Tin Whisker Growth Suppression Using NiO Sublayers Fabricated by Dip Coating
Abstract
1. Introduction
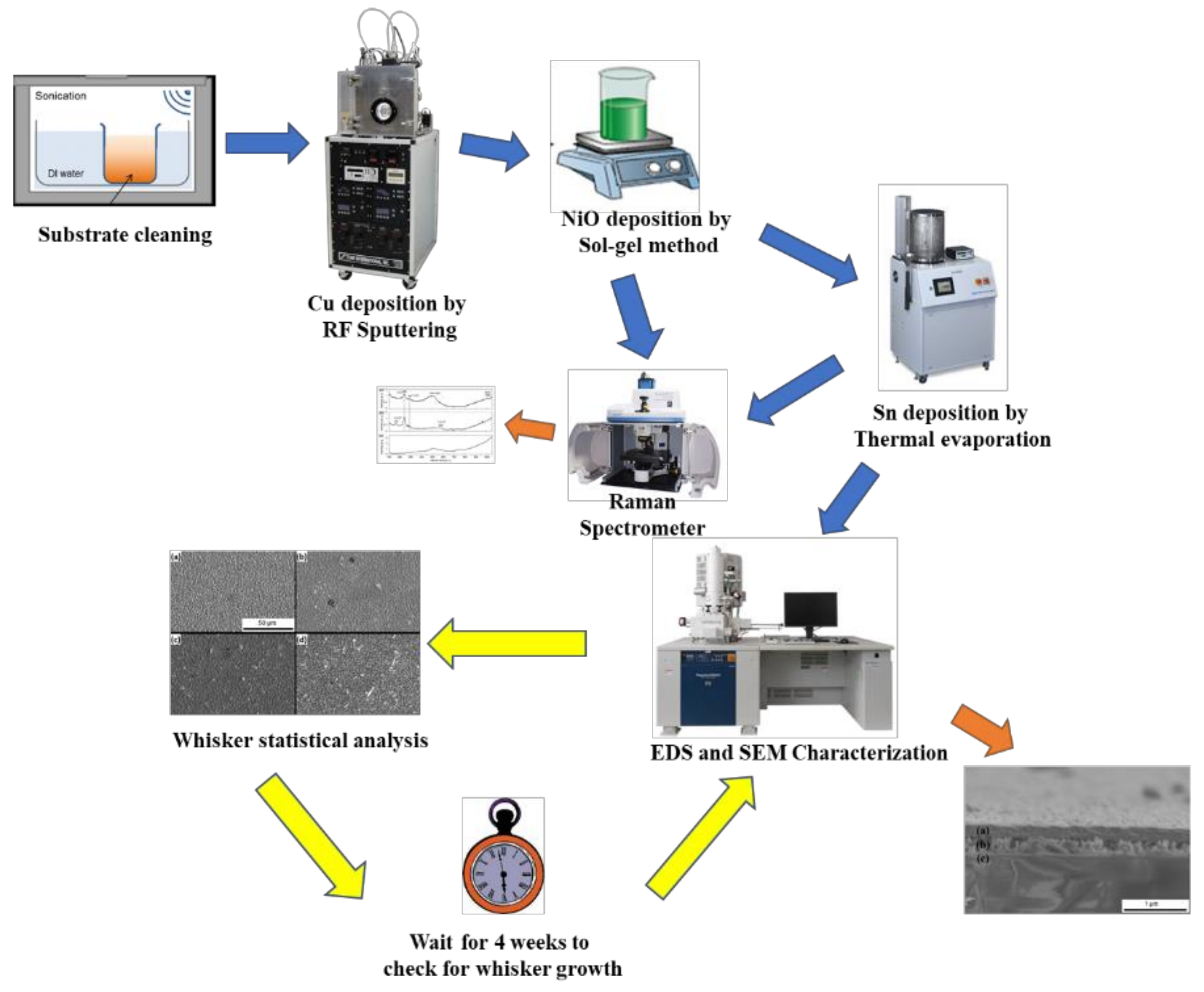
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Substrate Preparation
2.2. Sol–Gel Solution
2.3. Dip Coating Deposition
2.4. Tin Deposition
2.5. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
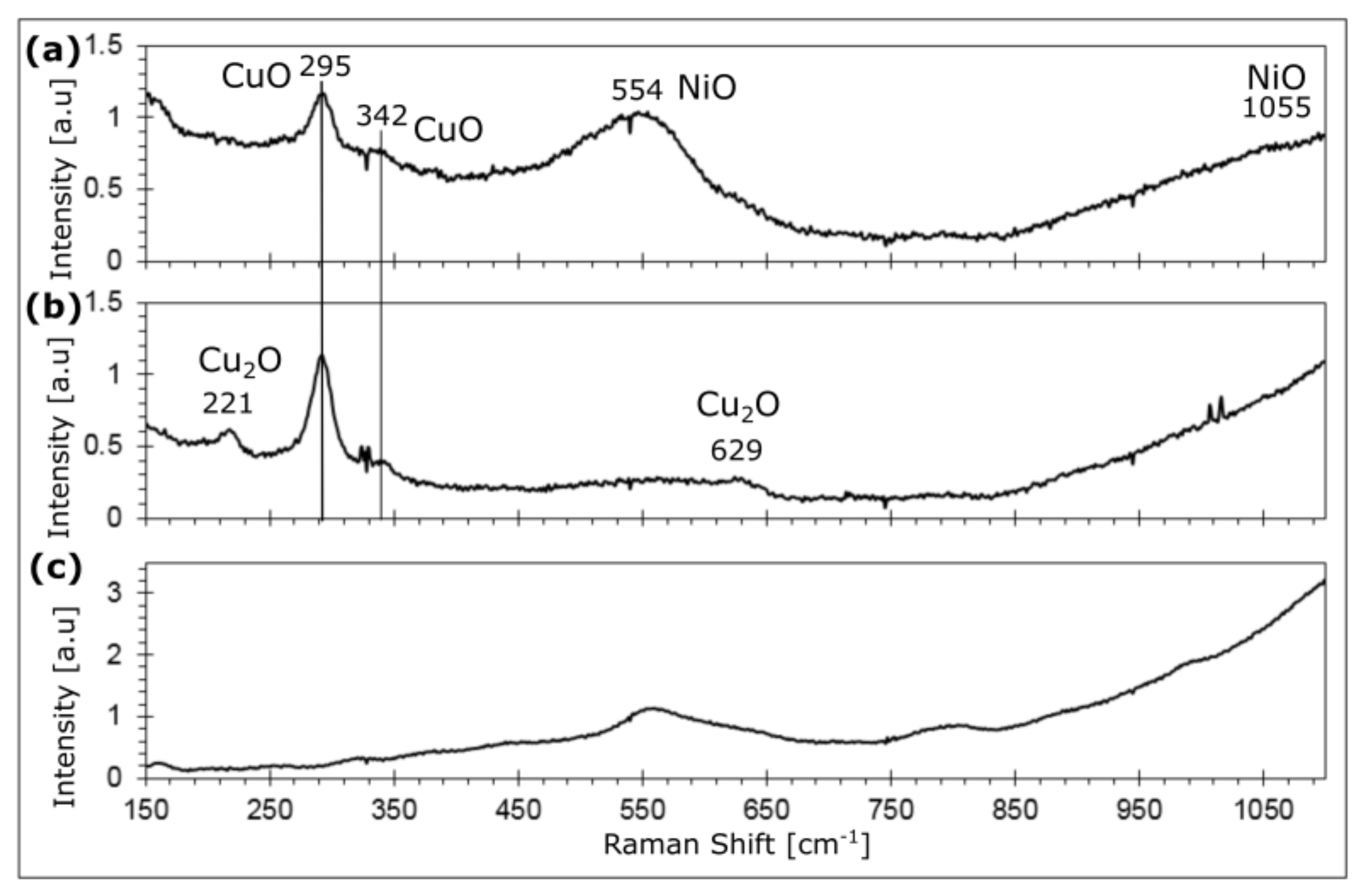
3.1. Characterization of the NiO Films
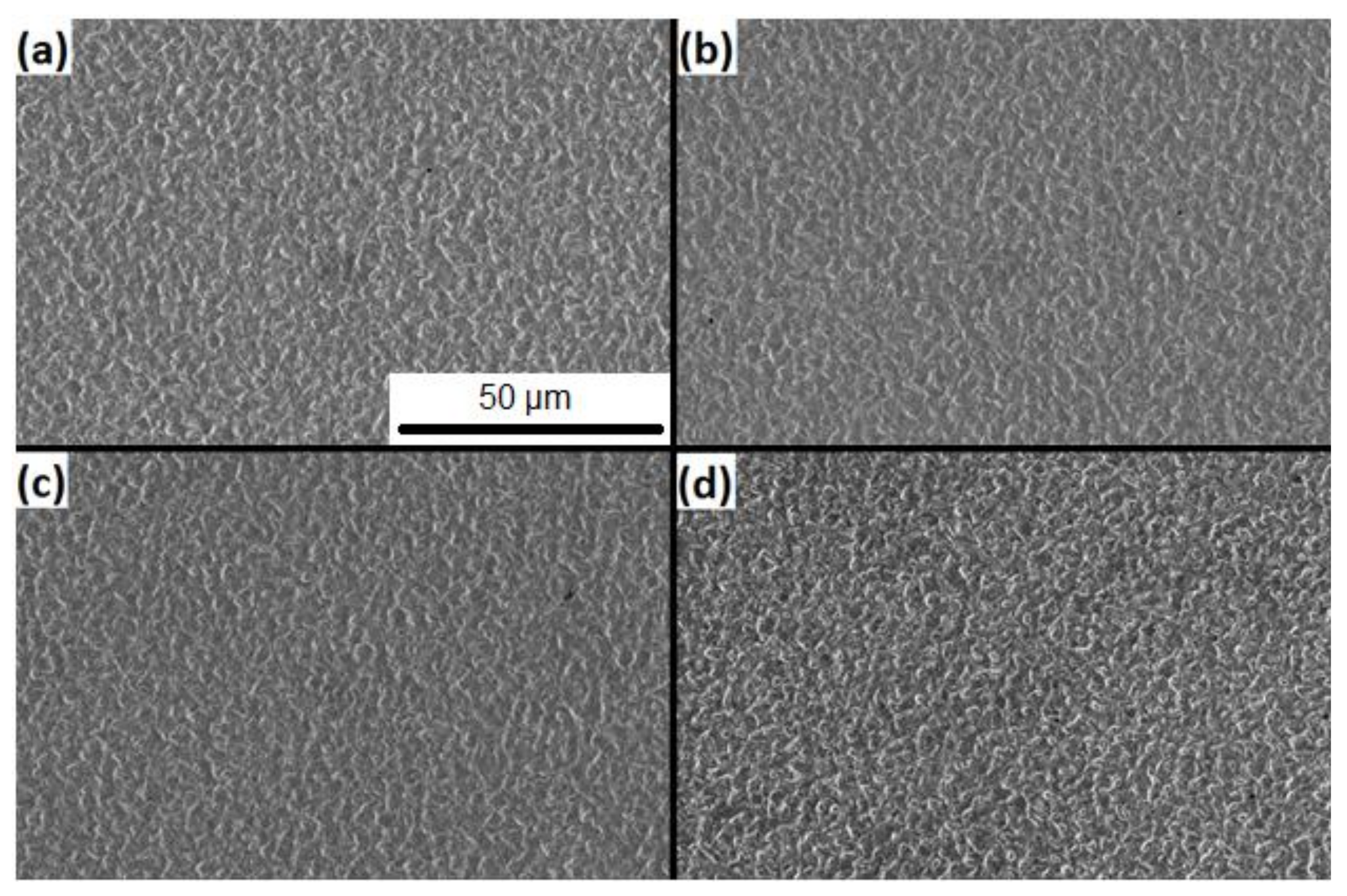
3.2. Sn Whisker Growth
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McDowell, M. Tin whiskers: A case study. In Proceedings of the 1993 IEEE Aerospace Applications Conference Digest, Steamboat Springs, CO, USA, 31 January 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Stupian, G.W. Tin Whiskers in Electronic Circuits; Aerospace Corporation: EL Segundo, CA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Leidecker, H.; Brusse, J. Tin Whiskers: A History of Documented Electrical System Failures. 2006. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/20060028088 (accessed on 9 October 2021).
- Coleman, R.; Sears, G. Growth of zinc whiskers. Acta Met. 1957, 5, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, R.V.; Price, B.; Cabrera, N. Slip of Zinc and Cadmium Whiskers. J. Appl. Phys. 1957, 28, 1360–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Hashimoto, H.; Barsoum, M.W. On the effect of environment on spontaneous growth of lead whiskers from commercial brasses at room temperature. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 3387–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, K.G.; Mendizza, A.; Arnold, S.M. Filamentary Growths on Metal Surfaces–“Whiskers”. Corrosion 1951, 7, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z. Spontaneous Growth of Metal Whiskers on Surfaces of Solids: A Review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 675–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-Z.; Lee, D. Spontaneous growth mechanism of tin whiskers. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 3701–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsoum, M.W.; Hoffman, E.N.; Doherty, R.D.; Gupta, S.; Zavaliangos, A. Driving Force and Mechanism for Spontaneous Metal Whisker Formation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 206104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Hino, M.; Takamizawa, M.; Nakai, K. Mechanism of generation and growth of whiskers on tin electroplating. Mater. Trans. 2008, 49, 2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianco, P.T.; Rejent, J.A. Dynamic Recrystallization (DRX) as the Mechanism for Sn Whisker Development. Part I: A Model. J. Electron. Mater. 2009, 38, 1815–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Crandall, E.R. Factors Governing Tin Whisker Growth; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Smetana, J. Theory of Tin Whisker Growth: “The End Game”. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 2007, 30, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, T.; Lin, H.; Chi, C. Rapid growth of tin whiskers on the surface of Sn–6.6Lu alloy. Scr. Mater. 2007, 56, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wilcox, G.D. Observations of the Spontaneous Growth of Tin Whiskers on Tin-Manganese Alloy Electrodeposits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 066104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusse, J.; Ewell, G.; Siplon, J. Tin whiskers: Attributes and mitigation. Cart. Eur. 2002, 16, 221–233. [Google Scholar]
- Brusse, J.A.; Ewell, G.J.; Siplon, J.P. Tin Whiskers: Attributes and Mitigation. In Proceedings of the 22nd Capacitor and Resistor Technology Symposium, New Orleans, LA, USA, 25–29 March 2002; pp. 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch, J.S.; Brusse, J. The Continuing Dangers of Tin Whiskers and Attempts to Control Them with Conformal Coating. NASA EEE Links Newsletter. 2001. Available online: https://nepp.nasa.gov/whisker/reference/tech_papers/kadesch2001-article-dangers-of-tin-whiskers-and-conformal-coat-study.pdf (accessed on 4 January 2022).
- 2021 RoHS Compliance Guide: Regulations, 10 Substances, Exemptions. Available online: https://www.rohsguide.com/ (accessed on 9 October 2021).
- Jo, J.-L.; Nagao, S.; Hamasaki, K.; Tsujimoto, M.; Sugahara, T.; Suganuma, K. Mitigation of Sn Whisker Growth by Small Bi Additions. J. Electron. Mater. 2014, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, B.S.; Dutta, I.; Bhassyvasantha, S.; Das Mahapatra, S. Recent Advances in Mitigation of Whiskers from Electroplated Tin. JOM 2019, 72, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadesch, J.S.; Leidecker, H.; Day, J.H. Effects of conformal coat on tin whisker growth. In Proceedings of the Institute of Managed Account Professionals Conference, Dearborn, MI, USA, 1–3 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrovska, A.; Kovacevic, R. Mitigation of Sn Whisker Growth by Composite Ni/Sn Plating. J. Electron. Mater. 2009, 38, 2516–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skwarek, A.; Pluska, M.; Ratajczak, J.; Czerwinski, A.; Witek, K.; Szwagierczak, D. Analysis of tin whisker growth on lead-free alloys with Ni presence under thermal shock stress. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2011, 176, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schetty, R. Minimization of tin whisker formation for lead-free electronics finishing. Circuit World 2001, 27, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diyatmika, I.M.W.; Chu, J.P.; Yen, Y.W.; Hsueh, C.H. Sn whisker mitigation by a thin metallic-glass underlayer in Cu-Sn. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 241912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpov, V.G. Electrostatic Theory of Metal Whiskers. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2014, 1, 044001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borra, V.; Georgiev, D.G.; Karpov, V.G.; Shvydka, D. Microscopic Structure of Metal Whiskers. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2018, 9, 054029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borra, V.S.V. Whiskers: The Role of Electric Fields in the Formation Mechanism and Methods for Whisker Growth Mitigation. University of Toledo. 2017. Available online: http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=toledo1513381893591481 (accessed on 9 October 2021).
- Borra, V.; Georgiev, D.G.; Karpov, V.G. Cultivating Metal Whiskers by Surface Plasmon Polariton Excitation. MRS Adv. 2016, 1, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borra, V.; Itapu, S.; Karpov, V.G.; Georgiev, D.G. Modification of Tin (Sn) metal surfaces by surface plasmon polariton excitation. Scr. Mater. 2021, 208, 114357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, S.; Osterman, M.; Pecht, M.; Dunlevey, F. Evaluation of pure tin plated copper alloy substrates for tin whiskers. Circuit World 2009, 35, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borra, V.; Itapu, S.; Georgiev, D.G. Sn whisker growth mitigation by using NiO sublayers. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 475309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itapu, S.; Georgiev, D.G.; Uprety, P.; Podraza, N.J. Modification of reactively sputtered NiOxthin films by pulsed UV laser irradiation. Phys. Status Solidi A 2017, 214, 1600414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borra, V.; Oudat, O.; Georgiev, D.G.; Karpov, V.G.; Shvydka, D. Metal whisker growth induced by localized, high-intensity DC electric fields. MRS Adv. 2018, 3, 3367–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killefer, M.; Borra, V.; Al-Bayati, A.; Georgiev, D.G.; Karpov, V.G.; Parsai, E.I.; Shvydka, D. Whisker growth on Sn thin film accelerated under gamma-ray induced electric field. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 405302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niraula, D.; McCulloch, J.; Warrell, G.R.; Irving, R.; Karpov, V.G.; Shvydka, D. Electric field stimulated growth of Zn whiskers. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 075201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Dutta, T.; Mal, S.; Narayan, J. Controlledp-type ton-type conductivity transformation in NiO thin films by ultraviolet-laser irradiation. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 013706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, E.; Tomozawa, A.; Torii, H.; Takayama, R. Preferred Orientations of NiO Films Prepared by Plasma-Enhanced Metalorganic Chemical Vapor Deposition. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 35, L328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Wu, M.; Qin, Z.; Xu, H. The electrochromic characteristics of sol gel-prepared NiO thin film. Nanotechnology 2003, 14, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, S.; Brückner, W. XPS depth profile analysis of non-stoichiometric NiO films. Surf. Interface Anal. 2004, 36, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Rahm, E.; Holze, R.; Wu, H. Electrode materials for lithium secondary batteries prepared by sol–gel methods. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2005, 50, 881–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, C.; Frye, G.; Hurd, A.; Ashley, C. Fundamentals of sol-gel dip coating. Thin Solid Film. 1991, 201, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.C. Preparation of copper oxide thin film by the sol–gel-like dip technique and study of their structural and optical properties. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2001, 68, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, P.S.; Venugopalan, V.P.; Das, D.A.; Dhara, S.; Pandiyan, R.; Tyagi, A.K. Antibiofilm activity of nano sized CuO. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Nanoscience, Engineering and Technology (ICONSET 2011), Chennai, India, 28 November 2011; pp. 580–583. [Google Scholar]
- Subedi, B.; Niraula, D.; Karpov, V.G. The stochastic growth of metal whiskers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 251604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölzl, J.; Schulte, F.K. Work function of metals. In Solid Surface Physics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1979; pp. 1–150. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.S.; Lee, C.; Yang, C.K. Atomic force microscopy and Raman spectroscopy studies on the oxidation of Cu thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 1995, 77, 5422–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Handoko, A.D.; Du, Y.; Xi, S.; Yeo, B.S. In Situ Raman Spectroscopy of Copper and Copper Oxide Surfaces during Electrochemical Oxygen Evolution Reaction: Identification of CuIII Oxides as Catalytically Active Species. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 2473–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelson, H.B. The work function of the elements and its periodicity. J. Appl. Phys. 1977, 48, 4729–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serag, M.F.; Abadi, M.; Habuchi, S. Single-molecule diffusion and conformational dynamics by spatial integration of temporal fluctuations. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalage, S.; Chougule, M.; Sen, S.; Joshi, P.; Patil, V. Sol–gel synthesis of nickel oxide thin films and their characterization. Thin Solid Film. 2012, 520, 4835–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koffyberg, F.P.; Benko, F.A. P-Type NiO as a Photoelectrolysis Cathode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1981, 128, 2476–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Element | Percentage (Atomic) |
|---|---|
| Carbon | 14% |
| Oxygen | 36% |
| Silicon | 2% |
| Nickel | 3% |
| Copper | 46% |
| Element | Percentage (Atomic) |
|---|---|
| Carbon | 1% |
| Oxygen | 6% |
| Nickel | 6% |
| Copper | 30% |
| Tin | 57% |
| C1 | C2 | S1 | S2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Density | Count | Density | Count | Density | Count | Density | |
| Initial | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 Weeks | 24 | 50.42 | 24 | 50.42 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 Weeks | 32 | 67.23 | 24 | 50.42 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 Weeks | 54 | 113.45 | 69 | 144.96 | 0 | 2.10 | 0 | 0 |
| 12 Weeks | 90 | 189.08 | 105 | 220.59 | 1 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 |
| 16 Weeks | 84 | 176.47 | 105 | 220.59 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 |
| 20 Weeks | 118 | 247.90 | 141 | 296.22 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 |
| 24 Weeks | 163 | 342.44 | 147 | 308.82 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 |
| 28 Weeks | 203 | 426.47 | 187 | 392.86 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 |
| 32 Weeks | 169 | 355.04 | 188 | 394.96 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buchanan, J.D.; Borra, V.; Islam, M.M.; Georgiev, D.G.; Itapu, S. Tin Whisker Growth Suppression Using NiO Sublayers Fabricated by Dip Coating. Condens. Matter 2022, 7, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat7010007
Buchanan JD, Borra V, Islam MM, Georgiev DG, Itapu S. Tin Whisker Growth Suppression Using NiO Sublayers Fabricated by Dip Coating. Condensed Matter. 2022; 7(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat7010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuchanan, Jacob D., Vamsi Borra, Md Maidul Islam, Daniel G. Georgiev, and Srikanth Itapu. 2022. "Tin Whisker Growth Suppression Using NiO Sublayers Fabricated by Dip Coating" Condensed Matter 7, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat7010007
APA StyleBuchanan, J. D., Borra, V., Islam, M. M., Georgiev, D. G., & Itapu, S. (2022). Tin Whisker Growth Suppression Using NiO Sublayers Fabricated by Dip Coating. Condensed Matter, 7(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat7010007







