Effects of Yacon (Smallanthus sonchifolius) Juice Byproduct Administered Using Different Feeding Methods on the Growth Performance, Digestive Enzyme Activity, Antioxidant Status, and Disease Resistance against Streptococcus iniae of Juvenile Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish and Experimental Diets
2.2. Feeding Trial
2.3. Growth Performance and Feed Utilization
2.4. Proximate Whole-Body Composition
2.5. Plasma Biochemical Indices and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
2.6. Lysozyme Activities
2.7. Digestive Enzyme Measurements
2.8. S.iniae Challenge
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance
3.2. Proximate Composition of Whole-Body and Plasma Biochemical Parameters
3.3. Lysozyme and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
3.4. Intestinal Digestive Enzyme Activities
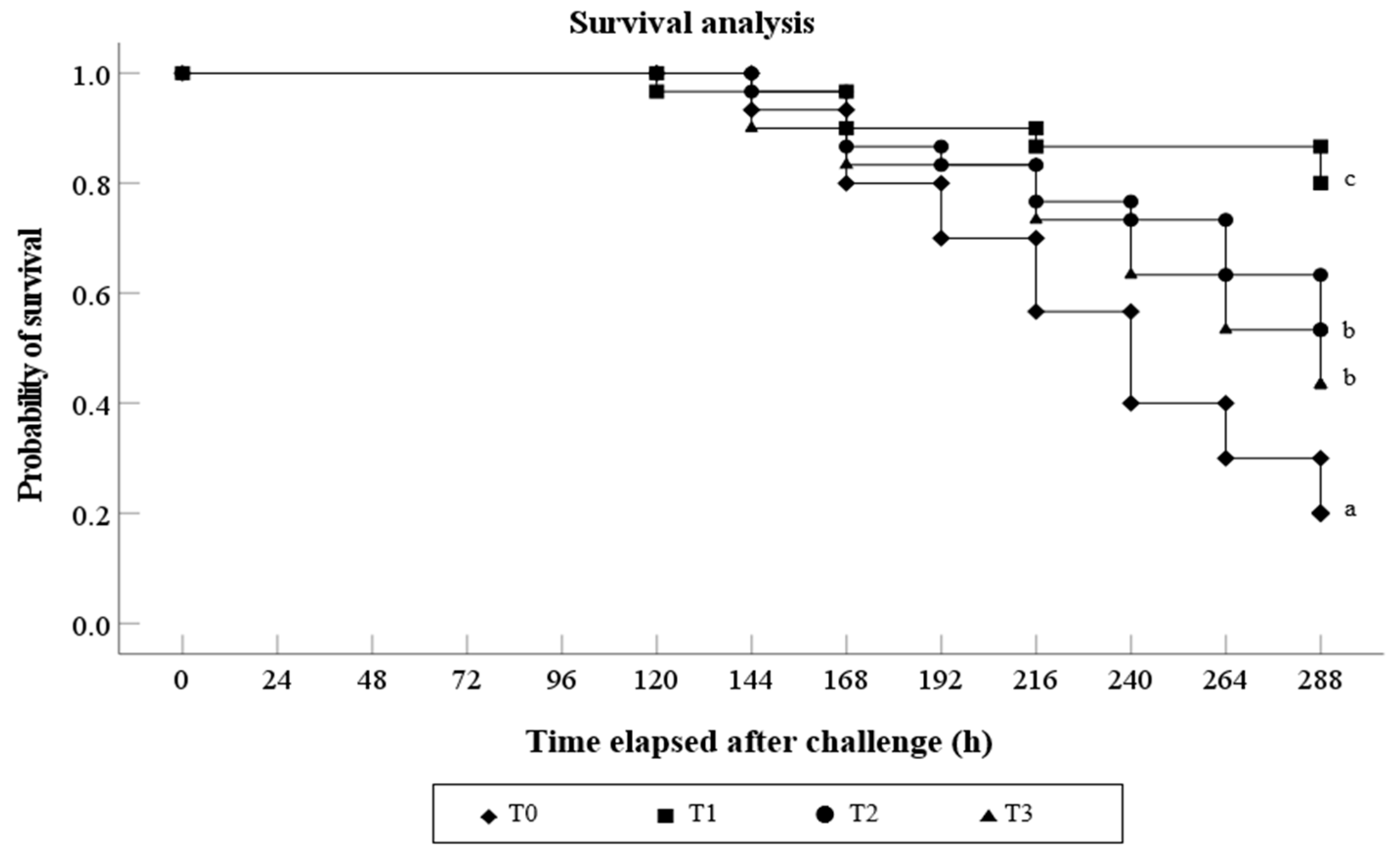
3.5. Challenge Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dawood, M.A.; Eweedah, N.M.; Moustafa Moustafa, E.; Shahin, M.G. Effects of feeding regimen of dietary Aspergillus oryzae on the growth performance, intestinal morphometry and blood profile of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac. Nutr. 2019, 25, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, P.; Kurian, A.; Lakshmi, S.; Musthafa, M.S.; Ringo, E.; Faggio, C. Effect of Leucas Aspera Against Aeromonas Hydrophila in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus): Immunity and Gene Expression Evaluation. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2021, 22, TRJFAS19802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggio, C.; Fazio, F.; Marafioti, S.; Arfuso, F.; Piccione, G. Oral administration of Gum Arabic: Effects on haematological parameters and oxidative stress markers in Mugil cephalus. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2015, 14, 60–72. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1834/11832 (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Guardiola, F.A.; Porcino, C.; Cerezuela, R.; Cuesta, A.; Faggio, C.; Esteban, M.A. Impact of data palm fruits extracts and probiotic enriched diet on antioxidant status, innate immune response and immune-related gene expression of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 52, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Sun, Y.Z.; Wang, A.; Zhou, Z. Probiotics as means of diseases control in aquaculture, a review of current knowledge and future perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 364982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, M.A.; El Basuini, M.F.; Yilmaz, S.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.; Alagawany, M.; Kari, Z.A.; Van Doan, H. Exploring the roles of dietary herbal essential oils in aquaculture: A review. Animals 2022, 12, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elumalai, P.; Kurian, A.; Lakshmi, S.; Faggio, C.; Esteban, M.A.; Ringø, E. Herbal immunomodulators in aquaculture. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 29, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paray, B.A.; El-Basuini, M.F.; Alagawany, M.; Albeshr, M.F.; Farah, M.A.; Dawood, M.A. Yucca schidigera usage for healthy aquatic animals: Potential roles for sustainability. Animals 2021, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reverter, M.; Bontemps, N.; Lecchini, D.; Banaigs, B.; Sasal, P. Use of plant extracts in fish aquaculture as an alternative to chemotherapy: Current status and future perspectives. Aquaculture 2014, 433, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutili, F.J.; Gatlin, D.M., III; Heinzmann, B.M.; Baldisserotto, B. Plant essential oils as fish diet additives: Benefits on fish health and stability in feed. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadifar, E.; Fallah, H.P.; Yousefi, M.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Adineh, H.; Yilmaz, S.; Paolucci, M.; Doan, H.V. The Gene Regulatory Roles of Herbal Extracts on the Growth, Immune System, and Reproduction of Fish. Animals 2021, 11, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiplakou, E.; Pitino, R.; Manuelian, C.L.; Simoni, M.; Mitsiopoulou, C.; Marchi, M.D.; Righi, R. Plant Feed Additives as Natural Alternatives to the Use of Synthetic Antioxidant Vitamins in Livestock Animal Products Yield, Quality, and Oxidative Status: A Review. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyva-López, N.; Lizárraga-Velázquez, C.E.; Hernández, C.; Sánchez-Gutiérrez, E.Y. Exploitation of Agro-Industrial Waste as Potential Source of bioactive Compounds for Aquaculture. Foods 2020, 9, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beigh, Y.A.; Ganai, A.M.; Ahmad, H.A. Utilisation of apple pomace as livetock feed: A review. Indian J. Small Rumin. 2015, 21, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.J.; Guroy, D.; Hassaan, M.S.; El-Ajnaf, S.M.; El-Haroun, E. Evaluation of co-fermented apple-pomace, molasses and formic acid generated sardine based fish silages as fishmeal substitutes in diets for juvenile European sea bass (Dicentrachus labrax) production. Aquaculture 2020, 521, 735087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paini, J.; Benedetti, V.; Ail, S.S.; Castaldi, M.J.; Baratieri, M.; Patuzzi, F. Valorization of wastes from the food production industry: A review towards an integrated agri-food processing biorefinery. Waste Biomass Valor. 2022, 13, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H. Regulation (EU) 2018/848: The New EU Organic Food Law. Eur. Food Feed L. Rev. 2019, 14, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Baldissera, M.D.; Souza, C.F.; Descovi, S.N.; Verdi, C.M.; Zeppenfeld, C.C.; da Silva, A.S.; Baldisserotto, B. Grape pomace flour ameliorates Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced bioenergetic dysfunction in gills of grass carp. Aquaculture 2019, 506, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikrishnan, R.; Devi, G.; Balasundaram, C.; Van Doan, H.; Jaturasitha, S.; Saravanan, K.; Ringø, E. Impact of cinnamaldehyde on innate immunity and immune gene expression in Channa striatus against Aphanomyces invadans. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 117, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frosi, I.; Montagna, I.; Colombo, R.; Milanese, C.; Papetti, A. Recovery of Chlorogenic Acids from Agri-Food Wastes: Updates on Green Extraction Techniques. Molecules 2021, 26, 4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Othman, S.; Jõudu, I.; Bhat, R. Bioactives from agri-food wastes: Present insights and future challenges. Molecules 2020, 25, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadniaye Motlagh, H.; Javadmanesh, A.; Safari, O. Improvement of non-specific immunity, growth, and activity of digestive enzymes in Carassius auratus as a result of apple cider vinegar administration to diet. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 46, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samavat, Z.; Mehrgan, M.S.; Jamili, S.; Soltani, M.; Shekarabi, S.P.H. Determination of grapefruit (Citrus paradisi) peel extract bio-active substances and its application in Caspian white fish (Rutilus Frisii kutum) diet: Growth, haemato-biochemical parameters and intestinal morphology. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 2496–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.; Wojeicchowski, J.P.; Cardoso, T.; Mafra, M.R.; Daltoé, M.L.M.; Masson, M.L. Lactobionic acid as a suitable food preservative for yacon juice. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Techonol. 2020, 64, 102400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojansivu, I.; Ferreira, C.L.; Salminen, S. Yacon, a new source of prebiotic oligosaccharides with a history of safe use. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, G.T.C.; Thomé, R.; Gabriel, D.L.; Tamashiro, W.M.; Pastore, G.M. Yacon (Smallanthus sonchifolius)-derived fructooligosaccharides improves the immune parameters in the mouse. Nutr. Res. 2012, 32, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.R.; Welch, R.; Rush, E.C.; Xiang, X.; Wang, X. A Sustainable Wholesome Foodstuff; Health Effects and Potential Dietotherapy Applications of Yacon. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, H.W.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, D.Y.; Sohn, M.Y.; Kwon, R.W.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, H.S. Effects of by-products from producing yacon (Smallanthus sonchifolius) juice as feed additive on growth performance, digestive enzyme activity, antioxidant status, related gene expression, and disease resistance against Streptococcus iniae in juvenile black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii). Aquaculture 2023, 569, 739383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, K.D.; Lim, H.J.; Kim, H.S. Effects of diet supplementation with plant juice processing by-products on juvenile black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii) growth performance, feed utilization, non-specific immunity, and disease resistance against Vibrio harveyi. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 21, 100831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.J. Effects of benzo [a] pyrene exposure on black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii): EROD activity, CYP1A protein, and immunohistochemical and histopathological alterations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 4033–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Qi, X.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Li, J. New insights on folliculogenesis and follicular placentation in marine viviparous fish black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii). Gene 2022, 827, 146444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amphan, S.; Unajak, S.; Printrakoon, C.; Areechon, N. Feeding-regimen of β-glucan to enhance innate immunity and disease resistance of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus Linn., against Aeromonas hydrophila and Flavobacterium columnare. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 87, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachibana, L.; Telli, G.S.; de Carla Dias, D.; Goncalves, G.S.; Ishikawa, C.M.; Cavalcante, R.B.; Ranzani-Paiva, M.J.T. Effect of feeding strategy of probiotic Enterococcus faecium on growth performance, hematologic, biochemical parameters and non-specific immune response of Nile tilapia. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 16, 100277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Guđmundsdottir, B.K.; Magnadottir, B. Humoral immune parameters of cultured Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2001, 11, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Jiménez, G.M.; Peña-Marín, E.S.; Maytorena-Verdugo, C.I.; Sepúlveda-Quiroz, C.A.; Jiménez-Martínez, L.D.; De la Rosa-García, S.; Alvarez-Villagomez, C.S. Incorporation of Fructooligosaccharides in Diets Influence Growth Performance, Digestive Enzyme Activity, and Expression of Intestinal Barrier Function Genes in Tropical Gar (Atractosteus tropicus) Larvae. Fishes 2022, 7, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poolsawat, L.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Yang, P.; Kabir Chowdhury, M.A.; Yusuf, A.; Leng, X. The potentials of fructooligosaccharide on growth, feed utilization, immune and antioxidant parameters, microbial community and disease resistance of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × O. aureus). Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 4430–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Olsen, R.E.; Gifstad, T.Ø.; Dalmo, R.A.; Amlund, H.; Hemre, G.I.; Bakke, A.M. Prebiotics in aquaculture: A review. Aquac. Nutr. 2010, 16, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, N.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Merrifield, D.L.; Barati, M.; Abadi, Z.H. Dietary supplementation of fructooligosaccharide (FOS) improves the innate immune response, stress resistance, digestive enzyme activities and growth performance of Caspian roach (Rutilus rutilus) fry. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.N.; Li, X.F.; Jiang, G.Z.; Zhang, D.D.; Tian, H.Y.; Li, J.Y.; Liu, W.B. Effects of dietary fructooligosaccharide levels and feeding modes on growth, immune responses, antioxidant capability and disease resistance of blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitroglou, A.; Merrifield, D.L.; Moate, R.; Davies, S.J.; Spring, P.; Sweetman, J.; Bradley, G. Dietary mannan oligosaccharide supplementation modulates intestinal microbial ecology and improves gut morphology of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 87, 3226–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, N.; Zhang, W.; Mai, K.; Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Ma, H. Effects of discontinuous administration of β-glucan and glycyrrhizin on the growth and immunity of white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2010, 306, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrifield, D.L.; Bradley, G.; Baker, R.T.M.; Davies, S.J. Probiotic applications for rainbow trout I. Effects on growth performance, feed utilization, intestinal microbiota and related health criteria. Aquacult. Nutr. 2009, 16, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assan, D.; Kuebutornye, F.K.A.; Hlordzi, V.; Chen, H.; Mraz, J.; Mustapha, U.F.; Abarike, E.D. Effects of probiotics on digestive enzymes of fish (finfish and shellfish); status and prospects: A mini review. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 257, 110653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Dakar, A.E.; Mohsen, M.; Abdelraouf, E.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Yokoyama, S. Effects of Using Exogenous Digestive Enzymes or Natural Enhancer Mixture on Growth, Feed Utilization, and Body Composition of Rabbitfish, Siganus rivulatus. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. B 2014, 4, 180–187. [Google Scholar]
- Abasubong, K.P.; Li, X.F.; Adjoumani, J.J.Y.; Jiang, G.Z.; Desouky, H.E.; Liu, W.B. Effects of dietary xylooligosaccharide prebiotic supplementation on growth, antioxidant and intestinal immune-related genes expression in common carp Cyprinus carpio fed a high-fat diet. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 106, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Meng, Z.; An, X.; Qi, J. Regulation of wheat bran feruloyl oligosaccharides in the intestinal antioxidative capacity of rats associated with the p38/JNK-Nrf2 signaling pathway and gut microbiota. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 6992–7002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Lin, Q. Effect of prebiotic xylooligosaccharides on growth performances and digestive enzyme activities of allogynogenetic crucian carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 35, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.L.; Cho, S.H.; Park, S.C.; Kwon, M.G. Ethanol extracts of yacon and ginger in diet of juvenile olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus): Effect on growth, feed utilization, body composition, plasma chemistry and challenge test against Vibrio anguillarum. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2021, 21, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggio, C.; Fedele, G.; Arfuso, F.; Panzera, M.; Fazio, F. Haematological and biochemical response of Mugil cephalus after acclimation to captivity. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2014, 55, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gobi, N.; Vaseeharan, B.; Chen, J.C.; Rekha, R.; Vijayakumar, S.; Anjugam, M.; Iswarya, A. Dietary supplementation of probiotic Bacillus licheniformis Dahb1 improves growth performance, mucus and serum immune parameters, antioxidant enzyme activity as well as resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila in tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 74, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doan, H.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Dawood, M.A.; Chitmanat, C.; Tayyamath, K. Effects of Cordyceps militaris spent mushroom substrate and Lactobacillus plantarum on mucosal, serum immunology and growth performance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 70, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.H.; Cheng, C.H.; Gua, W.R.; Guu, Y.K.; Cheng, W. Dietary administration of the probiotic, Saccharomyces cerevisiae P13, enhanced the growth, innate immune responses, and disease resistance of the grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnadóttir, B. Innate immunity of fish (overview). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006, 20, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.K.; Beck, B.R.; Kim, D.; Park, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.D.; Ringø, E. Prebiotics as immunostimulants in aquaculture: A review. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 40, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.M.; Chan, H.Y.E.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.Y. Green tea catechins upregulate superoxide dismutase and catalase in fruit flies. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Álvarez, R.M.; Morales, A.E.; Sanz, A. Antioxidant Defenses in Fish: Biotic and Abiotic Factors. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2005, 15, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaolong, G.; Caihuan, K.; Fucun, W.; Xian, L.; Ying, L. Effects of Bacillus lincheniformis feeding frequency on the growth, digestion and immunity of Haliotis discus hannai. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 96, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomax, A.P.; Calder, P.C. Probiotics, Immune Function, Infection and Inflammation: A Review of the Evidence from Studies Conducted in Humans. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 1428–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Experimental Diets | ||
|---|---|---|
| Basal Diet | YJB | |
| Jack mackerel meal | 520 | 520 |
| Fermented soybean meal | 120 | 120 |
| Wheat flour | 255 | 252.5 |
| YJB a | 0 | 2.5 |
| Fish oil | 40 | 40 |
| Soybean oil | 40 | 40 |
| Vitamin premix b | 10 | 10 |
| Mineral premix c | 10 | 10 |
| Choline | 5 | 5 |
| Proximate composition (g/kg) | ||
| Dry matter | 932 | 932 |
| Crude protein | 478 | 480 |
| Crude lipids | 133 | 132 |
| Ash | 91 | 96 |
| Experimental Diets | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | ||
| IBW (g) | 15.5 ± 0.02 | 15.5 ± 0.01 | 15.5 ± 0.03 | 15.5 ± 0.01 | 0.441 |
| FBW (g) | 37.3 ± 0.35 a | 40.9 ± 0.27 c | 39.7 ± 0.14 b | 38.0 ± 0.08 a | 0.001 |
| SR (%) | 98.3 ± 1.67 | 98.3 ± 1.67 | 100.0 ± 0.00 | 98.3 ± 1.67 | 0.802 |
| WG (g/fish) | 21.8 ± 0.34 a | 25.4 ± 0.28 c | 24.2 ± 0.13 b | 22.5 ± 0.08 a | 0.001 |
| SGR (%/day) | 1.79 ± 0.019 a | 1.98 ± 0.015 c | 1.92 ± 0.007 b | 1.83 ± 0.004 a | 0.001 |
| CF | 1.70 ± 0.036 | 1.74 ± 0.033 | 1.72 ± 0.021 | 1.72 ± 0.011 | 0.695 |
| VSI (%) | 10.45 ± 0.101 | 10.48 ± 0.202 | 10.50 ± 0.35 | 10.51 ± 0.096 | 0.988 |
| HSI (%) | 2.69 ± 0.044 | 2.72 ± 0.010 | 2.73 ± 0.073 | 2.71 ± 0.026 | 0.911 |
| FC (g/fish) | 24.0 ± 0.64 a | 27.1 ± 0.80 b | 25.7 ± 0.19 b | 24.4 ± 0.31 a | 0.008 |
| FE | 0.92 ± 0.004 a | 0.95 ± 0.004 b | 0.94 ± 0.002 b | 0.94 ± 0.004 a | 0.046 |
| PER | 1.89 ± 0.024 a | 1.96 ± 0.040 b | 1.96 ± 0.004 b | 1.92 ± 0.025 a | 0.011 |
| Experimental Diets | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | ||
| Moisture (%) | 70.0 ± 0.13 a | 69.8 ± 0.21 a | 70.6 ± 0.21 a | 69.9 ± 0.12 a | 0.059 |
| Crude protein (%) | 14.8 ± 0.12 a | 14.9 ± 0.15 a | 15.0 ± 0.26 a | 15.1 ± 0.41 a | 0.797 |
| Crude lipid (%) | 8.4 ± 0.12 a | 8.3 ± 0.12 a | 8.6 ± 0.36 a | 8.5 ± 0.06 a | 0.746 |
| Ash (%) | 4.2 ± 0.17 a | 4.2 ± 0.03 a | 4.1 ± 0.17 a | 4.1 ± 0.12 a | 0.896 |
| AST (U/L) | 38.7 ± 3.18 a | 34.3 ± 4.33 a | 36.3 ± 3.53 a | 32.3 ± 7.42 a | 0.821 |
| ALT (U/L) | 22.7 ± 2.85 a | 23.7 ± 2.40 a | 24.0 ± 0.58 a | 26.3 ± 0.67 a | 0.601 |
| T-CHO (mg/dL) | 171.7 ± 3.93 a | 173.0 ± 4.62 a | 179.7 ± 7.62 a | 172.0 ± 3.79 a | 0.681 |
| TP (g/dL) | 4.2 ± 0.32 a | 4.3 ± 0.41 a | 4.9 ± 0.26 a | 4.2 ± 0.35 a | 0.421 |
| GLU (mg/dL) | 113.7 ± 5.36 a | 111.0 ± 5.00 a | 110.3 ± 3.53 a | 117.0 ± 4.93 a | 0.753 |
| Experimental Diets | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | ||
| Lysozyme (U/mL) | 1.34 ± 0.019 a | 1.63 ± 0.022 c | 1.47 ± 0.010 b | 1.49 ± 0.046 b | 0.000 |
| SOD (U/mL) | 1.50 ± 0.065 a | 2.43 ± 0.065 c | 2.38 ± 0.056 c | 1.68 ± 0.035 b | 0.000 |
| CAT (nmol/min/mL) | 315.4 ± 3.26 a | 342.6 ± 3.36 b | 335.4 ± 4.21 b | 334.4 ± 3.84 b | 0.004 |
| GSH (µM) | 2.39 ± 0.342 a | 5.82 ± 0.642 c | 5.73 ± 0.690 c | 3.73 ± 0.316 b | 0.004 |
| Experimental Diets | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | ||
| Amylase (U/L) | 375.1 ± 13.0 a | 702.2 ± 17.8 b | 693.9 ± 16.8 b | 423.8 ± 16.0 a | 0.000 |
| Trypsin (U/L) | 33.0 ± 3.26 a | 55.8 ± 2.30 b | 54.0 ± 3.08 b | 39.8 ± 3.76 a | 0.002 |
| Lipase (U/L) | 48.2 ± 2.51 a | 76.2 ± 9.08 b | 67.9 ± 2.29 b | 50.3 ± 4.23 a | 0.015 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, H.Y.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, G.J.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, K.-T.; Kim, H.S. Effects of Yacon (Smallanthus sonchifolius) Juice Byproduct Administered Using Different Feeding Methods on the Growth Performance, Digestive Enzyme Activity, Antioxidant Status, and Disease Resistance against Streptococcus iniae of Juvenile Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii). Fishes 2024, 9, 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9070245
Oh HY, Lee TH, Lee GJ, Park SY, Kim K-T, Kim HS. Effects of Yacon (Smallanthus sonchifolius) Juice Byproduct Administered Using Different Feeding Methods on the Growth Performance, Digestive Enzyme Activity, Antioxidant Status, and Disease Resistance against Streptococcus iniae of Juvenile Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii). Fishes. 2024; 9(7):245. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9070245
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Hwa Yong, Tae Hoon Lee, Gyu Jin Lee, Seo Young Park, Ki-Tae Kim, and Hee Sung Kim. 2024. "Effects of Yacon (Smallanthus sonchifolius) Juice Byproduct Administered Using Different Feeding Methods on the Growth Performance, Digestive Enzyme Activity, Antioxidant Status, and Disease Resistance against Streptococcus iniae of Juvenile Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii)" Fishes 9, no. 7: 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9070245
APA StyleOh, H. Y., Lee, T. H., Lee, G. J., Park, S. Y., Kim, K.-T., & Kim, H. S. (2024). Effects of Yacon (Smallanthus sonchifolius) Juice Byproduct Administered Using Different Feeding Methods on the Growth Performance, Digestive Enzyme Activity, Antioxidant Status, and Disease Resistance against Streptococcus iniae of Juvenile Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii). Fishes, 9(7), 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9070245







