Abstract
The Channichthyidae, a monophyletic fish group belonging to the suborder Notothenioidei, are uniquely adapted to the polar environment. However, while their physiology has been extensively studied, studies on their ecology are relatively rare. Here, we investigated the trophic ecology of seven icefish species (Chaenodraco wilsoni, Chionobathyscus dewitti, Chionodraco hamatus, Dacodraco hunteri, Neopagetopis ionah, Pagetodes antarcticus and Pagetopsis macropterus) by using the traditional morphometric approach to assess the relationship between form and feeding function. The suction index (SI), the mechanical advantage in jaw closing (MA) and nine morphological traits related to feeding structures have been analysed. Icefish species are characterised by non-protractible, elongate jaws and a wide gape; such morphological features influence the low values of both MA and SI, supporting their ram-feeding habit. The ecomorphological differences among species resulted mainly determined by the anatomical structures related to SI. Such differences do not seem to be determined primarily by the type of prey, as is the case in other taxonomic groups of Notothenioidei, but rather by phylogenetic proximity. A 3D animation was developed to visualise the different feeding modes of two icefish species (C. hamatus and P. macropterus) which are characterised by different approaches to prey.
Key Contribution:
The trophic ecology of seven icefish species was investigated by using an ecomorphological approach. Based on the analysis of morphological traits, ram feeding emerged as the main feeding mode, shared within the family. Differently from other notothenioid lineages, the morphological differences among icefish species do not seem linked to trophic resource use but are rather influenced by phylogenetic relationships.
1. Introduction
The Southern Ocean fish fauna inhabiting the waters around Antarctica is dominated, both in terms of diversity and biomass, by a monophyletic lineage of fish, the Notothenioidei [1,2]. The suborder comprises 140 species in 45 genera: 30 distributed in non-Antarctic waters, 33 living in the sub-Antarctic and 77 Antarctic species [3]. Many species in this latter group are endemic to the coastal habitats of High Antarctica, where they live at sub-zero temperatures, and exhibit unique morphological, physiological and biochemical features [1,2,4,5]. Remarkably, Antarctic notothenioid fishes are a rare example of adaptive morphological radiation in the marine environment [6,7,8,9].
They have undergone evolutionary alteration of buoyancy and morphology associated with swimming and feeding in different strata of the water column leading to adaptive modifications that span from compensatory changes in body density [10,11] to morphological adaptations for foraging on different prey [12,13]. The rapid adaptive radiation and related modifications [9,14] make this group of fish particularly suitable for studying the ecomorphological relationships between the form of feeding structures and trophic ecology [15], deepening general knowledge of their ecological role and their ability to adapt to the availability of prey [13,16].
Within the Notothenioidei, the family Channichthyidae forms a monophyletic group, and is one of the most derived notothenioid clades, with regard to morphological characteristics [2,17,18,19,20]. The distribution of this family is restricted to the Southern Ocean, except Champsocephalus esox, which is found from the shelves of southern Patagonia and the Falklands to the Strait of Magellan [21,22]. The highest diversity of Channichthyidae has been found on the Antarctic continental shelf [23]. High-Antarctic species are distributed down to a depth of about 1667 m in the Weddell Sea, Ross Sea, Dumont d’Urville Sea and South Shetland Islands [22,24]. The bathymetric distribution varies according to age and species [22]. Larvae, post-larvae and juveniles are mainly distributed in the first 100 metres of the water column [16,22,25]. After 2–3 years, most species become predominantly bottom dwellers and feed on prey near the bottom. Other species (e.g., Champsocephalus gunnari, Pseudochaenichthys georgianus, Neopagetopsis ionah, Dacodraco hunteri) perform regular diurnal vertical migrations to feed in the water column [4,19] and can be considered semipelagic [26]. The Channichthyidae have been the focus of many studies dealing with their unique morphological and physiological adaptations (e.g., the complete lack of haemoglobin in the blood) [27,28,29,30], while studies on their trophic ecology are relatively rare [20].
In recent decades, with the development of morpho-functional studies on feeding structures, the importance of functional morphology of fish feeding biomechanisms is emerging as a powerful tool for gaining insights into the feeding ecology of species [31,32]. The relationship between morphology and prey use can be studied through the analysis of the trophic apparatus, which determines the feeding ability of a species, defined as the set of abilities to locate, chase, capture and successfully manipulate prey [33,34,35,36,37].
The fish’s feeding activity involves more than 20 skeletal components, driven by about 40 muscles [32]. However, to infer feeding strategies, a small number of key morphological traits are often analysed, including morpho-anatomical traits of the head and jaw regions. These provide valuable information on feeding performance and potential resource use. Although many studies are available on the diet of Antarctic fish, ecomorphological studies relating morphology to diet are few [13,38,39,40,41,42], and especially rare for icefish [43]. To evaluate fish feeding strategies, various biomechanical indices can be used, including the suction index (SI) and the mechanical advantage of jaw closure (MA) [31,35]. The SI evaluates suction feeding ability based on the transmission of muscle force to the buccal cavity [37]. High SI values indicate the ability to perform rapid jaw movements, while low values suggest slow jaw movements [38]. The MA represents the ability to generate force with the jaws and is inversely related to the speed of lower jaw movements [44]. Low MA denotes a high transmission speed and characterises species with weak jaws that close rapidly. Conversely, high MA is characteristic of species with strong force transmission due to strong jaws that close relatively slowly [37,38,44].
Three feeding methods are known in fish: suction feeding, ram feeding and manipulation [45]. In suction feeding, the predator expands the buccal cavity, creating a pressure gradient that pulls prey to move towards the mouth opening [31]. Fish that use this feeding strategy generally have small mouth openings, low MA and strong muscles allowing them to open their jaws quickly, resulting in high SI [31,38]. In ram feeding, the predator ingests free-swimming prey with a forward movement of the body and/or protruding jaws. Ram feeders are characterised by large buccal gape, moderate SI, low MA, non-robust oral jaws and moderate force-generating capability of the muscles [31]. Pure suction and pure ram feeding are relatively rare, and the combination of both appears to be the most commonly used [46]. Manipulation is a less common method, in which the jaws are applied directly to the prey and used to remove it from the substrate [31]. Predators using this feeding mode have strong jaws, a small mouth opening, a high MA and a powerful force-generating ability of the mandibular adductor allowing them to crush or grab prey from the substrate [31,44].
Here, we explored the ecomorphological diversity of seven species of Channichthyidae (Chaenodraco wilsoni, Chionobathyscus dewitti, Chionodraco hamatus, Dacodraco hunteri, Neopagetopis ionah, Pagetodes antarcticus and Pagetopsis macropterus). The traditional morphometric approach was used to investigate the relationship between form and function. In addition, models simulating the feeding mode were developed in 3D graphics for two species (C. hamatus and P. macropterus).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
A total of 46 specimens belonging to seven different species of Channichthyidae were analysed at the labs of the Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa in Wellington (Table 1). Samples were collected during the 2004, 2008 and 2012 New Zealand Antarctic expeditions to different areas of the Ross Sea by the R/V Tangaroa (see Table S1 for more details).

Table 1.
The Channichthyidae species investigated, their number and size range, the bathymetric ranges where they were sampled, life styles and main prey (P = pelagic; SP = semipelagic; D = demersal).
To compare individuals and species of different total lengths, morphological measurements were standardised to the standard length (SL) of each individual [32]. All specimens were stored in 70% ethanol (jar specimens) or 55% IPA (drum and tank specimens) at Te Papa Wellington.
2.2. Morphological Traits
To determine the feeding strategies of the species analysed, two morphological metrics have been calculated from measured traits: suction index (SI) and mechanical advantage in jaw closing (MA). Measures were taken in mm to the nearest 0.01 mm using dial callipers.
The model of SI (Figure 1a) is based on the transmission of force from the epaxial muscle to the buccal cavity, generating negative pressure to engulf prey. Following [47], SI was calculated as:
where CSAepax is the cross-sectional area of the epaxialis, Lin is the moment arm of the epaxialis and Lout is the moment arm of the buccal cavity (Figure 1a).
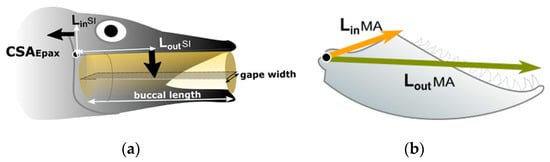
Figure 1.
Scheme of the traits and levers involved in feeding activities: (a) for calculating the suction index, modified from [37]; (b) lower jaw-closing lever mechanism for the calculation of the mechanical advantage, modified from [31].
One of the axes was measured from the supracleitro-posttemporal joint (S-PT) to the dorsal margin of the epaxialis, and the other as the lateral width of the epaxialis (Figure 1a). LinSI was calculated as the vertical distance between the centroid of the cross-section of the epaxialis muscles and the S-PT; LoutSI was measured from the SPT joint to the centre of the buccal cavity. Gape width (GW), the distance between the left and right coronoid processes of the mandible, and buccal length (BL), the distance between the anterior tip of the mandible and the depression in the sternohyoideus, were calculated to estimate the volume of the buccal cavity.
MA indicates the potential of a fish to generate force by its biting action. This results from the structure of the lower jaw, where the quadrate-articular joint serves as a fulcrum. The distance between this fulcrum and the insertion point of the mandibular adductor muscle represents the lever arm (LinMA). Conversely, the distance between the fulcrum and the most anterior tooth of the maxilla represents the exit arm (LoutMA) [31,38,48], and the ratio between LinMA and LoutMA results in MA (Figure 1b). See [37,38,44,49] for more details on how to carry out measurements for SI and MA.
2.3. Development of Three-Dimensional (3D) Deformable Models
To support the analysis and documentation of the aforementioned specimens, we investigated the adoption of 3D representations, starting with Pagetopsis macropterus.
We followed two approaches. Firstly, we digitised the specimens to reconstruct a model quantitatively similar to the original. However, due to their preservation in alcohol, the specimens are dehydrated with respect to the live fish. Secondly, a smoother, more natural model was manually crafted using Blender software. The result is less adherent to the actual specimen, but the gestalt is more suitable for dissemination. The digitisation process consists in the acquisition of real data for the reconstruction of a digital 3D model of the target.
Two main digitisation approaches are available: laser scanning and photogrammetry. The selection depends on the size and nature of the object to be digitised and the required resolution and accuracy [50,51]. Since the acquisition took place at the museum, it was simpler to adopt photogrammetry, as this required only a good camera and a cheap setting (cube, LED lights, turning table and tripod, see Figure 2a,b top) to achieve. The efficacy of this system has been proven on organic shapes using this method [52]. In total, we took 80 photos of the P. macropterus, with two different pitch angles (Figure 2b, bottom).
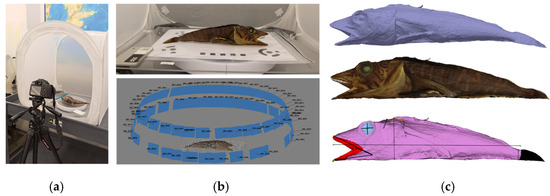
Figure 2.
Digitisation of the Pagetopsis macropterus: (a) the photo acquisition setting; (b) the registered images and the reconstructed points; and (c) the 3D mesh, textured and final annotated models.
The images were processed using the commercial software Agisoft Metashape 1.8.4 (https://www.agisoft.com/, accessed on 19 June 2024) to generate a triangle mesh of the fish and corresponding texture and to manually annotate landmarks (Figure 2c). For the documentation of the 3D model, we applied a method developed in [53] to manually select portions of a 3D model (points, lines or regions) and associate a label and numerical or textual attributes. Some measurements, like Euclidean and geodetic distance and thickness, can be automatically computed and annotated. Landmarks and annotations help to make the process of measurement and analysis fully documented and replicable.
As evident in Figure 2, the real acquisition and reconstruction have some limitations: for instance, the dorsal fin, being depressed against the body, was not reconstructed. As a result, the digitised model is good for documentation for scientific/museum research, but not for public display or education. For this purpose, we manually designed and animated a smoother model using Blender 4.1 software (https://www.blender.org/, accessed on 19 June 2024), free and cross-platform software for modelling, animation and rendering 2D and 3D objects and scenes. The resulting animation shows feeding action while swimming. We also modelled the Chionodraco hamatus to show two different feeding behaviours, as well as the Antarctic seabed (see Figure 3b).

Figure 3.
The models of the Pagetopsis macropterus (a) and Chionodraco hamatus (b) from the feeding animation sequence. The full 3D animations are provided in the Supplementary Materials.
2.4. Statistical Analyses
Statistical analyses were performed using the software R 4.0.2 (R Development Core Team 2020). Differences in suction index (SI) and mechanical advantage (MA) among the seven species were tested. Data were transformed in arcsin. After testing the normality and homoscedasticity of the distributions with Shapiro–Wilk and Levene tests, ANOVA was conducted when both assumptions were satisfied, and Welch’s ANOVA was used in the case of non-homoscedastic data. Tukey post hoc tests were employed to detect significant differences among species. Statistical significance was determined at α = 0.05. To show the differences in SI and MA values, boxplots were performed using the RStudio package.
To investigate which morphometric features explain the greatest variations among the seven species, a principal component analysis (PCA) involving 9 morphological traits was developed. The variables considered were the morphological traits used for the SI and MA metrics, plus eye diameter (ED) and head length (HL). The morphological measurements were standardised relative to the body size (SL) of each individual [32]. A hierarchical cluster analysis was developed to group species with similar morphological characteristics.
3. Results
The SI and MA mean and standard deviation values are summarised in Table 2. The mean SI value was highest in P. macropterus and lowest in C. wilsoni and C. dewitti; the highest value of MA was in C. hamatus, and the lowest value of MA was in P. macropterus.

Table 2.
Values of suction index (SI) and mechanical advantage (MA) in the seven species. The highest coefficients are in bold.
To determine if there were significant differences in SI and MA values among the species analysed, ANOVA tests were performed. Welch’s ANOVA test developed on SI values resulted in significant differences among the species (F(6,39) = 39.91, p < 0.0001). Tukey’s post hoc test showed that the SI values of N. ionah were significantly different from those of C. wilsoni, C. dewitti, C. hamatus, P. antarcticus and D. hunteri, while those of P. macropterus were significantly different from those of C. wilsoni, C. dewitti and D. hunteri (Figure 4a).
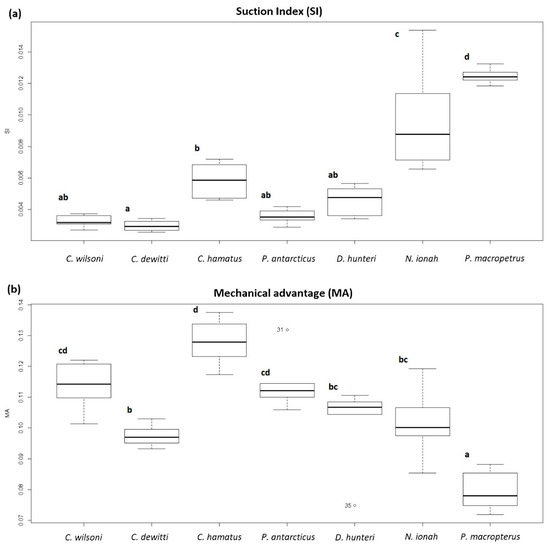
Figure 4.
Boxplots of the values of suction index (a) and mechanical advantage (b). Different letters in the boxplots indicate significant differences.
The ANOVA test developed on MA values resulted in significant differences among the species (F(6,39) = 19.86, p < 0.0001). Tukey’s post hoc test showed that the MA values of P. macropterus were significantly different from those of C. wilsoni, C. hamatus, P. antarcticus, D. hunteri and N. ionah, while those of C. hamatus were significantly different from those of C. dewitti, D. hunteri and N. ionah (Figure 4b).
Table 3 shows the mean values and standard deviations of the nine variables considered for the PCA. C. wilsoni had a larger ED and smaller HL, LinSI and LoutMA. C. dewitti was characterised by larger GW and lower BL and LinSI values. In C. hamatus, the highest LinMA value was found. In D. hunteri, the highest values of BL, LoutSI and LoutMA were measured. In N. ionah, the lowest value of ED was found. P. antarcticus showed the lowest values of GW, CSAepax and LinSI. P. macropterus showed the highest values of HL, CSAepax and LinSI and the lowest values of LoutSI and LinMA.

Table 3.
Mean values and standard deviations of the 9 morphological traits. Measures were standardised by SL. Traits: eye diameter (ED); head length (HL); gape width (GW); buccal length (BL); cross-sectional area of the epaxial muscle (CSAepax); in-lever of suction index (LinSI); out-lever of suction index (LoutSI); in-lever of mechanical advantage (LinMA); out-lever of mechanical advantage (LoutMA). The highest coefficients are in bold.
PCA explained 77.714% of the variance on the first three axes (Table 4). PC1 and PC2 are driven by traits directly related to SI: HL, CSAepax and LinSI strongly correlated with PC1, and LoutSI strongly correlated with PC2. None of the variables resulted in a correlation with coefficients higher than 0.800 with PC3 (Table 4).

Table 4.
Coefficients of the 9 traits selected to describe differences in the feeding apparatus of seven species of the icefish as resulting from the PCA after standardisation by SL. The driving morphological variables are in bold.
C. wilsoni, P. antarcticus and C. dewitti were distinct from the other four species along the PC1 axis and aggregated in a single cluster (Figure 5a,b). Two clusters emerged from the other four species, which were separated along the PC2 axis: one was composed of C. hamatus and D. hunteri, and the other of N. ionah and P. macropterus (Figure 5a,b).
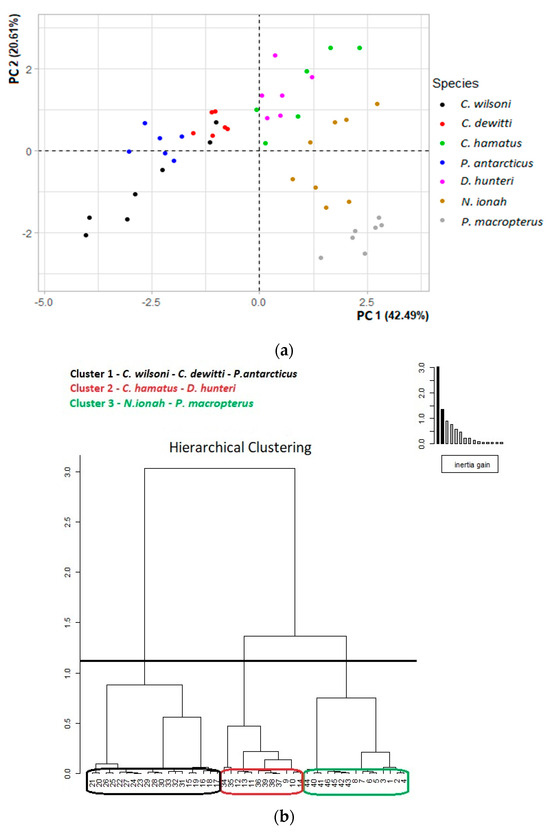
Figure 5.
(a) PCA plot developed on the 9 morphological traits of the feeding apparatus of the seven icefish species. (b) Cluster analysis performed after PCA.
4. Discussion
Studies on the diet of icefish have shown that they feed mainly on pelagic prey such as krill and other fish [1,17,38]. The body of icefish is elongate and tapered, with elongated heads and huge mouths equipped with a non-retractile jaw, without or with a reduced ascending process of the premaxilla [19,21,38]. In a first general observation, this morphology seems unsuitable for suction feeding of small planktonic prey or manipulative feeding involving high jaw force to capture benthic prey. Here, we deepened the morphological analysis of a group of icefish species, with the aim of highlighting how relative differences in traits and indices may indicate different feeding modes.
Based on our ecomorphological analysis of seven icefish species, and although slight differences were found among species, ram feeding emerges as the main feeding mode, providing support to previous hypotheses [38,42].
The shape and size of the icefish heads and mouths also explain the very low values of their biomechanical indices, much lower than those of any other Antarctic and non-Antarctic fish studied so far, which show ranges of SI values between 0.02 and 0.40 and MA values between 0.12 and 0.68 [37,38,54]. MA is heavily influenced by the size of the mouth, whereas light ecomorphological differences were detected among the seven species analysed, mainly related to anatomical structures determining the SI, as also shown by the PCA (Figure 4). The distribution of species along PC1, from left to right, exactly followed the SI gradient (from smallest to largest), as well as the length of the head. PC2 was also related to SI, but whereas the differentiations in PC1 were mainly related to the size of the epaxial muscle, the difference along PC2 occurs mainly in the LoutSI.
The cluster analysis developed by PCA showed that the icefish species analysed were grouped into three clusters (Figure 5b). The first cluster was composed of C. wilsoni, C. dewitti and P. antarcticus. These three species are phylogenetically close (Figure 6) and, despite living in different habitats and feeding on different prey, showed similar morphological features.
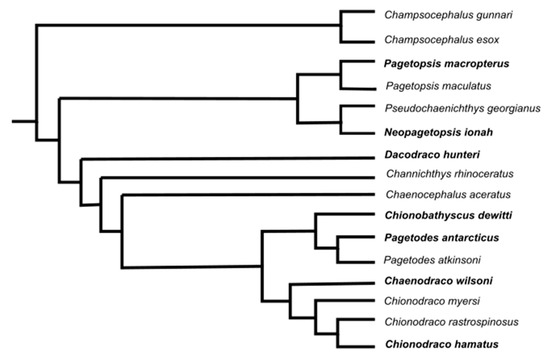
Figure 6.
Phylogenetic tree of the Channichthyidae, modified from [55]; species taxa investigated are in bold.
C. wilsoni is semipelagic species [1,28,56] performing regular diurnal migrations into the water column to feed. However, it remains dependent on krill or other euphausiids throughout its life, and only occasionally takes fish [19,57], which it is supposed to be able to grasp thanks to a relatively strong bite due to its MA value. C. dewitti is a deep-water demersal species that lives between 500 and 2000 m depth and that feeds mainly on fish, including various notothenioids, macrourids, mesopelagic fishes such as myctophids, and also large cephalopods [19,58]. Among the icefish species analysed in this study, C. dewitti had the lowest values of both SI and MA. This could be due to the fact that it has a huge mouth (the largest GW among the species analysed), which is needed to catch large prey but is disadvantageous for both suction feeding and biting. P. antarcticus is a demersal species that feeds on krill, benthic and mesopelagic fish. Unlike C. dewitti, it had the smallest GW among the icefish species studied, and its MA value was among the highest ones. In the case of relatively large prey, such as fish, it is able to retain with a relatively strong bite. P. antarcticus has the habit of exploiting the shallow section of the water column when young, taking krill and mysids. As it grows older, it switches to a benthic mode of life, targeting demersal fish and krill when they are on or near the bottom [59,60].
The second cluster was composed of the demersal C. hamatus and the semipelagic D. hunteri. Compared to the first cluster, in this case, the two species are phylogenetically distant but have similar diets, which probably represent the main forces that have led to their comparable morphology. C. hamatus showed higher MA and larger GW than the other icefishes, functional characteristics in line with its diet, composed mainly of fish [59]. It probably approaches the prey with its mouth open (very wide to catch large prey) and then closes its lower jaw with a bit of force (see 3D animation, S2). This slight pressure would allow C. hamatus to hold and manipulate prey before swallowing it. At Terra Nova Bay (western Ross Sea), this species commonly feeds on fish larvae and adults of other smaller notothenioids, such as the Antarctic silverfish Pleuragramma antarcticum [12,60], species of the genus Trematomus (Di Blasi, personal communication) and euphausiids (e.g., Euphausia crystallorophias). The latter may be caught by the action of the epaxial muscle, whose size supports a slight suction. The semipelagic D. hunteri also feeds on fish, mainly Pleuragramma antarcticum [28,61]. Due to its fragile and sluggish nature, silverfish can easily be grasped by D. hunteri, as can be inferred from its MA value.
The third cluster was composed of P. macropterus and N. ionah. The clustering of these two species seems to be driven by phylogenetic proximity and in part by prey types, although they live in distinct habitats. P. macropterus is a demersal species occurring on the continental shelf at depths between 5 and 655 m [21]. Our results suggest that P. macropterus, due to a more developed epaxialis muscle than the other icefish investigated, is able to produce a slight suction. In light of these results, we supposed that this species feeds by opening its mouth close to the prey (mainly euphausians), moving further towards them, exerting a light suction, and then closing its jaws (see 3D animation, S1). A similar feeding mechanism is also hypothesised for N. ionah, a semipelagic species that undertakes regular vertical migrations to feed in the water column, often at night [19]. Adult specimens have been taken in the top 100 m over 1000 m in the Ross Sea, gorging themselves on Pleuragramma antarcticum (Stewart, personal communication). Although this species is semipelagic, it clustered with the demersal P. macropterus, having a similar epaxial muscle size and SI. Like P. macropterus, N. ionah mainly feeds on crustaceans. However, based on its slightly higher MA, a higher degree of flexibility is expected in the diet of this latter species. Indeed, N. ionah is known to opportunistically take larger prey, including fishes.
Based on these findings, we can conclude that there is no common criterion according to which similarities and differences emerge between species. In two of the three cases, the grouped species are phylogenetically close, and the main morphological traits analysed were not shaped by ecological factors such as prey or habitat. In the third group, the species are relatively distant in the phylogenetic tree but have similar prey, and we inferred that they evolved similar morphological traits to capture them.
Our results support a previous study on the ecomorphological diversification of icefishes [43]. The authors discussed convergences among distantly related species and differences among closely related species of cryonotothenioids and justified such a pattern of morphological evolution with the periodic environmental perturbations of the Antarctic shelf areas [43]. The habitats along the Antarctic continental shelf are subject to drastic changes due to climatic variations affecting the entire water column and the action of the ice on the bottom. In such a dynamic scenario, species face continuous challenges and openings of new potential niches, resulting in divergences and convergences among species [43]. The environmental instability also induces the need for plasticity in the organisms, a characteristic that we can see in different species of icefish cryonotothenioids, which are known to periodically forage outside their buoyancy-based ecological niche [27,43,62]. This ecological and trophic plasticity must be considered as a driver for the diversification of this clade, as the availability of prey and habitat resources at different depths fluctuated during repeated perturbations of the Antarctic continental shelf [43,46].
Concerning the 3D technology used to create digital copies of the real specimens and animation sequences, we believe that they are a useful tool for supporting the conservation, study and dissemination of biological species. As mentioned, the models for animation were manually modelled on the gross shape of the digitised models. Indeed, the shape modifications induced by the pose on the rotating plane during the shooting stage and the deformation that occurred after the long conservation in ethanol or IPA made the shape of the specimen far from the original aspect of the alive exemplar. However, this required considerable manual work.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fishes9070247/s1, Table S1: Summary table. Videos S1 and S2: Three-dimensional animation of the feeding activity of two icefish species: Pagetopsis macropterus and Chionodraco hamatus.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, E.C.; methodology, E.C. and D.D.B.; software, A.S., M.M.; formal analysis, E.C. and D.D.B.; investigation, E.C. and A.L.S.; resources, E.C. and A.L.S.; data curation, E.C.; writing—original draft preparation, E.C.; writing—review and editing, D.D.B., L.G., A.L.S. and M.M.; supervision, E.C., D.D.B., L.G. and M.M.; project administration, E.C.; funding acquisition, E.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The study was supported by the Italian National Programme for Antarctic Research (PNRA) project 18_00106 “Ecomorphological Analysis and development of virtual mobile models of buccal apparatus of notothenioid fish species (EMPHASIS)”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed, and all necessary approvals have been obtained. The specimens were dead when we received them and processed them into the Nation Fish Collection here at Te Papa.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article and in the Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We would like to sincerely thank the staff of the Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa Wellington, New Zealand, for their kindness, helpfulness and precious logistical help; in particular, we thank Salme Kortet, Jeremy Barker and Carl Struthers. We also thank Giorgio Luciano for valuable support in consulting on animation. The NIWA scientists and crew of the R/V Tangaroa are thanked for their work in collecting specimens.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Eastman, J.T. Antarctic Fish Biology: Evolution in a Unique Environment; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Near, T.J.; Dornburg, A.; Eytan, R.I.; Keck, B.P.; Smith, W.L.; Kuhn, K.L.; Moore, J.A.; Price, S.A.; Burbrink, F.T.; Friedman, M.; et al. Phylogeny and tempo of diversification in the superradiation of spiny-rayed fishes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12738–12743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.T.; Eakin, R.R. Checklist of the species of notothenioid fishes. Antarct. Sci. 2021, 33, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kock, K.H. Antarctic Fish and Fisheries; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Mintenbeck, K.; Barrera-Oro, E.R.; Brey, T.; Jacob, U.; Knust, R.; Mark, F.C.; Moreira, E.; Strobel, A.; Arntz, W.E. Impact of climate change on fishes in complex Antarctic ecosystems. In Advances in Ecological Research; Academic Press: London, UK, 2012; Volume 46, pp. 351–426. [Google Scholar]
- Eastman, J.T.; McCune, A.R. Fishes on the Antarctic continental shelf: Evolution of a marine species flock? J. Fish. Biol. 2000, 57, 84–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ghigliotti, L.; Vacchi, M.; Pisano, E.; Detrich, H.W.; Albertson, R.C. Evolution in an extreme environment: Developmental biases and phenotypic integration in the adaptive radiation of antarctic notothenioids. BMC Evol. Biol. 2016, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landaeta, M.F.; Villegas, A.; Hüne, M. Shape, condition and diet of the pike icefish Champsocephalus esox (Teleostei: Channichthyidae): Evidence of phenotypic plasticity? Antarct. Sci. 2021, 33, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.T. The nature of the diversity of Antarctic fishes. Polar Biol. 2005, 28, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devries, A.L.; Eastman, J.T. Lipid sacs as a buoyancy adaptation in an Antarctic fish. Nature 1978, 271, 352–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voskoboinikova, O.S. Evolutionary significance of heterochronies in the development of the bony skeleton in fishes of the suborder Notothenioidei (Perciformes). J. Ichthyol. 2001, 41, 415–424. [Google Scholar]
- La Mesa, M.; Eastman, J.T.; Vacchi, M. The role of notothenioid fish in the food web of the Ross Sea shelf waters: A review. Polar Biol. 2004, 27, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlig, E.; Di Blasi, D.; Ghigliotti, L.; Pisano, E.; Faimali, M.; O’Driscoll, R.; Parker, S.; Vacchi, M. Diversification of feeding structures in three adult Antarctic nototheniid fish. Polar Biol. 2018, 41, 1707–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabosky, D.L.; Chang, J.; Title, P.O.; Cowman, P.F.; Sallan, L.; Friedman, M.; Kaschner, K.; Garilao, C.; Near, T.J.; Coll, M.; et al. An inverse latitudinal gradient in speciation rate for marine fishes. Nature 2018, 559, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motta, P.J.; Norton, S.F.; Luczkovich, J.J. Perspectives on the ecomorphology of bony fishes. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1995, 44, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingenberg, C.P.; Ekau, W. A combined morphometric and phylogenetic analysis of an ecomorphological trend: Pelagization in Antarctic fishes (Perciformes: Nototheniidae). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1996, 59, 143–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwami, T. Osteology and relationships of the family Channichthyidae. Mem. Natl. Inst. Polar Res. Ser. E 1985, 36, 1–69. [Google Scholar]
- Near, T.J.; Pesavento, J.J.; Cheng, C.H.C. Mitochondrial DNA, morphology, and the phylogenetic relationships of Antarctic icefishes (Notothenioidei: Channichthyidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 28, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kock, K.-H. Antarctic icefishes (Channichthyidae): A unique family of fishes. A review, Part I. Polar Biol. 2005, 28, 862–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, T.; Zizka, V.M.; Münster, J.; Klapper, R.; Mattiucci, S.; Kochmann, J.; Klimpel, S. Lighten up the dark: Metazoan parasites as indicators for the ecology of Antarctic crocodile icefish (Channichthyidae) from the north-west Antarctic Peninsula. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwami, T.; Kock, K.-H. Channichthyidae. In Fishes of the Southern Ocean; Gon, O., Heemstra, P.C., Eds.; J.L.B. Smith Institute of Ichthyology: Grahamstown, South Africa, 1990; pp. 381–399. [Google Scholar]
- Duhamel, G.; Hulley, P.A.; Causse, R.; Koubbi, P.; Vacchi, M.; Pruvost, P.; Vigetta, S.; Irisson, J.O.; Mormède, S.; Belchier, M.; et al. Biogeographic patterns of fish. In Biogeographic Atlas of the Southern Ocean; De Broyer, C., Koubbi, P., Griffiths, H.J., Raymond, B., d’Udekem d’Acoz, C., Van de Putte, A.P., Danis, B., David, B., Grant, S., et al., Eds.; Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 328–362. [Google Scholar]
- Causse, R.; Ozouf-Costaz, C.; Koubbi, P.; Lamy, D.; Eléaume, M.; Dettaï, A.; Duhamel, G.; Busson, F.; Pruvost, P.; Post, A.; et al. Demersal Ichthyofaunal Shelf Communities from the Dumont D’urville Sea (East Antarctica). Polar Sci. 2011, 5, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.T. Bathymetric distributions of notothenioid fishes. Polar Biol. 2017, 40, 2077–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, V.J.; Kellermann, A.K.; Koubbi, P.; North, A.W.; White, M.G. Antarctic larval fish assemblages: A review. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1993, 53, 416–449. [Google Scholar]
- Eastman, J.T. The buoyancy-based biotope axis of the evolutionary radiation of Antarctic cryonotothenioid fishes. Polar Biol. 2020, 43, 1217–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.T.; Hubold, G. The fish fauna of the Ross Sea, Antarctica. Antarct. Sci. 1999, 11, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wöhrmann, A.P.A. Aspects of Eco-Physiological Adaptations in Antarctic Fish. In Fishes of Antarctica; Springer: Milano, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidell, B.D.; Vayda, M.E.; Small, D.J.; Moylan, T.J.; Londraville, R.L.; Yuan, M.-L.; Rodnick, K.J.; Eppley, Z.A.; Costello, L. Variable expression of myoglobin among the hemoglobinless Antarctic icefishes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3420–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feller, G.; Gerday, C. Adaptations of the hemoglobinless Antarctic icefish (Channichthyidae) to hypoxia tolerance. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Physiol. 1997, 118, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, P.C.; Bellwood, D.R. Ecomorphology of feeding in coral reef fishes. In Coral reef fishes: Dynamics and Diversity in a Complex Ecosystem; Sale, P.F., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 33–55. [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, A.; Bellwood, D.R.; Hoey, A.S. Trophic ecomorphology of cardinalfish. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 322, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, P.C. Morphology and ecology: Functional basis of feeding constraints in Caribbean labrid fishes. Ecology 1988, 69, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnefeld, M.J.; Turingan, R.G.; Sloan, T.J. Functional morphological drivers of feeding mode in marine teleost fishes. Adv. Zool. Bot. 2014, 2, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidmark, N.J.; Pos, K.; Matheson, B.; Ponce, E.; Westneat, M.W. Functional morphology and biomechanics of feeding in fishes. In Feeding in Vertebrates; Bels, V., Whishaw, I., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 297–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delariva, R.L.; Neves, M.P. Morphological traits correlated with resource partitioning among small characin fish species coexisting in a Neotropical river. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2020, 29, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collar, D.C.; Wainwright, P.C. Discordance between morphological and mechanical diversity in the feeding mechanism of centrarchid fishes. Evolution 2006, 60, 2575–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansode, M.A.; Eastman, J.T.; Aronson, R.B. Feeding biomechanics of five demersal Antarctic fishes. Polar Biol. 2014, 37, 1835–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlig, E.; Di Blasi, D.; Pisano, E.; Vacchi, M.; Santovito, G.; Ghigliotti, L. Ecomorphological differentiation of feeding structures within the Antarctic fish species flock Trematominae (Notothenioidei) from Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frédérich, B.; Heindler, F.M.; Christiansen, H.; Dettai, A.; Van de Putte, A.P.; Volckaert, F.A.; Lepoint, G. Repeated morphological diversification in endemic Antarctic fishes of the genus Trematomus. Belg. J. Zool. 2022, 152, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landaeta, M.F.; Pareja, M.; Hüne, M.; Zenteno-Devaud, L.; Vera-Duarte, J.; Bernal-Durán, V.; Castillo, M.I.; La Mesa, M. Morphology and diet are decoupled in nearshore notothenoids from King George Island, West Antarctica. J. Fish Biol. 2023, 104, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastman, J.T. The Axes of Divergence for the Evolutionary Radiation of Notothenioid Fishes in Antarctica. Diversity 2024, 16, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, E.; Zapfe, K.L.; Yadav, J.; Frédérich, B.; Jones, C.D.; Economo, E.P.; Federman, S.; Near, T.J.; Dornburg, A. Periodic environmental disturbance drives repeated ecomorphological diversification in an adaptive radiation of Antarctic fishes. Am. Nat. 2022, 200, E221–E236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westneat, M.W. Skull biomechanics and suction feeding in fishes. In Fish Phisiology. Fish Biomechanics; Shadwick, R.E., Lauder, G.V., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2005; Volume 23, pp. 29–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liem, K.F. Acquisition of energy by teleosts: Adaptive mechanisms and evolutionary patterns. In Environmental physiology of fishes. NATO Advanced Study Institute Series; Ali, M.A., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1980; Volume 35, pp. 299–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, S.F.; Brainerd, E.L. Convergence in the feeding mechanics of ecomorphologically similar species in the Centrarchidae and Cichlidae. J. Exp. Biol. 1993, 176, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.M.; Wainwright, P.C.; Huskey, S.H.; Collar, D.C.; Turingan, R.G. Morphology predicts suction feeding performance in centrarchid fishes. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 3873–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westneat, M.W. Evolution of levers and linkages in the feeding mechanisms of fishes. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2004, 44, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlig, E.; Christiansen, J.S.; Di Blasi, D.; Ferrando, S.; Pisano, E.; Vacchi, M.; O’Driscoll, R.; Ghigliotti, L. Midtrophic fish feeding modes at the poles: An ecomorphological comparison of polar cod (Boreogadus saida) and Antarctic silverfish (Pleuragramma antarctica). Polar Biol. 2021, 44, 1629–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cignoni, P.; Scopigno, R. Sampled 3D models for CH applications: A viable and enabling new medium or just a technological exercise? ACM J. Comput. Cult. Herit. 2008, 1, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remondino, F.; Guarnieri, A.; Vettore, A. 3D modeling of Close-Range Objects: Photogrammetry or Laser Scanning? In Proceedings of the SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, Electronic Imaging 2005, San Jose, CA, USA, 16–20 January 2005; Volume 5665, pp. 216–225. [Google Scholar]
- Kano, Y. Bio-photogrammetry: Digitally archiving coloured 3D morphology data of creatures and associated challenges. Res. Ideas Outcomes 2022, 8, e86985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalas, A. A Framework for the Semantics-aware Modelling of Objects. PhD Thesis, University of Genoa, Genoa, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wainwright, P.C.; Richard, B.A. Predicting patterns of prey use from morphology of fishes. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1995, 44, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecointre, G. Phylogeny and Systematics of Antarctic Teleosts: Methodological and Evolutionary Issues. In Adaptation and Evolution in Marine Environments; di Prisco, G., Verde, C., Eds.; Volume 1 From Pole to Pole; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-J.; Bonillo, C.; Lecointre, G. Phylogeny of the Channichthyidae (Notothenioidei, Teleostei) based on two mitochondrial genes. In Fishes of Antarctica: A Biological Overview; Di Prisco, G., Pisano, E., Clarke, A., Eds.; Springer: Milan, Italy, 1998; pp. 287–298. [Google Scholar]
- Kock, K.H.; Gröger, J.; Jones, C.D. Interannual variability in the feeding of ice fish (Notothenioidei, Channichthyidae) in the southern Scotia Arc and the Antarctic Peninsula region (CCAMLR Subareas 48.1 and 48.2). Polar Biol. 2013, 36, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, A.F. New data on the diet of deep-sea icefish Chionobathyscus dewitti (Channichthyidae) in the Ross Sea in 2010. J. Ichthyol. 2011, 51, 692–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakhomov, E.A.; Tseitlin, V.B. Feeding pattern of nine species of Antarctic fish and assessment of their daily food consumption. Sel. Sci. Pap. CCAMLR 1992, 321–333. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, M.; Nemoto, T. The food of some Antarctic fish in the western Ross Sea in summer 1979. Polar Biol. 1984, 3, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Mesa, M.; Catalano, B.; Greco, S. Some biological characteristics of early larvae Dacodraco hunteri (Notothenioidei: Channichthyidae) in the western Ross Sea. Polar Biol. 2012, 35, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaux, R.; Barrera-Oro, E. Dietary overlap in inshore notothenioid fish from the Danco Coast, western Antarctic Peninsula. Polar Res. 2013, 32, 21319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).