Effects of Instability Neuromuscular Training Using an Inertial Load of Water on the Balance Ability of Healthy Older Women: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
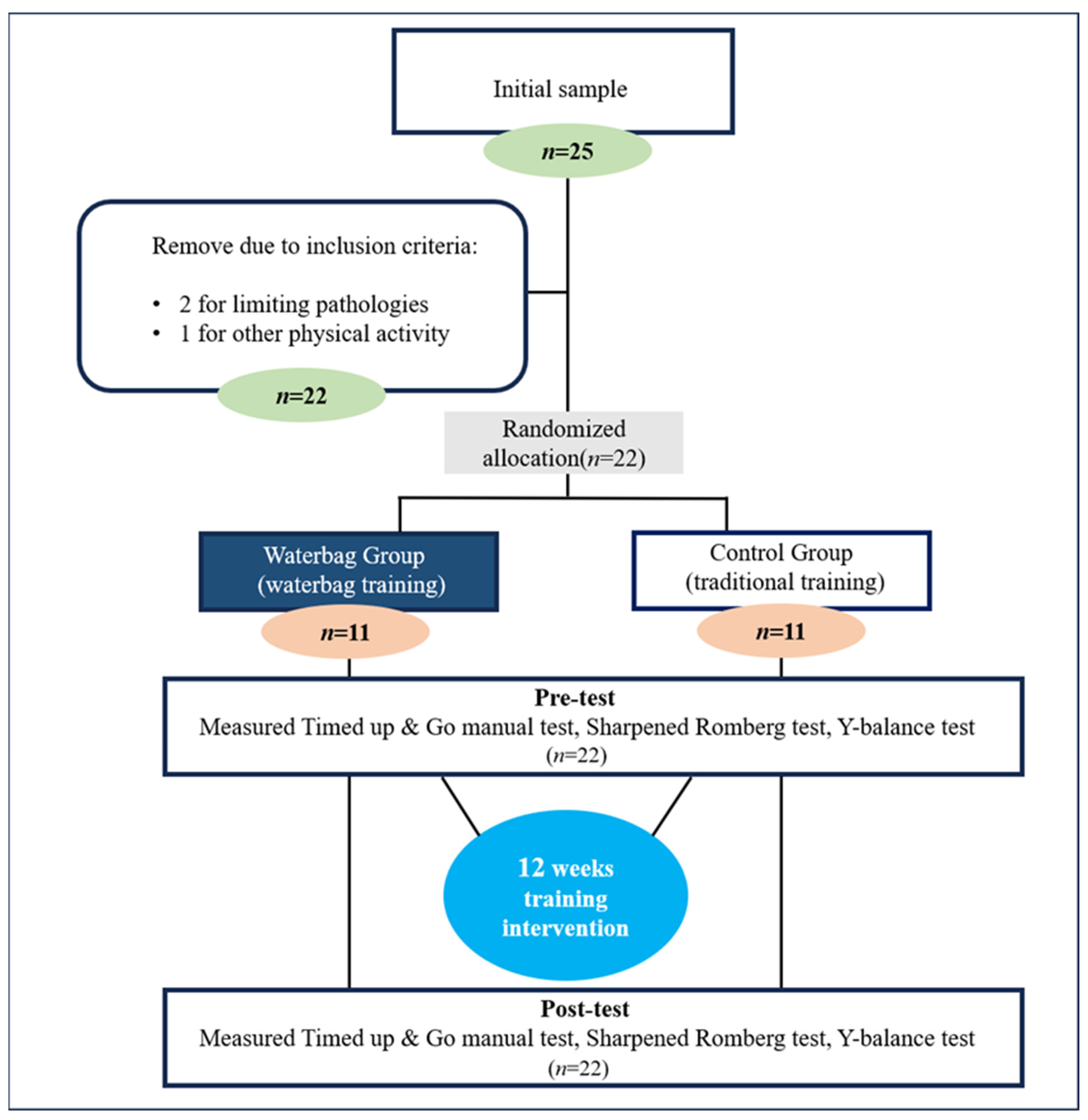
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Participants
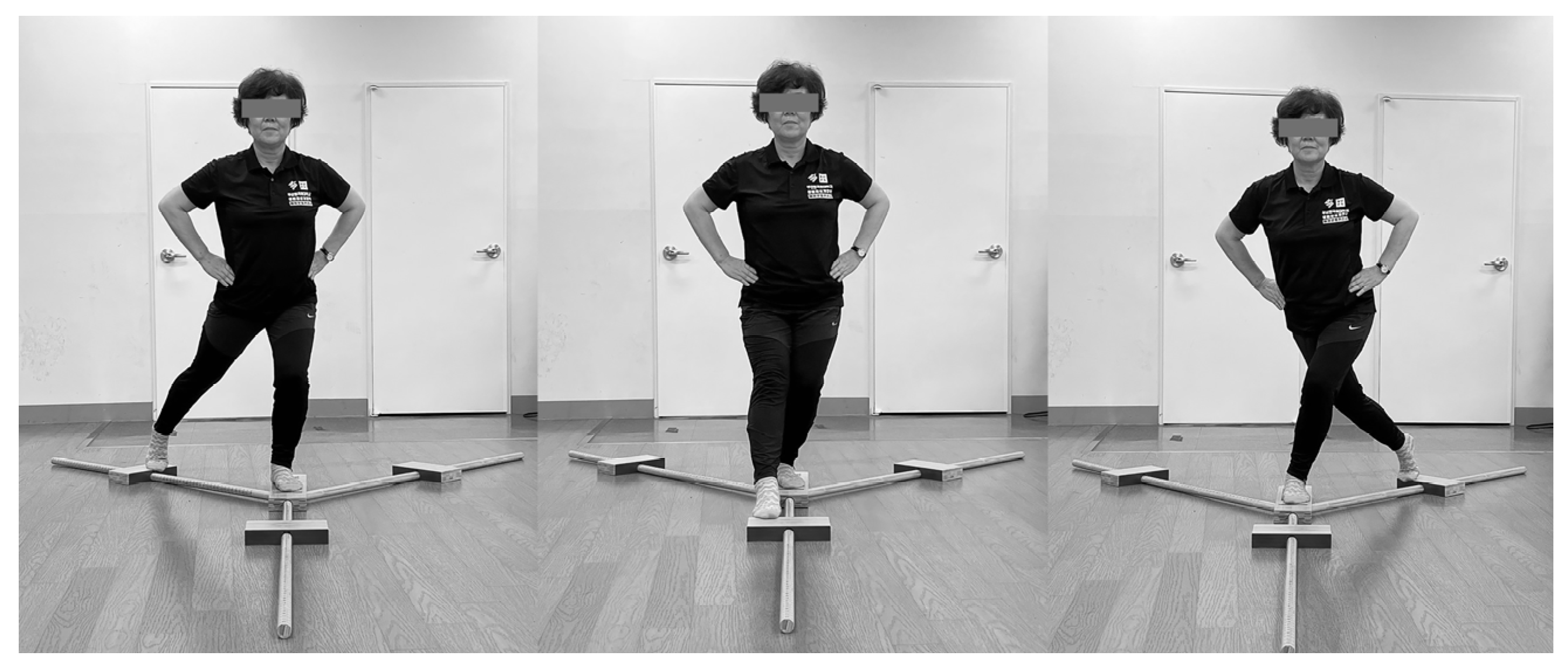
2.2. Instability Neuromuscular Training Using Waterbag Program
3. Measurements and Data Analysis
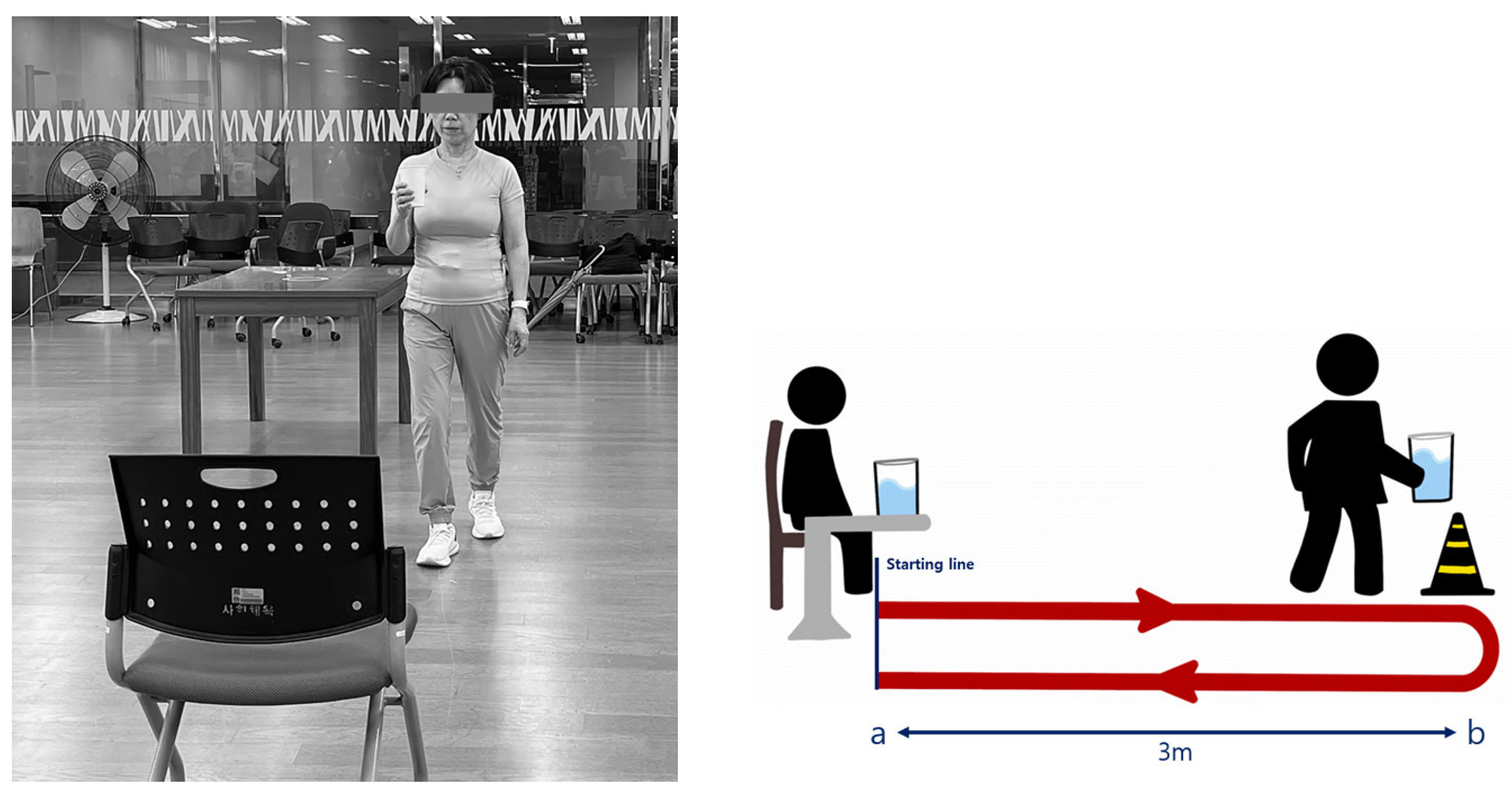
3.1. Gait Ability Outcomes
3.2. Dynamic Balance Outcome
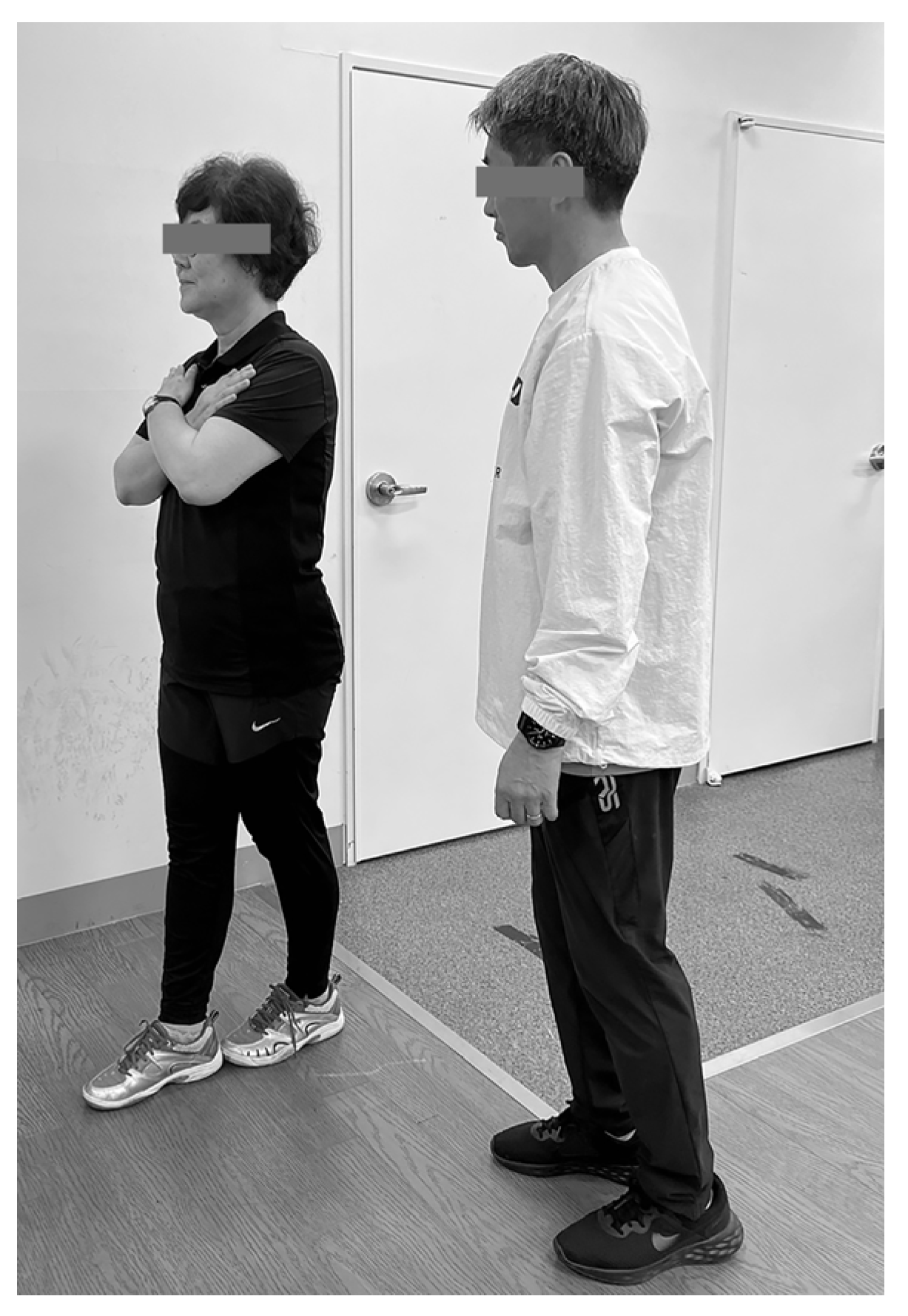
3.3. Lower Limb Reactive Ability and Static Balance Outcome
3.4. Data Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Gait Ability
4.2. Dynamic Balance
4.3. Lower Limb Reactive Ability and Static Stability
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, X.; He, R. The balance reaction ability of teenagers based on the evaluation model of unbalanced sports quotient. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 30, 5639893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamo, T.; Asahi, R.; Azami, M.; Hirofumi, O.; Tomoko, I.; Keisuke, S.; Yuusuke, N. Rate of torque development and the risk of falls among community dwelling older adults in Japan. Gait Posture 2019, 72, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubenstein, L.Z.; Josephson, K.R. Falls and their prevention in elderly people: What does the evidence show? Med. Clin. N. Am. 2006, 90, 807–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterling, D.A.; O’Connor, J.A.; Bonadies, J. Geriatric falls: Injury severity is high and disproportionate to mechanism. J. Trauma 2001, 50, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, G.C.; Low, S.L.; How, C.H. Approach to falls among the elderly in the community. Singapore Med. J. 2020, 61, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payette, H.; Roubenoff, R.; Jacpues, P.F.; Dinarellp, C.A.; Wilson, W.F.; Abad, L.W.; Harris, T. Insulin-like growth factor-1 and interleukin 6 predict sarcopenia in very old community-living men and women: The Framingham heart study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2003, 51, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barron, R.L.; Oster, G.; Grauer, A.; Crittenden, D.B.; Weycker, D. Determinants of imminent fracture risk in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Osteoporos. Int. 2020, 31, 2103–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasertsakul, T.; Kaimuk, P.; Chinjenpradit, W.; Limroongreungrat, W.; Charoensuk, W. The effect of virtual reality-based balance training on motor learning and postural control in healthy adults: A randomized preliminary study. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Długosz-Boś, M.; Filar-Mierzwa, K.; Stawarz, R.; Ścisłowska-Crarnecka, A.; Jankowicz-Szymańska, A.; Bac, A. Effect of three months pilates training on balance and fall risk in older women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, A.; Patti, A.; Bellafiore, M.; Battaglia, G.; Sahin, F.N.; Paoli, A.; Cataldo, M.C.; Mammina, C.; Palma, A. Group fitness activities for the elderly: An Innovative approach to reduce falls and injuries. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 26, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Guzmán, R.; Jiménez-Diaz, F.; Ramírez, C.; Esteban, P.; Abián-Vicén, J. Whole-body-vibration training and balance in recreational athletes with chronic ankle instability. J. Athl. Train. 2018, 53, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Amat, A.; Hita-Contreras, F.; Lomas-Vega, R.; Caballero-Martínez, I.; Alvarez, P.J.; Martínez-López, E. Effects of 12-week proprioception training program on postural stability, gait, and balance in older adults: A controlled clinical trial. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 2180–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, P.B.; Mrachacz-Kersting, N.; Oliveira, A.S.; Kersting, U.G. Effect of wobble board training on movement strategies to maintain equilibrium on unstable surfaces. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2018, 58, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picot, B.; Rémy-Neris, O.; Forestier, N. Proprioceptive postural control strategies differ among non-injured athletes. Neurosci. Lett. 2022, 769, 136366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behm, D.G.; Muehlbauer, T.; Kibele, A.; Granacher, U. Effects of strength training using unstable surfaces on strength, power and balance performance across the lifespan: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 1645–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brough, L.G.; Neptune, R.R. Individual muscle responses to mediolateral foot placement perturbations during walking. J. Biomech. 2022, 141, 111201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, S.C.; Blanchette, T.W.; Karwan, L.A.; Pearson, S.S.; O’neil, A.P.; Karlik, D.A. Core muscle activation during unstable biceps curl using a water-filled instability training tube. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 3212–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, S.C.; Albert, R.W. Compensatory muscle activation during unstable overhead squat using a water-filled training tube. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, I.B. The EMG analysis study according to weight and water bag vest during dush movement in badminton players. J. Converg. Sports Exerc. Sci. 2023, 21, 229–239. [Google Scholar]
- Wezenbeek, E.; Verhaeghe, L.; Laveyne, K.; Ravelingien, L.; Witvrouw, E.; Schuermans, J. The Effect of aquabag use on muscle activation in functional strength training. J. Sport Rehabil. 2022, 31, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccio, G.E.; Stoffregen, T.A. Affordances as constraints on the control of stance. Hum. Mov. Sci. 1988, 7, 265–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.P.; Si Tou, J.I.; Tse, M.M.; Ng, S.S. Reliability and validity of the Timed Up and Go Test with a motor task in people with chronic stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 98, 2213–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Yost, W.A. Relationship between postural stability and spatial hearing. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2013, 24, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahra, S.; Waris, M.; Ain, Q.U.; Sajjad, Y. Normative data of modified Romberg balance test for risk of fall in elderly population of Pakistan. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2023, 73, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Powden, C.J.; Dodds, T.K.; Gabriel, E.H. The reliability of the star excursion balance test and lower quarter y-balance test in healthy adults: A systematic review. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2019, 14, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonell, A.C.; Romero, J.A.; Soler, L.M. Relationship between the y balance test scores and soft tissue injury incidence in a soccer team. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2015, 10, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Asl, A.T.; Shojaedin, S.S.; Hadadnezhad, M. Comarison of effect of wobble board training with and without cognitive intervention on balance, ankle proprioception and jump landing kinetic parameters of men with chronic ankle instability: A randomized control trail. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 30, 888. [Google Scholar]
- Phirom, K.; Kamnardsiri, T.; Sungkarat, S. Beneficial effect interactive physical-cognitive game-based training on fall risk and cognitive performance of older adults. Int. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 21, 6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italo, S.; Giacomo, C.; Rosa, R.A. Instability tools and reactive motor tasks: Effects of 8 weeks training program on motor abilities in healthy women over 65 years old. J. Adv. Sports Phys. Educ. 2020, 3, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gary, L. ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription, 11th ed.; Walters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jehu, D.A.; Paquet, N.; Lajoie, Y. Balance and mobility training with or without concurrent cognitive training improves the timed up and go (TUG), TUG cognitive, and TUG manual in healthy older adults: An exploratory study. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 29, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, T.M.; Hacker, T.A.; Mollinger, L. Age-and gender-related test performance in community-dwelling elderly people: Six-minute walk test, berg balance scale, timed up & go test, and gait speeds. Phys. Ther. 2002, 82, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Podsiadlo, D.; Richardson, S. The timed ‘up & go’: A test of basic functional mobility for frail elderly persons. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1991, 39, 142–148. [Google Scholar]
- Shumway-Cook, A.; Brauer, S.; Woollacott, M. Predicting the probability for falls in community-dwelling older adults using the Timed Up & Go Test. Phys. Ther. 2000, 80, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chimera, N.J.; Warren, M. Use of clinical movement screening tests to predict injury in sport. World J. Orthop. 2016, 7, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghadir, A.H.; Iqbal, Z.A.; Iqbal, A.; Ahmed, H.; Ramteke, S.U. Effect of chronic ankle sprain on pain, range of motion, proprioception, and balance among athletes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canbaz, N.; Atılgan, E.; Tarakcı, E.; Papaker, M.G. Evaluation of balance after surgery for cerebellopontine angle tumor. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2019, 32, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffen, T.; Seney, M. Test-retest reliability and minimal detectable change on balance and ambulation tests, the 36 item short-form health survey, and the unified Parkinson disease rating scale in people with parkinsonism. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maden, T.K.; Bayramlar, K.Y.; Yakut, Y. The effect of cervical mobilization on balance and static plantar loading distribution in patients with multiple sclerosis: A randomized crossover study. Neurosciences 2022, 27, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas, C.H.M.; Carneiro, J.A.O.; Nobre, T.T.X.; Schettino, L.; Matos de Araujo, C.; Araújo dos Reis, L.; Fernandes, M.H. Analysis of plantar tactile sensitivity in older women after conventional proprioceptive training and exergame. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziechciaž, M.; Filip, R. Biological psychological and social determinants of old age: Bio-phycho-social aspects of human aging. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2014, 21, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, B.C.; Manini, T.M.; Wages, N.P.; Simon, J.E.; Clark, L.A. Voluntary vs electrically stimulated activation in age-related muscle weakness. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e1912052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almajid, R.; Tucker, C.; Wright, W.G.; Vasudevan, E.; Keshner, E. Visual dependence affects the motor behavior of older adults during the Timed Up and Go (TUG) test. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2020, 87, 104004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, J.; Burnfield, J.M. Gait Analysis: Normal and Pathological Function, 2nd ed.; Slack Incorporated: West Deptford, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Callisaya, M.L.; Blizzard, L.; Schmidt, M.D.; McGinley, J.L.; Srikanth, V.K. Sex modifies the relationship between age and gait: A population-based study of older adults. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2008, 63, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadjapong, U.; Yodkeeree, S.; Sungkarat, S.; Siviroj, P. Multicomponent exercise program reduces frailty and inflammatory biomarkers and Improves physical performance in community-dwelling older adults: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 7, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahedian-Nasab, N.; Jaberi, A.; Shirazi, F.; Kavousipor, S. Effect of virtual reality exercises on balance and fall in elderly people with fall risk: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junker, D.; Stöggle, T. The training effect of foam rolling on core strength endurance, balance, muscle performance and range of motion: A randomized controlled trial. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2019, 18, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.R.; Robertson, K.E.; Burnham, J.M.; Yonz, M.C.; Ireland, M.L.; Noehren, B. The relationship between hip strength and the Y balance test. J. Sport Rehabil. 2018, 27, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.K.; Kim, G.M.; Ha, S.M.; Oh, J.S. Correlation of the Y-Balance Test with Lower-limb Strength of Adult Women. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2014, 26, 641–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calatayud, J.; Colado, J.C.; Martin, F.; Casaña, J.; Jakobsen, M.D.; Andersen, L.L. Core muscle activity during the clean and jerk lift with barbell versus sandbags and water bags. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2015, 10, 803–810. [Google Scholar]
- Bahannon, R.W. Hand-grip dynamometry predicts future outcones in aging adults. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2008, 31, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.L.; Tan, K.C.B.; Bow, C.H.; Soong, C.S.S.; Loong, C.H.N.; Kung, A.W.C. Low handgrip strength is a predictor of osteoporotic fractures: Cross-sectional and prospective evidence from the Hong Kong osteoporosis study. Age 2012, 34, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shumway-Cook, A.; Horak, F.B. Assessing the influence of sensory interaction of balance. Suggestion from the field. Phys Ther. 1986, 66, 1548–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciniak, K.; Maciaszek, J.; Cyma-Wejchenig, M.; Szeklicki, R.; Stemplewski, R. The Effect of Nordic walking training with poles with an integrated resistance shock absorber on the body balance of women over the age of 60. Healthcare 2021, 9, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, W.R.; Alessio, H.M.; Mills, E.M.; Chen, T. Circumstances and consequences of falls in independent community-dwelling older adults. Age Ageing 1997, 26, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieterich, M.; Brandt, T. Perception of verticality and vestibular disorders of balance and falls. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Song, H.; Schmidt, C.; Chang, W.P.; Chien, J.H. The effect of mechanical vibration-based stimulation on dynamic balance control and gait characteristics in healthy young and older adults: A systematic review of cross-sectional study. Gait Posture 2023, 102, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbson, J.J. The Ecological Approach to Visual Perception; Houghton-Mifflin: Boston, MA, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Cardinale, M.; Bosco, C. The use of vibration as an exercise intervention. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2003, 31, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.; García-López, D.; González-Gallego, J.; Garatachea, N. Whole-body vibration training increases muscle strength and mass in older women: A randomized-controlled trial. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Stengel, S.; Kemmler, W.; Engelke, K.; Kalender, W.A. Effects of whole-body vibration on bone mineral density and falls: Results of the randomized contorrled ELVIS study with postmenopausal women. Osteoporos. Int. 2011, 22, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nairn, B.C.; Sutherland, C.A.; Drake, J.D.M. Motion and muscle activity are affected by instability location during a squat exercise. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Age (Year) | Height (cm) | Weight (kg) | BMI (kg/m2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WG (n = 11) | 74.91 ± 6.33 | 155.91 ± 6.35 | 55.13 ± 7.50 | 22.73 ± 3.37 |
| CG (n = 11) | 74.27 ± 7.92 | 152.49 ± 4.06 | 50.55 ± 7.72 | 24.37 ± 3.75 |
| Exercise | Program | Time |
|---|---|---|
| Warm-up | Dynamic stretching | 10 min |
| 1. Hip joint mobility with waterbag 1 | ||
| 2. Hip joint mobility with waterbag 2 | ||
| 3. Shoulder mobility and stability with waterbag | ||
| 4. Waterbag standing (hip hinge) 1 | ||
| Main | 5. Free walking while carrying waterbag | 40 min |
| 6. Waterbag standing 2 | ||
| 7. Waterbag squat (chair) | ||
| 8. Waterbag single leg over press | ||
| 9. Waterbag standing (hip hinge) 2 | ||
| 10. Waterbag single-leg hinge to standing | ||
| Cool-down | Static stretching and free walking | 10 min |
| Variables | Waterbag Group (n = 11) | Control Group (n = 11) | Group × Time # | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | 12 Weeks | ICC (2.1) | Pre | 12 Weeks | ICC (2.1) | F | p-Value | ηp2 | |
| MTUG | 13.69 ± 3.09 | 9.88 ± 2.03 a,b | 0.118 *** | 12.58 ± 2.13 | 11.98 ± 2.34 | 0.921 *** | 23.815 | 0.000 | 0.544 |
| SRT (EO) | 28.45 ± 2.69 | 29.54 ± 1.50 | 0.894 *** | 28.29 ± 2.64 | 28.63 ± 2.33 | 0.948 *** | 0.487 | 0.493 | 0.024 |
| SRT (EC) | 12.00 ± 7.25 | 16.81 ± 6.11 a,b | 0.57 | 12.60 ± 6.01 | 11.17 ± 5.61 | 0.873 *** | 43.114 | 0.000 | 0.683 |
| YBT (right) | 82.02 ± 6.19 | 92.13 ± 8.99 a,b | 0.642 *** | 81.25 ± 10.49 | 83.22 ± 10.52 | 0.961 *** | 24.627 | 0.000 | 0.552 |
| YBT (left) | 78.57 ± 8.95 | 89.65 ± 11.18 a,b | 0.742 *** | 79.04 ± 9.56 | 80.20 ± 9.98 | 0.982 *** | 57.964 | 0.000 | 0.743 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, S.; Park, I. Effects of Instability Neuromuscular Training Using an Inertial Load of Water on the Balance Ability of Healthy Older Women: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2024, 9, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk9010050
Kang S, Park I. Effects of Instability Neuromuscular Training Using an Inertial Load of Water on the Balance Ability of Healthy Older Women: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2024; 9(1):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk9010050
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Shuho, and Ilbong Park. 2024. "Effects of Instability Neuromuscular Training Using an Inertial Load of Water on the Balance Ability of Healthy Older Women: A Randomized Clinical Trial" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 9, no. 1: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk9010050
APA StyleKang, S., & Park, I. (2024). Effects of Instability Neuromuscular Training Using an Inertial Load of Water on the Balance Ability of Healthy Older Women: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 9(1), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk9010050






