A Reconfigurable Gripper for Dexterous Manipulation in Flexible Assembly
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- -
- Development of a multi-fingered high-DoF gripper, with anthropomorphic features.
- -
- Simple design and yet capable of grasping parts with varying geometrical and physical properties.
- -
- Providing a good tradeoff between (a) the dimensions and shape of the parts that it can grasp, including highly asymmetric objects, (b) the achieved gripping forces, and (c) the dynamic behavior of the fingers that can move at high speed and accelerations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design Principle
2.2. Mechanical Design
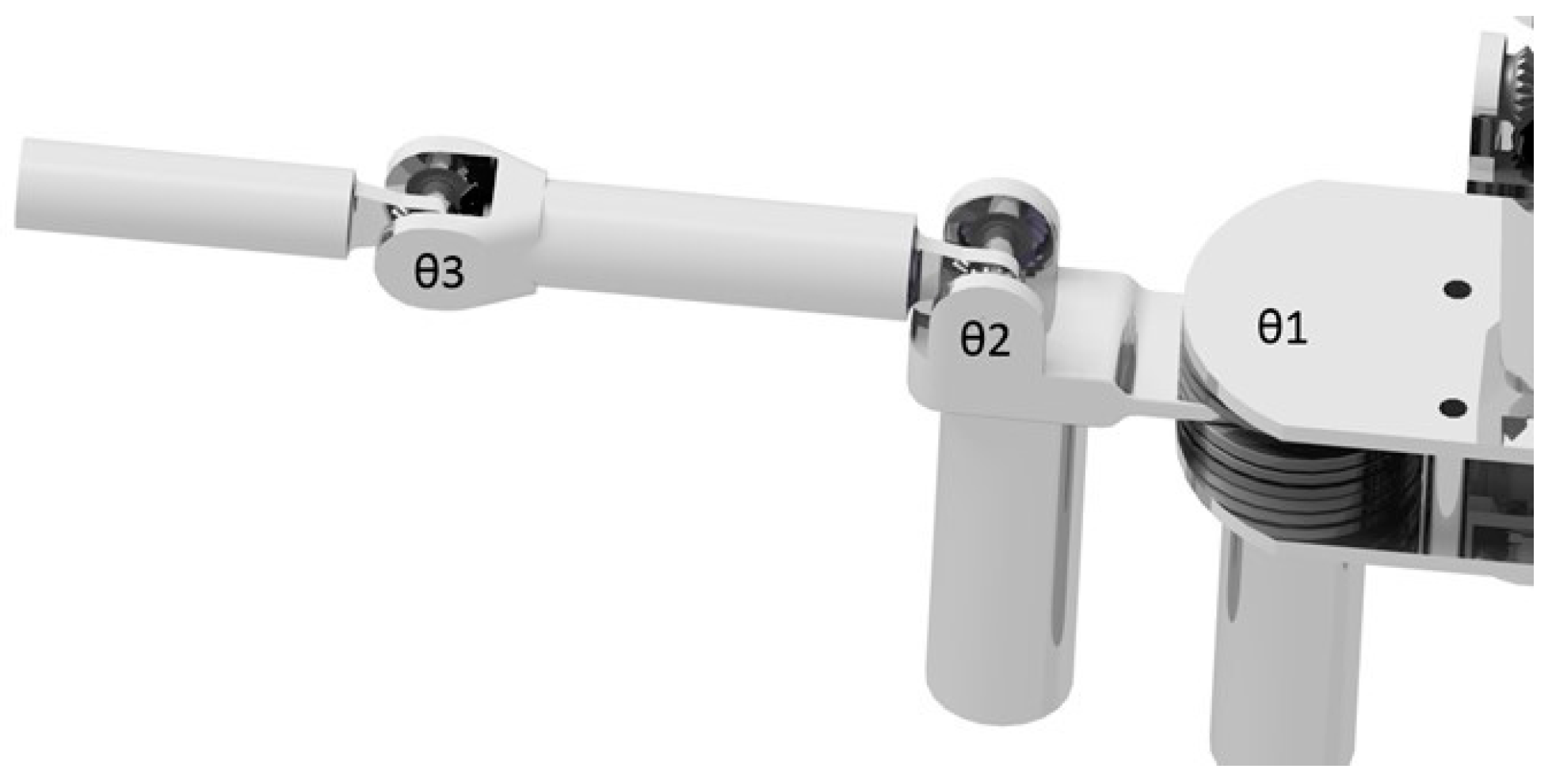
2.3. Kinematics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Actuation and Drive Electronics
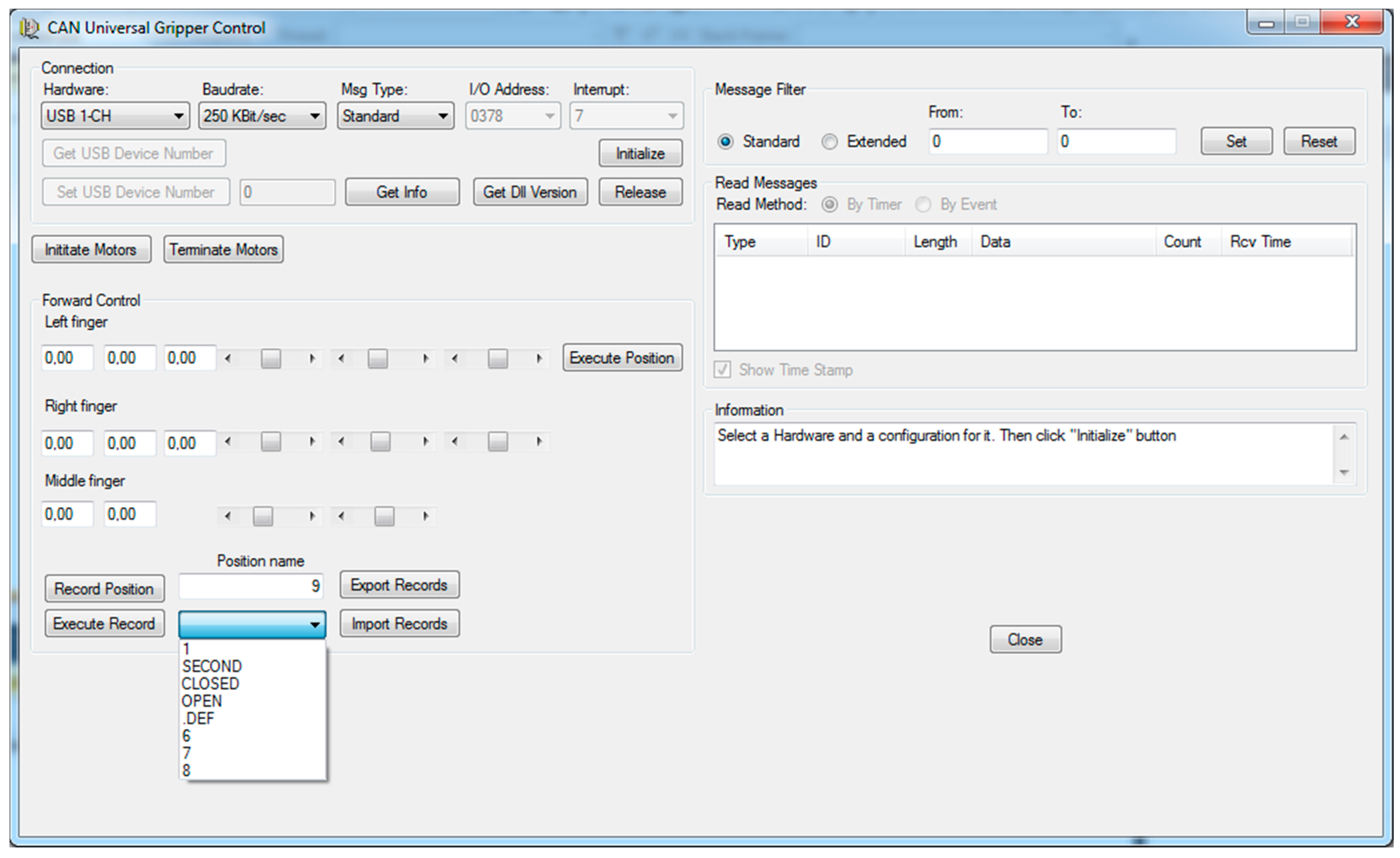
3.2. Gripper Control
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chryssolouris, G. Manufacturing Systems: Theory and Practice, 2nd ed.; Mechanical Engineering Series; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-387-25683-2. [Google Scholar]
- Krüger, J.; Wang, L.; Verl, A.; Bauernhansl, T.; Carpanzano, E.; Makris, S.; Fleischer, J.; Reinhart, G.; Franke, J.; Pellegrinelli, S. Innovative control of assembly systems and lines. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 66, 707–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalos, G.; Makris, S.; Papakostas, N.; Mourtzis, D.; Chryssolouris, G. Automotive assembly technologies review: Challenges and outlook for a flexible and adaptive approach. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2010, 2, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrinelli, S.; Pedrocchi, N.; Tosatti, L.M.; Fischer, A.; Tolio, T. Multi-robot spot-welding cells for car-body assembly: Design and motion planning. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2017, 44, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalos, G.; Makris, S.; Chryssolouris, G. The new assembly system paradigm. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2015, 28, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, S.; Michalos, G.; Eytan, A.; Chryssolouris, G. Cooperating robots for reconfigurable assembly operations: Review and challenges. Procedia CIRP 2012, 3, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, S.; Michalos, G.; Chryssolouris, G. Virtual commissioning of an assembly cell with cooperating robots. Adv. Decis. Sci. 2012, 2012, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakostas, N.; Michalos, G.; Makris, S.; Zouzias, D.; Chryssolouris, G. Industrial applications with cooperating robots for the flexible assembly. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2011, 24, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsarouchi, P.; Matthaiakis, S.-A.; Michalos, G.; Makris, S.; Chryssolouris, G. A method for detection of randomly placed objects for robotic handling. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2016, 14, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantoni, G.; Santochi, M.; Dini, G.; Tracht, K.; Scholz-Reiter, B.; Fleischer, J.; Kristoffer Lien, T.; Seliger, G.; Reinhart, G.; Franke, J.; et al. Grasping devices and methods in automated production processes. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 63, 679–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunk Parallel Gripper. Available online: https://schunk.com/de_en/gripping-systems/category/gripping-systems/schunk-grippers/parallel-gripper/ (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- Schunk Centric Gripper. Available online: https://schunk.com/br_en/gripping-systems/category/gripping-systems/schunk-grippers/centric-gripper/ (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- Adaptive Robot Gripper 2-Finger. Available online: http://robotiq.com/products/adaptive-robot-gripper/ (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- Townsend, W. The BarrettHand grasper—Programmably flexible part handling and assembly. Ind. Robot Int. J. 2000, 27, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, G.; González, A. A numerical simulation of the grasp operation by LARM Hand IV: A three finger robotic hand. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2011, 27, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukaya, N.; Toyama, S.; Asfour, T.; Dillmann, R. Design of the TUAT/Karlsruhe humanoid hand. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2000), Takamatsu, Japan, 30 October–5 November 2000; Volume 3, pp. 1754–1759. [Google Scholar]
- Kappassov, Z.; Khassanov, Y.; Saudabayev, A.; Shintemirov, A.; Varol, H.A. Semi-anthropomorphic 3D printed multigrasp hand for industrial and service robots. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Takamatsu, Japan, 4–7 August 2013; pp. 1697–1702. [Google Scholar]
- Robotic Hands (Self-contained) Prensilia s.r.l. Available online: http://www.prensilia.com/index.php?q=en/node/40 (accessed on 21 July 2017).
- Salisbury, J.K.; Craig, J.J. Articulated hands: Force control and kinematic issues. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1982, 1, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, S.; Iversen, E.; Knutti, D.; Johnson, R.; Biggers, K. Design of the Utah/M.I.T. Dextrous Hand. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Francisco, CA, USA, 7–10 April 1986; Volume 3, pp. 1520–1532. [Google Scholar]
- Lovchik, C.S.; Diftler, M.A. The Robonaut hand: A dexterous robot hand for space. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Detroit, MI, USA, 10–15 May 1999; Volume 2, pp. 907–912. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, Z.; Zhang, H.; Shang, X.; Wang, T.; Guo, W.; Gruver, W.A. Design and control of the BUAA four-fingered hand. In Proceedings of the ICRA IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Seoul, Korea, 21–26 May 2001; Volume 3, pp. 2517–2522. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.-R.; Huang, H.-P. NTU hand: A new design of dexterous hands. J. Mech. Des. 1998, 120, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, H.; Komatsu, T.; Uchiyama, K.; Kurimoto, T. Dexterous anthropomorphic robot hand with distributed tactile sensor: Gifu hand II. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Tokyo, Japan, 12–15 October 1999; Volume 2, pp. 782–787. [Google Scholar]
- Mouri, T.; Kawasaki, H.; Ito, S. Unknown object grasping strategy imitating human grasping reflex for anthropomorphic robot hand. J. Adv. Mech. Des. Syst. Manuf. 2007, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfass, J.; Grebenstein, M.; Liu, H.; Hirzinger, G. DLR-Hand II: Next generation of a dextrous robot hand. In Proceedings of the ICRA IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Seoul, Korea, 21–26 May 2001; Volume 1, pp. 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Melchiorri, C.; Palli, G.; Berselli, G.; Vassura, G. Development of the UB hand IV: Overview of design solutions and enabling technologies. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2013, 20, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexterous Hand—Shadow Robot Company. Available online: http://www.shadowrobot.com/products/dexterous-hand/ (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- SDH. Available online: https://schunk.com/ch_en/gripping-systems/series/sdh/ (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- elumotion.com: EH2—Elumotion Hand 2. Available online: http://www.elumotion.com/index.php/portfolio/project-title-1 (accessed on 21 July 2017).
- Namiki, A.; Imai, Y.; Ishikawa, M.; Kaneko, M. Development of a high-speed multifingered hand system and its application to catching. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–31 October 2003; Volume 3, pp. 2666–2671. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, M.; Carbone, G.; Ceccarelli, M.; Zhao, X. Analysis and design for changing finger posture in a robotic hand. Mech. Mach. Theory 2010, 45, 828–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutkosky, M.R. On grasp choice, grasp models, and the design of hands for manufacturing tasks. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1989, 5, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadali, S.; Kambiz, G.O.; Amir Ali, A.K. Modular framework kinematic and fuzzy reward reinforcement learning analysis of a radially symmetric six-legged robot. Life Sci. J. 2013, 10, 120–129. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.K. Introduction to Robotics; Tata McGraw-Hill: New Delhi, India, 2008; ISBN 978-0-07-066900-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kucuk, S.; Bingul, Z. Robot Kinematics: Forward and Inverse Kinematics. In Industrial Robotics: Theory, Modelling and Control; Cubero, S., Ed.; Pro Literatur Verlag: Augsburg, Germany; ARS: Linz, Austria, 2006; ISBN 978-3-86611-285-8. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Xu, C.; Pan, Q.; Zhao, X.; Li, X. Inverse kinematic analysis and evaluation of a robot for nondestructive testing application. J. Robot. 2015, 2015, 596327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MRPT—Empowering C++ Development in Robotics. Available online: http://www.mrpt.org/ (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- Corke, P.I. A robotics toolbox for MATLAB. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 1996, 3, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robotiq 3 Finger Adaptive Robot Gripper. Available online: https://robotiq.com/products/3-finger-adaptive-robot-gripper (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- Franchi, G.; Hauser, K. Technical Report: Use of Hybrid Systems to model the RobotiQ Adaptive Gripper. Available online: https://www.cs.indiana.edu/ftp/techreports/TR711.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- SCHUNK Dextrous Hand 2.0 (SDH 2.0). Available online: https://www.nist.gov/sites/default/files/documents/2017/05/09/9020173R1.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- Lauzier, N. Barrett Hand vs. Robotiq Adaptive Gripper. 2012. Available online: https://blog.robotiq.com/bid/52340/Barrett-Hand-vs-Robotiq-Adaptive-Gripper (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- Barret Hand. Available online: http://www.barrett.com/products-hand-specifications.htm (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- Larm Hand/ARMAND. Available online: http://www.mechanimata.it/flyers/ARMAND.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2017).
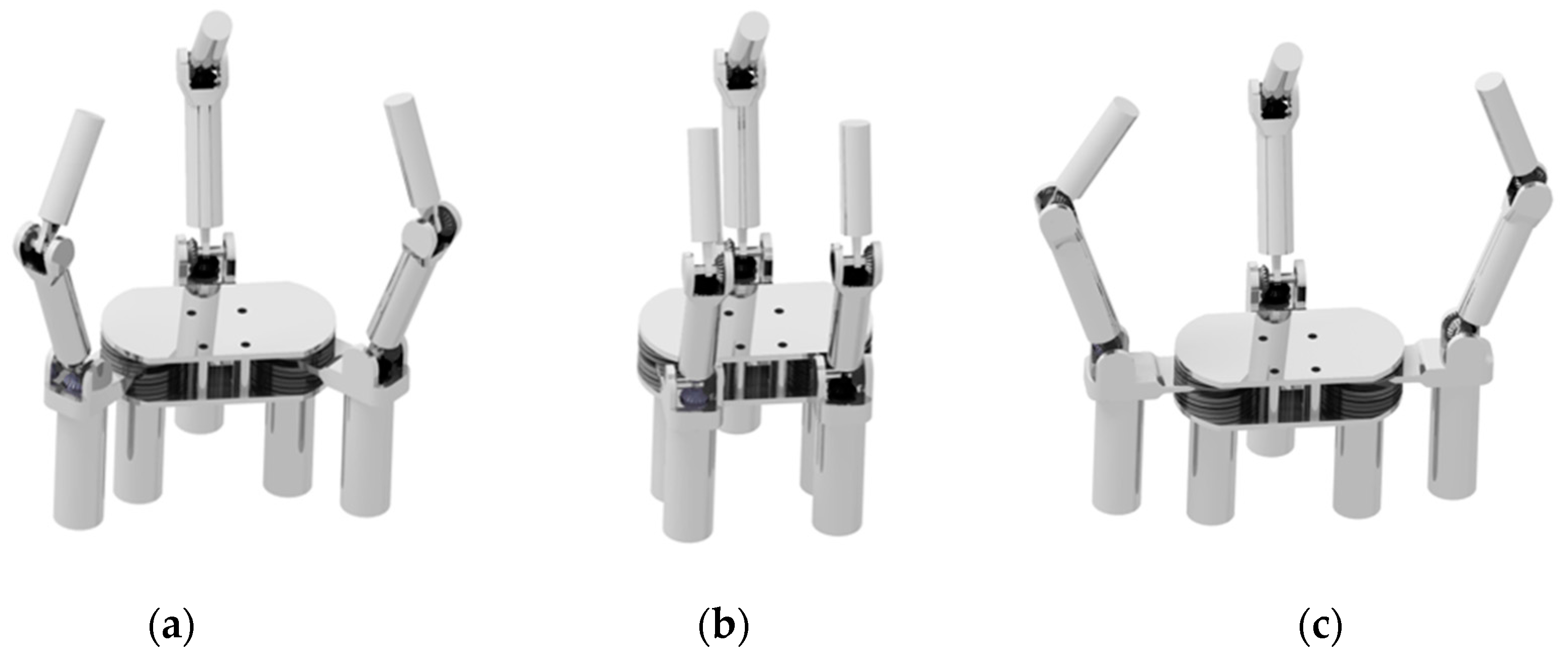
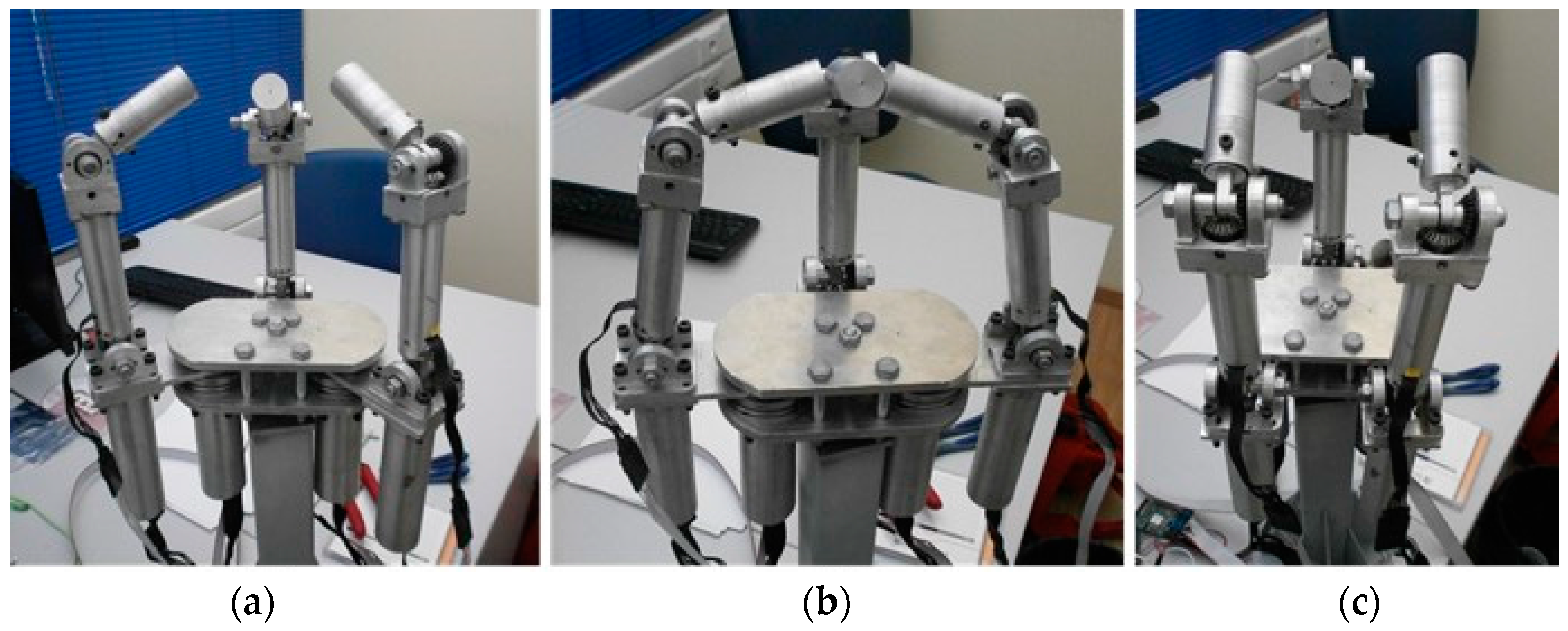

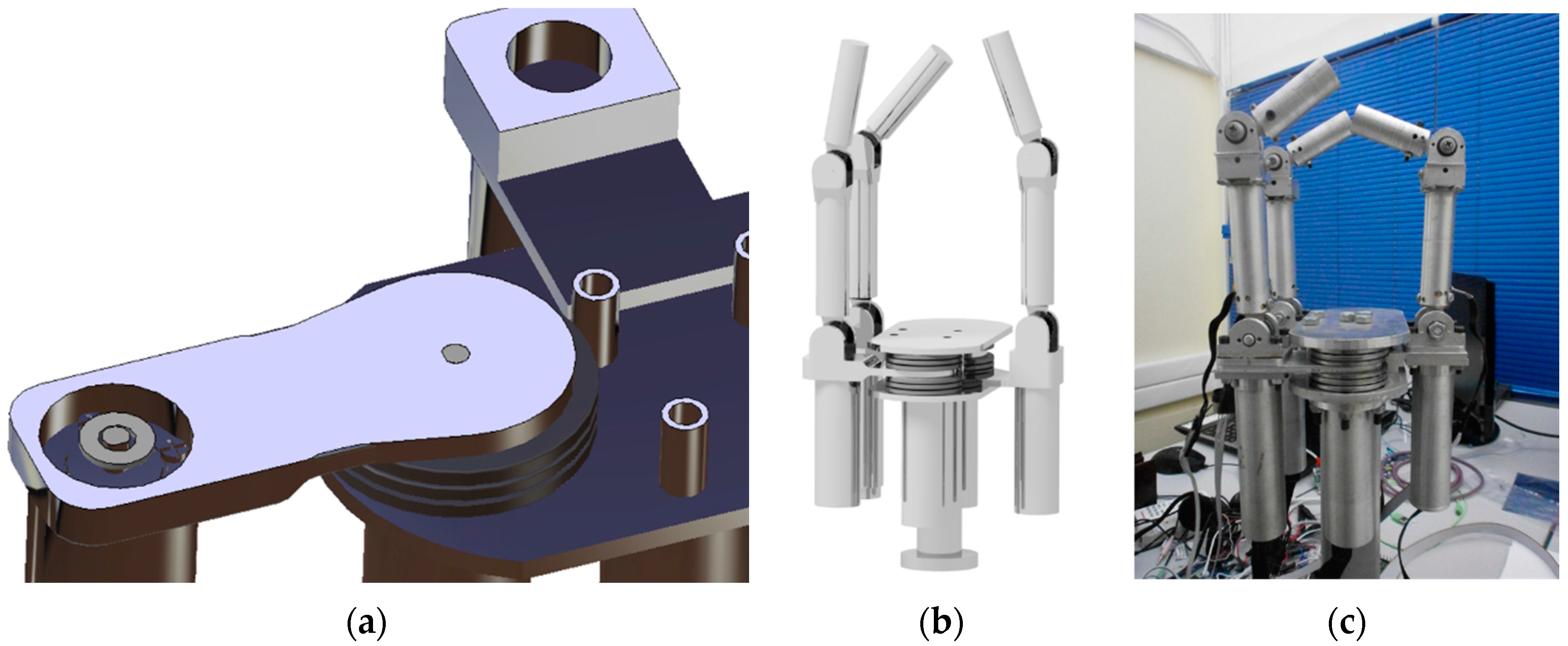






| Requirement Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Mechanical |
|
| Sensing |
|
| Control |
|
| Product |
|
| Link | θi | αi−1 | ai−1 | di |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | θ1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | θ2 | −π/2 | α2 | d2 |
| 3 | θ3 | 0 | α3 | 0 |
| 4 | θ4 | 0 | α4 | 0 |
| Characteristic | Fingertip DoF | Middle and Base Finger DoF |
|---|---|---|
| Motor type | DC brushless | DC brushless |
| Reduction rate | 25 | 29 |
| Max. speed (rpm) | 300 | 300 |
| Max. torque (Nm) | 1.5 | 8 |
| Size (mm) | Φ22 × 85 | Φ32 × 100 |
| Weight (g) | 100 | 200 |
| Sensor resolution | 4096 | 4096 |
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Max. speed (at tip) (m/s) | 24 (*1) |
| Max. force (at tip) (N) | 55 (*2) |
| Total DoF | 8 |
| Weight (kg) | ≈3.5 |
| Joint resolution (deg) | 0.0035 or 0.003 (*3) |
| Gripper | DoF (Total/Actuated) | Weight (kg) | Object Diameter for Encompassing (mm) | Maximum Payload (Encompassing Grip) (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Robotiq 3 Finger Gripper [40,41] | 10/4 | 2.3 | 20–155 | 100 |
| Schunk SDH [42] | 8/7 | 1.95 | 17–215 | N/A |
| Barret Hand [43,44] | 8/4 | 1.2 | Up to 240 | 60 |
| LARM Hand IV [45] | 9/3 | 1.5 | 10–100 | N/A |
| Proposed Gripper | 8/8 | 3.5 | Up to 215 | >150 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spiliotopoulos, J.; Michalos, G.; Makris, S. A Reconfigurable Gripper for Dexterous Manipulation in Flexible Assembly. Inventions 2018, 3, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions3010004
Spiliotopoulos J, Michalos G, Makris S. A Reconfigurable Gripper for Dexterous Manipulation in Flexible Assembly. Inventions. 2018; 3(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions3010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpiliotopoulos, Jason, George Michalos, and Sotiris Makris. 2018. "A Reconfigurable Gripper for Dexterous Manipulation in Flexible Assembly" Inventions 3, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions3010004
APA StyleSpiliotopoulos, J., Michalos, G., & Makris, S. (2018). A Reconfigurable Gripper for Dexterous Manipulation in Flexible Assembly. Inventions, 3(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions3010004








