The Laser Powder Bed Fusion of Nd2Fe14B Permanent Magnets: The State of the Art
Abstract
1. Introduction
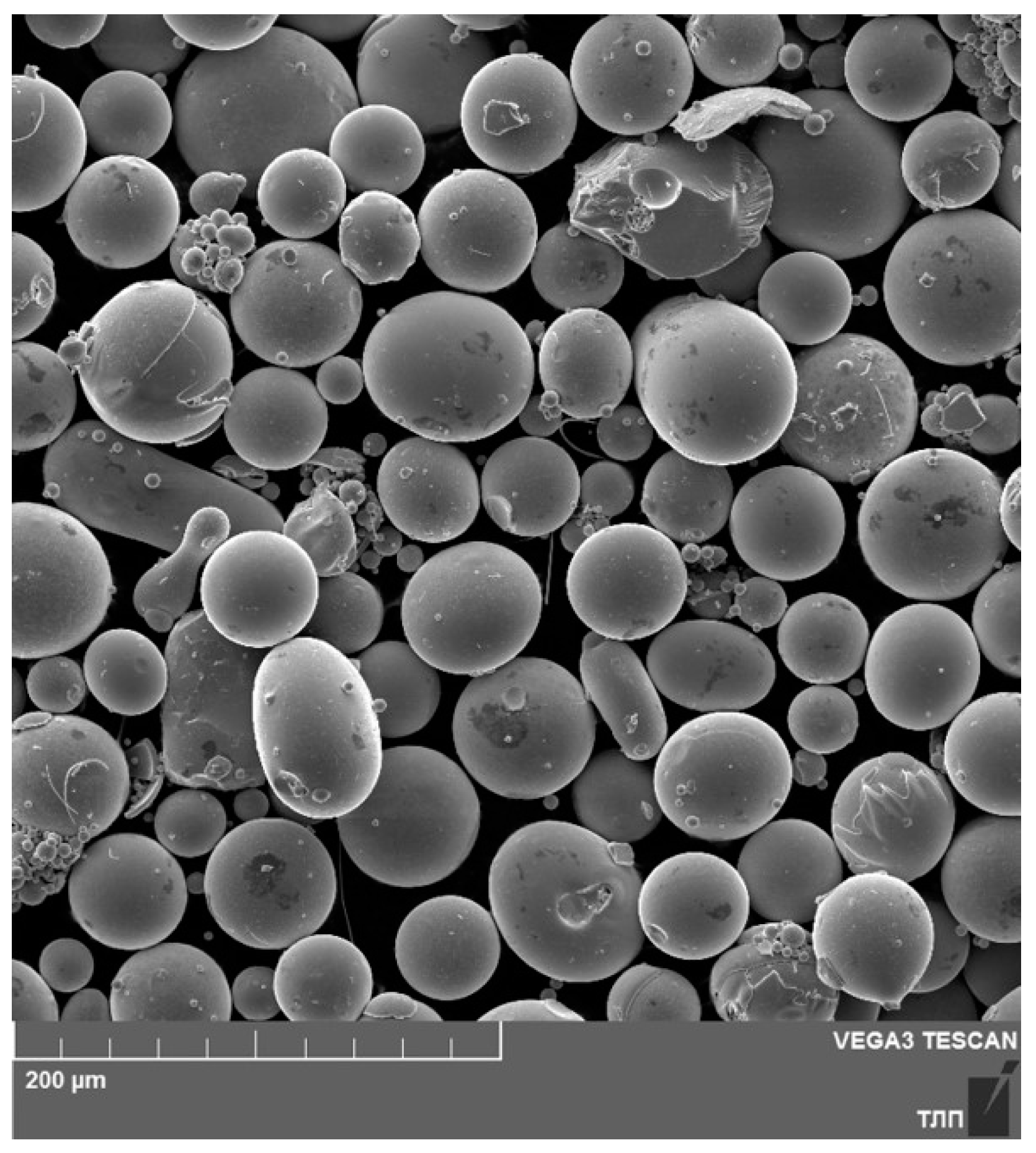
2. Initial Powder Materials
2.1. Powder Requirements
2.2. MQP-S Powder Grade
2.3. Alternatives to MQP-S Powder
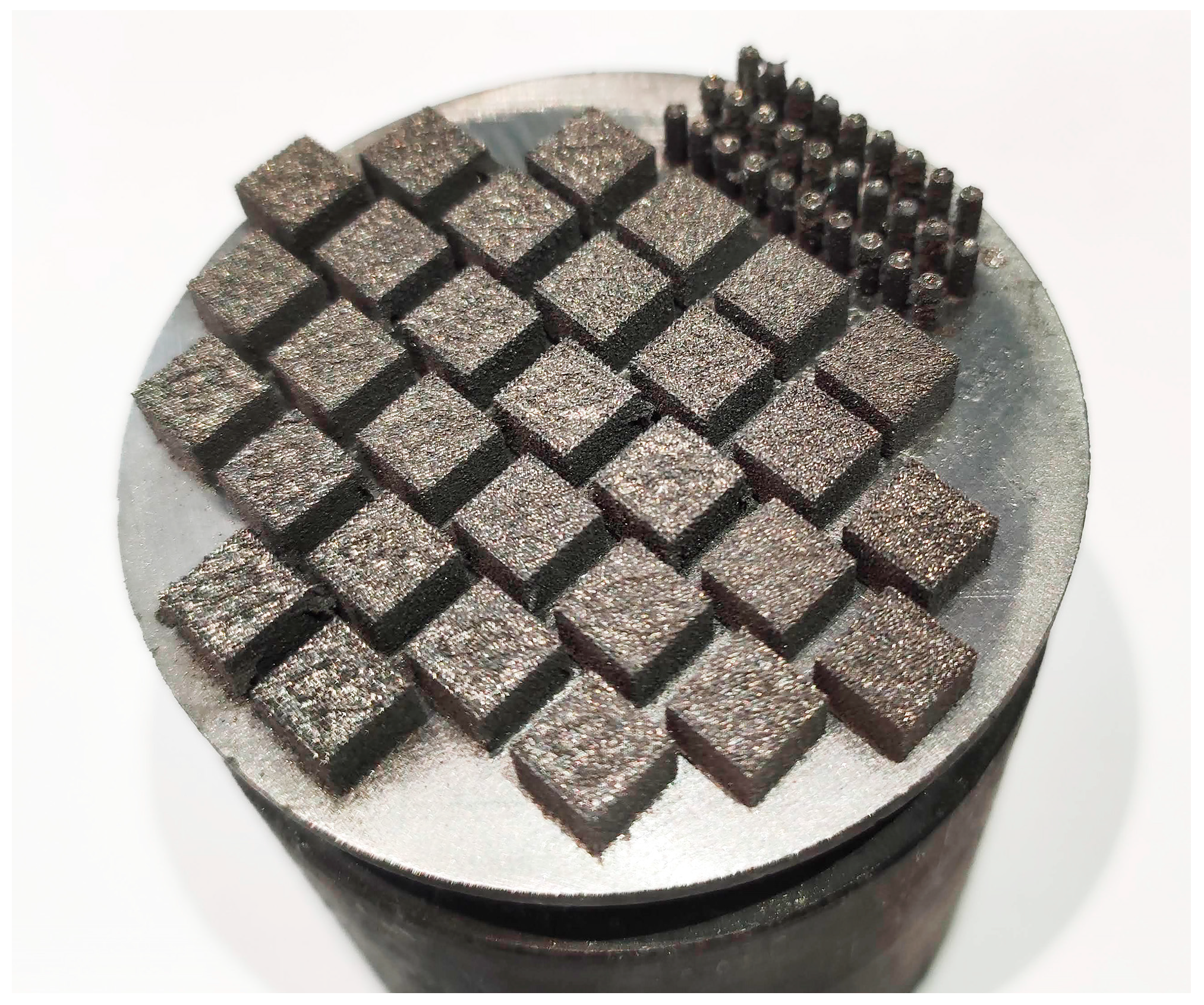
3. LPBF Process
3.1. LPBF Peculiarities
3.2. LPBF Process Parameters
3.3. Density and Scanning Strategies
4. Microstructure and Defects
4.1. REM-Lean MQP-S Material
4.2. Other Materials
4.3. Latest Achievements
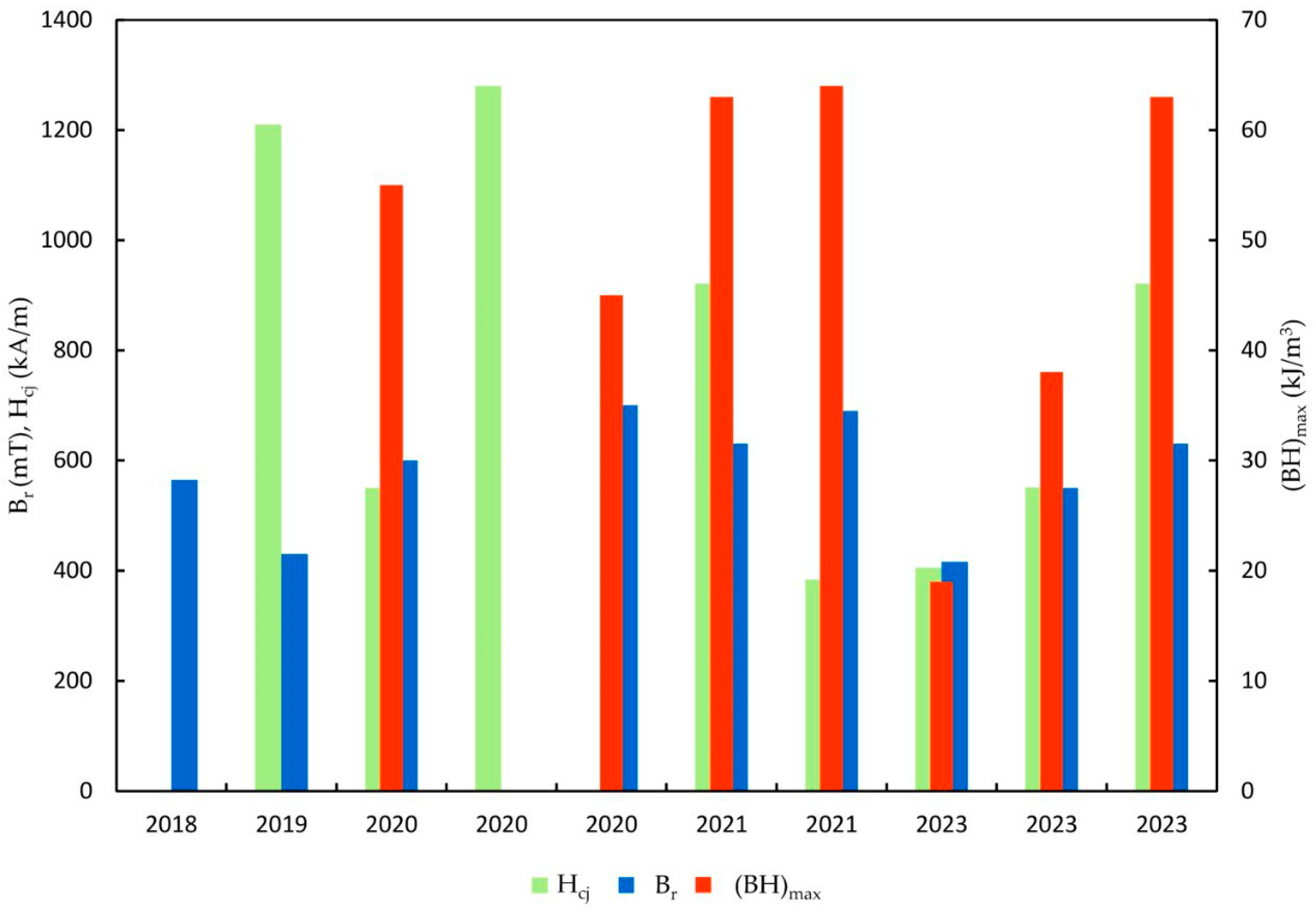
5. Magnetic Properties
5.1. LPBF vs. Conventional Methods
5.2. Dependance of Magnetic Properties on Process Parameters
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Refaie, A.; Osama, M. High Specific Power Electrical Machines: A System Perspective. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2019, 3, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemi, M. High Power Density Technologies for Large Generators and Motors for Marine Applications with Focus on Electrical Insulation Challenges. High Volt. 2020, 5, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, Y. Demagnetization Process of Nd-Fe-B Sintered and Ferrite Magnets. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2025, 579, 170854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poenaru, I.; Lixandru, A.; Güth, K.; Malfliet, A.; Yoon, S.; Škulj, I.; Gutfleisch, O. HDDR Treatment of Ce-Substituted Nd2Fe14B-Based Permanent Magnet Alloys—Phase Structure Evolution, Intergranular Processes and Magnetic Property Development. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 814, 152215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, H.; Liang, W.; Liu, Q.; Dong, H.; Jia, R.; Ma, W. Corrosion Resistance, Mechanical and Magnetic Properties of Cold-Sprayed Al Coating on Sintered NdFeB Magnet. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2021, 30, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kedous-Lebouc, A.; Dubus, J.-M.; Garbuio, L.; Personnaz, S. Direct Reuse Strategies of Rare Earth Permanent Magnets for PM Electrical Machines—An Overview Study. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 86, 20901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önal, M.A.R.; Dewilde, S.; Degri, M.; Pickering, L.; Saje, B.; Riaño, S.; Walton, A.; Binnemans, K. Recycling of Bonded NdFeB Permanent Magnets Using Ionic Liquids. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 2821–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Dong, S.; Li, Q.; Lu, X.; Chen, R.; Guo, S.; Yan, A.; Li, W. Performance Prediction Models for Sintered NdFeB Using Machine Learning Methods and Interpretable Studies. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 963, 171250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliesch, T. Injection Molded Permanent Magnets. In Modern Permanent Magnets; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 209–250. [Google Scholar]
- Croat, J.J. Compression Bonded NdFeB Permanent Magnets. In Modern Permanent Magnets; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 169–208. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.M.; Herchenroeder, J.W.; Smith, B.; Suda, M.; Brown, D.N.; Chen, Z. Recent Development in Bonded NdFeB Magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 239, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandha, K.; Ouyang, G.; Gupta, S.; Kunc, V.; Parans Paranthaman, M.; Nlebedim, I.C. Recycling of Additively Printed Rare-Earth Bonded Magnets. Waste Manag. 2019, 90, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, M.; Masuda, M.; Suzuki, S.; Machida, K. Recycling of Rare Earth Sintered Magnets as Isotropic Bonded Magnets by Melt-Spinning. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 374, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakotnik, M.; Harris, I.R.; Williams, A.J. Possible Methods of Recycling NdFeB-Type Sintered Magnets Using the HD/Degassing Process. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 450, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulkhair, N.T.; Simonelli, M.; Parry, L.; Ashcroft, I.; Tuck, C.; Hague, R. 3D Printing of Aluminium Alloys: Additive Manufacturing of Aluminium Alloys Using Selective Laser Melting. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 106, 100578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrpouya, M.; Tuma, D.; Vaneker, T.; Afrasiabi, M.; Bambach, M.; Gibson, I. Multimaterial Powder Bed Fusion Techniques. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2022, 28, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Tabary, S.A.A.B.; Rahmatabadi, D.; Ebrahimi, M.S.; Abrinia, K.; Hashemi, R. Review of Selective Laser Melting of Magnesium Alloys: Advantages, Microstructure and Mechanical Characterizations, Defects, Challenges, and Applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 1537–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzengue, A.G.B.; Mpofu, K.; Mathe, N.; Daniyan, I.; Muvunzi, R. An Experimental Investigation of Selective Laser Process Parameters on Aluminium Alloy (AlSi12). Procedia CIRP 2023, 118, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullane, A.; Murray, J.W.; Hyde, C.J.; Sankare, S.; Evirgen, A.; Clare, A.T. On the Use of Multiple Layer Thicknesses within Laser Powder Bed Fusion and the Effect on Mechanical Properties. Mater. Des. 2021, 212, 110256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, X.; Song, D.; Yu, A.; Tan, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Lin, X. Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure, Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Selective Laser Melted AlSi7Mg Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 945, 169278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.; Leary, M.; Lozanovski, B.; Downing, D.; Mazur, M.; Sarker, A.; Khorasani, A.; Jones, A.; Maconachie, T.; Bateman, S.; et al. Effect of Geometry on the Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Gyroid Structures Fabricated via SLM: A Numerical Study. Mater. Des. 2019, 184, 108165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahulan, N.; Sharma, S.S.; Rakesh, N.; Sambhu, R. A Short Review on Mechanical Properties of SLM Titanium Alloys Based on Recent Research Works. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 56, A7–A12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Li, P. Micropore-Propagation-Based Model of Fatigue Life Analysis of SLM Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Fatigue 2023, 167, 107352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarok, S.; Puspitasari, P.; Andoko, A.; Lubis, A.M.H.S.; Permanasari, A.A.; Abdullah, M.I.H.C. Failure Mechanism on Ti-6Al-4V Material Processed Using Selective Laser Melting (SLM). In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Advances in Manufacturing and Materials Engineering: ICAMME, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 9–10 August 2022; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 321–326. [Google Scholar]
- Metalnikov, P.; Ben-Hamu, G.; Eliezer, D. Corrosion Behavior of AM-Ti-6Al-4V: A Comparison between EBM and SLM. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 7, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Li, H.; Che, L.; Chen, S.; Zhang, P.; He, J.; Wu, Z.; Niu, S.; Li, X. Effects of HIP Process Parameters on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Fabricated by SLM. Metals 2023, 13, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Chen, C.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, K.; Guo, S. A High-Strength Heat-Resistant Al−5.7Ni Eutectic Alloy with Spherical Al3Ni Nano-Particles by Selective Laser Melting. Scr. Mater. 2021, 203, 114034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahari, T.; Nagoya, T.; Kakehi, K.; Sato, N.; Nakano, S. Microstructure and Creep Properties of Ni-Base Superalloy IN718 Built up by Selective Laser Melting in a Vacuum Environment. Metals 2020, 10, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplanskii, Y.Y.; Sentyurina, Z.A.; Loginov, P.A.; Levashov, E.A.; Korotitskiy, A.V.; Travyanov, A.Y.; Petrovskii, P.V. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the (Fe,Ni)Al-Based Alloy Produced by SLM and HIP of Spherical Composite Powder. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 743, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazeeva, A.K.; Staritsyn, M.V.; Bobyr, V.V.; Manninen, S.A.; Kuznetsov, P.A.; Klimov, V.N. Magnetic Properties of Fe–Ni Permalloy Produced by Selective Laser Melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 814, 152315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesyk, D.; Martinez, S.; Pedash, O.; Dzhemelinskyi, V.; Mordyuk, B. Combined Thermo-Mechanical Techniques for Post-Processing of the SLM-Printed Ni-Cr-Fe Alloy Parts. In Design, Simulation, Manufacturing: The Innovation Exchange; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 295–304. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A.; Takaichi, A.; Kajima, Y.; Hanawa, T.; Wakabayashi, N. Reusing the Co–Cr–Mo Support Structures of Selective Laser Melted Parts: Evaluation of Mechanical Properties and Microstructures. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2023, 36, e00608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, F.; Song, M.; Ni, S.; Liu, S. Microstructure Evolution, Martensite Transformation and Mechanical Properties of Heat Treated Co-Cr-Mo-W Alloys by Selective Laser Melting. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2023, 113, 106170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenbin, L.; Junhao, D.; Xiao, C.; You, W.; Xu, S.; Sai, Z. A 3D-Printed CuNi Alloy Catalyst with a Triply Periodic Minimal Surface for the Reverse Water-Gas Shift Reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 12, 314–320. [Google Scholar]
- Sankar, B.; Vinay, C.; Vishnu, J.; Shankar, K.V.; Gokul Krishna, G.P.; Govind, V.; Jayakrishna, A.J. Focused Review on Cu–Ni–Sn Spinodal Alloys: From Casting to Additive Manufacturing. Met. Mater. Int. 2023, 29, 1203–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreiev, A.; Hoyer, K.-P.; Hengsbach, F.; Haase, M.; Tasche, L.; Duschik, K.; Schaper, M. Powder Bed Fusion of Soft-Magnetic Iron-Based Alloys with High Silicon Content. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2023, 317, 117991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibaldi, M.; Ashcroft, I.; Lemke, J.N.; Simonelli, M.; Hague, R. Effect of Annealing on the Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Soft Magnetic Fe-Si Produced via Laser Additive Manufacturing. Scr. Mater. 2018, 142, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Hagedorn, Y.-C.; Meiners, W.; Meng, G.; Batista, R.J.S.; Wissenbach, K.; Poprawe, R. Densification Behavior, Microstructure Evolution, and Wear Performance of Selective Laser Melting Processed Commercially Pure Titanium. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 3849–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.C.; Savalani, M.M.; Lau, M.L.; Man, H.C. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Selective Laser Melted Magnesium. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 7447–7454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yu, C.; Ma, J.; Liu, W.; Shen, Z. Densification and Crack Suppression in Selective Laser Melting of Pure Molybdenum. Mater. Des. 2017, 129, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yuan, T.; Li, R.; Tang, J.; Wang, G.; Guo, K. Selective Laser Melting of Pure Tantalum: Densification, Microstructure and Mechanical Behaviors. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 707, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeshoji, T.-T.; Nakamura, K.; Yonehara, M.; Imai, K.; Kyogoku, H. Selective Laser Melting of Pure Copper. JOM 2018, 70, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, A.G.; Monguzzi, L.; Previtali, B. Selective Laser Melting of Pure Zn with High Density for Biodegradable Implant Manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 15, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Dong, S.; Deng, S.; Liao, H.; Coddet, C. Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Iron Parts Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. Opt. Laser Technol. 2014, 56, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Yadaiah, N.; Prakash, C.; Ramakrishna, S.; Dixit, S.; Gupta, L.R.; Buddhi, D. Laser Powder Bed Fusion: A State-of-the-Art Review of the Technology, Materials, Properties & Defects, and Numerical Modelling. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 20, 2109–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaćimović, J.; Binda, F.; Herrmann, L.G.; Greuter, F.; Genta, J.; Calvo, M.; Tomše, T.; Simon, R.A. Net Shape 3D Printed NdFeB Permanent Magnet. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, I.; Rosen, D.; Stucker, B.; Khorasani, M. Additive Manufacturing Technologies; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; ISBN 978-3-030-56126-0. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, K.-H.; Sawatzki, S.; Gauß, R.; Gutfleisch, O. Permanent Magnet Materials and Applications. In Handbook of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1369–1433. [Google Scholar]
- Pelevin, I.A.; Terekhin, E.A.; Ozherelkov, D.Y.; Tereshina, I.S.; Karpenkov, D.Y.; Bochkanov, F.Y.; Chernyshikhin, S.V.; Nalivaiko, A.Y.; Gromov, A.A. New Scanning Strategy Approach for Laser Powder Bed Fusion of Nd-Fe-B Hard Magnetic Material. Metals 2023, 13, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.; Sepehri-Amin, H.; Goertler, M.; Groenefeld, M.; Teliban, I.; Hono, K.; Suess, D. Coercivity Enhancement of Selective Laser Sintered NdFeB Magnets by Grain Boundary Infiltration. Acta Mater. 2019, 172, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volegov, A.S.; Andreev, S.V.; Selezneva, N.V.; Ryzhikhin, I.A.; Kudrevatykh, N.V.; Mädler, L.; Okulov, I.V. Additive Manufacturing of Heavy Rare Earth Free High-Coercivity Permanent Magnets. Acta Mater. 2020, 188, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosoni, O.; Borges Mendonça, E.; Reijonen, J.; Antikainen, A.; Schäfer, L.; Riegg, S.; Gutfleisch, O. High-Coercivity Copper-Rich Nd-Fe-B Magnets by Powder Bed Fusion Using Laser Beam Method. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 64, 103426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadroitsev, I.; Bertrand, P.; Smurov, I. Parametric Analysis of the Selective Laser Melting Process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 8064–8069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Périgo, E.A.; Jacimovic, J.; García Ferré, F.; Scherf, L.M. Additive Manufacturing of Magnetic Materials. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 30, 100870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MQP-S-11-9-20001. Available online: https://mqitechnology.com/product/mqp-s-11-9-20001/ (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Pelevin, I.A.; Ozherelkov, D.Y.; Chernyshikhin, S.V.; Nalivaiko, A.Y.; Gromov, A.A.; Chzhan, V.B.; Terekhin, E.A.; Tereshina, I.S. Selective Laser Melting of Nd-Fe-B: Single Track Study. Mater. Lett. 2022, 315, 131947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapley, M.; Gregory, S.D.; Pauls, J.P.; Tansley, G.; Busch, A. Influence of Powder Loading Fraction on Properties of Bonded Permanent Magnets Prepared By Selective Laser Sintering. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 8, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Shao, Y.; Yin, Y.; Chen, H.; Xu, H.; Liu, W.; Liu, M.; Zhong, C.; Yu, X.; Chen, J.; et al. Mass Production of Regenerated Sintered NdFeB Magnets with Improved Magnetic Properties Compared to Original Magnets. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2023, 36, e00615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, F.; Thielsch, J.; Drossel, W.-G. Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Nd-Fe-B Permanent Magnets Produced by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Scr. Mater. 2021, 201, 113921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, N.; Huber, F.; Franke, J. Influences of Process Parameters on Rare Earth Magnets Produced by Laser Beam Melting. In Proceedings of the 2017 7th International Electric Drives Production Conference (EDPC), Wuerzburg, Germany, 5–6 December 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Goll, D.; Trauter, F.; Loeffler, R.; Gross, T.; Schneider, G. Additive Manufacturing of Textured FePrCuB Permanent Magnets. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiya, T.; Liu, J.; Sepehri-Amin, H.; Ohkubo, T.; Hioki, K.; Hattori, A.; Hono, K. High-Coercivity Hot-Deformed Nd–Fe–B Permanent Magnets Processed by Nd–Cu Eutectic Diffusion under Expansion Constraint. Scr. Mater. 2014, 81, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawatzki, S.; Dirks, A.; Frincu, B.; Löwe, K.; Gutfleisch, O. Coercivity Enhancement in Hot-Pressed Nd-Fe-B Permanent Magnets with Low Melting Eutectics. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 17A705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Chen, R.; Yin, W.; Wang, J.; Tang, X.; Lee, D.; Yan, A. Enhanced Texture in Die-Upset Nanocomposite Magnets by Nd-Cu Grain Boundary Diffusion. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 072409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.Z.; Zheng, L.Y.; Marinescu, M.; Liu, J.F.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Textured Nd2Fe14B Flakes with Enhanced Coercivity. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 07A735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, C.; Hamada, N.; Mitarai, H.; Honkura, Y. Development of a Co-Free NdFeB Anisotropic Bonded Magnet Produced from the d-HDDR Processed Powder. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2001, 37, 2467–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehri-Amin, H.; Ohkubo, T.; Nishiuchi, T.; Hirosawa, S.; Hono, K. Coercivity Enhancement of Hydrogenation–Disproportionation–Desorption–Recombination Processed Nd–Fe–B Powders by the Diffusion of Nd–Cu Eutectic Alloys. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 1124–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F. Recent Progress of Grain Boundary Diffusion Process of Nd-Fe-B Magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 514, 167227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toujun, Z.; Bao, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, M.; Huang, X.; Wei, W.; Liu, R.; Xie, G. Optimizing Microstructure, Magnetic Properties and Mechanical Properties of Sintered NdFeB Magnet by Double Alloy Method and Grain Boundary Diffusion. Intermetallics 2023, 162, 108027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Bai, Q. Defect Formation Mechanisms in Selective Laser Melting. A Review. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 30, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, P.D.; Vijayananth, S.; Natarajan, M.P.; Jayabalakrishnan, D.; Arul, K.; Jayaseelan, V.; Elanchezhian, J. A Current State of Metal Additive Manufacturing Methods: A Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 59, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidrad, H.R.; Salemi, S. Effect of the Volume Energy Density and Heat Treatment on the Defect, Microstructure, and Hardness of L-PBF Inconel 625. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 5880–5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Mantri, S.A.; Ramanujan, R.V.; Banerjee, R. Additive Manufacturing of Magnetic Materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 114, 100688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, F.; Thielsch, J.; Drossel, W.-G. Laser Powder Bed Fusion of Nd–Fe–B Permanent Magnets. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 5, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalon, M.; Görtler, M.; Meier, B.; Arneitz, S.; Urban, N.; Mitsche, S.; Huber, C.; Franke, J.; Sommitsch, C. Influence of Melt-Pool Stability in 3D Printing of NdFeB Magnets on Density and Magnetic Properties. Materials 2019, 13, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Jang, Y.R.; Lee, H.-S.; Cho, J.-W.; Jang, T.; Eo, D.-R.; Lee, W. Microstructural Investigation of Nanocrystalline Nd-Fe-B Magnets Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Mater. Charact. 2024, 216, 114228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, P.; Salvemini, F.; Proper, S.; Luzin, V.; Simonsson, K.; Sjöström, S.; Hosseini, S.; Peng, R.L.; Moverare, J. A Study of the Influence of Novel Scan Strategies on Residual Stress and Microstructure of L-Shaped LPBF IN718 Samples. Mater. Des. 2022, 214, 110386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, T.; Kim, J.-Y.; Gurung, K.; Meyers, S.; Van Hooreweder, B.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, J.-K.; Lee, C.S. Impact of Laser Scanning Strategies on Microstructure in Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF) of Nanoparticle-Infused Pre-Alloyed Water-Atomized Iron Powder. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 891, 145989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; He, K.; Meng, X.; Xu, H.; Ming, G.; Du, Y.; Dai, K.; Dong, C. Influence of Laser Powder Bed Fusion Scanning Strategies on the Magnetic and Mechanical Properties of NdFeB. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1020, 179384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genç, K.; Toyting, S.; Galindo-Nava, E.; Todd, I.; Mumtaz, K. Laser Powder Bed Fusion of NdFeB and Influence of Powder Bed Heating on Density and Magnetic Properties. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 132, 5017–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caniou, R.; Rado, C.; Gaillard, G.-C.; Tosoni, O.; Flament, C.; Garandet, J.-P. Influence of Process Parameters on the Microstructure of Laser Printed NdFeB Alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 570, 170503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goll, D.; Trauter, F.; Bernthaler, T.; Schanz, J.; Riegel, H.; Schneider, G. Additive Manufacturing of Bulk Nanocrystalline FeNdB Based Permanent Magnets. Micromachines 2021, 12, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, N.; Sun, J. Pore Defects in Laser Powder Bed Fusion: Formation Mechanism, Control Method, and Perspectives. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 944, 169215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Plessis, A.; Yadroitsava, I.; Yadroitsev, I. Effects of Defects on Mechanical Properties in Metal Additive Manufacturing: A Review Focusing on X-Ray Tomography Insights. Mater. Des. 2020, 187, 108385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacimovic, J.; Christen, T.; Dénervaud, E. Self-Organized Giant Magnetic Structures via Additive Manufacturing in NdFeB Permanent Magnets. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 34, 101288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Aboulkhair, N.T.; Robertson, S.; Zhou, Z.; Bagot, P.A.J.; Moody, M.P.; Degano, M.; Ashcroft, I.; Hague, R.J.M. Amorphous-Crystalline Nanostructured Nd-Fe-B Permanent Magnets Using Laser Powder Bed Fusion: Metallurgy and Magnetic Properties. Acta Mater. 2023, 259, 119239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Kang, N.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Mansori, M.E.; Chen, J.; Yang, H.; Tan, H.; Lin, X. Toward Understanding the Microstructure Characteristics, Phase Selection and Magnetic Properties of Laser Additive Manufactured Nd-Fe-B Permanent Magnets. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2024, 6, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Vocabulary of Magnetism. Available online: https://www.arnoldmagnetics.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/Vocabulary-of-Magnetism.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Gutfleisch, O. Controlling the Properties of High Energy Density Permanent Magnetic Materials by Different Processing Routes. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2000, 33, R157–R172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, S. Current Status and Recent Topics of Rare-Earth Permanent Magnets. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 064001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Hirota, K.; Shimao, M.; Minowa, T.; Honshima, M. Magnetic Properties of Extremely Small Nd-Fe-B Sintered Magnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 3844–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Cao, J.; Yu, Z.; Song, W.; Yu, H.; Hussain, M.; Liu, Z. Grain Boundary Diffusion Sources and Their Coating Methods for Nd-Fe-B Permanent Magnets. Metals 2021, 11, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, C.; Shen, B. Nanocrystalline and Nanocomposite Permanent Magnets by Melt Spinning Technique. Chin. Phys. B 2018, 27, 117502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannesan, N.; Harris, I.R. Aspects of NdFeB HDDR Powders: Fundamentals and Processing. In Bonded Magnets; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 13–36. [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita, T. Magnetic Properties and Microstructures of the NdFeB Magnet Powder Produced by the HDDR Process(IV). In Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Rare-Earth Magnets and Their Applications; Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1990; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, T.; Oka, N.; Ohsuna, T.; Kaneko, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Shima, T. Enhancement of Coercivity for Nd-Fe-B Thin Films by the Infiltration of Nd-Cu Alloy Cap Layer. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 023903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.; Du, D.; Yi, C.; Xing, B.; Li, Y. Influences of Laser Spot Welding on Magnetic Property of a Sintered NdFeB Magnet. Metals 2016, 6, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, L.; Skokov, K.; Liu, J.; Maccari, F.; Braun, T.; Riegg, S.; Radulov, I.; Gassmann, J.; Merschroth, H.; Harbig, J.; et al. Design and Qualification of Pr–Fe–Cu–B Alloys for the Additive Manufacturing of Permanent Magnets. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2102148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


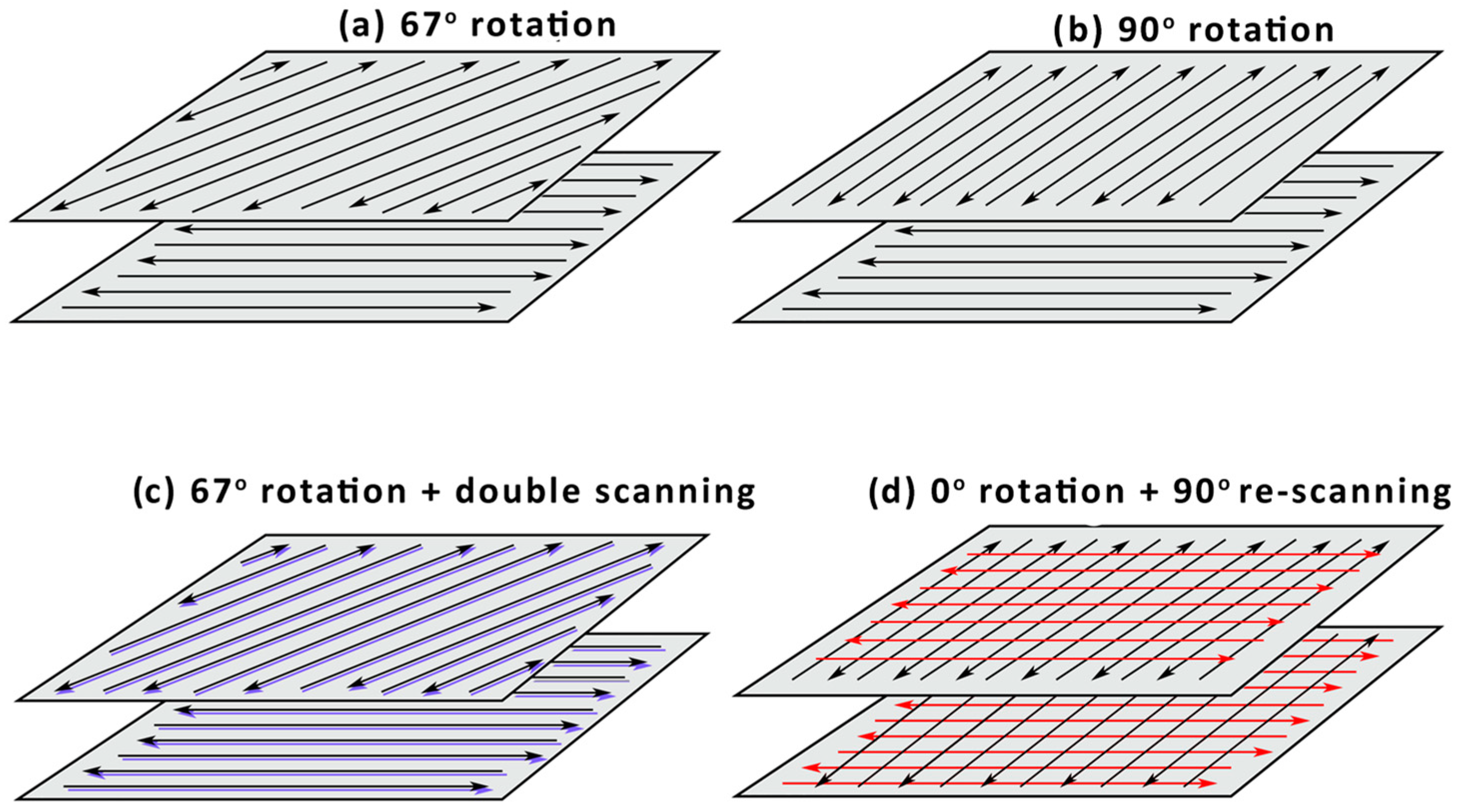

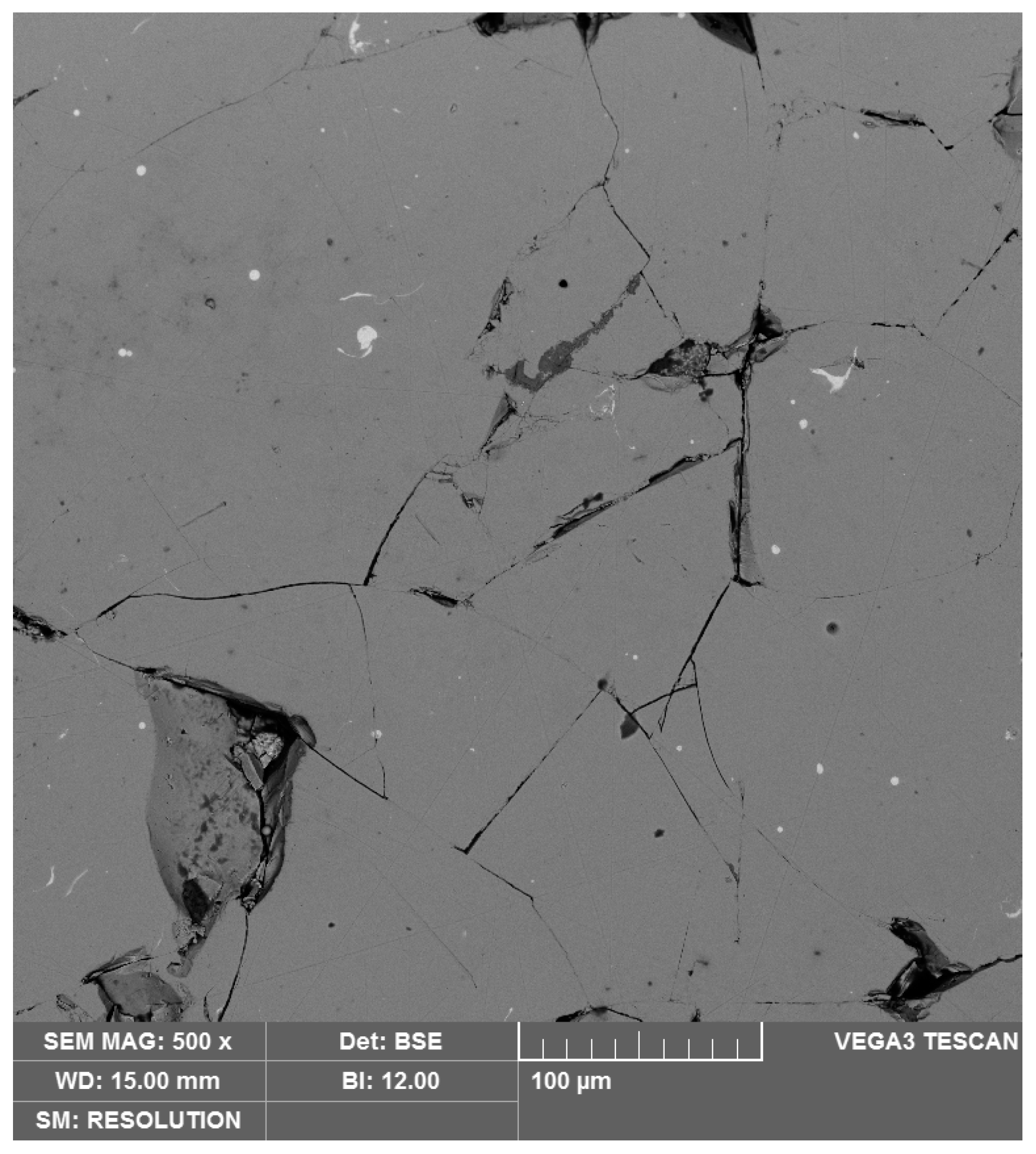

| Element | Manufacturer’s Data | Measured |
|---|---|---|
| Nd | 17.2 | 17.0 |
| Pr | 1.9 | 1.9 |
| Fe | 69.8 | 66.8 |
| Co | 2.8 | 2.9 |
| Ti | 2.1 | 2.1 |
| Zr | 4.3 | 4.7 |
| B | 1.7 | 2.7 |
| C | 0.1 | 0 |
| Cu | 0.1 | 0 |
| Infiltration | Powder | Hcj, kA/m | Br, mT | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Powder MQP-S-11-9 (datasheet) | 650–750 | 739–760 | [55] | ||
| (Pr0.5Nd0.5)3(Cu0.25Co0.75) | 80% MQP-B (nano) with 20% Inf. | 1280 | N/A | 2020 | [51] |
| Initial sample | MQP-S-11-9 | 522.4 | 436 | 2019 | [50] |
| Nd50Tb20Cu30 | MQP-S-11-9 | 1215.2 | 466 | ||
| Nd60Al10Ni10Cu20 | MQP-S-11-9 | 862.4 | 390 | ||
| Nd70Cu30 | MQP-S-11-9 | 842.4 | 464 | ||
| Nd80Cu20 | MQP-S-11-9 | 778.4 | 475 |
| Production Method | (BH)max (kJ/m3) | Hcj (kA/m) | Br (mT) | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sintered | 205–434 | 874–3180 | 1100–1500 |
|
|
| Hot-pressed magnetoplasts | 118–331 | 795–1987 | 1200–1400 |
|
|
| Bonded magnetoplasts | 47–94 | 556–1431 | 600–800 |
|
|
| Additive manufacturing | 42–64 | 675–1280 | 100–700 |
|
|
| Machine | Process Parameters | Material | Magnetic Properties | Ref. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P, W | Scan Velocity mm/s | Spot Size, µm | Layer Thickness, µm | Hatch Spacing, µm | (BH)max, kJ/m3 | Hcj, kA/m | Br, mT | |||
| Powder | 72.6 | 706 | 710 | |||||||
| M2 LPBF machine | 50–150 | 1000–2500 | 110 | 30 | 35–75 | MQP-S | 63 | 921 | 630 | [59] |
| TruFiber 1000 | 200 | 2000 | 46 | 50 | 30 | Nd-Pr-Zr-Ti-Co-Fe-B | 64 | 384 | 690 | [61] |
| AddSol D50 | 50, 100 | 1400 | 80 | 30 | 100 | MQP-S | 19 | 405 | 416 | [49] |
| Farsoon FS121M | 60 | 160 | 80 | 20 | 500 | Nd-Pr-Fe-Co-B-Zr-Ti | 55 | 550 | 600 | [75] |
| SLM125 | 150 | 750 | 70 | 50 | 70 | Nd-Pr-Dy-Fe-(CoCuAlGa)-B | 38 | 551 | 550 | [52] |
| AM125 | - | - | 40 | 30 | 100 | MQP-S | 63 | 921 | 630 | [86] |
| Farsoon S121M | 20–100 | 50–2000 | 100 | 20 | - | MQP-S | - | 1210 | 430 | [50] |
| Aconity3D | - | - | 100 | - | - | MQP-B+Inf | - | 1280 | - | [51] |
| Mlab Cusing R Gen.1 | 55 | 1800 | - | - | - | MQP-S | - | - | 564 | [60] |
| Model Realizer SLM 50 | 120 | 270 | 15–30 | 20 | 100 | MQP-S | 45 | - | 700 | [85] |
| E-Plus-3D M100T LPBF system | 160 | 1200 | 82 | - | 80 | LW-N-400 | 13.8 | 205.8 | 139 | [79] |
| Aconity Mini | 130 | 3500 | - | 20 | 20 | MQP-S | - | 700 | [80] | |
| Commercial LPBF machine Guangzhou Xinyuan Metal S & T Co | 100 | 1200 | - | 30 | 100 | MQP-S | 62 | 853 | 700 | [20] |
| BLT-S210 system | 120 | 1400 | - | 30 | 100 | MQP-S | 656 | 790 | [87] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pelevin, I.; Lyange, M.; Fedorenko, L.; Chernyshikhin, S.; Tereshina, I. The Laser Powder Bed Fusion of Nd2Fe14B Permanent Magnets: The State of the Art. Condens. Matter 2025, 10, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat10020022
Pelevin I, Lyange M, Fedorenko L, Chernyshikhin S, Tereshina I. The Laser Powder Bed Fusion of Nd2Fe14B Permanent Magnets: The State of the Art. Condensed Matter. 2025; 10(2):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat10020022
Chicago/Turabian StylePelevin, Ivan, Maria Lyange, Leonid Fedorenko, Stanislav Chernyshikhin, and Irina Tereshina. 2025. "The Laser Powder Bed Fusion of Nd2Fe14B Permanent Magnets: The State of the Art" Condensed Matter 10, no. 2: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat10020022
APA StylePelevin, I., Lyange, M., Fedorenko, L., Chernyshikhin, S., & Tereshina, I. (2025). The Laser Powder Bed Fusion of Nd2Fe14B Permanent Magnets: The State of the Art. Condensed Matter, 10(2), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/condmat10020022







