Chromatic Induction in Migraine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
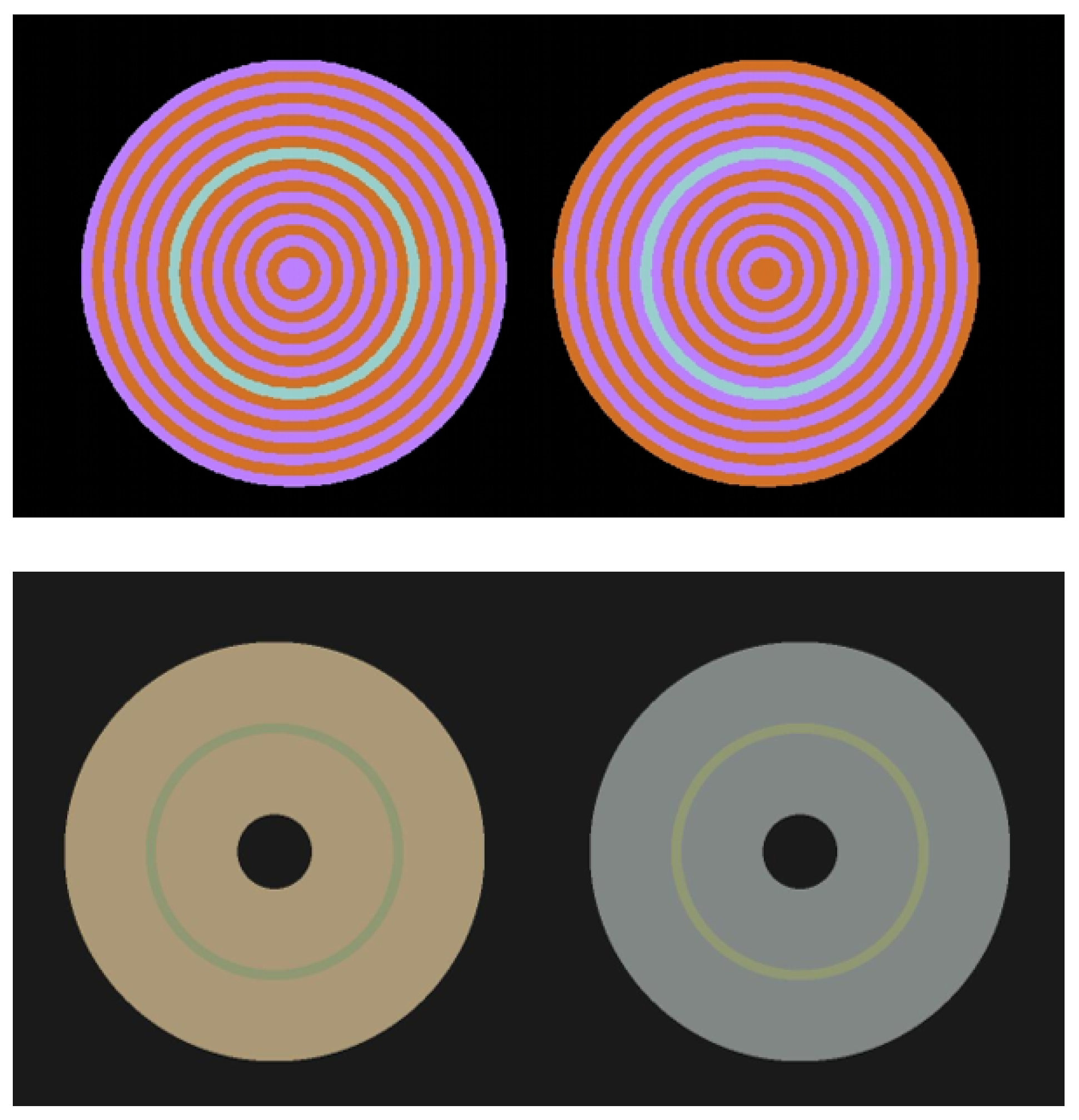
2.1. Stimuli
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Participants
2.4. Procedure
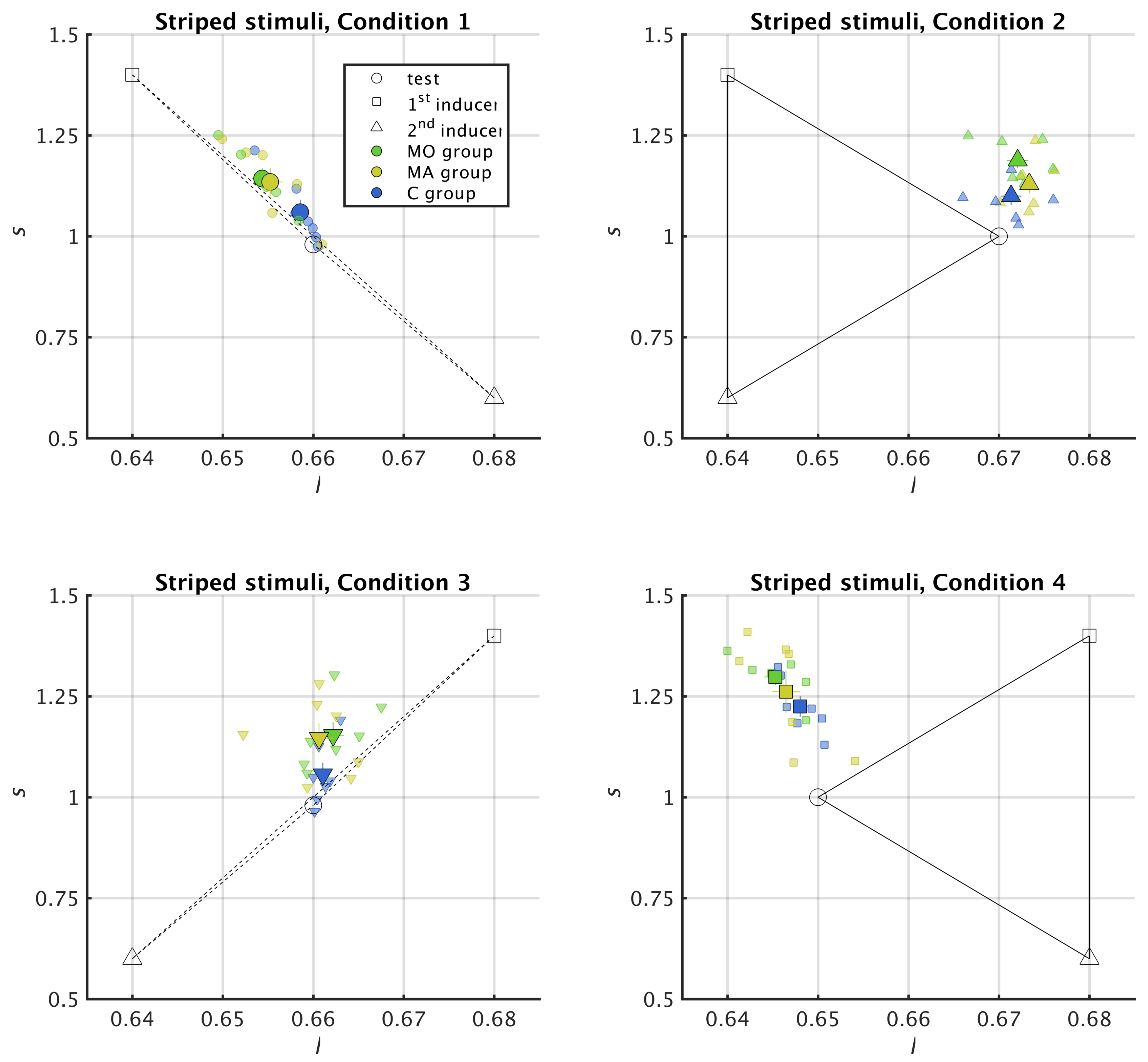
2.5. Reading Chromatic Induction in the MacLeod–Boynton Colour Space
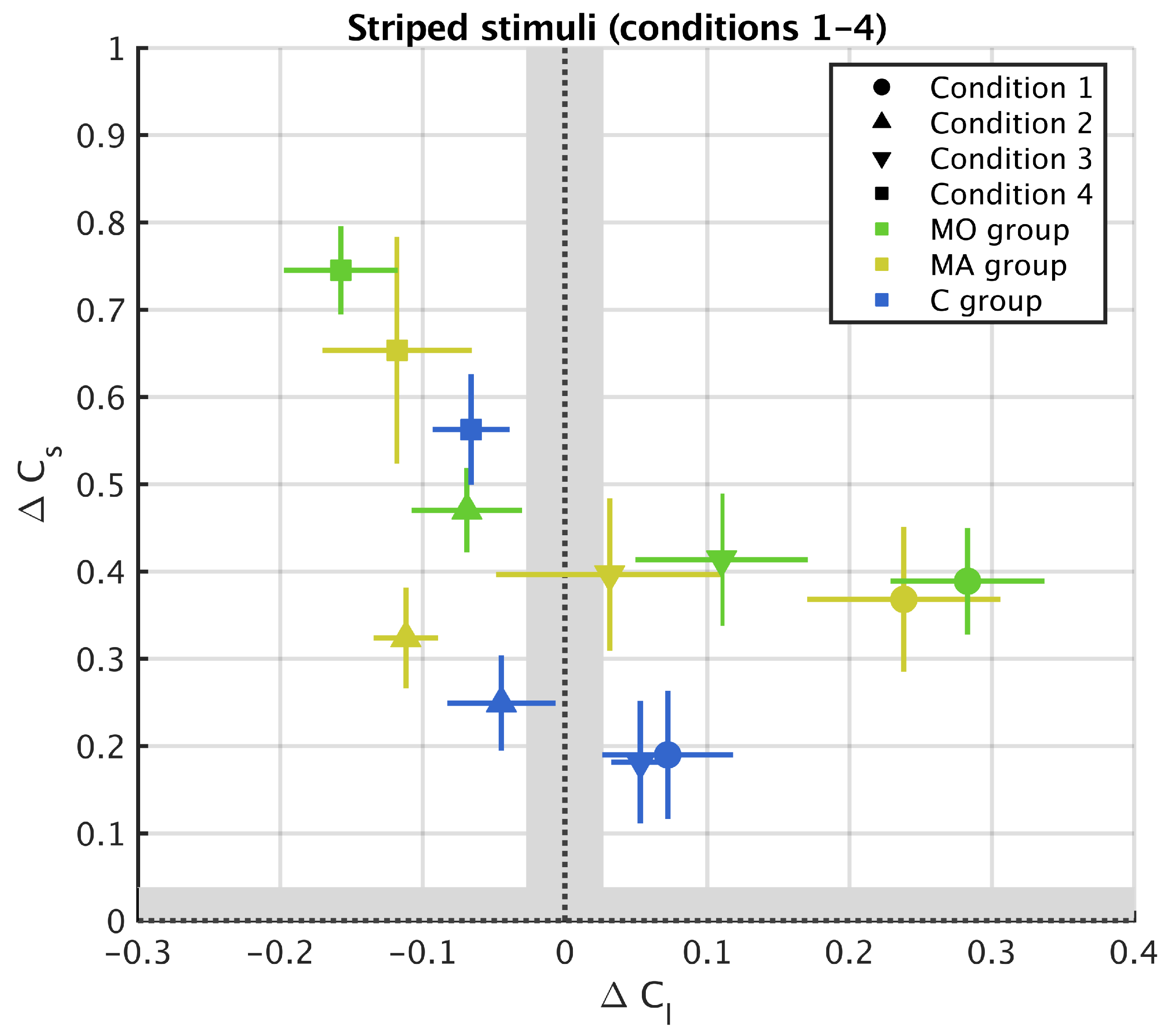
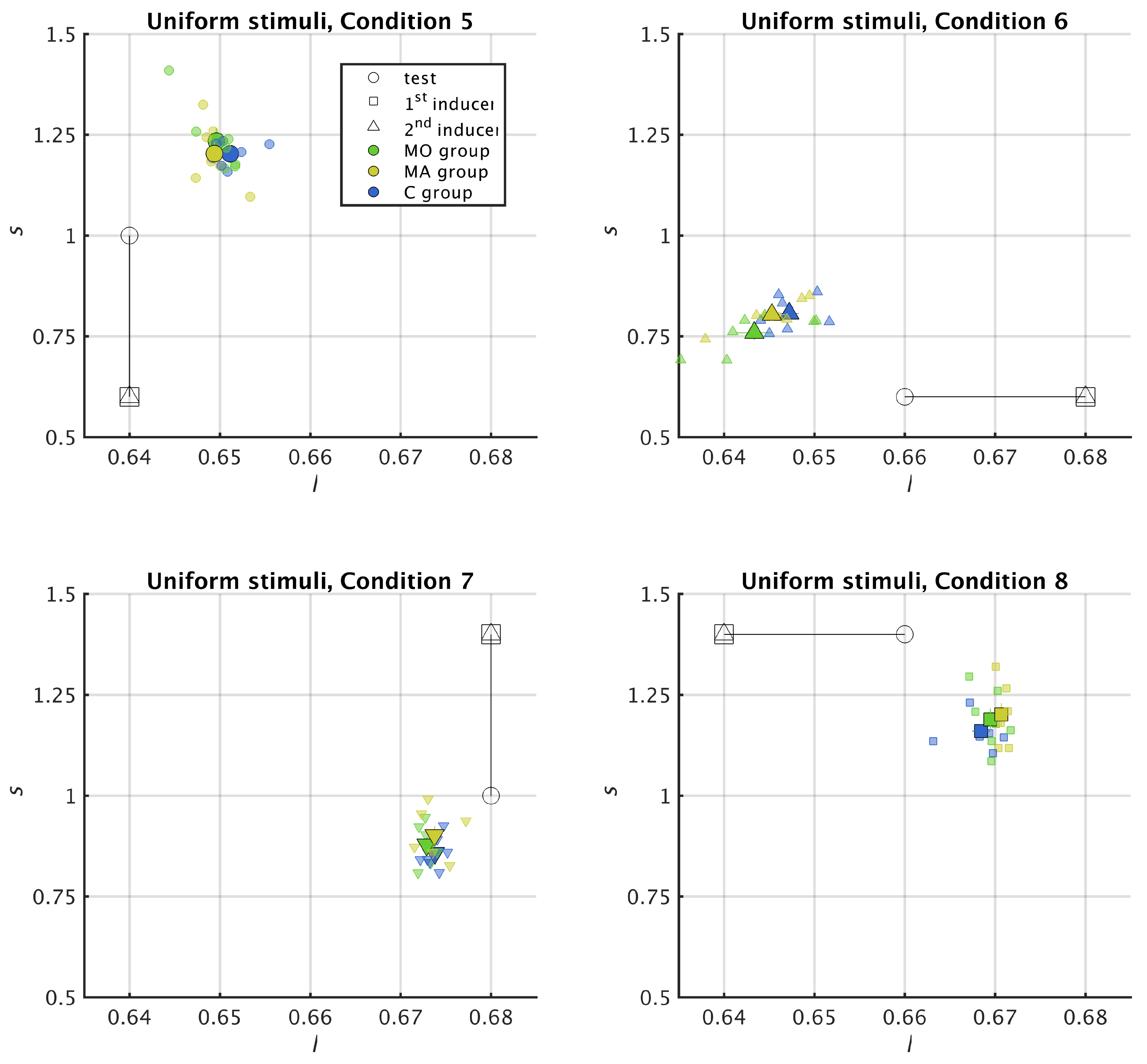
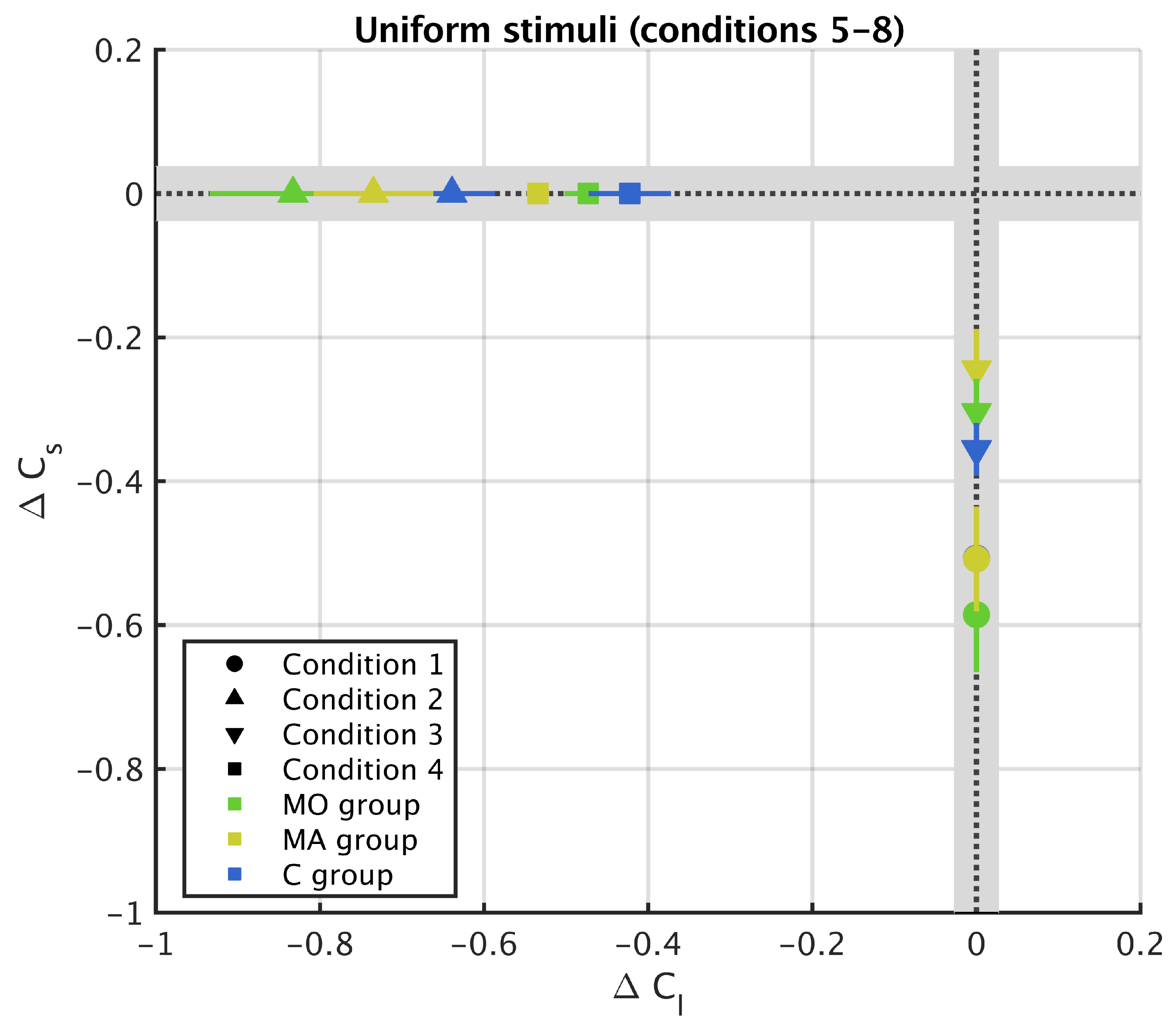
2.6. Metric for Chromatic Induction
2.7. Statistical Analysis
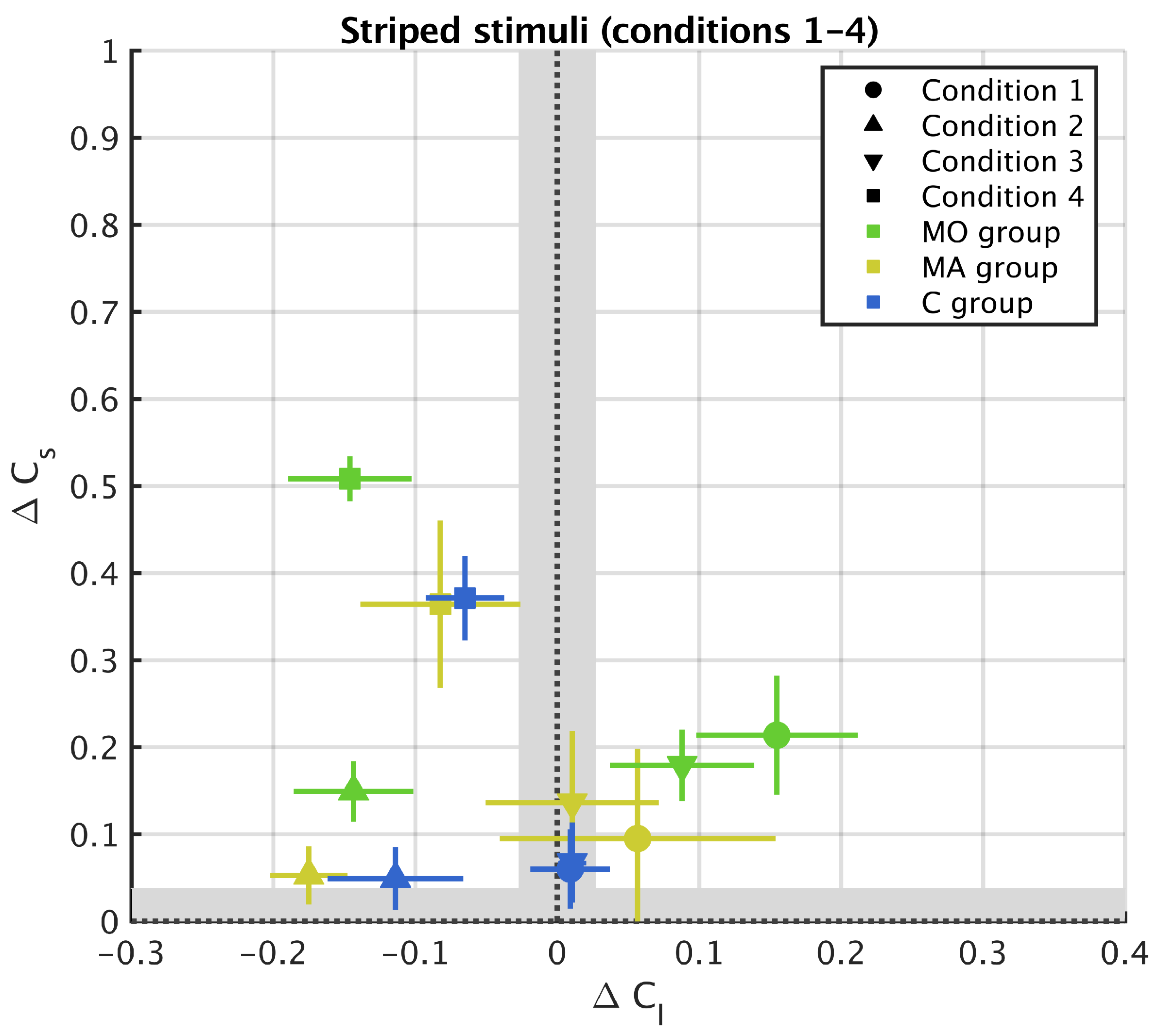
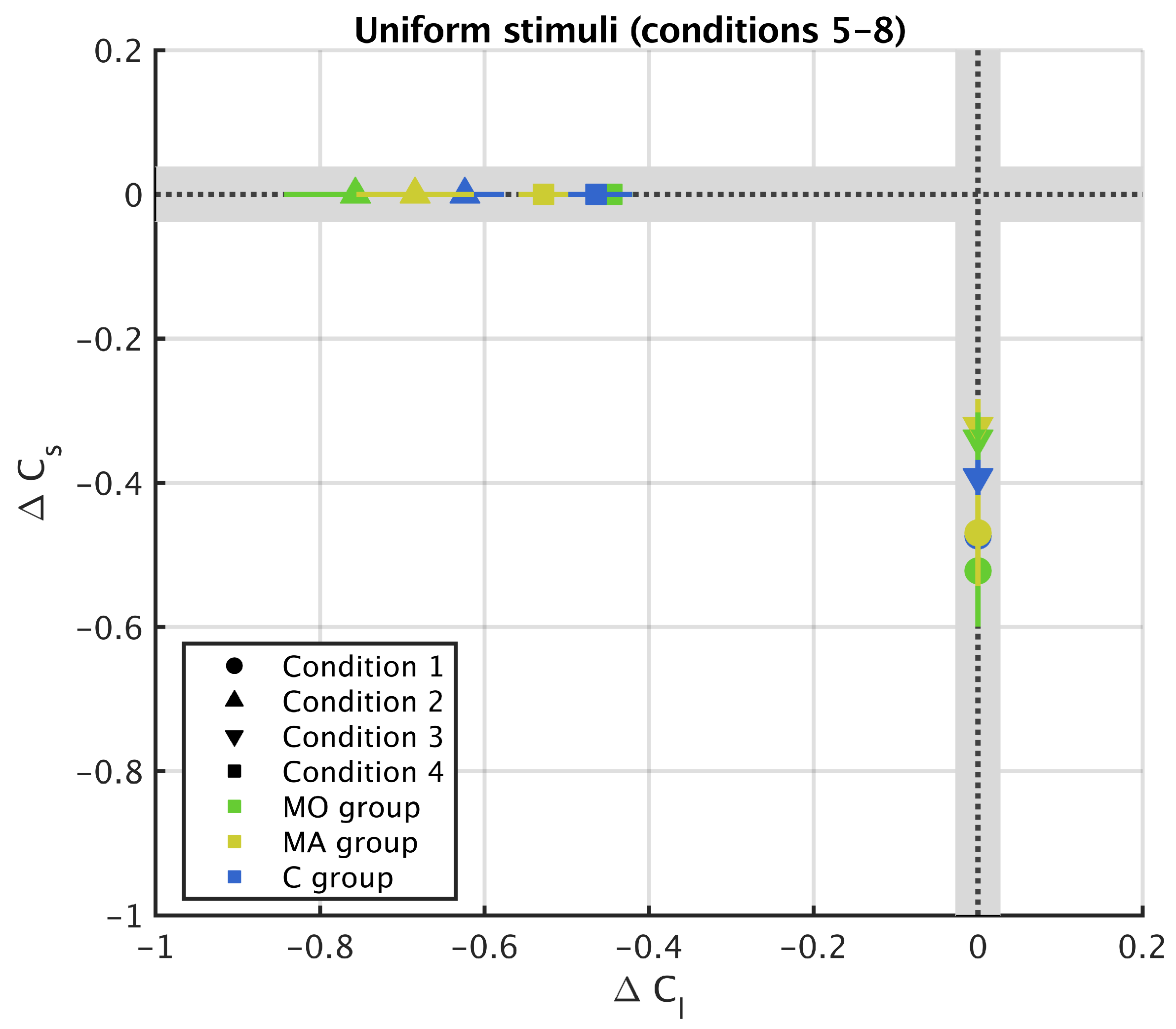
3. Results
3.1. Striped Surround
3.2. Uniform Surround
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| C | Healthy migraine-free control |
| JND | Just Noticeable Difference |
| M | Migraine |
| MA | Migraine with aura |
| MO | Migraine without aura |
Appendix A. Results from 11 Stripes Conditions
References
- Cao, D.; Shevell, S.K. Chromatic assimilation: Spread light or neural mechanism? Vis. Res. 2005, 45, 1031–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnier, P.; Shevell, S.K. Large shifts in color appearance from patterned chromatic backgrounds. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monnier, P.; Shevell, S.K. Chromatic induction from S-cone patterns. Vis. Res. 2004, 44, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otazu, X.; Parraga, C.A.; Vanrell, M. Toward a unified chromatic induction model. J. Vis. 2010, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, Q.; Yoshimi, B.; Flanigan, N.; Canova, A. Lateral interactions within color mechanism in simultaneous induced contrast. Vis. Res. 1992, 32, 1695–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, Q. Color and Brightness Induction: From Mach Bands to Three-Dimensional Configurations; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore, C.; Tobin, E. Lateral Inhibition between orientation detectors in the cat’s visual cortex. Exp. Brain Res. 1972, 15, 439–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, P.; Coombs, J.; Henry, G. Receptive fields of simple cells in the cat striate cortex. J. Physiol. 1973, 231, 31–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Heeger, D.J. Normalization of cell responses in cat striate cortex. Vis. Neurosci. 1992, 9, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelucci, A.; Bressloff, P. Contribution of feedforward, lateral and feedback connections to the classical receptive field center and extra-classical receptive field surround of primate V1 neurons. Prog. Brain Res. 2006, 154, 93–120. [Google Scholar]
- Otazu, X.; Vanrell, M.; Párraga, C.A. Multiresolution wavelet framework models brightness induction effects. Vis. Res. 2008, 48, 733–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerda-Company, X.; Otazu, X. Color induction in equiluminant flashed stimuli. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2019, 36, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penacchio, O.; Otazu, X.; Dempere-Marco, L. A Neurodynamical Model of Brightness Induction in V1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stovner, L.J.; Andree, C. Prevalence of headache in Europe: A review ofor the Eurolight project. J. Headache Pain 2010, 11, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelletti, P.; Birbeck, G.L.; Katsarava, Z.; Jensen, R.H.; Stovner, L.J.; Steiner, T.J. The Global Burden of Disease survey 2010, Lifting The Burden and thinking outside-the-box on headache disorders. J. Hedache Pain 2013, 14, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andress-Rothrock, D.; Wesley King, W.; Rothrock, J. An Analysis of Migraine Triggers in a Clinic-Based Population. J. Hedache Face Pain 2010, 50, 1366–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olesen, J.; Bes, A.; Kunkel, R.; Lance, J.W.; Nappi, G.; Pfaffenrath, V.; Rose, F.C.; Schoenberg, B.S.; Soyka, D.; Tfelt-Hansen, P.; et al. The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 629–808. [Google Scholar]
- Queiroz, L.P.; Rapoport, A.M.; Weeks, R.E.; Sheftell, F.D.; Siegel, S.E.; Baskin, S.M. Characteristics of migraine visual aura. J. Headache Face Pain 1997, 37, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hare, L.; Hibbard, P.B. Visual processing in migraine. Cephalalgia 2016, 36, 1057–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, S.; Wilkinson, F. Visual contrast gain control in migraine: Measures of visual cortical excitability and inhibition. Cephalalgia 2000, 20, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, A. Increased visual after-effects following pattern adaptation in migraine: A lack of intracortical excitation? Brain 2001, 124, 2310–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKendrick, A.M.; Vingrys, A.J.; Badcock, D.R.; Heywood, J.T. Visual dysfunction between migraine events. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 626–633. [Google Scholar]
- Antal, A.; Temme, J.; Nitsche, M.; Varga, E.; Lang, N.; Paulus, W. Altered motion perception in migraineurs: Evidence for interictal cortical hyperexcitability. Cephalalgia 2005, 25, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditchfield, J.A.; McKendrick, A.M.; Badcock, D.R. Processing of global form and motion in migraineurs. Vis. Res. 2006, 46, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, A.J. A Review of Motion and Orientation Processing in Migraine. Vision 2019, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, A.J. Tracking the Migraine Cycle Using Visual Tasks. Vision 2020, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, A.; Nimmosmith, I.; Tait, A.; McManus, C.; Della Sala, S.; Tilley, A.; Arnold, K.; Barrie, M.; Scott, S. A neurological basis for visual discomfort. Brain 1984, 107, 989–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlon, E.; Lovegrove, W.; Chekaluk, E.; Pattison, P. Measuring visual discomfort. Vis. Cogn. 1999, 6, 637–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, K.; St Louis, E.; Johnson, J.; McClelland, R.; Westmoreland, B.; Klass, D. Pattern-sensitive epilepsy: Electroclinical characteristics, natural history, and delineation of the epileptic syndrome. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, D.; Soso, M. Migraine and stripe-induced visual discomfort. Arch. Neurol. 1989, 46, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meldrum, B. Photosensitive epilepsy in man and the baboon. Electrophysiol. Epilepsy 1984, 1984, 51–77. [Google Scholar]
- Bigal, M.; Hetherington, H.; Pan, J.; Tsang, A.; Grosberg, B.; Avdievich, N.; Friedman, B.; Lipton, R. Occipital levels of GABA are related to severe headaches in migraine. Neurology 2008, 70, 2078–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, A. Colour vision in migraine: Selective deficits for S-cone discriminations. Cephalalgia 2005, 25, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zong, X.; Wilkins, A.; Jenkins, B.; Bozoki, A.; Cao, Y. fMRI evidence that precision ophthalmic tints reduce cortical hyperactivation in migraine. Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.; Chronicle, E.; Rolan, P.; Mulleners, W. Cortical hyperexcitability is cortical under-inhibition: Evidence from a novel functional test of migraine patients. Cephalalgia 2000, 20, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulleners, W.M.; Chronicle, E.P.; Palmer, J.E.; Koehler, P.J.; Vredeveld, J.W. Visual cortex excitability in migraine with and without aura. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2001, 41, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, G.; Pierelli, F.; Schoenen, J. Is The Cerebral Cortex Hyperexcitable or Hyperresponsive in Migraine? Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 1427–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, B.N.; McKendrick, A.M.; Vingrys, A.J. Abnormal inhibition-excitation imbalance in migraine. Cephalalgia 2016, 36, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, A.J. Color vision but not visual attention is altered in migraine. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2006, 46, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marinis, M.; Rinalduzzi, S.; Accornero, N. Impairment in color perception in migraine with and without aura. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2007, 47, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, A.J.; Hine, T.J.; Beaumont, H.M. Color and spatial frequency are related to visual pattern sensitivity in migraine. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2013, 53, 1087–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronicle, E.; Wilkins, A.; Coleston, D. Thresholds for detection of a target against a background grating suggest visual dysfunction in migraine with aura but not migraine without aura. Cephalalgia 1995, 15, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, A.J. Visual contrast processing in migraine. Cephalalgia 2000, 20, 865–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fach, C.; Sharpe, L.T. Assimilative hue shifts in color depend on bar width. Percept. Psychophys. 1986, 40, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, V.C.; Jin, P.Q.; Pokorny, J. The role of spatial frequency in color induction. Vis. Res. 2001, 41, 1007–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, D.A.; Boynton, R.M. Chromaticity diagram showing cone excitation by stimuli of equal luminance. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1979, 69, 1183–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MATLAB. Version 9.1.0 (R2016b); The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara, S. Tests for Colour-Blindness; Kanehara Shippan Co., Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Farnsworth, D. The Farnsworth Dichotomous Test for Color Blindness: Panel D-15; Psychological Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1947. [Google Scholar]
- Cerda-Company, X.; Otazu, X.; Sallent, N.; Parraga, C.A. The effect of luminance differences on color assimilation. J. Vis. 2018, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disraeli, B. General summary statistics. In Understanding Statistics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Chapter 2; pp. 36–83. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mulleners, W. Colour Vision Impairment in Migraine-Out of the Blue? Cephalalgia 2005, 25, 401–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibber, M.S.; Guedes, A.; Shepherd, A.J. Orientation discrimination and contrast detection thresholds in migraine for cardinal and oblique angles. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 5599–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKendrick, A.M.; Chan, Y.M.; Vingrys, A.J.; Turpin, A.; Badcock, D.R. Daily vision testing can expose the prodromal phase of migraine. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Experiment S (Striped Surround) | |||||||||
| Condition | Test Ring | 1st Inducer | 2nd Inducer | ||||||
| l | s | Y | l | s | Y | l | s | Y | |
| 1 | |||||||||
| 2 | |||||||||
| 3 | |||||||||
| 4 | |||||||||
| Experiment U (Uniform Surround) | |||||||||
| Condition | Test Ring | Inducer | |||||||
| l | s | Y | l | s | Y | ||||
| 5 | |||||||||
| 6 | |||||||||
| 7 | |||||||||
| 8 | |||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cerda-Company, X.; Penacchio, O.; Otazu, X. Chromatic Induction in Migraine. Vision 2021, 5, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision5030037
Cerda-Company X, Penacchio O, Otazu X. Chromatic Induction in Migraine. Vision. 2021; 5(3):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision5030037
Chicago/Turabian StyleCerda-Company, Xim, Olivier Penacchio, and Xavier Otazu. 2021. "Chromatic Induction in Migraine" Vision 5, no. 3: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision5030037
APA StyleCerda-Company, X., Penacchio, O., & Otazu, X. (2021). Chromatic Induction in Migraine. Vision, 5(3), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision5030037







