Abstract
The distribution of fish eggs and larvae (ichthyoplankton) reflects spawning and nursery areas as well as dispersal routes. This study’s goal is to demonstrate how the identification of ichthyoplankton species and stages and their spatial distribution among natural reefs (NRs) and artificial reefs (ARs) may serve as decision-making tools in conservation and fishery management. Natural reefs exhibited an eight-times higher abundance of eggs, as well as the highest abundance of larvae in the yolk-sac and preflexion phases. In contrast, ARs had the highest abundance of larvae in the flexion and postflexion phases. Natural reefs may serve as breeding grounds for Scaridae, Labridae, and Mugilidae; whereas, ARs may serve as breeding sites for Lutjanidae, Synodontidae, Carangidae, Fistularidae, and Haemulidae. Our study revealed differences between ARs and NRs, which demonstrate the potential of artificial reefs to expand the supply and settlement options of reef fishes and consequently can lead to increased fish production with potential benefits to adjacent fishing areas through connectivity. Thus, ARs as no-take sites can be effective tools for both fishery management and biodiversity conservation. The findings highlight the potential use of ichthyoplankton tools and the importance of considering both types of reefs in marine conservation and management efforts.
Keywords:
fish eggs and larvae; Gulf of California; spawning areas; shipwrecks; marine protected area Key Contribution:
Natural reefs may serve as breeding grounds for Scaridae, Labridae, and Mugilidae; whereas, ARs may serve as breeding sites for Lutjanidae, Synodontidae, Carangidae, Fistularidae, and Haemulidae. Our study revealed differences between ARs and NRs, which demonstrate the potential of artificial reefs to expand the supply and settlement options of reef fishes and consequently can lead to increased fish production with potential benefits to adjacent fishing areas through connectivity.
1. Introduction
Dispersal stages (e.g., the egg and larval stages) may have significant effects on the life cycle dynamics and ecology of reef fish populations, including economically important species [1,2,3,4,5,6].
Since the eggs and larvae (ichthyoplankton) of most marine fishes are found in the epipelagic zone, it was assumed that the ocean dynamics and the planktonic phase duration determine the dispersion distance (passive dispersal) [7,8]. Nevertheless, recent observations highlight the synchronization between spawning processes and hydrographic mesoscale structures (e.g., fronts and eddies) that can retain eggs and larvae or transport them to favorable sites and consequently may determine recruitment success by decreasing the random distribution of eggs and larvae [9,10,11]. Beyond flow patterns, the distribution and abundance of ichthyoplankton are primarily influenced by the distribution, abundance, and fecundity of the reproductive stocks [12,13,14], reflecting the spawning and nursery areas of the species, along with their dispersal routes [15,16,17].
Previous studies have shown that the distribution of fish eggs and larvae may vary depending on their developmental stages [16,18,19,20]. A high abundance of fish eggs and yolk-sac larvae is interpreted as an outcome of the production (biomass) of relevant reefs (natural and artificial reefs) [21,22,23,24,25]. A high presence of preflexion and flexion larvae cooccurring in areas with a high zooplankton concentration may indicate a favorable feeding habitat [26,27,28], whereas late postflexion larvae may indicate successful recruitment outcomes [15,29,30]. Therefore, the reliable identification of the early life stages of fish according to their different developmental stages and spatial distributions may reflect critical sites for the species ecology and, therefore, may be essential for the protection of the breeding and nursery areas of reef fish species [5,23].
The establishment of ARs can increase resource availability, provide protection from predation, and serve as breeding grounds for diverse fish species [23]. Recent analyses suggest artificial reefs may have aggregation and refugia effects on ichthyoplankton [22,23,24,25] and have shown high similarity in dominant species composition with natural reefs [31,32]. However, despite the apparent benefits of artificial reefs and their potential role as productive marine habitats, it remains difficult to determine the contribution of these new habitats to fish production within the relevant ecosystem’s range and in a conservation context.
The ongoing debate between “attraction” and “production” examines whether fish are primarily attracted to the new structure or whether artificial reefs increase fish production [33,34,35]. Quantifying egg production can serve as an initial step in assessing the potential for recruitment subsidies [5]. If artificial structures produce additional fish, reef deployment could help increase fishery yields. Conversely, if they function just as fish attractors, artificial reefs could inadvertently facilitate overexploitation by simplifying extraction for fishers [35,36,37,38].
Understanding the dual attraction versus production roles of artificial reefs is essential for their effective management as well as their role as potential conservation and restoration tools [39,40]. The role of ARs in affecting the distribution of the early stages of fish and their contribution to biomass production in the Gulf of California remain unknown.
The overall goal of this study is to identify the different developmental stages of ichthyoplankton (eggs and larvae) and compare their richness and abundance among artificial and natural reefs on the Espiritu Santo Archipelago (ESA) throughout an annual cycle. The differences in richness and abundance between natural and artificial reefs are expected to indicate the main spawning and favorable recruitment areas of fish species; that is, if ARs do indeed present favorable conditions for reproduction, it is reasonable to assume newly produced individuals will settle on the artificial reefs, contributing to biomass production. This study’s findings can provide valuable insights for conservation and fishery management, particularly in the context of marine protected area (MPA) planning.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Taking into account that we do not consider a record of adult fish, the present study was conducted on four natural reefs and four artificial reefs in the Espiritu Santo Archipelago, southern Gulf of California (Figure 1). The natural reefs include La Ballena, a large islet with a shallow rocky reef (7 m), El Gallo with coral patches on a rocky slope (9 m), El Corralito with corals on a vertical wall (17 m), and Swany Rock with coral communities at 12 m depth. The artificial reefs in the area are the Lapas 03 and Fang Ming shipwrecks deployed intentionally at 18 m and 20 m depths, respectively, in 1999; the Gunner C–59 wreck deployed at 20 m depth in 2004; and the Salvatierra wreck at 22 m depth, which sank in 1975. Four field surveys were conducted at each study site, covering an annual cycle: (1) September 2018 (warm season), (2) December 2018 (cold season), (3) March 2019 (cold season), and (4) June 2014 (warm season).
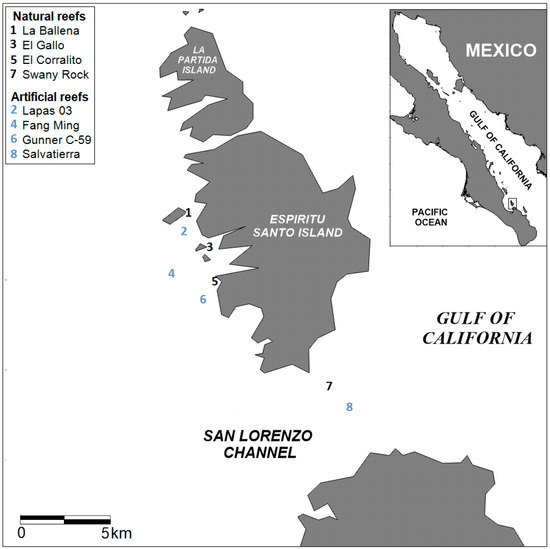
Figure 1.
The Espiritu Santo Archipelago (ESA) area with its natural and artificial reef sites (enlarged): (1) Ballena Island (partially protected area); (2) Lapas 03 wreck (no-take area); (3) El Gallo (partially protected area); (4) Fang Ming wreck (no-take area); (5) El Corralito (partially protected area); (6) Gunner C—59 Francisco Márquez (no-take area); (7) Swany Rock (partially protected area); (8) Salvatierra wreck (unprotected area).
2.2. Sampling Procedure In Situ
The ichthyoplankton samples were collected using a 2.5 m long conical net of a 333 µm mesh size attached to a 0.60 m diameter ring equipped with a flowmeter in the center to estimate the volume of filtered water. The horizontal tows were carried out on the sea’s surface with a circular path for 5 min each. All zooplankton samples were deposited in 250 mL plastic containers labeled with reference information and the geographic location and immediately fixed with 4% formalin buffered with borax (sodium borate). Temperature and salinity were taken after each sampling with a CastAway CTD.
2.3. Sampling Procedure in Laboratory
The zooplankton biomass was determined by the displacement volume method [41], excluding organisms whose individual volume exceeds 5 mL (e.g., juvenile fish, jellyfish, and siphonophores), and standardized to mL/1000 m3 of filtered water. The ichthyoplankton (eggs and fish larvae) was separated from the unfractionated samples using a stereo microscope and preserved with 4% formalin buffered with borax. The identification of eggs and larvae was carried out following the diagnostic characteristics established for each individual species [42,43,44,45]. Species without formal description were identified based on the scientific collection of eggs and fish larvae from the Mexican Pacific at the Interdisciplinary Center of Marine Sciences, National Polytechnic Institute (CICIMAR–IPN).
2.4. Breeding Habitat for Reef Fish
To surmise the fish species, the study reefs were used as breeding grounds, and fish eggs were quantified based on 11 stages of embryonic development [46]: early development (stages 1–5), medium development (stages 6–8), and late development (9–11). Fish larvae were classified according to the development of the notochord in stages of yolk-sac, pre-flexion, flexion, and post-flexion [47,48]. In order to compare the abundance across the reefs and months of the study, eggs and larval abundances were standardized to the number of eggs/larvae per 100 m
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The ichthyoplankton (eggs and fish larvae) community was characterized in terms of species richness (S) and abundance (N) and was further assessed using the Euclidean distance (Log(x + 1) data transformation) and multivariate ordination. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test (D) was used to examine the assumption of normality for the fish species abundance (Log(x + 1) transformed data). Multivariate non-metric multidimensional scaling ordination (nMDS) was used to compare fish assemblages (individual species abundance) between the natural and artificial reefs and between the seasons (warm and cold) of the study, which were tested for significance using a t-test. The nMDS analysis represents the samples as points in a low-dimensional space (2D and 3D). SIMPER analysis was performed to determine the average similarity and dissimilarity within and between the reefs and seasons of the study. The variability among samples (fish censuses) within each reef type and season of the study was compared with the MVDISP routine [49,50].
3. Results
3.1. Egg and Larva Distribution
A total of 106 taxa were recorded, of which 56 were identified at the species level, 24 at the genus level, 18 at the family level, 3 at the order level, and 5 were not identified (4 eggs and 1 larva). Of the total number of species recorded, 52 species were recorded in the egg stage (Table S1), and 79 species were recorded in the larval stage (Table S2); only 24 taxa were recorded in both developmental stages (eggs and larvae).
The same numbers of fish species in the egg stage were recorded in the natural and artificial reefs (44), of which 8 species were only in the natural reefs and 8 species were only in the artificial reefs (exclusive species), whereas the egg abundance was eight times higher in the natural reefs than in the artificial reefs, and the abundance was normally distributed (abundance, D = 0.045, p = 0.798).
In the egg stage, six species, Thalassoma lucasanum, Auxis rochei, Prionotus stephanophrys, Fistularia comersonii, Anisotremus davidsonni, and Harengula thrissina, were dominant in both reef types. Species of the family Scaridae, Labridae, and Mugilidae presented their highest abundances in the natural reefs, whereas 28 species were more abundant in the artificial reefs than in the natural reefs, including species of the families Haemulidae, Lutjanidae, Carangidae, Fistularidae, and Synodontidae.
In the larval stage, the highest number of species was recorded in the natural reefs, with 62 larval species, of which 21 were exclusive. In the artificial reefs, 47 larval species were recorded, of which 10 species were exclusive. The abundance of larvae in the natural reefs was 1.6 times higher than in the artificial reefs. The most abundant species in the natural reefs were Abudefduf troschelii, Labrisomidae sp. 1, Auxis rochei, and Diapterus peruvianus. However, the larvae of 30 species were more abundant in the artificial reefs, particularly Harengula thrissina and Benthosema panamense.
The Simper analysis recorded a dissimilarity between the two reef types of 77.80%; the species that contributed the most to this dissimilarity are Thalassoma lucasanum, Prionotus stephanophrys, Vinciguerria lucetia, Fistularia corneta, Scomber japonicus, and Benthosema panamense (Table 1). Nevertheless, there were no significant differences in the community composition of the icthyoplankton between the natural and artificial reefs (reef type, df = 15, t = 1.7, p = 0.099; Figure 2).

Table 1.
SIMPER (similarity/dissimilarity) and MVDISP (dispersion) values within and between the reefs (natural vs. artificial) and seasons (warm vs. cold) of the study. Higher values of dissimilarity indicate lower similarity between the samples. Higher values of multivariate dispersion indicate more variability among fish samples within each sample.
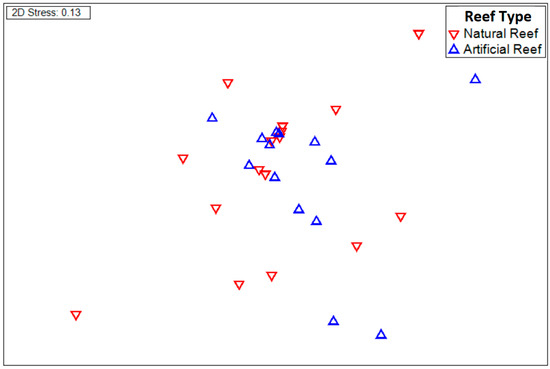
Figure 2.
nMDS plot of the 32 ichthyoplankton samples of the different study sites, based on species abundances by reef type (natural reefs and artificial reefs).
3.2. Egg Development Stage
Of the total number of eggs recorded in the study, 90.8% were in the early development stage, 5.6% in the medium development stage, and 3.6% in the late development stage. The highest number of eggs in the early development stage was recorded in the natural reefs (95% of the total). However, the highest abundance of medium (69.1%) and late (76.9%) stages was recorded in the artificial reefs.
The most abundant species in the early development stage were T. lucasamun, Halichoeres sp. 1, Prionotus stephanophrys, and F. comersonii. The most abundant species in the medium development stage were Auxis rochei, Harengula thrissina, Antennarius sp. 1, P. stephanophrys (only in the natural reefs), and Halichoeres sp. 1 (only in the artificial reefs). The most abundant species in the late stage were H. thrissina, Anisotremus davidsonni, P. stephanophrys (only in the natural reefs), and Auxis rochei (only in the artificial reefs). The artificial reefs presented a higher richness and abundance of eggs of the Lutjanidae and Synodontidae families. The Lutjanidae family was almost 7 times (6.8) more abundant in the artificial reefs compared to the natural reefs (mainly in the early development stage); however, the larval stage was absent at all the sampling sites. In contrast, 100% of the recorded ichthyoplankton from the Scaridae family corresponded to the early development stage, and 97.7% was recorded in the natural reefs.
Of the total larvae recorded, 12.6% were in the yolk-sac stage, 80.3% were in the preflexion stage, 6.4% were in the flexion stage, and 0.7% were in the postflexion stage. The natural reefs had the highest abundance of larvae in the yolk-sac and preflexion phases, while the artificial reefs had the highest abundance of larvae in the flexion and postflexion phases.
In the natural reefs, the most abundant yolk-sac larvae were Auxis rochei, Cirrhitichyhys oxicephalus, and Anisotremus davidsoni. In the artificial reefs, the most abundant yolk-sac larvae were Harengula thrissina, Auxis rochei, and Halichoeres sp. 1. Moreover, in the artificial reefs, species of the Carangidae, Mugilidae, Fistularidae, and Haemulidae families were most abundant in the three stages of egg development and in the first larval stage (yolk-sac).
In both reef types, Abudefduf troschelii was the most abundant larval species in the preflexion stage. Other abundant preflexion larvae species in the natural reefs were Labrisomidae sp. 1 and Pseudopeneus grandiscuamis. In the artificial reefs, Harengula thrissina and Benthosema panamense were also abundant in the preflexion stage.
In the natural reefs, nine species were recorded in the flexion stage; the most abundant were Diapterus peruvianus and Vinciguerria lucetia. In the artificial reefs, 17 species of larvae were recorded in the flexion stage; the most abundant were Labrisomidae sp. 1 and Vinciguerria lucetia. Caranx caballus presented a higher abundance in the flexion stage in the artificial reefs, while this stage was absent in the natural reefs.
Only four species were recorded in the postflexion larval stage; two species were present in the natural reefs (Hyporhamphus rosae and Oxyporhamphus micropterus) and three in the artificial reefs (Hemiramphus saltator, Hyporhamphus rosae, Hypsoblennius gentilis). The four species presented the same abundance, and none of the species were recorded at any other stage of development (neither in eggs nor larvae).
3.3. Seasonality (Warm Season vs. Cold Season)
Of the 106 taxa recorded, only 29 species were present in both seasons. During the warm season, 81 fish species were recorded, of which 52 were exclusive to that season. On the other hand, 48 species were recorded during the cold season, of which 20 were exclusive. The highest abundance (96.2%) was observed in the warm season, while only 3.8% of the abundance was recorded in the cold season.
A total of 69 species were more abundant in the warm season, while 28 species were more abundant in the cold season. Thalassoma lucasanum and Prionotus stephanophrys were abundant in both seasons of the study. Other abundant species in the warm season were Auxis rochei, Harengula thrissina, Fistularia comersonii, Anisotremus davidsonni, and Abudefduf troschelii. The most abundant species in the cold season were Fistularia corneta, Diodon holocanthus, Benthosema panamense, Vinciguerria lucetia, and Auxis thazard.
The Simper analysis recorded a dissimilarity between the two seasons of 88.91%. The species that contributed the most to this dissimilarity are Thalassoma lucasanum, Prionotus stephanophrys, Fistularia comersonii, Harengula thrissina, and Auxis rochei (Table 1). The non-metric multidimensional scaling ordination clearly separated the fish samples by season (Figure 3), with a higher observable dispersion among the samples belonging to the warm season compared to the cold season. Significant differences were found in the community composition between the warm and cold seasons (season, df = 15, t = 5.37, p < 0.001; Figure 3).
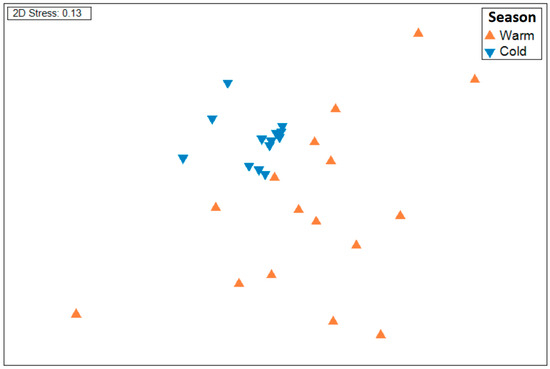
Figure 3.
nMDS plot of the 32 samples of the study based on species abundances by season (warm and cold).
4. Discussion
The reliable identification of reef fish’s early life stages is essential for the sound protection of their breeding and nursery sites [51]. However, the limited number of morphological characteristics and the high similarities between the different species during their early development make the identification of ichthyoplankton species challenging [52,53]. Consequently, few attempts have been made to study the dynamics of dispersal stages and their spatial distribution in ARs and MPA planning and siting. In the present study, we successfully identified the ichthyoplankton of the samples at both genus and species levels, which represents a significant contribution to filling the gap in addressing these challenges, particularly within the applied knowledge of artificial reefs.
Since the reproductive activities of fish determine the presence and distribution of their early developmental stages [16,53,54], the predominance of the egg stage (mainly early development) and yolk sac larvae in the ichthyoplankton samples implies that the studied reefs may serve as spawning grounds for various reef species [21,22,23,24,25]. Although the dominant ichthyoplankton species in both the natural and artificial reefs were nearly identical, supporting the hypothesis that a mimicking of fish communities may occur when artificial reefs are closer to natural reefs [40], the ichthyoplankton community assemblages varied at the species level. The differences suggest that the natural reefs in the ESA may serve as breeding grounds for species of the families Scaridae, Labridae, and Mugilidae, whereas the ARs may serve as breeding grounds for the families Lutjanidae, Synodontidae, Carangidae, Fistularidae, and Haemulidae, which indicates the potential of these novel habitats to expand spawning grounds and fish production in the Espiritu Santo Archipelago. This further contribution of the ARs could benefit adjacent fishing grounds through connectivity via the export of eggs and larvae (recruitment subsidies) [55,56], a phenomenon recorded in other artificial reefs around the world [23,57,58]. In addition, the present study highlights the potential attraction effect of artificial reefs on fish larvae, with special attention being paid to mesopelagic species like Benthosema panamense and pelagic species like Cetengraulis mysticetus and Hemiramphus saltator, which do not tend to naturally reside in reef areas.
The presence of almost all the developmental stages (from early-stage eggs to postflexion larvae) in the artificial reefs of the ESA suggests that they exhibit some aggregation effects, which may provide refuge for late stages of development, including contributions to the successful self-seeded recruitments of new generations. It has been shown that in situations where artificial reefs offer favorable conditions for reproduction, young recruits prefer to settle in artificial reefs rather than disperse in search of other natural habitats [58]; that is, the arrival of fish larvae to a suitable habitat may involve more than just physical dispersal processes [59,60]. This may be explained by the relatively strong swimming capabilities of species in the flexion and postflexion stages and their reliance on a range of environmental cues to respond to in order to eventually settle in reef habitats suitable in terms of food availability, reduced competition, and lower predation risk [61,62,63].
The results also indicate that, as fish development progresses, ichthyoplankton abundance decreases. This is an expected phenomenon due to the low survival rates during the early developmental stages, especially due to the fact that once the larvae have fully utilized the vitelline reserve, they rely on planktonic food, which is often scarce and could lead to starvation. This is a phase in fish life history that emphasizes the importance of survival beyond the preflexion stage [64,65].
The variations in abundance and species composition between the warm and cold seasons suggest that the assemblages of ichthyoplankton species are related to the alternating reproductive periods and mesoscale flow events in the Southern Gulf of California [66,67]. During the warm season, the Mexican Coastal Current intensifies, transporting warm water into the Gulf of California, raising the sea surface temperature [68,69], and providing favorable conditions for the reproduction of species of families like Labrids, Scarids, Pomacentrids, Haemulids, Mugilids, and others that live in shallow waters with a tropical and/or subtropical affinity for the Bay of La Paz [70,71].
Additionally, in the warm season, a strong synchronization of fish spawning has been observed with the formation of anticyclonic eddies in the northern part of La Paz Bay that transport eggs and larvae of oceanic and mesopelagic species like Auxis rochei, Etrumeus acuminatus, and Vinciguerria lucetia from the Gulf of California to favorable sites (for development) in La Paz Bay, influencing recruitment success and decreasing the random distribution of larvae [72,73,74]. In contrast, during the cold season when geostrophic current velocities in the northern entrance of La Paz Bay are weak [75], larvae of species like Fistularia corneta, Diodon holocanthus, and Benthosema panamense extend over a large part of the bay.
The results show a patchy distribution of ichthyoplankton with a clear spatial distribution characteristic for both the ARs and NRs in the studied area, suggesting that ARs, as no-take sites, can be an effective tool for both fishery management and biodiversity conservation [25,76]. However, to ensure that ARs indeed enhance productivity, further research is needed, specifically extended temporal and spatial (different depths) sampling, which will provide a comprehensive and more reliable layout of the long-term distribution patterns. These efforts will contribute to our understanding of the impact of ARs on local and regional productivity and their overall ecological role as management tools.
5. Conclusions
In the present study, we report the first preliminary characterization of the larval fish assemblage in the ARs deployed in the marine protected area of the Espiritu Santo Archipelago. The predominant occurrence of fish in the early developmental stages, such as eggs and yolk sac larvae, may indicate that the studied reefs serve as key spawning grounds for various reef fish species.
While the dominant species in the natural and artificial reef areas were similar, differences in the community structure and spatial distribution of the ichthyoplankton abundance suggest distinct spawning areas for different species. The artificial reefs in the Espiritu Santo Archipelago function as breeding sites for specific fish families, providing evidence of the potential of this new habitat type to expand spawning grounds, leading to increased fish production and potential benefits for adjacent fishing areas through the export of eggs and larvae.
Additionally, the presence of various developmental stages in the artificial reefs suggests successful recruitment, as newly produced individuals prefer settling in these reefs, indicating their role in supporting the successful development of a new generation of fish. This research exhibits the complex dynamics of ichthyoplankton in natural and artificial reefs, providing preliminary valuable information on the distribution, abundance, and developmental stages of several reef fish species. Although further research is needed, the findings highlight the importance of considering both types of reefs in marine conservation and management efforts.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fishes9050166/s1, Table S1: Total fish egg abundance (number of larvae per 100 m−3) present over the reefs and seasons of the study; Table S2: Total fish larvae abundance (number of larvae per 100 m−3) present over the reefs and seasons of the study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.A.S.-C. and J.M.B.-S.; methodology, C.A.S.-C. and R.J.S.-M.; formal analysis, C.A.S.-C. and R.J.S.-M.; investigation, C.A.S.-C.; resources, J.M.B.-S. and A.A.; data curation, C.A.S.-C. and R.J.S.-M.; writing—original draft preparation, C.A.S.-C.; writing—review and editing, A.A. and J.M.B.-S.; supervision, A.A.; project administration, A.A.; funding acquisition, J.M.B.-S. and A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Prince Albert II of Monaco Foundation, and the Explorers Club Grant (OceanX Grant) provided financial support.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Leis, J.M. What does larval fish biology tell us about the design and efficacy of Marine Protected Areas. In Aquatic Protected Areas: What Works Best and How Do We Know, Proceedings of the World Congress on Aquatic Protected Areas, Cairns, Australia; Australian Society for Fish Biology: Newcastle, Australia, 2003; pp. 170–180. [Google Scholar]
- Félix-Hackradt, F.C.; Hackradt, C.W.; Treviño-Otón, J.; Segovia-Viadero, M.; Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; García-Charton, J.A. Environmental determinants on fish post-larval distribution in coastal areas of south-western Mediterranean Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 129, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.L.; Maypa, A.P.; Almany, G.R.; Rhodes, K.L.; Weeks, R.; Abesamis, R.A.; Gleason, M.G.; Mumby, P.J.; White, A.T. Larval dispersal and movement patterns of coral reef fishes, and implications for marine reserve network design. Biol. Rev. 2015, 90, 1215–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.D.; Possingham, H.P.; Muelbert, J.H. Incorporating early life stages of fishes into estuarine spatial conservation planning. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2016, 26, 1013–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, A.B.; Davies, C.R.; Emslie, M.J.; Mapstone, B.D.; Russ, G.R.; Tobin, A.J.; Williams, A.J. Reproductive benefits of no-take marine reserves vary with region for an exploited coral reef fish. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Liu, B. Life History and Early Development of Fishes. In Biology of Fishery Resources; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortier, L.; Leggett, W.C. Fickian Transport and the Dispersal of Fish Larvae in Estuaries. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1982, 39, 1150–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norcross, B.L.; Shaw, R.F. Oceanic and estuarine transport of fish eggs and larvae: A review. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1984, 113, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattrick, P.; Weidberg, N.; Goschen, W.S.; Jackson, J.M.; McQuaid, C.D.; Porri, F. Larval fish assemblage structure at coastal fronts and the influence of environmental variability. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 347, 684502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Counsell, C.W.W.; Coleman, R.R.; Lal, S.S.; Bowen, B.W.; Franklin, E.C.; Neuheimer, A.B.; Powell, B.; Toonen, R.; Donahue, M.; Hixon, M.; et al. Interdisciplinary analysis of larval dispersal for a coral reef fish: Opening the black box. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2022, 684, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés-Rodríguez, Y.; Sánchez-Velasco, L.; Parés-Sierra, A.; Jiménez-Rosenberg, S.P.A.; Tenorio-Fernández, L.; Montes-Aréchiga, J.; Godínez-Sandoval, V. Distribution and transport of Fish larvae at the entrance of the Gulf of California (September, 2016). Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2022, 193, 103957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Witthames, P.R. Developments in understanding of fecundity of fish stocks in relation to egg production methods for estimating spawning stock biomass. Fish. Res. 2012, 117, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stige, L.C.; Yaragina, N.A.; Langangen, Ø.; Bogstad, B.; Stenseth, N.C.; Ottersen, G. Effect of a fish stock’s demographic structure on offspring survival and sensitivity to climate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowerre-Barbieri, S.K. Reproduction in relation to conservation and exploitation of marine fishes. In Reproductive Biology and Phylogeny of Fishes (Agnathans and Bony Fishes); CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 371–394. [Google Scholar]
- Somarakis, S.; Tsoukali, S.; Giannoulaki, M.; Schismenou, E.; Nikolioudakis, N. Spawning stock, egg production and larval survival in relation to small pelagic fish recruitment. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 617, 113–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceves-Medina, G.; Emilio, A.; Inda-Díaz, O.; Ubisha-Hernández, A.; Álvarez-Ramírez, I. Review of some aspects of the early life history of marine fish and their implications in the biogeographic distribution. CICIMAR Ocean 2020, 35, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Mitterwallner, P.; Shima, J.S. The relative influence of environmental cues on reproductive allocation of a highly iteroparous coral reef fish. Coral Reefs 2022, 41, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, P.L. Aggregation Spawning: Biological Aspects of the Early Life History. In Reef Fish Spawning Aggregations: Biology, Research and Management; Sadovy de Mitcheson, Y., Colin, P., Eds.; Fish & Fisheries Series; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamner, W.M.; Largier, J.L. Oceanography of the planktonic stages of aggregation spawning reef fishes. In Reef Fish Spawning Aggregations: Biology, Research and Management; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 159–190. [Google Scholar]
- Teodosio, M.A.; Paris, C.B.; Wolanski, E.; Morais, P. Biophysical processes leading to the ingress of temperate fish larvae into estuarine nursery areas: A review. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 183, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, J., Jr.; Pondella, D. Larval productivity of a mature artificial reef: The ichthyoplankton of King Harbor, California, 1974–1997. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2002, 59, S51–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, M.M.; Simons, R.D.; Love, M.S. Offshore oil production platforms as potential sources of larvae to coastal shelf regions off southern California. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2019, 95, 535–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegretti, C.B.; Grande, H.; Namiki, C.A.P.; Loose, R.H.; Brandini, F.P. A Preliminary assessment of larval fish assemblages on artificial reefs in the nearshore Southern Brazil. Ocean Coast. Res. 2021, 69, e21017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, H.; Yu, D.; Song, J.; Duan, G. The migration of viscous fish eggs in artificial reefs. Ecol. Model. 2022, 469, 109985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraufvelin, P.; Bergström, L.; Sundqvist, F.; Ulmestrand, M.; Wennhage, H.; Wikström, A.; Bergström, U. Rapid re-establishment of top-down control at a no-take artificial reef. Ambio 2022, 52, 556–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, T.; Olivar, M.P.; Hulley, P.A.; Fernández de Puelles, M.L. Feeding ecology of early life stages of mesopelagic fishes in the equatorial and tropical Atlantic. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2019, 76, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukel, M.R.; Gerard, T.; Kelly, T.; Knapp, A.N.; Laiz-Carrión, R.; Lamkin, J.; Landry, M.R.; Malca, E.; Selph, K.E.; Shiroza, A.; et al. Plankton food webs of the Gulf of Mexico spawning grounds of Atlantic Bluefin tuna. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiroza, A.; Malca, E.; Lamkin, J.T.; Trika, G.; Landry, M.R.; Stukel, M.R.; Laiz-Carrión, R.; Swalethorp, R. Active prey selection in developing larvae of Atlantic bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus) in spawning grounds of the Gulf of Mexico. J. Plankton Res. 2022, 44, 728–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Regal, M.A. Spawning seasons, spawning grounds and nursery grounds of some Red Sea fishes. Glob. J. Fish. Aqua. 2013, 6, 105–125. [Google Scholar]
- Reglero, P.; Ortega, A.; Balbín, R.; Abascal, F.J.; Medina, A.; Blanco, E.; de la Gándara, F.; Alvarez-Berastegui, D.; Hidalgo, M.; Rasmuson, L.; et al. Atlantic bluefin tuna spawn at suboptimal temperatures for their offspring. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20171405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granneman, J.E.; Steele, M.A. Fish growth, reproduction, and tissue production on artificial reefs relative to natural reefs. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 71, 2494–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Jiang, R.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, Z.; Chen, L.; Sui, Y.; Wang, S. Community structure of fish eggs and larvae in artificial reef area of Ma’an Archipelago. J. Fish. China 2019, 43, 1937–1951. [Google Scholar]
- Pickering, H.; Whitmarsh, D. Artificial reefs and fisheries exploitation: A review of the ‘attraction versus production’ debate, the influence of design and its significance for policy. Fish. Res. 1997, 31, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brickhill, M.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Connolly, R.M. Fishes associated with artificial reefs: Attributing changes to attraction or production using novel approaches. J. Fish Biol. 2005, 67, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layman, C.A.; Allgeier, J.E. An ecosystem ecology perspective on artificial reef production. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 57, 2139–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitmarsh, D.; Santos, M.N.; Ramos, J.; Monteiro, C.C. Marine habitat modification through artificial reefs off the Algarve (southern Portugal): An economic analysis of the fisheries and the prospects for management. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2008, 51, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, S.H.; Hamilton, C.D.; Spencer, G.C.; Ogston, H.O. Evaluating the Potential for Marine and Hydrokinetic Devices to Act as Artificial Reefs or Fish Aggregating Devices. Based on Analysis of Surrogates in Tropical, Subtropical, and Temperate US West Coast and Hawaiian Coastal Waters; No. DOE-HTH-0006389; HT Harvey & Associates: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.A.; Lowry, M.B.; Champion, C.; Suthers, I.M. A designed artificial reef is among the most productive marine fish habitats: New metrics to address ‘production versus attraction’. Mar. Biol. 2016, 163, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelson, A. Artificial reefs vs coral transplantation as restoration tools for mitigating coral reef deterioration: Benefits, concerns, and proposed guidelines. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2006, 78, 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- Komyakova, V.; Chamberlain, D.; Jones, G.P.; Swearer, S.E. Assessing the performance of artificial reefs as substitute habitat for temperate reef fishes: Implications for reef design and placement. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, S.H.; Hamilton, C.D.; Spencer, G.C.; Ogston, H.O. Collecting and Processing Data on Fish Eggs and Larvae in the California Current Region; NOAA Technical Report NMFS CIRC-370; National Marine Fisheries Service: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1972; Volume 370, 38p. Available online: https://repository.library.noaa.gov/view/noaa/3248 (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Jiménez-Rosenberg, S.P.A. Desarrollo Larvario de Eucinostomus cufrani Yáñez-Arancibia, 1978 (Pistes: Gerreidae). Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Baja California Sur, La Paz, Mexico, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Rosenberg, S.P.A. Descripción del Desarrollo Larvario de Eucinostomus gracilis y Larvario y Juvenil de Eucinostomus dowii y Diapterus peruvianus. Ph.D. Thesis, Depto. de Plancton y Ecología Marina, CICIMAR, La Paz, Mexico, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, H.G. Chauliodontidae: Viperfishes. In The Early Stages of Fishes in the California Current Region; Moser, H.G., Ed.; California Cooperative Oceanic Fisheries Investigations (CalCOFI) Atlas No. 33; Allen Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1996; pp. 297–299. 1505p. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, W.J. Early Stages of Atlantic Fishes: An Identification Guide for the Western Central North Atlantic; CRC Press: Boca Ratón, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ahlstrom, E.H. Influence of the Temperature on the Rate of Development of Pilchard Eggs in Nature. In Studies on the Pacific Pilchard or Sardine (Sardinops caerulaea); Special Scientific Report; U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1943; Volume 23, pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ahlstrom, E.H.; Moser, H.G. Eggs and larvae of fishes and their role in systematic investigatios and in fisheries. Rev. Des Trav. De L’institut Des Pêches Marit. 1976, 40, 379–398. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, A.W.; Ahlstrom, E.H.; Moser, H.G. Early Life History Stages of Fishes and Their Characters. In Ontogeny and Systematics of Fishes; Moser, H.G., Ed.; American Society of Ichthyologists and Herptetologists: Glen Allen, VA, USA, 1984; Volume 1, pp. 11–22. Available online: https://swfsc-publications.fisheries.noaa.gov/publications/CR/1984/8447.PDF (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman, R.J.; Matcher, G.F.; Vink, T.J.; Froneman, P.W. Preliminary evidence for the organisation of a bacterial community by zooplanktivores at the top of an estuarine planktonic food web. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grol, M.G.; Rypel, A.L.; Nagelkerken, I. Growth potential and predation risk drive ontogenetic shifts among nursery habitats in a coral reef fish. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 502, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogan, M.W. Distribution and retention of larval fishes near reefs in the Gulf of California. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 115, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, A.L.M.; Gómez-Gutiérrez, J.; Aburto-Oropeza, O.; Saldierna-Martínez, R.J.; Johnson, A.F.; Harada, A.E.; Sánchez-Uvera, A.R.; Erisman, B.; Arvizú, D.I.C.; Burton, R.S. DNA sequencing of fish eggs and larvae reveals high species diversity and seasonal changes in spawning activity in the southeastern Gulf of California. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 592, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatés, A.; Olivar, M.P.; Salat, J.; Palomera, I.; Alemany, F. Physical and biological processes controlling the distribution of fish larvae in the NW Mediterranean. Prog. Oceanogr. 2007, 74, 355–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Port, A.; Montgomery, J.C.; Smith, A.N.H.; Croucher, A.E.; McLeod, I.M.; Lavery, S.D. Temperate marine protected area provides recruitment subsidies to local fisheries. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 284, 20171300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, C.; Hock, K.; Krueck, N.C.; Tyazhelnikov, V.; Mumby, P.J. An MPA design approach to benefit fisheries: Maximising larval export and minimising redundancy. Diversity 2021, 13, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.S.; Sanchez-Jerez, P.; dos Santos, L.N.; Zalmon, I.R. Could artificial reefs increase access to estuarine fishery resources? Insights from a long-term assessment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 242, 106858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, I.D.; da Silva Santos, J.L.; Costa, L.L.; Lima, J.S.; Zalmon, I.R. Reproductive potential and production role of artificial reefs-Southeastern Brazil. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 265, 107710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leis, J.M.; Fisher, R. Swimming speed of settlement-stage reef-fish larvae measured in the laboratory and in the field: A comparison of critical speed and in situ speed. In Proceedings of the 10th International Coral Reef Symposium, Okinawa, Japan, 28 June–3 July 2006; pp. 438–445. [Google Scholar]
- Barth, P.; Berenshtein, I.; Besson, M.; Roux, N.; Parmentier, E.; Banaigs, B.; Lecchini, D. From the ocean to a reef habitat: How do the larvae of coral reef fishes find their way home? A state of art on the latest advances. Vie Milieu 2015, 65, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, R. Swimming speeds of larval coral reef fishes: Impacts on self-recruitment and dispersal. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 285, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, G.; Artema, J. The use of chemical cues in habitat recognition and settlement. In Chemical Ecology in Aquatic Systems; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 72–89. [Google Scholar]
- Huijbers, C.M.; Nagelkerken, I.; Lössbroek, P.A.; Schulten, I.E.; Siegenthaler, A.; Holderied, M.W.; Simpson, S.D.A. Test of the senses: Fish select novel habitats by responding to multiple cues. Ecology 2012, 93, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, S.; Caldarone, E.M.; Chícharo, M.A.; Clemmesen, C.; Faria, A.M.; Faulk, C.; Folkvord, A.; Holt, G.J.; Høie, H.; Kanstinger, P.; et al. On the edge of death: Rates of decline and lower thresholds of biochemical condition in food-deprived fish larvae and juveniles. J. Mar. Syst. 2012, 93, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China, V.; Holzman, R. Hydrodynamic starvation in first-feeding larval fishes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8083–8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, D.A.; Findley, L.T.; Kerstitch, A.N. Reef Fishes of the Sea of Cortez: The Rocky-Shore Fishes of the Gulf of California, Revised ed.; University of Texas Press: Austin, TX, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Farach, E.B.; López, J.; García, R.; Nevárez, M.O.; Lluch, D.B.; Ortega, S. Temporal Variability of Oceanic Mesoscale Events in the Gulf of California. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantoja, D.A.; Marinone, S.G.; Parés-Sierra, A.; Gómez-Valdivia, F. Numerical modeling of seasonal and mesoscale hydrography and circulation in the Mexican Central Pacific. Cienc. Mar. 2012, 38, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Martínez, J.; Farach Espinoza, E.B.; Herrera-Cervantes, H.; García Morales, R. Long-Term Variability in Sea Surface Temperature and Chlorophyll a Concentration in the Gulf of California. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceves-Medina, G.; Emilio, A.; Inda-Díaz, O.; Ubisha-Hernández, A.; Álvarez-Ramírez, I. Fish larvae assemblages in the Gulf of California. J. Fish Biol. 2004, 65, 832–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Armas, R.; Funes-Rodríguez, R.; Amador-Buenrostro, A. Larval fish community structure in a seamount of the Gulf of California. Hidrobiológica 2008, 18, 77–88. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Velasco, L.; Jimenéz-Rosenberg, S.P.; Shirasago, B.; Obeso-Nieblas, M. Distribution and abundance of fish larvae in the Bahia de La Paz (Gulf of Califórnia) and their relation to hidrographic variability during Summer (1997–1998). Deep Sea Res. 2004, 51, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Catala, F.; Beier, E.J.; Sánchez-Velasco, L.; Godínez, V.M.; Sánchez-Pérez, E.D.; Barton, E.D. Water masses and larval fish habitats in the Pacific tropical-subtropical convergence off Mexico. Cont. Shelf Res. 2021, 230, 10457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavín, M.F.; Castro, R.; Beier, E.; Godínez, V.M. Mesoscale eddies in the southern Gulf of California during summer: Characteristics and interaction with the wind stress. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 1367–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Cervantes, H. Sea surface temperature, ocean color and wind forcing patterns in the Bay of La Paz, Gulf of California: Seasonal variability. Atmósfera 2019, 32, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, E.; Metaxas, A.; Scheibling, R.E. A systematic review of artificial reefs as platforms for coral reef research and conservation. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).