Generation of DC, AC, and Second-Harmonic Spin Currents by Electromagnetic Fields in an Inversion-Asymmetric Antiferromagnet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Formulation of the Problem
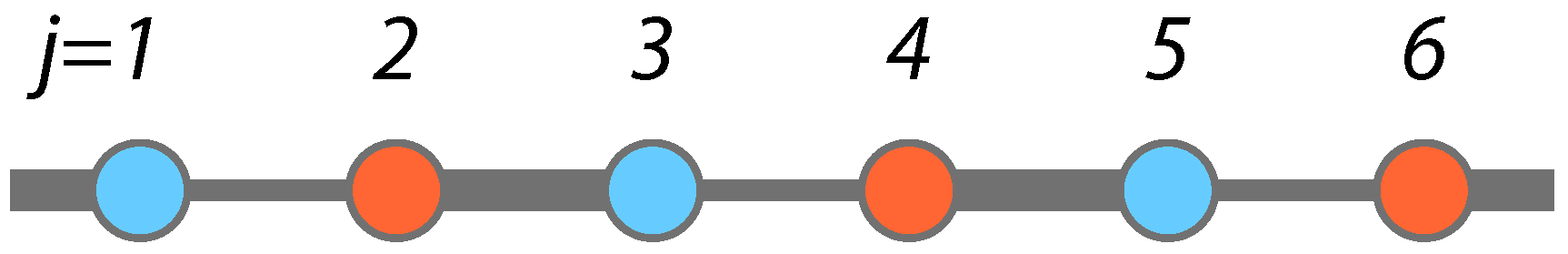
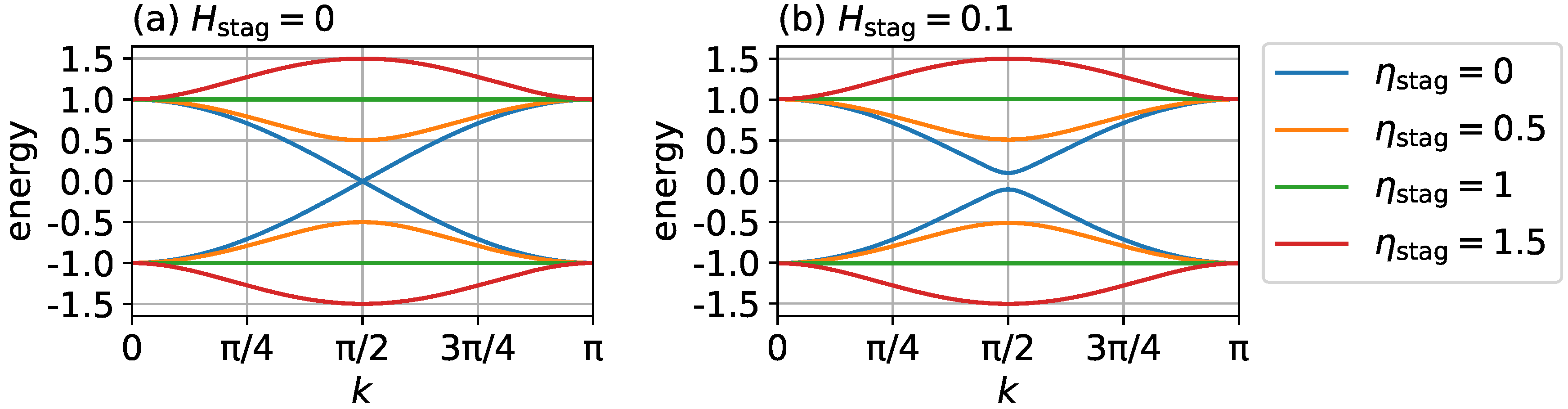
2.1. Time-Independent Hamiltonian
2.2. Coupling to AC Electric Field: Difference- and Sum-Frequency Mechanisms
2.3. Total Hamiltonian and Spin Current
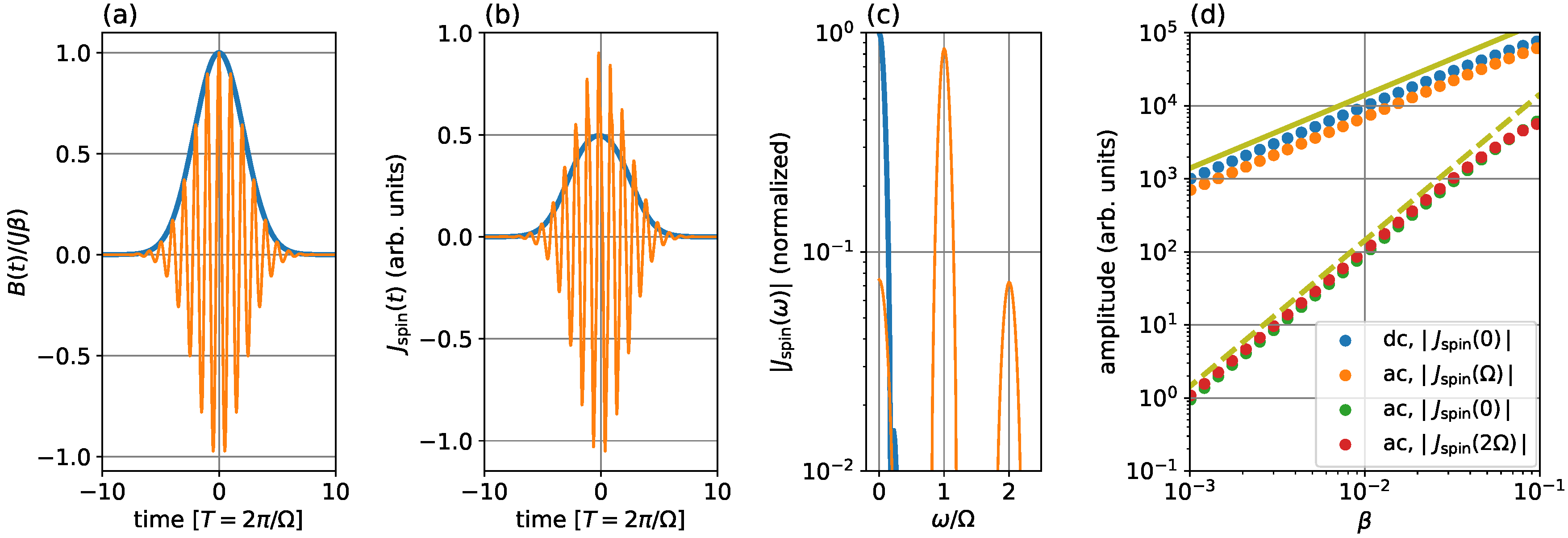
3. Results
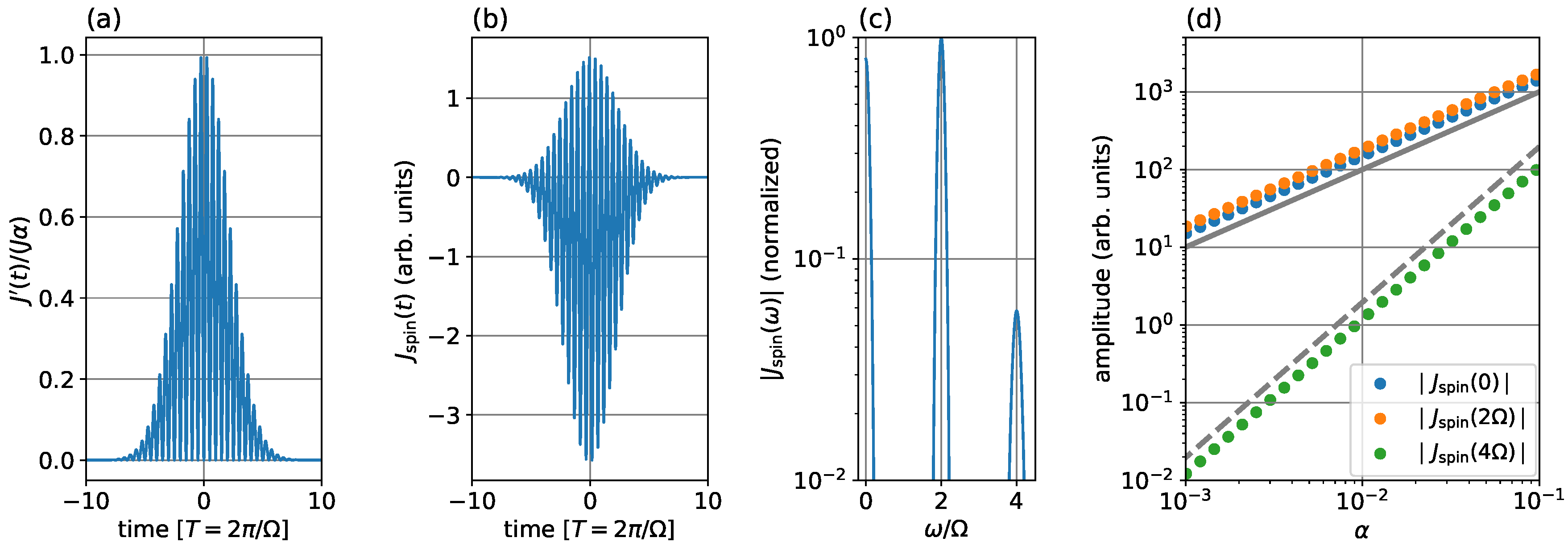
3.1. DC and Second-Harmonic Spin Currents
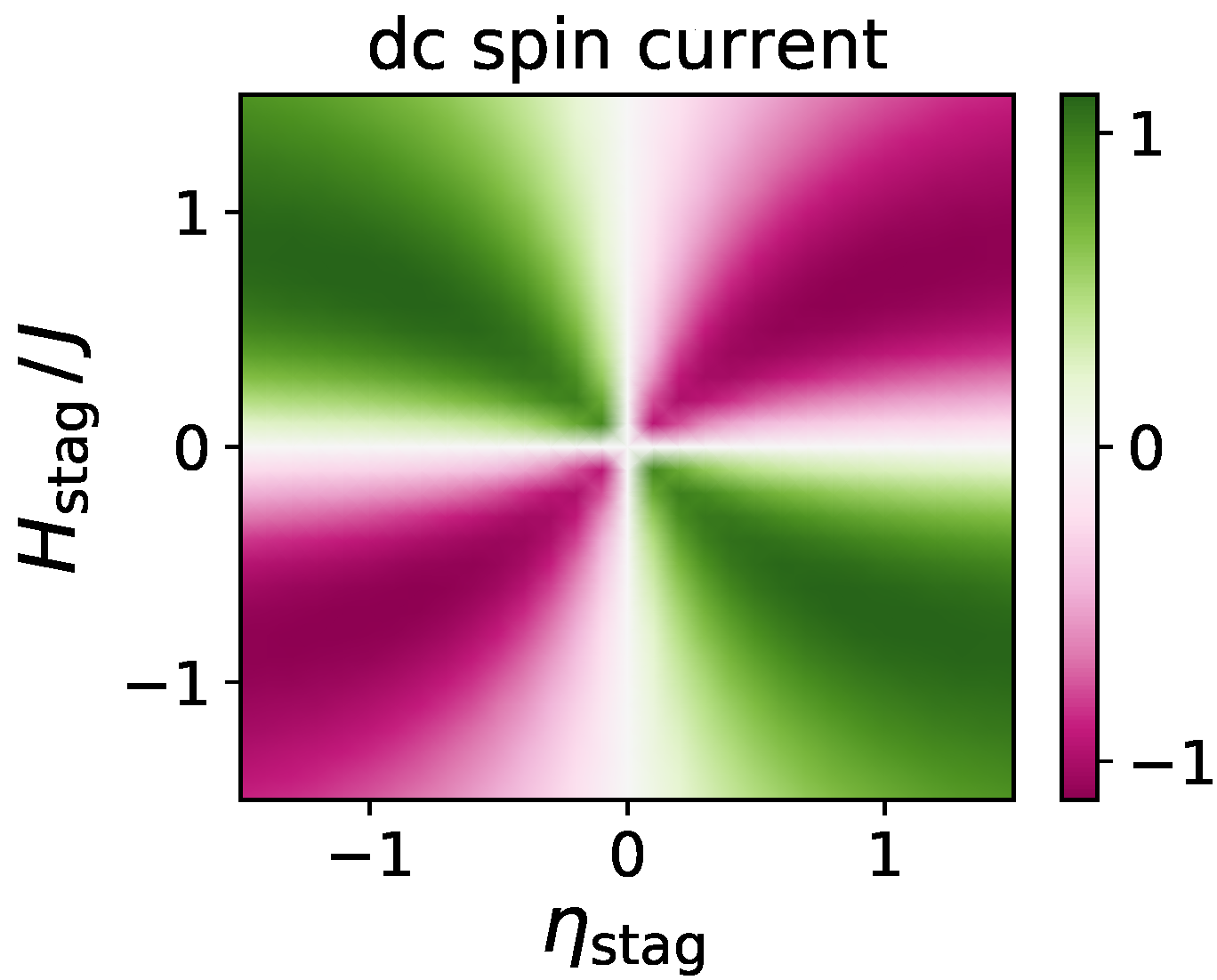
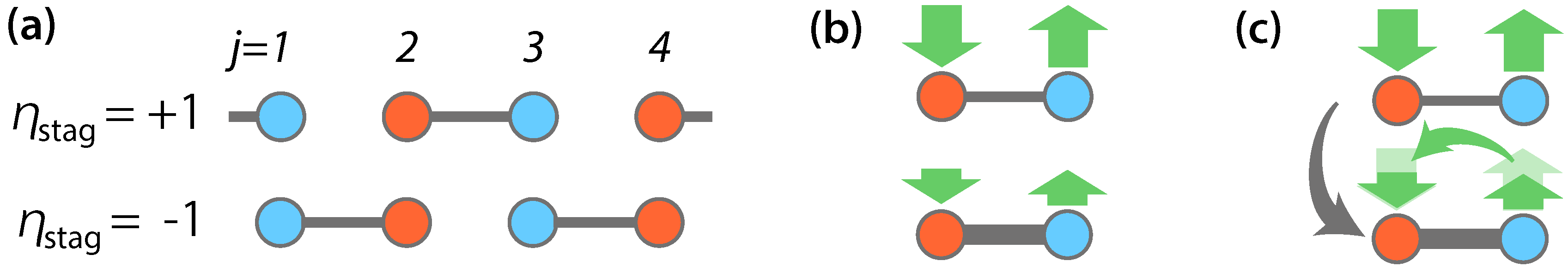
3.2. Direction of DC Spin Current
3.3. Mechanism of Spin Current Generation
3.4. DC Spin Current Generation by External Magnetic Field
4. Discussion and Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Fermionization
5.2. Quantum Master Equation
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Žutić, I.; Fabian, J.; Sarma, S.D. Spintronics: Fundamentals and applications. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2004, 76, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirilyuk, A.; Kimel, A.V.; Rasing, T. Ultrafast optical manipulation of magnetic order. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2010, 82, 2731–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, S.; Valenzuela, S.O.; Saitoh, E.; Kimura, T. (Eds.) Spin Current (Series on Semiconductor Science and Technology); Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sinova, J.; Žutić, I. New moves of the spintronics tango. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyakonov, M.I.; Perel, V.I. Possibility of orienting electron spins with current. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. Lett. 1971, 13, 467. [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch, J.E. Spin Hall Effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 1834–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, Y.K.; Myers, R.C.; Gossard, A.C.; Awschalom, D.D. Observation of the Spin Hall Effect in Semiconductors. Science 2004, 306, 1910–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uchida, K.; Takahashi, S.; Harii, K.; Ieda, J.; Koshibae, W.; Ando, K.; Maekawa, S.; Saitoh, E. Observation of the spin Seebeck effect. Nature 2008, 455, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, G.E.W.; Saitoh, E.; van Wees, B.J. Spin caloritronics. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumak, A.V.; Vasyuchka, V.; Serga, A.; Hillebrands, B. Magnon spintronics. Nat. Phys. 2015, 11, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumak, A.V.; Serga, A.A.; Hillebrands, B. Magnon transistor for all-magnon data processing. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krawczyk, M.; Grundler, D. Review and prospects of magnonic crystals and devices with reprogrammable band structure. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2014, 26, 123202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltz, V.; Manchon, A.; Tsoi, M.; Moriyama, T.; Ono, T.; Tserkovnyak, Y. Antiferromagnetic spintronics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2018, 90, 15005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimel, A.V.; Kirilyuk, A.; Tsvetkov, A.; Pisarev, R.V.; Rasing, T. Laser-induced ultrafast spin reorientation in the antiferromagnet TmFeO3. Nature 2004, 429, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, S.; Ideue, T.; Kubota, M.; Kozuka, Y.; Takagi, R.; Nakamura, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Kawasaki, M.; Tokura, Y. Thermal Generation of Spin Current in an Antiferromagnet. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 266601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Chen, K.; Zhang, S.; Chien, C. Enhancement of Thermally Injected Spin Current through an Antiferromagnetic Insulator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 186601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naka, M.; Hayami, S.; Kusunose, H.; Yanagi, Y.; Motome, Y.; Seo, H. Spin current generation in organic antiferromagnets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimel, A.V.; Kirilyuk, A.; Usachev, P.A.; Pisarev, R.V.; Balbashov, A.M.; Rasing, T. Ultrafast non-thermal control of magnetization by instantaneous photomagnetic pulses. Nature 2005, 435, 655–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, T.; Van Aken, B.B.; Duong, N.P.; Lottermoser, T.; Fiebig, M. Ultrafast spin and lattice dynamics in antiferromagnetic Cr2O3. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 155406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, R.; Jin, Z.; Li, G.; Ma, G.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, X. Terahertz magnetic field induced coherent spin precession in YFeO3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 61102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishitani, J.; Nagashima, T.; Hangyo, M. Terahertz radiation from antiferromagnetic MnO excited by optical laser pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 81907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, Y.; Hirori, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Kageyama, H.; Tanaka, K. Antiferromagnetic resonance excitation by terahertz magnetic field resonantly enhanced with split ring resonator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 22410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizuka, H.; Sato, M. Rectification of Spin Current in Inversion-Asymmetric Magnets with Linearly Polarized Electromagnetic Waves. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 197702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishizuka, H.; Sato, M. Theory for shift current of bosons: Photogalvanic spin current in ferrimagnetic and antiferromagnetic insulators. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.02734. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, T.N.; Sato, M. High-harmonic generation by electric polarization, spin current, and magnetization. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.00146. [Google Scholar]
- Mentink, J.H.; Balzer, K.; Eckstein, M. Ultrafast and reversible control of the exchange interaction in Mott insulators. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.W. Antiferromagnetism. Theory of Superexchange Interaction. Phys. Rev. 1950, 79, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, S.; Oka, T.; Aoki, H. Probing and controlling spin chirality in Mott insulators by circularly polarized laser. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 014406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chinzei, K.; Ikeda, T.N.; Tsunetsugu, H. Laser-induced DC spin current. Unpublished work. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rezende, S.M.; Azevedo, A.; Rodríguez-Suárez, R.L. Introduction to antiferromagnetic magnons. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 126, 151101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sachdev, S. Quantum Phase Transitions; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Breuer, H.P.; Petruccione, F. The Theory of Open Quantum Systems; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ikeda, T.N. Generation of DC, AC, and Second-Harmonic Spin Currents by Electromagnetic Fields in an Inversion-Asymmetric Antiferromagnet. Condens. Matter 2019, 4, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat4040092
Ikeda TN. Generation of DC, AC, and Second-Harmonic Spin Currents by Electromagnetic Fields in an Inversion-Asymmetric Antiferromagnet. Condensed Matter. 2019; 4(4):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat4040092
Chicago/Turabian StyleIkeda, Tatsuhiko N. 2019. "Generation of DC, AC, and Second-Harmonic Spin Currents by Electromagnetic Fields in an Inversion-Asymmetric Antiferromagnet" Condensed Matter 4, no. 4: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat4040092




