The Complexity of Skeletal Transverse Dimension: From Diagnosis, Management, and Treatment Strategies to the Application of Collaborative Cross (CC) Mouse Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Transverse Deficiency and Working/Nonworking Interferences
1.2. Transverse Deficiency and the Periodontium
2. Materials and Methods
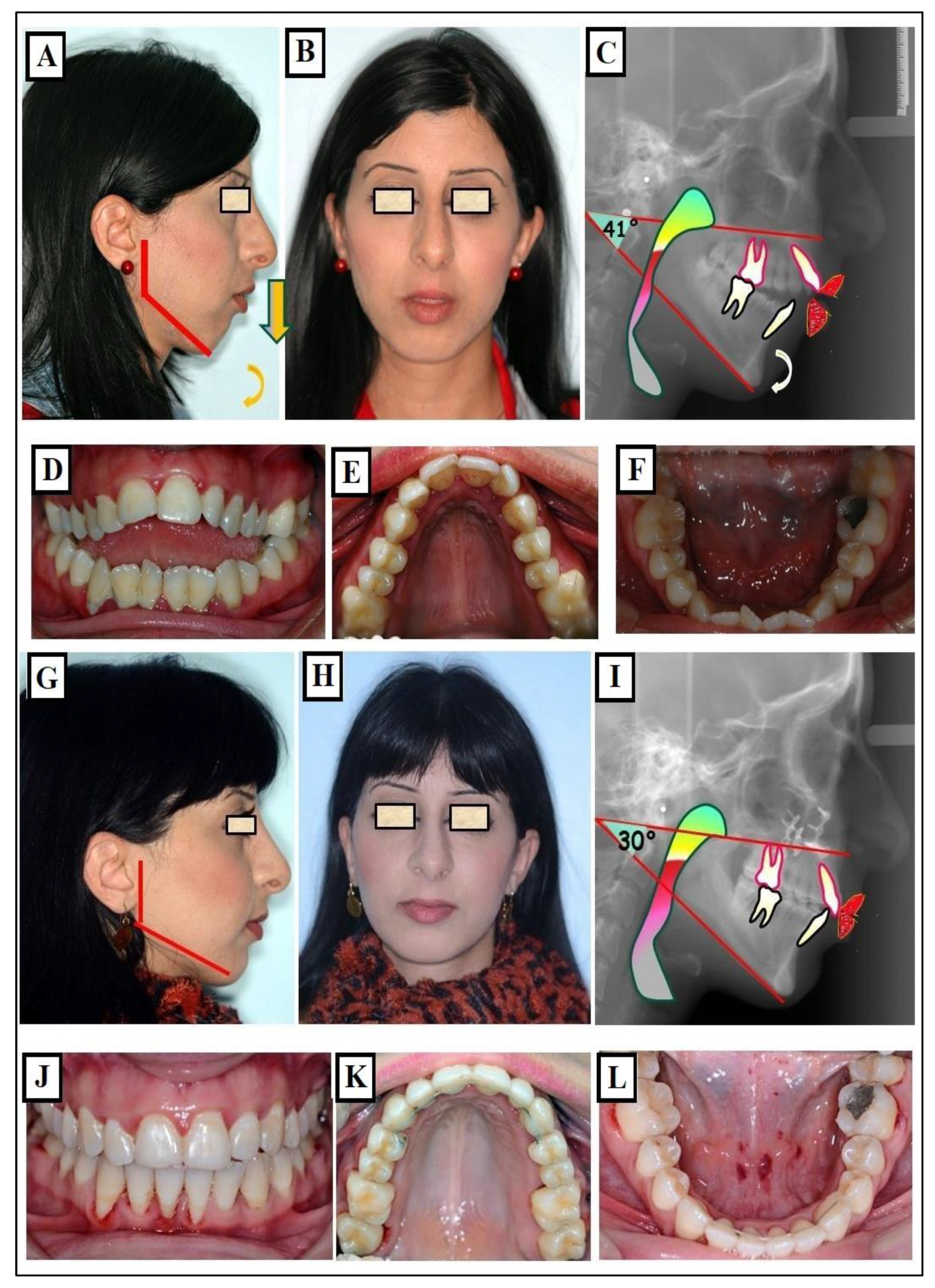
2.1. Diagnosis
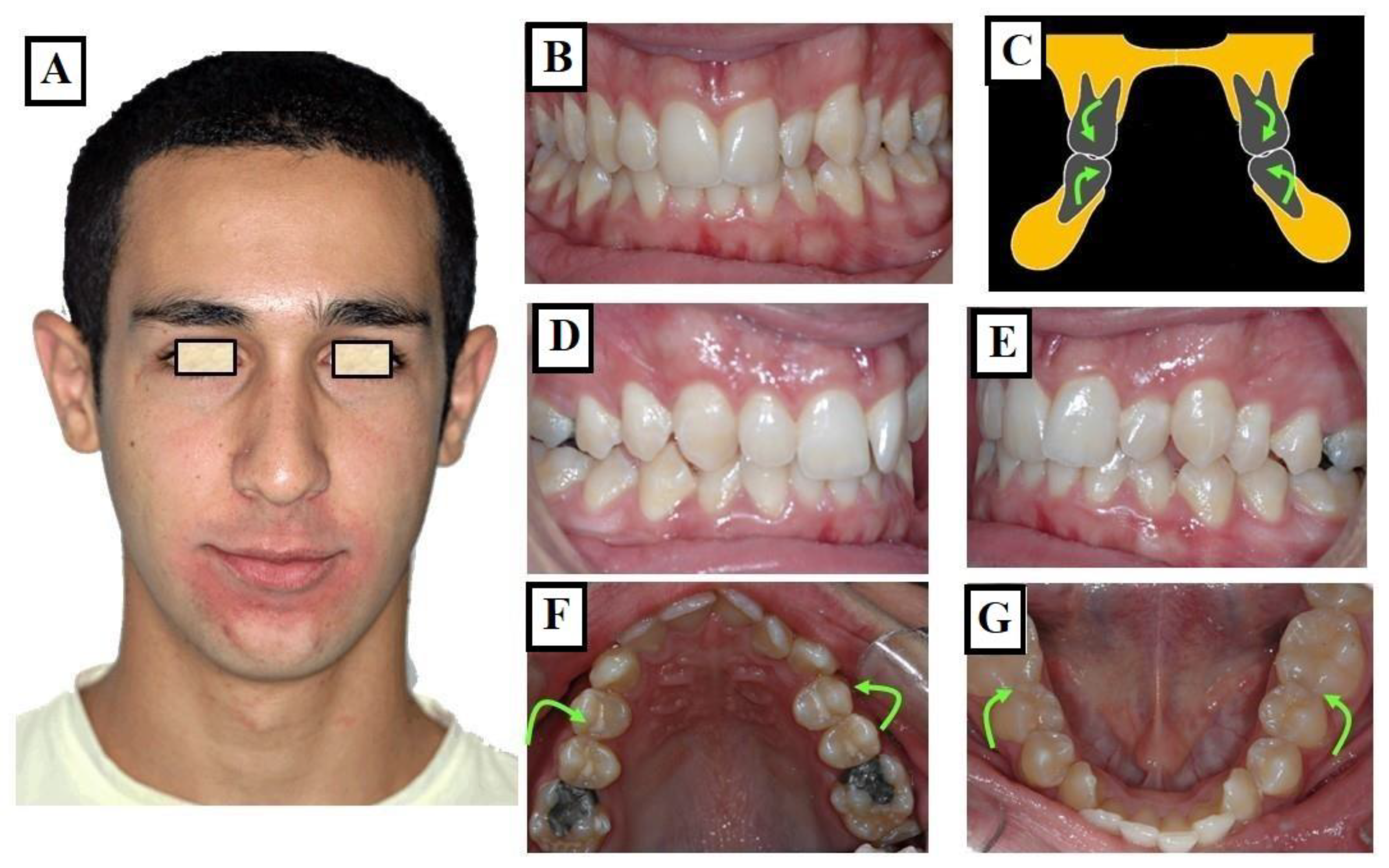
2.2. Narrow Upper and Lower Jaw
2.3. Dental Expansion
2.4. Transverse Deficiency and the Airway
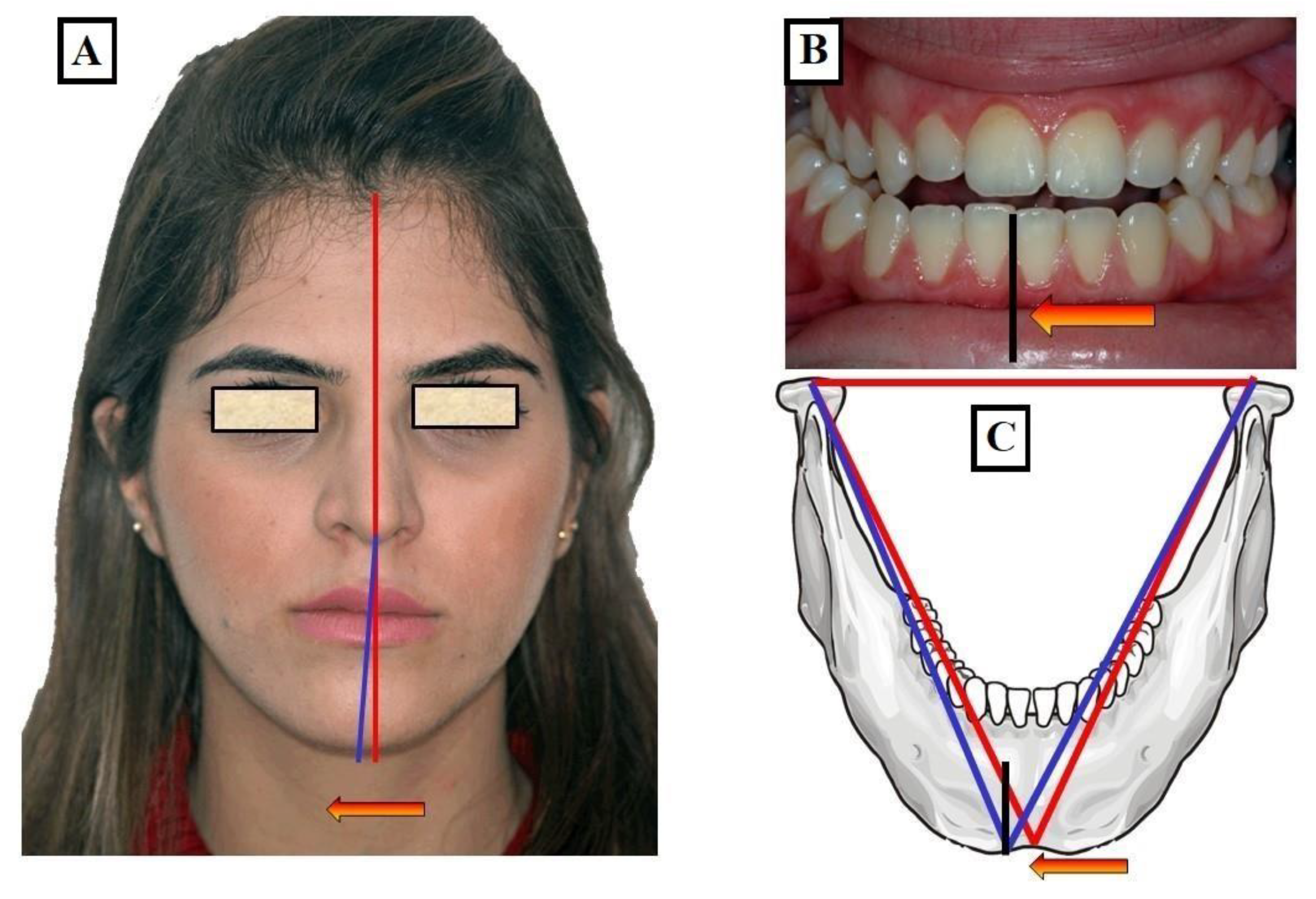
2.5. Methods of Transverse Diagnosis
3. Results
3.1. The Causes of the Discrepancy in Jaw Widths Can Be
3.1.1. Functional
3.1.2. Dentoalveolar
3.1.3. Skeletal
3.1.4. Combination
3.2. Expanding the Narrow Maxilla
3.2.1. Passive Expansion
3.2.2. Orthodontic Expansion
3.2.3. Orthopedic Expansion
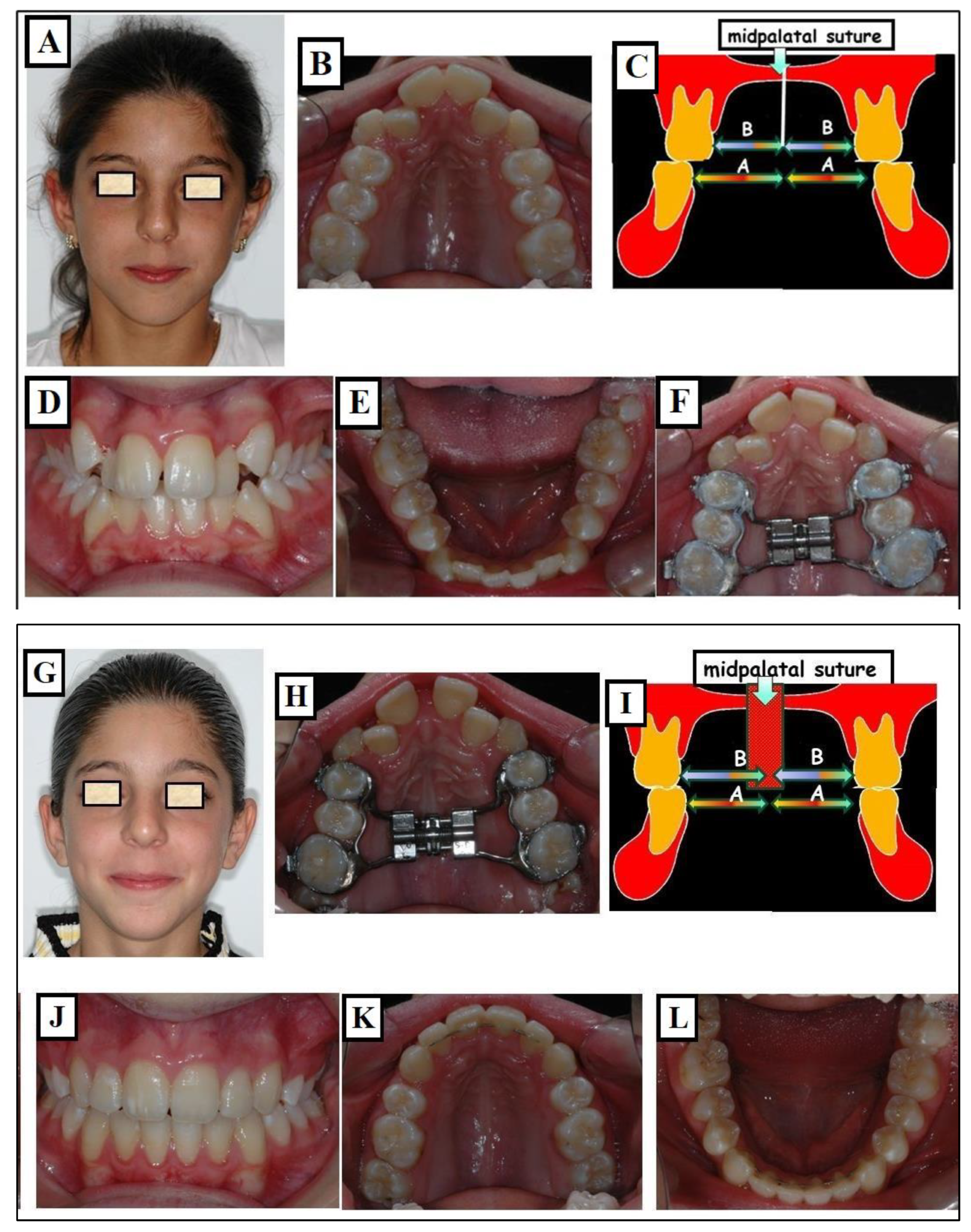
Conventional Rapid Maxillary Expansion (RME or RPE)
Micro-Implant-Assisted Rapid Palatal Expander (MARPE)
Surgically Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion (SARPE)
Absolute Surgically Palatal Expansion (ASPE)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrews, L.F. The six keys to normal occlusion. Am. J. Orthod. 1972, 62, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamburrino, R.K.; Boucher, N.S.; Vanarsdall, R.L.; Secchi, A. The transverse dimension: Diagnosis and relevance to functional occlusion. RWISO J. 2010, 2, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ricketts, R.M. Introducing Computerized Cephalometrics, 1st ed.; Rocky Mountain Data Systems: Denver, CO, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, C.C. The use of cephalometrics as an aid to planning and assessing orthodontic treatment. Am. J. Orthod. 1960, 46, 721–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, W.B. Analysis of the dentofacial profile. Angle Orthod. 1956, 26, 191–212. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, L.F. Syllabus of the Andrews Orthodontic Philosophy, 9th ed.; Lawrence F. Andrews: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- McNamara, J.A.; Brudon, W.L.; Kokich, V.G. Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics, 2nd ed.; Needham Press: Needham, MA, USA, 2001; ISBN 9780963502230. [Google Scholar]
- Vanarsdall, R.L. Transverse dimension and long-term stability. Semin. Orthod. 1999, 5, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordray, F.E. Three-dimensional analysis of models articulated in the seated condylar position from a deprogrammed asymptomatic population: A prospective study. Part 1. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2006, 129, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utt, T.W.; Meyers, C.E.; Wierzba, T.F.; Hondrum, S.O. A three-dimensional comparison of condylar position changes between centric relation and centric occlusion using the mandibular position indicator. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1995, 107, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, S.D. Condylar axis position, as determined by the occlusion and measured by the CPI instrument, and signs and symptoms of temporomandibular dysfunction. Angle Orthod. 1999, 69, 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Tamburrino, R.; Secchi, A.; Katz, S.; Pinto, A. Assessment of the three-dimensional condylar and dental positional relationships in CR-to-MIC Shifts. Rev. Mex. Ortod. 2014, 2, e224–e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McNamara, J.A., Jr.; McClatchey, L.M.; Graber, L.W. Part B: Treatment Timing and Mixed Dentition Therapy. In Orthodontics: Current Principles and Techniques; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bin Dakhil, N.; Bin Salamah, F. The diagnosis methods and management modalities of maxillary transverse discrepancy. Cureus 2021, 13, e20482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, P.M.; Vanarsdall, R.L., Jr.; Levrini, M.; Read, R. An evaluation of anterior temporal and masseter muscle activity in appliance therapy. Angle Orthod. 1999, 69, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, E.H.; Lundquist, D.O. Anterior guidance: Its effect on electromyographic activity of the temporal and masseter muscles. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1983, 49, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manns, A.; Chan, C.; Miralles, R. Influence of group function and canine guidance on electromyographic activity of elevator muscles. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1987, 57, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okano, N.; Baba, K.; Igarashi, Y. Influence of altered occlusal guidance on masticatory muscle activity during clenching. J. Oral Rehabil. 2007, 34, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, J.A. Maxillary transverse deficiency. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2000, 117, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarver, D.M.; Proffit, W.R. Special Considerations in Diagnosis and Treatment Planning, 5th ed.; Elsevier Mosby: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Harrel, S.K. Occlusal forces as a risk factor for periodontal disease. Periodontol. 2000 2003, 32, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, S. Occlusal considerations in periodontics. In A Guide to Good Occlusal Practice; BDJ Clinician’s Guides; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 165–189. ISBN 978-3-030-79224-4. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanan, R. Comparative Analysis of Occlusal Force Distribution Using T-Scan in Chronic Periodontitis Patients before and after Periodontal Therapy. Scholast. Med. Sci. 2023, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ricketts, R.M. Forum on the tonsile and adenoid problem in orthodontics-Respiratory obstruction syndrome. Am. J. Orthod. 1968, 54, 494–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comyn, F.; Gislason, T.; Pack, A.; Maislin, G.; Arnardottir, E.; Benediktsdottir, B.; Juliusson, S.; Einarsdottir, H.; Schwab, R. MRI comparison of craniofacial structures in sleep apneic patients. In B66. The Upper Airway: Control of Function and Pathophysiology; American Thoracic Society: New York, NY, USA, 2009; p. A3596. [Google Scholar]
- Rakosi, T.; Jonas, I.; Graber, T.M. Color atlas of dental medicine, Orthodontic-Diagnosis. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1994, 105, 613. [Google Scholar]
- Redmond, W.R. Digital models: A new diagnostic tool. J. Clin. Orthod. JCO 2001, 35, 386–387. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, S.D.; Southard, K.A.; Southard, T.E. Early Transverse Treatment. Semin. Orthod. 2005, 11, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, A.J. Rapid expansion of the maxillary dental arch and nasal cavity by opening the midpalatal suture. Angle Orthod. 1961, 31, 73–90. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, S.; Dawson, D.; Southard, K.A.; Lee, A.N.; Casko, J.S.; Southard, T.E. Transverse molar movements during growth. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2003, 124, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilander, B.; Lennartsson, B. A study of children with unilateral posterior crossbite, treated and untreated, in the deciduous dentition--occlusal and skeletal characteristics of significance in predicting the long-term outcome. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2002, 63, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, J.D.; Bell, W.H.; Williams, C.E.; Kennedy, J.W. Control of the transverse dimension with surgery and orthodontics. Am. J. Orthod. 1980, 77, 284–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, N.J.; Vanarsdall, R.L.; Barber, H.D. Diagnosis and treatment of transverse maxillary deficiency. Int. J. Adult Orthod. Orthognath. Surg. 1995, 10, 75–96. [Google Scholar]
- Betts, N.J. Surgically assisted maxillary expansion. Atlas Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. 2016, 24, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricketts, R.M. Perspectives in the clinical application of cephalometrics: The first fifty years. Angle Orthod. 1981, 51, 115–150. [Google Scholar]
- Suri, L.; Taneja, P. Surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion: A literature review. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2008, 133, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchi, A.; Carrafiello, G.; Cacciafesta, V.; Norcini, A. Three-dimensional digital modeling and setup. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2006, 129, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawchuk, D.; Currie, K.; Vich, M.L.; Palomo, J.M.; Flores-Mir, C. Diagnostic methods for assessing maxillary skeletal and dental transverse deficiencies: A systematic review. Korean J. Orthod. 2016, 46, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, K.F.; Boucher, N.; Chung, C.-H. Effects of bonded rapid palatal expansion on the transverse dimensions of the maxilla: A cone-beam computed tomography study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2010, 137, S79–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiliç, N.; Oktay, H. Effects of rapid maxillary expansion on nasal breathing and some nasorespiratory and breathing problems in growing children: A literature review. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2008, 72, 1595–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira De Felippe, N.L.; Da Silveira, A.C.; Viana, G.; Kusnoto, B.; Smith, B.; Evans, C.A. Relationship between rapid maxillary expansion and nasal cavity size and airway resistance: Short- and long-term effects. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2008, 134, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyneke, J.P.; Conley, R.S. Surgical/orthodontic correction of transverse maxillary discrepancies. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 32, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, P.E. New definition for relating occlusion to varying conditions of the temporomandibular joint. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1995, 74, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guichet, N.F. Biologic laws governing functions of muscles that move the mandible. Part I. Occlusal programming. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1977, 37, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, A.J. Palatal expansion: Just the beginning of dentofacial orthopedics. Am. J. Orthod. 1970, 57, 219–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, J.A., Jr.; Riolo, M.L.; Enlow, D.H. Growth of the maxillary complex in the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta) This study was supported in part by United States Public Health Service Grants HD-02272 and DE-03610. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1976, 44, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baccetti, T.; Franchi, L.; Cameron, C.G.; McNamara, J.A. Treatment timing for rapid maxillary expansion. Angle Orthod. 2001, 71, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Angelieri, F.; Franchi, L.; Cevidanes, L.H.S.; Gonçalves, J.R.; Nieri, M.; Wolford, L.M.; McNamara, J.A. Cone beam computed tomography evaluation of midpalatal suture maturation in adults. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, A.J. The treatment of maxillary deficiency by opening the midpalatal suture. Angle Orthod. 1965, 35, 200–217. [Google Scholar]
- Proffit, W.R.; Fields, H.W.; Larson, B.; Sarver, D.M. Contemporary Orthodontics, 6th ed.; Elsevier Mosby: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Proffit, W.R.; Turvey, T.A.; Phillips, C. The hierarchy of stability and predictability in orthognathic surgery with rigid fixation: An update and extension. Head Face Med. 2007, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, Í.; Oktay, H.; Demirci, M. The effect of rapid maxillary expansion on conductive hearing loss. Angle Orthod. 1996, 66, 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, R.A. A review of maxillary expansion in relation to rate of expansion and patient’s age. Am. J. Orthod. 1982, 81, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Mathur, R. Maxillary Expansion. Int. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2010, 3, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleall, J.F.; Bayne, D.I.; Posen, J.M.; Subtelny, J.D. Expansion of the midpalatal suture in the monkey. Angle Orthod. 1965, 35, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Storey, E. Tissue response to the movement of bones. Am. J. Orthod. 1973, 64, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, E.P. Slow maxillary expansion: A clinical study of the skeletal versus dental response to low-magnitude force. Am. J. Orthod. 1978, 73, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacson, R.J.; Ingram, A.H. Forces produced by rapid maxillary expansion: II. Forces present during treatment. Angle Orthod. 1964, 34, 261–270. [Google Scholar]
- Brunetto, D.P.; Sant’Anna, E.F.; Machado, A.W.; Moon, W. Non-surgical treatment of transverse deficiency in adults using Microimplant-assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion (MARPE). Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2017, 22, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, T.; Zhao, B.; Wang, C.; Xiao, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhao, G.; Ke, J. Efficacy of different designs of mandibular expanders: A 3-dimensional finite element study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2020, 157, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lines, P.A. Adult rapid maxillary expansion with corticotomy. Am. J. Orthod. 1975, 67, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, L.J.; White, R.P.; Proffit, W.R.; Turvey, T.A. Segmental LeFort I osteotomy for management of transverse maxillary deficiency. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1997, 55, 728–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehman, J.A.; Haas, A.J.; Haas, D.G. Surgical orthodontic correction of transverse maxillary deficiency: A simplified approach. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1984, 73, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraut, R.A. Surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion by opening the midpalatal suture. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1984, 42, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, J.W.; Bell, W.H.; Kimbrough, O.L.; James, W.B. Osteotomy as an adjunct to rapid maxillary expansion. Am. J. Orthod. 1976, 70, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bays, R.A.; Greco, J.M. Surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion: An outpatient technique with long-term stability. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1992, 50, 110–113; discussion 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koudstaal, M.J.; Poort, L.J.; van der Wal, K.G.H.; Wolvius, E.B.; Prahl-Andersen, B.; Schulten, A.J.M. Surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion (SARME): A review of the literature. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2005, 34, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossaz, C.F.; Byloff, F.K.; Richter, M. Unilateral and bilateral corticotomies for correction of maxillary transverse discrepancies. Eur. J. Orthod. 1992, 14, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northway, W.M.; Meade, J.B. Surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion: A comparison of technique, response, and stability. Angle Orthod. 1997, 67, 309–320. [Google Scholar]
- Glassman, A.S.; Nahigian, S.J.; Medway, J.M.; Aronowitz, H.I. Conservative surgical orthodontic adult rapid palatal expansion: Sixteen cases. Am. J. Orthod. 1984, 86, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.-H.; Woo, A.; Zagarinsky, J.; Vanarsdall, R.L.; Fonseca, R.J. Maxillary sagittal and vertical displacement induced by surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2001, 120, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mommaerts, M.Y. Transpalatal distraction as a method of maxillary expansion. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1999, 37, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.L.; Pangrazio-Kulbersh, V.; Borgula, T.; Kaczynski, R. Stability of orthopedic and surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion over time. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1998, 114, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyt, N.M.F.; Mommaerts, M.Y.; Abeloos, J.V.S.; De Clercq, C.A.S.; Neyt, L.F. Problems, obstacles and complications with transpalatal distraction in non-congenital deformities. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2002, 30, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishara, S.E.; Staley, R.N. Maxillary expansion: Clinical implications. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1987, 91, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mew, J. Long-term effect of rapid maxillary expansion. Eur. J. Orthod. 1993, 15, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velázquez, P.; Benito, E.; Bravo, L.A. Rapid maxillary expansion. A study of the longterm effects. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1996, 109, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogrel, M.A.; Kaban, L.B.; Vargervik, K.; Baumrind, S. Surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion in adults. Int. J. Adult Orthod. Orthognath. Surg. 1992, 7, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zahl, C.; Gerlach, K. Palatinaldistraktor. Mund Kiefer Gesichtschir. 2002, 6, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proffit, W.R.; Turvey, T.A.; Phillips, C. Orthognathic surgery: A hierarchy of stability. Int. J. Adult Orthod. Orthognath. Surg. 1996, 11, 191–204. [Google Scholar]
- Woods, M.; Wiesenfeld, D.; Probert, T. Surgically-assisted maxillary expansion. Aust. Dent. J. 1997, 42, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Thomas, N.; Hatch, N.E.; Hu, M.; Liu, F. Postnatal craniofacial skeletal development of female c57bl/6ncrl mice. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Toamih-Atamni, H.J.; Lone, I.M.; Binenbaum, I.; Mott, R.; Pilalis, E.; Chatziioannou, A.; Iraqi, F.A. Mapping novel QTL and fine mapping of previously identified QTL associated with glucose tolerance using the collaborative cross mice. Mamm. Genome 2023, 35, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.J.; Ackert-Bicknell, C.L. Genetic regulation of bone strength: A review of animal model studies. Bonekey Rep. 2015, 4, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuyinu, E.L.; Narayanan, G.; Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Animal models of osteoarthritis: Classification, update, and measurement of outcomes. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2016, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, I.M.; Midlej, K.; Nun, N.B.; Iraqi, F.A. Intestinal cancer development in response to oral infection with high-fat diet-induced Type 2 diabetes (T2D) in collaborative cross mice under different host genetic background effects. Mamm. Genome 2023, 34, 56–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lone, I.M.; Iraqi, F.A. Genetics of murine type 2 diabetes and comorbidities. Mamm. Genome 2022, 33, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durrant, C.; Tayem, H.; Yalcin, B.; Cleak, J.; Goodstadt, L.; de Villena, F.P.-M.; Mott, R.; Iraqi, F.A. Collaborative Cross mice and their power to map host susceptibility to Aspergillus fumigatus infection. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lone, I.M.; Nun, N.B.; Ghnaim, A.; Schaefer, A.S.; Houri-Haddad, Y.; Iraqi, F.A. Highfat diet and oral infection induced type 2 diabetes and obesity development under different genetic backgrounds. Anim. Models Exp. Med. 2023, 6, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, I.M.; Zohud, O.; Nashef, A.; Kirschneck, C.; Proff, P.; Watted, N.; Iraqi, F.A. Dissecting the Complexity of Skeletal-Malocclusion-Associated Phenotypes: Mouse for the Rescue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehia, R.; Lone, I.M.; Yehia, I.; Iraqi, F.A. Studying the Pharmagenomic effect of Portulaca oleracea extract on anti-diabetic therapy using the Collaborative Cross mice. Phytomed. Plus 2023, 3, 100394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohud, O.; Lone, I.M.; Midlej, K.; Obaida, A.; Masarwa, S.; Schröder, A.; Küchler, E.C.; Nashef, A.; Kassem, F.; Reiser, V.; et al. Towards genetic dissection of skeletal class III malocclusion: A review of genetic variations underlying the phenotype in humans and future directions. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lone, I.M.; Zohud, O.; Midlej, K.; Awadi, O.; Masarwa, S.; Krohn, S.; Kirschneck, C.; Proff, P.; Watted, N.; Iraqi, F.A. Narrating the Genetic Landscape of Human Class I Occlusion: A Perspective-Infused Review. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watted, N.; Lone, I.M.; Zohud, O.; Midlej, K.; Proff, P.; Iraqi, F.A. Comprehensive Deciphering the Complexity of the Deep Bite: Insight from Animal Model to Human Subjects. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lone, I.M.; Zohud, O.; Midlej, K.; Proff, P.; Watted, N.; Iraqi, F.A. Skeletal Class II Malocclusion: From Clinical Treatment Strategies to the Roadmap in Identifying the Genetic Bases of Development in Humans with the Support of the Collaborative Cross Mouse Population. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghnaim, A.; Lone, I.M.; Nun, N.B.; Iraqi, F.A. Unraveling the host genetic background effect on internal organ weight influenced by obesity and diabetes using collaborative cross mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



















Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Watted, N.; Lone, I.M.; Midlej, K.; Zohud, O.; Awadi, O.; Masarwa, S.; Watted, A.; Paddenberg, E.; Krohn, S.; Kirschneck, C.; et al. The Complexity of Skeletal Transverse Dimension: From Diagnosis, Management, and Treatment Strategies to the Application of Collaborative Cross (CC) Mouse Model. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2024, 9, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk9010051
Watted N, Lone IM, Midlej K, Zohud O, Awadi O, Masarwa S, Watted A, Paddenberg E, Krohn S, Kirschneck C, et al. The Complexity of Skeletal Transverse Dimension: From Diagnosis, Management, and Treatment Strategies to the Application of Collaborative Cross (CC) Mouse Model. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2024; 9(1):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk9010051
Chicago/Turabian StyleWatted, Nezar, Iqbal M. Lone, Kareem Midlej, Osayd Zohud, Obaida Awadi, Samir Masarwa, Ali Watted, Eva Paddenberg, Sebastian Krohn, Christian Kirschneck, and et al. 2024. "The Complexity of Skeletal Transverse Dimension: From Diagnosis, Management, and Treatment Strategies to the Application of Collaborative Cross (CC) Mouse Model" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 9, no. 1: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk9010051
APA StyleWatted, N., Lone, I. M., Midlej, K., Zohud, O., Awadi, O., Masarwa, S., Watted, A., Paddenberg, E., Krohn, S., Kirschneck, C., Proff, P., & Iraqi, F. A. (2024). The Complexity of Skeletal Transverse Dimension: From Diagnosis, Management, and Treatment Strategies to the Application of Collaborative Cross (CC) Mouse Model. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 9(1), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk9010051








