Parametric Study of an Air Charged Franchot Engine with Novel Hot and Cold Isothermalizers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Plain Cylinder
1.2. Heat Exchanger
1.3. Isothermalizer
2. Materials and Methods
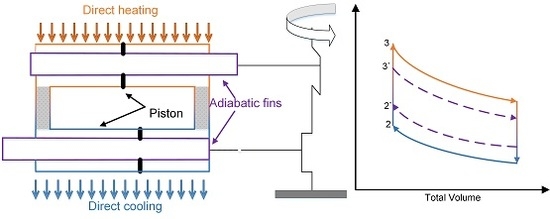
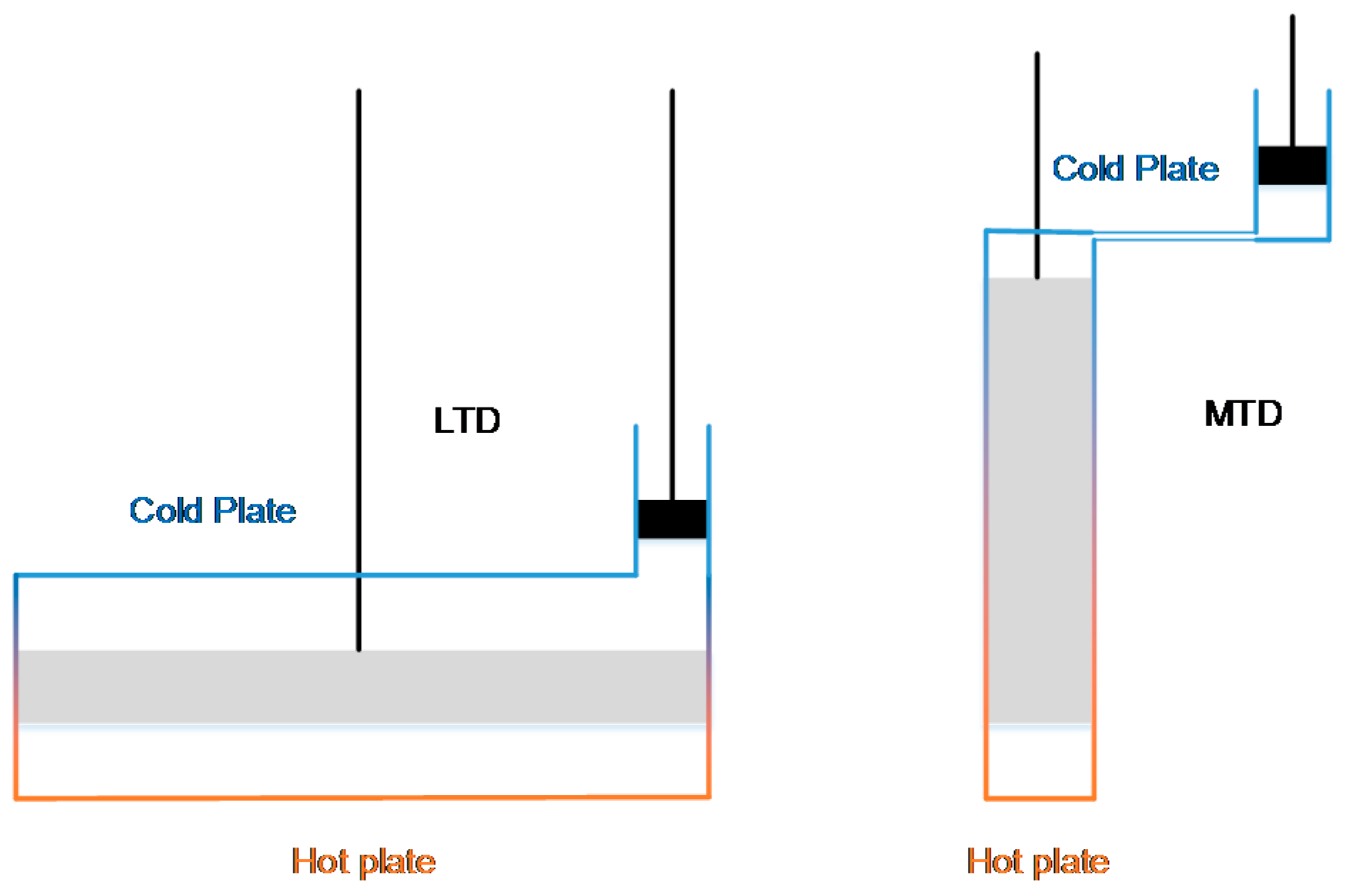
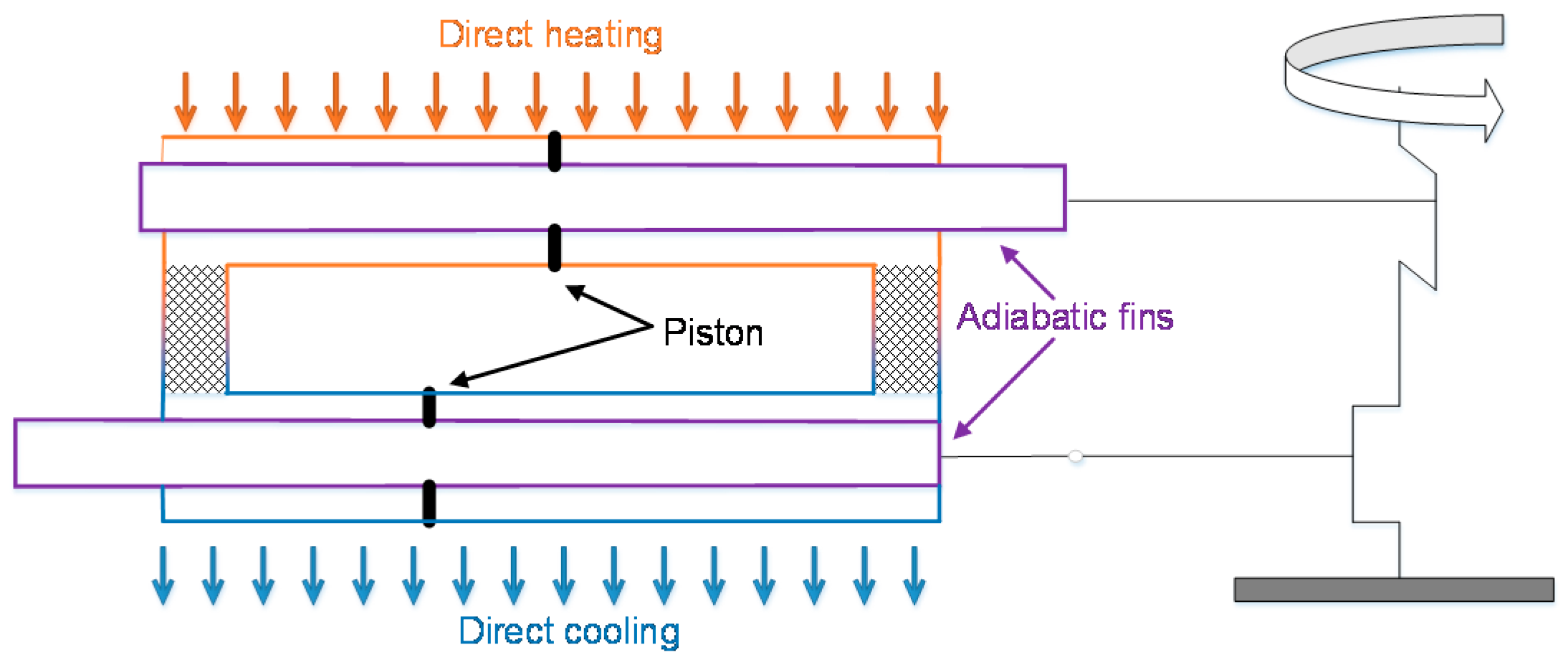
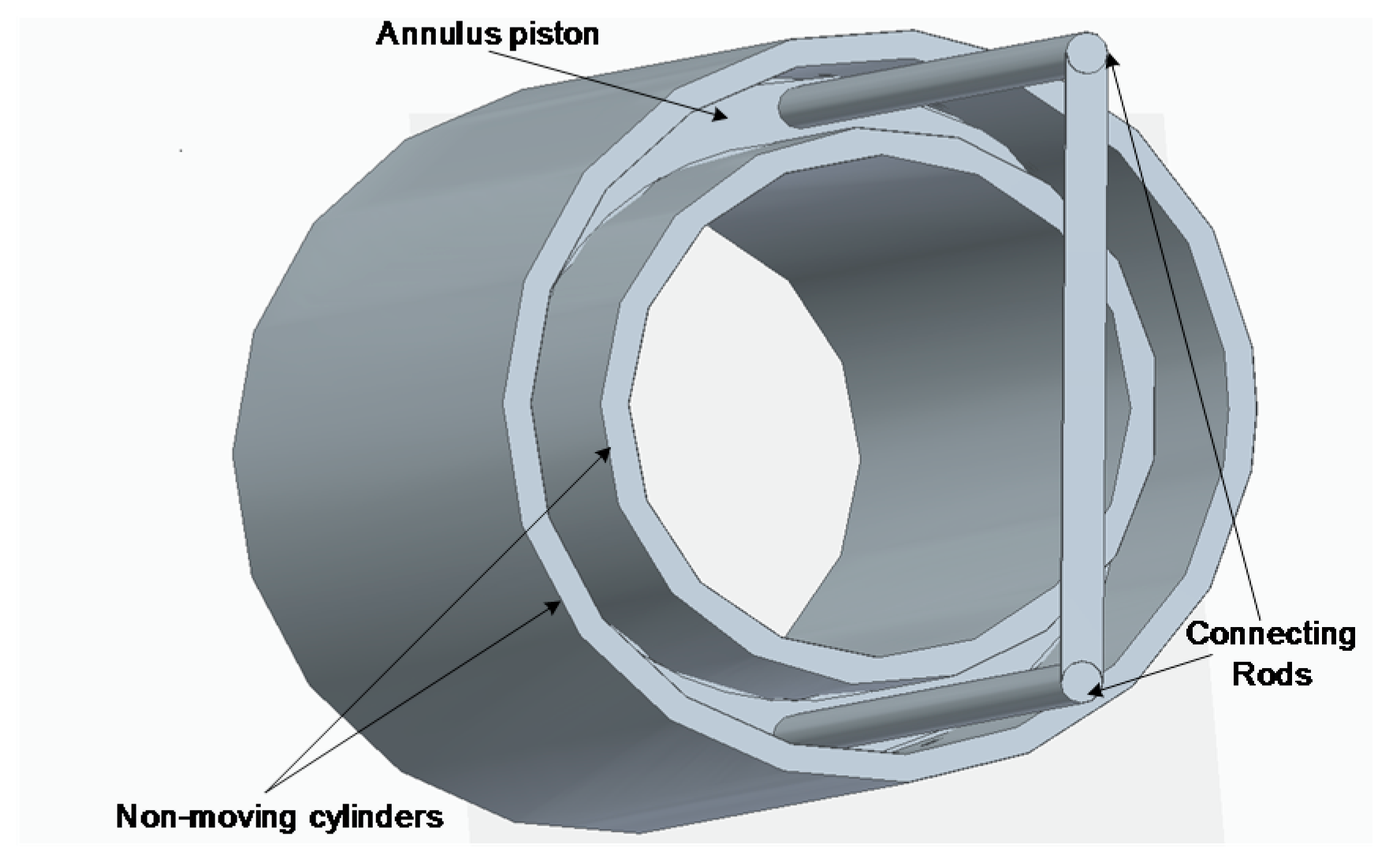
2.1. Isothermalizing the Franchot Engine
2.2. Mathematical Modelling
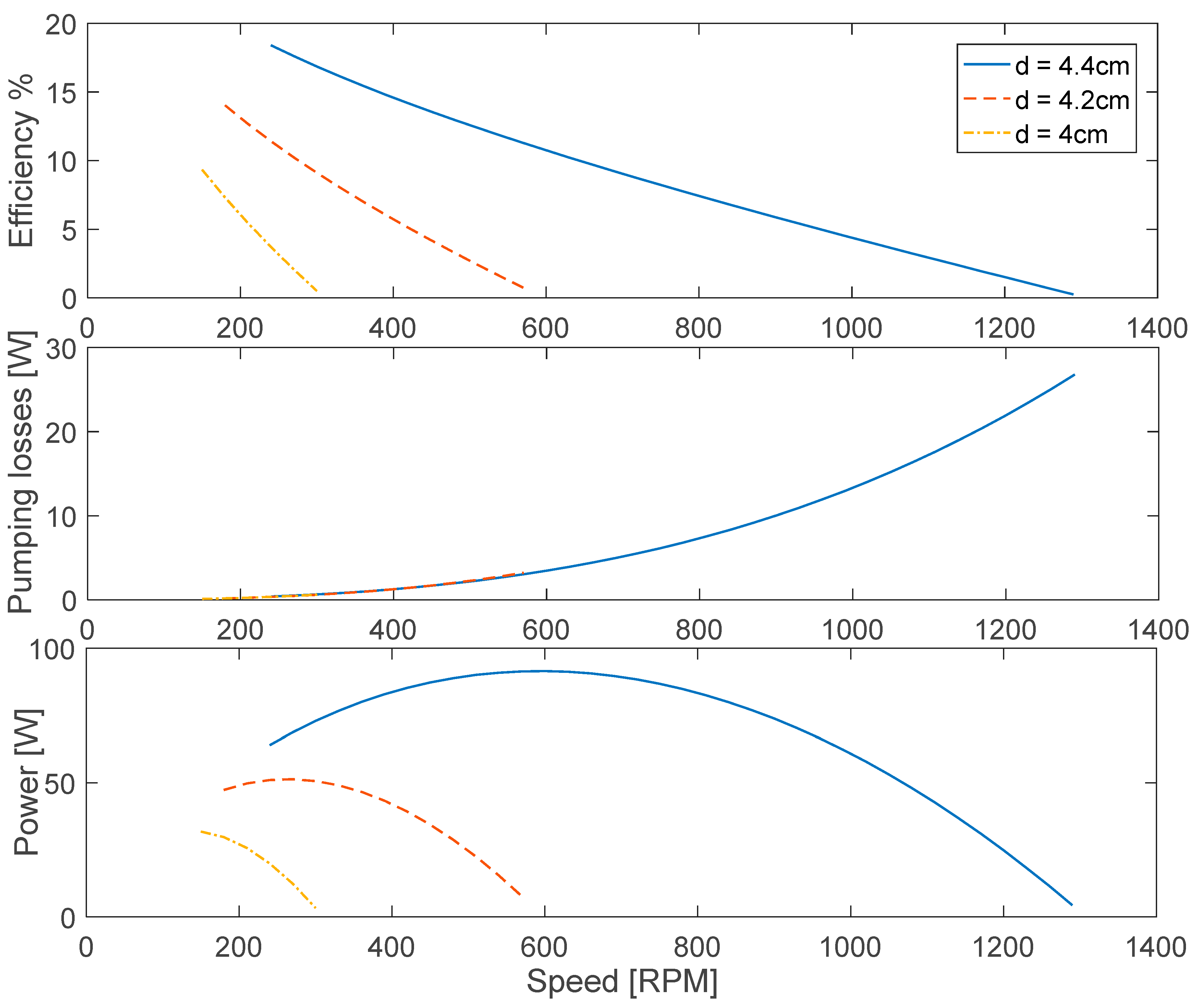
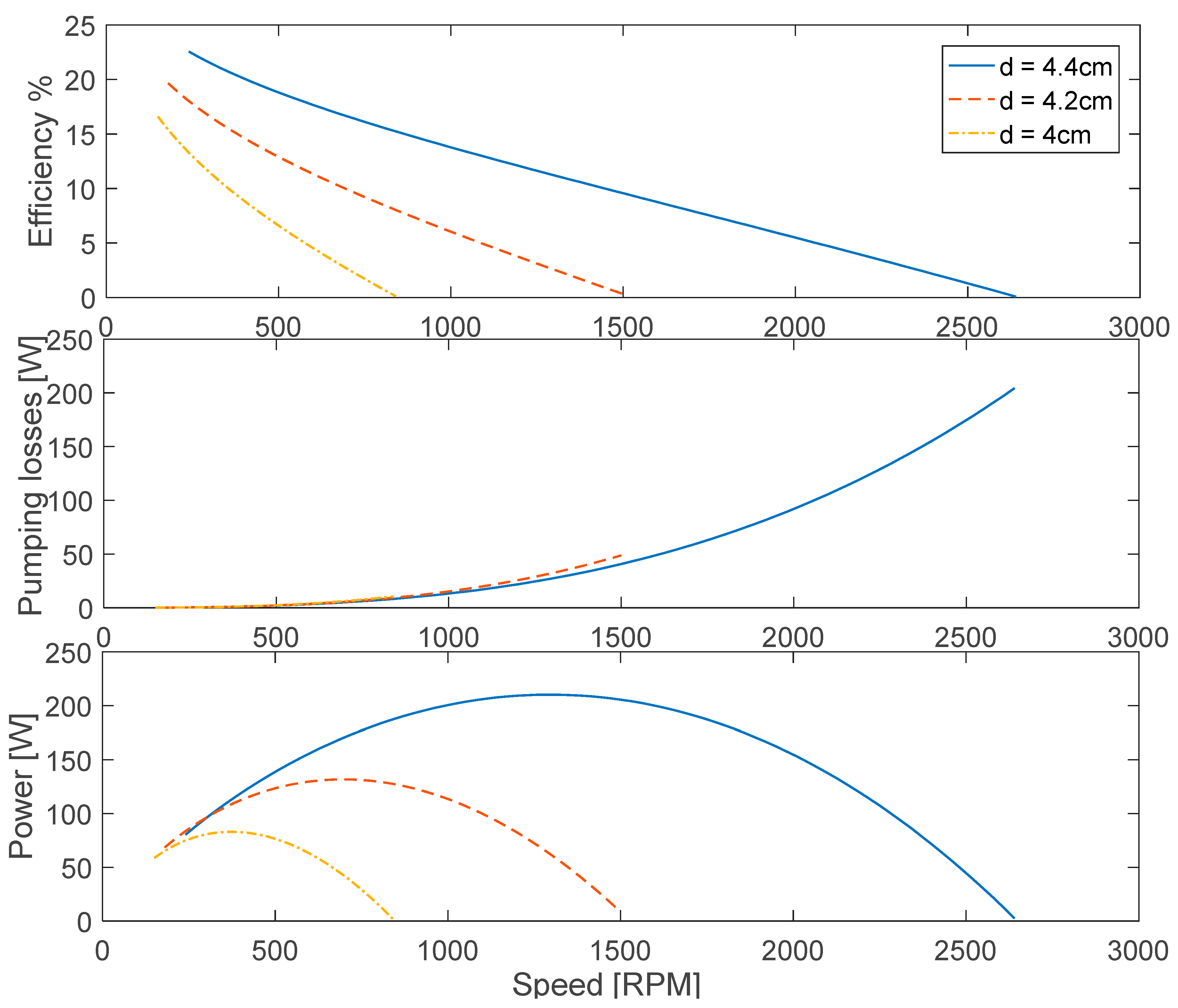
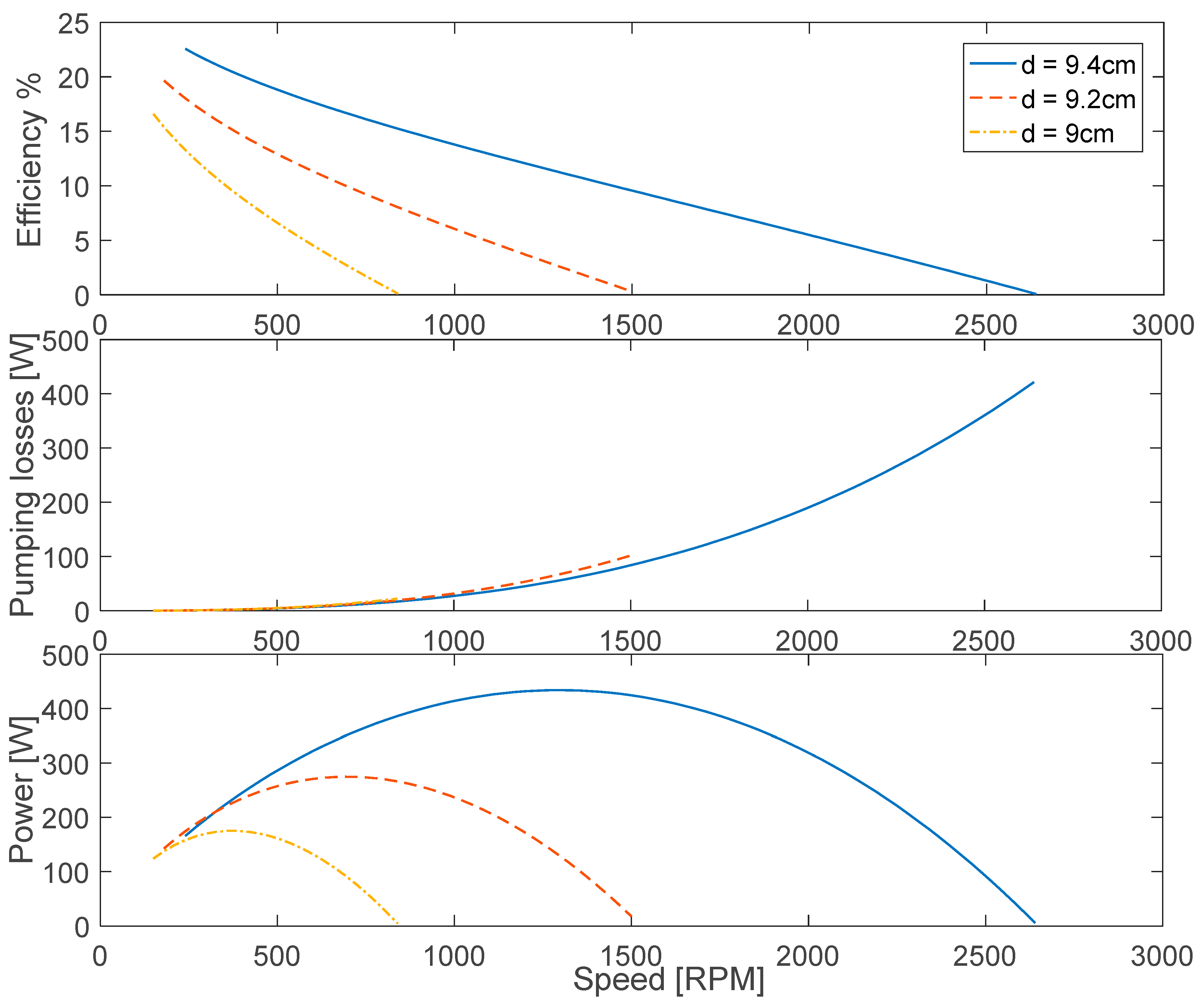
3. Results and Discussion
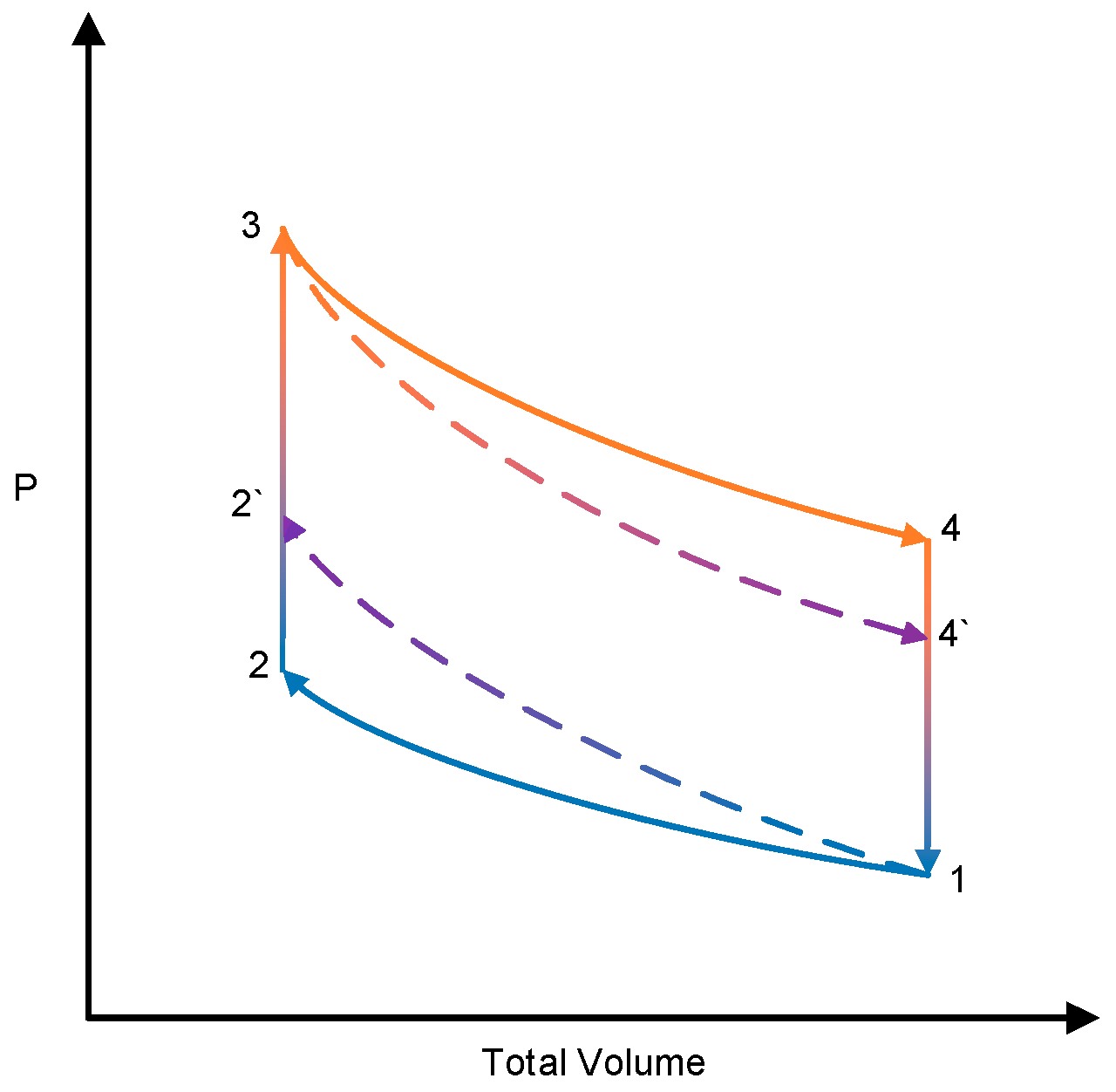
3.1. Influence of the Adiabatic Fin
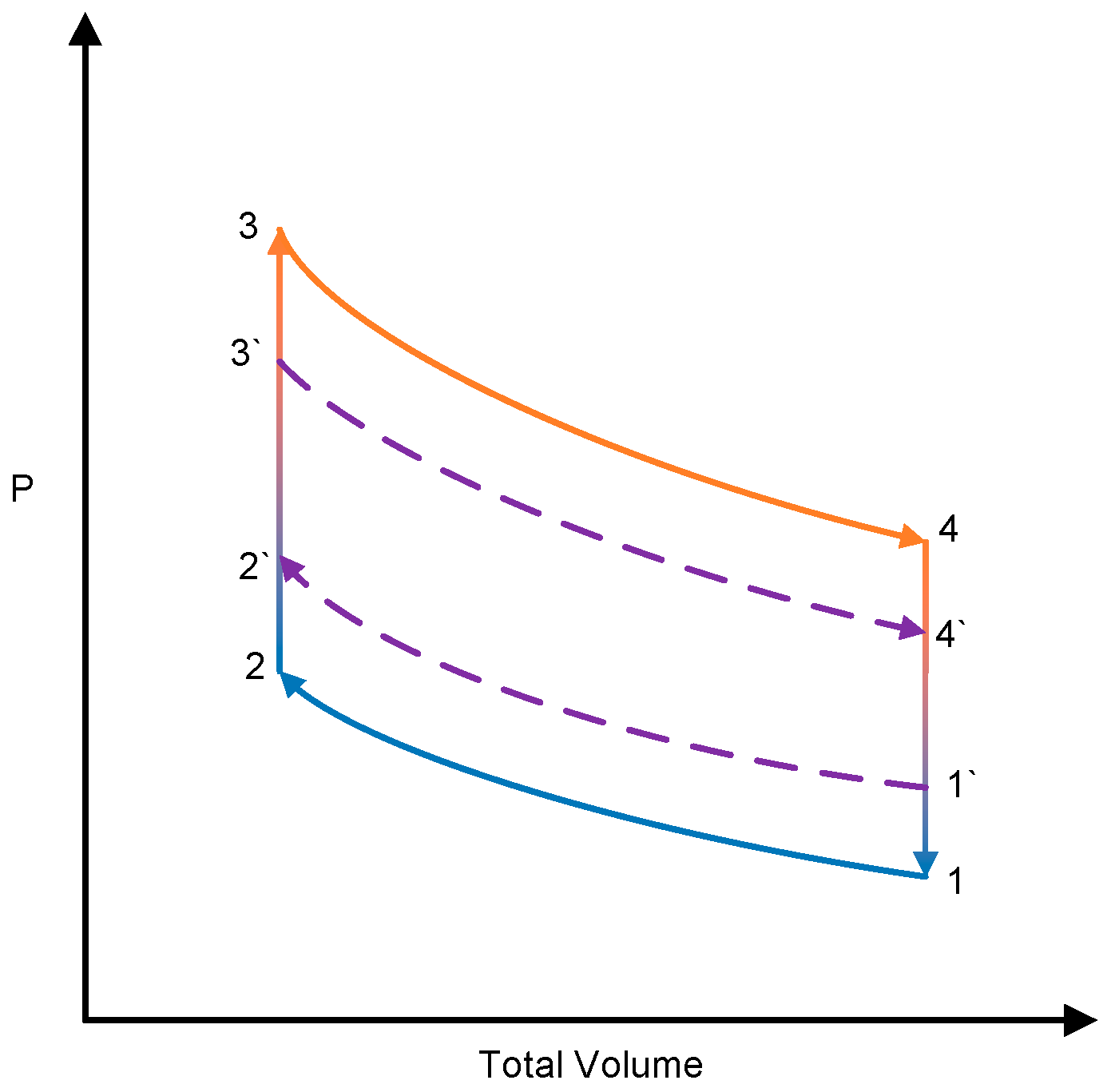
3.2. Influence of the Isothermal Fins
3.3. Optimised Response
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kongtragool, B.; Wongwises, S. A four power-piston low-temperature differential Stirling engine using simulated solar energy as a heat source. Sol. Energy 2008, 82, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongtragool, B.; Wongwises, S. Performance of a twin power piston low temperature differential Stirling engine powered by a solar simulator. Sol. Energy 2007, 81, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shazly, J.H.; Hafez, A.Z.; el Shenawy, E.T.; Eteiba, M.B. Simulation, design and thermal analysis of a solar Stirling engine using MATLAB. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 79, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongtragool, B.; Wongwises, S. A review of solar-powered Stirling engines and low temperature differential Stirling engines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2003, 7, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongtragool, B.; Wongwises, S. Performance of low-temperature differential Stirling engines. Renew. Energy 2007, 32, 547–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Sanders, S.R.; Dubey, S.; Choo, F.H.; Duan, F. Stirling cycle engines for recovering low and moderate temperature heat: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 62, 89–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, J.M.; Friedrich, D. Performance investigation of a novel Franchot engine design. Int. J. Energy Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Ven, J.D. Mobile hydraulic power supply: Liquid piston Stirling engine pump. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 2317–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauwens, L. Adiabatic Losses in Stirling Refrigerators. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 1996, 118, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, H.; Commisso, M.B.; Lorentzen, B. Maximum Obtainable Efficiency For Engines and Refrigerators Based on The Stirling Cycle. In Proceedings of the 25th Intersociety Energy Conversion Engineering Conference, Reno, Nevada, 12–17 August 1990; Volume 5, pp. 366–371. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann, C.; Ṕrise, J.A.D.R. Numerical prediction of the instantaneous regenerator and in-cylinder heat transfer of a stirling engine. Int. J. Energy Res. 1991, 15, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thombare, D.G.; Verma, S.K. Technological development in the Stirling cycle engines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G. Cryocoolers Part 2: Applications; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Hoegel, B. Thermodynamics-Based Design of Stirling Engines for Low-Temperature Heat Sources; University of Canterbury: Christchurch, New Zealand, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- El-Ehwany, A.A.; Hennes, G.M.; Eid, E.I.; El-Kenany, E.A. Development of the performance of an alpha-type heat engine by using elbow-bend transposed-fluids heat exchanger as a heater and a cooler. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. A new approach to determining the intermediate temperatures of endoreversible combined cycle power plant corresponding to maximum power. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 91, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.; Senft, J.R. Free Piston Stirling Engines, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1985; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Kongtragool, B.; Wongwises, S. Thermodynamic analysis of a Stirling engine including dead volumes of hot space, cold space and regenerator. Renew. Energy 2006, 31, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoumi, Y.; Tlili, I.; Nasrallah, S.B. Design and performance optimization of GPU-3 Stirling engines. Energy 2008, 33, 1100–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, C.D. Stirling machines: Adiabatic to isothermal. In Proceedings of the International Stirling Engine Conference (ISEC3), Rome, Italy, 1 June 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Haywood, D. Investigation of Stirling-type Heat-Pump and Refrigerator Systems Using Air as the Refrigerant. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseinzade, H.; Sayyaadi, H.; Babaelahi, M. A new closed-form analytical thermal model for simulating Stirling engines based on polytropic-finite speed thermodynamics. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 90, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Ven, J.D.; Li, P.Y. Liquid piston gas compression. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 2183–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curzon, F.L.; Ahlborn, B. Efficiency of a Carnot engine at maximum power output. Am. J. Phys. 1975, 43, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, W.R.M. Stirling Engine Design Manual, 2nd ed.; DOE/NASA/3194-I; U.S. Department of Energy Conservation and Renewable Energy Office of Vehicle and Engine R&D: Washington, DC, USA, 1983.
- Hauser, S.G.; Martini, W.R.; Scheffler, W.A. Experimental measurements of enhanced heat transfer in a Stirling engine model with interleaving fins. In Proceedings of the 16th Intersociety Energy Conversion Engineering Conference, (A82-11701 02-44), Atlanta, GA, USA, 9–14 August 1981; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1981; Volume 2, pp. 1925–1928. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, G.M. Isothermalizer System. US Patent 4,446,698, 8 May 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, A.; Schiefelbein, K. Stirling Engine with Injection of Heat Transfer Medium. US Patent 5,638,684, 17 June 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.S.; Weaver, S.P.; Nuel, B.P.; Vermeer, W.H. Direct Contact Thermal Exchange Heat Engine or Heat Pump. US Patent 2009/0038307 Al, 12 February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fette, P. A Stirling Engine Able to Work with Compound Fluids Using Heat Energy of Low to Medium Temperatures. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Stirling Engine Conference, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 26–28 May 1993; pp. 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Hoegel, B.; Pons, D.; Gschwendtner, M.; Tucker, A. Theoretical investigation of the performance of an Alpha Stirling engine for low temperature applications. In Proceedings of the ISEC the 15th International Stirling Engine Conference, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 27–29 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Costea, M.; Feidt, M. The effect of the overall heat transfer coefficient variation on the optimal distribution of the heat transfer surface conductance or area in a Stirling engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 1998, 39, 1753–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, Y.U.F.; Iwamoto, S.; Matsuo, M. Heat Transfer on a Small Stirling Engine. J. Mar. Eng. Soc. Jpn. 1990, 25, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuosa, M.; Saari, K.; Kankkunen, A.; Tveit, T.-M. Oscillating flow in a stirling engine heat exchanger. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2012, 45–46, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.S.; Cheng, P. Experimental studies on the onset of turbulence and frictional losses in an oscillatory turbulent pipe flow. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 1996, 17, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name | Symbol | Value/Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Stroke length | Le, Lc | 50 cm |
| Bore diameter | De, Dc | 5 cm |
| Charge gas density | ρ | 1.225 kg/m3 |
| Clearance length | re, rc | 0.1 mm |
| Regenerator volume | Vr | 0 cm3 |
| Out of Phase angle | θ | 90 degree |
| Hot, cold temperatures | Th, Tk | 450 K, 300 K |
| Working gas | Air | |
| Gas constant | R | 287 J/kg·K |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daoud, J.M.; Friedrich, D. Parametric Study of an Air Charged Franchot Engine with Novel Hot and Cold Isothermalizers. Inventions 2017, 2, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions2040035
Daoud JM, Friedrich D. Parametric Study of an Air Charged Franchot Engine with Novel Hot and Cold Isothermalizers. Inventions. 2017; 2(4):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions2040035
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaoud, Jafar M., and Daniel Friedrich. 2017. "Parametric Study of an Air Charged Franchot Engine with Novel Hot and Cold Isothermalizers" Inventions 2, no. 4: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions2040035
APA StyleDaoud, J. M., & Friedrich, D. (2017). Parametric Study of an Air Charged Franchot Engine with Novel Hot and Cold Isothermalizers. Inventions, 2(4), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions2040035