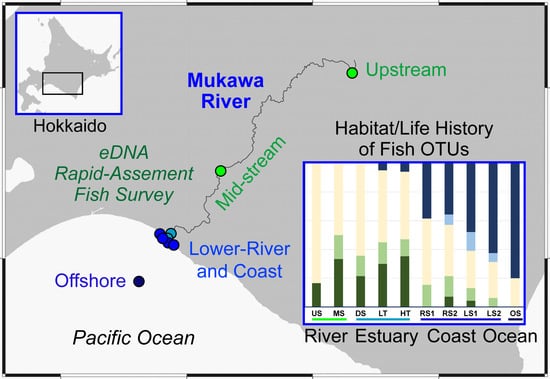
Environmental DNA Characterization of the Fish Species Composition in the Mukawa River and Adjacent Habitats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
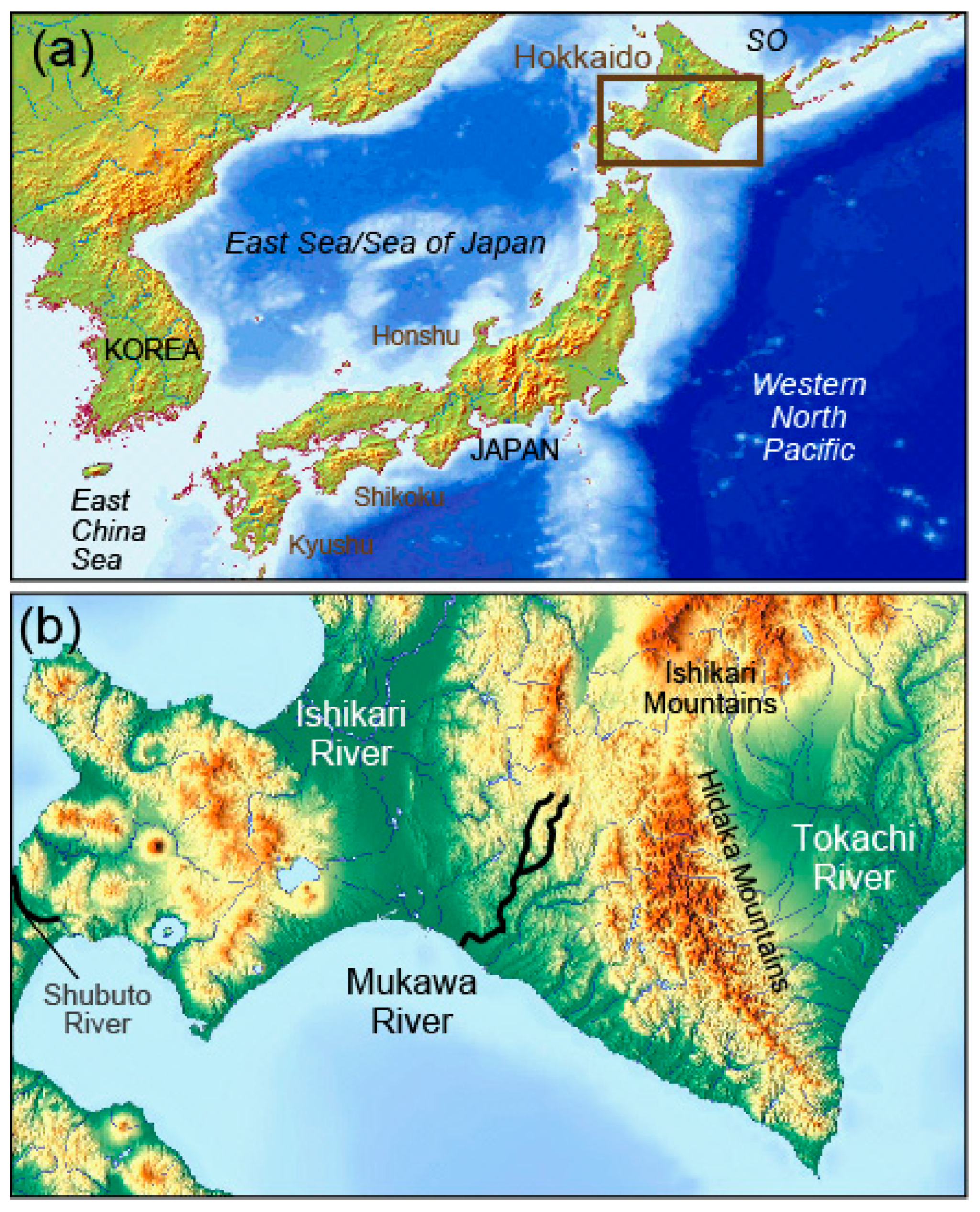
2.1. Water Sampling
2.2. Molecular Experiments on eDNA
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
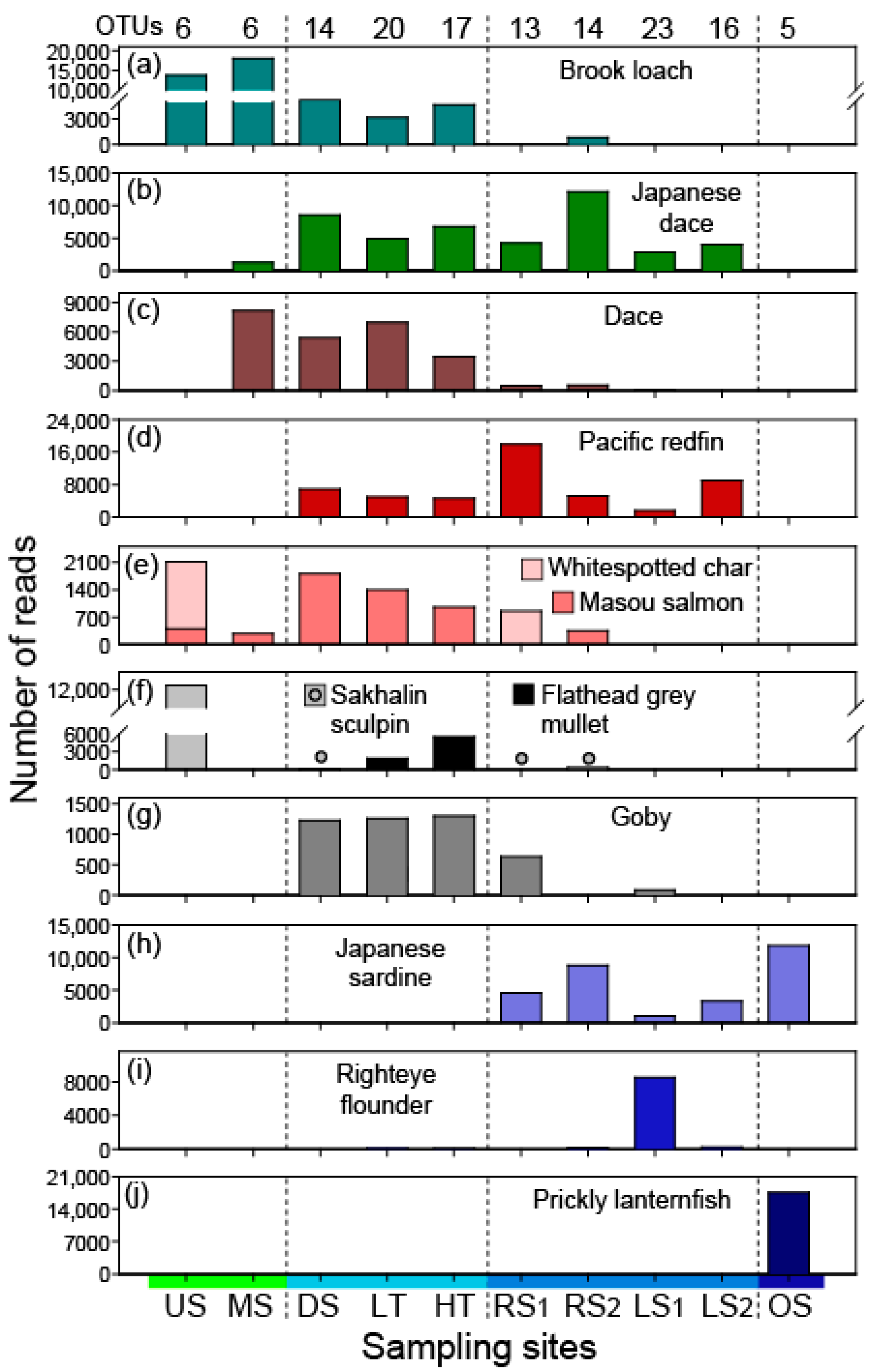
3.1. Species Detections in Each Environment
3.2. Proportions of Fish Types by Habitat Groups
3.3. Similarity of Species Compositions


4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kai, Y.; Motomura, H.; Matsuura, K. (Eds.) Fish Diversity in Japan; Springer: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, H.; Matsuura, K. Geography, currents, and fish diversity of Japan. In Fish Diversity in Japan; Kai, Y., Motomura, H., Matsuura, K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura, C.; Omura, T.; Furumai, H.; Tockner, K. Present state of rivers and streams in Japan. River Res. Appl. 2005, 21, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoya, K. Freshwater Fishes of Japan; Yama-Kei Publishers: Tokyo, Japan, 2015. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Hosoya, K. Conservation of Freshwater Fish Diversity in Japan. In Fish Diversity in Japan; Kai, Y., Motomura, H., Matsuura, K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 395–408. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-16-7427-3_23.
- Itakura, H.; Kitagawa, T.; Miller, M.J.; Kimura, S. Declines in catches of Japanese eels in rivers and lakes across Japan: Have riverbank and lakeshore revetments reduced fishery catches? Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 11, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuma, M.; Hosoya, K.; Nagata, Y. Distribution of the freshwater fishes of Japan: An historical overview. In Fish Biology in Japan: An Anthology in Honour of Hiroya Kawanabe; Developments in environmental biology of, fishes, Yuma, M., Nakamura, I., Fausch, K.D., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 97–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, Y.; Inoue, M.; Kawaguchi, Y. Stream fish habitat science and management in Japan: A review. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2001, 4, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Tominaga, K.; Nakajima, J.; Kakioka, R.; Tabata, R. Japanese Freshwater Fishes: Biogeography and Cryptic Diversity. In Species Diversity of Animals in Japan; Diversity and Commonality in Animals; Motokawa, M., Kajihara, H., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2017; pp. 183–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, M. The dam-related decline of freshwater fish diversity—analyses of the data collected from Hokkaido during the last half century. Jpn. J. Ecol. 2005, 55, 349–357. [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima, M.; Kameyama, S.; Kaneko, M.; Nakao, K.; Steel, E.A. Modelling the effects of dams on freshwater fish distributions in Hokkaido, Japan. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 1511–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Fukushima, M.; Kameyama, S.; Fukushima, T.; Matsushita, B. How do dams affect freshwater fish distributions in Japan? Statistical analysis of native and nonnative species with various life histories. Ecol. Res. 2008, 23, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, Y. Fish diversity of subarctic waters in Japan. In Fish Diversity in Japan; Kai, Y., Motomura, H., Matsuura, K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 111–124. [Google Scholar]
- Goto, A.; Nakanishi, T.; Utoh, H.; Hamada, K. A preliminary study of the freshwater fish fauna of rivers in southern Hokkaido. Bull. Fac. Fish. Hokkaido Univ. 1978, 29, 118–130. [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki, Y.; Senou, H.; Terui, A.; Washitani, I. Illustrated checklist of fishes from the Shubuto River System, southwestern Hokkaido, Japan. Check List 2013, 9, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakae, M.; Matsuura, K. Ichthyology and collection building in Japan. In Fish Diversity in Japan; Kai, Y., Motomura, H., Matsuura, K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 33–60. [Google Scholar]
- Yatsuyanagi, T.; Araki, H. Understanding seasonal migration of Shishamo smelt in coastal regions using environmental DNA. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsuyanagi, T.; Ishida, R.; Sakata, M.K.; Kanbe, T.; Mizumoto, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kamada, S.; Namba, S.; Nii, H.; Minamoto, T.; et al. Environmental DNA monitoring for short-term reproductive migration of endemic anadromous species, Shishamo smelt (Spirinchus lanceolatus). Environ. DNA 2020, 2, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.; Goto, A.; Jeon, S.-R. Speciation and dispersal of Tribolodon species (Pisces, Cyprinidae) around the Sea of Japan. Zool. Sci. 2002, 19, 1291–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, H. Life-histories and genetic divergence in three species of Tribolodon (Cyprinidae). Mem. Fac. Fish. Hokkaido Univ. 1995, 42, 1–98. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2115/21893.
- Akamatsu, Y.; Tsuzuki, T.; Yokoyama, R.; Funahashi, Y.; Ohta, M.; Azegami, M.; Naito, D.; Inui, R. Comparative study between fish collection by National Census on River Environment and environmental DNA metabarcoding. J. Japan Soc. Civil Eng. Ser. B1 Hydraul. Eng. 2018, 74, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavergne, E.; Kume, M.; Ahn, H.; Henmi, Y.; Terashima, Y.; Ye, F.; Kameyama, S.; Kai, Y.; Kadowaki, K.; Kobayashi, S.; et al. Effects of forest cover on richness of threatened fish species in Japan. Conservation Biol. 2022, 36, e13449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, M.; Yamamoto, J.; Sudo, K.; Muzugaki, S.; Montani, S.; Tanaka, H. Influence of a river flood on the environment of fishing ground in the Mukawa coast, Hokkaido. J. Japan Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. B2 (Coast. Eng.) 2012, 68, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, M.; Yamamoto, J.; Sudo, K.; Muzugaki, S.; Montani, S. Effect of snowmelt flood for primary production in Mukawa coast, Hokkaido. J. Japan Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. B2 (Coast. Eng.) 2013, 692, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meador, M.R.; Matthews, W.J. Spatial and temporal patterns in fish assemblage structure of an intermittent Texas stream. Amer. Midl. Nat. 1992, 127, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humpl, M.; Pivnicka, K. Fish assemblages as influenced by environmental factors in streams in protected areas of the Czech Republic. Ecol. Freshw. Fish. 2006, 15, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.M.; Holder, T.L.; Fiorillo, R.A.; Williams, L.R.; Thomas, R.B.; Warren, M.L. Distribution, abundance, and diversity of stream fishes under variable environmental conditions. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 63, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdorff, T.; Pont, D.; Hugueny, B.; Chessel, D. A probabilistic model characterizing fish assemblages of French rivers: A framework for environmental assessment. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pont, D.; Hugueny, B.; Oberdorff, T. Modelling habitat requirement of European fishes: Do species have similar responses to local and regional constraints? Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeinghaus, D.J.; Winemiller, K.O.; Birnbaum, J.S. Local and regional determinants of stream fish assemblage structure: Inferences based on taxonomic vs. functional groups. J. Biogeogr. 2007, 34, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coble, A.A.; Flinders, C.A.; Homyack, J.A.; Penaluna, B.E.; Cronn, R.C.; Weitemier, K. eDNA as a tool for identifying freshwater species in sustainable forestry: A critical review and potential future applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1157–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenekar, T. The current state of eDNA research in freshwater ecosystems: Are we shifting from the developmental phase to standard application in biomonitoring? Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 1263–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Masuda, R.; Sato, Y.; Sado, T.; Araki, H.; Kondoh, M.; Minamoto, T.; Miya, M. Environmental DNA metabarcoding reveals local fish communities in a species-rich coastal sea. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, H. Variation of Japanese eel eDNA in sequentially changing conditions in different sample volumes. J. Fish. Biol. 2020, 97, 1238–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongo, Y.; Nishijima, S.; Kanamori, Y.; Sawayama, S.; Yokouchi, K.; Kanda, N.; Oori, S.; Onitsuka, T.; Kurogi, H.; Yamazaki, T.; et al. Fish environmental DNA in Tokyo Bay: A feasibility study on the availability of environmental DNA for fisheries. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 47, 101950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kume, M.; Lavergne, E.; Ahn, H.; Terashima, Y.; Kadowaki, K.; Ye, F.; Kameyama, S.; Henmi, Y.; Kai, Y.; Yamashita, Y.; et al. Factors structuring estuarine and coastal fish communities across Japan using environmental DNA metabarcoding. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, G.; Yamauchi, H.; Shigeyoshi, M.; Ashino, K.; Yonashiro, C.; Asami, M.; Goto, Y.; Duda, J.J.; Yamanaka, H. Using eDNA metabarcoding to establish targets for freshwater fish composition following river restoration. Global Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 43, e02448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Sato, Y.; Sado, T.; Minamoto, T.; Miya, M. Comparing local- and regional-scale estimations of the diversity of stream fish using eDNA metabarcoding and conventional observation methods. Freshw. Biol. 2018, 63, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamura, A.; Hayami, K.; Sakata, M.K.; Minamoto, T. Environmental DNA revealed the fish community of Hokkaido Island, Japan, after invasion by rainbow trout. Biodiv. Data J. 2020, 8, e56876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minegishi, Y.; Wong, M.K.-S.; Kanbe, T.; Araki, H.; Kashiwabara, T.; Ijichi, M.; Kogure, K.; Hyodo, S. Spatiotemporal distribution of juvenile chum salmon in Otsuchi Bay, Iwate, Japan, inferred from environmental DNA. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizumoto, H.; Mitsuzuka, T.; Araki, H. An environmental DNA survey on distribution of an endangered salmonid Species, Parahucho perryi, in Hokkaido, Japan. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 569425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Iijima, T.; Kakuzen, W.; Watanabe, S.; Yamada, Y.; Okamura, A.; Horie, N.; Mikawa, N.; Miller, M.J.; Kojima, T.; et al. Release of eDNA by different life history stages and during spawning activities of laboratory-reared Japanese eels for interpretation of oceanic survey data. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, A.; Watanabe, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Miller, M.J.; Fukuba, T.; Miwa, T.; Okino, T.; Minamoto, K.; Tsukamoto, K. First use of oceanic environmental DNA to study the spawning ecology of the Japanese eel Anguilla japonica. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 609, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Higuchi, T.; Kuroki, M.; Watanabe, S.; Miller, M.J.; Okino, T.; Miwa, T.; Tsukamoto, T. Environmental DNA detects a possible Japanese eel spawning event near a video-recorded anguillid eel in the open ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2022, 689, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, A.; Yamazaki, A.; Ahn, H.; Yamanaka, H.; Kameyama, S.; Masuda, R.; Azuma, N.; Kimura, S.; Karaki, T.; Kurokawa, Y.; et al. Distribution of Japanese eel Anguilla japonica revealed by environmental DNA. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, O.E. Global biodiversity scenarios for the year 2100. Science 2000, 287, 1770–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gozlan, R.E.; St-Hilaire, S.; Feist, S.W.; Martin, P.; Kent, M.L. Disease threats on European fish. Nature 2005, 435, 1045–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.; Knowler, D.J.; Leveque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.; et al. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worm, B.; Barbier, E.B.; Beaumont, N.; Duffy, J.E.; Folke, C.; Halpern, B.S.; Jackson, J.B.C.; Lotze, H.K.; Micheli, F.; Palumbi, S.R.; et al. Impacts of biodiversity loss on ocean ecosystem services. Science 2006, 314, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulthard, S.; Johnson, D.; McGregor, J.A. Poverty, sustainability and human wellbeing: A social wellbeing approach to the global fisheries crisis. Global Environ. Change 2011, 21, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamoto, T.; Miya, M.; Sado, T.; Seino, S.; Doi, H.; Kondoh, M.; Nakamura, K.; Takahara, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamanaka, H.; et al. An illustrated manual for environmental DNA research: Water sampling guidelines and experimental protocols. Environ. DNA. 2021, 3, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andruszkiewicz, E.A.; Starks, H.A.; Chavez, F.P.; Sassoubre, L.M.; Block, B.A.; Boehm, A.B. Biomonitoring of marine vertebrates in Monterey Bay using eDNA metabarcoding. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakabo, T. Fishes of Japan with Pictorial Keys to the Species, 3rd ed.; Tokai University Press: Kanagawa, Japan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima, J. Loaches of Japan; Yama-Kei Publishers: Tokyo, Japan, 2017. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, J.S. Fishes of the World, 4th ed.; Wiley John & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team, 2020. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Borcard, D.; Gillet, F.; Legendre, P. Numerical Ecology with R; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kindt, R.; Coe, R. Tree Diversity Analysis: A Manual and Software for Common Statistical Methods for Ecological and Biodiversity Studies; World Agroforestry Centre: Nairobi, Kenya, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Guttman, L. Some necessary conditions for common-factor analysis. Psychometrika 1954, 19, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontier, S. Étude de la décroissance des valeurs propres dans une analyse en composantes principales: Comparaison avec le modd́le du bâton brisé. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1976, 25, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meire, P.; Ysebaert, T.; Damme, S.V.; Van den Bergh, M.E.T.; Struyf, E. The Scheldt estuary: A description of a changing ecosystem. Hydrobiologia 2005, 540, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, J.E.; Thrush, S.F.; Dayton, P.D. Habitat variation, species diversity and ecological functioning in a marine system. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 366, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, S.; Vasconcelos, R.P.; Fonseca, V.F.; Tanner, S.E.; Reis-Santos, P.; Costa, M.J.; Cabral, H.N. Predicting fish community properties within estuaries: Influence of habitat type and other environmental features. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 107, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, P.; Zimmermann, N.E.; Graham, C.H.; Lavergne, S.; Pellissier, L.; Münkemüller, T.; Thuiller, W. The productivity-biodiversity relationship varies across diversity dimensions. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, K. Invasions of rainbow trout and brown trout in Japan: A comparison of invasiveness and impact on native species. Ecol. Freshw. Fish. 2020, 29, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, K. Ups and downs of non-native and native stream-dwelling salmonids: Lessons from two contrasting river. Ecological Res. 2021, 37, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, G.J.A.; Jones, M.L. A rapid assessment approach to prioritizing streams for control of Great Lakes sea lampreys (Petromyzon marinus): A case study in adaptive management. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 65, 2471–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pederson, J.; Carlton, J.T.; Bastidas, C.; David, A.; Grady, S.; Green-Gavrielidis, L.; Hobbs, N.-V.; Kennedy, C.; Knack, J.; McCuller, M.; et al. 2019 Rapid Assessment Survey of marine bioinvasions of southern New England and New York, USA, with an overview of new records and range expansions. BioInvasions Rec. 2021, 10, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.R.; McKenna, S.A. A Marine Rapid Assessment of the Togean and Banggai Islands, Sulawesi, Indonesia; RAP Bulletin of Biological Assessment 20; Conservation International: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tiberti, R.; Buchaca, T.; Cruset, E.; Iacobelli, L.; Maini, M.; Victor, O.; Mariangels, P.; Quim, P.R.; Ibor, S.; Marc, V.; et al. Evaluation of visual encounter surveys as a method for the rapid assessment of fish presence and relative density in high mountain lakes. Aquatic Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2022, 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajemian, M.J.; Wetz, J.J.; Shipley-Lozano, B. Rapid assessment of fish communities on submerged oil and gas platform reefs using remotely operated vehicles. Fish. Rese. 2015, 167, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minchin, D.; White, B. A rapid assessment method for an invasive mollusc in an Irish lake. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2014, 5, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Davison, P.I.; Copp, G.H. A rapid assessment of non-native fish distributions in two English river basins using environmental, D.N.A.J. Vertebr. Biol. 2023, 72, 22068. [Google Scholar]
- Goto, A. Alternative life-history styles of Japanese freshwater sculpins revisited. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1990, 28, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamate, T.; Maekawa, K. Life cycle of masu salmon (Oncorhynchus masou) in Shumarinai Lake, northern Hokkaido, Japan. Eurasian J. Forest Res. 2000, 1, 39–42. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2115/22122.
- Ahn, H.; Kume, M.; Terashima, Y.; Ye, F.; Kameyama, S.; Miya, M.; Yamashita, Y.; Kasai, A. Evaluation of fish biodiversity in estuaries using environmental DNA metabarcoding. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafferty, K.D.; Garcia-Vedrenne, A.E.; McLaughlin, J.P.; Childress, J.N.; Morse, M.F.; Jerde, C.L. At Palmyra Atoll, the fish-community environmental DNA signal changes across habitats but not with tides. J. Fish Biol. 2021, 98, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, W.A.; Barry, P.; Dokai, W.; Maselko, J.; Olson, J.; Baetscher, D. Leveraging eDNA metabarcoding to characterize nearshore fish communities in Southeast Alaska: Do habitat and tide matter? Environ. DNA 2022, 4, 868–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.H.; Piermarini, P.M.; Choe, K.P. The multifunctional fish gill: Dominant site of gas exchange, osmoregulation, acid-base regulation, and excretion of nitrogenous waste. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 97–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laporte, M.; Berger, C.S.; García-Machado, E.; Côté, G.; Morissette, O.; Bernatchez, L. Cage transplant experiment shows weak transport effect on relative abundance of fish community composition as revealed by eDNA metabarcoding. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, T.; Yamanaka, H. Meta-analyses of environmental DNA downstream transport and deposition in relation to hydrogeography in riverine environments. Freshw. Biol. 2022, 67, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Driessche, C.; Everts, T.; Neyrinck, S.; Brys, R. Experimental assessment of downstream environmental DNA patterns under variable fish biomass and river discharge rates. Environ. DNA 2023, 5, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, T.; Foreman, M.; Chandler, P.; Kashiwai, M. Coastal Oyashio south of Hokkaido, Japan. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2004, 34, 1477–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


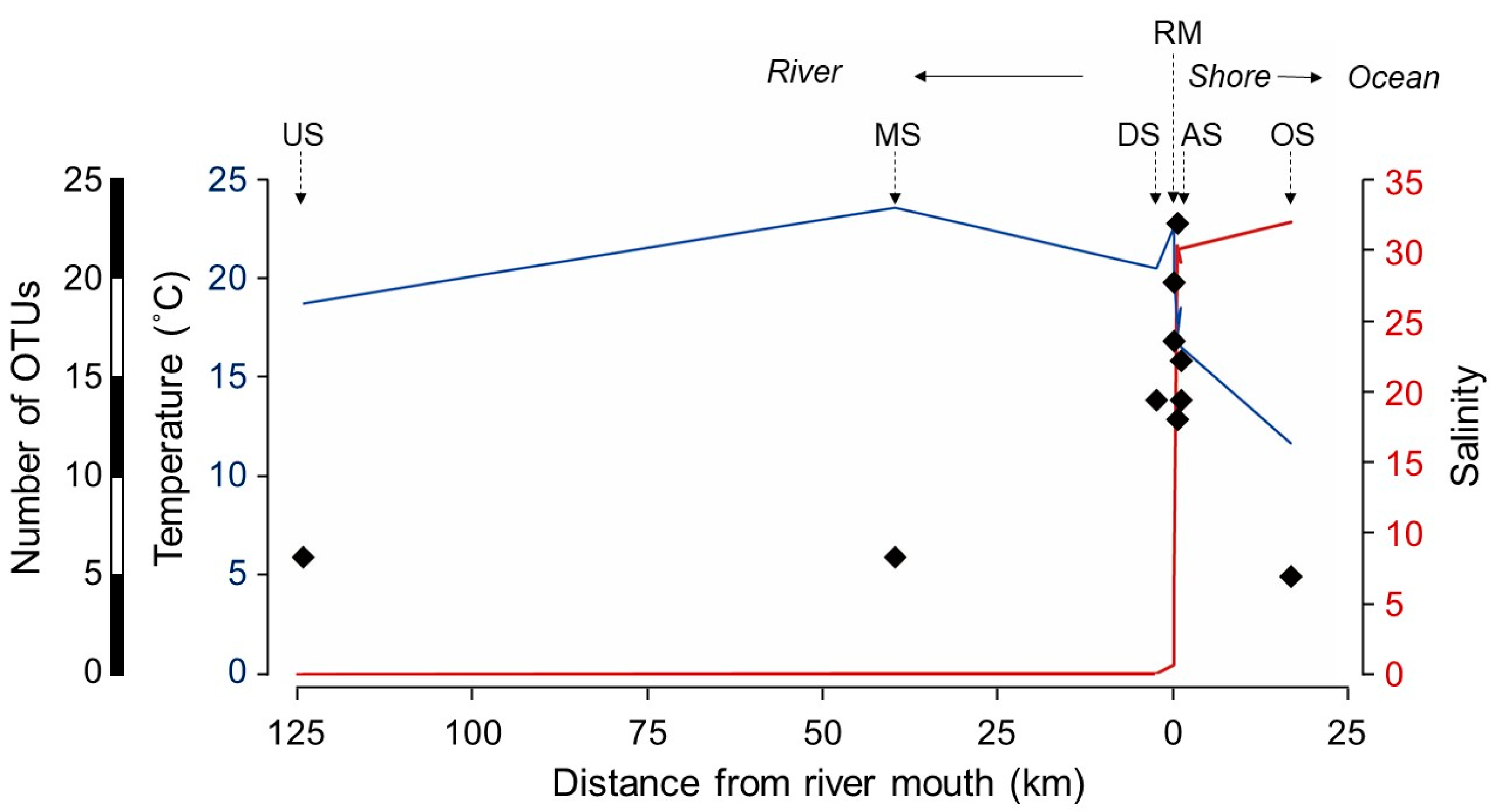
| Station | Code | Lat | Long | Dist | Temp | Sal | Vol | Conc | OTU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upstream | US | 43.0433 | 142.6577 | 125 | 18.9 | 0 | 0.5 | 5240.6 | 6 |
| Midstream | MS | 42.7587 | 142.1368 | 40 | 23.8 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 1617.6 | 6 |
| Downstream | DS | 42.5752 | 141.9359 | 2.5 | 20.7 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 1497.7 | 14 |
| River mouth at low tide | LT | 42.5616 | 141.9239 | 0 | 22.8 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 932.1 | 20 |
| River mouth at high tide | HT | 42.5614 | 141.9231 | 0 | 20.5 | 6.1 | 0.3 | 2149.7 | 17 |
| Right shore 1 (500 m) | RS1 | 42.5687 | 141.9121 | 0.5 | 17.9 | 30.6 | 0.4 | 514.3 | 13 |
| Right shore 2 (1 km) | RS2 | 42.5702 | 141.9098 | 1 | 18.7 | 29.4 | 0.4 | 3232.7 | 14 |
| Left shore 1 (500 m) | LS1 | 42.5586 | 141.9263 | 0.5 | 17.2 | 30.3 | 0.5 | 5110.6 | 23 |
| Left shore 2 (1 km) | LS2 | 42.5561 | 141.9286 | 1 | 16.7 | 30.4 | 0.6 | 4258.8 | 16 |
| Offshore | OS | 42.4343 | 141.8076 | 16.8 | 11.8 | 32.3 | 3.0 | 4000.7 | 5 |
| Negative control | NC | - | - | - | - | - | 0.5 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahn, H.; Miller, M.J. Environmental DNA Characterization of the Fish Species Composition in the Mukawa River and Adjacent Habitats. Fishes 2024, 9, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9040147
Ahn H, Miller MJ. Environmental DNA Characterization of the Fish Species Composition in the Mukawa River and Adjacent Habitats. Fishes. 2024; 9(4):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9040147
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhn, Hyojin, and Michael J. Miller. 2024. "Environmental DNA Characterization of the Fish Species Composition in the Mukawa River and Adjacent Habitats" Fishes 9, no. 4: 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9040147
APA StyleAhn, H., & Miller, M. J. (2024). Environmental DNA Characterization of the Fish Species Composition in the Mukawa River and Adjacent Habitats. Fishes, 9(4), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9040147