Effects of Different Durations at Fixed Intensity Exercise on Internal Load and Recovery—A Feasibility Pilot Study on Duration as an Independent Variable for Exercise Prescription
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subject Characteristics
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurements and Analysis
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Peak Values during CLE
3.2. Loss of Performance during CLE
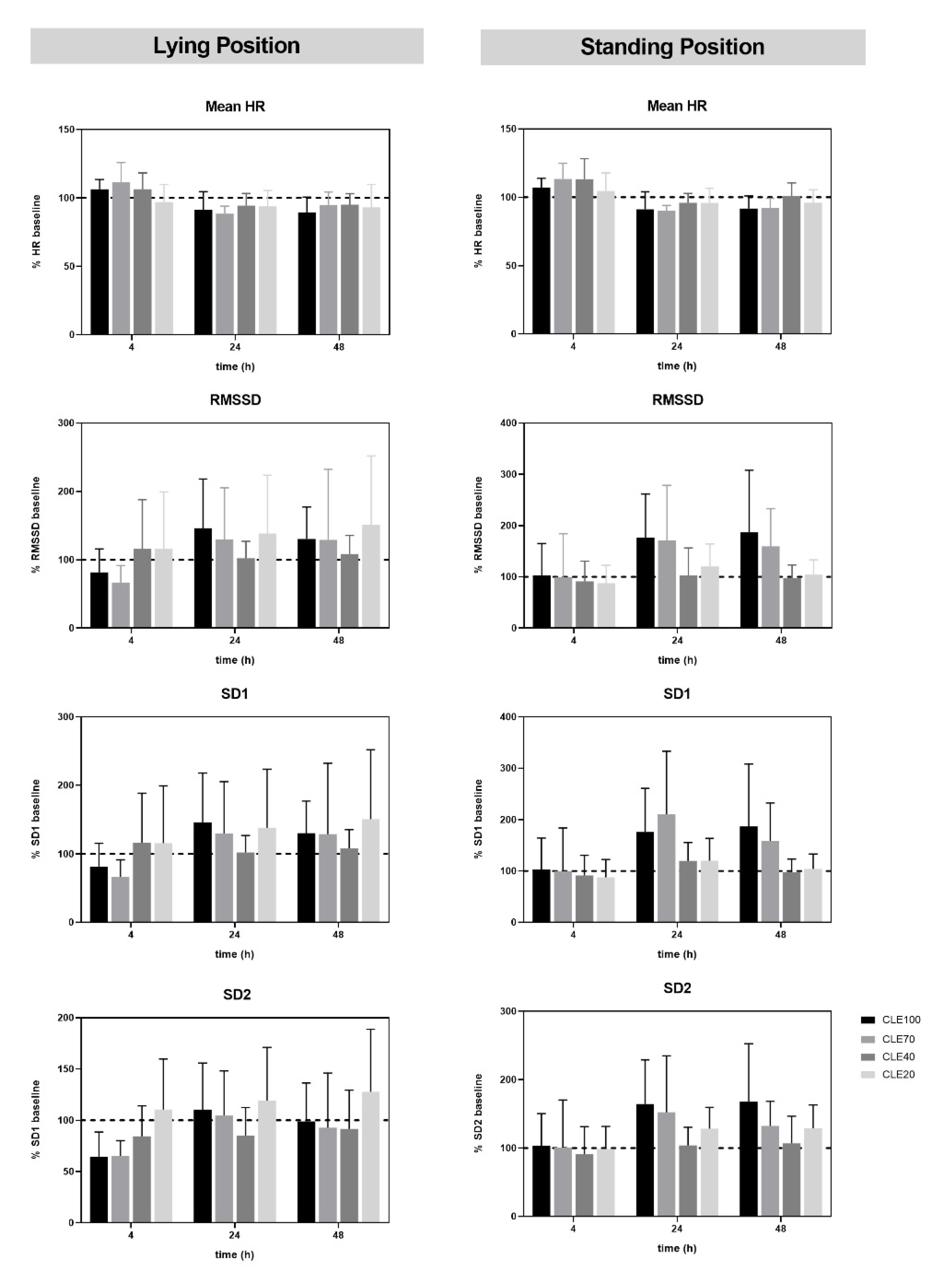
3.3. Recovery after CLE Compared to Baseline Values
3.4. HRV in Orthostatic Tests
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iannetta, D.; Inglis, E.C.; Mattu, A.T.; Fontana, F.Y.; Pogliaghi, S.; Keir, D.A.; Murias, J.M. A Critical Evaluation of Current Methods for Exercise Prescription in Women and Men. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 52, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnet, K.; Kelsch, E.; Zieff, G.; Moore, J.B.; Stoner, L. How Fitting Is FITT? A Perspective on a Transition from the Sole Use of Frequency, Intensity, Time, and Type in Exercise Prescription. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 199, 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamnick, N.A.; Pettitt, R.W.; Granata, C.; Pyne, D.B.; Bishop, D.J. An Examination and Critique of Current Methods to Determine Exercise Intensity. Sports Med. 2020, 50, 1729–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, H.A.; Bell, G.J. The Interactions of Intensity, Frequency and Duration of Exercise Training in Altering Cardiorespiratory Fitness. Sports Med. 1986, 3, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, P.; Tschakert, G. Special Needs to Prescribe Exercise Intensity for Scientific Studies. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2010, 2011, 209302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hofmann, P.; Tschakert, G. Intensity- and Duration-Based Options to Regulate Endurance Training. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tremblay, M.S.; Copeland, J.L.; Van Helder, W. Influence of Exercise Duration on Post-Exercise Steroid Hormone Responses in Trained Males. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 94, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschakert, G.; Handl, T.; Weiner, L.; Birnbaumer, P.; Mueller, A.; Groeschl, W.; Hofmann, P. Exercise Duration: Independent Effects on Acute Physiologic Responses and the Need for an Individualized Prescription. Physiol. Rep. 2022, 10, e15168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesisoglou, A.; Nicolo, A.; Passfield, L. Cycling Performance and Training Load: Effects of Intensity and Duration. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2021, 16, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, R.K.; Wonisch, M.; Corra, U.; Cohen-Solal, A.; Vanhees, L.; Saner, H.; Schmid, J.-P. Methodological Approach to the First and Second Lactate Threshold in Incremental Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil. 2008, 15, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzani, A.; Hamm, L.F.; Jones, A.M.; McBride, P.E.; Moholdt, T.; Stone, J.A.; Urhausen, A.; Williams, M.A. Aerobic Exercise Intensity Assessment and Prescription in Cardiac Rehabilitation: A Joint Position Statement of the European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention and Rehabilitation, the American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation and the Canadian Association of Cardiac Rehabilitation. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2013, 20, 442–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezzani, A.; Corrà, U.; Giordano, A.; Colombo, A.; Psaroudaki, M.; Giannuzzi, P. Upper Intensity Limit for Prolonged Aerobic Exercise in Chronic Heart Failure. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platonov, V.N. Belastung—Ermüdung—Leistung; Philippka-Sportverlag: Münster, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, G.A.; Fahey, T.D.; Baldwin, K.M. Exercise Physiology: Human Bioenergetics and Its Applications, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bahr, R.; Ingnes, I.; Vaage, O.; Sejersted, O.M.; Newsholme, E.A. Effect of Duration of Exercise on Excess Postexercise O2 Consumption. J. Appl. Physiol. 1987, 62, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gore, C.J.; Withers, R.T. The Effect of Exercise Intensity and Duration on the Oxygen Deficit and Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1990, 60, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlock, D.A.; Fissinger, J.A.; Melby, C.L. Effect of Exercise Intensity and Duration on Postexercise Energy Expenditure. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1989, 21, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chad, K.E.; Wenger, H.A. The Effect of Exercise Duration on the Exercise and Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption. Can. J. Sport Sci. 1988, 13, 204–207. [Google Scholar]
- Viru, A.A. Adaptation in Sports Training; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Viru, A.A.; Smirnova, T.; Karelson, K.; Snegovskaya, V. Determinants and Modulators of Hormonal Responses to Exercise. Biol. Sport 1996, 13, 169–187. [Google Scholar]
- Passfield, L.; Murias, J.M.; Sacchetti, M.; Nicolo, A. Validity of the Training-Load Concept. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2022, 17, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impellizzeri, F.M.; Marcora, S.M.; Coutts, A.J. Internal and External Training Load: 15 Years On. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2019, 14, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnley, M.; Jones, A.M. Power–Duration Relationship: Physiology, Fatigue, and the Limits of Human Performance. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2018, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaikkonen, P.; Hynynen, E.; Mann, T.; Rusko, H.; Nummela, A. Can HRV Be Used to Evaluate Training Load in Constant Load Exercises? Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, S.; Haugen, O.; Kuffel, E. Autonomic Recovery after Exercise in Trained Athletes: Intensity and Duration Effects. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hynynen, E.; Vesterinen, V.; Rusko, H.; Nummela, A. Effects of Moderate and Heavy Endurance Exercise on Nocturnal HRV. Int. J. Sports Med. 2010, 31, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myllymäki, T.; Rusko, H.; Syväoja, H.; Juuti, T.; Kinnunen, M.L.; Kyröläinen, H.; George, K.P. Effects of Exercise Intensity and Duration on Nocturnal Heart Rate Variability and Sleep Quality. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hautala, A.J.; Kiviniemi, A.M.; Tulppo, M.P. Individual Responses to Aerobic Exercise: The Role of the Autonomic Nervous System. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2009, 33, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelwyn, G.J.; Wong, L.E.; Kennedy, M.D.; Eves, N.D. The Effect of Hypoxia and Exercise on Heart Rate Variability, Immune Response, and Orthostatic Stress. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2013, 23, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garet, M.; Tournaire, N.; Roche, F.; Laurent, R.; Lacour, J.R.; Barthélémy, J.C.; Pichot, V. Individual Interdependence between Nocturnal ANS Activity and Performance in Swimmers. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004, 36, 2112–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdillon, N.; Schmitt, L.; Yazdani, S.; Vesin, J.M.; Millet, G.P. Minimal Window Duration for Accurate HRV Recording in Athletes. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamelin, F.X.; Berthoin, S.; Bosquet, L. Validity of the Polar S810 Heart Rate Monitor to Measure R-R Intervals at Rest. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2006, 38, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borg, G. Perceived Exertion as an Indicator of Somatic Stress. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 1970, 2, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, P.; Pokan, R.; von Duvillard, S.P.; Seibert, F.J.; Zweiker, R.; Schmid, P. Heart Rate Performance Curve during Incremental Cycle Ergometer Exercise in Healthy Young Male Subjects. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1997, 29, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, MI, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A.M.; Grassi, B.; Christensen, P.M.; Krustrup, P.; Bangsbo, J.; Poole, D.C. Slow Component of VO2 Kinetics: Mechanistic Bases and Practical Applications. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 2046–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colosio, A.L.; Caen, K.; Bourgois, J.G.; Boone, J.; Pogliaghi, S. Bioenergetics of the VO2 Slow Component between Exercise Intensity Domains. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2020, 472, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellinger, P. Functional Overreaching in Endurance Athletes: A Necessity or Cause for Concern? Sports Med. 2020, 50, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, N.; Reaburn, P.; Driller, M.; Argus, C. Age-Related Changes in Performance and Recovery Kinetics in Masters Athletes: A Narrative Review. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2016, 24, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krüger, R.L.; Aboodarda, S.J.; Jaimes, L.M.; Samozino, P.; Millet, G.Y. Cycling Performed on an Innovative Ergometer at Different Intensities–Durations in Men: Neuromuscular Fatigue and Recovery Kinetics. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 44, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maresh, C.M.; Abraham, A.; De Souza, M.J.; Deschenes, M.R.; Kraemer, W.J.; Armstrong, L.E.; Maguire, M.S.; Gabaree, C.L.; Hoffman, J.R. Oxygen Consumption Following Exercise of Moderate Intensity and Duration. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1992, 65, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivy, J.L.; Costill, D.L.; van Handel, P.J.; Essig, D.A.; Lower, R.W. Alteration in the Lactate Threshold with Changes in Substrate Availability. Int. J. Sports Med. 1981, 2, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautala, A.; Tulppo, M.P.; Mäkikallio, T.H.; Laukkanen, R.; Nissilä, S.; Huikuri, H.V. Changes in Cardiac Autonomic Regulation after Prolonged Maximal Exercise. Clin. Physiol. 2001, 21, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iellamo, F.; Legramante, J.M.; Pigozzi, F.; Spataro, A.; Norbiato, G.; Lucini, D.; Pagani, M. Conversion from Vagal to Sympathetic Predominance with Strenuous Training in High-Performance World Class Athletes. Circulation 2002, 105, 2719–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pichot, V.; Roche, F.; Gaspoz, J.M.; Enjolras, F.; Antoniadis, A.; Minini, P.; Costes, F.; Busso, T.; Lacour, J.R.; Barthelemy, J.C. Relation between Heart Rate Variability and Training Load in Middle-Distance Runners. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tulppo, M.P.; Mäkikallio, T.H.; Takala, T.E.S.; Seppänen, T.; Huikuri, H.V. Quantitative Beat-to-Beat Analysis of Heart Rate Dynamics during Exercise. Am. J. Physiol. 1996, 271, H244–H252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezzani, A.; Grassi, B.; Jones, A.M.; Giordano, A.; Corrà, U.; Porcelli, S.; Della Bella, S.; Taddeo, A.; Giannuzzi, P. Speeding of Pulmonary VO2 On-Kinetics by Light-to-Moderate-Intensity Aerobic Exercise Training in Chronic Heart Failure: Clinical and Pathophysiological Correlates. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 2189–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchheit, M.; Simpson, M.B.; Al Haddad, H.; Bourdon, P.C.; Mendez-Villanueva, A. Monitoring Changes in Physical Performance with Heart Rate Measures in Young Soccer Players. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pind, R.; Hofmann, P.; Mäestu, E.; Vahtra, E.; Purge, P.; Mäestu, J. Increases in RPE Rating Predict Fatigue Accumulation Without Changes in Heart Rate Zone Distribution After 4-Week Low-Intensity High-Volume Training Period in High-Level Rowers. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 735565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, A.; Sustercich, W.; Edgerton, K.; Cortis, C.; Jaime, S.J.; Mikat, R.P.; Porcari, J.P.; Foster, C. Effect of Progressive Fatigue on Session RPE. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2020, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
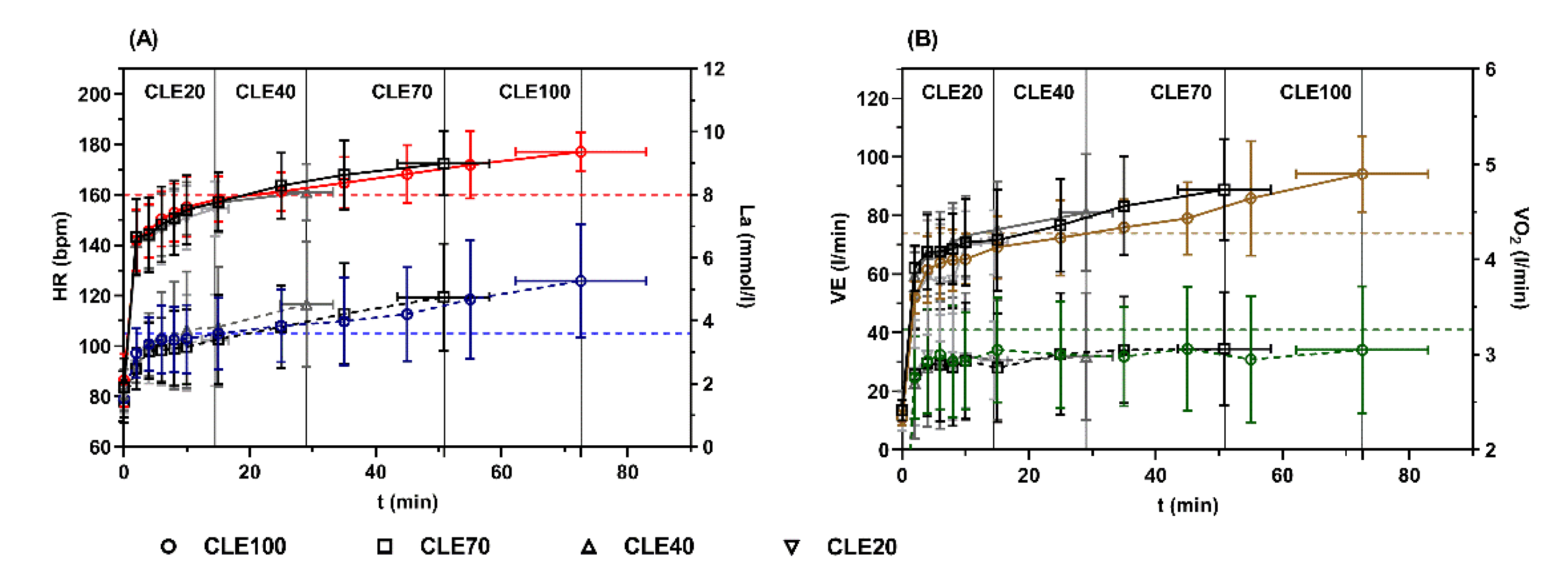

| HR [bpm] | La [mmol/L] | P [W] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LTP1 | 118 ± 8 | 1.83 ± 0.37 | 1.17 ± 0.42 | 106 ± 24 |
| VT1 | 118 ± 10 | 1.80 ± 0.46 | 1.19 ± 0.38 | 103 ± 0.71 |
| LTP2 | 160 ± 10 | 3.26 ± 0.55 | 3.59 ± 1.00 | 212 ± 34 |
| VT2 | 161 ± 10 | 3.26 ± 0.56 | 3.66 ± 1.14 | 213 ± 38 |
| Max | 187 ± 11 | 3.86 ± 0.75 | 12.31 ± 1.92 | 299 ± 48 |
| P LTP1 | CLE20 (W) | CLE40 (W) | CLE70 (W) | CLE100 (W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| baseline | 113 ± 16 | 107 ± 16 | 107 ± 18 | 106 ± 21 |
| Rec4 | 112 ± 16 | 109 ± 17 | 108 ± 17 | 107 ± 19 |
| Rec24 | 108 ± 17 | 108 ± 17 | 107 ± 17 | 106 ± 21 |
| Rec48 | 112 ± 16 | 109 ± 19 | 108 ± 20 | 104 ± 19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Birnbaumer, P.; Weiner, L.; Handl, T.; Tschakert, G.; Hofmann, P. Effects of Different Durations at Fixed Intensity Exercise on Internal Load and Recovery—A Feasibility Pilot Study on Duration as an Independent Variable for Exercise Prescription. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2022, 7, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk7030054
Birnbaumer P, Weiner L, Handl T, Tschakert G, Hofmann P. Effects of Different Durations at Fixed Intensity Exercise on Internal Load and Recovery—A Feasibility Pilot Study on Duration as an Independent Variable for Exercise Prescription. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2022; 7(3):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk7030054
Chicago/Turabian StyleBirnbaumer, Philipp, Lena Weiner, Tanja Handl, Gerhard Tschakert, and Peter Hofmann. 2022. "Effects of Different Durations at Fixed Intensity Exercise on Internal Load and Recovery—A Feasibility Pilot Study on Duration as an Independent Variable for Exercise Prescription" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 7, no. 3: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk7030054
APA StyleBirnbaumer, P., Weiner, L., Handl, T., Tschakert, G., & Hofmann, P. (2022). Effects of Different Durations at Fixed Intensity Exercise on Internal Load and Recovery—A Feasibility Pilot Study on Duration as an Independent Variable for Exercise Prescription. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 7(3), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk7030054







