The Dynamic Change in the Neutrophil–Lymphocyte Ratio and Systemic Inflammatory Response Index After Undergoing an Intensive Resistance-Based Exercise Program
Abstract
1. Introduction
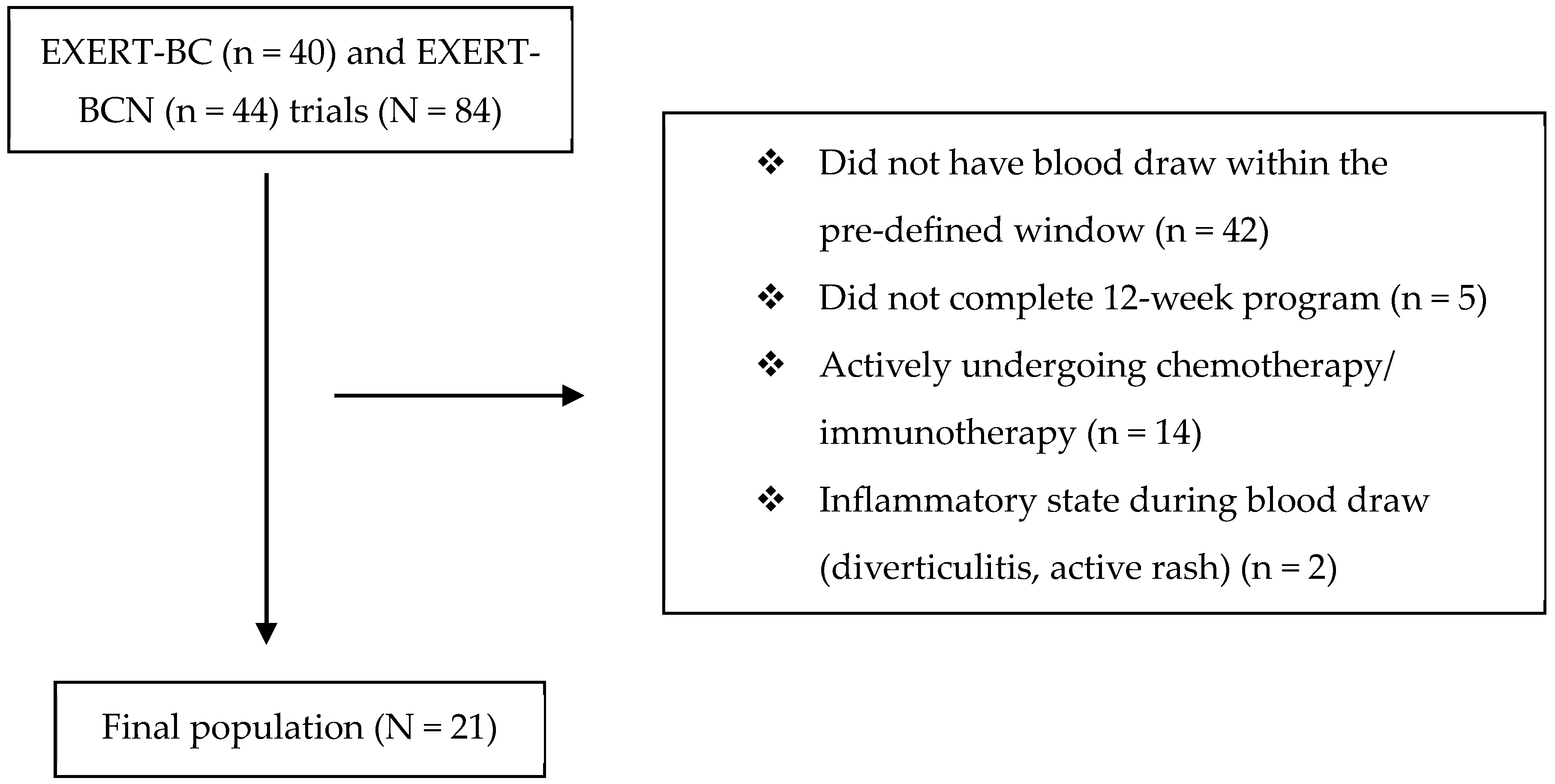
2. Methods
Statistics
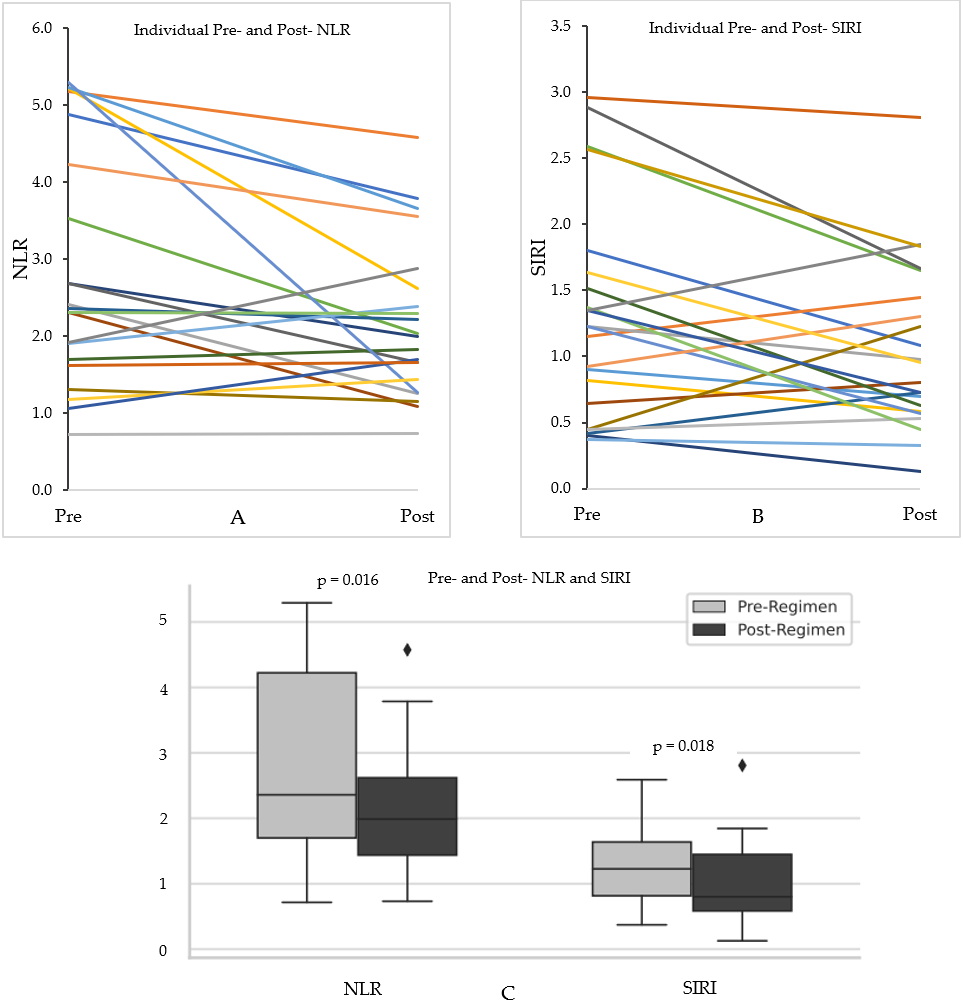
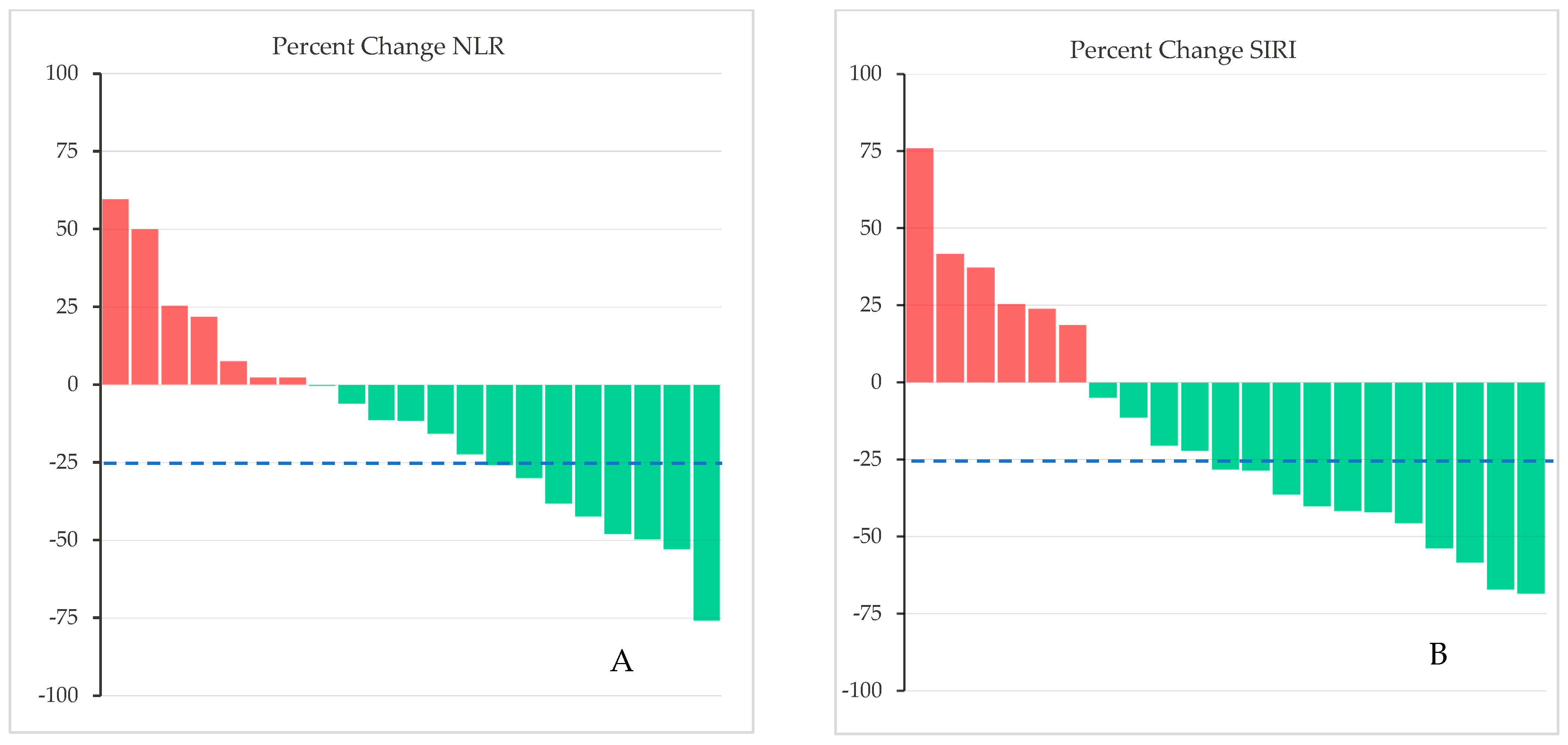
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mandsager, K.; Harb, S.; Cremer, P.; Phelan, D.; Nissen, S.E.; Jaber, W. Association of cardiorespiratory fitness with long-term mortality among adults undergoing exercise treadmill testing. JAMA Network Open 2018, 1, e183605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemanne, D.; Cassileth, B.; Gubili, J. The role of physical activity in cancer prevention, treatment, recovery, and survivorship. Oncology 2013, 27, 580–585. [Google Scholar]
- Cannioto, R.A.; Hutson, A.; Dighe, S.; McCann, W.; McCann, S.E.; Zirpoli, G.R.; Barlow, W.; Kelly, K.M.; DeNysschen, C.A.; Hershman, D.L.; et al. Physical activity before, during, and after chemotherapy for high-risk breast cancer: Relationships with survival. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021, 113, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougherty, T.P.; Meyer, J.E. Comparing lifestyle modifications and the magnitude of their associated benefit on cancer mortality. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, M.A.; Bayes, S.; Newton, R.U.; Zissiadis, Y.; Spry, N.A.; Taaffe, D.R.; Hart, N.H.; Galvão, D.A. Implementation barriers to integrating exercise as medicine in oncology: An ecological scoping review. J. Cancer Surviv. Res. Pract. 2022, 16, 865–881, Erratum in J. Cancer Surviv. Res. Pract. 2022, 16, 1504–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courneya, K.S.; Vardy, J.L.; O’Callaghan, C.J.; Gill, S.; Friedenreich, C.M.; Wong, R.K.S.; Dhillon, H.M.; Coyle, V.; Chua, N.S.; Jonker, D.J.; et al. Structured exercise after adjuvant chemotherapy for colon cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 393, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forget, P.; Khalifa, C.; Defour, J.-P.; Latinne, D.; Van Pel, M.-C.; De Kock, M. What is the normal value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio? BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.-H.; Huang, D.-H.; Chen, Z.-Y. Prognostic role of systemic immune-inflammation index in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 75381–75388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Jung, E.J.; Kim, J.-M.; Lee, H.S.; Kwag, S.-J.; Park, J.-H.; Park, T.; Jeong, S.-H.; Jeong, C.-Y.; Ju, Y.-T. Dynamic changes of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts breast cancer prognosis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Xia, S.; Lu, L.; Dai, T.; Li, A.; Chen, Y.; Gao, E. Prognostic value of the systemic inflammation response index (Siri) before and after surgery in operable breast cancer patients. Cancer Biomark. Sect. A Dis. Markers 2020, 28, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasapis, C.; Thompson, P.D. The effects of physical activity on serum C-reactive protein and inflammatory markers: A systematic review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 45, 1563–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walzik, D.; Joisten, N.; Zacher, J.; Zimmer, P. Transferring clinically established immune inflammation markers into exercise physiology: Focus on neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio and systemic immune-inflammation index. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 121, 1803–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Chen, P.J.; Chen, W.H. Diet and exercise improve neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in overweight adolescents. Int. J. Sports Med. 2011, 32, 982–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çinar, M.A.; Erkiliç, A. Effect of aerobic exercise on neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-lymphocyte ratio, and lymphocyte-monocyte ratio in burn patients: A randomized controlled trial. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. JPRAS 2024, 95, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, D.J.; Peluso, C.; Hilton, C.; Coopey, S.B.; Gomez, J.; Rosenberg, J.; Beriwal, S.; Hyde, P.N.; Champ, C.E. Exert-bcn: An exercise regimen designed to improve body composition, functional capacity, and strength after treatment for breast cancer with nutrition optimization. JCO Oncol. Pract. 2025, OP-24-00954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, D.J.; Peluso, C.; Hilton, C.; Velasquez, F.; Annichine, A.; Matsko, K.; Rosenberg, J.; Diaz, A.K.; Hyde, P.; Beriwal, S.; et al. EXERT-BC: A pilot study of an exercise regimen designed to improve functional mobility, body composition, and strength after the treatment for breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e7001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Q.; Zhuang, L.; Shen, Y.; Geng, Y.; Yu, S.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Meng, Z.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z. A novel systemic inflammation response index (Siri) for predicting the survival of patients with pancreatic cancer after chemotherapy. Cancer 2016, 122, 2158–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, B.; Ju, X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Y. A novel prognostic marker systemic inflammation response index (Siri) for operable cervical cancer patients. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhu, D.; Wu, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, R.; Jiang, J.; Wu, C. A novel systemic inflammation response index (Siri) for predicting postoperative survival of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 65, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, X. A systemic inflammation response index (Siri)-based nomogram for predicting the recurrence of early stage hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2022, 45, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ge, H.; Miao, Z.; Shao, S.; Shi, H.; Dong, C. Dynamic changes in the systemic inflammation response index predict the outcome of resectable gastric cancer patients. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 577043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, C.-H.; Bhoo-Pathy, N.; Ng, K.-L.; Jabir, R.S.; Tan, G.-H.; See, M.-H.; Jamaris, S.; Taib, N.A. Utility of pre-treatment neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio as prognostic factors in breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairey, A.S.; Courneya, K.S.; Field, C.J.; Bell, G.J.; Jones, L.W.; Martin, B.S.; Mackey, J.R. Effect of exercise training on C-reactive protein in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors: A randomized controlled trial. Brain Behav. Immun. 2005, 19, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagstrom, A.D.; Marshall, P.W.M.; Lonsdale, C.; Papalia, S.; Cheema, B.S.; Toben, C.; Baune, B.T.; Fiatarone Singh, M.A.; Green, S. The effect of resistance training on markers of immune function and inflammation in previously sedentary women recovering from breast cancer: A randomized controlled trial. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 155, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champ, C.; Rosenberg, J.; Peluso, C.; Hilton, C.; Carpenter, D. Long-term exercise adherence and body composition after completion of an intense resistance training regimen during and after treatment for breast cancer. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2025, 27 (Suppl. S6), suaf083.029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Total Population (N = 21) | Those with an Increase in the SIRI (n = 6) | Those with a Decrease in the SIRI (n = 15) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yrs) [range] | 56 [40–69] | 52 [40–58] | 57 [42–69] |
| Race | |||
| White | 18 (86%) | 5 (83%) | 13 (87%) |
| Black | 3 (14%) | 1 (17%) | 2 (13%) |
| Stage | |||
| 0 | 2 (10%) | 1 (17%) | 1 (7%) |
| 1 | 13 (61%) | 4 (67%) | 9 (60%) |
| 2 | 4 (19%) | 0 (0%) | 4 (27%) |
| 3 | 2 (10%) | 1 (17%) | 1 (7%) |
| Prior Chemotherapy (%) | 8 (38%) | 2 (33%) | 6 (40%) |
| Received Radiotherapy (%) | 16 (76%) | 3 (50%) | 13 (87%) |
| Current adjuvant endocrine therapy (%) | 13 (62%) | 4 (67%) | 9 (60%) |
| BMI (kg/m2) [IQR] | 30.3 [25.6–35.6] | 31.5 [27.4–34.9] | 29.8 [25.3–34.5] |
| Time between initial CBC and intake (days) [IQR] | 64 [26–103] | 86 [73–106] | 55 [14–91] |
| Time after outtake and final CBC (days) [IQR] | 57 [18–79] | 56 [16–101] | 57 [25–76] |
| Total Population (N = 21) | Those with an Increase in the SIRI (n = 6) | Those with a Decrease in the SIRI (n = 15) | Mann-Whitney p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-exercise NLR [IQR] | 2.26 [1.70–4.22] | 1.76 [1.29–1.92] | 2.69 [2.33–5.03] | 0.016 |
| Pre-exercise SIRI [IQR] | 1.23 [0.82–1.64] | 0.78 [0.50–1.10] | 1.37 [1.06–2.18] | 0.061 |
| Post-exercise NLR [IQR] | 1.99 [1.44–2.62] | 1.99 [1.66–2.36] | 1.99 [1.26–3.09] | 0.904 |
| Post-exercise SIRI [IQR] | 0.80 [0.59–1.45] | 1.05 [0.75–1.41] | 0.73 [0.57–1.36] | 0.484 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dougherty, T.P.; Carpenter, D.J.; Peluso, C.; Champ, C.E. The Dynamic Change in the Neutrophil–Lymphocyte Ratio and Systemic Inflammatory Response Index After Undergoing an Intensive Resistance-Based Exercise Program. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2025, 10, 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10040436
Dougherty TP, Carpenter DJ, Peluso C, Champ CE. The Dynamic Change in the Neutrophil–Lymphocyte Ratio and Systemic Inflammatory Response Index After Undergoing an Intensive Resistance-Based Exercise Program. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2025; 10(4):436. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10040436
Chicago/Turabian StyleDougherty, Timothy P., David J. Carpenter, Chris Peluso, and Colin E. Champ. 2025. "The Dynamic Change in the Neutrophil–Lymphocyte Ratio and Systemic Inflammatory Response Index After Undergoing an Intensive Resistance-Based Exercise Program" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 10, no. 4: 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10040436
APA StyleDougherty, T. P., Carpenter, D. J., Peluso, C., & Champ, C. E. (2025). The Dynamic Change in the Neutrophil–Lymphocyte Ratio and Systemic Inflammatory Response Index After Undergoing an Intensive Resistance-Based Exercise Program. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 10(4), 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10040436






