Acute Effect of Submaximal Exercise on Respiratory System Impedance in Healthy Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethical Approval
2.2. Study Location
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Recruitment and Selection of Participants
2.5. Evaluation
2.6. Impulse Oscillometry System—IOS
2.7. Six-Minute Walk Test—6MWT
2.8. Spirometry
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| O2 | Oxygen |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| IOS | Impulse Oscillometry System |
| 6MWT | 6-min walk test |
| STROBE | Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology |
| TV | Tidal volume |
| Hz | Hertz |
| R5 | Total resistance of the respiratory system |
| R20 | Resistance of larger-caliber airways |
| R5-R20 | Resistance of smaller-caliber airways |
| X5 | Total reactance of the respiratory system |
| Fres | Resonant frequency |
| AX | Reactance area |
| HR | Heart rate |
| RR | Respiratory rate |
| SpO2 | Peripheral oxygen saturation |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| ATS | American Thoracic Society |
| ERS | European Respiratory Society |
| FVC | Forced vital capacity |
| RV | Residual volume |
| TLC | Total lung capacity |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| FEV1 | Force expiratory volume in the first second |
| kPa/L/s | Kilopascals per liter per second |
| kPa/L | Kilopascals per liter |
References
- West, J.B. Fisiologia Respiratória: Princípios Básicos, 9th ed.; Artmed: Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil, 2013; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Fishman, A.P. Handbook of Physiology. The Respiratory System. Circulation and Nonrespiratory Functions; American Physiological Society (APS): Bethesda, MD, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Hlastala, M.P. Physiology of Respiration; Oxford University Press: Cary, NC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Leff, A.R. Respiratory Physiology: Basics and Applications; W.B. Saunders Co.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Vogiatzis, I.; Zakynthinos, S. Factors Limiting Exercise Tolerance in Chronic Lung Diseases. In Organizador. Comprehensive Physiology [Internet], 1st ed.; Prakash, Y.S., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1779–1817. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cphy.c110015 (accessed on 30 April 2024).
- Albuquerque, C.G.D.; Andrade, F.M.D.D.; Rocha, M.A.D.A.; Oliveira, A.F.F.D.; Ladosky, W.; Victor, E.G.; Rizzo, J.Â. Determining respiratory system resistance reactance by impulse oscillometry in obese individuals. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2015, 41, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppenheimer, B.W.; Berger, K.I.; Segal, L.N.; Stabile, A.; Coles, K.D.; Parikh, M.; Goldring, R.M. Airway Dysfunction in Obesity: Response to Voluntary Restoration of End Expiratory Lung Volume. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroli, R.G.; Santos, D.O.D.; Souza, H.C.D.D.; Perossi, L.; Ribeiro, M.A.; Perossi, J.; Baddini-Martinez, J.A.; Gastaldi, A.C. Effects of Controlled Voluntary Increase in the Ventilatory Demand on Respiratory System Resistance in Healthy and Non-Cystic Fibrosis Bronchiectasis Subjects: A Cross-Sectional Study. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2021, 57, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmberg, L.P.; Mäkelä, M.J.; Mattila, P.S.; Hammarén-Malmi, S.; Pelkonen, A.S. Exercise-induced changes in respiratory impedance in young wheezy children and nonatopic controls. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2008, 43, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiller, N.B.; Cao, M.; Lin, F.; Yuan, W.; Wang, C.Y.; Abbasi, A.; Calmelat, R.; Soriano, A.; Rossiter, H.B.; Casaburi, R.; et al. Dynamic airway function during exercise in COPD assessed via impulse oscillometry before and after inhaled bronchodilators. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 131, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brashier, B.; Salvi, S. Measuring lung function using sound waves: Role of the forced oscillation technique and impulse oscillometry system. Breathe 2015, 11, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostveen, E.; MacLeod, D.; Lorino, H.; Farre, R.; Hantos, Z.; Desager, K.; Marchal, F. The forced oscillation technique in clinical practice: Methodology, recommendations and future developments. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 22, 1026–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, J.; Smidt, U. Impulse Oscillometry. Analysis of Lung Mechanics in General Practice and the Clinic, Epidemiology and Experimental Research; PMI-Verlagsgruppe: Frankfurt, Germany, 1994; pp. 149–160. [Google Scholar]
- ATS Statement: Guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 111–117. [CrossRef]
- Britto, R.R.; Probst, V.S.; Andrade, A.F.D.D.; Samora, G.A.R.; Hernandes, N.A.; Marinho, P.E.M.; Karsten, M.; Pitta, F.; Parreira, V.F. Reference equations for the six-minute walk distance based on a Brazilian multicenter study. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2013, 17, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, B.L.; Steenbruggen, I.; Miller, M.R.; Barjaktarevic, I.Z.; Cooper, B.G.; Hall, G.L.; Hallstrand, T.S.; Kaminsky, D.A.; McCarthy, K.; McCormack, M.C.; et al. Standardization of Spirometry 2019 Update. An Official American Thoracic Society and European Respiratory Society Technical Statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, e70–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.A.D.C.; Sato, T.; Rodrigues, S.C. Novos valores de referência para espirometria forçada em brasileiros adultos de raça branca. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2007, 33, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porojan-Suppini, N.; Fira-Mladinescu, O.; Marc, M.; Tudorache, E.; Oancea, C. Lung Function Assessment by Impulse Oscillometry in Adults. TCRM 2020, 16, 1139–1150; Erratum in 2021, 17, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assumpção, M.S.D.; Ribeiro, J.D.; Wamosy, R.M.G.; Parazzi, P.L.F.; Schivinski, C.I.S. Oscilometria de Impulso e Espirometria em Escolares Submetidos ao Teste de Caminhada de Seis Minutos. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2018, 36, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parshall, M.B.; Schwartzstein, R.M.; Adams, L.; Banzett, R.B.; Manning, H.L.; Bourbeau, J.; Calverley, P.M.; Gift, A.G.; Harver, A.; Lareau, S.C.; et al. An Official American Thoracic Society Statement: Update on the Mechanisms, Assessment, and Management of Dyspnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotshall, R.W. Airway Response during Exercise and Hyperpnoea in Non-Asthmatic and Asthmatic Individuals. Sports Med. 2006, 36, 513–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, D.E.; Revill, S.M.; Webb, K.A. Dynamic Hyperinflation and Exercise Intolerance in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, S.D.; Daviskas, E. The mechanism of exercise-induced asthma is …. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Noord, J.; Clement, J.; Cauberghs, M.; Mertens, I.; Van De Woestijne, K.; Demedts, M. Total respiratory resistance and reactance in patients with diffuse interstitial lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 1989, 2, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokai, R.; Ito, S.; Iwano, S.; Uchida, A.; Aso, H.; Kondo, M.; Ishiguro, N.; Kojima, T.; Hasegawa, Y. Respiratory mechanics measured by forced oscillation technique in rheumatoid arthritis-related pulmonary abnormalities: Frequency-dependence, heterogeneity and effects of smoking. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, D.A.; Simpson, S.J.; Berger, K.I.; Calverley, P.; De Melo, P.L.; Dandurand, R.; Dellacà, R.L.; Farah, C.S.; Farré, R.; Hall, G.L.; et al. Clinical significance and applications of oscillometry. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2022, 31, 210208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelson, E.D.; Grassman, E.D.; Peters, W.R. Pulmonary mechanics by spectral analysis of forced random noise. J. Clin. Investig. 1975, 56, 1210–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, M.D. Clinical Application of Forced Oscillation. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 14, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczka, D.W.; Dellaca, R.L. Oscillation Mechanics of the Respiratory System: Applications to Lung Disease. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 39, 337–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Anthropometric Variables (n = 50) | |
|---|---|
| Male | 21 |
| Female | 29 |
| Sedentary | 10/50 |
| Age (Years) | Mean and standard deviation |
| 32.22 ± 11.60 | |
| Weight (Kg) | 69.62 ± 14.18 |
| Height (m) | 1.68 ± 0.09 |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 24.3 ± 3.87 |
| Spirometry parameters (n = 41) | |
| CVF (L) | 4.32 ± 1.20 |
| %CVF | 98.85 ± 13.47 |
| VEF1 (L) | 3.62 ± 0.99 |
| %VEF1 | 99.24 ± 14.41 |
| VEF1/CVF | 83.87 ± 6.73 |
| %VEF1/CVF | 99.61 ± 6.89 |
| FEF25–75% (L/min) | 3.94 ± 1.32 |
| %FEF25–75% | 98.15 ± 27.21 |
| Parameters | Pre-6MWT | Post-6MWT | p |
|---|---|---|---|
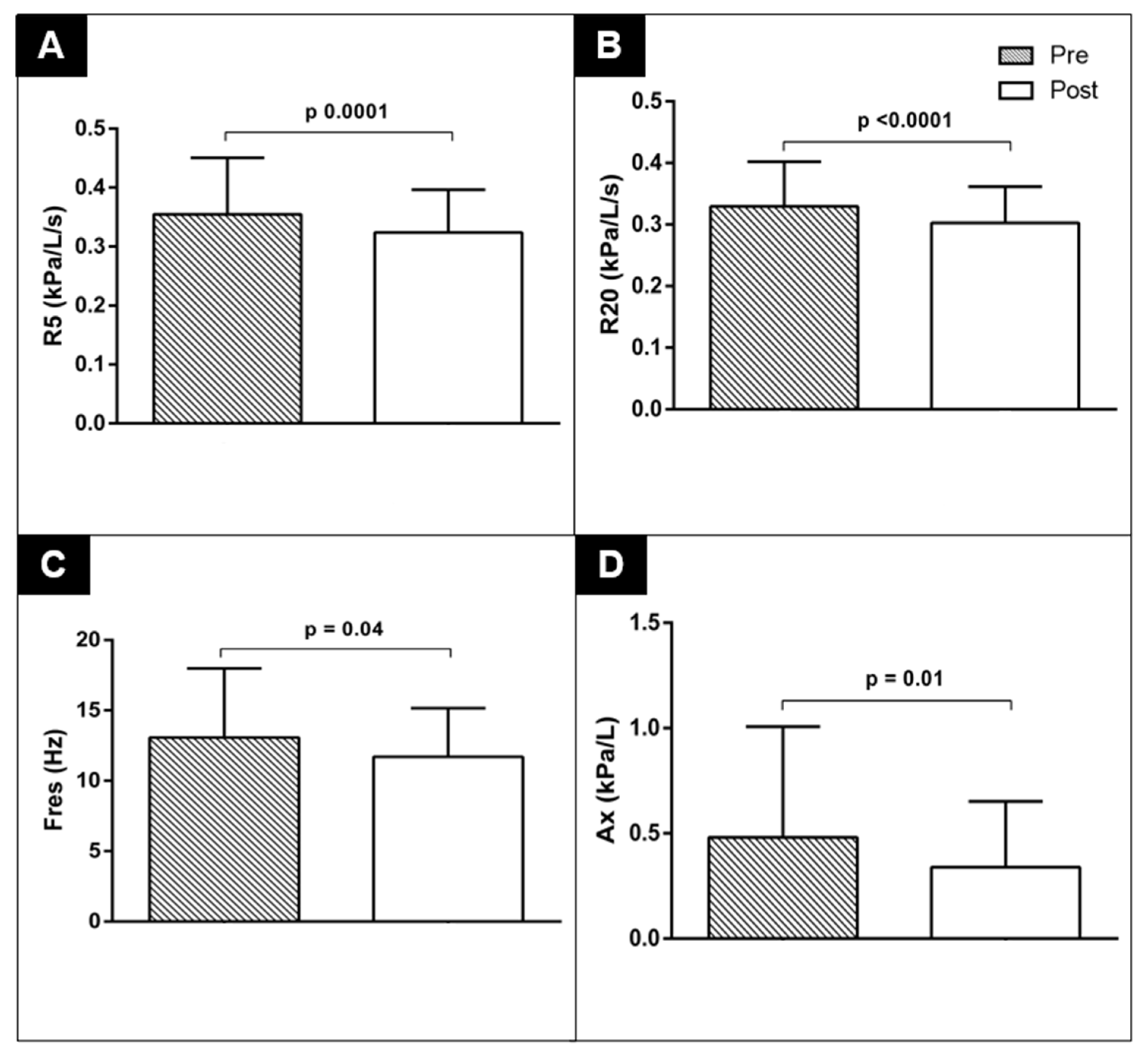
| R5 (kPa/L/s) | 0.35 ± 0.10 | 0.32 ± 0.07 | 0.0001 |
| %R5 (kPa/L/s) | 113.70 ± 30.26 | 103.36 ± 21.68 | <0.0001 |
| R20 (kPa/L/s) | 0.33 ± 0.07 | 0.30 ± 0.06 | <0.0001 |
| %R20 (kPa/L/s) | 126.24 ± 26.30 | 115.98 ± 21.38 | <0.0001 |
| R5-R20 (kPa/L/s) | 0.03 ± 0.04 | 0.02 ± 0.04 | 0.19 |
| %R5-R20 (kPa/L/s) | 55.50 ± 90.28 | 43.33 ± 79.88 | 0.07 |
| X5 (kPa/L/s) | −0.13 ± 0.05 | −0.10 ± 0.04 | <0.0001 |
| Fres (Hz) | 13.07 ± 4.93 | 11.70 ± 3.45 | 0.0042 |
| AX (kPa/L) | 0.48 ± 0.53 | 0.34 ± 0.31 | 0.01 |
| Distance covered in the 6MWT (m) | 623.34 ± 42.6 | ||
| %prev TC6 | 96.6 ± 7.4 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Furquim, T.H.d.C.; Santos, D.O.d.; Perossi, J.; Lima, F.C.; Silveira, J.M.; Gastaldi, A.C. Acute Effect of Submaximal Exercise on Respiratory System Impedance in Healthy Adults. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2025, 10, 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10040403
Furquim THdC, Santos DOd, Perossi J, Lima FC, Silveira JM, Gastaldi AC. Acute Effect of Submaximal Exercise on Respiratory System Impedance in Healthy Adults. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2025; 10(4):403. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10040403
Chicago/Turabian StyleFurquim, Thales Henrique do Carmo, Daniele Oliveira dos Santos, Jéssica Perossi, Fernanda Cristina Lima, Janne Marques Silveira, and Ada Clarice Gastaldi. 2025. "Acute Effect of Submaximal Exercise on Respiratory System Impedance in Healthy Adults" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 10, no. 4: 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10040403
APA StyleFurquim, T. H. d. C., Santos, D. O. d., Perossi, J., Lima, F. C., Silveira, J. M., & Gastaldi, A. C. (2025). Acute Effect of Submaximal Exercise on Respiratory System Impedance in Healthy Adults. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 10(4), 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10040403






