Controlling Electrical Conduction through Noble Metal Thin Films by Surface Plasmon Resonance
Abstract
1. Introduction
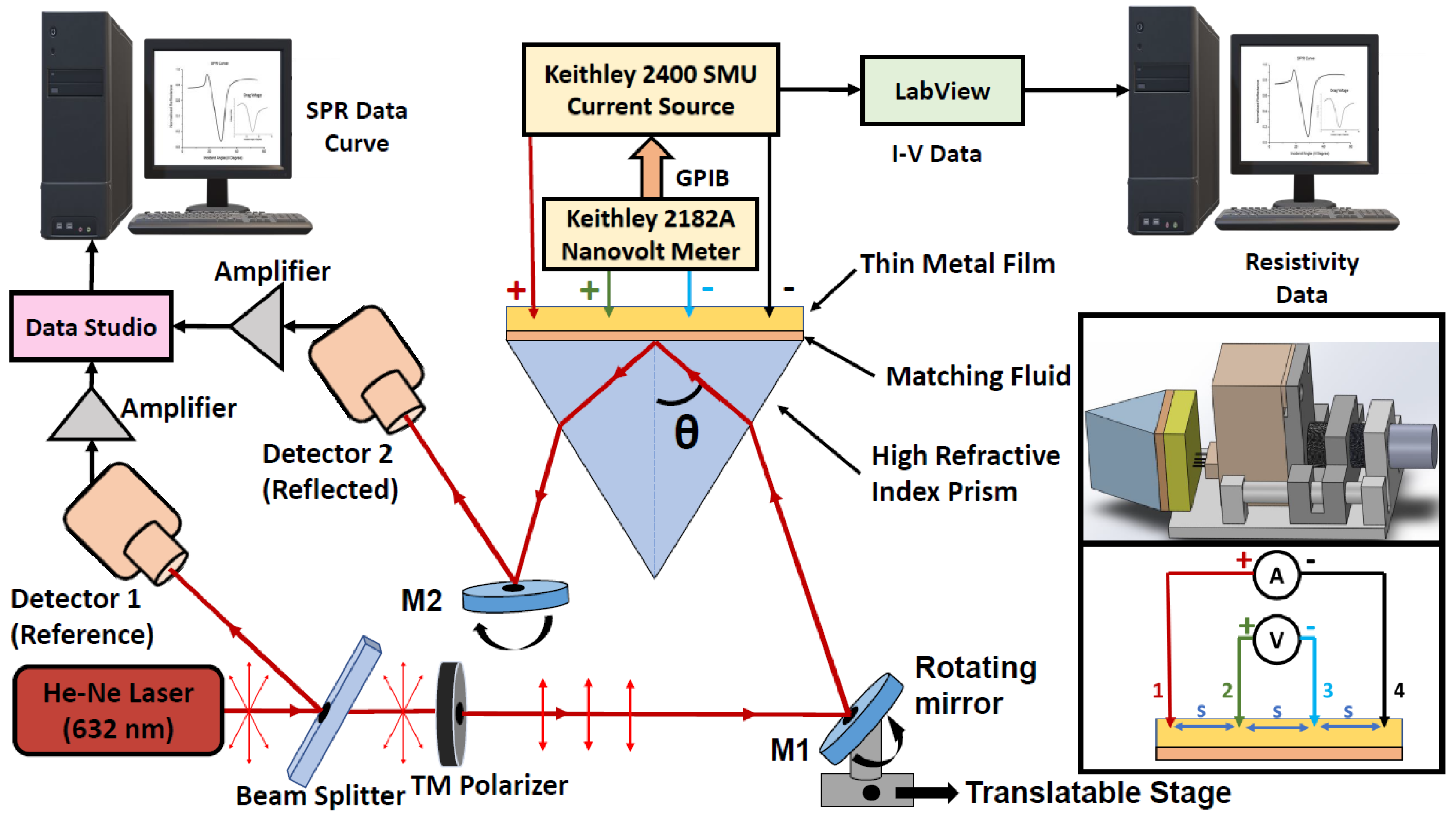
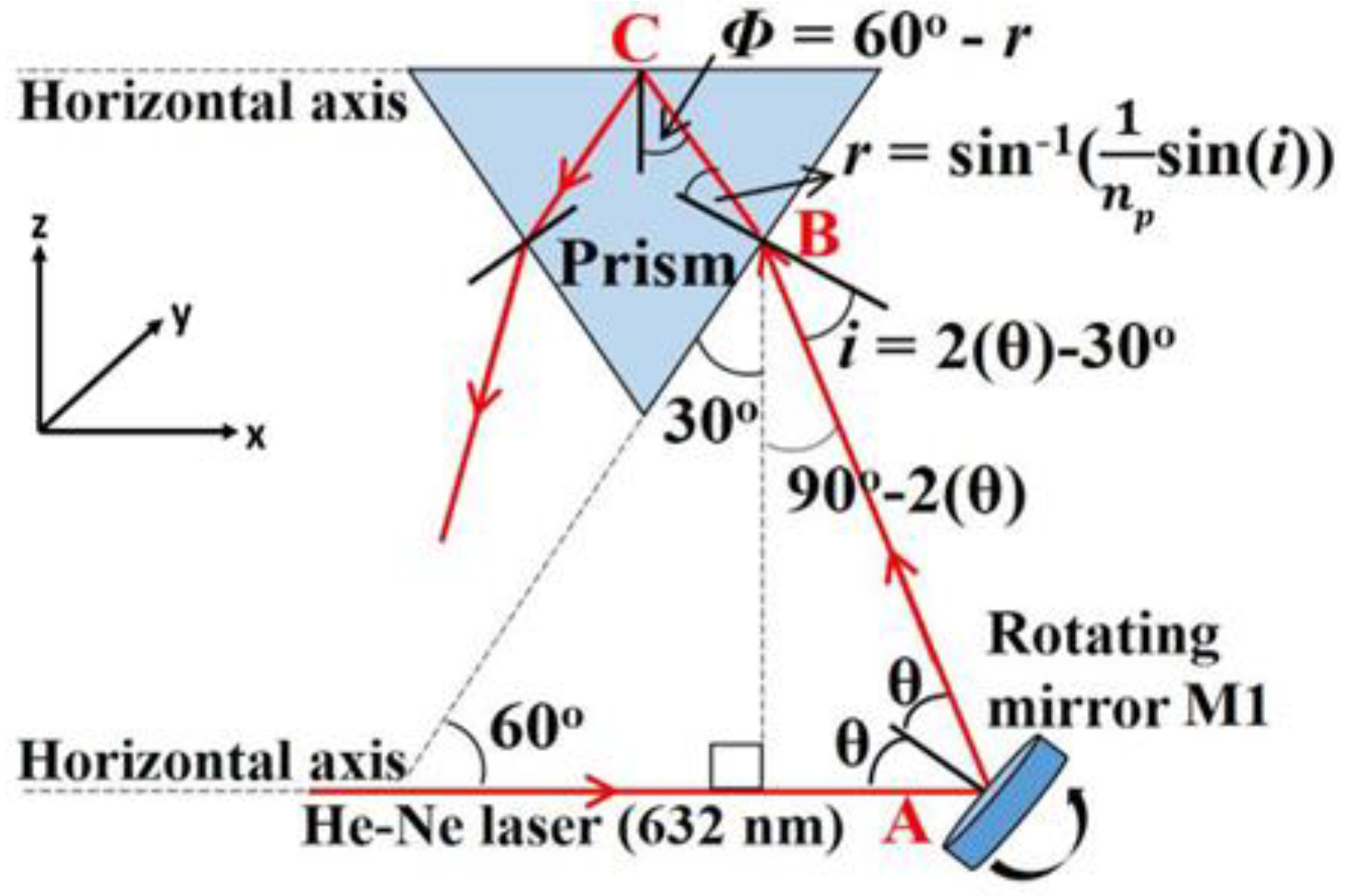
2. Experimental Details
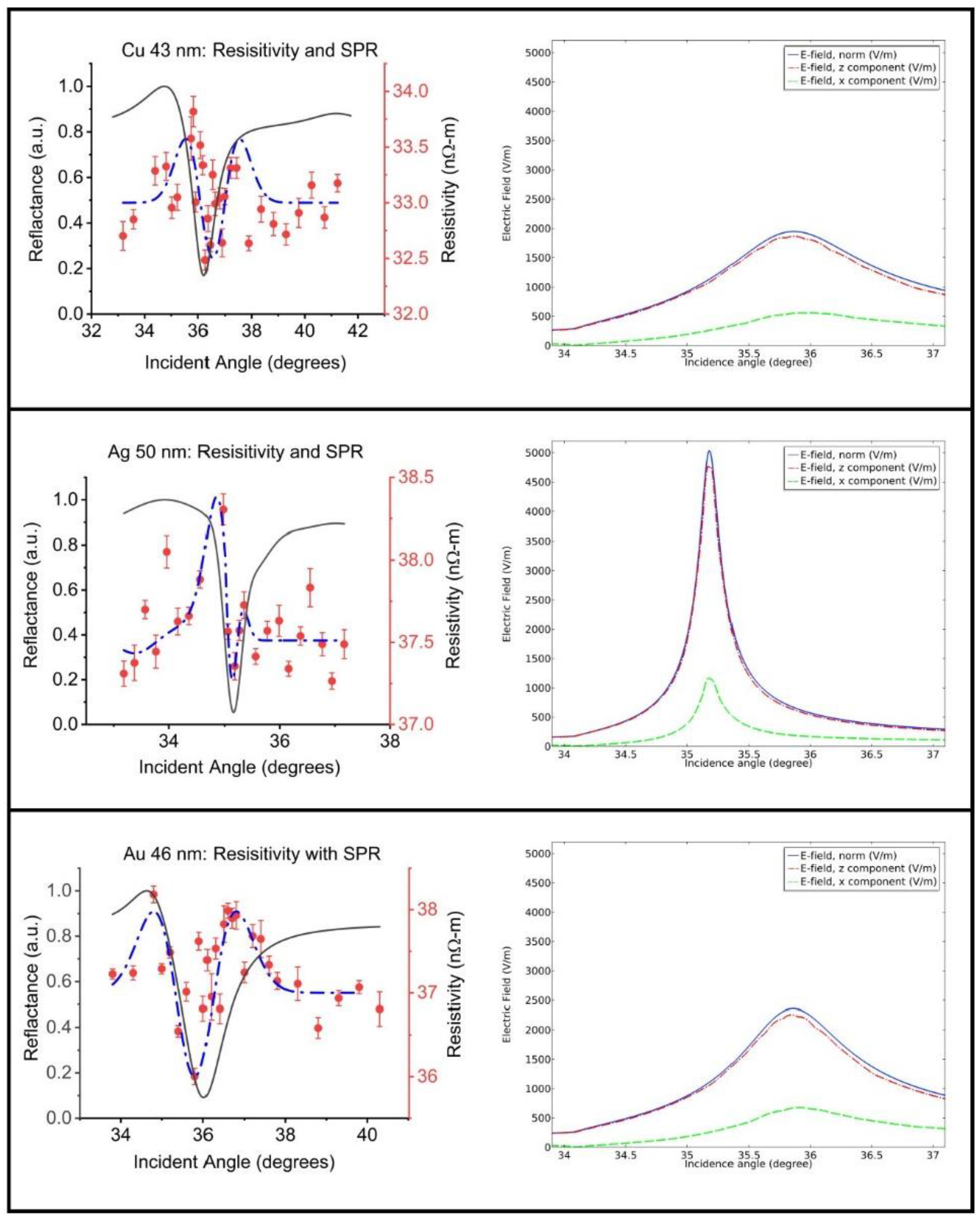
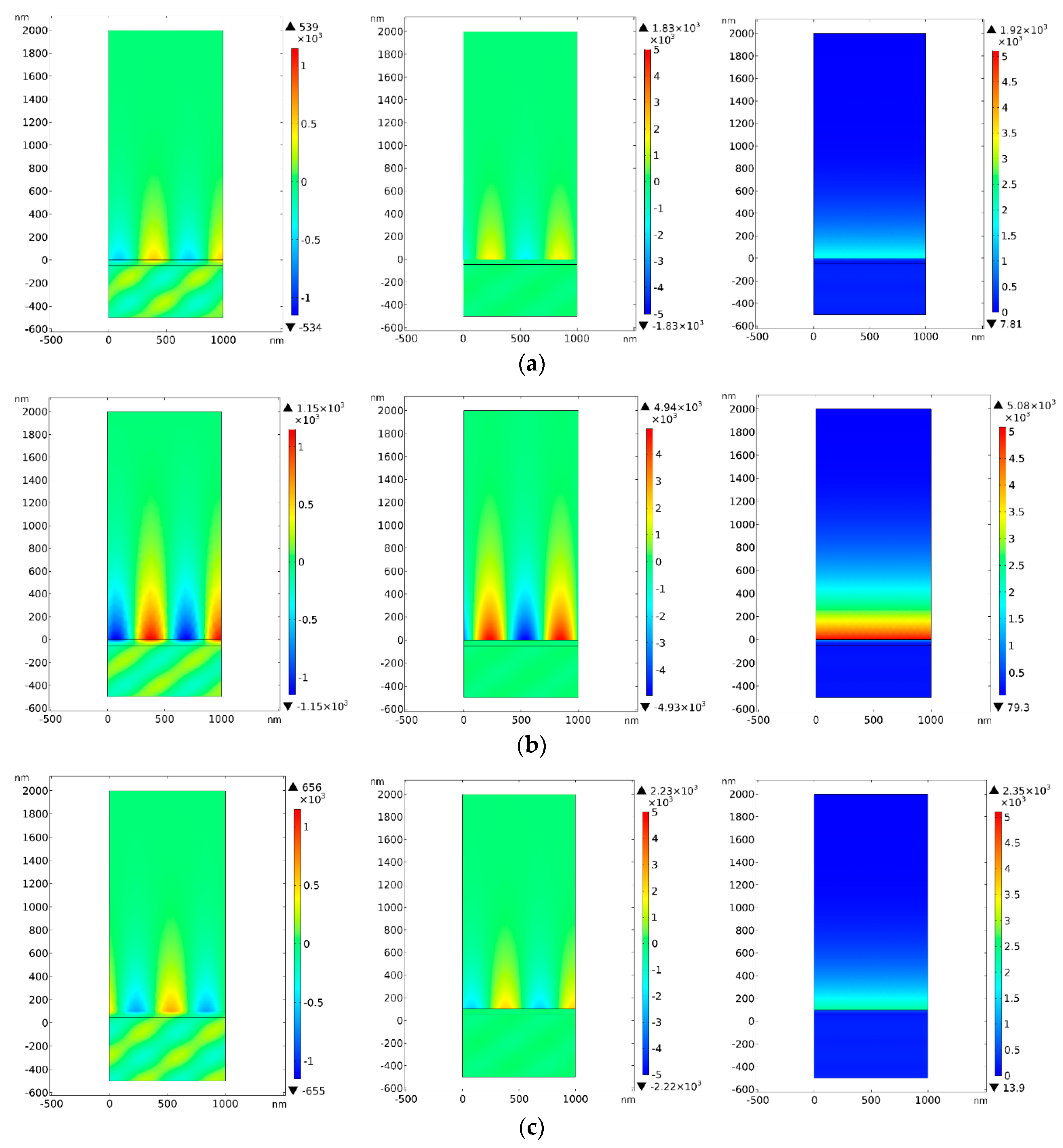
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raether, H. Surface Plasmons on Smooth and Rough Surfaces and on Gratings; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Novotny, L.; Hecht, B. Principles of Nano-Optics, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pitarke, J.M.; Silkin, V.M.; Chulkov, E.V.; Echenique, P.M. Theory of surface plasmons and surface-plasmon polaritons. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2007, 70, 1–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayats, A.V.; Smolyaninov, I.I.; Maradudin, A.A. Nano-optics of surface plasmon polaritons. Phys. Rep. 2005, 408, 131–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayats, A.V.; Smolyaninov, I.I. Near-field photonics: Surface plasmon polaritons and localized surface plasmons. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2003, 5, S16–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.C. Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensors: Fundamental Concepts, Selected Techniques, Materials, and Applications. In Advances in Sensors: Reviews’ Book Series; Yurish, S.Y., Ed.; IFSA Publishing: Barcelona, Spain, 2018; Volume 5, pp. 25–77. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, R.H. Plasma Losses by Fast Electrons in Thin Films. Phys. Rev. 1957, 106, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittel, C. Introduction to Solid State Physics, 7th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Homola, J.; Koudela, I.; Yee, S.S. Surface plasmon resonance sensors based on diffraction gratings and prism couplers: Sensitivity comparison. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1999, 54, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneipp, K.; Flemming, J. Surface Enhanced Raman-Scattering (Sers) of Nucleic-Acids Adsorbed on Colloidal Silver Particles. J. Mol. Struct 1986, 145, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pines, D. Electron Interaction in Solids. Can. J. Phys. 1956, 34, 1379–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, D.; Pines, D. Screening of Electronic Interactions in a Metal. Phys. Rev. 1950, 80, 903–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pines, D.; Bohm, D. A Collective Description of Electron Interactions. Collective Vs Individual Particle Aspects of the Interactions. Phys. Rev. 1952, 85, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, D.; Pines, D. A Collective Description of Electron Interactions. Coulomb Interactions in a Degenerate Electron Gas. Phys. Rev. 1953, 92, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, J.W. Mechanisms for Superconductivity in Transition Metals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1963, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohlich, H. Superconductivity in Metals with Incomplete Inner Shells. J. Phys. Part C Solid 1968, 1, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K.; Sharma, S. C. plasmon based sensor with order-of-magnitude higher sensitivity to electric field induced changes in dielectric environment at metal/nematic liquid-crystal unterface. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2014, 216, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K.; Sharma, S.C.; Hozhabri, N. High performance surface plasmon sensors: Simulations and measurements. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 093105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K.; Sharma, S.C.; Hozhabri, N. Hafnium dioxide as a dielectric for highly-sensitive waveguide-coupled surface plasmon resonance sensors. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 045217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K.; Singh, A.; Sharma, S.C. Evidence for surface plasmons in a liquid crystal containing gold nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Sharma, S.C. A fixed detector Kretschmann configuration optical system to study surface plasmon excitations. Opt. Laser Technol. 2014, 56, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K. Bimetallic Waveguide-Coupled Sensors for Tunable Plasmonic Devices. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Texas at Arlington, Arlington, TX, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Akafzade, H. Theoretical and Experimental Probes of Dispersion in Two-Dimensional Materials. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Texas at Arlington, Arlington, TX, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, A.; Sharma, S.C. New Metamaterial as a Broadband Absorber of Sunlight with Extremely High Absorption Efficiency. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 035209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, D.; Huang, K.; Pines, D. Role of Subsidiary Conditions in the Collective Description of Electron Interactions. Phys. Rev. 1957, 107, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, D.; Pines, D. A Collective Description of Electron Interactions. Magnetic Interactions. Phys. Rev. 1951, 82, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, H. Theory of Dielectrics; Dielectric Constant and Dielectric Loss, 2nd ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1958; p. 192. [Google Scholar]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, S.C.; Khichar, V.; Akafzade, H.; Zinn, D.; Hozhabri, N. Controlling Electrical Conduction through Noble Metal Thin Films by Surface Plasmon Resonance. Condens. Matter 2020, 5, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat5030052
Sharma SC, Khichar V, Akafzade H, Zinn D, Hozhabri N. Controlling Electrical Conduction through Noble Metal Thin Films by Surface Plasmon Resonance. Condensed Matter. 2020; 5(3):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat5030052
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Suresh C., Vivek Khichar, Hussein Akafzade, Douglas Zinn, and Nader Hozhabri. 2020. "Controlling Electrical Conduction through Noble Metal Thin Films by Surface Plasmon Resonance" Condensed Matter 5, no. 3: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat5030052
APA StyleSharma, S. C., Khichar, V., Akafzade, H., Zinn, D., & Hozhabri, N. (2020). Controlling Electrical Conduction through Noble Metal Thin Films by Surface Plasmon Resonance. Condensed Matter, 5(3), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat5030052





