Abstract
Flux as well as spatial and angular resolution for a microbeam small-angle X-ray scattering set-up, comprising Laue optics and multiple focusing elements are modeled within five-dimensional phase space analysis. A variety of X-ray optics configurations for highest angular resolution and for highest spatial resolution are analyzed.
1. Introduction
Microbeam small-angle X-ray scattering, in short microSAXS, adds another dimension to the well-established small-angle scattering technique [1]. Not only can spatially inhomogeneous samples be studied in detail [2,3], but also microfluidic sample environments become accessible by the technique [4,5]. A microbeam small-angle X-ray scattering (microSAXS) experiment has to overcome contradictory requirements: for a high resolution in SAXS the beam should have as low a divergence as possible. In order to obtain high spatial resolution the beam has to be focused to micron size, introducing enhanced divergence. The design challenge is how to achieve the desired scanning resolution while maintaining a reasonable scattering resolution at a good photon flux.
The considerations presented here are inspired by the Sector 2b and 3b side-bounce stations at the upgraded Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source. Both stations feature a fixed scattering angle of 2θB = 36°, which corresponds to fixed beam energies of 9.7 keV, 15.9 keV, and 22.5 keV for the diamond 111, 220, and 400 reflections, respectively. Due to heatload concerns the Laue geometry is favorable, as it minimizes X-ray absorption. An attractive feature of the Laue geometry is Laue focusing [6,7] which results in 1:1 focusing of the beam for symmetric cut crystals. This focusing effect has to be taken into account for properly designing the main focusing optics. In the following it is shown how phase space analysis (PSA) can be used as a convenient tool for determining flux, gain, as well as spatial and angular resolution and thus modelling the beamline in its entirety.
2. Method
PSA was introduced for synchrotron radiation X-ray optics by Matsushita and Kaminaga [8,9], inspired by methods used in accelerator science. Here the variant by Pedersen and Riekel [10] will be used with extension to the full five-dimensional phase space [11]. A photon beam is considered as a distribution of rays with slight deviations in position , angle and energy from the optical axis. We follow here the convention that lie in the horizontal plane, in the vertical plane and points along the beam direction. PSA relies on the paraxial approximation which works well for X-ray optics where typically all rays are close to the optical axis. By approximation of all distribution functions by Gaussians [10], a particularly compact formulation can be found [11].
The X-ray flux emitted by an undulator can be determined from the on-axis brilliance and the phase space density :
The phase space density can be written in compact matrix form as
Here is the vector of the five phase space variables, and its transposed. The source matrix for the on-axis radiation of an undulator in a straight section is diagonal and contains the inverse beam variances. A Cornell Compact Undulator [12] has a source brightness of 5.6 × 1017 photons/mm2/mrad2/0.1% bandwidth for the considered photon energy at an electron energy of 6 GeV and a current of 200 mA. The deviations of individual rays from the optical axis are assumed to have a normal distribution with standard deviations and are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Source parameters of a Cornell Compact Undulator.
As the beam propagates through the optical system, the phase space density matrices are modified according to:
is the acceptance matrix of the nth optical element and is the transformation matrix of the previous phase space density matrix by the optical element. The following expressions for the and matrices will be relevant to our considerations.
2.1. Flight Path of Length L without Aperture
Flight paths are assumed to have a diameter large enough to not clip the beam, i.e., all rays are accepted. The transformation matrix describes the evolution of the phase space density as the beam propagates along the flight path.
2.2. Laue Monochromator
Acceptance and Transformation matrices for a Laue monochromator are given by [10,13]
18° corresponds to the fixed Bragg angle, is derived from the Darwin width of the 220 reflection 0.016 in 0.1% band width in the Gaussian approximation:
and b to the asymmetry parameter [9,10,13].
where is the miscut angle. For demonstration purposes we will focus here solely on the case of a symmetric 220 reflection with and .
2.3. Focusing Element–Compound Refractive Lens
Compound refractive lenses [14] have a finite aperture of a typical diameter 0.5 mm. In the Gaussian approximation the positional variance is obtained from . The focal length of the lens is given by .
2.4. Reflection and Transmission Factors
Beam attenuation factors due to the transmission of X-ray windows and compound refractive lenses, or due to reflections from monochromators and mirrors enter the analysis as simple multiplicative factors for the flux. We will assume that there is only a single 0.5 mm Beryllium window at end of the incident flight path which has a transmission of 98% [15]. The reflection factor from a typical X-ray mirror is of similar order [15]. Flat X-ray mirrors are used for the suppression of higher order harmonics of the monochromator. For a perfect-crystal Laue monochromator the maximum reflected intensity is 50% [16].
The transmission of a compound refractive lense can be determined using the online calculator by RXOptics [17]. For a compound refractive lens with a focal length of 250 mm we need 85 Be lenses with a minimum curvature radius of 0.05 mm and a transmission of 23%. We will also consider generating a secondary source point using a second compound refractive lens with a focal length of 1 m which will need 19 Be single lenses and yield a transmission of 62%.
2.5. Intensities and Marginal Widths along the Beam Path
The power of the Gaussian approximation lies therein, that instead of solving high-dimensional integrals the flux at any position along the beam path can be determined directly from the transformed phase space density matrices [11]:
Another important concept is marginal standard deviations [18], for instance the standard deviation in x with all other phase space variables integrated over. These provide the actual measurable beam parameters and can again be expressed by determinants [11]:
where is the matrix obtained from by crossing out the row and column and corresponds to either or . Note that all expressions are analytical functions along the beam path and intensities and marginal beam widths can be obtained at any point along the beam path.
If all acceptances were trivial e.g., all acceptance matrices , the flux would be preserved throughout the optical system, as all T matrices merely shear the source density distribution which preserves the phase space volume and thus the flux. In contrast, apertures and crystal acceptance, as well as attenuation factors, reduce the intensity, and the goal is to optimize flux impinging on the sample while attaining the target beam parameters. The highest resolution obtained in small-angle scattering is both a function of beam size at the detector and the beam divergence; this makes microSAXS an interesting challenge in optics optimization.
3. Application
Depending on the experimental requirements the anticipated beamline should be capable of performing both high resolution SAXS (mode A) and scanning microbeam SAXS with either 10 µm or 1 μm resolution (modes B and C). Here it is assumed that the focusing elements can be removed from the beam path for a quick change-over between configurations. Most advantageous for ease of operation are on-axis focusing elements, such as X-ray compound refractive lenses or Fresnel zone plates. Figure 1 provides an overview of the three optics configurations discussed below. In the following we will focus on the medium beam energy of 15.9 keV, as obtained with a symmetric Laue 220 reflection.
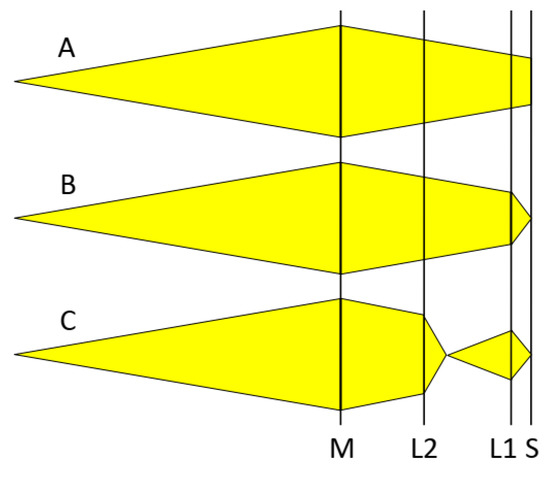
Figure 1.
Operating modes A, B, and C, shown in the horizontal plane. M is a diamond monochromator crystal with Laue focusing, S is the sample position. L1 is the primary focusing lens. L2 is the secondary focusing lens creating a virtual source point for L1 in configuration C.
3.1. Configuration A: Laue Focusing Only
This configuration is the best to achieve high angular resolution. The beam has a 1:1 Laue focusing which preserves the divergence of the source, but reduces the beam widths. Although the detector is upstream of the 1:1 focus point, the beam diameter is reduced significantly. Note that Laue focusing is only effective in the horizontal plane. However, the vertical beam size and divergence at the source are a factor of 10 smaller than in the horizontal plane, as is typical for synchrotron sources, and hence prefocusing is not as essential as in the horizontal plane.
The phase space description is in this case:
= 16.8 m is the distance between undulator and Laue monochromator crystal which is unusually short compared with other synchrotron sources operating at 6 GeV. This length is the same for all configurations; thus the beam matrices and remain the same for all three configurations. The distance from monochromator to sample is = 7.25 m. We chose the maximum sample–detector distance = 5 m for all our considerations. Of particular interest in this configuration are the beam matrices and which contain the flux and beam widths at sample and detector, respectively. For the flux and gain calculation we also need the reflection factor as well as the window transmission:
The results of the calculation for all configurations are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Flux, beam size and divergence (as standard deviations), resolution, and gain for modes A, B, and C. For beam size, divergence, and resolution the top and bottom numbers correspond to the horizontal and vertical dimensions, respectively.
3.2. Configuration B: Laue Focusing and Focusing Element
In configuration B we introduce another focusing element (or “lens” in short) close to the sample. and are the same as before. = 7 m is now the distance between monochromator and lens, and = 0.25 m the distance from lens to the sample. Compound refractive lenses with a parabolic profile have an aperture of typically = 0.5 mm; Fresnel zone plates can even have smaller apertures.
As the lens is in a convergent beam due to the Laue focusing, the optical distances for source and image are now:
Note that is negative, as the virtual source point of the lens is downstream of the lens. The focusing length is then given in the thin lens approximation as
In configuration B the beam matrices and contain all of the beam information at sample and detector, respectively. The transmission/reflection factor now contains the transmission of the compound refractive lens:
3.3. Configuration C: Laue Focusing and Two Lenses
In order to achieve focusing down to 1 µm, we have to use two lenses. Lens L1 remains the same as in configuration B. Lens L2 is located = 1.5 m downstream from the monochromator and focuses the Laue-focused beam to a secondary source point at = 1 m. The distance from the secondary source point to lens L1 is = 5 m. The distance of lens L1 to the sample is = 0.25 m, as before.
For the lens parameters we have this time:
and for the reflection transmission factor
4. Results and Discussion
We are now ready to calculate actual numbers, such as the flux and the beamsize at the sample, the beamsize at the detector, and the q-resolution. For the minimum scattering vector q we use the rule-of-thumb that the beamstop should be about three times as wide as the beam, so that at least 99% of the direct beam intensity is absorbed. The first resolvable peak is thus at . This yields a minimum scattering angle which corresponds to the minimum of the scattering vector . This in turn provides the maximum resolvable d-spacing
which we will refer to as the resolution. The values for the three configurations are provided in Table 2. Finally we will estimate the gain of the microfocusing optics. The gain is defined as the flux in the microbeam focus per unfocused flux through a pinhole of the same size as the focal spot [19]. Within the phase space analysis framework, the gain can be obtained as
for configuration B as well as for configuration C using instead of , respectively.
Our calculations are based on the use of a perfect diamond Laue crystal, such as grown with the high temperature/high pressure method. Despite the narrow Darwin width of the diamond 220 reflection of 0.016 × 10−3, such a crystal would yield a flux of 1.3 × 1012 photons/s at 15.9 keV beam energy. When averaged over the beam divergence, the marginal distribution of yields an effective energy acceptance of 4.3 eV. A mosaic crystal would have an enhanced acceptance and yield a higher flux, however at higher divergence and thus lower scattering resolution and a larger focal spot.
Within reasonable optical parameters, the resolution for single-lens focusing in configuration B is limited to a spot size of around 8 µm. Only with two lenses (configuration C) can a horizontal spot size of 1 µm be achieved. In this case the vertical beamsize is even smaller. This makes configuration C attractive for grazing incidence scattering, because the size of the beam footprint on the sample is reduced. A smaller footprint avoids geometric smearing [20], in particular for wide-angle scattering. Nonetheless, the 20-times higher flux at the sample and the round beam, both in beam size and divergence, makes configuration B an attractive option for experiments requiring high intensity, but resolution. In addition, the scattering resolution at the detector is close to isotropic, eliminating the need of resolution corrections.
5. Conclusions
PSA offers a straightforward way to obtain beam parameters and estimates of overall beamline performance, such as flux and resolution. The results are available essentially instantaneous and thus a variety of optics configurations can be simulated efficiently. PSA is the tool of choice for initial beamline layout, predicting the performance of a perfect optical system for a finite distribution of rays. When the basic layout is established, more powerful (but more time-consuming methods) such as ray tracing [21] can be used for the critical components. The good agreement of PSA and ray tracing has been demonstrated [22]. We have discussed here a variety of configurations suitable for a microSAXS beamline, meeting the constraints of the sector 2b and 3b beamlines.
Funding
Part of this work was performed at the Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source with funding by the National Science Foundation via award DMR-1332208.
Acknowledgments
Tom Krawczik, Alan Pauling, and Aaron Lyndaker are to be thanked for sharing lay-out parameters of the beamline with me. Special thanks to Stanislav Stoupin for providing the Darwin widths of the diamond reflections and stimulating discussions on the Laue geometry. I would like to acknowledge Andrey Ivashov for the use of his excellent program “SMath” [23] with which all calculations were performed.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Riekel, C. New avenues in X-ray microbeam experiments. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2000, 63, 233–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, S.V.; Burghammer, M.; Riekel, C.; Müller-Buschbaum, P.; Diethert, A.; Panagiotou, P.; Walter, H. Self-assembled gradient nanoparticle-polymer multilayers investigated by an advanced characterisation method: Microbeam grazing incidence X-ray scattering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 1935–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Cornaby, S.; Kamperman, M.; Smilgies, D.-M. Nanocomposite characterization on multiple length scales using μSAXS. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2011, 18, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollack, L.; Tate, M.W.; Darnton, N.C.; Knight, J.B.; Gruner, S.M.; Eaton, W.A.; Austin, R.H. Compactness of the denatured state of a fast-folding protein measured by submillisecond small-angle X-ray scattering. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 10115–10117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, J.S.; Cornaby, S.; Andresen, K.; Kwok, L.; Park, H.Y.; Qiu, X.; Smilgies, D.-M.; Bilderback, D.H.; Pollack, L. Focusing capillary optics for use in solution small-angle X-ray scattering. J. Appl. Cryst. 2007, 40, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez del Rio, M.; Grübel, G.; Als-Nielsen, J.; Nielsen, M. Focusing characteristics of dia-mond crystal X-ray monochromators. An experimental and theoretical comparison. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1995, 66, 5148–5152. [Google Scholar]
- Kvardakov, V.V.; Somenkov, V.A.; Lynn, J.W.; Mildner, D.F.R.; Chen, H. Laue focusing effect and its applications. Physica B 1998, 241–243, 1210–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, T.; Kaminaga, U. A systematic method of estimating the performance of X-ray optical systems for synchrotron radiation. I. Description of various optical elements in position-angle space for ideally monochromatic X-rays. J. Appl. Cryst. 1980, 13, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, T.; Kaminaga, U. A systematic method of estimating the performance of X-ray optical systems for synchrotron radiation. II. Treatment in position-angle-wavelength space. J. Appl. Cryst. 1980, 13, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, J.S.; Riekel, C. Resolution function and flux at the sample for small-angle X-ray scattering calculated in position-angle-wavelength space. J. Appl. Cryst. 1991, 24, 893–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smilgies, D.-M. Compact matrix formalism for phase space analysis of complex optical systems. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, E106–E115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanks, J.; Barley, J.; Barrett, S.; Billing, M.; Codner, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Lyndaker, A.; Rice, D.; Rider, N.; et al. Accelerator design for the Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source upgrade. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 2019, 22, 021602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvyd’ko, Y. Theory and optical design of X-ray echo spectrometers. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 96, 023804. [Google Scholar]
- Lengeler, B.; Schroer, C.; Tümmler, J.; Benner, B.; Richwin, M.; Snigirev, A.; Snigireva, I.; Drakopoulos, M. Imaging by parabolic refractive lenses in the hard X-ray range. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 1999, 6, 1153–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for X-ray Optics (CXRO). Available online: https://henke.lbl.gov/optical_constants/ (accessed on 21 July 2020).
- Grübel, G.; Abernathy, D.; Vignaud, G.; Sanchez del Rio, M.; Freund, A. A diamond double-crystal transmission monochromator for the TROIKA II station at ESRF. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1996, 67, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RX Optics—Design Parameters. Available online: https://www.rxoptics.de/design-parameters/ (accessed on 20 July 2020).
- Kreyszig, E. Advanced Engineering Mathematics, 4th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 885–889. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.; Szebenyi, T.; Pfeifer, M.; Woll, A.; Smilgies, D.-M.; Finkelstein, K.; Dale, D.; Wang, Y.; Vila Comamala, J.; Gillilan, R.; et al. Application of CHESS single-bounce capillaries at synchrotron beamlines. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 493, 012034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smilgies, D.-M. Scherrer grain-size analysis adapted to grazing-incidence scattering with area detectors. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez del Rio, M.; Canestrari, N.; Jiang, F.; Franco Cerrina, F. SHADOW3: A new version of the synchrotron X-ray optics modelling package. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2011, 18, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrero, C.; Smilgies, D.-M.; Riekel, C.; Gatta, G.; Daly, P. Extending the possibilities in phase space analysis of synchrotron radiation X-ray optics. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, E116–E124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SMath Studio. Available online: https://en.smath.com/view/SMathStudio/summary (accessed on 21 June 2019).
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).