Relevance of Reactive Fe:S Ratios for Sulfur Impacts on Arsenic Uptake by Rice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil
2.2. Soil and Planting Preparation
2.3. Plant-Growth and Sampling
2.4. Harvest and Post-Trial Ppreparations
- The standing water was decanted
- The soil/root mass was lifted out and put into a larger tub for root cleaning
- A 10–15 g soil sample was immediately taken from the middle of the soil/root lump with a spatula and put in a 20 mL plastic scintillation vial, flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen, quickly transferred to a freeze-dryer chamber and freeze-dried under vacuum for 3–5 days. The samples were stored in the dark at room temperature in a glove bag (95% N2/5% H2 atmosphere).
- The root mass was carefully loosened from the soil and thoroughly cleaned with several liters of DI water in the tub until the rinsing water was free from soil particles.
2.5. Analytical Procedures
2.6. Statistical Analyses and Data Treatment
3. Results
3.1. Biomass and As Uptake
3.2. Soil Solution
3.3. Soil As and S Speciation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAOSTAT. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: http://faostat3.fao.org/home/E (accessed on 3 February 2015).
- Fendorf, S.; Michael, H.A.; van Geen, A. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Groundwater Arsenic in South and Southeast Asia. Science 2010, 328, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meharg, A.A.; Rahman, M.M. Arsenic Contamination of Bangladesh Paddy Field Soils: Implications for Rice Contribution to Arsenic Consumption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meharg, A.A.; Williams, P.N.; Adomako, E.; Lawgali, Y.Y.; Deacon, C.; Villada, A.; Cambell, R.C.J.; Sun, G.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Feldmann, J.; Raab, A.; Zhao, F.-J.; Islam, R.; Hossain, S.; Yanai, J. Geographical Variation in Total and Inorganic Arsenic Content of Polished (White) Rice. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1612–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.N.; Price, A.H.; Raab, A.; Hossain, S.A.; Feldmann, J.; Meharg, A.A. Variation in Arsenic Speciation and Concentration in Paddy Rice Related to Dietary Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5531–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Minamikawa, R.; Hattori, K.H.; Kurishima, K.; Kihou, N.; Yuita, K. Arsenic Behavior in Paddy Fields during the Cycle of Flooded and Non-flooded Periods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.F.; Yamaji, N.; Mitani, N.; Xu, X.-Y.; Su, Y.-H.; McGrath, S.P.; Zhao, F.-J. Transporters of arsenite in rice and their role in arsenic accumulation in rice grain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9931–9935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedin, M.J.; Feldmann, J.; Meharg, A.A. Uptake Kinetics of Arsenic Species in Rice Plants. Plant Physiol. 2002, 128, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, F.-J.; Meharg, A.A.; Raab, A.; Feldmann, J.; McGrath, S.P. Mechanisms of Arsenic Hyperaccumulation in Pteris vittata. Uptake Kinetics, Interactions with Phosphate, and Arsenic Speciation. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetterlein, D.; Szegedi, K.; Ackermann, J.; Mattusch, J.; Neue, H.-U.; Tanneberg, H.; Jahn, R. Competitive Mobilization of Phosphate and Arsenate Associated with Goethite by Root Activity. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1811–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catarecha, P.; Segura, M.D.; Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; García-Ponce, B.; Lanza, M.; Solano, R.; Paz-Ares, J.; Leyva, A. A mutant of the Arabidopsis phosphate transporter PHT1;1 displays enhanced arsenic accumulation. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.-J.; McGrath, S.P.; Meharg, A.A. Arsenic as a food chain contaminant: mechanisms of plant uptake and metabolism and mitigation strategies. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 535–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, P.K.; Kim, K. A review of the arsenic concentration in paddy rice from the perspective of geoscience. Geosci. J. 2013, 17, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfferth, A.L.; Fendorf, S. Silicate Mineral Impacts on the Uptake and Storage of Arsenic and Plant Nutrients in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 13176–13183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zia, Z.; Bakhat, H.F.; Saqib, Z.A.; Shah, G.M.; Fahad, S.; Ashraf, M.R.; Hammad, H.M.; Naseem, W.; Shahid, M. Effect of water management and silicon on germination, growth, phosphorus and arsenic uptake in rice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 144, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.-J.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Smith, F.A.; Smith, S.E. Do phosphorus nutrition and iron plaque alter arsenate (As) uptake by rice seedlings in hydroponic culture? New Phytol. 2004, 162, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-J.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Smith, F.A.; Smith, S.E. Do iron plaque and genotypes affect arsenate uptake and translocation by rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.) grown in solution culture? J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, A.; Tripathi, P.; Dwivedi, S.; Dubey, S.; Shri, M.; Kumar, S.; Tripathi, P.K.; Dave, R.; Kumar, A.; Singh, R.; Adhikari, B.; Bag, M.; Tripathi, R.D.; Trivedi, P.K.; Chakrabarty, D.; Tuli, R. Arsenic tolerances in rice (Oryza sativa) have a predominant role in transcriptional regulation of a set of genes including sulphur assimilation pathway and antioxidant system. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, S.; Tripathi, R.D.; Tripathi, P.; Kumar, A.; Dave, R.; Mishra, S.; Singh, R.; Sharma, D.; Rai, U.N.; Chakrabarty, D.; Trivedi, P.K.; Adhikari, B.; Bag, M.K.; Dhankher, O.P.; Tuli, R. Arsenate exposure affects amino acids, mineral nutrient status and antioxidants in rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 9542–9549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Ohkura, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Maejima, Y.; Arao, T. Arsenic distribution and speciation near rice roots influenced by iron plaques and redox conditions of the soil matrix. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, D.; Wu, S.-C.; Wu, F.-Y.; Deng, H.; Wong, M.-H. Effects of root anatomy and Fe plaque on arsenic uptake by rice seedlings grown in solution culture. Environ. Pollut. Barking Essex 1987 2010, 158, 2589–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Ye, Z.; Li, H.; Wu, S.; Deng, D.; Zhu, Y.; Wong, M. Do radial oxygen loss and external aeration affect iron plaque formation and arsenic accumulation and speciation in rice? J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 2961–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, X.Q.; Wong, M.H.; Yang, Y.; Dong, H.Y.; Qiu, R.L.; Ye, Z.H. The effects of radial oxygen loss on arsenic tolerance and uptake in rice and on its rhizosphere. Environ. Pollut. Barking Essex 1987 2012, 165, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravin, M.N.; Travassac, F.; Floch, M.L.; Hinsinger, P.; Garnier, J.-M. Oxygen input controls the spatial and temporal dynamics of arsenic at the surface of a flooded paddy soil and in the rhizosphere of lowland rice (Oryza sativa L.): A microcosm study. Plant Soil 2008, 312, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.Y.; Stroud, J.L.; Ma, J.F.; McGrath, S.P.; Zhao, F.J. Mitigation of arsenic accumulation in rice with water management and silicon fertilization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3778–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talukder, A.S.M.H.M.; Meisner, C.A.; Sarkar, M.A.R.; Islam, M.S.; Sayre, K.D.; Duxbury, J.M.; Lauren, J.G. Effect of water management, arsenic and phosphorus levels on rice in a high-arsenic soil–water system: II. Arsenic uptake. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 80, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Huang, J.; Ouyang, Y.; Wu, L.; Song, J.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Han, C.; Zhou, L.; Huang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Christie, P. Water management affects arsenic and cadmium accumulation in different rice cultivars. Environ. Geochem. Health 2013, 35, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, M.F. Arsenic toxicity and potential mechanisms of action. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 133, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnegan, P.M.; Chen, W. Arsenic Toxicity: The Effects on Plant Metabolism. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, D.K.; Srivastava, S.; Huang, H.G.; Romero-Puertas, M.C.; Sandalio, L.M. Arsenic Tolerance and Detoxification Mechanisms in Plants. In Detoxification of Heavy Metals; Sherameti, I., Varma, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 169–179. ISBN 978-3-642-21407-3, 978-3-642-21408-0. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, G.J.; Lou-Hing, D.E.; Meharg, A.A.; Price, A.H. Rice–arsenate interactions in hydroponics: whole genome transcriptional analysis. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 2267–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmöger, M.E.V.; Oven, M.; Grill, E. Detoxification of Arsenic by Phytochelatins in Plants. Plant Physiol. 2000, 122, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, R.; Singh, P.K.; Tripathi, P.; Shri, M.; Dixit, G.; Dwivedi, S.; Chakrabarty, D.; Trivedi, P.K.; Sharma, Y.K.; Dhankher, O.P.; Corpas, F.J.; Barroso, J.B.; Tripathi, R.D. Arsenite Tolerance is Related to Proportional Thiolic Metabolite Synthesis in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 64, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, G.; Singh, A.P.; Kumar, A.; Mishra, S.; Dwivedi, S.; Kumar, S.; Trivedi, P.K.; Pandey, V.; Tripathi, R.D. Reduced arsenic accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) shoot involves sulfur mediated improved thiol metabolism, antioxidant system and altered arsenic transporters. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 99, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Akkarakaran, J.J.; Sounderajan, S.; Shrivastava, M.; Suprasanna, P. Arsenic toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) is influenced by sulfur supply: Impact on the expression of transporters and thiol metabolism. Geoderma 2016, 270, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, E.D.; Johnston, S.G.; Kocar, B.D. Arsenic Mobility during Flooding of Contaminated Soil: The Effect of Microbial Sulfate Reduction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13660–13667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couture, R.-M.; Rose, J.; Kumar, N.; Mitchell, K.; Wallschläger, D.; Van Cappellen, P. Sorption of Arsenite, Arsenate, and Thioarsenates to Iron Oxides and Iron Sulfides: A Kinetic and Spectroscopic Investigation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5652–5659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocar, B.D.; Borch, T.; Fendorf, S. Arsenic repartitioning during biogenic sulfidization and transformation of ferrihydrite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 980–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Day, P.A.; Vlassopoulos, D.; Root, R.; Rivera, N. The influence of sulfur and iron on dissolved arsenic concentrations in the shallow subsurface under changing redox conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13703–13708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Mikutta, C.; Kretzschmar, R. Arsenite Binding to Sulfhydryl Groups in the Absence and Presence of Ferrihydrite: A Model Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3822–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langner, P.; Mikutta, C.; Kretzschmar, R. Arsenic sequestration by organic sulphur in peat. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, J.; Berg, M. Impact of sulfate reduction on the scale of arsenic contamination in groundwater of the Mekong, Bengal and Red River deltas. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowers, H.A.; Breit, G.N.; Foster, A.L.; Whitney, J.; Yount, J.; Uddin, M.N.; Muneem, A.A. Arsenic incorporation into authigenic pyrite, Bengal Basin sediment, Bangladesh. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, Q.-Z.; Duan, G.-L.; Huang, Y.-C. Influence of sulphur on arsenic accumulation and metabolism in rice seedlings. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2011, 72, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Xia, X.; Hu, Z.; Ziadi, N.; Liu, C. Excessive sulfur supply reduces arsenic accumulation in brown rice. Plant Soil Environ. 2013, 59, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.-Y.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.-G.; Cao, Z.-H.; Smith, F.A. Sulfur (S)-induced enhancement of iron plaque formation in the rhizosphere reduces arsenic accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Bao, P.; Zhu, Y.-G. Arsenic bioavailability to rice plant in paddy soil: influence of microbial sulfate reduction. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 1960–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, M.; Stengel, C.; Pham, T.K.T.; Pham, H.V.; Sampson, M.L.; Leng, M.; Samreth, S.; Fredericks, D. Magnitude of arsenic pollution in the Mekong and Red River Deltas--Cambodia and Vietnam. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 372, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyfferth, A.L.; McCurdy, S.; Schaefer, M.V.; Fendorf, S. Arsenic Concentrations in Paddy Soil and Rice and Health Implications for Major Rice-Growing Regions of Cambodia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4699–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; He, P.; Li, S.; Lin, B. Mineralization of organic sulfur in paddy soils under flooded conditions and its availability to plants. Geoderma 2005, 125, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocar, B.D.; Polizzotto, M.L.; Benner, S.G.; Ying, S.C.; Ung, M.; Ouch, K.; Samreth, S.; Suy, B.; Phan, K.; Sampson, M.; Fendorf, S. Integrated biogeochemical and hydrologic processes driving arsenic release from shallow sediments to groundwaters of the Mekong delta. Arsen. Groundw. South-East Asia Emphas. Cambodia Vietnam 2008, 23, 3059–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRRI International Rice Research Institute. Available online: http://irri.org (accessed on 13 May 2013).
- Almkvist, G.; Boye, K.; Persson, I. K-edge XANES analysis of sulfur compounds: an investigation of the relative intensities using internal calibration. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2010, 17, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Moon, H.S.; Myneni, S.C.B.; Jaffé, P.R. Effect of dissimilatory iron and sulfate reduction on arsenic dynamics in the wetland rhizosphere and its bioaccumulation in wetland plants (Scirpus actus). J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobermann, A.; Fairhurst, T.H. Rice: Nutrient Disorders & Nutrient Management; Potash & Phosphate Institute, Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada, International Rice Research Institute, Oxford Graphic Printers Pte Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2000; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, S.; Panda, P.; Mishra, S.; Dey, M.; Choudhury, S.; Sahoo, L.; Panda, S.K. Arsenic stress in rice: Redox consequences and regulation by iron. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 80, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.B.; Jahiruddin, M.; Loeppert, R.H.; Panaullah, G.M.; Islam, M.R.; Duxbury, J.M. The effects of iron plaque and phosphorus on yield and arsenic accumulation in rice. Plant Soil 2008, 317, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Liu, W.-J.; Meharg, A.A. Direct evidence showing the effect of root surface iron plaque on arsenite and arsenate uptake into rice (Oryza sativa) roots. New Phytol. 2005, 165, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyfferth, A.L.; Webb, S.M.; Andrews, J.C.; Fendorf, S. Arsenic Localization, Speciation, and Co-Occurrence with Iron on Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Roots Having Variable Fe Coatings. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8108–8113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wan, X.; Zheng, G.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Guo, L.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Guo, Q.; Xu, R.; Zhou, G.; Peters, M.; Zhu, G.; Wei, R.; Tian, L.; Han, X. Interaction between sulfur and lead in toxicity, iron plaque formation and lead accumulation in rice plant. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 128, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.Y.H.; Lu, J.; Hu, Z.Y. Influence of Sulfur Supply on the Iron Accumulation in Rice Plants. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2014, 45, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

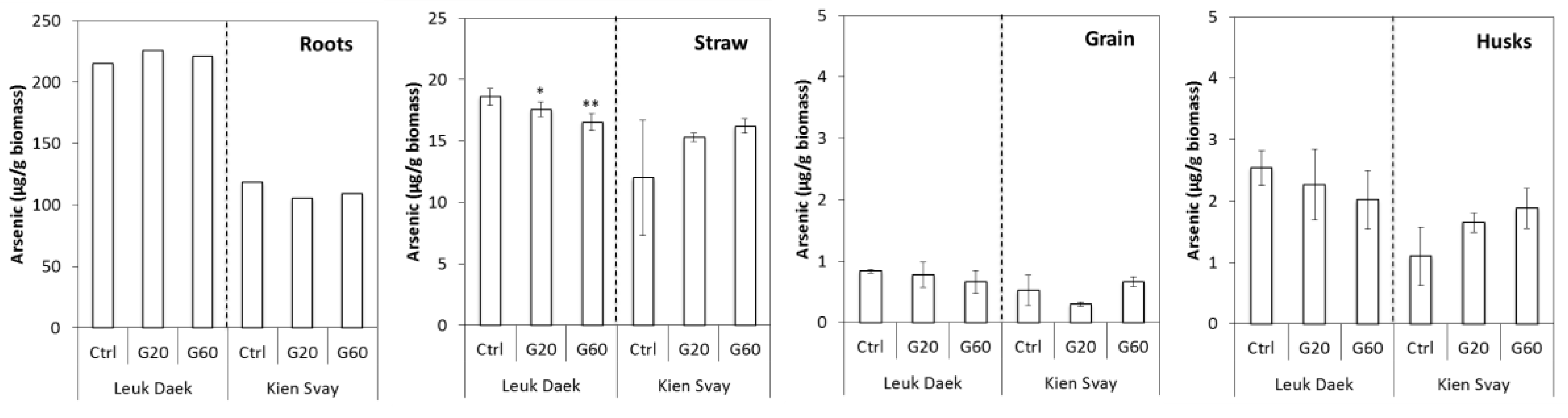
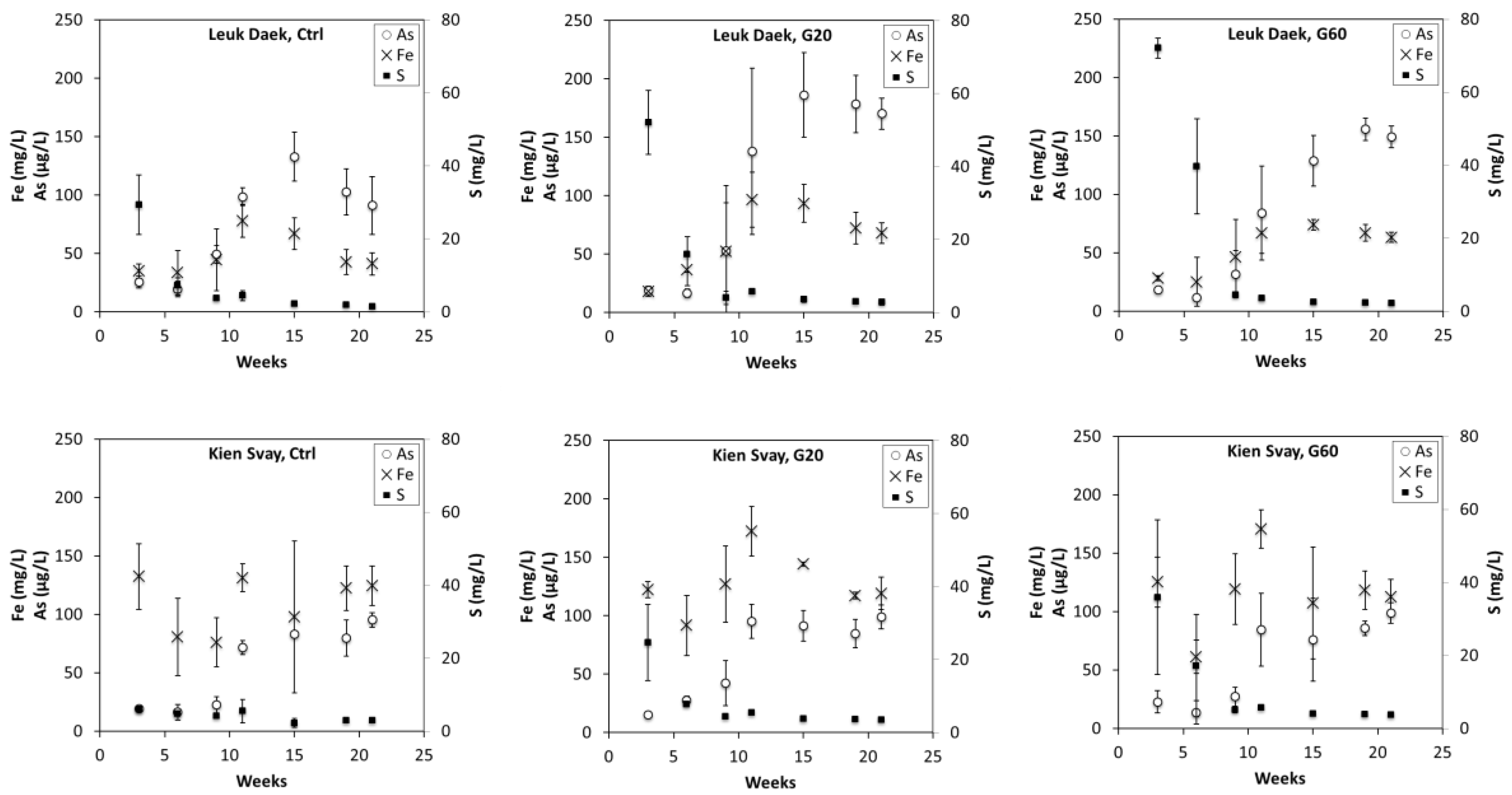
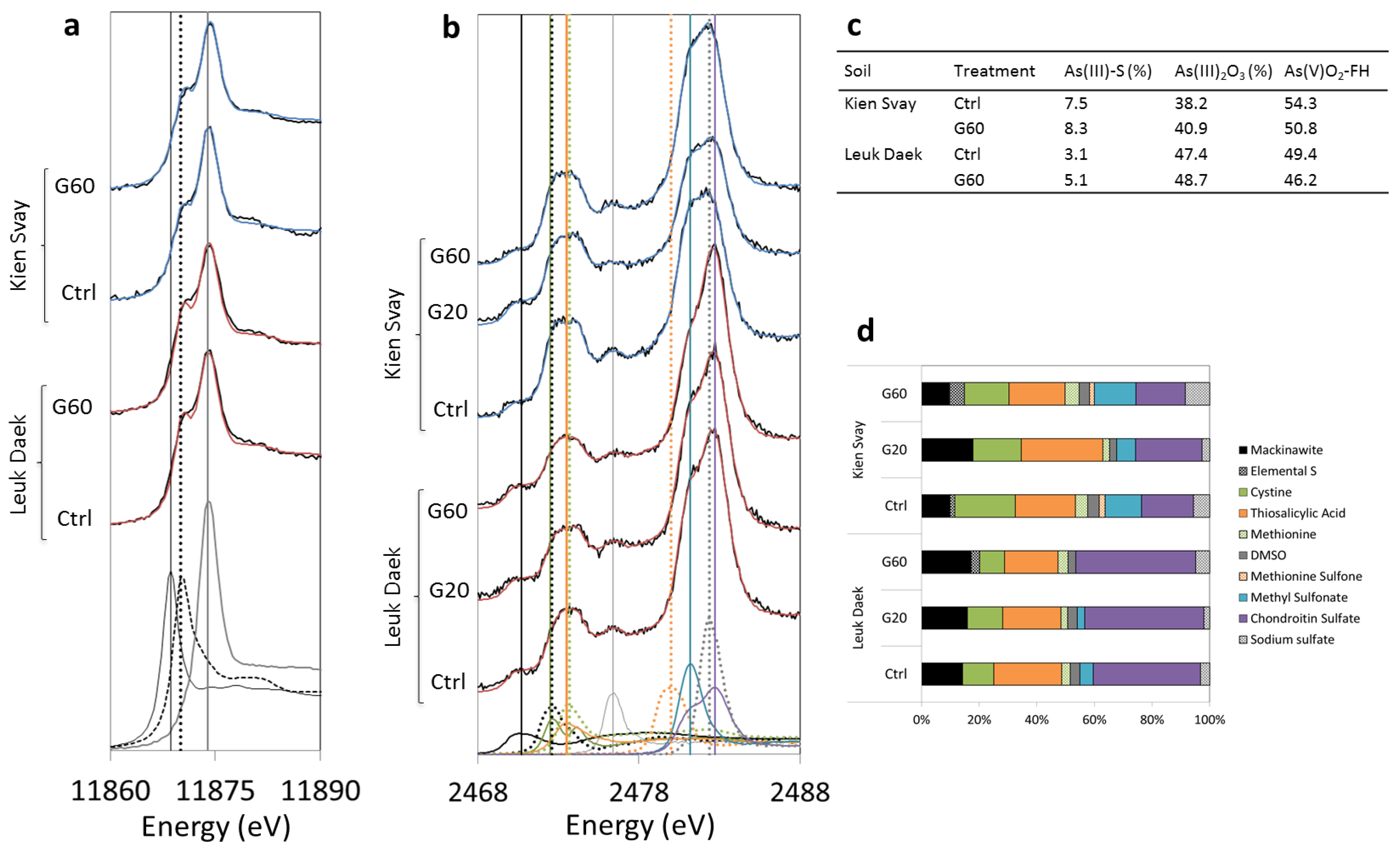
| Soil | Treatment | As in Plaque (µg g−1 Root Biomass) | As in Root (µg g−1 Root Biomass) | Fe in Plaque (mg g−1 Root Biomass) | Fe in Root (mg g−1 Root Biomass) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kien Svay | Ctrl | 76.8 ± 6.9 | 61.8 ± 1.4 | 16.8 ± 2.5 | 6.61 ± 0.39 |
| G60 | 33.4 ± 6.5 | 52.8 ± 2.6 | 7.4 ± 1.0 | 6.9 ± 1.5 | |
| Leuk Daek | Ctrl | 92.3 ± 1.9 | 76.5 ± 1.0 | 11.1 ± 0.06 | 7.84 ± 0.30 |
| G60 | 52 ± 32 | 59.7 ± 3.2 | 9.2 ± 3.5 | 7.0 ± 0.52 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boye, K.; Lezama-Pacheco, J.; Fendorf, S. Relevance of Reactive Fe:S Ratios for Sulfur Impacts on Arsenic Uptake by Rice. Soils 2017, 1, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/soils1010001
Boye K, Lezama-Pacheco J, Fendorf S. Relevance of Reactive Fe:S Ratios for Sulfur Impacts on Arsenic Uptake by Rice. Soils. 2017; 1(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/soils1010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoye, Kristin, Juan Lezama-Pacheco, and Scott Fendorf. 2017. "Relevance of Reactive Fe:S Ratios for Sulfur Impacts on Arsenic Uptake by Rice" Soils 1, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/soils1010001
APA StyleBoye, K., Lezama-Pacheco, J., & Fendorf, S. (2017). Relevance of Reactive Fe:S Ratios for Sulfur Impacts on Arsenic Uptake by Rice. Soils, 1(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/soils1010001






