Food Web Structure and Ecosystem Functions of the Water Source in the Middle Route of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
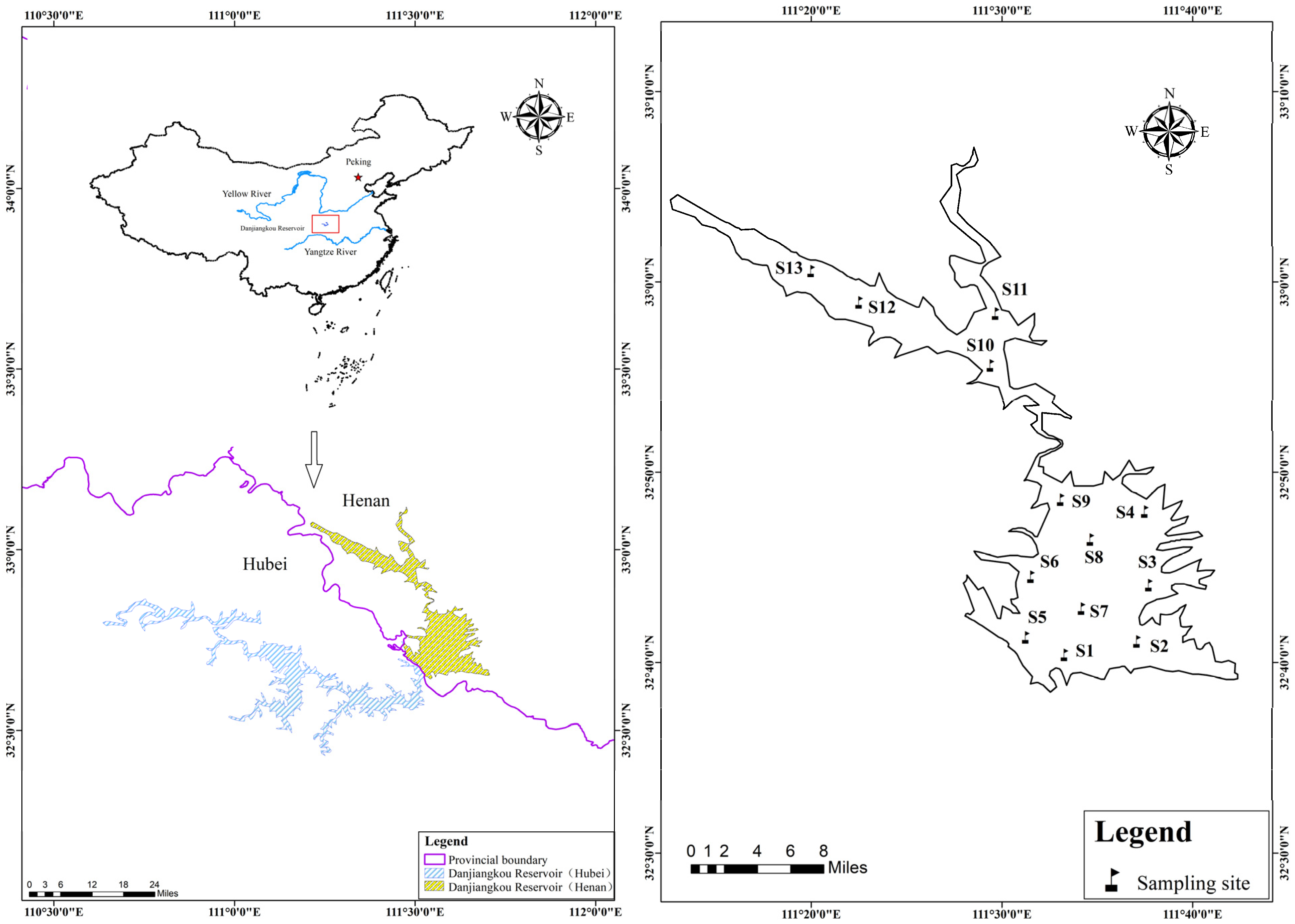
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Procedure
2.2. Ecopath Modelling Approach
2.3. Functional Groups
2.4. Data Sources and Parameter Estimation
2.4.1. Biomass (B)
2.4.2. Production (P) and P/B Coefficient
2.4.3. Q/B Coefficient
2.4.4. EE (Ecological Efficiency)
2.4.5. Diet Composition Matrix
2.5. Model Debugging
3. Results
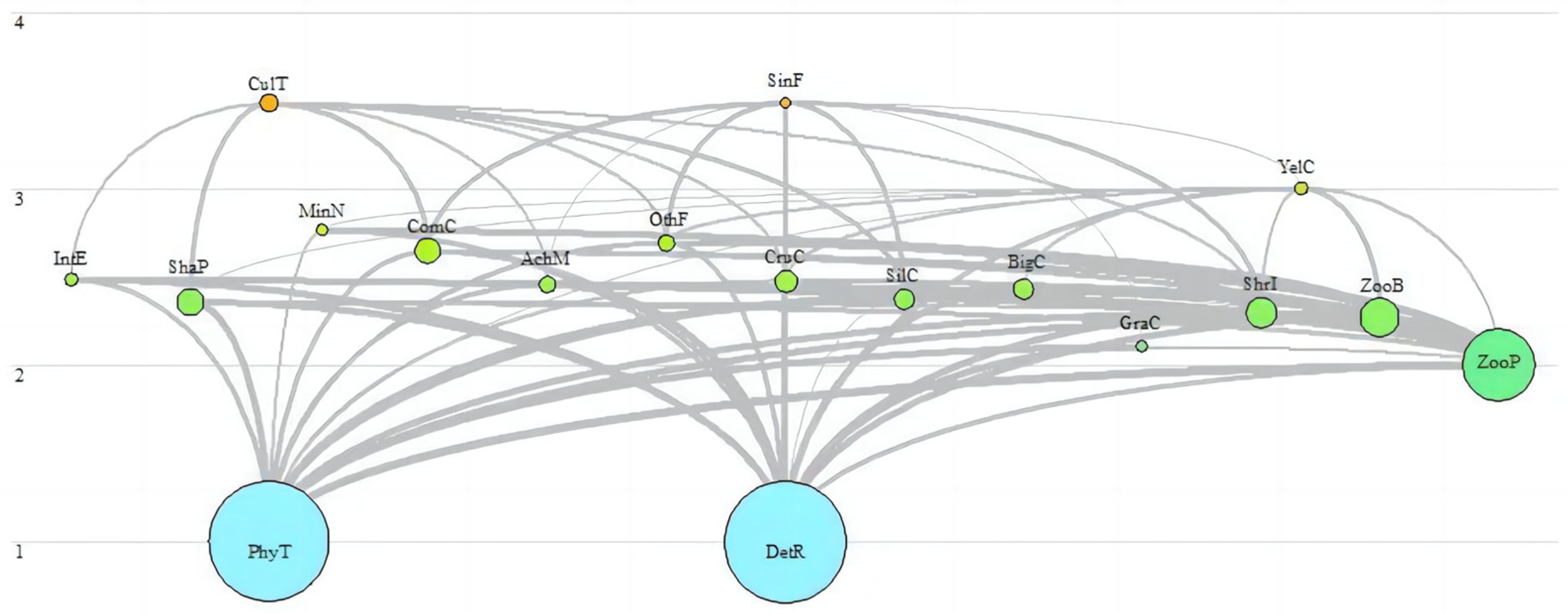
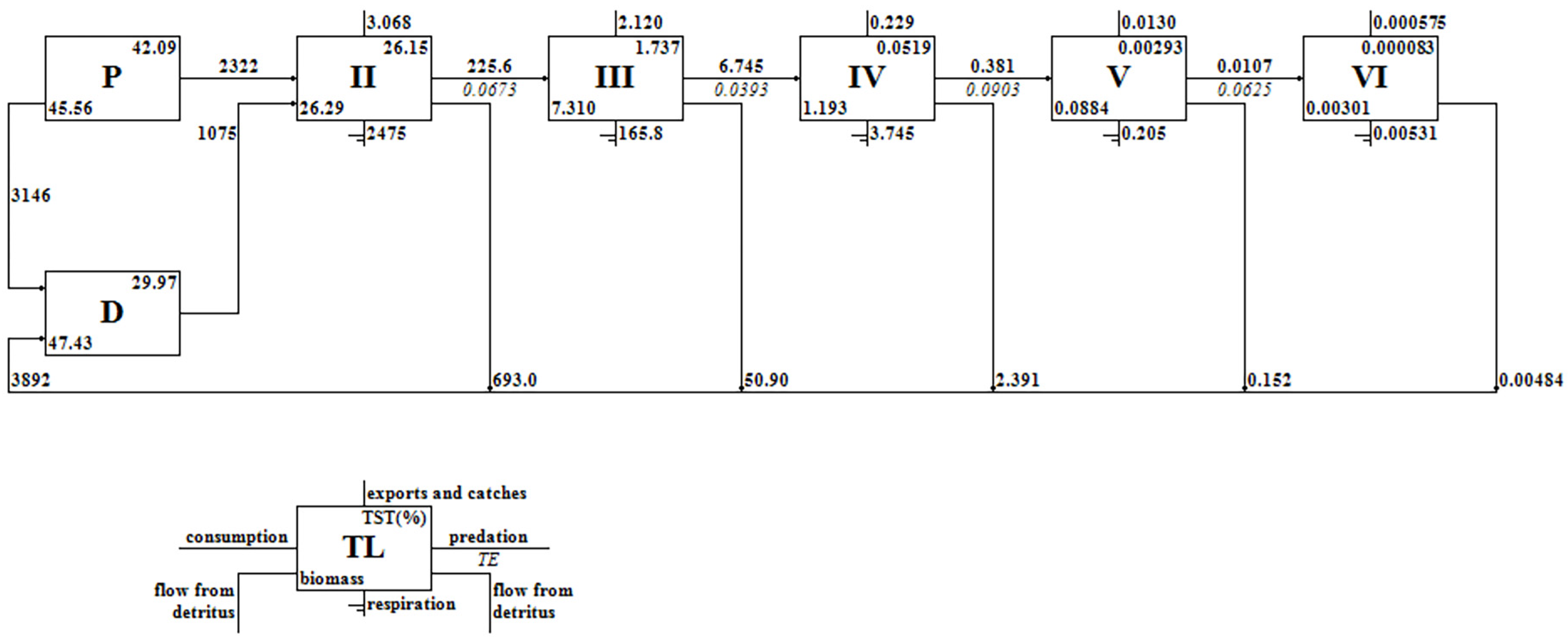
3.1. Trophic Level and Energy Flow Distribution
3.2. Efficiency of Energy Flow and Conversion between Trophic Levels
3.3. The Overall Characteristics of the Dan Reservoir
| Parameter | Dan Reservoir | Qiandao Lake [23] | Chaohu Lake [24] | Gehu Lake [25] | Taihu Lake [30] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sum of all consumption (t·km−2·a−1) | 3629.178 | 5733.298 | 4486.67 | 2665.828 | 2320.373 |
| Sum of all exports (t·km−2·a−1) | 2822.619 | 5425.390 | 16,796.6 | 2184.73 | 1238.119 |
| Sum of all respiratory flows (t·km−2·a−1) | 2644.581 | 1623.460 | 1308.45 | 829.088 | 799.961 |
| Sum of all flows into detritus (t·km−2·a−1) | 3892.074 | 7330.43 | 18,411.37 | 2892.898 | 3029.265 |
| Total system throughput (t·km−2·a−1) | 12,988.45 | 20,112.58 | 41,003.08 | 8562.544 | 7387.718 |
| Sum of all production (t·km−2·a−1) | 5725.961 | 7341.1 | 17,937.42 | 1974.82 | 2401.587 |
| Mean trophic level of the catch | 2.61 | 2.575 | 2.87 | 2.56 | 2.603 |
| Calculated total net primary production (t·km−2·a−1) | 5467.2 | 7058.526 | 17,703.42 | 1815.238 | 2038.080 |
| Total primary production/total respiration | 2.067322 | 4.348 | 13.53 | 2.189 | 2.548 |
| Total primary production/total biomass | 67.96619 | 109.472 | 137.92 | 3.509 | 15.592 |
| Total biomass/total throughput | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.060 | 0.018 |
| Total biomass (excluding detritus) (t·km−2) | 80.44 | 64.478 | 128.36 | 517.286 | 130.709 |
| Connectance index | 0.274 | 0.219 | 0.20 | 0.219 | 0.210 |
| System omnivory index | 0.217 | 0.1 | 0.092 | 0.189 | 0.067 |
| Finn’s cycling index (%) | 2.856 | 11.13 | 3.32 | 7.99 | 21.65 |
| Finn’s mean path length | 2.376 | 2.853 | 2.37 | 2.841 | 3.625 |
4. Discussion
4.1. Nutritional Structure and Overall Characteristics of the Dan Reservoir
4.2. Energy Transfer Efficiency of the Dan Reservoir
4.3. Strategies for Ecosystem-Based Management in the Dan Reservoir
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Polovina, J.J. Model of a coral reef ecosystem. Coral Reefs 1984, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, V.; Walters, C.J.; Pauly, D. Ecopath with Ecosim: A User’s Guide; University of British Columbia: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2005; Volume 12, 154p. [Google Scholar]
- Janjua, M.Y.; Tallman, R.F. A mass-balanced Ecopath model of Great Slave Lake to support an ecosystem approach to fisheries management: Preliminary Results. Can. Tech. Rep. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 3138, vi+32 p. [Google Scholar]
- Gorokhova, E.; Hansson, S.; Höglander, H.; Andersen, C.M. Stable isotopes show food web changes after invasion by the predatory cladoceran Cercopagis pengoi in a Baltic Sea bay. Oecologia 2005, 143, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faye, D.; Morais, T.D.; Raffray, J.; Sadio, O.; Thiaw, O.T.; Le Loc’h, F. Structure and seasonal variability of fish food webs in an estuarine tropical marine protected area (Senegal): Evidence from stable isotope analysis. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 92, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.; Matsuishi, T.; Arhonditsis, G. Elucidation of ecosystem attributes of an oligotrophic lake in Hokkaido, Japan, using Ecopath with Ecosim (EwE). Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Hu, M.H.; Liu, Q.G. Study on the feeding habits and trophic levels of the gillnet catches of Qiandao Lake in autumn by stable isotope technology. Shanghai Ocean Univ. 2014, 23, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.J.; Shi, X.H.; Wu, H.; Li, Y.L.; Li, X.X.; Chen, L.Q.; Liu, Q.G. Food Web Structure in Qingcaosha Reservoir of Shanghai, China. J. Hydroecol. 2019, 40, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Abobi, S.M. Fisheries Assessment and Trophic Modelling of Tono, Bontanga and Golinga Reservoirs, Ghana. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bremen, Bremen, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, V.; Pauly, D. ECOPATH II-a software for balancing steady-state ecosystem models and calculating network characteristics. Ecol. Model. 1992, 61, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnickson, D.; Chagaris, D.; Allen, M. Exploring Impacts of River Discharge on Forage Fish and Predators Using Ecopath With Ecosim. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 689950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W. Eco-environmental impact of inter-basin water transfer projects: A review. Environm. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 12867–12879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.W.; Gao, S.S.; Li, M.L.; Chen, Y.; Nicola, F.; Robert, C.; Li, Y.Y.; Chen, Z.J. Vertical Distribution Characteristics and Driving Factors of Bacterioplankton and Nitrogen Phosphorus Cycle Genes in Danjiangkou Reservoir. Environ. Sci. 2023, 1–17. Available online: https://link.oversea.cnki.net/doi/10.13227/j.hjkx.202307255 (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Pan, Y.D.; Guo, S.J.; Li, Y.Y.; Yin, W.; Qi, P.C.; Shi, J.W.; Hu, L.Q.; Li, B.; Bi, S.G.; Zhu, J.Y. Effects of water level increase on phytoplankton assemblages in a drinking water reservoir. Water 2018, 10, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.S.; Xiong, M.T.; Yin, Z.; Liu, J.S. Studies on the Fishery Fishing and Community Structure of Fish in the Danjiangkou Reservoir. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2018, 46, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, D.; Wang, G.T.; Xi, B.W.; Yao, W.J.; Nie, P. A New Species of Allocreadium (Trematoda: Allocreadiidae) from Freshwater Fishes in the Danjiangkou Reservoir in China. J. Parasitol. 2008, 94, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Xu, C.; Sun, Y.; Shi, L.; Zhou, L.; Jeppesen, E.; Chen, J.; Xie, P. Can the “10-year fishing ban” rescue biodiversity of the Yangtze River? Innovation 2022, 3, 100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Shao, M.L.; Cai, Q.H.; Xu, Y.Y.; Wang, L.; Kong, L.H. Macroinvertebrate community structure and the biological assessment to the water quality of the Danjiangkou Reservoir. J. Lake Sci. 2010, 22, 281–290. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.G. Aquatic Environmental Protection Oriented Fishery in Lake Qiandaohu and Its Influences on Lake Ecosystem; East China Normal University: Shanghai, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- McGregor, M.A. Using Ecopath Modeling to Describe Historical Conditions for a Large, Boreal Lake Ecosystem prior to European Settlement. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2014, 34, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Zhou, X.; Huang, L.; Zheng, X.; Du, J.; Yu, W.; Chen, G.; Hu, W.; Gao, S. The ecological functions and risks of expansive bivalve-macroalgae polyculture: A case study in Sansha Bay, China. Aquaculture 2022, 560, 738549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.F.; Xiao, X.Z.; Wang, Y.C.; Hu, S.; Wang, Y. Ecosystem structure and function of the main channel of the middle route of south-north water diversion project. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 5391–5402. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Zheng, Y.C.; Chang, J.B. Evaluation of the effect of stocking silver carp and bighead carp on the ecosystem of Qiandao Lake using Ecopath model. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 6853–6862. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, E.S.; Li, Y.K.; Zang, R.W.; Wang, H. A preliminary analysis of the ecosystem structure and functioning of Lake Chaohu based on Ecopath model. J. Fish. China 2014, 38, 417–425. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, P.Q.; Hu, Z.J.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Q.G. Quantitative analysis on the structure and function of the Gehu lake ecosystem based on ecopath model. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2010, 2, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, D.Y.; Yang, G.R. The feeding habits of six fierce fish species in Danjiangkou Reservoir. Reserv. Fish. 1992, 3, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ulanowicz, R.E. Ecosystem trophic foundations: Lindeman exonerate. In Evolution, Order and Complexity; Routledge: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Janjua, M.Y.; Gerdeaux, D. Preliminary trophic network analysis of subalpine Lake Annecy (France) using an Ecopath model. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2009, 2, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guo, C.B.; Chen, Y.S.; Li, W.; Xie, S.G.; Lek, S. Food web structure and ecosystem properties of the largest impounded lake along the eastern route of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Ecol. Inform. Int. J. Ecoinform. Comput. Ecol. 2018, 43, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.H.; Xu, D.P.; Ren, L.; Xu, P. Assessment of the ecological carrying capacity of silver and bighead carp in the Taihu Lake based on Ecopath model. J. Fish. Sci. China 2021, 28, 785–795. [Google Scholar]
- Odum, E.P. The Strategy of Ecosystem Development. Science 1969, 164, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulanowicz, R.E. Growth and Development:Ecosystems Phenomenology. Q. Rev. Biol. 1987, 62, 337–338. [Google Scholar]
- Han, R.; Chen, Q.; Wang, L.; Tang, X. Preliminary investigation on the changes in trophic structure and energy flow in the Yangtze estuary and adjacent coastal ecosystem due to the Three Gorges Reservoir. Ecol. Inform. 2016, 36, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Lenton, T.M.; Winder, M.; Sommer, U. Regime shifts in marine ecosystems: Detection, dynamics, and early warnings. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20130263. [Google Scholar]
- Hornborg, L.K.; Bouwman, A.F.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Slomp, C.P. Global environmental consequences of human modification of nitrogen and phosphorus flows through the Holocene. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 345–360. [Google Scholar]
- Garibaldi, L.; Dearing, J.A. Ecosystem-based fisheries management in a human-dominated world. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2016, 21, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, D.; Ulanowicz, R.E. The seasonal dynamics of an estuarine ecosystem: A network approach. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 194, 176–186. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, C.M.; Regaudie, D.; Cole, J.J. The role of aquatic vegetation in the coastal carbon sink. Ecology 2013, 94, 771–777. [Google Scholar]
- Post, E.; Pedersen, C.; Wilmers, C.C.; Forchhammer, M.C. Phenological responses to climate change in an Arctic ungulate. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 3003–3012. [Google Scholar]
- Halpern, B.S.; Frazier, M.; Potapenko, J.; Casey, K.S.; Koeve, W.; Longo, C.; Lowndes, J.S.; Rockwood, R.C.; Selig, E.R.; Selkoe, K.A.; et al. Spatial and temporal changes in cumulative human impacts on the world’s ocean. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, T. Ecosystem resilience and the role of energy cycling. Ecol. Complex. 2011, 8, 262–266. [Google Scholar]
- Ulanowicz, R.E.; Abarca-Arenas, L. An informational perspective on ecosystem development and health. Ecol. Model. 2017, 343, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.K.; Liu, E.S.; Wang, H.; Gong, Y. Analysis on the ecosystem structure and function of Lake Taihu based on Ecopath model. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 25, 2033–2040. [Google Scholar]
- Lun, F.; Zhou, B.X.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.X.; Li, Y.Y. Investigation of fish resources in Danjiangkou Reservoir in Henan province. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2016, 45, 150–155. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.P.; Huang, G.; Jiang, C.J.; Zhang, W.C.; Wang, Q.D.; Yao, L.G. Characteristics and historical changes of the fish assemblage in the Danjiangkou Reservoir. Biodivers. Sci. 2020, 28, 1202–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapanand, T.; Jutagatee, T.; Wongrat, P.; Lekcholayut, T.; Meksumpun, C.; Janekitkarn, S.; Rodloi, A.; Moreau, J.; Wongrat, L. Trophic relationships and ecosystem characteristics in a newly-impounded man-made lake in Thailand. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2009, 16, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, A.C.; Inger, R.; Bearhop, S.; Jackson, A.L.; Rands, S. Source Partitioning Using Stable Isotopes: Coping with Too Much Variation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panikkar, P.; Khan, M.F.; Desai, V.R.; Shrivastava, N.P.; Sharma, A.P. Characterizing trophic interactions of a catfish dominated tropical reservoir ecosystem to assess the effects of management practices. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2015, 98, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, S.E.; Patten, B.C.; Straškraba, M. Ecosystems emerging: 4. growth. Ecol. Model. 2000, 126, 249–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Huang, Y.B.; Wang, B.L.; Mi, W.J.; Song, Q.Y.; Xu, Y.Z.; Bi, Y.H. The analysis of food web structure in the area in front of the Three Gorges Dam using the stable isotope technology. Ecol. Sci. 2020, 39, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Loáiciga, H.A.; Du, Y. Opportunities and challenges of interbasin water transfer: A literature review with bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics 2015, 105, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Code | Functional Group | Main Species Composition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CulT | Culters | Culter alburnus, Chanodichthys mongolicus, Chanodichthys erythropterus, Chanodichthys dabryi, Culter oxycephaloides |
| 2 | SinF | Sinipercine fish | Siniperca chuatsi, Siniperca kneri |
| 3 | YelC | Yellow catfish | Tachysurus fulvidraco, Tachysurus vachellii |
| 4 | IntE | Intermittent | Hyporhamphus intermedius |
| 5 | ShaP | Sharpbelly | Hemiculter leucisculus, Hemiculter bleekeri |
| 6 | MinN | Minnows | Saurogobio dabryi, Squalidus argentatus |
| 7 | ComC | Common carp | Cyprinus carpio |
| 8 | AchM | Acheilognathus macropterus | Acheilognathus macropterus |
| 9 | CruC | Crucian carp | Carassius auratus |
| 10 | SilC | Silver carp | Hypophthalmichthys molitrix |
| 11 | BigC | Bighead carp | Hypophthalmichthys nobilis |
| 12 | GraC | Grass carp | Ctenopharyngodon idella |
| 13 | OthF | Other fish | Sinobdella sinensis, Rhinogobius giurinus, Protosalanx hyalocranius, Neosalanx tangkahkeii, Sarcocheilichthys nigripinnis, Labeo rohita, Pseudorasbora parva, Pseudolaubuca sinensis, Microphysogobio microstomus, Rhodeus sinensis, Abbottina rivularis, Opsariichthys macrolepis, Cobitis sinensis, Pseudobrama simoni, Sinibrama macrops, Misgurnus anguillicaudatus, Paramisgurnus dabryanus, Acheilognathus rhombeus, Channa argus, Silurus meridionalis |
| 14 | ShrI | Shrimp | Macrobrachium nipponense |
| 15 | ZooB | Zoobenthos | Bellamya aeruginosa, Cristaria plicata, Chironomid, Limnodrilus |
| 16 | ZooP | Zooplankton | Zooplankton |
| 17 | PhyT | Phytoplankton | Phytoplankton |
| 18 | DetR | Detritus | Organic detritus |
| Prey | Predator | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | |
| CulT | 0.009 | |||||||||||||||
| SinF | 0.001 | |||||||||||||||
| YelC | 0.001 | |||||||||||||||
| IntE | 0.056 | |||||||||||||||
| ShaP | 0.204 | 0.01 | ||||||||||||||
| MinN | 0.001 | |||||||||||||||
| ComC | 0.197 | 0.211 | ||||||||||||||
| AchM | 0.07 | 0.037 | ||||||||||||||
| CruC | 0.091 | 0.15 | 0.068 | |||||||||||||
| SilC | 0.12 | 0.217 | 0.125 | |||||||||||||
| BigC | 0.192 | 0.168 | ||||||||||||||
| GraC | 0.13 | |||||||||||||||
| OthF | 0.014 | |||||||||||||||
| ShrI | 0.061 | 0.201 | 0.124 | 0.164 | 0.05 | 0.031 | 0.205 | 0.133 | ||||||||
| ZooB | 0.215 | 0.131 | 0.102 | 0.329 | 0.245 | 0.21 | 0.2 | 0.109 | 0.158 | |||||||
| ZooP | 0.069 | 0.322 | 0.232 | 0.135 | 0.271 | 0.154 | 0.175 | 0.172 | 0.377 | 0.435 | 0.106 | 0.1 | 0.269 | |||
| PhyT | 0.024 | 0.182 | 0.318 | 0.106 | 0.168 | 0.276 | 0.146 | 0.107 | 0.586 | 0.247 | 0.391 | 0.392 | 0.306 | 0.735 | ||
| DetR | 0.234 | 0.365 | 0.348 | 0.266 | 0.266 | 0.329 | 0.274 | 0.479 | 0.037 | 0.318 | 0.503 | 0.35 | 0.425 | 0.265 | ||
| Groups | Trophic Level | B (t/km2) | P/B (1/a) | Q/B (1/a) | EE | P/Q |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CulT | 3.50 | 1.10 | 0.98 | 3.35 | 0.83 | 0.29 |
| SinF | 3.49 | 0.09 | 1.06 | 3.87 | 0.81 | 0.27 |
| YelC | 3.01 | 0.41 | 1.01 | 4.62 | 0.73 | 0.22 |
| IntE | 2.49 | 0.60 | 1.48 | 5.33 | 0.77 | 0.28 |
| ShaP | 2.36 | 2.36 | 1.14 | 7.45 | 0.87 | 0.15 |
| MinN | 2.77 | 0.32 | 1.29 | 5.11 | 0.79 | 0.25 |
| ComC | 2.65 | 2.13 | 1.34 | 6.20 | 0.76 | 0.22 |
| AchM | 2.46 | 0.97 | 1.03 | 5.73 | 0.67 | 0.18 |
| CruC | 2.70 | 0.90 | 1.16 | 4.56 | 0.79 | 0.25 |
| SilC | 2.48 | 1.59 | 1.21 | 8.70 | 0.77 | 0.14 |
| BigC | 2.38 | 1.46 | 2.03 | 9.10 | 0.80 | 0.22 |
| GraC | 2.44 | 1.27 | 2.09 | 10.20 | 0.85 | 0.20 |
| OthF | 2.11 | 0.20 | 1.55 | 10.12 | 0.70 | 0.15 |
| ShrI | 2.30 | 2.85 | 3.40 | 12.56 | 0.74 | 0.27 |
| ZooB | 2.27 | 4.26 | 4.14 | 75.00 | 0.82 | 0.06 |
| ZooP | 2.00 | 14.13 | 15.00 | 200.00 | 0.89 | 0.08 |
| PhyT | 1.00 | 45.56 | 120.00 | 0.42 | ||
| DetR | 1.00 | 47.43 | 0.28 |
| Trophic Level | Import | Export | Consumption by Predators | Flow to Detritus | Total Throughput |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VI | 0.00531 | 0.000775 | 0.000000 | 0.00464 | 0.0107 |
| V | 0.205 | 0.0176 | 0.0107 | 0.147 | 0.381 |
| IV | 3.745 | 0.266 | 0.381 | 2.353 | 6.745 |
| III | 165.8 | 2.177 | 6.745 | 50.84 | 225.6 |
| II | 2475 | 3.068 | 225.6 | 693.0 | 3396 |
| I | 0.000 | 2817 | 3396 | 3146 | 9359 |
| Total | 2645 | 2823 | 3629 | 3892 | 12,988 |
| Source | Trophic Level | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II | III | IV | V | VI | |
| Producer | 7.003 | 3.744 | 9.220 | 6.278 | 5.362 |
| Detritus | 6.145 | 4.394 | 8.612 | 6.174 | 5.364 |
| Total flow | 6.732 | 3.930 | 9.030 | 6.248 | 5.363 |
| From detritus | 39% | ||||
| Ecosystem | 6.205% | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Gu, K.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Duan, J.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Q. Food Web Structure and Ecosystem Functions of the Water Source in the Middle Route of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Fishes 2024, 9, 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9060202
Zhang Y, Gu K, Wang X, Zhang J, Duan J, Hu Z, Liu Q. Food Web Structure and Ecosystem Functions of the Water Source in the Middle Route of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Fishes. 2024; 9(6):202. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9060202
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuanyuan, Kaidi Gu, Xinyu Wang, Ji’ao Zhang, Jiaoyang Duan, Zhongjun Hu, and Qigen Liu. 2024. "Food Web Structure and Ecosystem Functions of the Water Source in the Middle Route of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project" Fishes 9, no. 6: 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9060202
APA StyleZhang, Y., Gu, K., Wang, X., Zhang, J., Duan, J., Hu, Z., & Liu, Q. (2024). Food Web Structure and Ecosystem Functions of the Water Source in the Middle Route of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Fishes, 9(6), 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9060202






