Oxidative Stress and Ultrastructural Analysis in Heart, Aorta, Skeletal Muscle and Lung of Rats Treated with N-Acetylcysteine or Rutin After Sprint Running
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Exercise Device and Software
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Analysis
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
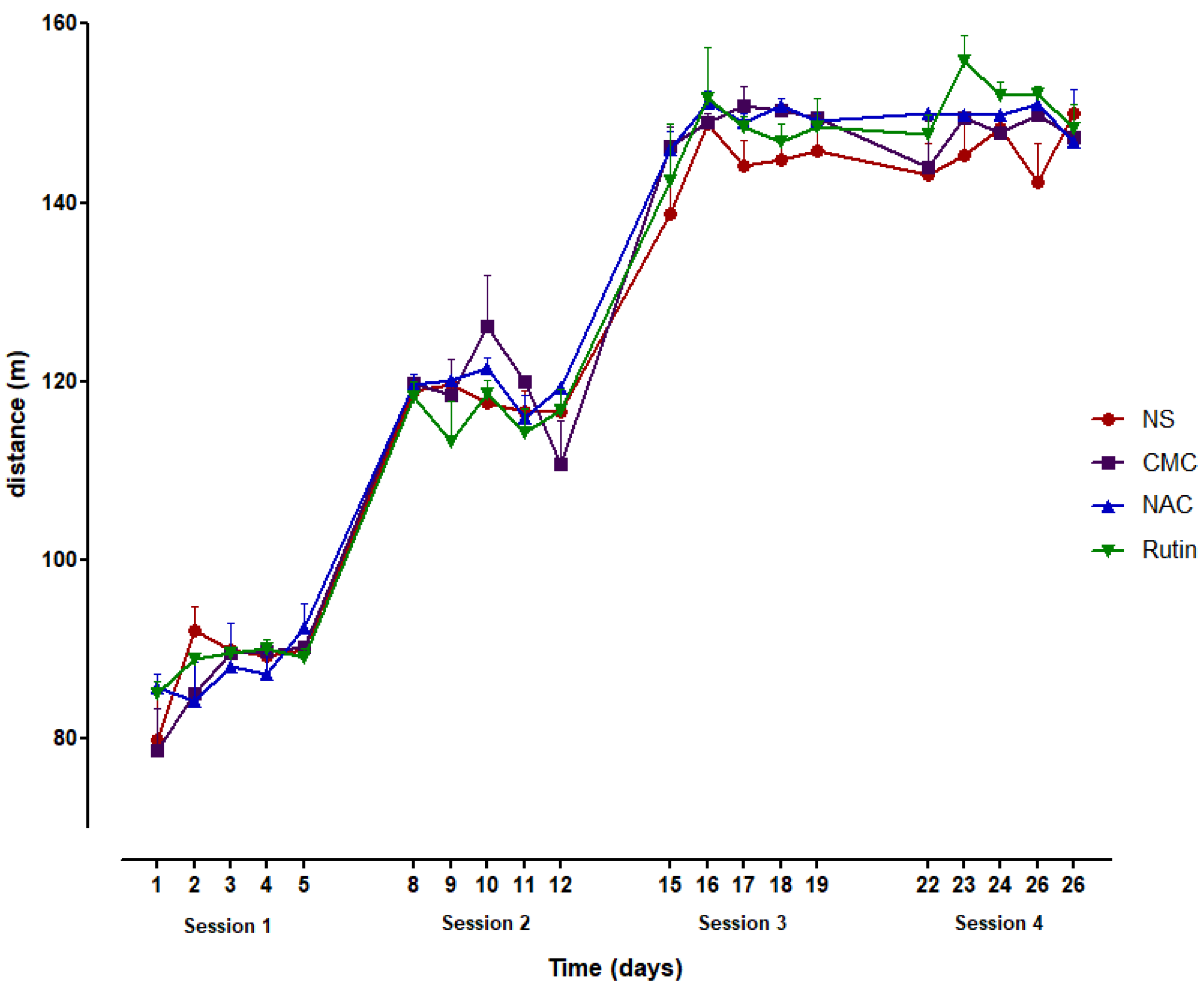
3.1. Treadmill Running
3.2. Physical Effort Effects on the Heart
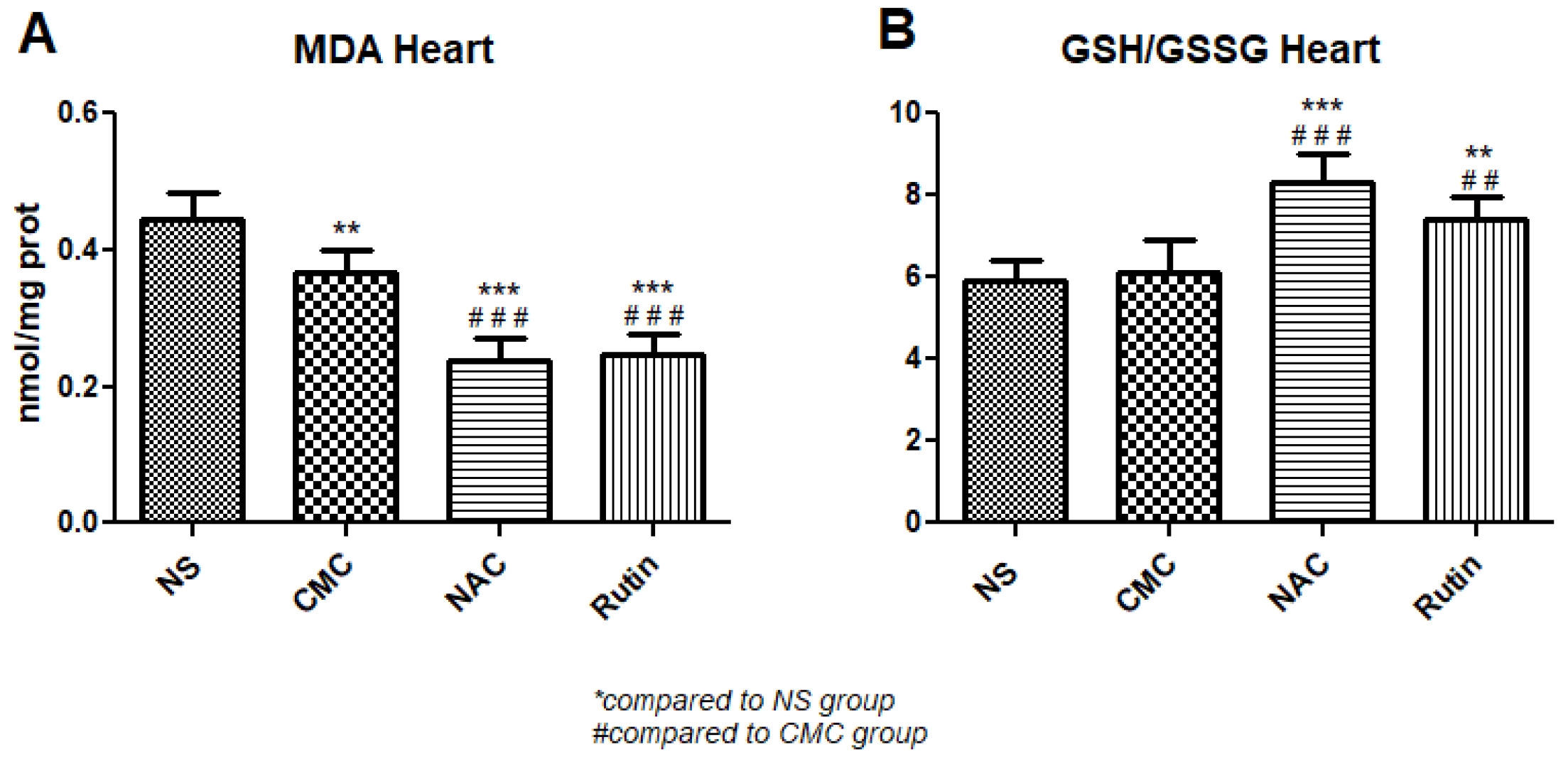
3.2.1. Oxidative Stress in Heart
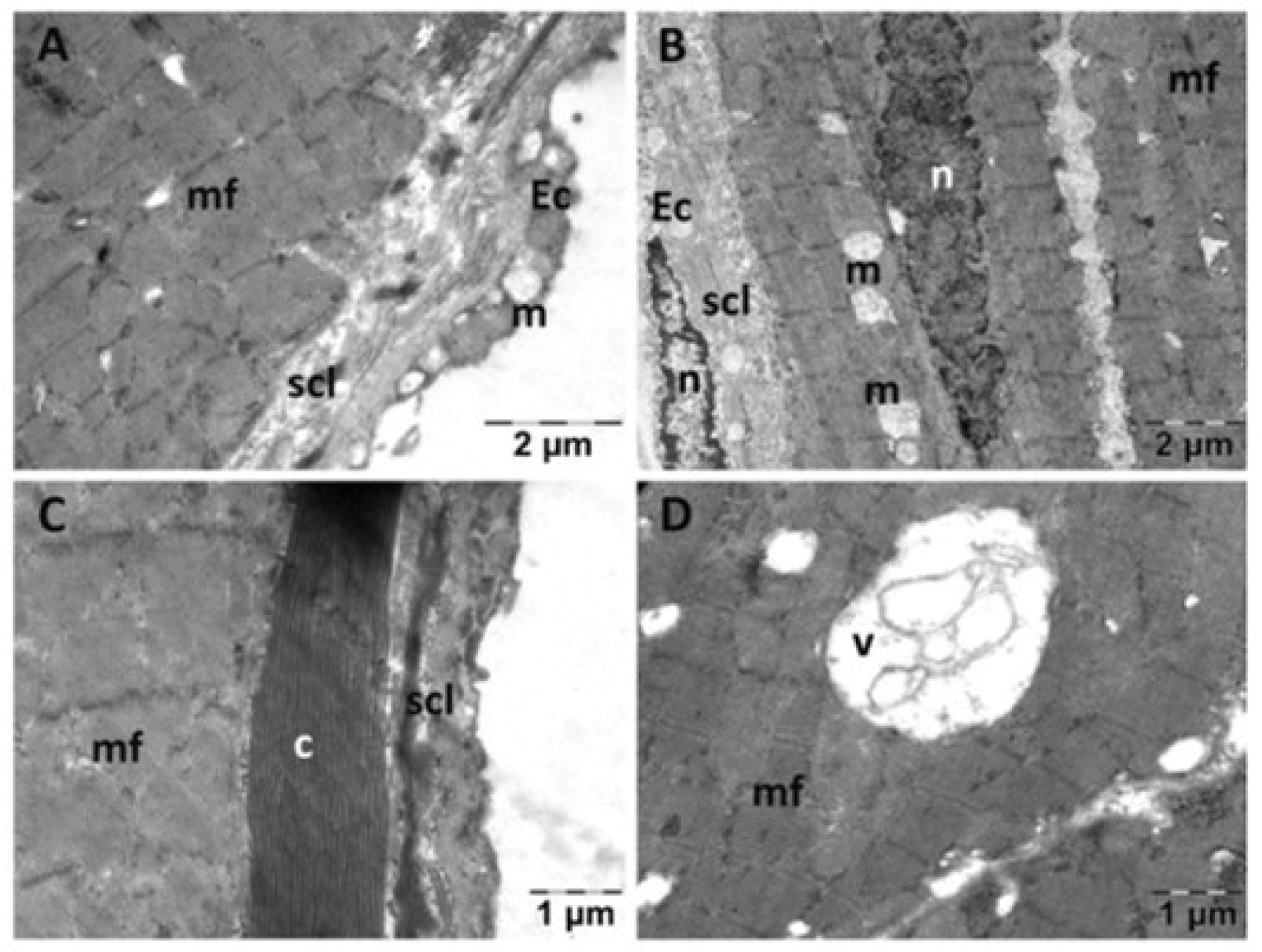
3.2.2. Heart Transmission Electron Microscopy
3.3. Physical Effort Effects on the Aorta
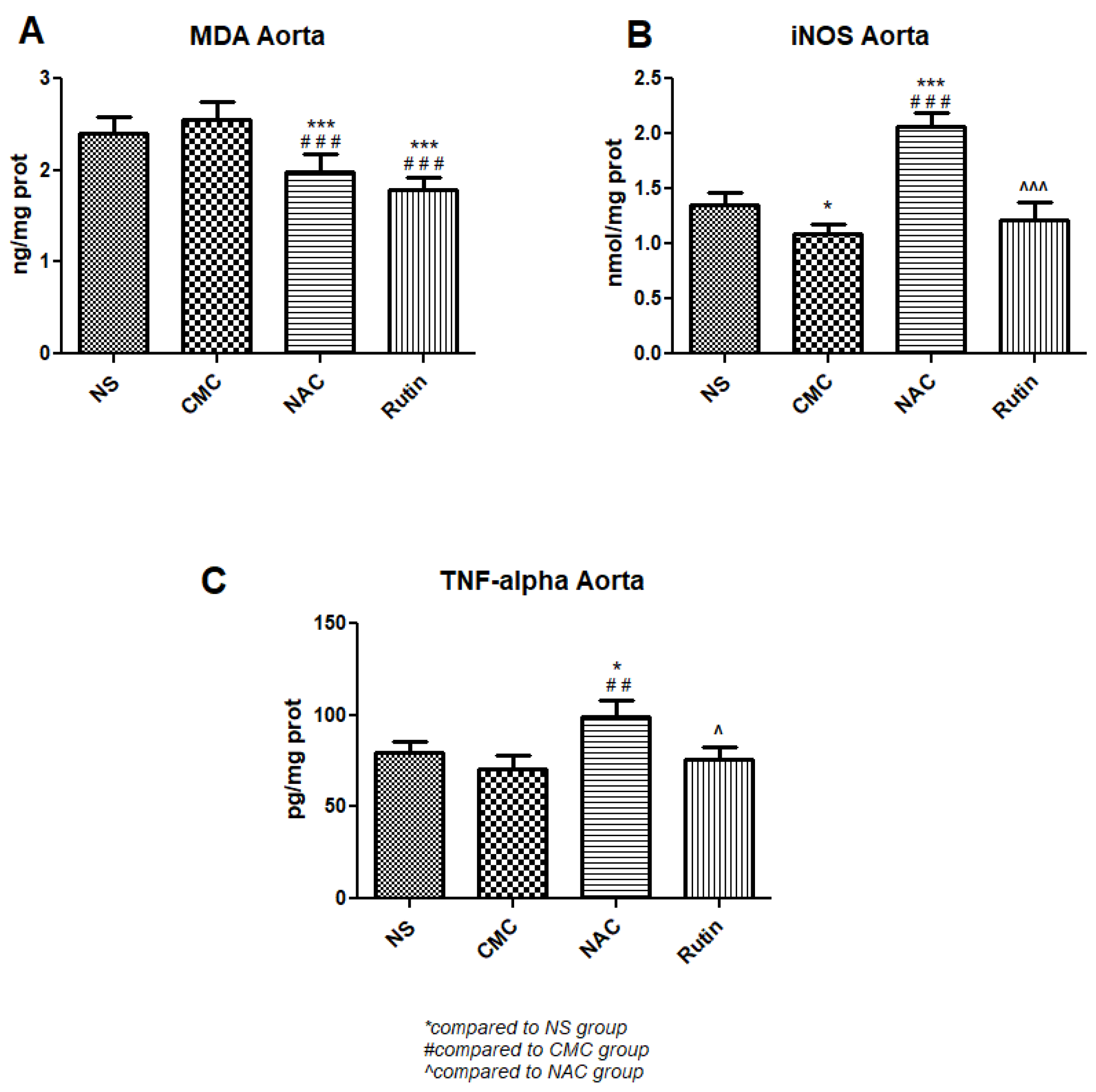
3.3.1. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in the Aorta
3.3.2. Aorta Transmission Electron Microscopy
3.4. Physical Effort Effects in the Lung
3.4.1. Oxidative Stress in the Lung
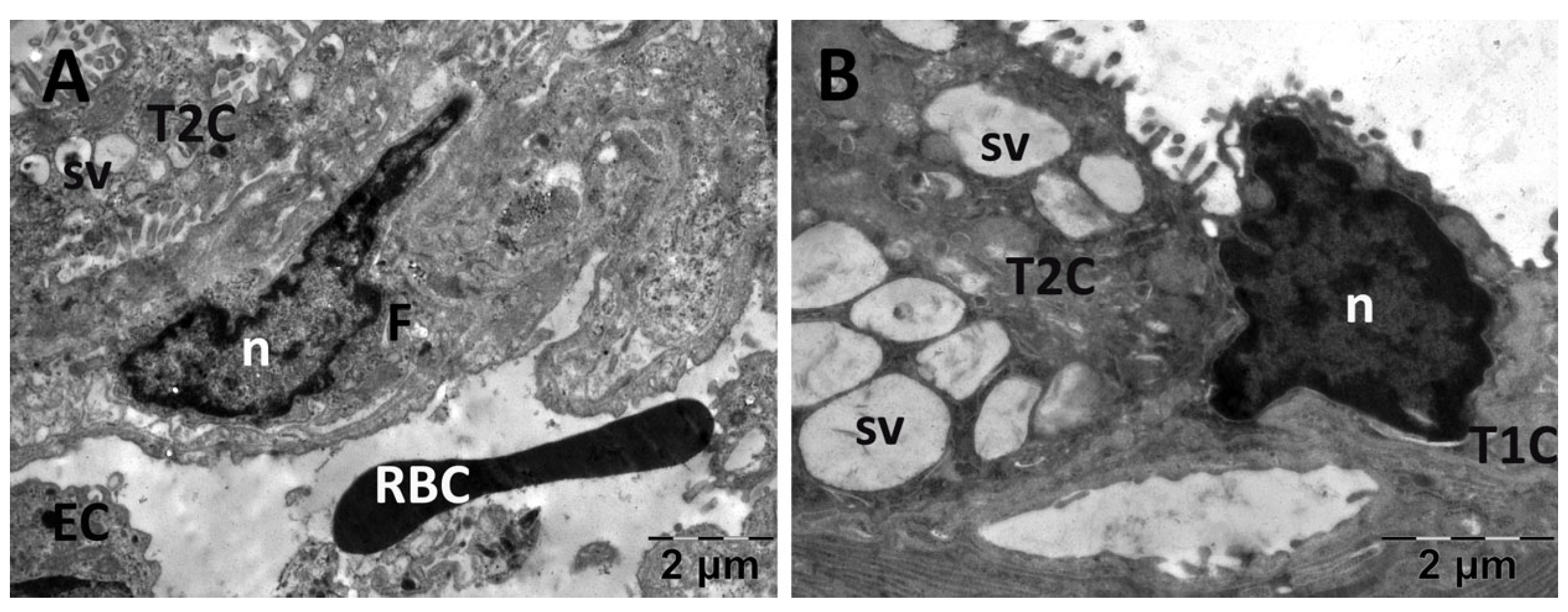
3.4.2. Lung Transmission Electron Microscopy
3.5. Physical Effort Effects on the Gastrocnemius Muscle
3.5.1. Oxidative Stress in the Gastrocnemius Muscle
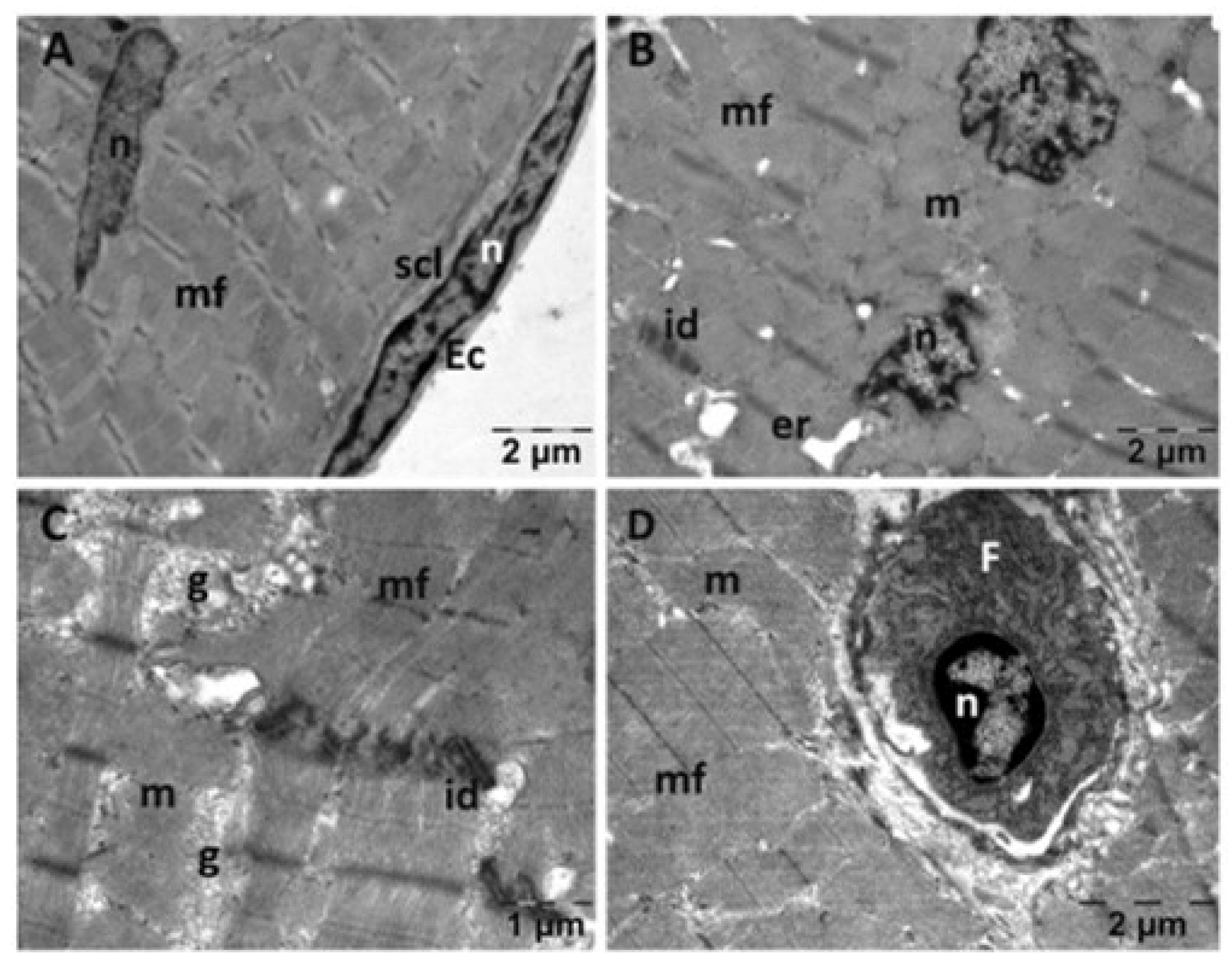
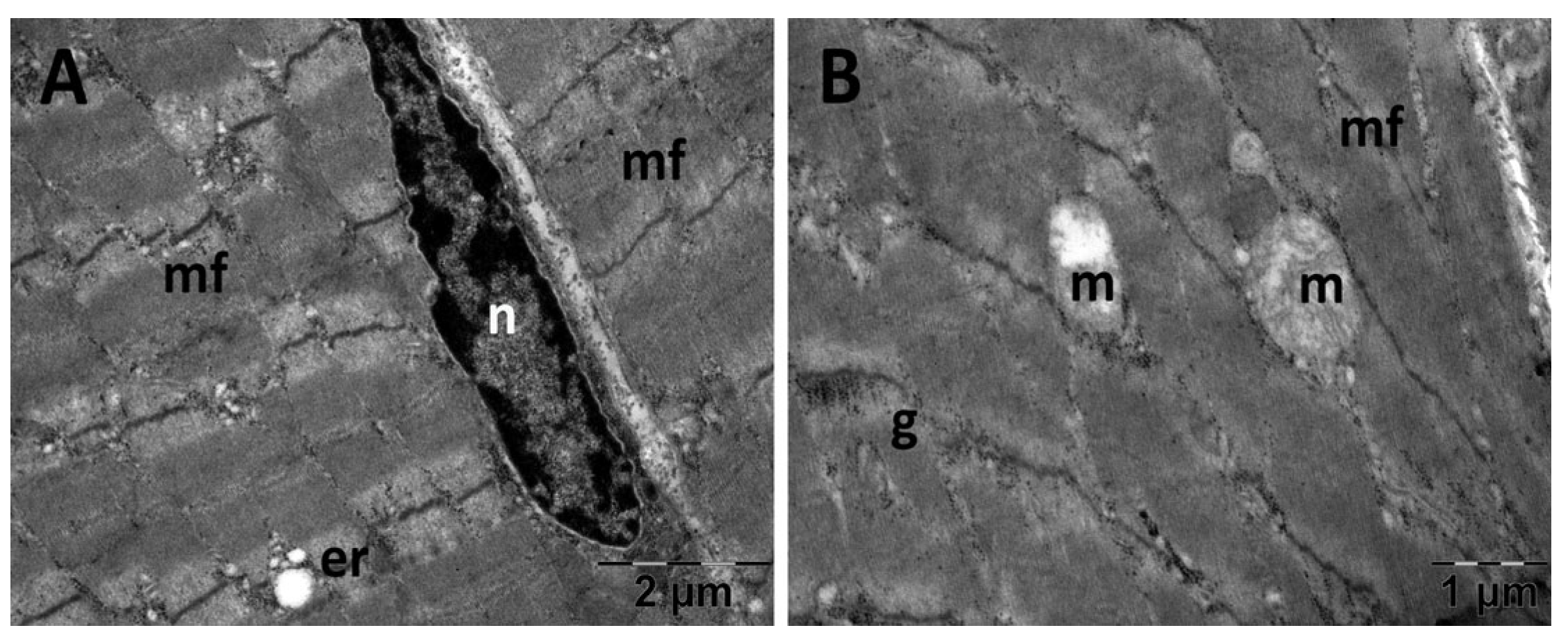
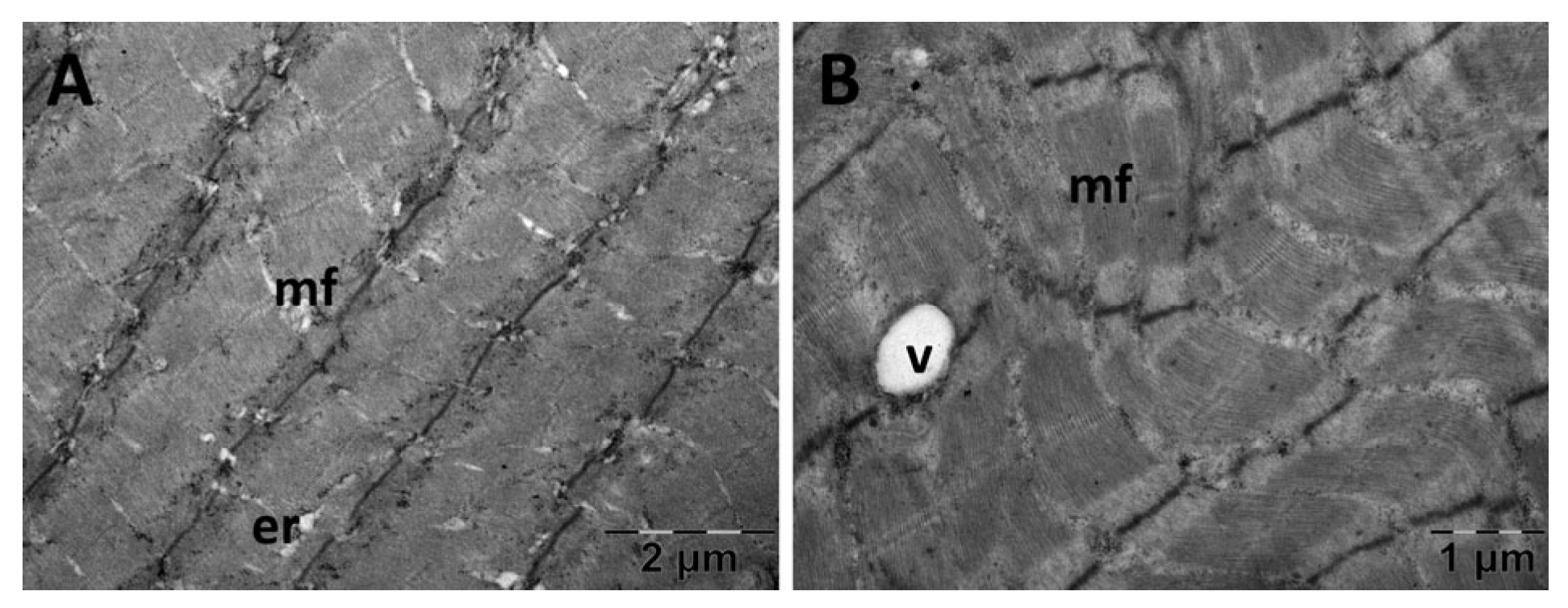
3.5.2. Muscle Transmission Electron Microscopy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arazi, H.; Eghbali, E.; Suzuki, K. Creatine Supplementation, Physical Exercise and Oxidative Stress Markers: A Review of the Mechanisms and Effectiveness. Nutrients 2021, 13, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, T.; Muraoka, I. Exercise-Induced Oxidative Stress and the Effects of Antioxidant Intake from a Physiological Viewpoint. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, S.K.; Deminice, R.; Ozdemir, M.; Yoshihara, T.; Bomkamp, M.P.; Hyatt, H. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: Friend or foe? J. Sport Health Sci. 2020, 9, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Effects of Exercise-Induced ROS on the Pathophysiological Functions of Skeletal Muscle. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 3846122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atakan, M.M.; Li, Y.; Kosar, S.N.; Turnagol, H.H.; Yan, X. Evidence-Based Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training on Exercise Capacity and Health: A Review with Historical Perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeting, A.J.; Cormack, S.J.; Morgan, S.; Aughey, R.J. When Is a Sprint a Sprint? A Review of the Analysis of Team-Sport Athlete Activity Profile. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, W.W.; Kraus, W.E.; Powell, K.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Janz, K.F.; Jakicic, J.M.; Troiano, R.P.; Sprow, K.; Torres, A.; Piercy, K.L.; et al. High-Intensity Interval Training for Cardiometabolic Disease Prevention. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quindry, J.C.; Franklin, B.A.; Chapman, M.; Humphrey, R.; Mathis, S. Benefits and Risks of High-Intensity Interval Training in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2019, 123, 1370–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suarez, V.J.; Bustamante-Sanchez, A.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Martinez-Guardado, I.; Martin-Rodriguez, A.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. Antioxidants and Sports Performance. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Chuang, C.C.; Yang, W.; Zuo, L. Redox Mechanism of Reactive Oxygen Species in Exercise. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulios, A.; Papanikolaou, K.; Draganidis, D.; Tsimeas, P.; Chatzinikolaou, A.; Tsiokanos, A.; Jamurtas, A.Z.; Fatouros, I.G. The Effects of Antioxidant Supplementation on Soccer Performance and Recovery: A Critical Review of the Available Evidence. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, J.; Aboul-Enein, B.H.; Duchnik, E.; Marchlewicz, M. Antioxidative properties of phenolic compounds and their effect on oxidative stress induced by severe physical exercise. J. Physiol. Sci. 2022, 72, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somerville, V.; Bringans, C.; Braakhuis, A. Polyphenols and Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 1589–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojarczuk, A.; Dzitkowska-Zabielska, M. Polyphenol Supplementation and Antioxidant Status in Athletes: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2022, 15, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Lazaro, D.; Dominguez-Ortega, C.; Busto, N.; Santamaria-Pelaez, M.; Roche, E.; Gutierez-Abejon, E.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J. Influence of N-Acetylcysteine Supplementation on Physical Performance and Laboratory Biomarkers in Adult Males: A Systematic Review of Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadowski, M.; Zawieja, E.; Chmurzynska, A. The impact of N-acetylcysteine on lactate, biomarkers of oxidative stress, immune response, and muscle damage: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e70198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, K.; Braakhuis, A. Performance and Side Effects of Supplementation with N-Acetylcysteine: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 1619–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeshpurkar, A.; Saluja, A.K. The Pharmacological Potential of Rutin. Saudi Pharm J 2017, 25, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, M.; Morand, P.C.; Levillain, P.; Lemonnier, A. Improved Fluorometric Determination of Malonaldehyde. Clin. Chem. 1991, 37/7, 1273–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.-L. Measurement of Protein Thiol Groups and Glutathione in Plasma. Methods Enzymol. 1994, 233, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vats, P.; Singh, S.N.; Singh, S.B. Glutathione Metabolism under High-Altitude Stress and Effect of Antioxidant Supplementation. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2008, 79, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koval’skii, I.V.; Krasnyuk, I.I.; Krasnyuk, I.I.; Nikulina, O.I.; Belyatskaya, A.V.; Kharitonov, Y.Y.; Feldman, N.B.; Lutsenko, S.V. Mechanisms of Rutin Pharmacological Action (Review). Pharm. Chem. J. 2014, 48, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, A.J.; Tan, Y.; Li, L.; Chang, J.; Syrris, P.; Hessabi, M.; Rahbar, M.H.; Willerson, J.T.; Cheong, B.Y.; Liu, C.Y.; et al. Hypertrophy Regression With N-Acetylcysteine in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HALT-HCM): A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Pilot Study. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arica, V.; Demir, I.H.; Tutanc, M.; Basarslan, F.; Arica, S.; Karcoiglu, M.; Ozturk, H.; Nacar, A. N-acetylcysteine prevents doxorubucine-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2013, 32, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oluranti, O.I.; Alabi, B.A.; Michael, O.S.; Ojo, A.O.; Fatokun, B.P. Rutin prevents cardiac oxidative stress and inflammation induced by bisphenol A and dibutyl phthalate exposure via NRF-2/NF-kappaB pathway. Life Sci. 2021, 284, 119878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umarani, V.; Muvvala, S.; Ramesh, A.; Lakshmi, B.V.; Sravanthi, N. Rutin potentially attenuates fluoride-induced oxidative stress-mediated cardiotoxicity, blood toxicity and dyslipidemia in rats. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2015, 25, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, T.; Khan, I.; Iqbal, H.; Usman, S.; Naeem, N.; Faizi, S.; Salim, A. Rutin and quercetagetin enhance the regeneration potential of young and aging bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the rat infarcted myocardium. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2023, 478, 1759–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Lv, J.; Ni, H. Rutin alleviates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury in myocardial cells by up-regulating SIRT1 expression. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 297, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.J.; Ha, Y.M.; Jin, Y.C.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Seo, H.G.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, S.S.; Kim, Y.S.; et al. Rutin from Lonicera japonica inhibits myocardial ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis in vivo and protects H9c2 cells against hydrogen peroxide-mediated injury via ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt signals in vitro. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siti, H.N.; Jalil, J.; Asmadi, A.Y.; Kamisah, Y. Roles of rutin in cardiac remodeling. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lan, Z.; Ming, L. Mo Yanzhi Protective Effects of Rutin on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Heart Injury in Mice. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 43, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellem, L.; Srour, B.; Javaux, G.; Chazelas, E.; Chassaing, B.; Viennois, E.; Debras, C.; Salamé, C.; Druesne-Pecollo, N.; Esseddik, Y.; et al. Food Additive Emulsifiers and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in the NutriNet-Santé Cohort: Prospective Cohort Study. BMJ 2023, 382, e076058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunturk, E.E.; Yucel, B.; Gunturk, I.; Yazici, C.; Yay, A.; Kose, K. The effects of N-acetylcysteine on cisplatin induced cardiotoxicity. Bratisl. Med. J. 2019, 120, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi, Y. Exercise Is a Double-Edged Sword for Endothelial Function. Hypertens. Res. 2015, 39, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosun, M.; Olmez, H.; Unver, E.; Arslan, Y.K.; Cimen, F.K.; Ozcicek, A.; Aktas, M.; Suleyman, H. Oxidative and pro-inflammatory lung injury induced by desflurane inhalation in rats and the protective effect of rutin. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 30, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Li, A.; Gong, C.; Ning, X.; Wang, Z. Protective effect of rutin against bleomycin induced lung fibrosis: Involvement of TGF-beta1/alpha-SMA/Col I and III pathway. Biofactors 2020, 46, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, V.; Yuksel, V.; Chousein, S.; Tastekin, E.; Iscan, S.; Sagiroglu, G.; Canbaz, S.; Sunar, H. The effects of sildenafil and n-acetylcysteine on ischemia and reperfusion injury in gastrocnemius muscle and femoral artery endothelium. Vascular 2015, 23, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





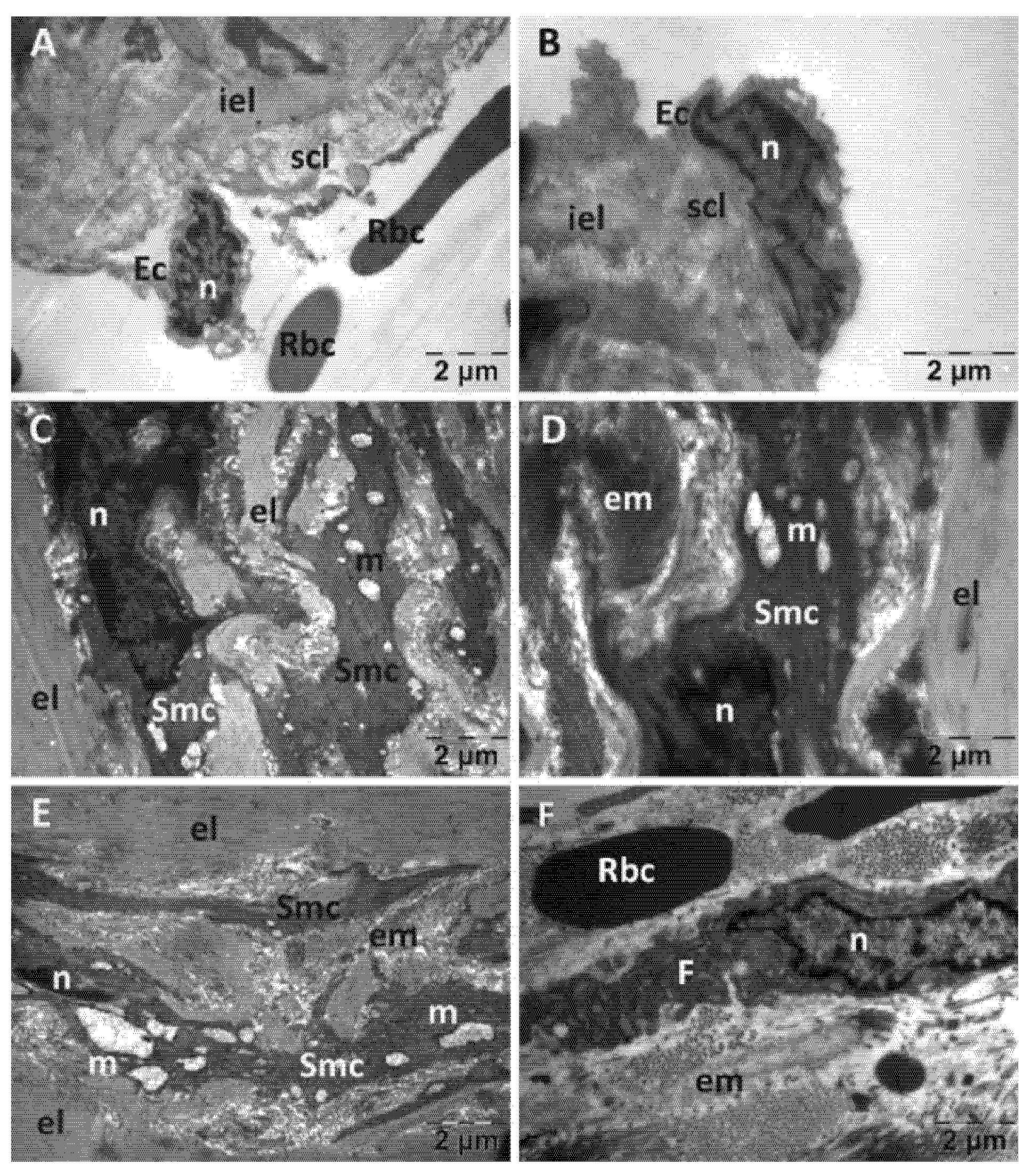




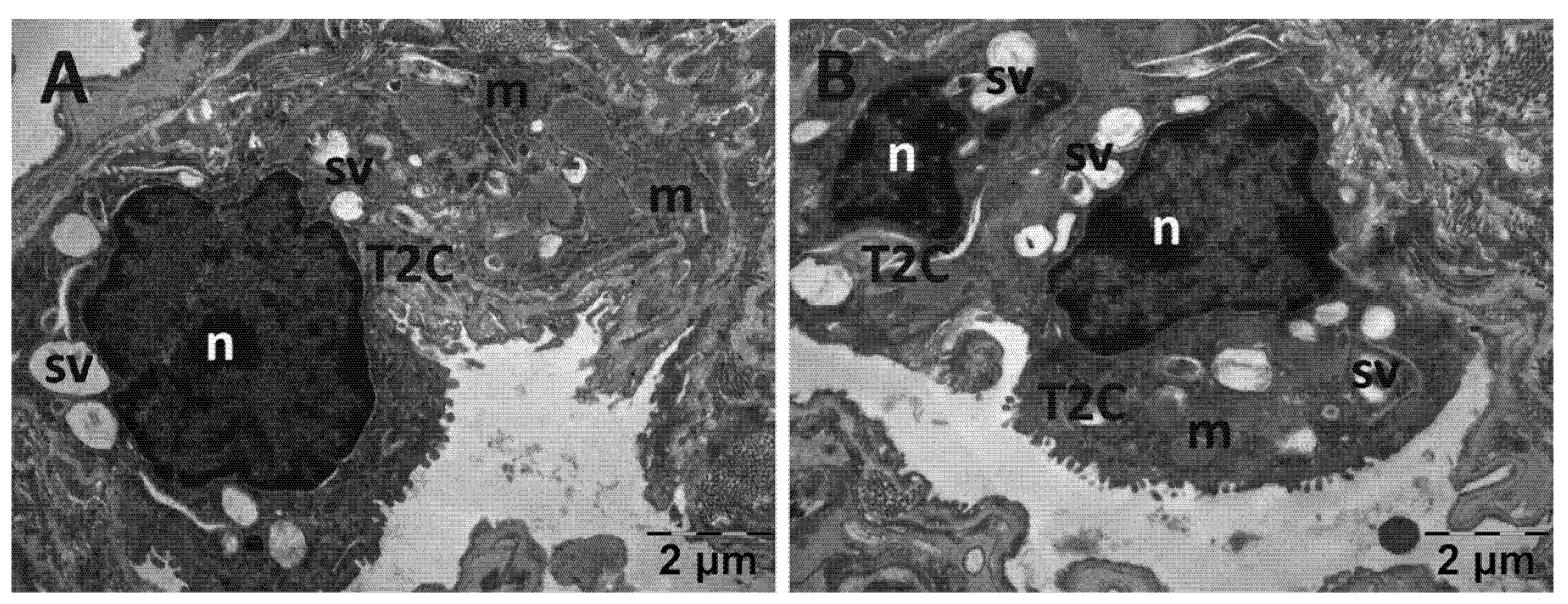



| Week | Belt Velocity (cm/s) | Duration (min) | Frequency (days/week) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 | 5 | 5 |
| 2 | 40 | 5 | 5 |
| 3 | 50 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 50 | 5 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moldovan, M.; Muntean, M.; Schauer, S.A.; Moldovan, R.; Mitrea, D.-R. Oxidative Stress and Ultrastructural Analysis in Heart, Aorta, Skeletal Muscle and Lung of Rats Treated with N-Acetylcysteine or Rutin After Sprint Running. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2025, 10, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020206
Moldovan M, Muntean M, Schauer SA, Moldovan R, Mitrea D-R. Oxidative Stress and Ultrastructural Analysis in Heart, Aorta, Skeletal Muscle and Lung of Rats Treated with N-Acetylcysteine or Rutin After Sprint Running. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2025; 10(2):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020206
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoldovan, Mădălina, Mara Muntean, Sandra Andrea Schauer, Remus Moldovan, and Daniela-Rodica Mitrea. 2025. "Oxidative Stress and Ultrastructural Analysis in Heart, Aorta, Skeletal Muscle and Lung of Rats Treated with N-Acetylcysteine or Rutin After Sprint Running" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 10, no. 2: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020206
APA StyleMoldovan, M., Muntean, M., Schauer, S. A., Moldovan, R., & Mitrea, D.-R. (2025). Oxidative Stress and Ultrastructural Analysis in Heart, Aorta, Skeletal Muscle and Lung of Rats Treated with N-Acetylcysteine or Rutin After Sprint Running. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 10(2), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10020206








