, S.; Ahmad, S.; Mudhar, H.S.; Meeny, A.; Lako, M.; Figueiredo, F. Successful Application of Ex Vivo Expanded Human Autologous Oral Mucosal Epithelium for the Treatment of Total Bilateral Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 2135–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimazaki, J.; Satake, Y.; Higa, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Noma, H.; Tsubota, K. Long-term outcomes of cultivated cell sheet transplantation for treating total limbal stem cell deficiency. Ocul. Surf. 2020, 18, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Ou, S.; Ren, J.; Sun, H.; He, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, H.; Qu, Y.; Liu, T.; Jeyalatha, V.; et al. Tissue engineered corneal epithelium derived from clinical-grade human embryonic stem cells. Ocul. Surf. 2020, 18, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, R.; Ishikawa, Y.; Sasamoto, Y.; Katori, R.; Nomura, N.; Ichikawa, T.; Araki, S.; Soma, T.; Kawasaki, S.; Sekiguchi, K.; et al. Nishida KCo-ordinated ocular development from human iPS cells recovery of corneal function. Nature 2016, 531, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.; Foulsham, W.; Amouzegar, A.; Mittal, S.K.; Chauhan, S.K. The therapeutic application of mesenchymal stem cells at the ocular surface. Ocul. Surf. 2019, 17, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilmarinen, T.; Laine, J.; Juuti-Uusitalo, K.; Numminen, J.; Seppänen-Suuronen, R.; Uusitalo, H.; Skottman, H. Towards a defined, serum- and feeder-free culture of stratified human oral mucosal epithelium for ocular surface reconstruction. Acta Ophthalmol. 2012, 91, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCorry, M.C.; Puetzer, J.L.; Bonassar, L.J. Characterization of mesenchymal stem cells and fibrochondrocytes in three-dimensional co-culture: Analysis of cell shape, matrix production, and mechanical performance. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirjamshidi, H.; Milani, B.; Sagha, H.; Movahedan, A.; Shafiq, M.; Lavker, R.; Yue, B.; Djalilian, A. Limbal fibroblast conditioned media: A non-invasive treatment for limbal stem cell deficiency. Mol. Vis. 2011, 17, 658–666. [Google Scholar]
- Cejkova, J.; Trosan, P.; Cejka, C.; Lencova, A.; Zajicova, A.; Javorkova, E.; Kubinova, S.; Sykova, E.; Holan, V. Suppression of alkali-induced oxidative injury in the cornea by mesenchymal stem cells growing on nanofiber scaffolds and transferred onto the damaged corneal surface. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 116, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cui, X.; Liu, X.; Yu, M.; Yang, C.; Li, X. Polysaccharide Hydrogel Combined with Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promotes the Healing of Corneal Alkali Burn in Rats. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Mittal, S.K.; Foulsham, W.; Elbasiony, E.; Singhania, D.; Sahu, S.K.; Chauhan, S.K. Therapeutic efficacy of different routes of mesenchymal stem cell administration in corneal injury. Ocul. Surf. 2019, 17, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews, S.; Chidambaram, J.; Lanjewar, S.; Mascarenhas, J.; Prajna, N.V.; Muthukkaruppan, V.; Chidambaranathan, G.P. In Vivo Confocal Microscopic Analysis of Normal Human Anterior Limbal Stroma. Cornea 2015, 34, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Chen, S.-Y.; Zhu, Y.-T.; Tseng, S.C. Integration of BMP/Wnt signaling to control clonal growth of limbal epithelial progenitor cells by niche cells. Stem Cell Res. 2014, 12, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiwaki-Dantas, M.C.; Dantas, P.; Reggi, J.R.A. Ipsilateral limbal translocation for treatment of partial limbal deficiency secondary to ocular alkali burn. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2001, 85, 1031–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohaina, C.M.; Then, K.Y.; Ng, A.M.H.; Halim, W.H.; Zahidin, A.Z.M.; Bin Saim, A.; Idrus, R.B. Reconstruction of limbal stem cell deficient corneal surface with induced human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on amniotic membrane. Transl. Res. 2014, 163, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrbach, J.; Süsskind, D.; Grüb, M. Der Melanozyt und das Auge: Eine Übersicht unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Kornea. Klin. Mon. Für Augenheilkd. 2011, 229, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polisetti, N.; Gießl, A.; Zenkel, M.; Heger, L.; Dudziak, D.; Naschberger, E.; Stich, L.; Steinkasserer, A.; Kruse, F.E.; Schlötzer-Schrehardt, U. Melanocytes as emerging key players in niche regulation of limbal epithelial stem cells. Ocul. Surf. 2021, 22, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziasko, M.A.; Tuft, S.J.; Daniels, J.T. Limbal melanocytes support limbal epithelial stem cells in 2D and 3D microenvironments. Exp. Eye Res. 2015, 138, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Xu, L.; Fan, Q.; Ren, S. Association between Corneal Stiffness Parameter at the First Applanation and Keratoconus Severity. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qassim, A.; Mullany, S.; Abedi, F.; Marshall, H.; Hassall, M.M.; Kolovos, A.; Knight, L.S.; Nguyen, T.; Awadalla, M.S.; Chappell, A.; et al. Corneal Stiffness Parameters Are Predictive of Structural and Functional Progression in Glaucoma Suspect Eyes. Ophthalmol. 2021, 128, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomasy, S.M.; Raghunathan, V.K.; Miyagi, H.; Evashenk, A.T.; Sermeno, J.C.; Tripp, G.K.; Morgan, J.; Murphy, C.J. Latrunculin B and substratum stiffness regulate corneal fibroblast to myofibroblast transformation. Exp. Eye Res. 2018, 170, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruri, D.P.; Miron-Mendoza, M.; Kivanany, P.B.; Hack, J.M.; Schmidtke, D.W.; Petroll, W.M.; Varner, V.D. ECM Stiffness Controls the Activation and Contractility of Corneal Keratocytes in Response to TGF-β1. Biophys. J. 2020, 119, 1865–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Q.; Deng, S.X. The application of human amniotic membrane in the surgical management of limbal stem cell deficiency. Ocul. Surf. 2019, 17, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calonge, M.; Pérez, I.; Galindo, S.; Nieto-Miguel, T.; López-Paniagua, M.; Fernández, I.; Alberca, M.; García-Sancho, J.; Sánchez, A.; Herreras, J.M. A proof-of-concept clinical trial using mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of corneal epithelial stem cell deficiency. Transl. Res. 2019, 206, 18–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramuta, T.Ž.; Kreft, M.E. Human Amniotic Membrane and Amniotic Membrane–Derived Cells: How Far Are We from Their Use in Regenerative and Reconstructive Urology? Cell Transplant. 2018, 27, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deihim, T.; Yazdanpanah, G.; Niknejad, H. Different Light Transmittance of Placental and Reflected Regions of Human Amniotic Membrane That Could Be Crucial for Corneal Tissue Engineering. Cornea 2016, 35, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknejad, H.; Yazdanpanah, G.; Ahmadiani, A. Induction of apoptosis, stimulation of cell-cycle arrest and inhibition of angiogenesis make human amnion-derived cells promising sources for cell therapy of cancer. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 363, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levis, H.; Daniels, J.T. Recreating the Human Limbal Epithelial Stem Cell Niche with Bioengineered Limbal Crypts. Curr. Eye Res. 2016, 41, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdanpanah, G.; Shah, R.; Somala, S.R.R.; Anwar, K.N.; Shen, X.; An, S.; Omidi, M.; Rosenblatt, M.I.; Shokuhfar, T.; Djalilian, A.R. In-situ porcine corneal matrix hydrogel as ocular surface bandage. Ocul. Surf. 2021, 21, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, A.P.; Ahearne, M. Strategies for developing decellularized corneal scaffolds. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 108, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.Y.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, H.J.; Ko, J.H.; Wee, W.R.; Lee, J.H. Comparative observation of freeze-thaw-induced damage in pig, rabbit, and human corneal stroma. Veter-Ophthalmol. 2009, 12, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoeruek, E.; Bayyoud, T.; Maurus, C.; Hofmann, J.; Spitzer, M.S.; Bartz-Schmidt, K.-U.; Szurman, P. Decellularization of porcine corneas and repopulation with human corneal cells for tissue-engineered xenografts. Acta Ophthalmol. 2011, 90, e125–e131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahearne, M.; Lynch, A.P. Early Observation of Extracellular Matrix-Derived Hydrogels for Corneal Stroma Regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2015, 21, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, M.A.; Gemeinhart, R.; Yue, B.Y.; Djalilian, A.R. Decellularized Human Cornea for Reconstructing the Corneal Epithelium and Anterior Stroma. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2012, 18, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanpanah, G.; Jiang, Y.; Rabiee, B.; Omidi, M.; Rosenblatt, M.I.; Shokuhfar, T.; Pan, Y.; Naba, A.; Djalilian, A.R. Fabrication, Rheological, and Compositional Characterization of Thermoresponsive Hydrogel from Cornea. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2021, 27, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanpanah, G.; Jabbehdari, S.; Djalilian, A.R. Emerging Approaches for Ocular Surface Regeneration. Curr. Ophthalmol. Rep. 2019, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myung, D.; Farooqui, N.; Zheng, L.L.; Koh, W.; Gupta, S.; Bakri, A.; Noolandi, J.; Cochran, J.R.; Frank, C.W.; Ta, C.N. Bioactive interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels that support corneal epithelial wound healing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2009, 90, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Fernandes-Cunha, G.M.; Na, K.; Hull, S.M.; Myung, D. Bio-Orthogonally Crosslinked, In Situ Forming Corneal Stromal Tissue Substitute. Adv. Heal. Mater. 2018, 7, e1800560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.B.; Lawrence, B.D.; Gao, X.R.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, A.; Guaiquil, V.H.; Rosenblatt, M.I. Micro- and Nanoscale Topographies on Silk Regulate Gene Expression of Human Corneal Epithelial Cells. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 6388–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, K.N.; Bobba, S.; Richardson, A.; Park, M.; Watson, S.L.; Wakefield, D.; Di Girolamo, N. Native and synthetic scaffolds for limbal epithelial stem cell transplantation. Acta Biomater. 2018, 65, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radosevich, M.; Goubran, H.A.; Burnouf, T. Fibrin Sealant: Scientific Rationale, Production Methods, Properties, and Current Clinical Use. Vox Sang. 1997, 72, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atrah, H.I. Fibrin glue. BMJ 1994, 308, 933–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowacki, J.; Mizuno, S. Collagen scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomolecules 2008, 89, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.; Zhao, B.; Bentley, A.J.; Brahma, A.; MacNeil, S.; Martin, F.L.; Rimmer, S.; Fullwood, N.J. Corneal epithelialisation on surface-modified hydrogel implants. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2011, 22, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myung, D.; Koh, W.; Bakri, A.; Zhang, F.; Marshall, A.; Ko, J.; Noolandi, J.; Carrasco, M.; Cochran, J.R.; Frank, C.W.; et al. Design and fabrication of an artificial cornea based on a photolithographically patterned hydrogel construct. Biomed. Microdevices 2007, 9, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akcam, H.T.; Unlu, M.; Karaca, E.E.; Yazici, H.; Aydin, B.; Hondur, A.M. Autologous serum eye-drops and enhanced epithelial healing time after photorefractive keratectomy. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2018, 101, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azari, A.; Rapuano, C.J. Autologous Serum Eye Drops for the Treatment of Ocular Surface Disease. Eye Contact Lens 2015, 41, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harritshøj, L.H.; Nielsen, C.; Ullum, H.; Hansen, M.B.; Julian, H.O. Ready-made allogeneic ABO-specific serum eye drops: Production from regular male blood donors, clinical routine, safety and efficacy. Acta Ophthalmol. 2014, 92, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreimei, M.; Sorkin, N.; Boutin, T.; Slomovic, A.R.; Rootman, D.; Chan, C. Patient-reported outcomes of autologous serum tears for the treatment of dry eye disease in a large cohort. Ocul. Surf. 2019, 17, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semeraro, F.; Forbice, E.; Braga, O.; Bova, A.; Di Salvatore, A.; Azzolini, C. Evaluation of the Efficacy of 50% Autologous Serum Eye Drops in Different Ocular Surface Pathologies. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripa, M.; Jabbehdari, S.; Yazdanpanah, G.; Lukacs, E.; Karcher, B.; Iqbal, O.; Bouchard, C. The Role of Multisystem Disease in Composition of Autologous Serum tears and ocular surface symptom improvement. Ocul. Surf. 2020, 18, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, N.; Yin, G.H.W.; Noharet, R.; Ghazouane, R.; Grimaud, F.; Aboudou, H.; Darque, A.; Delmotte, N.; Veran, J.; Hoffart, L.; et al. A retrospective analysis of characteristic features of responder patients to autologous serum eye drops in routine care. Ocul. Surf. 2019, 17, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; de la Fuente, M.; Muruzabal, F.J.; Riestra, A.; Merayo-Lloves, J.; Orive, G. Plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF) eye drops stimulates scarless regeneration compared to autologous serum in the ocular surface stromal fibroblasts. Exp. Eye Res. 2015, 135, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.M.; Shin, Y.T.; Kim, H.K. Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on persistent corneal epithelial defect after infec-tious keratitis. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 56, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, N.G.; Jeng, B.H. Blood-derived topical therapy for ocular surface diseases. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 100, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, M.Y.; Igua, A.M.; Mora, A.M. Randomised, prospective clinical trial of platelet-rich plasma injection in the management of severe dry eye. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 103, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire, V.; Andollo, N.; Etxebarria, J.; Hernaez-Moya, R.; Duran, J.A.; Morales, M.C. Corneal wound healing promoted by 3 blood derivatives: An in vitro and in vivo comparative study. Cornea 2014, 33, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradaran-Rafii, A.; Asl, N.S.; Ebrahimi, M.; Jabbehdari, S.; Bamdad, S.; Roshandel, D.; Eslani, M.; Momeni, M. The role of amniotic membrane extract eye drop (AMEED) in in vivo cultivation of limbal stem cells. Ocul. Surf. 2018, 16, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, S.C.G. HC-HA/PTX3 Purified from Amniotic Membrane as Novel Regenerative Matrix: Insight Into Relationship between Inflammation and Regeneration. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, ORSFh1–ORSFh8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-Y.; Han, B.; Zhu, Y.-T.; Mahabole, M.; Huang, J.; Beebe, D.C.; Tseng, S.C.G. HC-HA/PTX3 Purified from Amniotic Membrane Promotes BMP Signaling in Limbal Niche Cells to Maintain Quiescence of Limbal Epithelial Progenitor/Stem Cells. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 3341–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirassa, P.; Rosso, P.; Iannitelli, A. Ocular Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) and NGF Eye Drop Application as Paradigms to Investigate NGF Neuroprotective and Reparative Actions. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1727, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambiase, A.; Sacchetti, M.; Bonini, S. Nerve growth factor therapy for corneal disease. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2012, 23, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonini, S.; Lambiase, A.; Rama, P.; Sinigaglia, F.; Allegretti, M.; Chao, W.; Mantelli, F.; Bonini, S.; Lambiase, A.; Rama, P.; et al. Phase II Randomized, Double-Masked, Vehicle-Controlled Trial of Recombinant Human Nerve Growth Factor for Neurotrophic Keratitis. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 1332–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, S.-I.; Ho, T.-C.; Chen, S.-L.; Cheng, H.-C.; Lan, Y.-W.; Hsieh, J.-W.; Wang, C.-T.; Tsao, Y.-P. Pigment Epithelial-Derived Factor Peptide Regenerated Limbus Serves as Regeneration Source for Limbal Regeneration in Rabbit Limbal Deficiency. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.-C.; Chen, S.-L.; Wu, J.-Y.; Ho, M.-Y.; Chen, L.-J.; Hsieh, J.-W.; Cheng, H.-C.; Tsao, Y.-P. PEDF promotes self-renewal of limbal stem cell and accelerates corneal epithelial wound healing. Stem Cells 2013, 31, 1775–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, H.; Ong, H.S.; Riau, A.K.; Stanzel, T.P.; Mehta, J.S.; Yam, G.H.-F. Current Trends and Future Perspective of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Exosomes in Corneal Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, A.; Baiju, I.; Bhat, I.A.; Pandey, S.; Bharti, M.; Verma, M.; Singh, A.P.; Ansari, M.M.; Chandra, V.; Saikumar, G.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned media: A novel alternative of stem cell therapy for quality wound healing. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 5555–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes-Cunha, G.M.; Na, K.-S.; Putra, I.; Lee, H.J.; Hull, S.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Blanco, I.J.; Eslani, M.; Djalilian, A.R.; Myung, D. Corneal Wound Healing Effects of Mesen-chymal Stem Cell Secretome Delivered within a Viscoelastic Gel Carrier. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2018, 8, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslani, M.; Putra, I.; Shen, X.; Hamouie, J.; Afsharkhamseh, N.; Besharat, S.; Rosenblatt, M.I.; Dana, R.; Hematti, P.; Djalilian, A.R. Corneal Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Are Directly Antiangiogenic via PEDF and sFLT-1. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 5507–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslani, M.; Putra, I.; Shen, X.; Hamouie, J.; Tadepalli, A.; Anwar, K.N.; Kink, J.A.; Ghassemi, S.; Agnihotri, G.; Reshetylo, S.; et al. Cornea-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Therapeutically Modulate Macrophage Immunophenotype and Angiogenic Function. Stem Cells 2018, 36, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhao, J.; Yu, S.; Tang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; He, X.; et al. exoRBase: A database of circRNA, lncRNA and mRNA in human blood exosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D106–D112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, B.K.; Zhang, H.; Becker, A.; Matei, I.; Huang, Y.; Costa-Silva, B.; Zheng, Y.; Hoshino, A.; Brazier, H.; Xiang, J.; et al. Double-stranded DNA in exosomes: A novel biomarker in cancer detection. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skotland, T.; Sandvig, K.; Llorente, A. Lipids in exosomes: Current knowledge and the way forward. Prog. Lipid Res. 2017, 66, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livshits, M.A.; Khomyakova, E.; Evtushenko, E.; Lazarev, V.N.; Kulemin, N.; Semina, S.E.; Generozov, E.; Govorun, V.M. Isolation of exosomes by differential centrifugation: Theoretical analysis of a commonly used protocol. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böing, A.N.; van der Pol, E.; Grootemaat, A.E.; Coumans, F.A.W.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. Single-step isolation of extracellular vesicles by size-exclusion chromatography. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, L.M.; Wang, M.Z. Overview of Extracellular Vesicles, Their Origin, Composition, Purpose, and Methods for Exosome Isolation and Analysis. Cells 2019, 8, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaeekia, R.; Rabiee, B.; Putra, I.; Shen, X.; Park, Y.J.; Hematti, P.; Eslani, M.; Djalilian, A.R. Effect of Human Corneal Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-derived Exosomes on Corneal Epithelial Wound Healing. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 5194–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shojaati, G.; Khandaker, I.; Funderburgh, M.L.; Mann, M.M.; Basu, R.; Stolz, D.B.; Geary, M.L.; Dos Santos, A.; Deng, S.X.; Funderburgh, J.L. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reduce Corneal Fibrosis and Inflammation via Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Delivery of miRNA. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2019, 8, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harting, M.T.; Srivastava, A.K.; Zhaorigetu, S.; Bair, H.; Prabhakara, K.S.; Toledano Furman, N.E.; Vykoukal, J.V.; Ruppert, K.A.; Cox, C.S., Jr.; Olson, S.D. Inflamma-tion-stimulated mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate inflammation. Stem Cells 2018, 36, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knickelbein, J.E.; Liu, B.; Arakelyan, A.; Zicari, S.; Hannes, S.; Chen, P.; Li, Z.; Grivel, J.; Chaigne-Delalande, B.; Sen, H.N.; et al. Modulation of immune responses by extra-cellular vesicles from retinal pigment epithelium. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 4101–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shigemoto-Kuroda, T.; Oh, J.Y.; Kim, D.-K.; Jeong, H.J.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Park, J.W.; Kim, T.W.; An, S.Y.; Prockop, D.J.; et al. MSC-derived Extracellular Vesicles Attenuate Immune Responses in Two Autoimmune Murine Models: Type 1 Diabetes and Uveoretinitis. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 8, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witwer, K.W.; Van Balkom, B.W.M.; Bruno, S.; Choo, A.; Dominici, M.; Gimona, M.; Hill, A.F.; De Kleijn, D.; Koh, M.; Lai, R.C.; et al. Defining mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC)-derived small extracellular vesicles for therapeutic applications. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1609206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Rhim, W.-K.; Seo, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, C.G.; Han, D.K. Comparative Analysis of MSC-Derived Exosomes Depending on Cell Culture Media for Regenerative Bioactivity. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2021, 18, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtam, T.A.; Kovalev, R.A.; Varfolomeeva, E.Y.; Makarov, E.M.; Kil, Y.V.; Filatov, M.V. Exosomes are natural carriers of exogenous siRNA to human cells in vitro. Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Kong, Y. Exosomes Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Modulate miR-126 to Ameliorate Hyperglycemia-Induced Retinal Inflammation Via Targeting HMGB1. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amin, S.; Jalilian, E.; Katz, E.; Frank, C.; Yazdanpanah, G.; Guaiquil, V.H.; Rosenblatt, M.I.; Djalilian, A.R. The Limbal Niche and Regenerative Strategies. Vision 2021, 5, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision5040043
Amin S, Jalilian E, Katz E, Frank C, Yazdanpanah G, Guaiquil VH, Rosenblatt MI, Djalilian AR. The Limbal Niche and Regenerative Strategies. Vision. 2021; 5(4):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision5040043
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmin, Sohil, Elmira Jalilian, Eitan Katz, Charlie Frank, Ghasem Yazdanpanah, Victor H. Guaiquil, Mark I. Rosenblatt, and Ali R. Djalilian. 2021. "The Limbal Niche and Regenerative Strategies" Vision 5, no. 4: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision5040043
APA StyleAmin, S., Jalilian, E., Katz, E., Frank, C., Yazdanpanah, G., Guaiquil, V. H., Rosenblatt, M. I., & Djalilian, A. R. (2021). The Limbal Niche and Regenerative Strategies. Vision, 5(4), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision5040043




