Abstract
Spiral thermal surface waves arising from self-propulsion of the camphor-driven objects are reported. Spiral thermal waves were registered for dissolution and evaporation-guided self-propulsion. Soluto-capillarity is accompanied by thermo-capillarity under self-propulsion of camphor boats. The jump in the surface tension due to the soluto-capillarity is much larger than that due to the thermo-capillarity. The spiral patterns inherent for the surface thermal waves are imposed by the self-rotational motion of camphor grains. The observed thermal effect is related to the adsorption of camphor molecules at the water/vapor interface. The observed spirals are shaped as Archimedean ones.
1. Introduction
The fascinating phenomenon of spiral waves was registered within various experimental contexts, including the formation of spiral galaxies [1], rotating liquids [2,3,4] and insect populations [5]. The particular case of spiral waves is thermal waves, in which spirals are formed with 2D thermal fields, inherent for example for the Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction [6,7,8,9]. Recall that the Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction represents the reaction–diffusion system, including bromine and an acid and giving rise to a nonlinear chemical oscillator, acting far from thermodynamic equilibrium and giving rise to fascinating spatial patterns, the focus of recent extensive research [6,7,8,9]. We demonstrate spiral thermal waves emerging from the self-propulsion of camphor boats, floating on water. The phenomenon of self-propulsion attracted much attention of investigators during the past decade [10,11,12,13,14,15]. Self-propulsion was successfully exploited recently for micro-robotics applications as well as for the generation of electrical power [16,17,18]. One of the most studied self-propelled objects is the so called “camphor boat” studied first by Lord Rayleigh [19] The motion of camphor boats is usually related to the soluto-capillary interfacial (Marangoni) flows [12,13,20,21,22,23]. Camphor decreases the surface tension of water, and the boat is driven by differences in the surface tension around it [20,21]. Obviously, motion becomes possible due to the breaking of symmetry of the surface tension field surrounding the camphor boat [20,21,22,23,24,25]. The breaking of symmetry may arise from the non-uniform dissolution of camphor. We demonstrate that thermal Marangoni flows accompanying the self-propulsion of camphor boats may be non-negligible and also contribute to the self-propulsion. Moreover, the self-propulsion of camphor boats gives rise to the spiral thermal fields, resembling those inherent for the Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction [6,7,8,9].
2. Results
The experimental system is shown schematically in Figure 1a,b. Generally self-propulsion of the camphor-driven objects is possible under two scenarios, namely under evaporation and dissolution of camphor [19,20,21,25]. Both of the regimes were studied experimentally. When the self-propulsion was guided by dissolution of camphor, the grains were placed directly on the water surfaces, as shown in Figure 1a. A special rotator, depicted in Figure 1b, was designed for the study of the evaporation-guided self-propulsion. Camphor was placed in the polymer tubing, with a diameter of 1 mm.
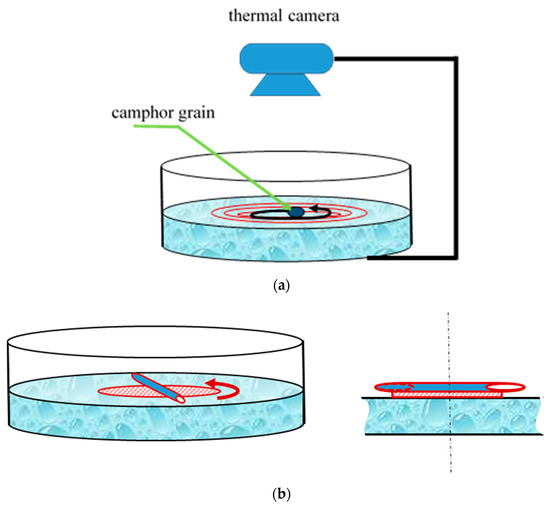
Figure 1.
(a) Sketch of the experimental unit used for the study of spiral thermal waves arising from the self-propulsion of camphor grains. The self-propulsion is guided by the dissolution of camphor. (b) A sketch of the special rotator enabling the study of the evaporation–guided self-propulsion is depicted. The polymer disk prevented direct contact of camphor with water.
Thermal imaging of the water/vapor interface registered spiral thermal waves such as those depicted in Figure 2a–c and presented in the Supplementary Movie S1. Spiral waves were observed in the circular and rectangular vessels. Clockwise and counter-clockwise rotation of water was observed within the spiral thermal waves generated by camphor grains and rotors driven by the evaporation of camphor. Evaporation-induced rotation may be controlled by the shape of polymer tubing. It should be emphasized that the spiral thermal waves emerged from both the dissolution- and evaporation-guided self-propulsion (see Supplementary Movies S1 and S2). The maximal thermal contrast observed in the course of the motion of grain and rotation of the rotor was . Thus, the soluto-capillary Marangoni flows are accompanied in the reported experimental situation with the thermo-capillary ones. Recall that the co-occurrence of the soluto- and thermo-capillary flows takes place even for the famous phenomenon of “wine tears” [26]. Let us estimate the contributions of thermo- and soluto-capillarity to the effect of self-propulsion. The total change in the surface tension is expressed as follows:
where represents the contribution of soluto-capillarity, whereas is the term due to the thermo-capillarity. The value of the was established in Ref. [27] experimentally as . Assuming for the temperature gradient of the surface tension (see Ref. [28]) and , we estimate . Thus, we conclude that the interrelation takes place and the motion of camphor boats is mainly due to the soluto-capillarity. However, the thermal effect may be of primary importance for the understanding of the self-propulsion, when the strong exponential dependency of water viscosity is considered [28]. Thus, thermal waves play an essential role in the breaking of the symmetry, resulting in the motion of the camphor boat [23].
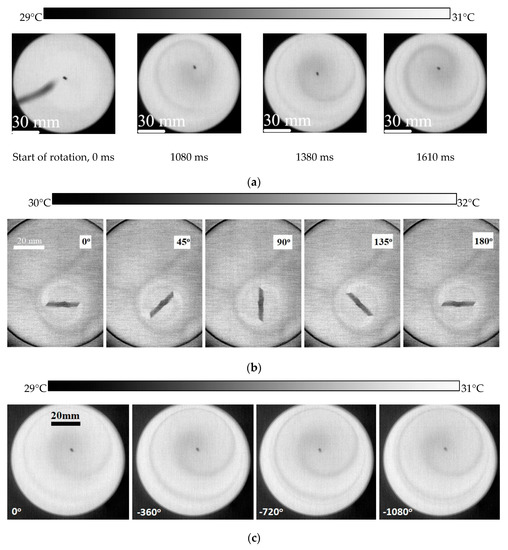
Figure 2.
(a) The sequence of thermal images representing spiral thermal surface waves, generated under the dissolution-guided self-propulsion of camphor grains. Thermographic images were taken in the course of motion of the camphor grain. Brighter pixels correspond to the higher temperatures. (b) The sequence of thermal images representing spiral thermal waves in the stationary regime, generated under the evaporation-guided self-propulsion of the rotor, shown in Figure 1b. Degrees illustrate the rotation of the polymer tubing filled with camphor. Thermographic images were taken in the course of the rotation. Brighter pixels correspond to the higher temperatures. (c) Thermal images illustrating the stationary regime of rotation of the camphor sample are shown. Degrees illustrate the rotation of the camphor grain. The spiral thermal surface wave is clearly seen.
3. Discussion
The thermal spirals evolved towards the walls of vessels during ca 0.5–1 s and afterwards remained stable (in other words, stationary, see for example Figure 2b,c) during ca 10 s. The radial temporal displacement of the labeled water particle, located at the water/vapor surface, is shown in Figure 3 (for the details, see Section 4). It is recognized from Figure 3, that at the initial stage of propagation, taking place ca 0.4 s, the radial displacement of the marker occurs with the constant velocity This means that, at this stage, the spiral is an Archimedean one, described in the polar coordinates by the equation:
where λ is the wavelength of the Archimedean spiral and c denotes the initial radial location of the camphor grain. Actually, and were registered. It should be emphasized that the angular frequency coincides with the frequency of self-rotation of the camphor grain.

Figure 3.
The temporal dependence of the radial displacement of the marker taken in the course of the spiral wave propagation is depicted.
It was demonstrated that the eventual Archimedean geometry of the spiral appearing under the Belousov–Zhabotinsky reactions may be independent of their chemical kinetic basis and arises from the symmetry considerations [29]. It was demonstrated in the seminal paper by Alan Turing that formation of spiral patterns in initially homogeneous reaction–diffusion systems, such as Belousov–Zhabotinsky reactions, becomes possible due to the spontaneous breaking of symmetry [30]. Contrastingly, in our experiments, the spiral geometry is imposed by the self-rotational motion of the camphor grain. This conclusion is supported by the fact that the angular frequency appearing in Equation (2) coincides with that of the self-rotation of the camphor grain.
We are far from an exhaustive, quantitative explanation of the observed spiral, thermal waves. However, qualitative arguments will be useful for understanding of the phenomenon. What is the physico-chemical source of the observed thermal waves? One of these sources is enthalpy of the chemical reaction of dissolution of camphor by water. However, thermal waves were observed in the situation when the disc-like rotator, shown in Figure 1b, blocked the dissolution of camphor in water. Thus, it is plausible to relate the formation of the thermal waves to formation of the adsorbed layer of camphor molecules surrounding the self-propelled object. The suggested mechanism implies transport of the camphor molecules from the vapor phase to the water/vapor interface, followed by the heat release. The spatially-temporal periodic nature of formation of this layer was discussed in Ref. [31]. The enthalpy of periodic adsorption, in turn, (consider that adsorption is always exothermic) may give rise to the reported thermal waves. The role of the adsorption of the volatile elements (which is camphor in our case) in the evolution of Marangoni flows was discussed in Ref. [32]. It is reasonable to relate the formation of the observed spiral thermal patterns to the capillary–gravity waves, generated by the self-propelled camphor boats [32]. The formation of Archimedian spiral patterns of capillary–gravity waves created by rotating floating bodies was reported in Ref. [33]. The similarity of waves created by floating bodies to the Cherenkov radiation was discussed in Refs. [33,34,35,36,37]. It should be emphasized that the formation of stable spiral thermal patterns was observed under the velocities of the self-propulsion , which are much smaller than the threshold one (where ρ is the water density), necessary for formation of steady capillary–gravity waves under straight uniform self-propulsion [34,35,36,37]. This effect was explained in Ref. [34], in which it was demonstrated that no velocity threshold exists for the steady spiral wave patterns, appearing under the circular motion of the self-propelled bodies, explored in our experiments.
Let us estimate the dimensionless numbers, governing the evolving of spiral thermal waves, which are the Reynolds (Re) and Prandtl (Pr) numbers:
where and are viscosity, specific heat and thermal conductivity of water at the conditions of the experiment, respectively, v and L are the characteristic velocity and dimension correspondingly [12,13]. Assuming, and , we estimate and . This means that the propagation of spiral waves occurs within the laminar regime; however, both momentum and heat dissipate through the fluid at about the same rate under the evolving of the spiral thermal waves. The last consideration makes the exact quantitative analysis of the phenomenon extremely challenging.
4. Materials and Methods
Vessels of various shapes were used for the study of the self-propulsion: Petri dishes (Corning Crystal Polystyrene) with the diameters of 140 mm and 85 mm, square polystyrene vessels with dimensions of 210 × 210 mm and 110 × 180 mm. The de-ionized water, used as supporting liquid, was purified by a synergy UV water purification system from Millipore SAS (Molsheim, France) and its specific resistivity was at 25 °C. The vessels were filled with de-ionized water; the height of the supporting liquid hl was 7 ± 1 mm. Camphor grains with dimensions of (4 ± 1) × (4 ± 1) × (6 ± 2) mm were prepared from Camphor (96%), supplied by Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). The temperature of water varied within the range of 25–35 °C. All the experiments were performed under atmospheric pressure.
The self-propelled motion of camphor grains and propagation of spiral thermal waves was visualized with the Therm-App TAS19AQ-1000-HZ thermal camera. The resolution was: 384 × 288 pixels (>110.000 pixels); the LWIR (longwave infrared) measurements were carried out at the wavelength of 7.5–14 μm, the accuracy of the thermal camera was: NEDT (noise equivalent differential temperature) < 0.07 °C, and the frame rate was 26 frames/s.
Quantitative treatment of the thermal movies was carried out as follows: a straight line was built along the camphor boat, and the location of crests of thermal waves located on this straight line were fixed. The location of the first crest of the thermal wave was called the “marker”, which was used for the calculation of the radial velocity v appearing in Equation (2).
5. Conclusions
To conclude, we report the fascinating phenomenon of propagation of spiral thermal waves emerging from the motion of camphor-driven floating self-propelled objects. The soluto-capillarity mainly guides the self-propulsion. Thermo-capillarity, in turn, gives rise to propagation of the spiral Archimedean thermal waves, resembling those observed under Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction [6,7,8,9]. It reasonable to suggest that the spiral geometry of the observed thermal waves is imposed by the self-rotational motion of the camphor grain, and this is in contrast to the spiral patterns inherent for reaction–diffusion systems, in which spiral patterns emerge under the spontaneous breaking of the symmetry of the system [30]. We relate the observed thermal effect to the adsorption of camphor molecules at the water/vapor interface [31,32]. It seems reasonable to assume that spiral thermal surface waves reflect the quasi-periodic distribution of camphor at the water/vapor interface [31]. The reported effect is important for understanding of the self-propulsion of floating bodies, exploited recently for micro-robotics and micro-fluidics applications and also for the ecologically friendly generation of electrical energy [16,17,18,38,39].
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2410-3896/5/3/51/s1, Supplementary Movie S1: Spiral thermal waves arising from the self-propulsion of camphor grain; Supplementary Movie S2: Spiral thermal waves arising from the self-propulsion of camphor filled rotator.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.B.; Methodology, E.B.; A.V.; Validation, A.V.; M.F.; I.L.; Investigation, A.V.; M.F.; I.L.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, E.B.; Writing—Review & Editing A.V.; E.B.; Visualization, M.F.; I.L.; A.V.; Supervision, E.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
That authors are thankful to Mrs. Yelena Bormashenko for her kind help in preparing this manuscript. The authors are indebted to Professor Oleg Gendelman for extremely fruitful discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| 2D | two-dimensional |
| ca | Circa (approximately) |
| Re | Reynolds number |
| Pr | Prandtl number |
References
- Lin, C.C.; Shu, F.H. On the Spiral Structure of Disc Galaxies, II. Outline of the Theory of Density Waves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1966, 55, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liao, X.; Chan, K.H.; Zhang, K. On Nonlinear Multiarmed Spiral Waves in Slowly Rotating Fluid System. Phys. Fluids 2010, 22, 011701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkley, D. Linear Stability Analysis of Rotating Spiral Waves in Excitable Media. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 2090–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Net, M.; Mercader, I.; Knobloch, E. Binary Fluid Convection in a Rotating Cylinder. Phys. Fluids 1995, 7, 1553–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassell, M.P.; Comins, H.N.; May, R.M. Spatial Structure and Chaos in Insect Population Dynamics. Nature 1991, 353, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keener, J.P.; Tyson, J.J. Spiral Waves in the Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction. Phys. D 1986, 21, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, P. Chemical Oscillations and Spiral Waves. In Spirals and Vortices. The Frontiers Collection; Tsuji, K., Müller, S., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Adamatzky, A.; Fullarton, C.; Phillips, N.; Costello, B.D.L.; Draper, T.C. Thermal Switch of Oscillation Frequency in Belousov–Zhabotinsky Liquid Marbles. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 190078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamatzky, A.; Holley, J.; Dittrich, P.; Gorecki, J.; Costello, B.D.L.; Zauner, K.-P.; Bull, L. On Architectures of Circuits Implemented in Simulated Belousov–Zhabotinsky Droplets. BioSystems 2012, 109, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, S. Capillarity-Driven Migration of Small Objects: A Critical Review. Eur. Phys. J. E 2019, 42, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosseau, Q.; Usabiaga, F.B.; Lushi, E.; Wu, Y.; Ristroph, L.; Zhang, J.; Ward, M.; Shelley, M.J. Relating Rheotaxis and Hydrodynamic Actuation Using Asymmetric Gold-Platinum Phoretic Rods. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 178004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimienta, V.; Antoine, C. Self-Propulsion on Liquid Surfaces. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 19, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryazantsev, Y.S.; Velarde, M.G.; Guzmán, E.; Rubio, R.G.; Ortega, F.; Montoya, J.-J. On the Autonomous Motion of Active Drops or Bubbles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 527, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, C.H.; Evans, G.M.; Gendelman, O.; Bormashenko, E.; Nguyen, A.V. A Floating Self-Propelling Liquid Marble Containing Aqueous Ethanol Solutions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 101006–101012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Hu, Z.; Chu, F.; Wu, X. Enhanced and Guided Self-Propelled Jumping on the Superhydrophobic Surfaces with Macrotexture. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 115, 163701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, M.; Vilk, A.; Legchenkova, I.; Shoval, S.; Bormashenko, E. Mini-Generator of Electrical Power Exploiting the Marangoni Flow Inspired Self-Propulsion. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 15265–15268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sun, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Wei, J.; Li, J.; Dong, L.; Yan, D.; Hu, A.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Z. Self-Propelled Droplet-Based Electricity Generation. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 23164–23169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Q.; Huang, X. Marangoni Effect-Driven Motion of Miniature Robots and Generation of Electricity on Water. Langmuir 2017, 33, 12609–12615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayleigh, L. Measurements of the Amount of Oil Necessary in Order to Check the Motions of Camphor upon Water. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1890, 47, 364–367. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashima, Y.; Nagayama, M.; Nakata, S. A Camphor Grain Oscillates While Breaking Symmetry. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 5353–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suematsu, N.J.; Nakata, S. Evolution of Self-Propelled Objects: From the Viewpoint of Nonlinear Science. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 6308–6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, S.; Kohira, M.I.; Hayashima, Y. Mode Selection of a Camphor Boat in a Dual-Circle Canal. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2000, 322, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyano, Y.; Kitahata, H.; Nakata, S.; Gorecki, J. On a Simple Model That Explains Inversion of a Self-Propelled Rotor under Periodic Stop-And-Release-Operations. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2020, 30, 023105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadmor, R.; Baksi, A.; Gulec, S.; Jadhav, S.; N’Guessan, H.E.; Sen, K.; Somasi, V.; Tadmor, M.; Wasnik, P.; Yadav, S. Drops That Change Their Mind: Spontaneous Reversal from Spreading to Retraction. Langmuir 2019, 35, 15734–15738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bormashenko, E.; Bormashenko, Y.; Grynyov, R.; Aharoni, H.; Whyman, G.; Binks, B.P. Self-Propulsion of Liquid Marbles: Leidenfrost-Like Levitation Driven by Marangoni Flow. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 9910–9915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venerus, D.C.; Simavilla, D.N. Tears of Wine: New Insights on an Old Phenomenon. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suematsu, N.J.; Sasaki, T.; Nakata, S.; Kitahata, H. Quantitative Estimation of the Parameters for Self-Motion Driven by Difference in Surface Tension. Langmuir 2014, 30, 8101–8108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, W.M. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 91st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Winfree, A.T.; Delong, M.R. Spiral Waves of Chemical Activity. Science 1972, 175, 634–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turing, A.M. The Chemical Basis of Morphogenesis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 1952, 237, 37–72. [Google Scholar]
- Nakata, S.; Hiromatsu, S.-I. Intermittent Motion of a Camphor Float. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 224, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadmor, R. Marangoni Flow Revisited. J. Coll. Interf. Sci. 2009, 332, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Ma, K.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, J.; Li, L.; Yang, W.; Gong, Y.; Cai, L.; Gong, K. Cell Cycle Arrest and Senescence in P53-Wild Type Renal Carcinoma by Enhancer RNA—P53-Bound Enhancer Regions 2(p53BER2) through p53-Dependent Pathway. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 695–699. [Google Scholar]
- Chepelianskii, A.D.; Chevy, F.; Raphaël, E. Capillary-Gravity Waves Generated by a Slow Moving Object. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 074504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Closa, F.; Chepelianskii, A.D.; Raphaël, E. Capillary-Gravity Waves Generated by a Sudden Object Motion. Phys. Fluids 2010, 22, 052107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghelea, T.; Steinberg, V. Onset of Wave Drag Due to Generation of Capillary-Gravity Waves by a Moving Object as a Critical Phenomenon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 2557–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burghelea, T.; Steinberg, V. Wave Drag Due to Generation of Capillary-Gravity Surface Waves. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 66, 051204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenkel, M.; Whyman, G.; Shulzinger, E.; Starostin, A.; Bormashenko, E. Self-Propelling Rotator Driven by Soluto-Capillary Marangoni Flows. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 131604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, J.; Hou, J. Curvature-Driven Bubbles or Droplets on the Spiral Surface. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).