Direct Assessment of Alcohol Consumption in Mental State Using Brain Computer Interfaces and Grammatical Evolution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
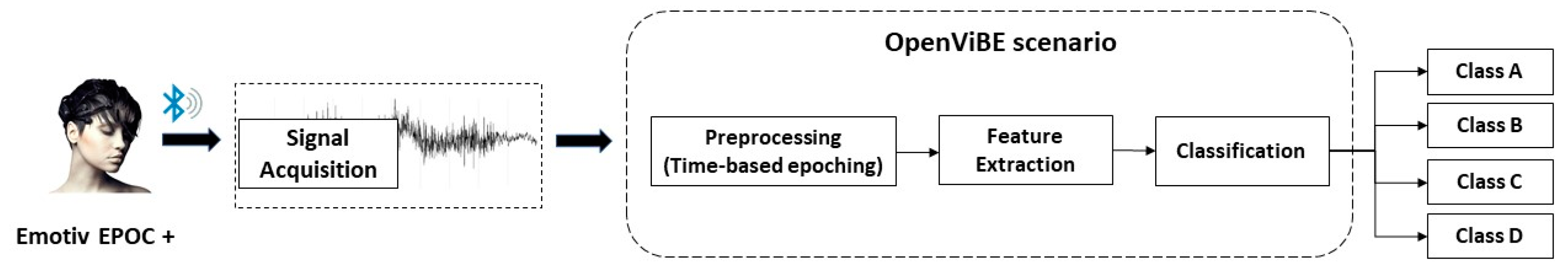
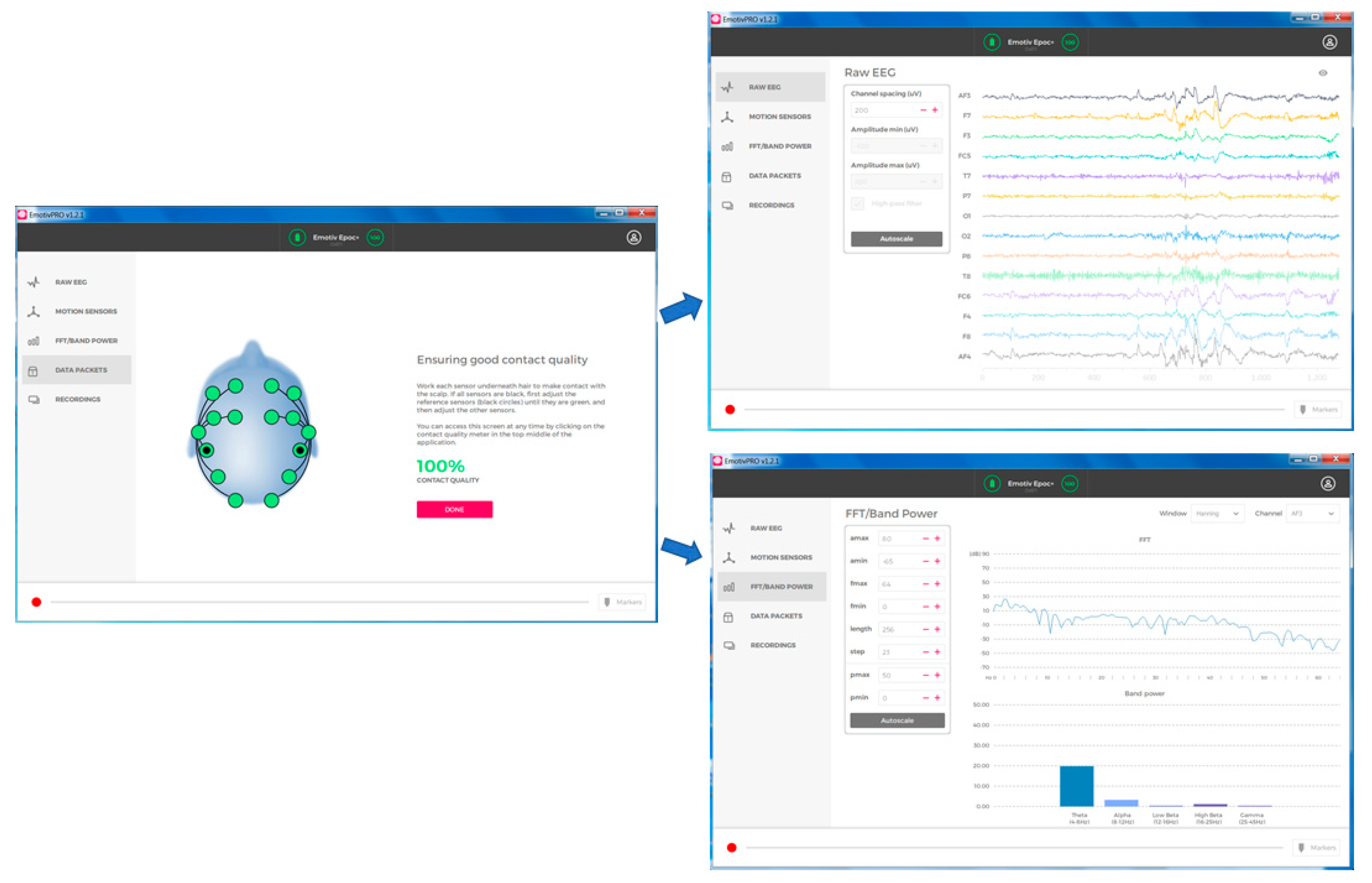
3.1. Brain Computer Interface Devices and Software
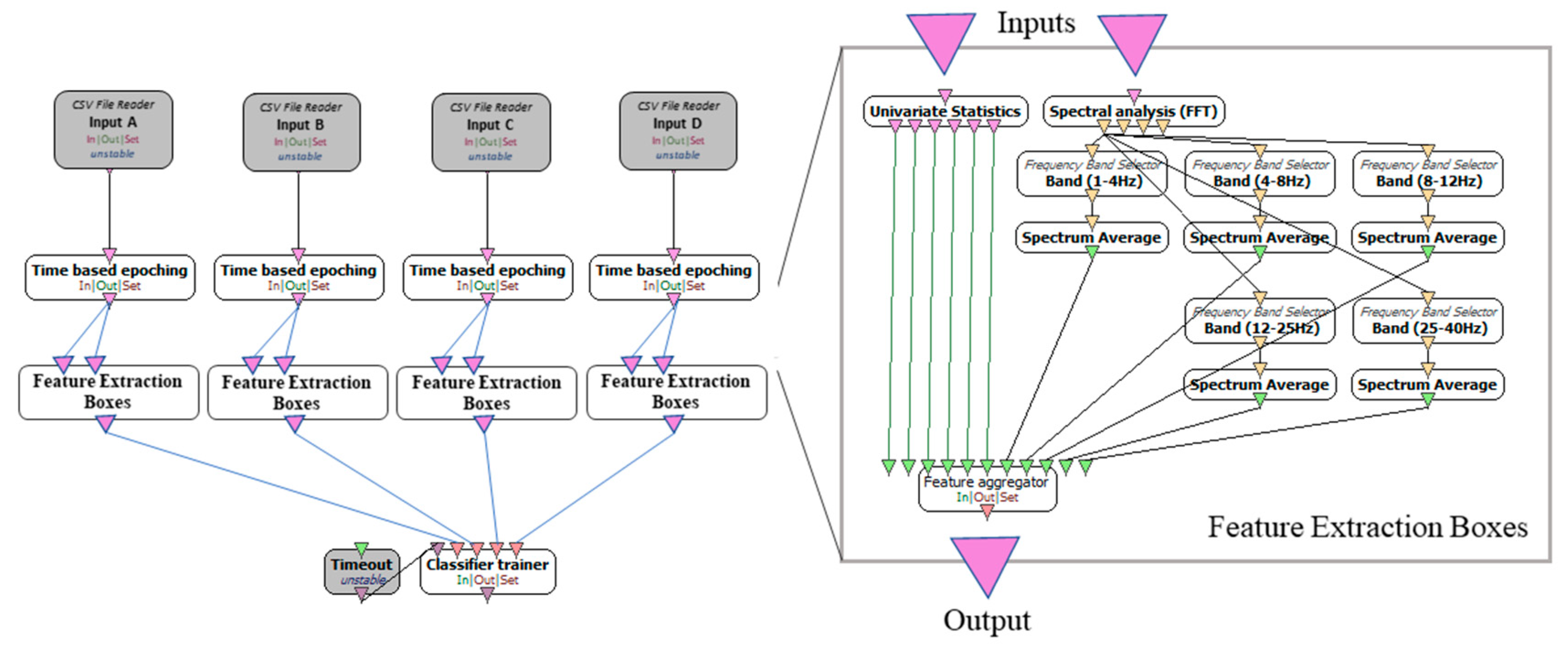
3.2. Feature Extraction
3.3. Classification Using Grammatical Evolution
- The next element from the vector is taken (denoted as V).
- The production rule is selected using the scheme Rule = V mod R, where R is the number of production rules for the current non-terminal symbol.
| Algorithm 1 |
1. Initialization step
(a) For i = 1 to NG do
3. Evaluation step
|
4. Experimental Results
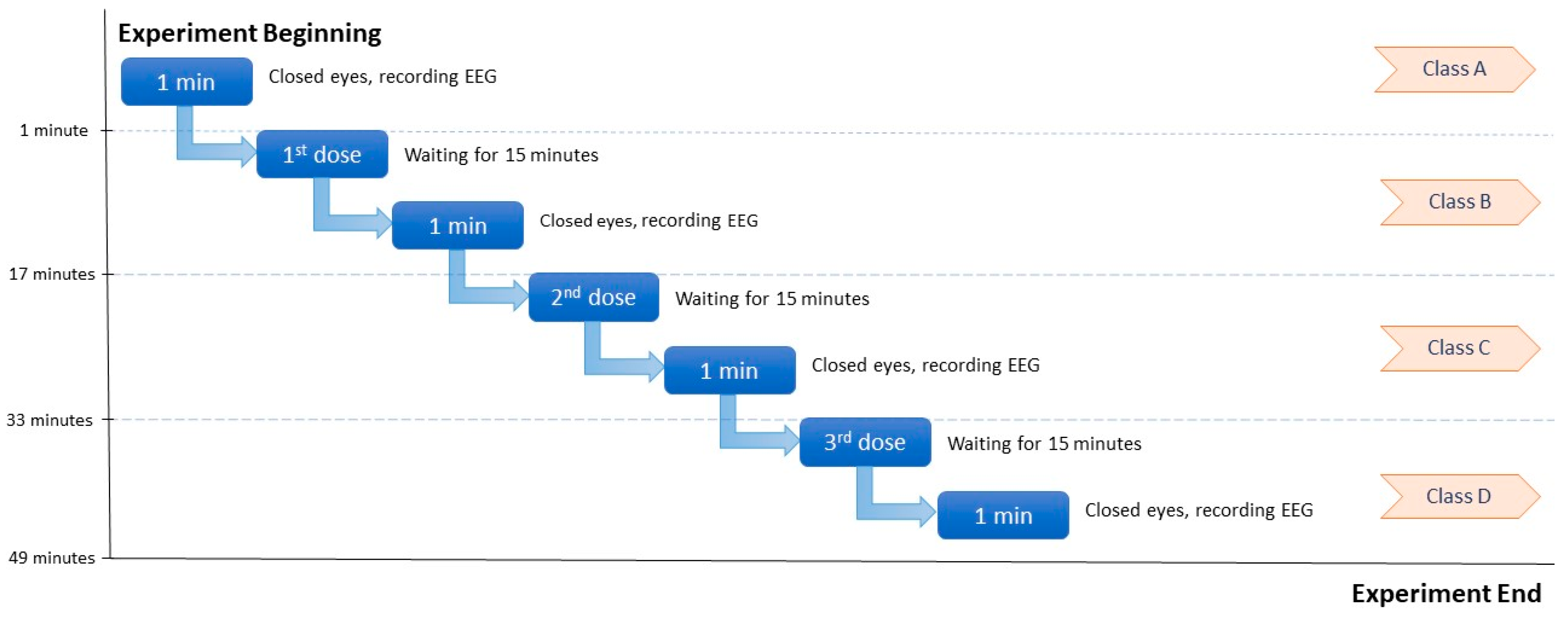
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Experimental Procedure
4.3. Classification Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Townshend, J.M.; Duka, T. Binge drinking, cognitive performance and mood in a population of young social drinkers. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2005, 29, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, U.R.; Bhat, S.; Adeli, H.; Adeli, A. Computer-aided diagnosis of alcoholism-related EEG signals. Epilepsy Behav. 2014, 41, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horne, J.A.; Reyner, L.A.; Barrett, P.R. Driving impairment due to sleepiness is exacerbated by low alcohol intake. Occup. Environ. Med. 2003, 60, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, P.R.; Horne, J.A.; Reyner, L.A. Early evening low alcohol intake also worsens sleepiness-related driving impairment. Hum. Psychopharmacol. Clin. Exp. 2005, 20, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, I.; Baba, S.; Ozaki, K.; Li, S. Using brain waves as transparent biometrics for on-demand driver authentication. Int. J. Biom. 2013, 5, 288–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, Y.S.; Somani, S.B.; Shete, V.V. Biometric user authentication using brain waves. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), Coimbatore, India, 26–27 August 2016; Volume 2, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pallavi, T.; Harish, G. Implementation of EEG based driver’s attention tracking and habitats monitoring system. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES), Coimbatore, India, 21–22 October 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossan, A.; Kashem, F.B.; Hasan, M.M.; Naher, S.; Rahman, M.I. A smart system for driver’s fatigue detection, remote notification and semi-automatic parking of vehicles to prevent road accidents. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Medical Engineering, Health Informatics and Technology (MediTec), 17–18 December 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledezma-Zavala, E.; Ramrez-Mendoza, R.A. Towards a new framework for advanced driver assistance systems. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 2018, 12, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- [Volkswagen News]. Volkswagen @ IAA 2017: The visionary Car Finder [Video File]. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bTvT5oxeQpQ (accessed on 25 September 2017).
- [Renault Sverige]. Renault KADJAR Presents Team Will Power [Video File]. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9_6uHjZyg_w (accessed on 31 October 2017).
- De Bruin, E.A.; Stam, C.J.; Bijl, S.; Verbaten, M.N.; Kenemans, J.L. Moderate-to-heavy alcohol intake is associated with differences in synchronization of brain activity during rest and mental rehearsal. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2006, 60, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtney, K.E.; Polich, J. Binge drinking effects on EEG in young adult humans. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 2325–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachman, N.T.; Tjandrasa, H.; Fatichah, C. Alcoholism classification based on EEG data using Independent Component Analysis (ICA), Wavelet de-noising and Probabilistic Neural Network (PNN). In Proceedings of the 2016 International Seminar on Intelligent Technology and Its Applications (ISITIA), Lombok, Indonesia, 28–30 July 2016; pp. 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Mumtaz, W.; Kamel, N.; Ali, S.S.A.; Malik, A.S. An EEG-based functional connectivity measure for automatic detection of alcohol use disorder. Artif. Intell. Med. 2018, 84, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boha, R.; Molnár, M.; Gaál, Z.A.; Czigler, B.; Róna, K.; Kass, K.; Klausz, G. The acute effect of low-dose alcohol on working memory during mental arithmetic: I. Behavioral measures and EEG theta band spectral characteristics. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2009, 73, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnár, M.; Boha, R.; Czigler, B.; Gaál, Z.A.; Benyovszky, M.; Róna, K.; Klausz, G. The acute effect of low-dose alcohol on working memory during mental arithmetic: II. Changes of nonlinear and linear EEG-complexity in the theta band, heart rate and electrodermal activity. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2009, 73, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karungaru, S.; Yoshida, T.; Seo, T.; Fukumi, M.; Terada, K. Monotonous Tasks and alcohol consumption effects on the brain by EEG analysis using neural networks. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Appl. 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Martin, A.; Hernández-González, M.; Guevara, M.A.; Santana, G.; Gumá-Díaz, E.; Amezcua, C. Effects of alcohol on the performance of the Tower of London task in relation to the menstrual cycle: An electroencephalographic study. Behav. Pharmacol. 2012, 23, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, J.; Malone, S.M.; Iacono, W.G. Impact of alcohol use on EEG dynamics of response inhibition: A cotwin control analysis. Addict. Biol. 2018, 23, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarraf, J.; Chakrabarty, S.; Pattnaik, P.K. EEG based oscitancy classification system for accidental prevention. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Frontiers in Intelligent Computing: Theory and Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 235–243. [Google Scholar]
- Cernea, D.; Olech, P.S.; Ebert, A.; Kerren, A. Controlling in-vehicle systems with a commercial eeg headset: Performance and cognitive load. In Proceedings of IRTG 1131—Visualization of Large and Unstructured Data Sets Workshop 2011; OASIcs-OpenAccess Series in Informatics; Schloss Dagstuhl-Leibniz-Zentrum für Informatik: Wadern, Germany, 2012; Volume 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, T.O.; Andreessen, L.M.; Berg, A.; Bleuel, M.; Pawlitzki, J.; Zawallich, L.; Krol, L.R.; Gramann, K. Evaluation of a dry EEG system for application of passive brain-computer interfaces in autonomous driving. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, R.; Naik, G.R.; Nguyen, T.N.; Ling, S.H.; Tran, Y.; Craig, A.; Nguyen, H.T. Driver fatigue classification with independent component by entropy rate bound minimization analysis in an EEG-based system. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Informat. 2017, 21, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renard, Y.; Lotte, F.; Gibert, G.; Congedo, M.; Maby, E.; Delannoy, V.; Bertrand, O.; Lécuyer, A. OpenViBE: An Open-Source Software Platform to Design, Test and Use Brain-Computer Interfaces in Real and Virtual Environments1. Presence Teleoperat. Virtual Environ. 2010, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, M.; Ryan, C. Grammatical Evolution: Evolutionary Automatic Programming in an Arbitrary Language; Springer US: New York, NY, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-1-4615-0447-4. [Google Scholar]
- Tzallas, A.T.; Tsoulos, I.; Tsipouras, M.G.; Giannakeas, N.; Androulidakis, I.; Zaitseva, E. Classification of EEG signals using feature creation produced by grammatical evolution. In Proceedings of the 24th Telecommunications Forum (TELFOR), Belgrade, Serbia, 22–23 November 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2015-2020, 8th ed.; Skyhorse Publishing Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-5107-2604-8.
- Roine, R.P.; Gentry, R.T.; Lim, R.T., Jr.; Helkkonen, E.; Salaspuro, M.; Lieber, C.S. Comparison of blood alcohol concentrations after beer and whiskey. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1993, 17, 709–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, M.C., Jr.; Teigen, E.L.; Ramchandani, V.A. Absorption and peak blood alcohol concentration after drinking beer, wine, or spirits. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleiss, J.L.; Levin, B.; Paik, M.C. Statistical Methods for Rates and Proportions, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-0-4714-4542-5. [Google Scholar]
| Features | Feature Details |
|---|---|
| Time-based features | Mean value |
| Variance | |
| Range (max–min) | |
| Median value | |
| Inter-Quantile Range | |
| Percentiles | |
| Spectral features | Spectrum average in gamma band (25–40 Hz) |
| Spectrum average in beta band (12–25 Hz) | |
| Spectrum average in alpha band (8–12 Hz) | |
| Spectrum average in theta band (4–8 Hz) | |
| Spectrum average in delta band (1–4 Hz) |
| Feature Selection | Classifier | Scenario 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moderate Drinkers | Heavy Drinkers | ||
| Principal Component Analysis | Decision Tree | 54.39%, (t = 29.285) * | 63.33%, (t = 24.141) * |
| Linear Discriminant Analysis | 55.58%, (t = 40,239) * | 65.19%, (t = 20.725) * | |
| MultiLayer Perceptron | 66.53%, (t = 14.567) * | 80.06%, (t = 8.398) * | |
| k-Nearest Neighbor | 66.89%, (t = 18.075) * | 73.97%, (t = 14.633) * | |
| Information Gain | Decision Tree | 58.99%, (t = 28.769) * | 59.51%, (t = 20.057) * |
| Linear Discriminant Analysis | 53.15%, (t = 35.698) * | 50.27%, (t = 22.019) * | |
| MultiLayer Perceptron | 55.43%, (t = 23.535) * | 58.89%, (t = 15.690) * | |
| k-Nearest Neighbor | 62.92%, (t = 26.112) * | 60.33%, (t = 32.457) * | |
| Correlation Attribute Evaluation | Decision Tree | 59.71%, (t = 28.387) * | 72.57%, (t = 17.691) * |
| Linear Discriminant Analysis | 50.31%, (t = 21.372) * | 59.41%, (t = 18.706) * | |
| MultiLayer Perceptron | 56.77%, (t = 31.751) * | 69.79%, (t = 10.324) * | |
| k-Nearest Neighbor | 63.22%, (t = 34.711) * | 76.60%, (t = 8.508) * | |
| Entropy-based | Decision Tree | 58.42%, (t = 31.053) * | 70.15%, (t = 20.633) * |
| Linear Discriminant Analysis | 49.54%, (t = 22.118) * | 58.21%, (t = 26.308) * | |
| MultiLayer Perceptron | 60.07%, (t = 30.640) * | 71.49%, (t = 11.294) * | |
| k-Nearest Neighbor | 62.25%, (t = 19.294) * | 73.35%, (t = 15.475) * | |
| Grammatical Evolution | 85.55 | 87.53 | |
| Feature Selection | Classifier | Scenario 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moderate Drinkers | Heavy Drinkers | ||
| Principal Component Analysis | Decision Tree | 54.96%, (t = 36.905) * | 60.90%, (t = 23.464) * |
| Linear Discriminant Analysis | 55.07%, (t = 20.997) * | 67.98%, (t = 13.365) * | |
| MultiLayer Perceptron | 68.28%, (t = 14.641) * | 80.89%, (t = 8.469) * | |
| k-Nearest Neighbor | 76.35%, (t = 3.451) *** | 84.04%, (t = 4.335) ** | |
| Information Gain | Decision Tree | 50.31%, (t = 20.493) * | 58.73%, (t = 17.948) * |
| Linear Discriminant Analysis | 44.68%, (t = 26.378) * | 51.92%, (t = 18.690) * | |
| MultiLayer Perceptron | 48.91%, (t = 21.261) * | 61.00%, (t = 22.797) * | |
| k-Nearest Neighbor | 57.08%, (t = 22.712) * | 62.91%, (t = 20.325) * | |
| Correlation Attribute Evaluation | Decision Tree | 52.07%, (t = 18.237) * | 75.83%, (t = 8.038) * |
| Linear Discriminant Analysis | 40.24%, (t = 27.991) * | 59.35%, (t = 25.952) * | |
| MultiLayer Perceptron | 48.35%, (t = 25.775) * | 68.24%, (t = 18.666) * | |
| k-Nearest Neighbor | 56.30%, (t = 16.395) * | 75.57%, (t = 11.341) * | |
| Entropy-based | Decision Tree | 50.98%, (t = 18.085) * | 51.91%, (t = 31.298) * |
| Linear Discriminant Analysis | 49.28%, (t = 29.809) * | 52.33%, (t = 28.626) * | |
| MultiLayer Perceptron | 53.98%, (t = 23.165) * | 49.12%, (t = 22.302) * | |
| k-Nearest Neighbor | 53.61%, (t = 14.929) * | 50.01%, (t = 31.960) * | |
| Grammatical Evolution | 80.52% | 88.70% | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tzimourta, K.D.; Tsoulos, I.; Bilero, T.; Tzallas, A.T.; Tsipouras, M.G.; Giannakeas, N. Direct Assessment of Alcohol Consumption in Mental State Using Brain Computer Interfaces and Grammatical Evolution. Inventions 2018, 3, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions3030051
Tzimourta KD, Tsoulos I, Bilero T, Tzallas AT, Tsipouras MG, Giannakeas N. Direct Assessment of Alcohol Consumption in Mental State Using Brain Computer Interfaces and Grammatical Evolution. Inventions. 2018; 3(3):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions3030051
Chicago/Turabian StyleTzimourta, Katerina D., Ioannis Tsoulos, Thanasis Bilero, Alexandros T. Tzallas, Markos G. Tsipouras, and Nikolaos Giannakeas. 2018. "Direct Assessment of Alcohol Consumption in Mental State Using Brain Computer Interfaces and Grammatical Evolution" Inventions 3, no. 3: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions3030051
APA StyleTzimourta, K. D., Tsoulos, I., Bilero, T., Tzallas, A. T., Tsipouras, M. G., & Giannakeas, N. (2018). Direct Assessment of Alcohol Consumption in Mental State Using Brain Computer Interfaces and Grammatical Evolution. Inventions, 3(3), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions3030051








