Abstract
Cadmium (Cd) is a common environmental pollutant that accumulates mainly in the kidneys and thus endangers the physiological health of aquatic animals. Selenium (Se) is a natural antidote to heavy metals that antagonises heavy metal toxicity and enhances the antioxidant capacity of organisms. Lactobacillus plantarum (L. plantarum) can reduce the toxicity of heavy metals through adsorption, reduction and metabolism. Studies have confirmed that the biological synthesis of Se nanoparticles (Bio-SeNPs) using bacterial microorganisms is simple, safe and less toxic than the synthesis of inorganic and organic Se, but the effect on Cd-induced immunosuppression is un-known. One hundred and eighty Bulatmai barbel (Luciobarbus capito: L. capito) plants were randomly divided into control (C), Cd and Cd + Se-enriched L. plantarum groups (S1L1-Cd) and fed for 28 days. The analysis methods included histopathology, test kits, transcriptomics and real-time quantitative PCR. The addition of selenium-enriched L. plantarum significantly attenuated cadmium-induced pathological changes such as glomerular atrophy, detachment of renal tubular epithelial cells, mild swelling, and interstitial inflammatory cell infiltration. Cd stress can lead to significant decreases in RBC, HCT, WBC, LZM, C3, and IgM levels, and the addition of Se-enriched L. plantarum can significantly reverse the changes in these indicators. Transcriptomic analysis revealed 488 DEGs in the Cd groups, 301 of which were upregulated and 187 of which were downregulated. There were 1474 DEGs in the S1L1-Cd group, of which 720 were upregulated and 754 were downregulated. In addition, GO enrichment analysis revealed that the biological regulation of the most differentially expressed genes involved metal ion binding, ATP binding and nucleotide inclusion. KEGG enrichment analysis revealed six of the most enriched pathways: oxidative phosphorylation, Huntington disease, retrograde endocannabinoid signalling, natural killer cell-mediated cyto-toxicity, the IL-17 signalling pathway, and leukocyte transient migration. Moreover, we selected 12 DEGs for qRT-PCR, which showed that the qRT-PCR results were consistent with our RNA-Seq results. Our results suggest that Se-enriched L. plantarum can enhance immunity and alleviate Cd exposure-mediated immunosuppression in L. capito.
Key Contribution:
Our results suggest that Se-enriched L. plantarum can enhance immunity and alleviate Cd exposure-mediated immunosuppression in L. capito.
1. Introduction
The main sources of Cd pollution include polyvinyl chloride (PVC) products, colour pigments, industrial corrosive reagents, and phosphate fertilisers [1]. Bulatmai barbel belongs to Cypriniformes, Cyprinidae, and Barbinae, and is mainly found in the inland rivers of the southern Caspian Sea and the Aral Sea system, Uzbekistan, Iran and Turkey [2,3]. Heavy metal contamination of water bodies has led to heavy metal stress in Bulatmai barbel, severely affecting growth and development [3,4,5,6]. In addition, environmental Cd leakage can occur in tissues or organs such as the kidneys of living organisms [4,7]. Cd poses a great threat to the survival of aquatic animals due to its long half-life and low excretion rate from the body. Cd enters the bloodstream from the intestines of carp and accumulates in the kidneys over a long period of time, leading to renal dysfunction [1]. Cd stress disrupts cell physiological signalling cascades, gene expression, molecular transport and metabolic regulation in aquatic animals [8]. Cd exposure induced aberrant autophagy and pyroptosis in duck kidney tubular epithelial cells [9]. Cd can inhibit the function of T cells and B cells, thereby affecting the humoral immune function of aquatic animals and mediating the development of inflammatory responses that increase the burden on the immune system [10,11]. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated through in vitro experiments that Cd can directly interfere with signalling pathways, where cell activation and differentiation are altered, ultimately leading to cytokine production, which in turn affects the status and function of immune cells [11]. Cd exposure results in a significant increase in the serum IL-17 mRNA level [12]; this may be attributed to the effect of Cd on innate immune cells, which are required for the differentiation of cytokine-producing T cells [13]. Therefore, the increased accumulation of Cd in fish is causing great damage to the aquaculture industry, food safety and public health.
Se has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and heavy metal antagonistic functions; enhances reproductive function; and promotes basal metabolism in organisms. Se affects the immune function of the body in three ways: cellular immunity, humoral immunity and nonspecific immunity. Se can enhance the secretion of IL-1 and IL-2 by lymphocytes, stimulate the formation of immunoglobulins, and increase the levels of IgG and IgM [14]. Nano-Se is a new form of Se supplementation, and the addition of nano-Se to feed im-proves the activity of antioxidant enzymes in the L. capito liver [15]. Studies have shown that low doses of Se can promote the proliferation of hepatocytes in mice under arsenic (As) stress while attenuating the degree of lipid peroxidation in liver and kidney tissues, indicating that Se can antagonise arsenic toxicity [16,17,18]. It has been reported that Se can alleviate Cd toxicity by forming Se-Cd complexes with Cd, thereby reducing the bioavailability of Cd and reducing oxidative damage in different organs and tissues, such as the liver, kidneys, bones and blood [19].
Probiotics are defined as live beneficial microorganisms that, when ingested in moderation, may help the host regulate the intestinal flora. Probiotics will have beneficial effects on the host by colonising and altering the intestinal microbial population [20]. Feeding L. plantarum enhanced kidney antioxidant enzyme activity and reduced Cd toxicity in mice under Cd stress [21]. Probiotics can convert inorganic Se to nano-Se through bio-transformation, which reduces Se toxicity while increasing the biological activity of the probiotics, making Se conversion more efficient. Shang et al. carried out a Se enrichment test on six strains of Bacillus sphaericus and reported that the highest Se enrichment and Se conversion efficiency were found in Bacillus subtilis, with an enrichment content of 281.813 μg/mL and a Se conversion rate of 56% [22]. Studies have shown that probiotics have the ability to adsorb the heavy metal Cd, which can reach saturation adsorption and very high removal efficiency within one hour [23,24]. However, there are few studies on the mechanism of Cd removal by Se-enriched L. plantarum.
Studies have demonstrated that Se and L. plantarum have antagonistic effects on heavy metals, reducing their accumulation, promoting the immune response and modu-lating the inflammatory response [17,25,26]. However, most of these studies focused on Se or L. plantarum alone to antagonise heavy metal toxicity, and few studies have utilised the biotransformation of L. plantarum from sodium selenite to Se nanoparticles to antago-nise heavy metals. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the effect of Se-enriched L. plantarum in feed on the immune regulation of L. capito and its potential role in alleviating the adverse effects of Cd toxicity through transcriptomics.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs and Reagents
Sodium selenite (Sinopharm Group Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Hitachi Aerospace Corporation, Tokyo, Japan), Cd chloride (Tianjin Tianli Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China), RNA fixative (Dalian Meilun Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Dalian, China), MRS medium and MRS broth culture (Qingdao Haibo, Qingdao, China) were used.
2.2. Preparation of Se-Enriched Lactic Acid Bacteria
The detailed experimental procedures used for the adsorptive transformation of inorganic Se by L. plantarum have been described previously [1]. Briefly, 200 μL of L. plantarum and 200 µg/mL sodium selenite were added to 10 mL of MRS broth and incubated aerobically and statically for 24 h at 37 °C. The obtained Se-enriched L. plantarum solution was centrifuged at 3500 r/s for 5 min, after which the supernatant was discarded, and the Se in the solution was washed away three times. The precipitated cells obtained were dried in an oven at 37 °C. Bacterial powder (0.1 g) was mixed well with concentrated nitric acid (65% HNO3). The digestion reaction was carried out on a hot plate until the sample was completely dissolved. The Se concentration was determined by an AA-6300 (Shimadzu, Japan) atomic absorption spectrometer
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy Observation of Se and Morphological Distribution of Bacteria
The L. plantarum strain was incubated in MRS medium at 37 °C for 12 h, transferred to 24-well plates and incubated in MRS medium containing 200 g/mL Na2SeO3 at 37 °C for 24 h. Then, the bacteria were fixed with glutaraldehyde at 2.5% v/v/v and left at room temperature for 1 h before being washed three times with PBS. The bacteria were dehydrated in a series of gradients of ethanol (30% to 100%), the ethanol was replaced with 100% tert-butanol, the bacteria were then dried and coated with gold in a vacuum freeze dryer, and the samples were scanned using a HITACHI SU8010 emission field scanning electron microscope (Hitachi Aerospace Corporation, Dallas, TX, USA).
2.4. Experimental Design
L. capito (76.2 ± 1.1 g) was procured from a specialized aquatic fry farm (Jilin province, China) and transferred to the laboratory. A total of 270 L. capito individuals were randomly and equally assigned to 9 aquariums (90 × 50 × 50 cm, 30 fish/aquarium). L. capito was randomly reared in a tempered glass fish tank with three experimental groups—control (C), Cd and Se-enriched Cd (S1L1-Cd)—with three replicates for each group, and the culture experiment lasted for 28 d. Cd was added to the water (0.05 mg/L), and Se and Cd concentrations were set according to previous studies [1]. Feeds were supplemented with Se-enriched L. plantarum (nano-Se level of 5 mg/kg and L. plantarum content of 108 CFU/kg), and all feeds were stored at 4 °C until use. To maintain the activity of L. plantarum, all the finished feeds were stored at 4 °C and fed within 2 d. The feeds were stored at 4 °C and fed within 2 d. The water was changed once a day, half of it at a time, and the corresponding Cd was added according to the test concentration to maintain the set Cd concentration in the water.
The fish were fasted for 12 h before the end of the experiment, and six fish were removed from each group. One study recommended a minimum of 4 to 6 fish to obtain 80% statistical significance in biochemical/immunological parameters [27]. Whole blood was collected from the tail vein of the fish for biochemical analysis. The fish were euthanised with 300 mg/L of methane-sulfonate-222. The kidneys of the fish were collected. The kidneys were rinsed with precooled saline and then quickly placed in liquid nitrogen for 1.5 h. The kidneys were finally stored in a freezer at −80 °C for transcriptome sequencing and qRT-PCR. This study was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Jilin Agricultural Science and Technology University (approval code: 20221011).
2.5. Blood and Serum Immunological Tests
Blood was subsequently collected. Haematological indices were determined using an animal blood cell analyser (Mindray BC-2800Vet, Shenzhen, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Serum creatinine (Cr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), uric acid (UA), C3, C4, and immunoglobulin M (IgM) levels and lysozyme (LZM) activity were measured using an ELISA kit (Nanjing Jianjian Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China).
2.6. Kidney Tissue Sections
Renal histological sections were fixed in 10% neutral-buffered formalin for histological examination. The formalin-fixed tissues were embedded in paraffin and processed using standard paraffin techniques. Sections stained with haematoxylin and eosin were processed according to standard protocols [28]. Finally, the sample sections were observed on an Axioskop microscope (IX71. Olympus, Hamburg, Germany).
2.7. Transcriptome
Sequencing was performed by Hangzhou Lianchuan Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Hangzhou, China) using a NovaSeq 6000 system (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). The raw data obtained were filtered to maximise the data quality. Contaminated, low-quality and unidentified bases were removed. A window quality scan of sequencing reads was performed. The default scanning window was 6 bp. The portion of the reads from the beginning of the window to the end of the 3′ window was truncated when the average quality value in the window was less than 20. FastQC software was used for data quality control, with 90% valid data and 90% valid data for Q20 and Q30. Truncated sequences with N contents greater than 5% were removed. FastQC was used to assess sequence quality, including the number of valid reads, Q20, Q30 and GC content (http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/) (accessed on 18 May 2023). The expression levels of the unigenes were determined as transcripts per million (TPM) values. After obtaining reads for genes. Differentially expressed unigenes with statistical significance (|log2-fold change| ≥ 2, p < 0.05) were screened using the R package edgeR (3.12.1).
2.8. Gene Ontology and Enrichment Analysis
Unigenes were obtained by reassembling the transcriptome using Trinity 2.4.0. All newly assembled gene sequences (UniGene) were compared and annotated with the NR, GO, EggNog and KEGG databases. Biological effects of differentially expressed genes were demonstrated using GO (http://www.geneontology.org) (accessed on 18 May 2023); signalling pathways between differentially expressed genes were analysed using KEGG (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/) (accessed on 18 May 2023). The GO and KEGG classes were significantly enriched (p < 0.05).
2.9. qRT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted from the kidneys of L. capito according to the instructions of the Simply P Total RNA Extraction Kit (Hangzhou Bozhi Science and Technology Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China). cDNA was reverse transcribed using 1 μg of total RNA according to the instructions of the PrimeScript™ RT kit and gDNA Eraser (Beijing Baozhi Physical Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). For quantitative real-time fluorescence PCR (qRT-PCR), qRT-PCR was performed on a QuantStudio 6 real-time PCR system. The sequences of primers used for gene expression analysis are shown in Table 1. The relative expression of each gene relative to that of the internal reference gene β-actin was calculated according to the 2−ΔΔCT method.

Table 1.
Primer sequences for polymerase chain reactions.
2.10. Data Analysis
The data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (mean ± SD) of each group. Differences in means between groups were analysed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), and multiple comparisons were performed using Tukey’s method and then tested using the data analysis software SPSS 20.0. Differences with a p value < 0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance.
3. Results
3.1. Se-Enriched Lactic Acid Bacteria
As shown in Figure 1A, the L. plantarum surface was smooth. As shown in Figure 1B, spherical Se nanoparticles (red arrows) were visibly attached to the surface of L. plantarum. Zhang et al. [29] also obtained similar findings.
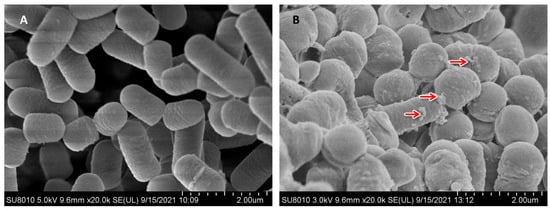
Figure 1.
Morphology of control (A) and Se-enriched L. plantarum (B) in 200 mg/L Se was analysed by scanning electron microscopy. Nano-selenium particles (red arrow).
3.2. Kidney Histology and Morphology
As shown in Figure 2, kidney sections from the control group (A) show normal glomeruli, proximal tubules and distal tubules, and after Cd stress (B) show glomerular atrophy, vacuolisation of the tubular epithelial cell lining, mild swelling and epithelial cell detachment, and a large number of inflammatory cells infiltrating the renal interstitium. After feeding with Se-enriched L. plantarum, pathological changes in glomerular structure were significantly reduced, the renal tubular structure was normal, and the number of inflammatory cells in the renal interstitium was significantly reduced.
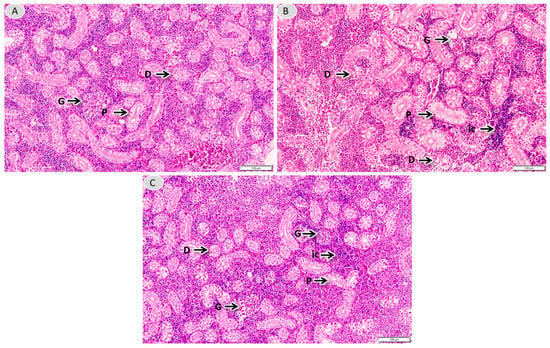
Figure 2.
Histopathological observations of the kidneys. Kidneys’ morphology in group C (A), Cd (B) and SL-Cd (C) (kidney tissues were fixed and stained with H&E. Original magnification ×400). G: glomerulus; D: distal tubule; P: proximal tubule; ic: inflammatory cells.
3.3. Haemocyte Parameters and Serum Immune Responses
As shown in Figure 3, Cd exposure can cause cytotoxicity, which is a decrease in fish immune functions. In this study, the haematological indices of L. capito were determined under Cd or Se-enriched L. plantarum treatment. As expected, Cd exposure resulted in a significant decrease in blood RBC, HCT and WBC counts, while the S1L1-Cd group had significantly greater RBC, HCT and WBC counts.
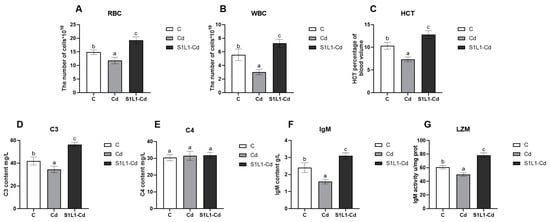
Figure 3.
Blood and serum immune parameters of red blood cells (A) and leucocytes (B), HCT (C), complement 3, C3 (D) complement 4, C4 (E), IgM (F), and lysozyme activity, LZM (G), of L. capito after Cd or S1L1-Cd. Data are expressed as the mean ± S.D (n = 5). Bar graphs with different letter superscripts, values are significantly different from each other.
The serum LZM, C3, C4 and IgM levels are nonspecific immune indicators that are important for resisting pathogen invasion and maintaining the health of fish. In this study, the serum levels of LZM, C3 and IgM were significantly lower in the Cd group than in the control group. The serum levels of LZM, C3, and IgM were significantly greater in the S1L1-Cd group than in the Cd and control groups. However, there was no significant change in the serum level of C4, and its mechanism of action needs to be further investigated and discussed. These results show that the addition of selenium-enriched L. plantarum to the feed could improve the immune function of L. capito and alleviate cadmium-induced immunosuppression.
3.4. Kidney Damage Indicators
The three indicators of blood urea nitrogen (BUN), inosine (CR), and uric acid (UA) in serum are sensitive serological indicators of kidney injury (Figure 4). Their levels can directly reflect kidney function. In this study, compared with those in the control group, the serum Cr, BUN, and UA levels in the Cd group were significantly greater. Compared with those in the Cd group, the levels of serum Cr, BUN and UA significantly decreased in the S1L1-Cd group, but elevated compared to the control group. This result shows that selenium-enriched L. plantarum can attenuate cadmium stress-induced renal injury.
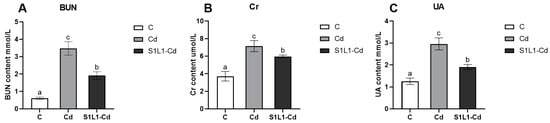
Figure 4.
Serum biochemical parameters of L. capito under Cd or S1L1-Cd. BUN (A), CR (B), and UA (C). Data are expressed as the mean ± S.D. (n = 5). Values with different superscripts are significant (p < 0.05), as determined by Tukey’s test.
3.5. Transcriptome
The quality control results of the transcriptome sequencing are shown in Table 2. The three samples in Group C obtained 38,813,784, 42,393,916 and 42,578,024 readings, and the samples in group Cd obtained 37,924,708, 41,503,984 and 41,839,558 readings, respectively. The 46,031,170, 42,993,436 and 39,382,828 readings were obtained for the S1L1_Cd group. The differences in gene expression in the kidney tissues of L. capito plants treated with Cd and L. plantarum are shown in Figure 5A. There were 488 DEGs in the control group and the Cd group, of which 301 genes were upregulated and 187 genes were downregulated. There were 1474 DEGs in the C and S1L1-Cd groups, of which 720 genes were upregulated and 754 genes were downregulated. A total of 989 DEGs were expressed in the S1L1-Cd and Cd groups; 510 genes were upregulated, and 497 genes were downregulated. A Venn diagram can more directly show the overlap of differential gene expression. As shown in Figure 5B, two significantly differentially expressed genes were found in all the groups. The cluster analysis of differential gene expression is shown in Figure 5C. The two differentially expressed genes were TRINITY_DN15244_c0_g1 (agr2) and TRINITY_DN16045_c0_g1.

Table 2.
Transcriptome sequencing quality control results.
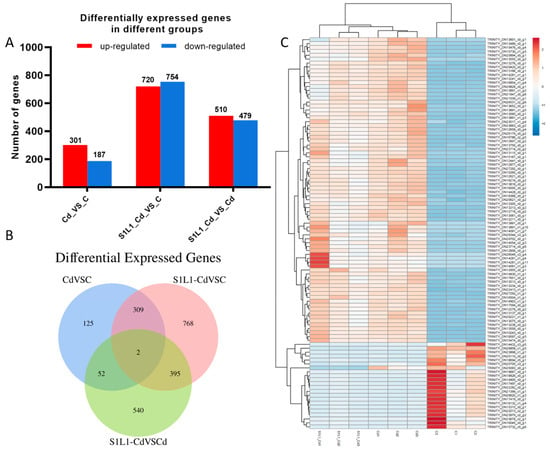
Figure 5.
Differentially expressed genes (A), Venn diagram (B), and heatmap of the differentially expressed genes (C) in L. capito treated with Cd and Se-enriched L. plantarum. Note: Red represents upregulated genes, blue represents downregulated genes. C: the control group; S1L1-Cd: the S1L1-Cd group; Cd: the Cd group; n = 3.
We used GO enrichment to analyse DEGs in L. capito plants treated with Cd- or Se-enriched L. plantarum. DNA templates (transcriptional regulation) and signal transduction were significantly enriched. Membranes, membrane components and cellular components of the nucleus were significantly enriched. The molecular functions of metal ion binding, ATP binding, and nucleotide inclusion were the most highly differentially expressed genes (Figure 6A).
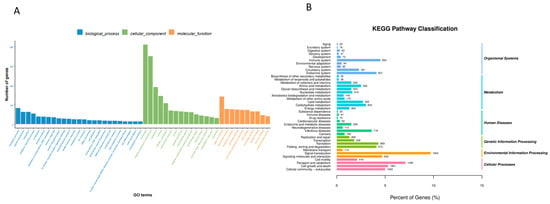
Figure 6.
GO (A) and KEGG (B) enrichment results.
The KEGG database annotates differentially expressed gene enrichment pathways. Our results showed that the enriched pathways were as follows: environmental information processing, cellular processes, and human diseases (Figure 6B). The kidney tissue enrichment pathways consisted of four main categories: organismal systems, metabolism, human diseases, genetic information processing, environmental information processing and cellular processes. The six pathways with the greatest enrichment were signal transduction, endocrine system, cell growth and death, cellular community eukaryotes, signalling molecules and interaction and immune system. The 20 pathways with the most significant enrichment in KEGG pathways were analysed. Research has shown that Cd is closely related to signalling pathways related to kidney immune injury. The following six of the most closely related enrichment pathways were identified: oxidative phosphorylation, Huntington disease, retrograde endocannabinoid signalling, natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity, the IL-17 signalling pathway, and leukocyte transendothelial migration (Figure 7).
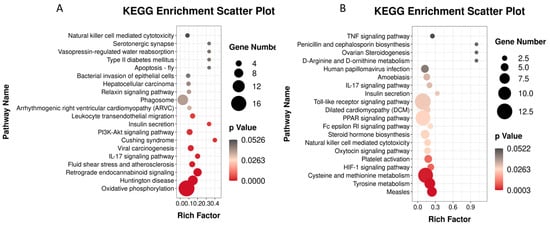
Figure 7.
Enrichment analysis of KEGG in brain transcriptome of L. capito. (A) (Cd vs. C), (B) (S1L1-Cd vs. C).
3.6. qRT-PCR Validation
Twelve DEGs from L. capito kidneys were randomly selected for qRT-PCR to verify the reliability and reproducibility of the RNA-Seq data (Figure 8). HSP90AB1, hsp70, and HSPA4L expression levels were significantly greater in the Cd group than in the control group, and agr2 and VMO1 expression levels were lower in the Cd group than in the control group (Figure 8A). The results showed that the expression levels of MT-CO1, MT-ND4, HSP90AB1, and HSPA8 in the S1L1-Cd group were significantly greater than those in the control group, and the expression levels of agr2, VMO1, IL1B, and tnfaip8l2a were lower than those in the control group (Figure 8B).
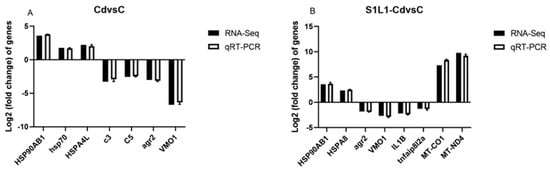
Figure 8.
The comparison genes for RNA-Seq and qRT-PCR. X-axis represents genes and Y-axis represents relative fold change ((A): Cd vs. C; (B): S1L1-Cd vs. C). The data of this study are presented as mean ± SD of three parallel measurements (n = 3).
4. Discussion
Cd is a toxic heavy metal, and Cd is widely present in natural aquatic environments. Long-term exposure to Cd or excessive Cd intake can cause serious damage to the physiological functions of aquatic animals and oxidative stress [30]. The kidneys are the main target organs of Cd exposure, and Cd is mainly excreted through the kidneys when it enters the body of aquatic animals. When the Cd concentration is too high, the kidneys are unable to efficiently excrete Cd, which leads to the accumulation of Cd in the kidneys, thus causing kidney damage [31]. A study reported that Cd exposure can lead to severe damage to the histological structure of the kidney in male rats and that Se can reduce Cd accumulation and alleviate kidney damage [32]. In this study, we found that Cd stress caused glomerular atrophy, vacuolisation of the tubular epithelial cell lining, mild swelling and epithelial cell detachment in renal tissues, whereas the lesions were significantly attenuated by the addition of Se-enriched L. plantarum to the feed, which suggests that Cd exposure causes damage to the kidney tissues of L. capito and that Se-enriched L. plantarum alleviates Cd damage to the kidneys.
A study revealed that Cd concentrations were greater than 0.1 mg/kg in the muscle, liver and kidneys of carp (Cyprinus carpio) and catfish (Silurus glanis) from the Buško Blato region of Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Cd accumulation reached its highest level in the kidneys [33]. Cd has been shown to have toxic effects on the hepatopancreas, cardiovascular, immune and reproductive systems [34,35]. Cd stress can lead to significant changes in blood biochemical indices in aquatic animals. Similarly, acute Cd exposure led to a significant reduction in blood WBC, RBC, and HCT levels in mice [35]. Similar results were obtained by Simsek, where Cd-containing feeds led to anaemia in mice by causing a reduction in erythrocyte, leukocyte, and ANAE-positive T-lymphocyte counts as well as Hb, PCV, and MCHC values in mouse groups. In the present study, our results also revealed a decrease in RBC, HGB and HCT, which may be due to the inhibition of erythropoiesis induced by Cd chloride, whereas the increase in leucocytes may be a result of enhanced immunomodulation of the organism affected by oxidative stress [36].
Serum creatinine (Cr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and uric acid (UA) are the main indicators for evaluating renal function. Heavy metal exposure can lead to a significant increase in serum Cr, BUN, and UA [37]. Fluoride exposure was also found to cause oxidative damage and nephropathy in mice and significantly increased urea nitrogen (BUN), creatine and serum creatinine levels [38]. Studies have confirmed that Se can attenuate hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)]-induced renal dysfunction by lowering the serum levels of BUN and CRE [39]. In the present study, long-term Cd exposure resulted in significantly higher levels of serum Cr, BUN, and UA in L. capito, which suggests that Cd can cause renal dysfunction. Compared with those in the Cd group, the Se-enriched Cd group had significantly lower serum Cr, BUN, and UA levels, which suggests that Se-enriched L. plantarum can alleviate the damage caused by Cd in the kidney to a certain extent. Fish are lower metameric vertebrates with relatively low specific immune responses, and the nonspecific immune system is of great importance to scleractinian fishes under abiotic stress. Lysozyme is an important component of nonspecific immunity in fish and is widely present in fish mucus and serum, where it activates phagocytic complements in addition to lysing bacteria [40].
In addition, IgM is an important measure of humoral immunity and health in fish. External oxidative stress has a significant effect on the level of immunity in fish. When Takifugu rubripes were subjected to nitrite stress, the serum LZM and IgM levels decreased significantly, leading to immune dysfunction and immunotoxicity [41]. It has also been found that ammonia exposure results in significantly lower concentrations of C3, C4, IgM and LZM and reduced immune function in redfin puffer [42]. In the present study, we found that Cd stress resulted in a significant reduction in the levels of C3, IgM and LZM in L. capito, whereas there was no significant change in the level of C4. Se and L. plantarum have growth-promoting, immune-enhancing and antioxidant functions [43]. L. plantarum belongs to a branch of Lactobacillus, and it has been shown that Lactobacillus has growth-promoting, immune-enhancing and disease-resistant functions. The administration of Lactobacillus to loaches significantly increased C3, C4, IgM and LZM levels and enhanced humoral immunity [44]. In our study, the addition of Se-enriched L. plantarum to the feed after Cd exposure increased the C3, IgM and LZM levels, suggesting that Se-enriched L. plantarum alleviated Cd-induced immunosuppression in L. capito.
The transendothelial migration of leukocytes is the process by which leukocytes pass through the vascular endothelium into tissues and is essential for the functioning of the immune system because it allows leukocytes to reach damaged cells or tissues [45]. In the inflammatory response, leukocyte migration across the endothelium is an important factor. Through transendothelial migration, leukocytes can reach damaged tissues while removing pathogens and waste products from damaged tissues, promoting tissue repair and regeneration [46]. Lymphocytes are an important part of the immune system that makes up an organism. Humoral immunity is mediated by antibodies produced by B lymphocytes (B cells); antibodies recognise extracellular microorganisms, bind to them (blocking host cell infection in this way) and promote phagocytosis for microbial uptake and destruction; and T lymphocytes (T cells), the mediators of cell-mediated immunity, destroy intracellular microorganisms [47].
IL-17 is a bridge between innate and adaptive immunity, as it is produced by adaptive and ‘innate’ T cells and activates the gene expression program typical of the innate immune response; IL-17 has been implicated in a variety of diseases, and IL-17 activates the nf-κB and MAPK pathways, which regulate the production of inflammatory mediators [48]. In recent years, the IL-17 family has attracted much attention from a wide range of medical researchers. One study showed that IL-17 and IL-23 levels were significantly greater in AIH patients than in chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients and healthy controls [49]. In addition, IL-17 can promote oxidative stress-induced hepatocyte apoptosis through the Nrf2/Keap1 signalling pathway [50,51]. In the present study, Cd exposure significantly enriched leukocyte transendothelial migration and the IL-17, TNF and nrf-κB signalling pathways, revealing that Cd exposure promotes oxidative stress-mediated inflammatory responses in L. capito. In contrast, the addition of Se-enriched L. plantarum to the feed significantly reversed the changes in the expression levels of these inflammatory factors, revealing that Se-enriched L. plantarum mitigated Cd-mediated immune responses by modulating inflammatory factors.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our study showed that Cd exposure causes damage to the kidneys of L. capito. Cd exposure induced immunosuppression and further reduced immune levels through haematological and immunological parameters. Cd regulates immune and inflammatory responses by activating the transendothelial migration pathway of leukocytes. KEGG pathway analysis revealed that Cd stress significantly enriched the IL-17 signalling pathway, which is involved in the inflammatory response. In contrast, the addition of Se-enriched L. plantarum to the feed significantly alleviated renal tissue injury. The Se-enriched L. plantarum treatment significantly reversed the effects of Cd stress on haematological and immunological parameters and alleviated Cd exposure-induced renal injury through the transendothelial migratory pathway, and the IL-17 signalling pathway was involved in the inflammatory response. Overall, the present study revealed the potential mechanism by which Se-enriched L. plantarum alleviates Cd-induced renal pathology and provided a theoretical basis for assessing the toxic effects of Cd in fish.
Author Contributions
Q.S.: Conceptualization, formal analysis, investigations, methodology, visualization, writing—original draft. Y.P.: investigations, farming techniques, surveys. Y.Q.: farming techniques, surveys, visualization. Z.D.: methodology, formal analysis, visualization. Y.M.: farming techniques, visualization. Y.Z.: farming techniques, surveys, visualization. Z.Z.: farming techniques, surveys, visualization. J.L.: formal analysis. B.M.: investigations, methodology. B.Y.: conceptualization, formal analysis, methodology, project management, resources, supervision, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Jilin province science and technology development planning grant program (Grant No. YDZJ202201ZYTS612) and Jilin city science and technology innovation development plan project (Grant No. 20230103009).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Jilin Agricultural Science and Technology University (approval code: 20221011).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Jilin Agricultural University Aquatic Nursery Farm (China, Jilin) for providing animal care and facilities for this research project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The effects of cadmium toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.L.; Xu, W.; Wei, Y.Y.; Xu, Q.Y. The complete mitochondrial genome of Barbus capito (Cypriniformes, Cyprinidae). Mitochondr Dna. 2013, 24, 326–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canli, M.A.Y.O.; Ay, Ö.; Kalay, M. Levels of Heavy Metals (Cd, Pb, Cu, Cr and Ni) in Tissue of Cyprinus carpio, Barbus capitoand Chondrostoma regiumfrom the Seyhan River, Turkey. Turk. J. Zool. 1998, 22, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Koca, S.; Koca, Y.B.; Yildiz, Ş.; Gürcü, B. Genotoxic and histopathological effects of water pollution on two fish species, Barbus capito pectoralis and Chondrostoma nasus in the Büyük Menderes River, Turkey. Biol. Trace Element. Res. 2008, 122, 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, X.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Li, Z.; Geng, L.; Teng, X. Transcriptome analysis revealed the mechanism of Luciobarbus capito (L. capito) adapting high salinity: Antioxidant capacity, heat shock proteins, immunity. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 192, 115017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Xu, W.; Che, X.; Cui, J.; Shang, X.; Teng, X.; Jia, Z. Effect of arsenic stress on the intestinal structural integrity and intestinal flora abundance of Cyprinus carpio. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1179397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satarug, S.; Garrett, S.H.; Sens, M.A.; Sens, D.A. Cadmium, environmental exposure, and health outcomes. Environ. Health Persp. 2010, 118, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, A.; Kumar, A.; Lal, A.; Pant, M. Cellular mechanisms of cadmium-induced toxicity: A review. Int. J. Environ. Heal. Res. 2014, 24, 378–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hu, Z.; Hu, R.; Pi, S.; Wei, Z.; Wang, C.; Yang, F.; Xing, C.; Nie, G.; Hu, G. New insights into crosstalk between pyroptosis and autophagy co-induced by molybdenum and cadmium in duck renal tubular epithelial cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Bevan, M.J. CD8+ T cells: Foot soldiers of the immune system. Immunity 2011, 35, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellino, F.; Germain, R.N. Cooperation between CD4+ and CD8+ T cells: When, where, and how. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 24, 519–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, T.; Mitra, P.; Singh, P.; Sharma, S.; Purohit, P.; Sharma, P. Effect of occupational co-exposure to lead and cadmium on selected immunomodulatory cytokines. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2022, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucovic, D.; Aleksandrov, A.P.; Mirkov, I.; Ninkov, M.; Kulas, J.; Zolotarevski, L.; Vukojevic, V.; Mutic, J.; Tatalovic, N.; Kataranovski, M. Oral cadmium exposure affects skin immune reactivity in rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe. 2018, 164, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minetti, G. Mevalonate pathway, selenoproteins, redox balance, immune system, Covid-19: Reasoning about connections. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 144, 110128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Xu, W.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Geng, L. Effects of exposure to cadmium (Cd) and selenium-enriched Lactobacillus plantarum in Luciobarbus capito: Bioaccumulation, antioxidant responses and intestinal microflora. COMP Biochem. Phys. C 2022, 257, 109352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Wu, Q.; Deng, H.; Yu, Y.; Tang, W.; Deng, Y.; Deng, J. Effects of selenium on the immunotoxicity of subacute arsenic poisoning in chickens. Biol. Trace Element. Res. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liang, J.; Jiang, C.; Cui, J.; Hong, L.; Hao, Z.; Teng, X. Se alleviated Pb-caused neurotoxicity in chickens: SPS2-GPx1-GSH-IL-2/IL-17-NO pathway, selenoprotein suppression, oxidative stress, and inflammatory injury. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Yu, W.; Hao, Z.; Qiu, M.; Cui, J.; Tang, Y.; Liu, H. Molecular mechanism of selenium against lead-induced apoptosis in chicken brainstem relating to heat shock protein, selenoproteins, and inflammatory cytokines. Ecotox Environ Safe. 2024, 272, 116028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banni, M.; Chouchene, L.; Said, K.; Kerkeni, A.; Messaoudi, I. Mechanisms underlying the protective effect of zinc and selenium against cadmium-induced oxidative stress in zebrafish Danio rerio. Biometals 2011, 24, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G. Probiotics: Definition, scope and mechanisms of action. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 30, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shang, X.; Geng, L.; Che, X.; Wei, H.; Tang, S.; Xu, W. Dietary Selenium-Rich Lactobacillus plantarum Alleviates Cadmium-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Bulatmai barbel Luciobarbus capito. Fishes 2023, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Sun, Q.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Mao, Q.; Li, Y. Reducingmercury accumulation in common carp using selenium-enriched Bacillus subtilis. Aquacult Rep. 2021, 19, 100609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, F.; Halttunen, T.; Tahvonen, R.; Salminen, S. Probiotic bacteria as potential detoxification tools: Assessing their heavy metal binding isotherms. Can. J. Microbiol. 2006, 52, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teemu, H.; Seppo, S.; Jussi, M.; Raija, T.; Kalle, L. Reversible surface binding of cadmium and lead by lactic acid and bifidobacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 125, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Kumar, V.; Panwar, R.; Ram, C. Efficacy of indigenous probiotic Lactobacillus strains to reduce cadmium bioaccessibility-an in vitro digestion model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Qu, D.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM8661 modulates bile acid enterohepatic circulation and increases lead excretion in mice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1455–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnon, M.M.; Hodson, P.V. Field studies using fish biomarkers–How many fish are enough? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2871–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, N.; Izawa, T.; Kuwamura, M.; Higashiguchi, N.; Kezuka, C.; Kurata, O.; Yamate, J. The first case of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus (ISKNV) infection in aquarium-maintained mandarin fish, S iniperca chuatsi (B asilewsky), in Japan. J. Fish. Dis. 2014, 37, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhong, M.; Zhou, R.; Qin, W.; Si, Y. Se (IV) reduction and extracellular biosynthesis of Nano-Se (0) by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 and Shewanella putrefaciens. Process Biochem. 2023, 130, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, N.K.; Gaw, S.; Brooks, B.W.; Glover, C.N. Oxidative stress in the galaxiid fish, Galaxias maculatus, exposed to binary waterborne mixtures of the pro-oxidant cadmium and the anti-oxidant diclofenac. Environ. Pollt. 2019, 247, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Cruz, E.Y.; Amador-Martínez, I.; Aranda-Rivera, A.K.; Cruz-Gregorio, A.; Chaverri, J.P. Renal damage induced by cadmium and its possible therapy by mitochondrial transplantation. Chem-Biol. Interact. 2022, 361, 109961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imed, M.; Fatima, H.; Abdelhamid, K. Protective effects of selenium (Se) and zinc (Zn) on cadmium (Cd) toxicity in the liver of the rat: Effects on the oxidative stress. Ecotox Environ. Safe 2009, 72, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Has-Schön, E.; Bogut, I.; Vuković, R.; Galović, D.; Bogut, A.; Horvatić, J. Distribution and age-related bioaccumulation of lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), cadmium (Cd), and arsenic (As) in tissues of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) and European catfish (Sylurus glanis) from the Buško Blato reservoir (Bosnia and Herzegovina). Chemosphere 2015, 135, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buha, A.; Wallace, D.; Matovic, V.; Schweitzer, A.; Oluic, B.; Micic, D.; Djordjevic, V. Cadmium exposure as a putative risk factor for the development of pancreatic cancer: Three different lines of evidence. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1981837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andjelkovic, M.; Buha Djordjevic, A.; Antonijevic, E.; Antonijevic, B.; Stanic, M.; Kotur-Stevuljevic, J.; Bulat, Z. Toxic effect of acute cadmium and lead exposure in rat blood, liver, and kidney. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remyla, S.R.; Ramesh, M.; Sajwan, K.S.; Senthil Kumar, K. Influence of zinc on cadmium induced haematological and bio-chemical responses in a freshwater teleost fish Catla catla. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 34, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaz, M.A.; Nisa, Z.U.; Mehmood, A.; Anjum, M.S.; Shahzad, K. Metal-induced nephrotoxicity to diabetic and non-diabetic Wistar rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 31111–31118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Verma, P.K.; Sood, S.; Yousuf, R.; Raina, R. Oxidative renal damage induced by fluoride and dimethoate and its mitigation by Zingiber officinale in Wistar rats. Research Square 2022, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hao, D.; Wang, J.; Zhu, R.; Liu, W.; Liu, C. Selenium regulates the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway to protect broilers from hexavalent chromium-induced kidney dysfunction and apoptosis. Ecotox Environ. Safe. 2022, 239, 113629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnadóttir, B. Innate immunity of fish (overview). Fish. Shellfish. Immun. 2006, 20, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.Q.; Fei, F.; Huo, H.H.; Huang, B.; Meng, X.S.; Zhang, T.; Liu, B.L. Impact of nitrite exposure on plasma biochemical parameters and immune-related responses in Takifugu rubripes. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 218, 105362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Liu, B.L.; Han, C.; Huang, B.; Lei, J.L. Effects of ammonia exposure on stress and immune response in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 3149–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, M.H.; Mahdavi, M.; Setayesh, N.; Esfandyar, M.; Shahverdi, A.R. Selenium nanoparticle-enriched Lactobacillus brevis causes more efficient immune responses in vivo and reduces the liver metastasis in metastatic form of mouse breast cancer. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Gao, C.; Du, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, M.; Shan, X.; Wang, G. Effects of single or conjoint administration of lactic acid bacteria as potential probiotics on growth, immune response and disease resistance of snakehead fish (Channa argus). Fish. Shellfish. Immun. 2020, 102, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, W.A. Mechanisms of transendothelial migration of leukocytes. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, W.A. How endothelial cells regulate transmigration of leukocytes in the inflammatory response. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, A.W., Jr. The immune cells in adipose tissue. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2013, 15, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffen, S.L. An overview of IL-17 function and signaling. Cytokine. 2008, 43, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Tang, Y.; You, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liang, S.; Han, X.; Ma, X. Interleukin-17 contributes to the pathogenesis of autoimmune hepatitis through inducing hepatic interleukin-6 expression. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Song, X.; Hu, Q.; Pan, W. IL-17 enhances oxidative stress in hepatocytes through Nrf2/keap1 signal pathway activation. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Patho. 2018, 11, 3318. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Shen, F.; Liu, J.; Tang, H.; Teng, X.; Yang, F.; Liu, H. Luteolin enhanced antioxidant capability and induced pyroptosis through NF-κB/NLRP3/Caspase-1 in splenic lymphocytes exposure to ammonia. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 919, 170699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).