Effects of Iron Amendments on the Speciation of Arsenic in the Rice Rhizosphere after Drainage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pot Experiment
2.2. Eh, pH and Soil Solution Analyses
2.3. Soil and Root Sampling from Rice-Cultivation Pots
2.4. Speciation of As by X-ray Absorption Near Edge Structure Spectroscopy
2.5. Analyses of Rice Grain
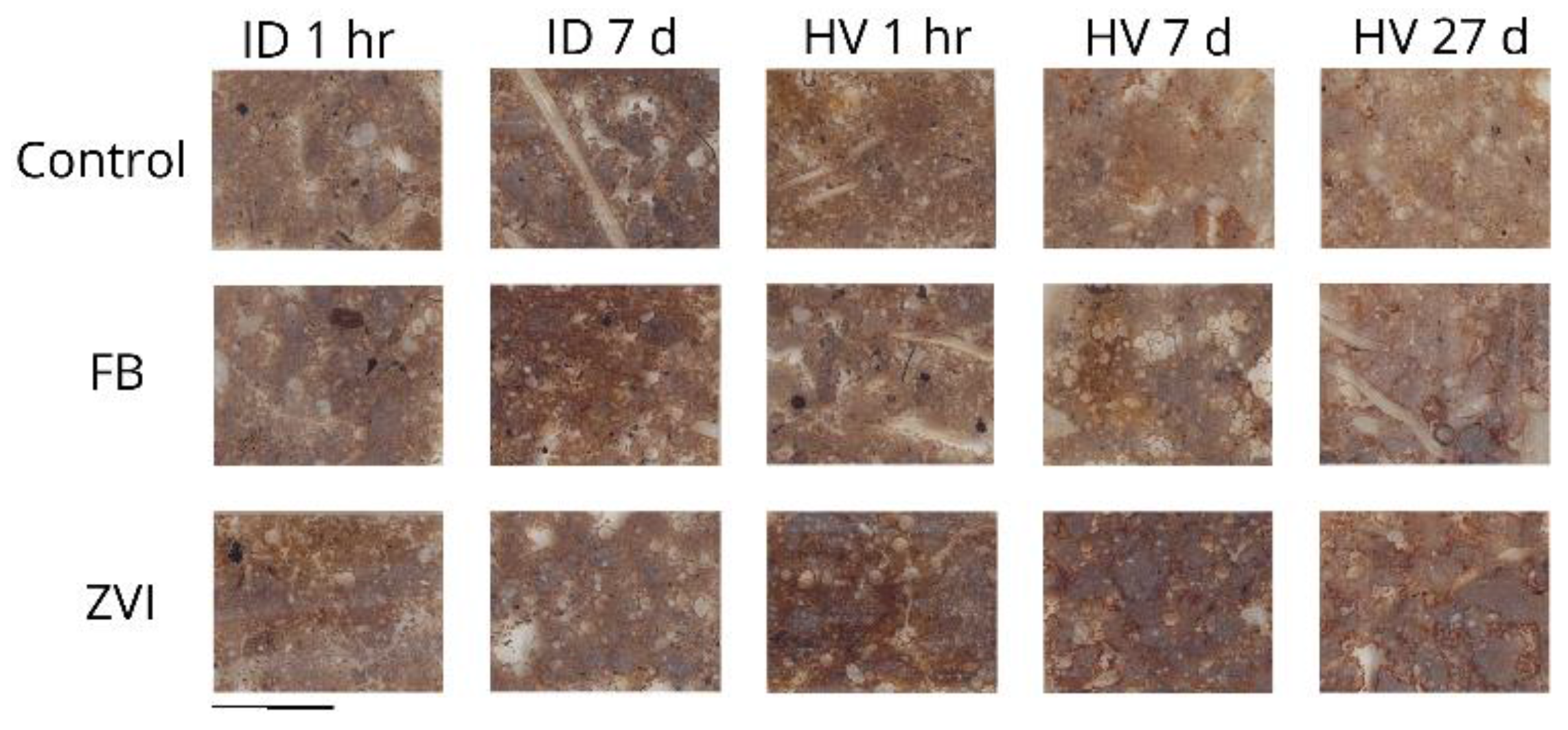
2.6. Preparation of Soil Thin-Sections
2.7. Statistic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Observation of the Soil Thin-Sections
3.2. Soil Redox Potential, pH and As and Fe Dissolution in the Soil Solution
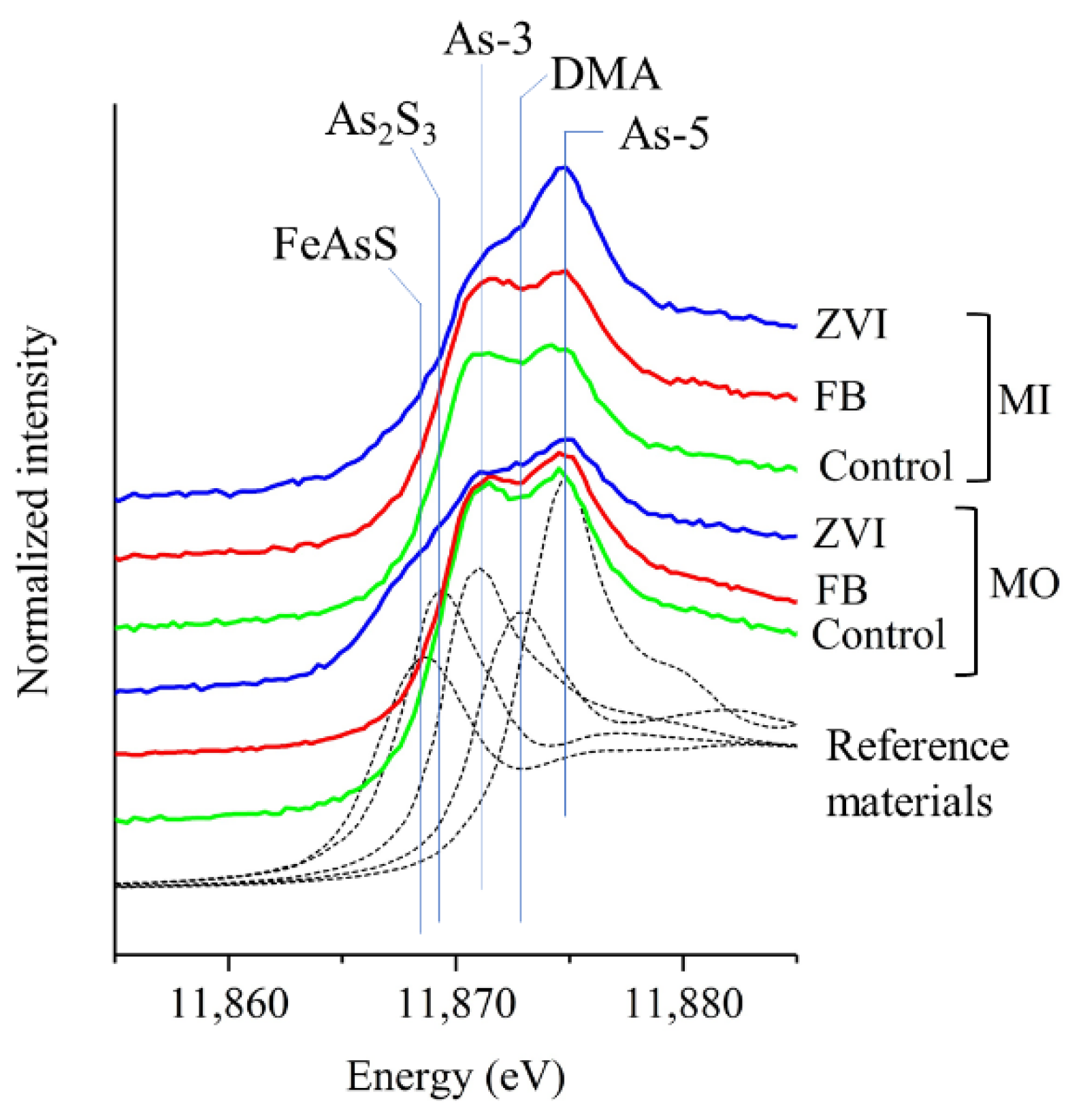
3.3. As Speciation
3.3.1. Root-Attached Materials (RZ)
3.3.2. Bulk Soil (MO and MI)
4. Discussion
4.1. Deposition of Fe Hydroxide after Drainage
4.1.1. Intermittent Drainage
4.1.2. Drainage at Harvest
4.1.3. Deposition of Fe Plaques Around Roots
4.2. Oxidation of As after Drainage
4.3. Influence of Fe Amendments
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stone, R. Food safety—Arsenic and paddy rice: A neglected cancer risk? Science 2008, 321, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, B.A.; Goldberg, S. Arsenic(III) and arsenic(V) absorption on three California soils. Soil Sci. 1997, 162, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Minamikawa, R.; Hattori, K.H.; Kurishima, K.; Kihou, N. Arsenic behavior in paddy fields during the cycle of flooded and non-flooded periods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Nakamura, T.; Dong, D.; Takahashi, Y.; Amachi, S.; Makino, T. Arsenic release from flooded paddy soils is influenced by speciation, Eh, pH, and iron dissolution. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arao, T.; Kawasaki, A.; Baba, K.; Mori, S.; Matsumoto, S. Effects of water management on cadmium and arsenic accumulation and dimethylarsinic acid concentrations in Japanese rice. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 9361–9367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickson, R.T.; McArthur, J.M.; Ravenscroft, P.; Burgess, W.G.; Ahmed, K.M. Mechanism of arsenic release to groundwater, Bangladesh and west Bengal. Appl. Geochem. 2000, 15, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Y.; McGrath, S.P.; Meharg, A.A.; Zhao, F.J. Growing rice aerobically markedly decreases arsenic accumulation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5574–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Jimenez, E.; Meharg, A.A.; Smolders, E.; Manzano, R.; Becerra, D.; Sanchez-Llerena, J.; Albarran, A.; Lopez-Pinero, A. Sprinkler irrigation of rice fields reduces grain arsenic but enhances cadmium. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 485, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyuma, K. Paddy Soil Science; Kyoto University Press: Kyoto, Japan; Trans Pacific Press: Melbourne, Australia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Makino, T.; Nakamura, K.; Katou, H.; Ishikawa, S.; Ito, M.; Honma, T.; Miyazaki, N.; Takehisa, K.; Sano, S.; Matsumoto, S.; et al. Simultaneous decrease of arsenic and cadmium in rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants cultivated under submerged field conditions by the application of iron-bearing materials. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2016, 62, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Kasuga, J.; Makino, T.; Arao, T. Evaluation of the effects of application of iron materials on the accumulation and speciation of arsenic in rice grain grown on uncontaminated soil with relatively high levels of arsenic. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2016, 125, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Kasuga, J.; Taiki, N.; Makino, T.; Arao, T. Inhibition of arsenic accumulation in Japanese rice by the application of iron and silicate materials. Catena 2015, 135, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, A.; Baba, K.; Akahane, I.; Makino, T. Use of water-treatment residue containing polysilicate-iron to stabilize arsenic in flooded soils and attenuate arsenic uptake by rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2016, 62, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, A.; Baba, K.; Yamaguchi, N.; Akahane, I.; Makino, T. The effects of soil amendments on arsenic concentrations in soil solutions after long-term flooded incubation. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2015, 61, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, A.; Makino, T.; Yamaguchi, N.; Taniguchi, H. Arsenic immobilization in anaerobic soils by application of by-product iron materials obtained from the casting industry. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Zhu, Y.G.; Smith, F.A. Effects of iron and manganese plaques on arsenic uptake by rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.) grown in solution culture supplied with arsenate and arsenite. Plant Soil 2005, 277, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, J.M.; Travassac, F.; Lenoble, V.; Rose, J.; Zheng, Y.; Hossain, M.S.; Chowdhury, S.H.; Biswas, A.K.; Ahmed, K.M.; Cheng, Z. Temporal variations in arsenic uptake by rice plants in Bangladesh: The role of iron plaque in paddy fields irrigated with groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4185–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syu, C.H.; Jiang, P.Y.; Huang, H.H.; Chen, W.T.; Lin, T.H.; Lee, D.Y. Arsenic sequestration in iron plaque and its effect on as uptake by rice plants grown in paddy soils with high contents of as, iron oxides, and organic matter. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2013, 59, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dong, F.; Lu, Y.; Yan, Q.; Shim, H. Mechanisms controlling arsenic uptake in rice grown in mining impacted regions in south China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Seshadri, B.; Bolan, N.; Saint, C.P.; Kirkham, M.B.; Chowdhury, S.; Yamaguchi, N.; Lee, D.Y.; Li, G.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; et al. Root iron plaque on wetland plants as a dynamic pool of nutrients and contaminants. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 138, pp. 1–96. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.J.; Zhu, Y.G.; Hu, Y.; Williams, P.N.; Gault, A.G.; Meharg, A.A.; Charnock, J.M.; Smith, F.A. Arsenic sequestration in iron plaque, its accumulation and speciation in mature rice plants (Oryza sativa L.). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5730–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyfferth, A.L.; Webb, S.M.; Andrews, J.C.; Fendorf, S. Arsenic localization, speciation, and co-occurrence with iron on rice (Oryza sativa L.) roots having variable Fe coatings. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8108–8113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Ohkura, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Maejima, Y.; Arao, T. Arsenic distribution and speciation near rice roots influenced by iron plaques and redox conditions of the soil matrix. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Li, F.B.; Li, B.; Liu, C.P.; Wang, Q.; Lei, J. Arsenic mobility and bioavailability in paddy soil under iron compound amendments at different growth stages of rice. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syu, C.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Jiang, P.-Y.; Chen, M.-K.; Lee, D.-Y. Comparison of as sequestration in iron plaque and uptake by different genotypes of rice plants grown in as-contaminated paddy soils. Plant Soil 2014, 374, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violante, A.; Barberis, E.; Pigna, M.; Boero, V. Factors affecting the formation, nature, and properties of iron precipitation products at the soil-root interface. J. Plant Nutr. 2003, 26, 1889–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frommer, J.; Voegelin, A.; Dittmar, J.; Marcus, M.A.; Kretzschmar, R. Biogeochemical processes and arsenic enrichment around rice roots in paddy soil: Results from micro-focused X-ray spectroscopy. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 62, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultra, V.U.; Nakayama, A.; Tanaka, S.; Kang, Y.M.; Sakurai, K.; Iwasaki, K. Potential for the alleviation of arsenic toxicity in paddy rice using amorphous iron-(hydr)oxide amendments. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2009, 55, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Furuya, M.; Yamaguchi, N.; Makino, T. Zerovalent iron with high sulfur content enhances the formation of cadmium sulfide in reduced paddy soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2016, 80, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, X.; Li, Y.; Shen, X. Uptake and accumulation characteristics of arsenic and iron plaque in rice at different growth stages. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2015, 46, 2509–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H.; Eickhorst, T.; Tippkötter, R. Monitoring of root growth and redox conditions in paddy soil rhizotrons by redox electrodes and image analysis. Plant Soil 2010, 341, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfferth, A.L.; Ross, J.; Webb, S.M. Evidence for the root-uptake of arsenite at lateral root junctions and root apices in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Soils 2017, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.T.; Yamaguchi, N.; Makino, T.; Amachi, S. Effect of soil microorganisms on arsenite oxidation in paddy soils under oxic conditions. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2014, 60, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Katou, H. Arsenic and cadmium solubilization and immobilization in paddy soils in response to alternate submergence and drainage. In Competitive Sorption and Transport of Heavy Metals in Soils and Geological Media; Selim, H.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 379–404. [Google Scholar]
- Arao, T.; Kawasaki, A.; Baba, K.; Matsumoto, S. Effects of arsenic compound amendment on arsenic speciation in rice grain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuramata, M.; Sakakibara, F.; Kataoka, R.; Abe, T.; Asano, M.; Baba, K.; Takagi, K.; Ishikawa, S. Arsenic biotransformation by Streptomyces sp isolated from rice rhizosphere. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 1897–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Arai, Y.; Sparks, D.L. Multiscale assessment of methylarsenic reactivity in soil. 2. Distribution and speciation in soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4300–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Arai, Y.; Sparks, D.L. Multiscale assessment of methylarsenic reactivity in soil. 1. Sorption and desorption on soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4293–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Gao, K.T.; Jin, J.; Lin, H.Z.; Xu, X.Y. Analysis of ZVI corrosion products and their functions in the combined ZVI and anaerobic sludge system. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 12747–12756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Bao, P.; Zhu, Y.G. Arsenic bioavailability to rice plant in paddy soil: Influence of microbial sulfate reduction. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 1960–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, R.D.; Smyth, D.J.A.; Blowes, D.W.; Spink, L.E.; Wilkin, R.T.; Jewett, D.G.; Weisener, C.J. Treatment of arsenic, heavy metals, and acidity using a mixed PVI-compost PRB. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1970–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kober, R.; Welter, E.; Ebert, M.; Dahmke, A. Removal of arsenic from groundwater by zerovalent iron and the role of sulfide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8038–8044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ona-Nguema, G.; Morin, G.; Wang, Y.H.; Foster, A.L.; Juillot, F.; Calas, G.; Brown, G.E. XANES evidence for rapid arsenic(III) oxidation at magnetite and ferrihydrite surfaces by dissolved O2 via Fe2+-mediated reactions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5416–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Eh | pH | As | Fe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mV | µmol L−1 | mmol L−1 | ||
| Days of flooding | ||||
| 50 d (6 d before intermittent drainage) | −234 ± 6a | 6.70 ± 0.04a | 3.05 ± 0.42a | 4.85 ± 0.20a |
| 72 d (41 d before drainage at harvest) | −229 ± 8a | 6.81 ± 0.02b | 3.51 ± 0.52a | 3.82 ± 0.20b |
| 78 d (35 days before drainage at harvest) | −226 ± 3a | 6.75 ± 0.02ab | 3.96 ± 0.62a | 4.32 ± 0.44ab |
| Materials | ||||
| Control | −236 ± 3a | 6.71 ± 0.03a | 5.46 ± 0.18a | 5.08 ± 0.33a |
| FB | −235 ± 4a | 6.80 ± 0.04a | 3.00 ± 0.21b | 3.80 ± 0.18b |
| ZVI | −221 ± 10a | 6.72 ± 0.03a | 1.81 ± 0.21c | 4.39 ± 0.24ab |
| Analysis of Variance | ||||
| Days of flooding | n.s. | * | n.s. | ** |
| Materials | n.s. | n.s. | ** | * |
| Days of flooding x Materials | n.s. | n.s. | - | - |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamaguchi, N.; Ohkura, T.; Hikono, A.; Yamaguchi, H.; Hashimoto, Y.; Makino, T. Effects of Iron Amendments on the Speciation of Arsenic in the Rice Rhizosphere after Drainage. Soils 2017, 1, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/soils1010006
Yamaguchi N, Ohkura T, Hikono A, Yamaguchi H, Hashimoto Y, Makino T. Effects of Iron Amendments on the Speciation of Arsenic in the Rice Rhizosphere after Drainage. Soils. 2017; 1(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/soils1010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamaguchi, Noriko, Toshiaki Ohkura, Atsuko Hikono, Hiroshi Yamaguchi, Yohey Hashimoto, and Tomoyuki Makino. 2017. "Effects of Iron Amendments on the Speciation of Arsenic in the Rice Rhizosphere after Drainage" Soils 1, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/soils1010006
APA StyleYamaguchi, N., Ohkura, T., Hikono, A., Yamaguchi, H., Hashimoto, Y., & Makino, T. (2017). Effects of Iron Amendments on the Speciation of Arsenic in the Rice Rhizosphere after Drainage. Soils, 1(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/soils1010006





