Real-Time Precision in 3D Concrete Printing: Controlling Layer Morphology via Machine Vision and Learning Algorithms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
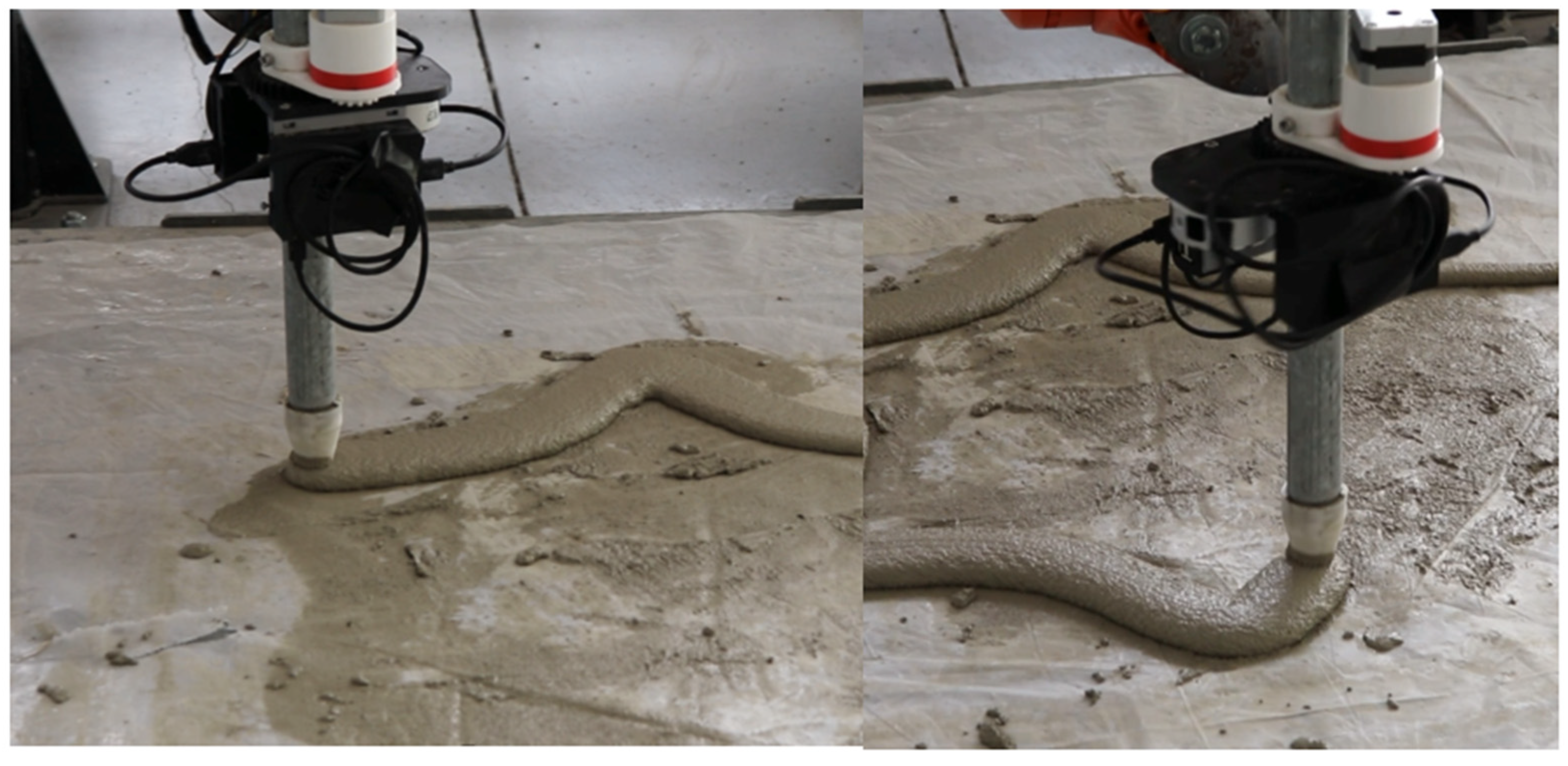
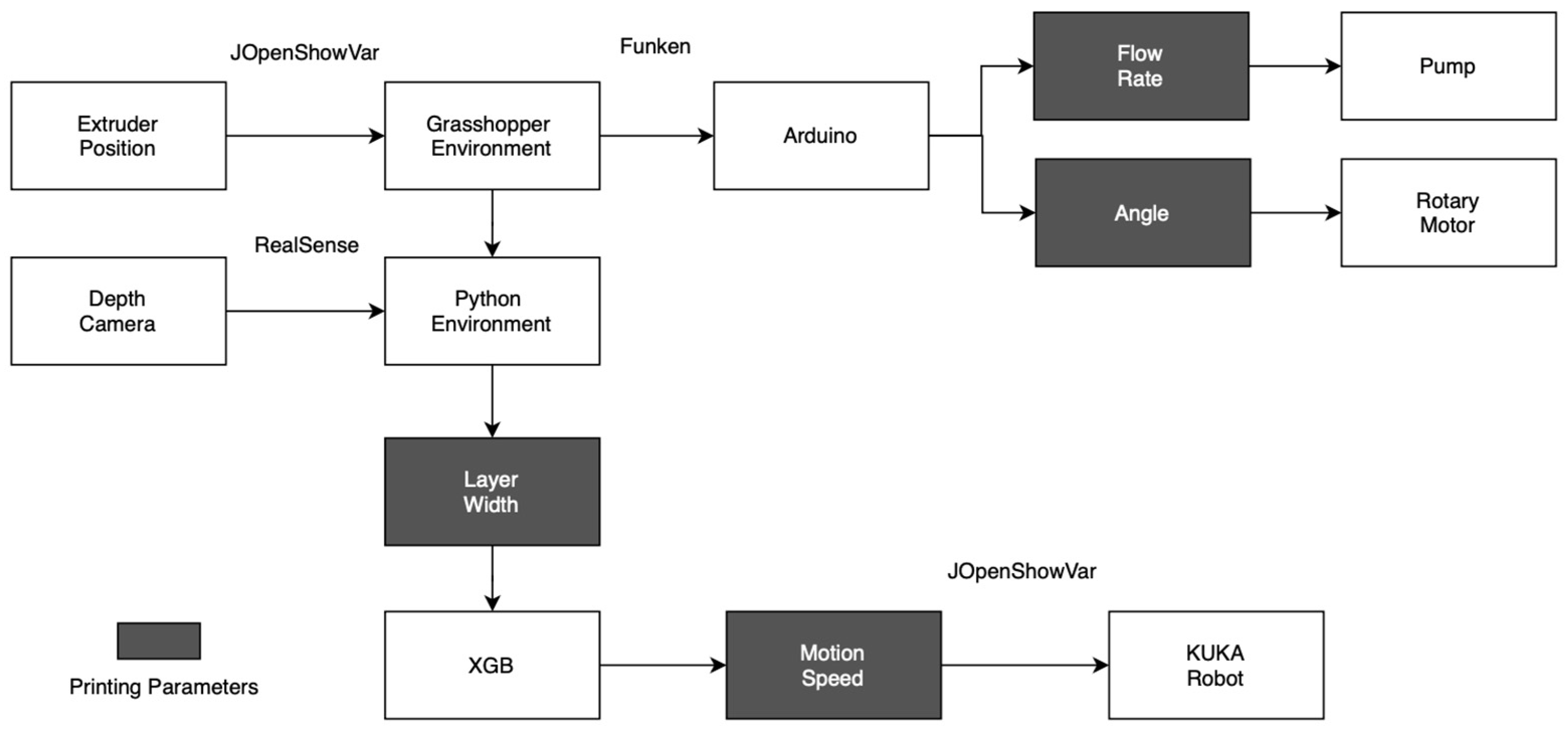
2.1. Fabrication Framework
2.2. Machine Learning Framework
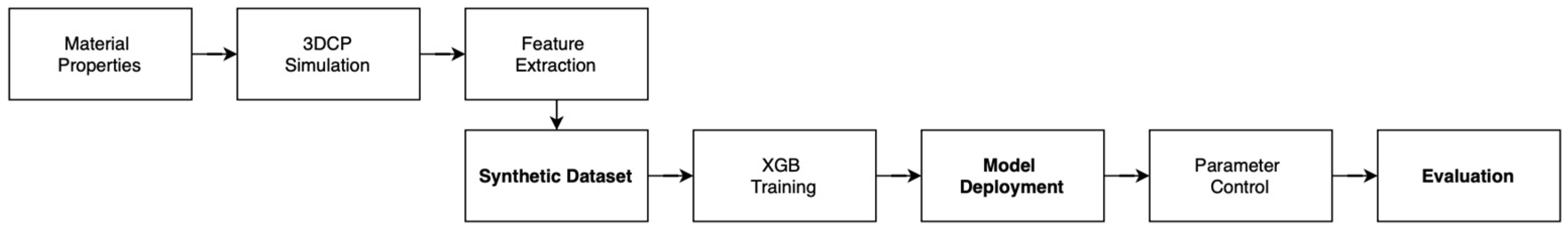
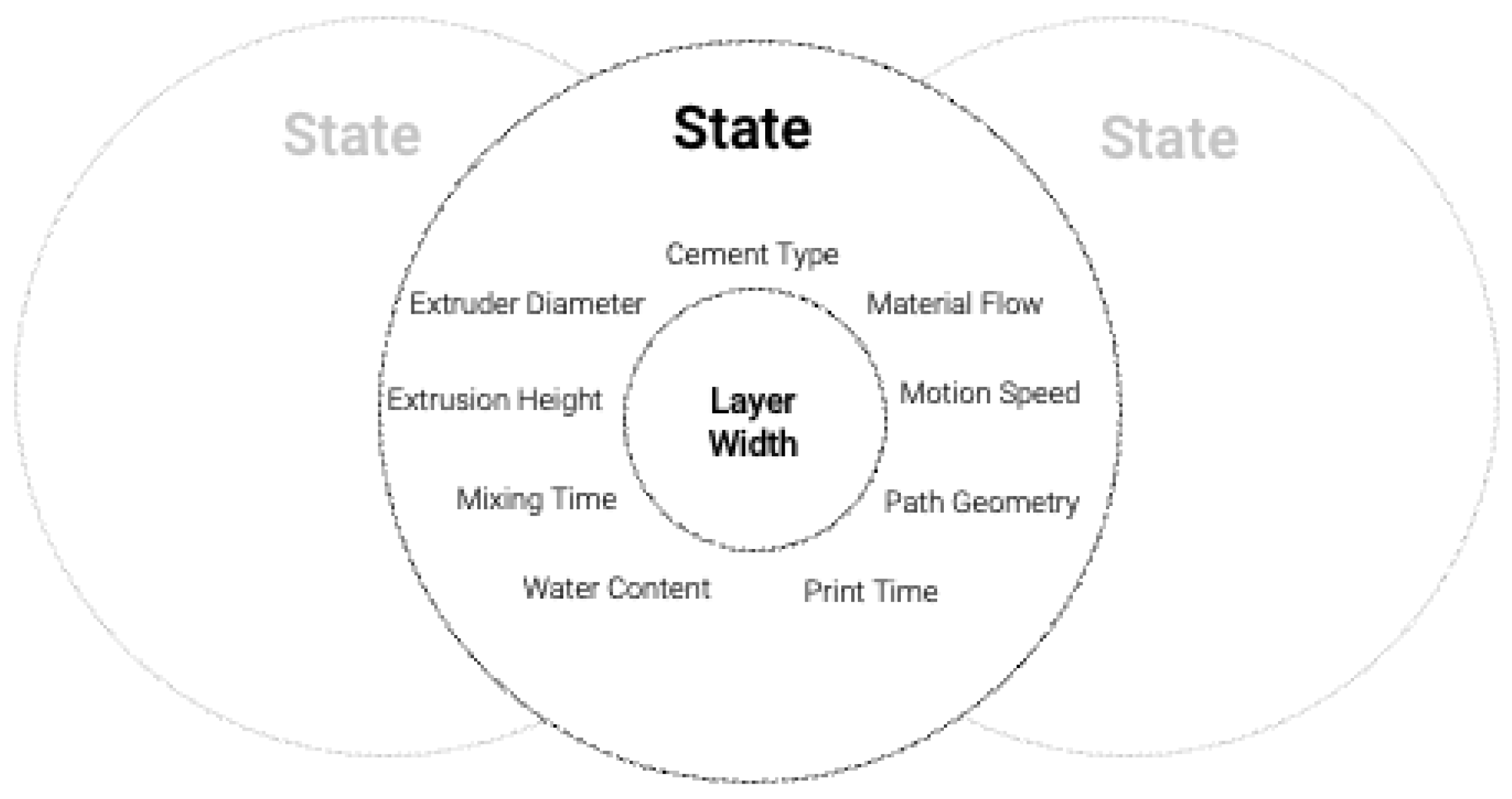
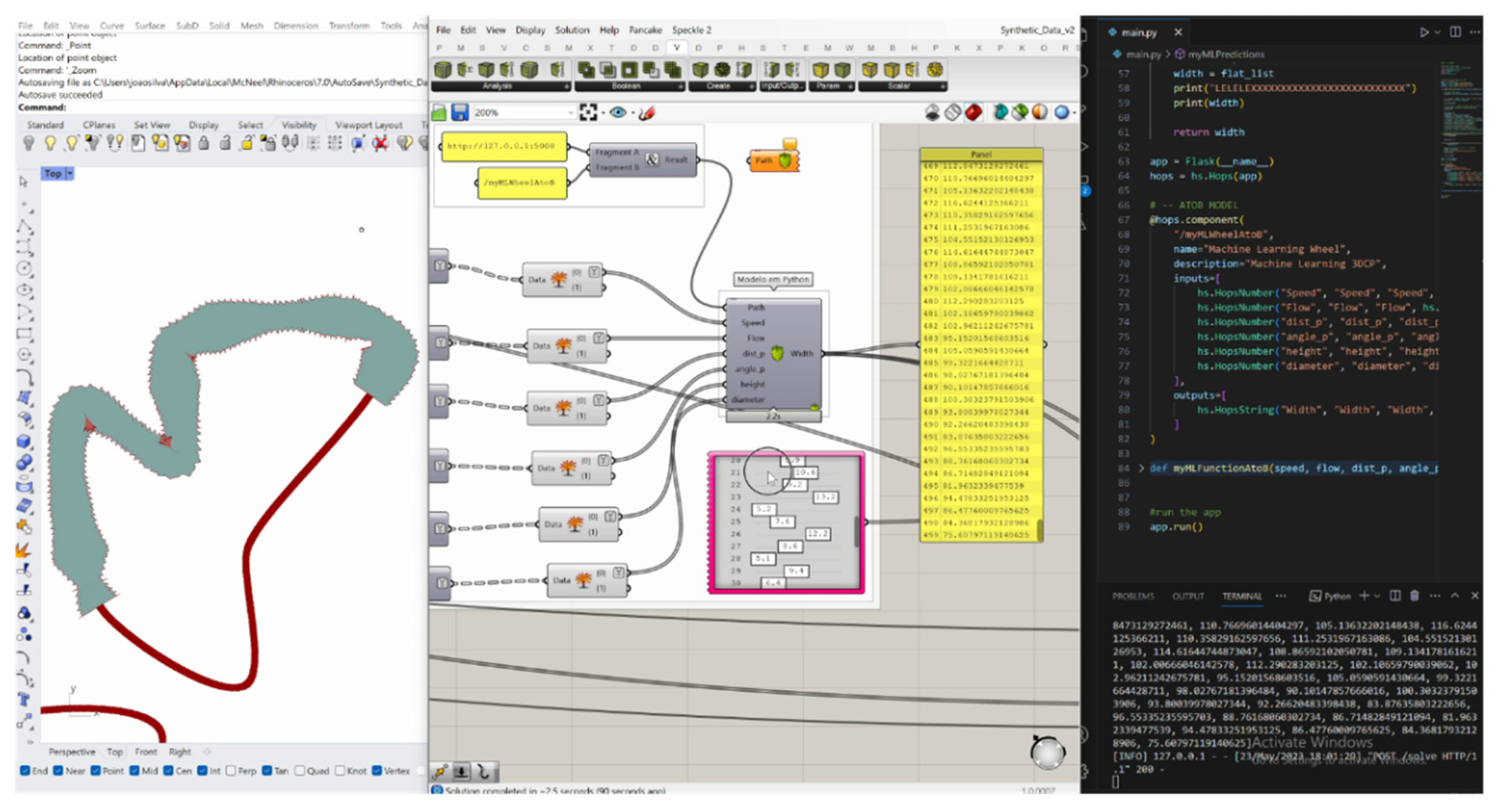
2.2.1. Data Pipeline
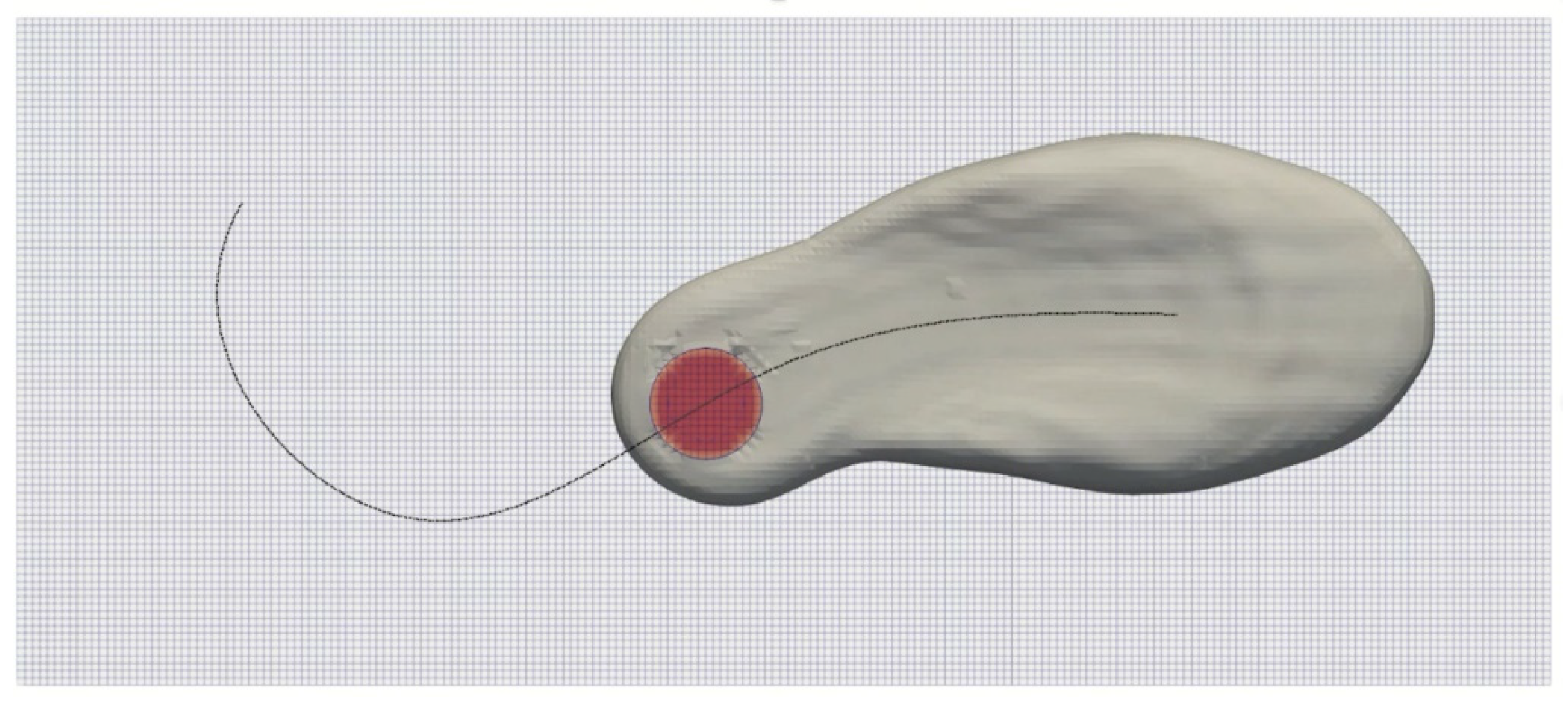
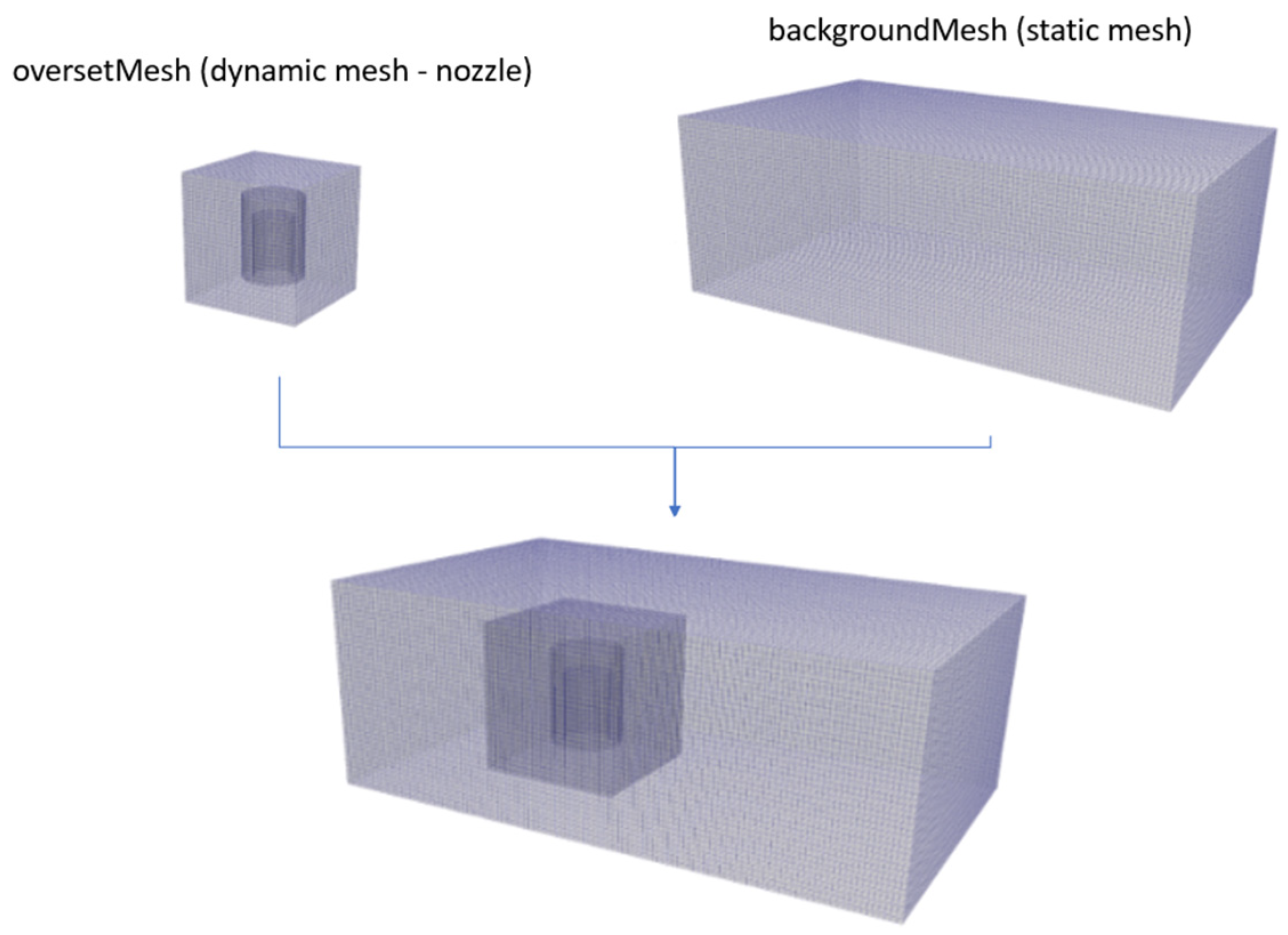
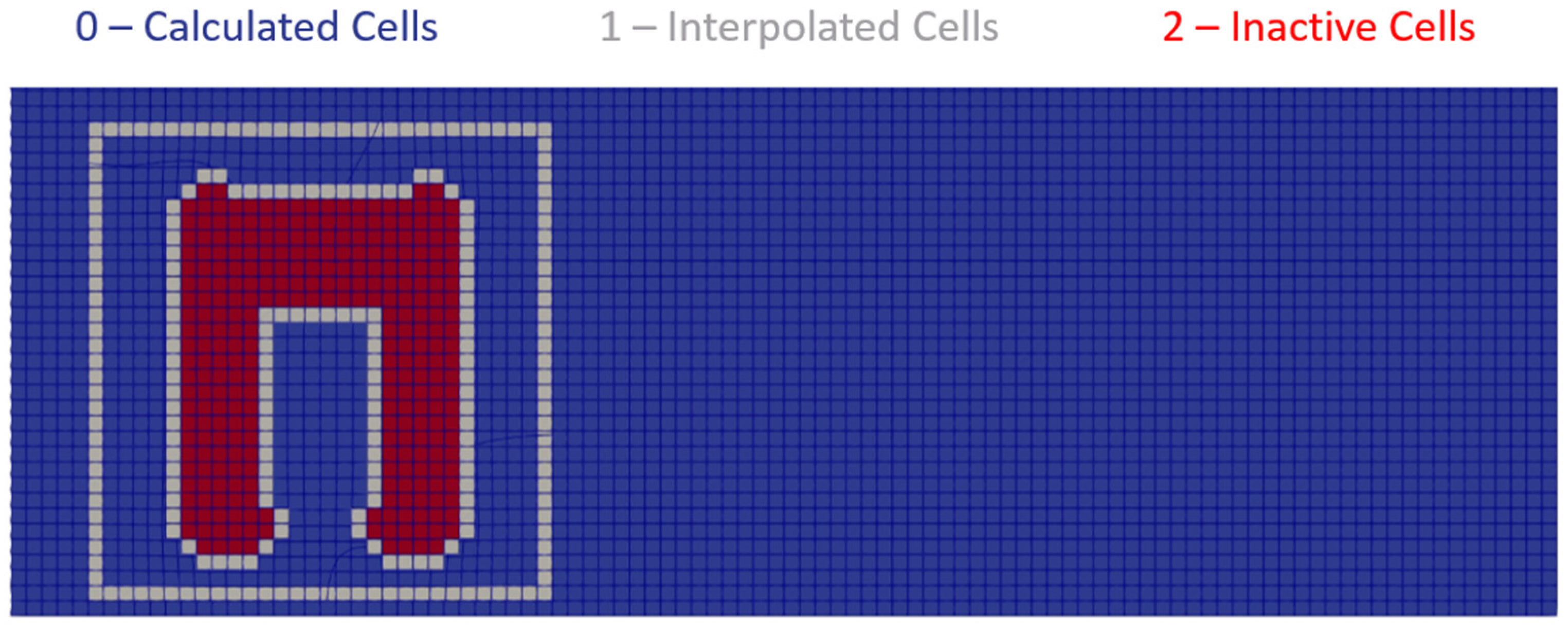
2.2.2. Numerical Simulation
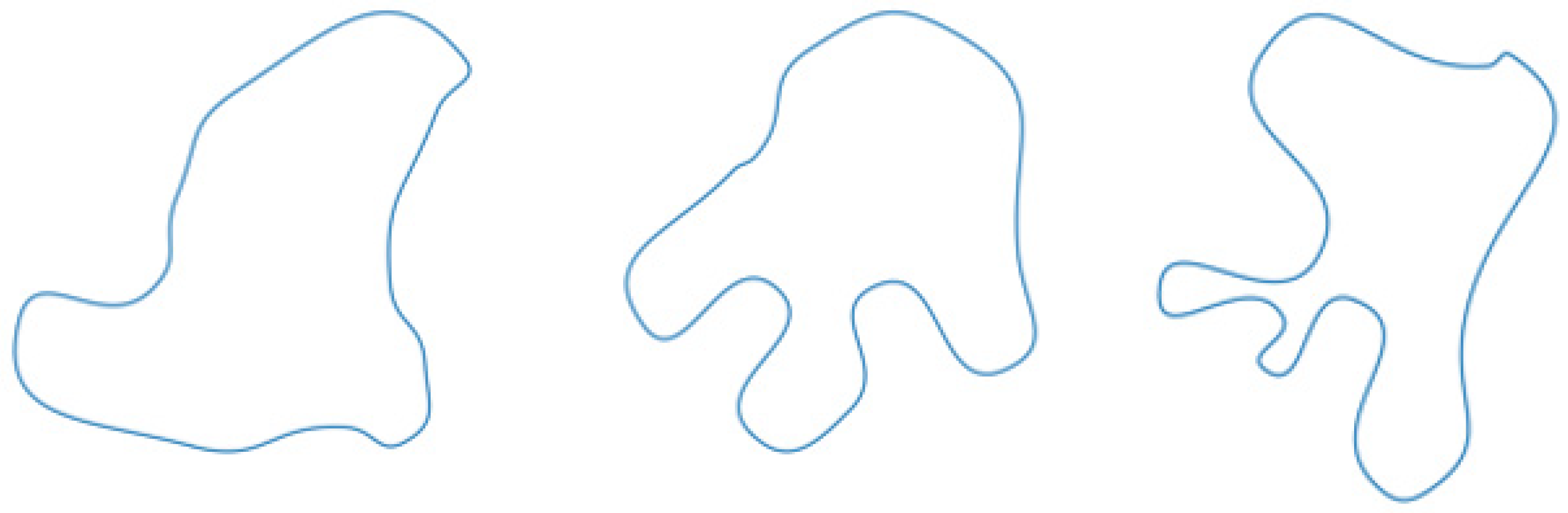
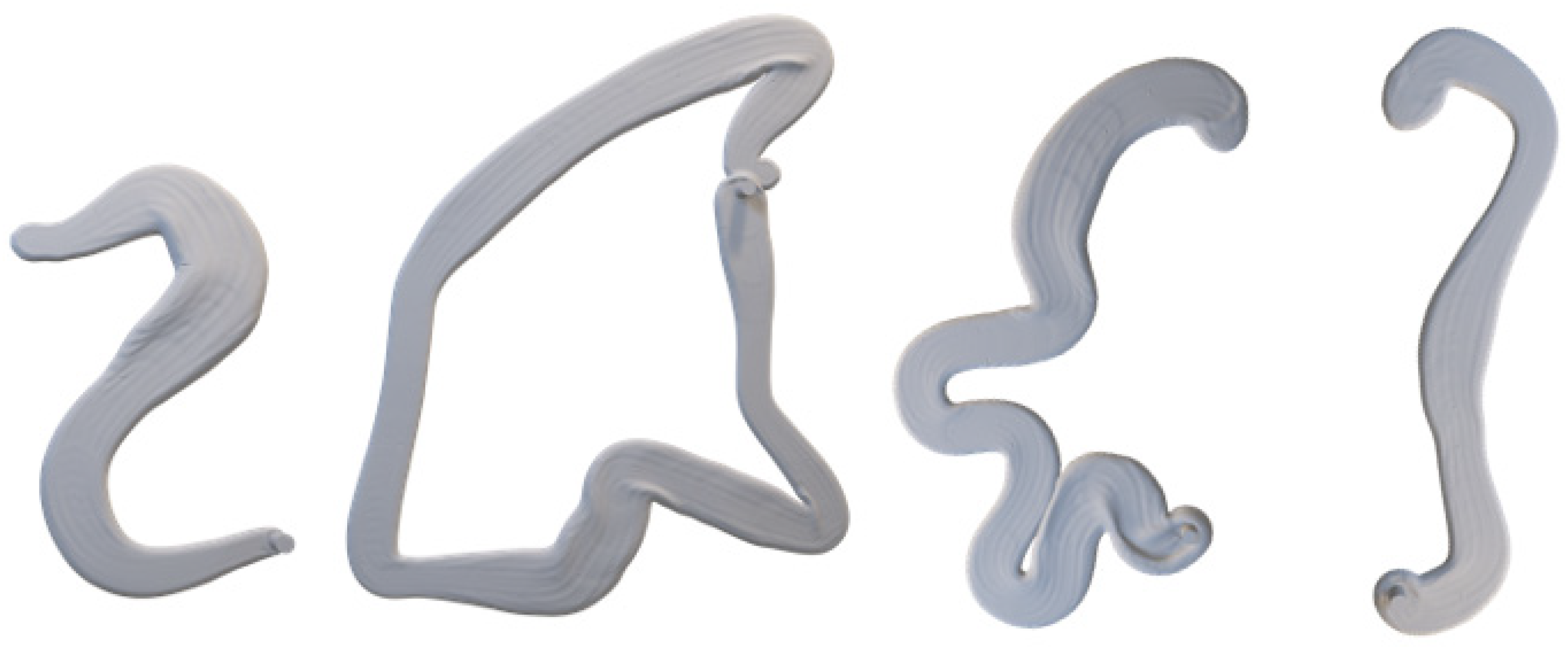
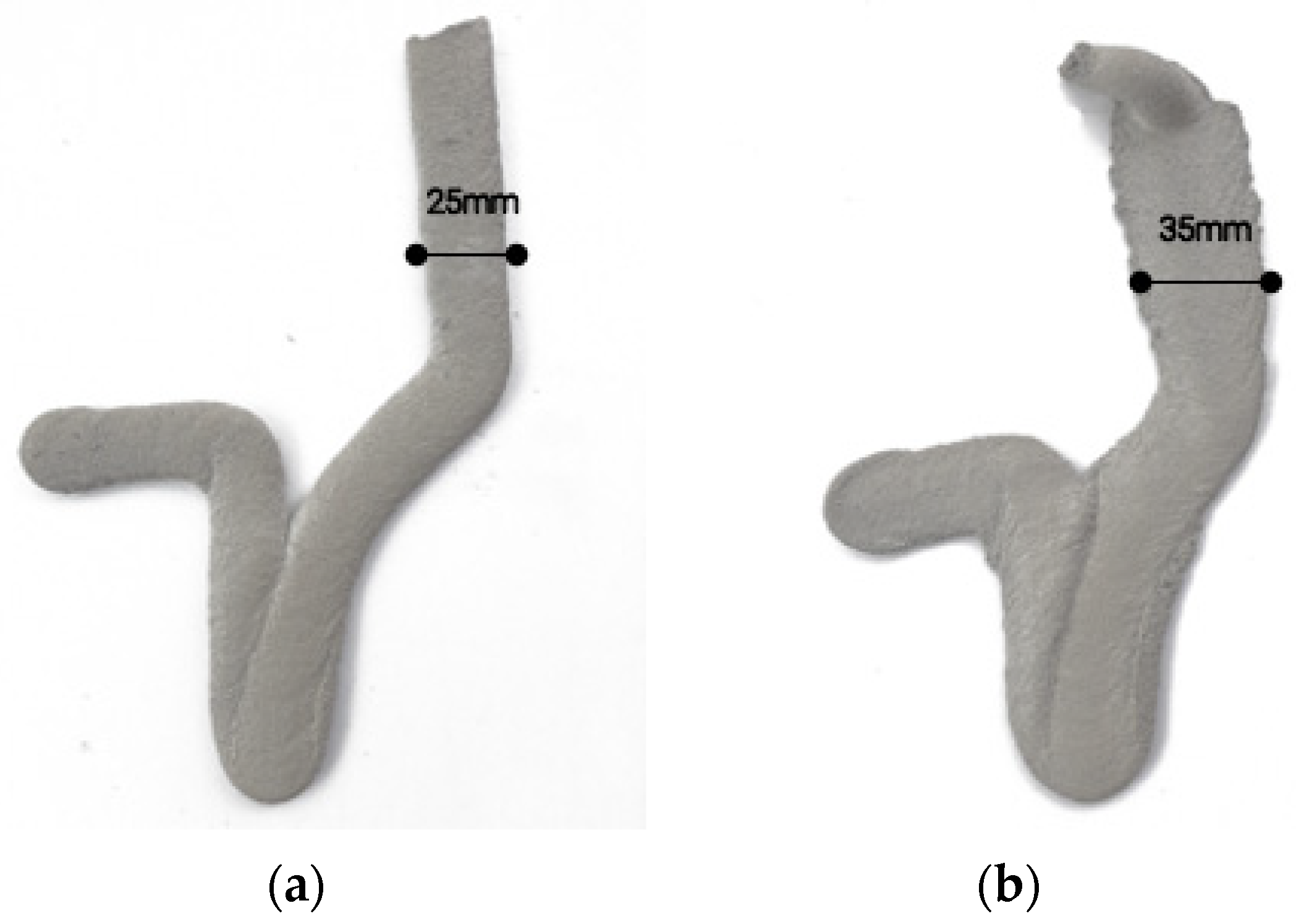
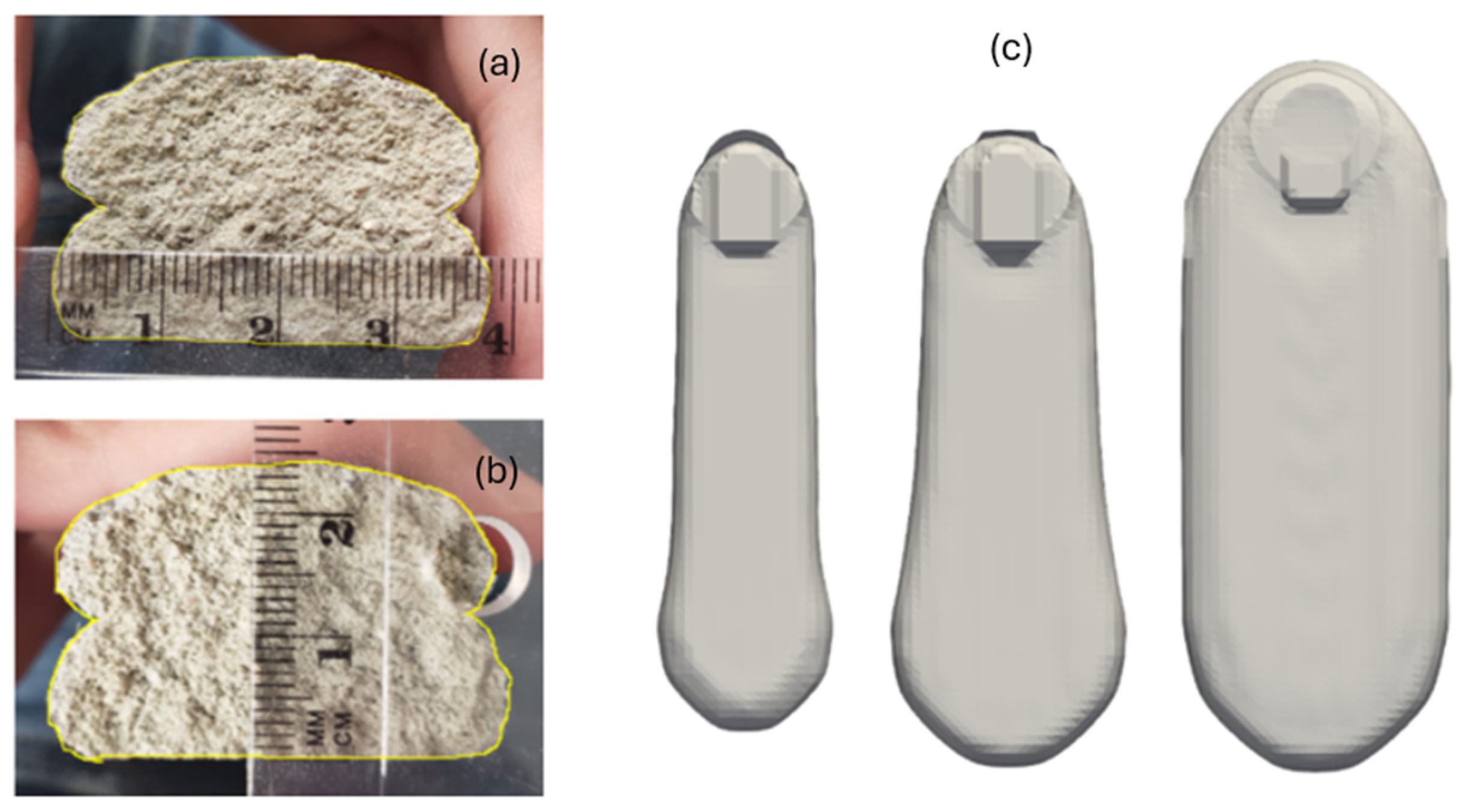
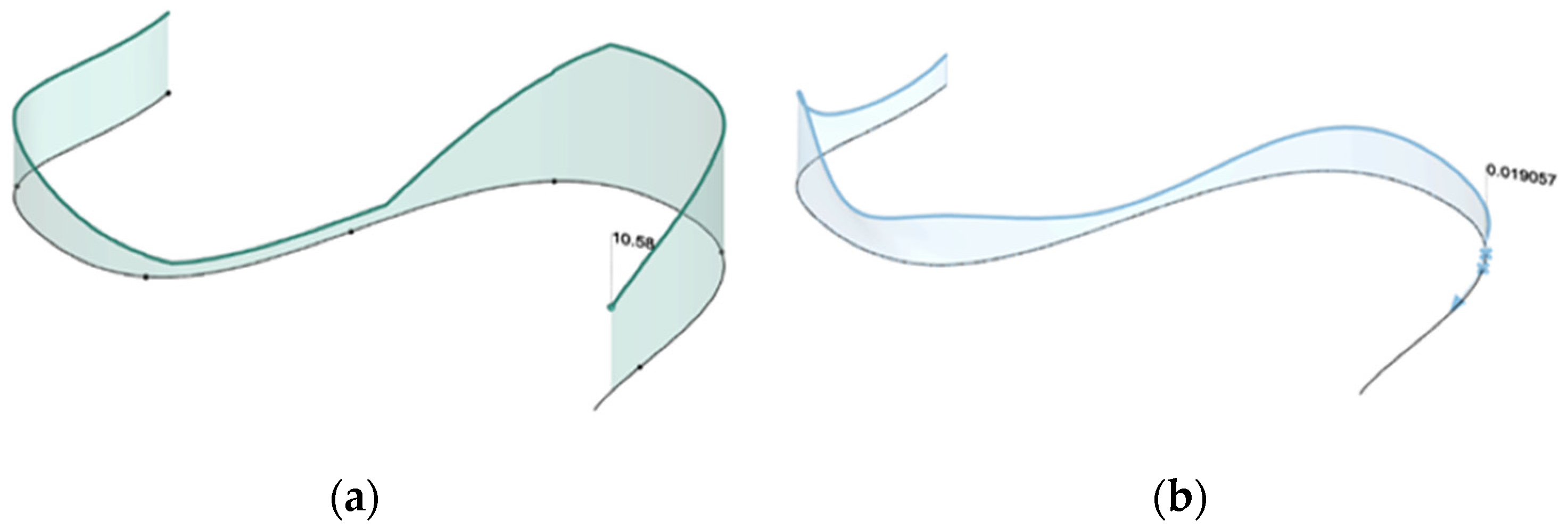
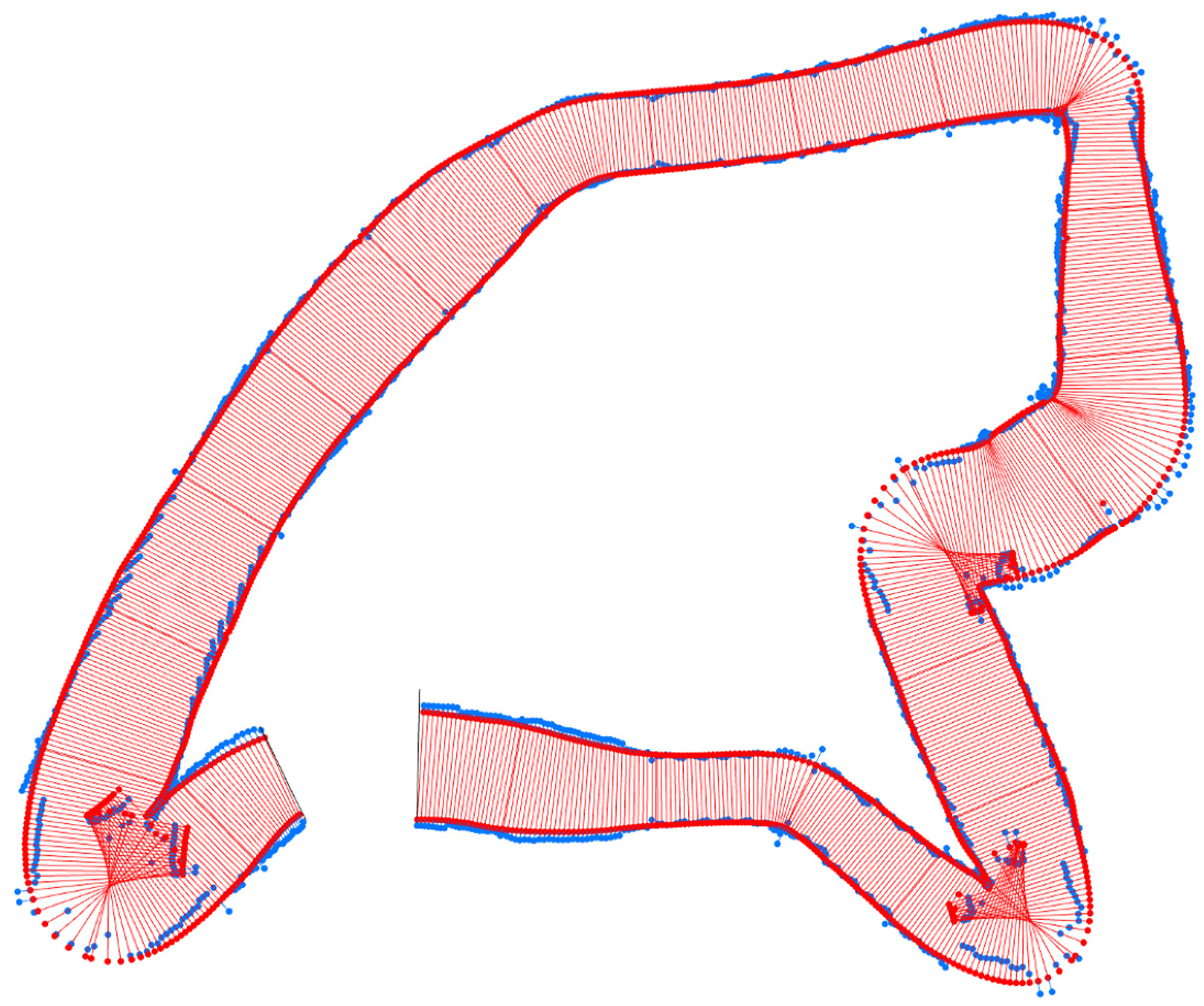
2.2.3. Dataset Generation
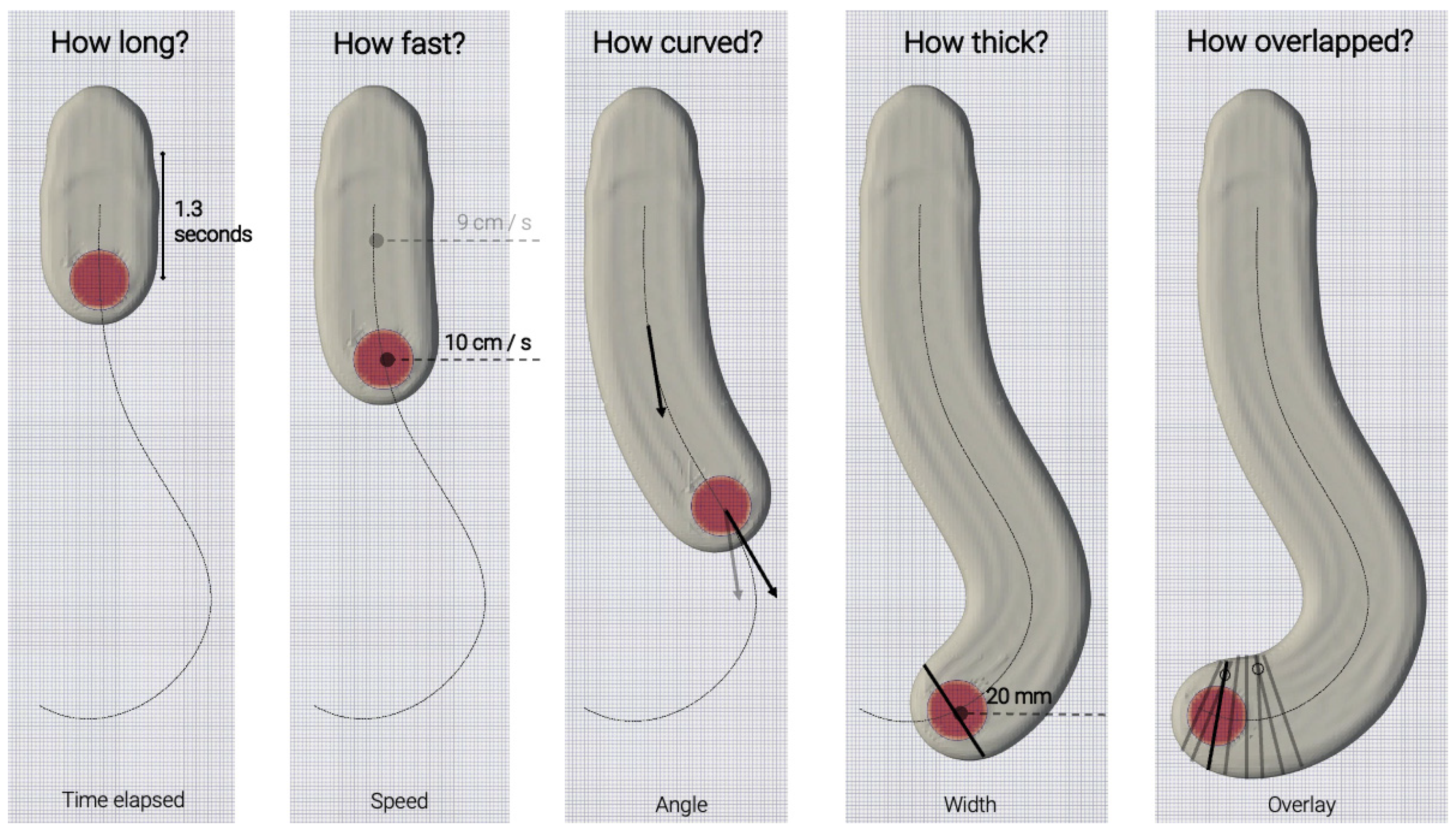
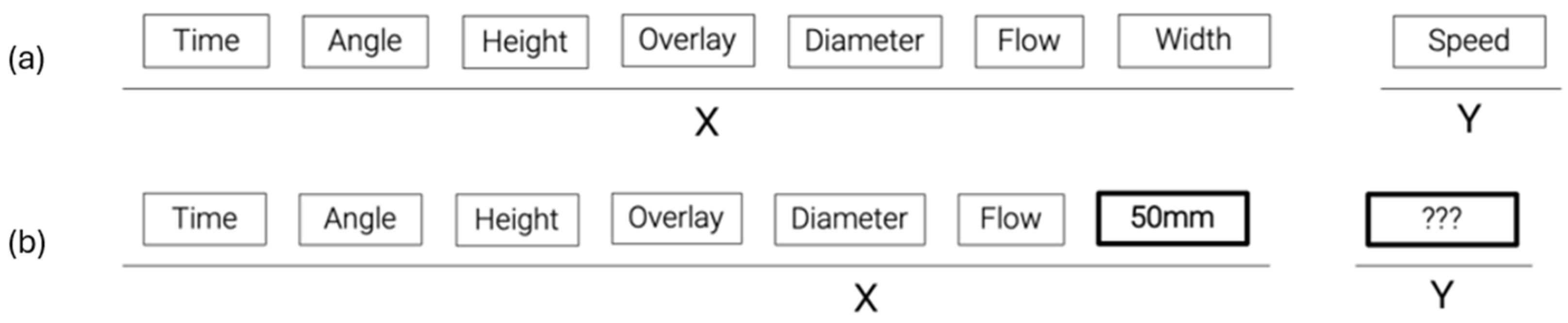
- Time (s)—The time elapsed since the start of the print until reaching that position;
- Speed (cm/s)—The motion speed of the extruder at that location;
- Flow (m/s)—The material flow at that location;
- Distance (mm)—The distance between that location and the previous location sampled in the dataset;
- Angle (degrees)—The difference in angle between the tangent vector at that location and the previous datapoint (important to distinguish between the type of motion being executed—straight, curved, etc.);
- Height (cm)—The distance of the extruder tip to the deposition plane (printing base or previous layer);
- Diameter (cm)—The diameter of the extruder;
- Width (cm)—The width of the layer at that location;
- Overlay—The number of intersections between a perpendicular line to the printing path drawn at that location and previous locations.
3. Results and Discussion
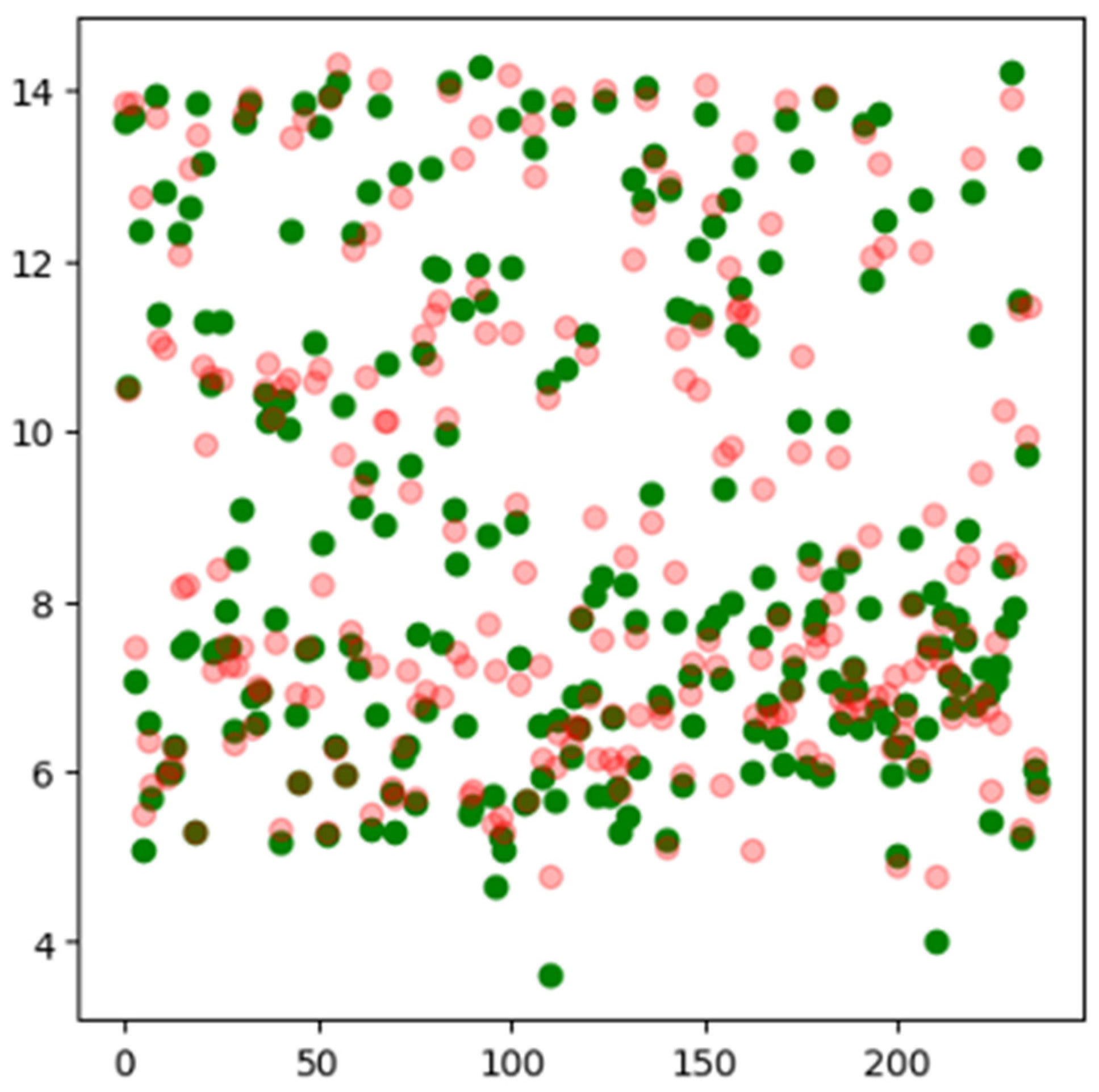
3.1. Algorithm: Training and Inference
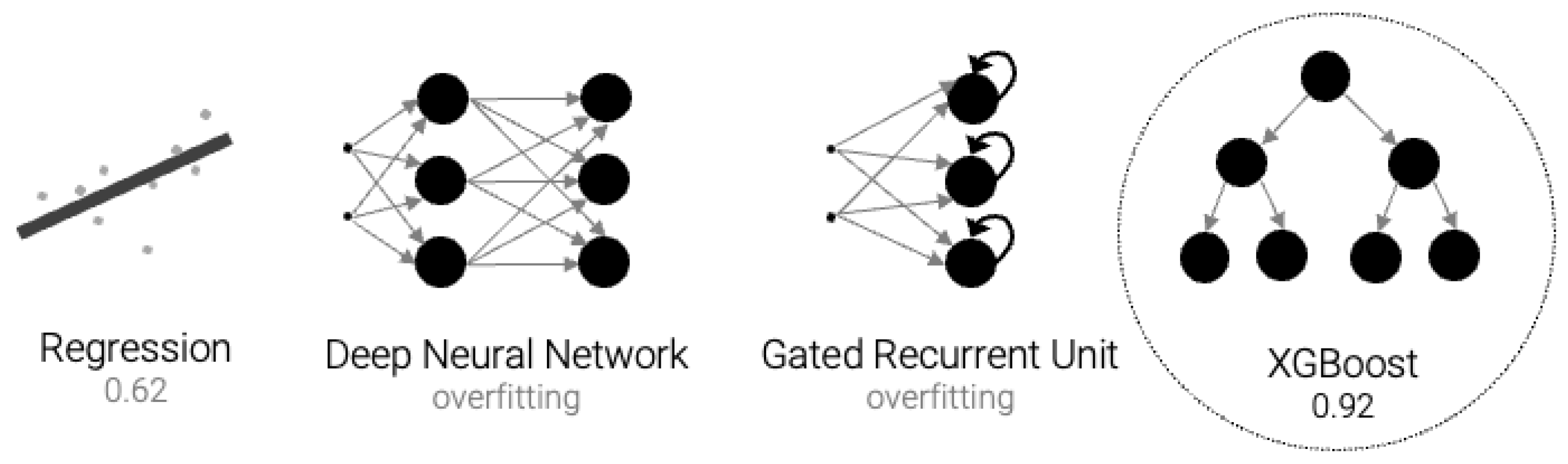
3.1.1. Model Architecture
3.1.2. Model Application
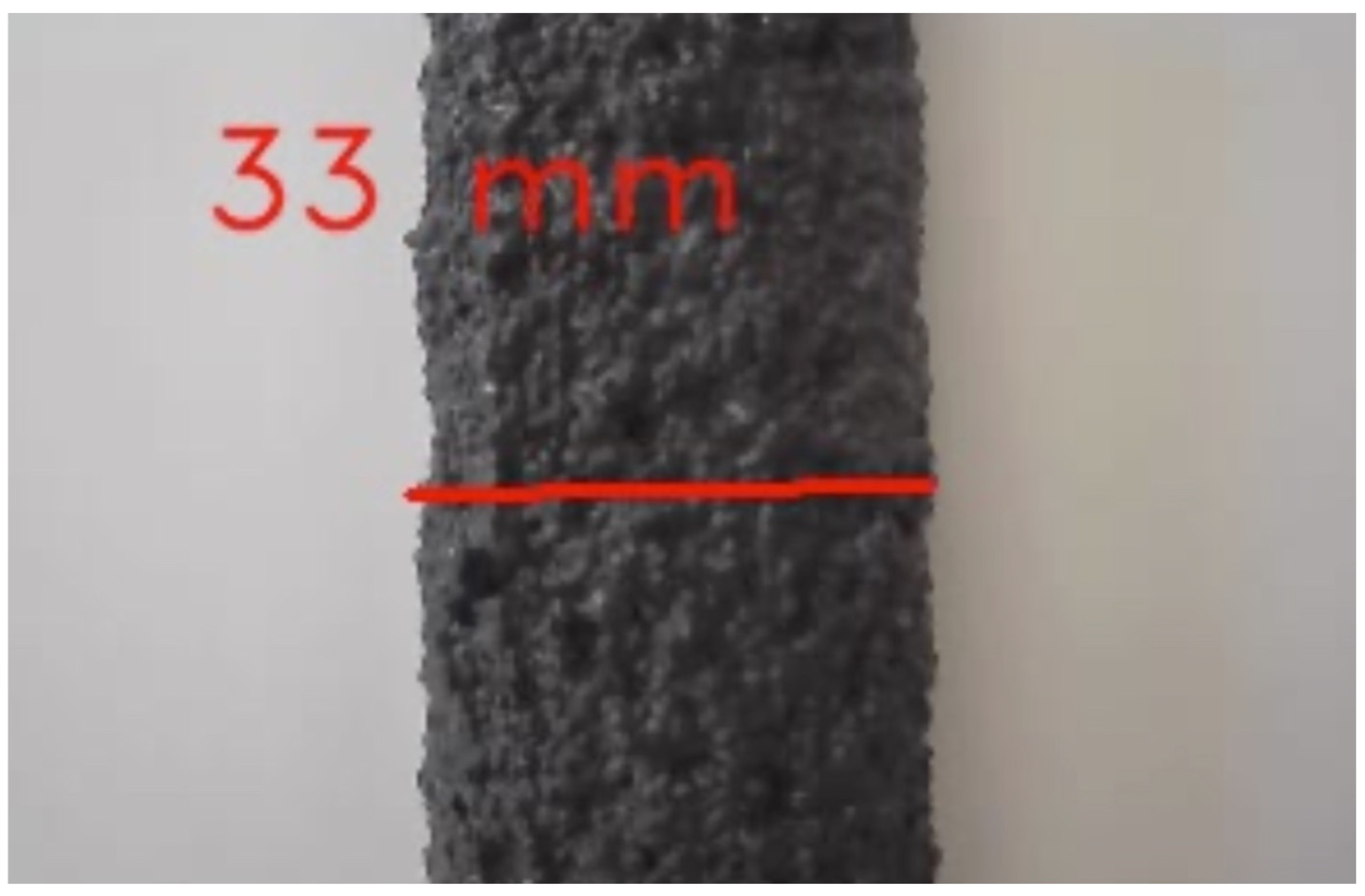
3.2. Computer Vision System
3.3. Real-Time Deployment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Schutter, G.; Lesage, K.; Mechtcherine, V.; Nerella, V.N.; Habert, G.; Agusti-Juan, I. Vision of 3D printing with concrete—Technical, economic and environmental potentials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 112, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Sanchez, F.; Zhou, H. 3-D printing of concrete: Beyond horizons. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 133, 106070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.C.; van Zijl, G.P.A.G.; Gibson, I. A review of 3D concrete printing systems and materials properties: Current status and future research prospects. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2018, 24, 784–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhdar, Y.; Tuck, C.; Binner, J.; Terry, A.; Goodridge, R. Additive manufacturing of advanced ceramic materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 116, 100736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baduge, S.K.; Navaratnam, S.; Abu-Zidan, Y.; McCormack, T.; Nguyen, K.; Mendis, P.; Zhang, G.; Aye, L. Improving performance of additive manufactured (3D printed) concrete: A review on material mix design, processing, interlayer bonding, and reinforcing methods. Structures 2021, 29, 1597–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minář, J.; Pilnaj, D.; Uřičář, J.; Veselý, P.; Dušek, K. Application of solid-phase microextraction arrows for characterizing volatile organic compounds from 3D printing of acrylonitrile-styrene-acrylate filament. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1705, 464180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradski, G. The OpenCV Library. Dr. Dobb’s J. Softw. Tools 2000, 25, 122–125. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, G.; Nicholas, P. Encoded Images: Representational protocols for integrating cGANs in iterative computational design processes. In ACADIA 2020 Distributed Proximities: Proceedings of the 40th Annual Conference of the Association for Computer Aided Design in Architecture, Online, 24–30 October 2020; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 218–227. [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen, M.R.; Nicholas, P.; Tamke, M.; Gatz, S.; Sinke, Y.; Rossi, G. Towards machine learning for architectural fabrication in the age of industry 4.0. Int. J. Archit. Comput. 2020, 18, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, M.A.; Visan, A.I.; Ristoscu, C.; Mihailescu, I.N. Artificial neural network algorithms for 3D printing. Materials 2021, 14, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, G.D.; Sing, S.L.; Yeong, W.Y. A review on machine learning in 3D printing: Applications, potential, and challenges. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 63–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, G.L.; Goh, G.D.; Pan, J.W.; Teng, P.S.P.; Kong, P.W. Automated Service Height Fault Detection Using Computer Vision and Machine Learning for Badminton Matches. Sensors 2023, 23, 9759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golnabi, H.; Asadpour, A. Design and application of industrial machine vision systems. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2007, 23, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langeland, S.A. Automatic Error Detection in 3D Pritning Using Computer Vision. Master’s Thesis, The University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sutjipto, S.; Tish, D.; Paul, G.; Vidal-Calleja, T.; Schork, T. Towards Visual Feedback Loops for Robot-Controlled Additive Manufacturing. In Robotic Fabrication in Architecture, Art and Design 2018; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Peng, X.; Chen, Y. Fast and Accurate Defects Detection for Additive Manufactured Parts by Multispectrum and Machine Learning. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 10, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garfo, S.; Muktadir, M.A.; Yi, S. Defect Detection on 3D Print Products and in Concrete Structures Using Image Processing and Convolution Neural Network. J. Mechatron. Robot. 2020, 4, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delli, U.; Chang, S. Automated Process Monitoring in 3D Printing Using Supervised Machine Learning. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 26, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Remond, S.; Gallias, J.L. Influence of cement grouts composition on the rheological behaviour. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macosko, C.W. Rheology Principles, Measurements, and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Güneyisi, E.; Gesoglu, M.; Naji, N.; Ipek, S. Evaluation of the rheological behavior of fresh self-compacting rubberized concrete by using the Herschel-Bulkley and modified Bingham models. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2016, 16, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konan, N.A.; Rosenbaum, E.; Massoudi, M. On the Response of a Herschel–Bulkley Fluid Due to a Moving Plate. Polymers 2022, 14, 3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feys, D.; Verhoeven, R.; De Schutter, G. Evaluation of time independent rheological models applicable to fresh self-compacting concrete. Appl. Rheol. 2007, 17, 56244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenFOAM, The Open Source CFD Toolbox. Available online: https://www.openfoam.com/ (accessed on 11 April 2023).
- OpenFOAM: User Guide: Overset. Available online: https://www.openfoam.com/documentation/guides/v2112/doc/guide-overset.html (accessed on 17 May 2023).
- FeltusChristophe. Learning Algorithm Recommendation Framework for IS and CPS Security. Int. J. Syst. Softw. Secur. Prot. 2022, 13, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefas, A.; Rossi, A.; Tessmann, O. Funken Serial Protocol Toolkit for Interactive Prototyping. In Proceedings of the 36th eCAADe Conference, Łódź, Poland, 17–21 September 2018; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Sanfilippo, F.; Hatledal, L.I.; Zhang, H.; Fago, M.; Pettersen, K.Y. Controlling Kuka industrial robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2015, 22, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Density [ρ] | 2070 kg/m3 |
| Yield Stress [τ0] | 8.28 kPa |
| Consistency Index [K] | 20.7 Pa.s1.56 |
| Viscosity Exponent [n] | 1.56 |
| Patch | Pressure, p | Velocity, U |
|---|---|---|
| inlet | fixed flux | fixed value Uin |
| overset | overset | overset |
| nozzle Walls | fixed flux | 0 |
| outlet | constant atmospheric pressure | null normal gradient |
| floor | fixed flux | 0 |
| Time [s] | Speed [cm/s] | Flow [m/s] | Distance [mm] | Angle [degree] | Height [cm] | Diameter [cm] | Width [cm] | Overlay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.26344 | 11.3 | 0.233 | 30 | 0.036599 | 12 | 20 | 57.427403 | 0 |
| 7.22211 | 10.0 | 0.264 | 40 | 0.035724 | 12 | 20 | 57.337229 | 2 |
| 1.24866 | 12.7 | 0.264 | 60 | 0.033314 | 12 | 40 | 56.499766 | 0 |
| 3.27521 | 8.4 | 0.264 | 30 | 0.031016 | 8 | 20 | 55.649535 | 0 |
| 2.30175 | 8.9 | 0.264 | 30 | 0.028557 | 12 | 40 | 55.088962 | 3 |
| 15.3283 | 9.1 | 0.264 | 12 | 0.026146 | 10 | 20 | 57.243402 | 0 |
| 33.35485 | 7.7 | 0.292 | 30 | 0.023822 | 12 | 40 | 58.402407 | 0 |
| 64.3814 | 11.3 | 0.292 | 14 | 0.021642 | 12 | 20 | 63.236045 | 11 |
| 114.40795 | 11.0 | 0.292 | 30 | 0.01961 | 8 | 10 | 63.371653 | 0 |
| 26.43449 | 8.3 | 0.292 | 15 | 0.017804 | 10 | 20 | 63.022733 | 5 |
| 88.46104 | 12.3 | 0.307 | 15 | 0.015641 | 12 | 25 | 60.956338 | 0 |
| 179.48759 | 10.0 | 0.307 | 45 | 0.013088 | 14 | 20 | 61.726337 | 3 |
| 57.51414 | 10.0 | 0.307 | 76 | 0.010921 | 6 | 25 | 66.683418 | 1 |
| 61.54069 | 9.6 | 0.331 | 10 | 0.009159 | 12 | 20 | 63.430119 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, J.M.; Wagner, G.; Silva, R.; Morais, A.; Ribeiro, J.; Mould, S.; Figueiredo, B.; Nóbrega, J.M.; Cruz, P.J.S. Real-Time Precision in 3D Concrete Printing: Controlling Layer Morphology via Machine Vision and Learning Algorithms. Inventions 2024, 9, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions9040080
Silva JM, Wagner G, Silva R, Morais A, Ribeiro J, Mould S, Figueiredo B, Nóbrega JM, Cruz PJS. Real-Time Precision in 3D Concrete Printing: Controlling Layer Morphology via Machine Vision and Learning Algorithms. Inventions. 2024; 9(4):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions9040080
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, João M., Gabriel Wagner, Rafael Silva, António Morais, João Ribeiro, Sacha Mould, Bruno Figueiredo, João M. Nóbrega, and Paulo J. S. Cruz. 2024. "Real-Time Precision in 3D Concrete Printing: Controlling Layer Morphology via Machine Vision and Learning Algorithms" Inventions 9, no. 4: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions9040080
APA StyleSilva, J. M., Wagner, G., Silva, R., Morais, A., Ribeiro, J., Mould, S., Figueiredo, B., Nóbrega, J. M., & Cruz, P. J. S. (2024). Real-Time Precision in 3D Concrete Printing: Controlling Layer Morphology via Machine Vision and Learning Algorithms. Inventions, 9(4), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions9040080






