Abstract
This study evaluates the relative and combined effectiveness of seaweed rafts and light traps in attracting juvenile fish, focusing on diel variations in juvenile fish assemblage in the tropical coastal waters of Gaolong Bay, Wenchang City, Hainan Province. Sampling was conducted in May 2023 during various time periods using self-made artificial drifting seaweed rafts and light traps. The nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis was employed to compare the diversity and catch per unit effort of juvenile fish across different time periods and sampling methods. The Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance, heatmaps, and Principal Coordinates Analysis were used to analyze and visualize the differences between juvenile fish assemblages. Our findings indicate that light traps were particularly effective during nocturnal periods, capturing a diverse array of species and achieving the highest richness and evenness indices. Seaweed rafts demonstrated the lowest diversity indices, largely due to the dominance of specific species, which likely contributed to the competitive exclusion of other species. Seaweed rafts showed significant effectiveness during noon, providing critical habitat and shelter that attracted juvenile fish despite the lower diversity. While each method demonstrated specific advantages, their combined approach did not significantly improve juvenile fish aggregation compared to the individual method. These findings underscore the importance of considering diel and tidal cycles in the selection of sampling methods, as aligning the method with the time of day can greatly enhance the accuracy of biodiversity assessments, leading to more informed conservation and management strategies for tropical coastal waters.
Keywords:
juvenile fish assemblage; seaweed raft; light traps; aggregation effect; diel patterns; sampling method Key Contribution:
Explores the comparative and combined efficacy of two juvenile fish sampling methods: drifting seaweed raft and light traps. The results highlight the distinct advantages of using drifting seaweed rafts during daytime and light traps during nighttime for effective juvenile fish monitoring.
1. Introduction
Coastal zones are recognized for their high primary productivity and significant economic contributions, serving as crucial nurseries for juvenile fish [1]. The intertidal and shallow subtidal zones exhibit dynamic ecological interplay with mangroves, seagrass beds, coral reefs, and other critical habitats, promoting ecological connectivity. These areas offer essential ecological services including spawning, nursing, and foraging habitats, which are critical for the ontogenetic development of numerous marine fish species, thereby supporting the reproductive and juvenile stages crucial for sustaining fish populations [2,3,4]. However, these nurseries are increasingly vulnerable to anthropogenic impacts, underlining the importance of monitoring juvenile fish diversity and abundance. Such assessments are integral to understanding the health and sustainability of fishery stocks and the ecological integrity of these habitats [1,5,6,7]. They provide insight into the efficacy of marine biodiversity conservation strategies and the resilience of fish populations, which are pivotal for formulating adaptive fishery management practices [8].
Floating seaweeds, dislodged from the benthic zone due to physical or biological forces, serve as floating microhabitats on the marine surface [9]. These floating seaweeds are critically linked with marine life, particularly fish. Over 333 species across 96 families are associated with floating seaweeds and other floating substrates, predominantly during their juvenile stages [10,11]. Studies have shown that naturally floating seaweeds and fresh seaweeds detached from the substrate attract juvenile fish and invertebrates [12,13,14]. Floating seaweeds contribute to habitat complexity and provide essential services such as refuge and foraging grounds [15], facilitating juvenile fish survival by offering shelter from predators and enhanced feeding opportunities [16]. Floating seaweeds predominantly collect in dynamic marine areas like estuaries, nearshore regions, or oceanic fronts [9], regions known for their elevated planktonic biodiversity compared to open ocean waters. Field observations, particularly in regions like Hainan Island, China, highlight the practical implications of these floating ecosystems, where local fishers exploit natural seaweed rafts to capture juvenile fish for commercial purposes. Species such as Kyphosus lembus, Caranx sexfasciatus, Histrio histrio, Siganus fuscescens, and Abudefduf vaigiensis, frequently found around these natural assemblages, become targeted for ornamental and commercial fisheries, reflecting a direct interaction between ecological phenomena and local economic activities [17].
Previous research on floating seaweeds and their associated fish communities has largely focused on open, deep waters (>50 m), primarily assessing the ecological significance of these floating complexes. Preliminary findings have shown nocturnal predominance in juvenile fish aggregation around floating seaweeds [18,19]. However, the influence of diel variations, specifically changes in juvenile fish aggregation behavior between day and night, remains underexplored. This gap limits our understanding of the role of floating seaweed and other structures as fish aggregating devices. To address this gap, our research compared the effectiveness of seaweed rafts and light traps during the diel cycle and light traps at night in aggregating juvenile fish in Gaolong Bay, Wenchang coast, Hainan Island. Specifically, we used seaweed rafts, light traps, and a combination of both at night to attract nocturnal species that are sensitive to artificial lighting, whereas during the day, we utilized seaweed rafts to observe natural aggregation behavior without the influence of artificial light. By employing these two methods at various times of the diel cycle, our investigation aims to determine the diel dynamics of juvenile fish assemblage and to provide novel insights into species-specific preferences. Our findings could provide a foundational approach for coastal juvenile fishery surveys, thereby improving the accuracy of juvenile fish resource assessment and leading to more informed conservation and management strategies for tropical coastal waters.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Our research was conducted from 19 to 21 May 2023, in the shallow zone of Gaolong Bay at Wenchang, located on the eastern coast of Hainan Island within the northern South China Sea, which is rich in juvenile fish resources [20]. This region is characterized by its tropical climate and ecological diversity (Figure 1). Governed by a tropical monsoon climate, Gaolong Bay exhibits pronounced seasonal variations in inshore and wind currents, significantly affecting local marine habitats. A critical ecological feature, the Qiongdong coastal upwelling, occurs from April to September, channeling substantial nutrients towards the coast and substantially boosting primary productivity and biodiversity in the region [21]. Furthermore, Gaolong Bay experiences mixed semi-diurnal tides, with tidal levels fluctuating between approximately 0.5 m at neap tides and 2.0 m at spring tides. The Gaolong Bay’s diverse benthic habitats, including sandy and stony substrates, seagrass beds, and coral reefs, form a rich mosaic habitat supporting a wide spectrum of marine organisms. This area’s heterogeneity makes it an ideal location for studying juvenile fish assemblage, especially during their peak breeding season from April to September. During this peak period, various juvenile fish species are observed seeking refuge shelter under the naturally formed floating seaweeds on the water’s surface, such as Sargassum spp., coinciding with significant episodes of algal blooms, thereby providing a unique natural laboratory for our research [22].
Figure 1.
Location of Gaolong Bay, Wenchang coast, Hainan Island, China, showing the sampling site from 19 to 21 May 2023.
2.2. Fish Sampling
We developed simple sampling devices integrating elements from floating seaweeds (Sargassum spp.) and artificial light traps (Figure 2). The devices were constructed using a fine-mesh net (1 × 1 mm) with a 73 cm diameter at the opening, attached to a floater to maintain its position just below the water surface (approximately 15 cm deep). An anchor system was employed to stabilize the structure against tidal movements. To simulate seaweed rafts, we collected local seaweeds from adjacent seabeds, ensuring they were fresh and in a pre-decomposition state to optimize their attractiveness to fish, following protocols suggested in prior studies [23]. Each seaweed raft was designed to approximate an area of about 0.4 m2 and weighed around 4 kg when wet. The light traps comprised a waterproof, white LED lamp capable of continuous operation for over 4 h, strategically placed within the net to attract nocturnal and crepuscular juvenile fish.
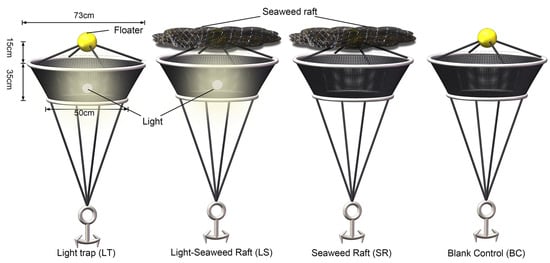
Figure 2.
Self-made sampling devices used in the study, showing the main structures of four kinds of sampling devices, including light trap (LT); seaweed raft (SR), light trap–seaweed raft (LS), and blank control (BC).
We preconditioned all experimental setups in situ for 24 h before commencing the data collection process. The experimental design included four distinct groups to evaluate the efficiency of different sampling methodologies: the light traps, the seaweed rafts, the light trap–seaweed raft, and the blank control. Each treatment was replicated three times within each sampling session to ensure temporal consistency and minimize potential biases from day-to-day variations. Samples were collected from three different locations about 50 m from the shore, with 30 m separating each device, chosen based on similar environmental conditions (depth, substrate type, and proximity to the shore) to ensure comparability. The water depth during the study was 1.0 to 1.5 m.
Sampling sessions were structured to cover various times of the day: including late night (01:00–03:30, ebb tide), dawn (04:00–06:30, flood tide), and early night (22:00–00:30, flood tide), from 19 May to 21 May 2023. Additionally, the seaweed raft and the blank control groups were also conducted during noon (11:00–13:30, ebb tide) and dusk (17:00–19:30, flood tide), the time of sunrise and sunset in the study area is 06:00 and 19:00 in local times, respectively. The entire research period coincided with a neap tide and the sea was calm during the sampling sessions, with the highest wave less than 2 m. The mean wave height was 1.0 ± 0.2 m during the study period (National Meteorological Data Center, https://data.cma.cn/, accessed on 25 May 2023). To ensure independence of sampling times, each set of devices was deployed and retrieved at the end of each sampling session, and fish were collected by hand nets and removed before redeployment for the next session. This approach prevented fish accumulation from previous periods, ensuring that each sampling time represented an independent dataset.
Captured fish were immediately preserved in a 4% seawater formalin solution for 4 h, and then stored in 75% ethanol for laboratory analysis. The growth stages of all collected fish were determined through careful morphological examination. All fin rays were fully developed, and scales were visible, with the only difference from adult fish being body size proportions. Therefore, all specimens were classified as juveniles. Juvenile fishes were identified morphologically to the lowest taxonomic level in the laboratory. The body length (BL, mm) was measured using either a dissecting microscope (Nikon SMZ1270, Nikon Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) or a vernier caliper, with an accuracy of 0.1 mm.
2.3. Analysis
The total number of fish captured by each sampling device within a specified timeframe was quantified as the Catch Per Unit Effort (CPUE, ind./net). The Index of Relative Importance (IRI) was calculated for each species into dominant species (IRI > 100), common species (100 > IRI ≥ 10), or rare species (IRI < 10). The formula was IRI = N% × F%, where N% is the percentage of individuals of a particular species relative to the total number of individuals of all species captured, and F% is the percentage of samples of a particular species to the total number of collected samples [24].
The Shapiro–Wilk test showed that the data did not meet the conditions of normality after various transformations (e.g., natural logarithm, square, square root, and reciprocal). Therefore, the nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis test was conducted to assess the influence of different sampling methods and sampling times on CPUE and species diversity parameters. For instances where significant differences emerged, Dunn’s post hoc test was applied for pairwise comparisons [25]. Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance (PERMANOVA) was employed to assess whether sampling methods and sampling time had an impact on juvenile fish assemblage [21]. A heatmap was constructed to display clustering patterns, illustrating similarities within the juvenile fish assemblage. The similarity percentage analysis (SIMPER) was applied to identify specific species that contributed significantly to within-group similarity and between-group differences. Species diversity of fish assemblage was measured using the Shannon–Wiener diversity index (H′), Margalef species richness index (D′), and Pielou’s evenness index (J′):
where S represents the number of species in the sample, N is the total number of individuals in the sample, and Pi is the proportion of the i-th species in the sample. Principal Coordinates Analysis (PCoA) is a statistical method used to visualize the relative distances between samples in a multivariate data set. In this study, PCoA based on the Bray–Curtis similarity distance matrix was used to analyze the similarity among fish assemblage. Before analysis, we transformed all original data using a log (x + 1) transformation to stabilize the variance. The clustering heatmap, PERMANOVA, and Principal Coordinates Analysis were conducted in the R programming environment using the “pheatmap”, “vegan” and “ade4” packages, respectively. Species diversity calculations and SIMPER analyses were conducted using the software PRIMER5 (Version 5.2.9).
H′ = −∑(Pi ln Pi),
D′ = (S − 1)/ln N,
J′ = H′/ln S
3. Results
3.1. Diversity and CPUE of Juvenile Fish Assemblage
A total of 955 juvenile fish were collected, belonging to 15 families, 19 genera, and 21 species (Table 1). The blank control group only yielded 17 individuals, comprising 5 species from 5 genera in 5 families. Due to the significantly lower performance of the BC group (p < 0.05) compared to the active sampling methods, data from the BC group were excluded from further analysis to avoid skewing the results and to focus on comparing the more effective sampling approaches. The control group was used primarily for qualitative comparison to establish a baseline of natural aggregation in the absence of stimuli. To evaluate the influence of diel patterns on fish assemblages and differentiate the performance of the seaweed raft group at different times, we categorized the collections from the seaweed raft into nighttime (including early night, late night, and dawn) and daytime (including noon and dusk) groups. The nighttime seaweed raft group yielded 7 species from 6 genera across 6 families, whereas the daytime seaweed raft group yielded 9 species from 7 genera across 6 families. In comparison, the light trap method captured 12 species from 12 genera across 11 families, and the light trap–seaweed raft combination collected 9 species from 9 genera across 8 families. A temporal analysis of species numbers across different periods revealed that the late-night period had the highest species count, followed by dawn, noon, early night, and dusk, with dusk yielding the fewest species.

Table 1.
Species, body length range, index of relative importance (IRI), and occurrence of juvenile fish assemblage collected by seaweed raft and light traps in the coastal water.
Further analysis of fish assemblage diversity indices showed that the light trap group (1.36 ± 0.51) had the highest species richness index (D’), followed by the light trap–seaweed raft group (1.05 ± 0.37) and the daytime seaweed raft group (0.89 ± 0.21). The nighttime seaweed raft group exhibited the lowest species richness (0.73 ± 0.25). In terms of evenness (J’), the light trap–seaweed raft group (0.64 ± 0.06) ranked highest, followed by the light trap group (0.59 ± 0.16) and the nighttime seaweed raft group (0.55 ± 0.05), with the daytime seaweed raft group (0.49 ± 0.05) showing the lowest evenness. The Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H’) mirrored these findings, with the light trap–seaweed raft group (1.16 ± 0.48) having the highest diversity, followed by the light trap group (1.06 ± 0.24), daytime seaweed raft group (0.79 ± 0.15), and finally the nighttime seaweed raft group (0.75 ± 0.1). These diversity parameters did not show significant differences across the groups. (Table 2, p > 0.05).

Table 2.
Juvenile fish assemblage diversity and the proportion of the dominant species by different sampling methods.
The analysis of CPUE revealed no significant differences across the various sampling methods (p > 0.05). However, a general trend was observed, where the daytime seaweed raft had the highest CPUE, followed by the light trap and the light trap–seaweed raft, with the nighttime seaweed raft group showing the lowest CPUE. Temporal factors were identified as the primary drivers of CPUE variations (p < 0.05). Among the periods, CPUE was highest at noon (ebb tide), followed by late night (ebb tide), early night (flood tide), and dawn (flood tide), with dusk (flood tide) showing the lowest CPUE (Figure 3).
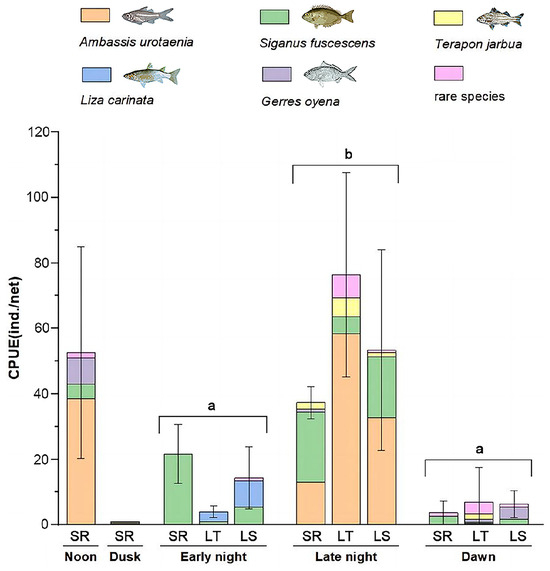
Figure 3.
CPUE, species composition and distribution of the juvenile fish assemblages collected by light trap (LT), seaweed raft (SR), light trap–seaweed raft (LS) at different sampling times. The species composition showed the domain, comment species, and all the rare species. Statistical significance was assessed using the Kruskal–Wallis test, where identical letters above the bars indicate no significant difference (p > 0.05) between groups, and different letters indicate a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05).
3.2. Dominant Species
The dominant species identified across all sampling methods included S. fuscescens, Ambassis urotaenia, and Terapon jarbua. The body length distribution of A. urotaenia ranged from 13.9 to 33.5 mm, with an average of 23.62 mm. For S. fuscescens, body lengths ranged from 17.1 to 34.4 mm, with an average of 26.92 mm. The body length distribution of G. oyena ranged from 11.2 to 19.6 mm, with an average of 16.42 mm (Figure 4). Common species within the assemblages were Liza carinata and Gerres oyena, while the remaining 12 species were considered rare. Among the dominant species, A. urotaenia was the most abundant, accounting for 53.94% of all juvenile fish collected. However, S. fuscescens exhibited a higher relative importance index (IRI) of 2241.71, compared to 2125.09 for A. urotaenia. Together, these two species constituted 87.42% of the total fish count (Table 1). Heatmap analyses revealed that S. fuscescens was consistently present across all sampling periods, whereas A. urotaenia and T. jarbua were predominantly found during the late-night period and were less frequent at other times (Figure 5). The proportion of S. fuscescens was highest in the nighttime seaweed raft samples and during early night periods, whereas its presence was lowest in light trap samples and during noon periods.
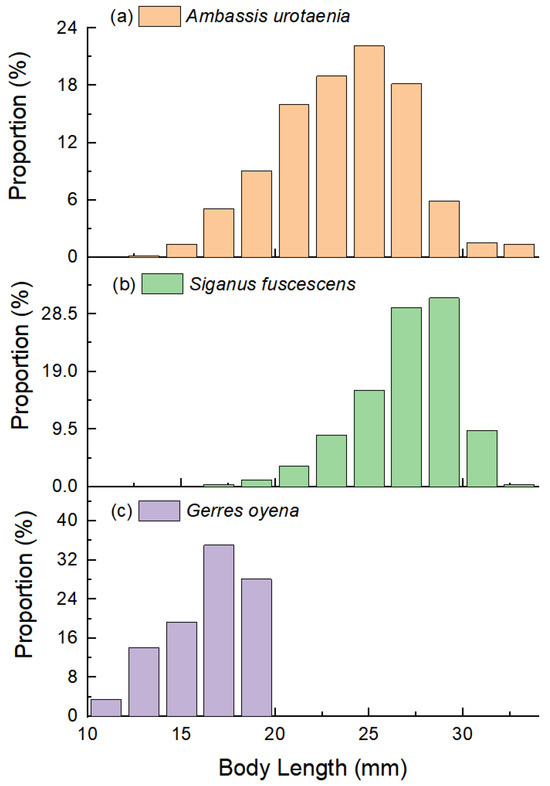
Figure 4.
Body length distribution of the dominant species. (a) Ambassis urotaenia; (b) Siganus fuscescens; (c) Gerres oyena.
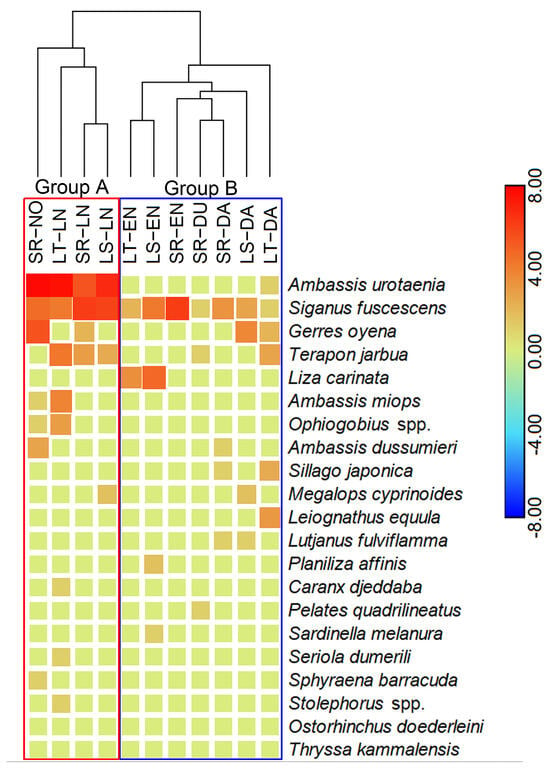
Figure 5.
The clustering patterns of the juvenile fish assemblages and group-specific contributions to the differences of fish assemblages collected by light trap (LT), seaweed raft (SR), light trap–seaweed raft (LS) during the diel periods. Abbreviations of the juvenile fish assemblages were formed by sampling methods and sampling time; for example, SR-NO represents the fish assemblage collected by seaweed raft during the noon. Sampling times: noon (NO), dusk (DU), late night (LN), dawn (DA), early night (EN).
3.3. Differences in Juvenile Fish Assemblage Structure
There were no statistically significant differences in fish assemblage structure across the different sampling methods (F = 1.17, p > 0.05), but significant differences were observed across different sampling times (F = 11.09, p < 0.05). PERMANOVA analysis indicated that the sampling method accounted for 5.2% of the variation in fish assemblages, while sampling time explained 49.4% of the variation. The interaction between the sampling method and time accounted for 5.2% of the variation. PCoA demonstrated that the first and second principal coordinates explained 29.64% and 20.22% of the total variance in fish assemblage structure, respectively, totaling 49.86% of the variance. When grouped by sampling time (Figure 6), the 90% confidence interval ellipses for the early night and dawn periods showed partial overlap, whereas the late-night period was distinctly separated from the other time periods. This separation indicates that fish assemblages during the late-night period may differ significantly from those at other times.
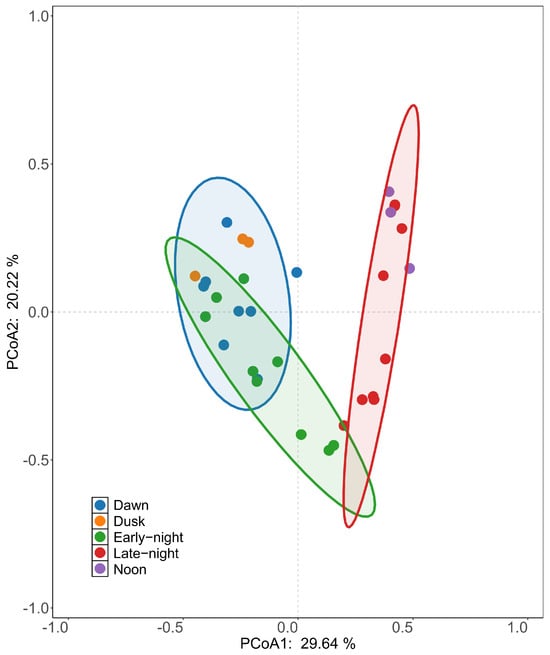
Figure 6.
Points of the same color represent fish assemblages during a specific period, with the degree of dispersion reflecting the extent of divergence among assemblages.
Hierarchical clustering analysis further segregated the assemblages into two distinct groups (Figure 5). Group A, which included data from the noon and late-night samplings, displayed similar assemblage characteristics and differed significantly from Group B, which encompassed assemblages from the other sampled time slots. SIMPER analysis revealed an average dissimilarity of 80.75% between the two assemblage groups. This variation was primarily driven by the species A. urotaenia, S. fuscescens, G. oyena, and T. jarbua, which together contributed to more than 80% of the observed intergroup variance.
4. Discussion
Our study underscored the effectiveness of different sampling methods (i.e., the light traps, the seaweed raft, the light trap–seaweed raft) in attracting and assessing juvenile fish assemblages across various diel periods. Light traps proved particularly effective for nocturnal sampling, yielding higher catch rates, especially for small and light-sensitive species, as supported by previous studies [26,27]. This is evidenced by the highest richness and evenness indices observed in the light trap group, highlighting the strong attraction of artificial light at night, which draws in a greater diversity and number of juvenile fish [28]. The nocturnal light environment not only attracts fish but also influences their behavior and ecological interactions [29,30]. Additionally, the gathering of fish in light devices may be associated with the mass accumulation of plankton [31]. The juvenile fish from the light trap–seaweed raft exhibited the highest Shannon–Wiener diversity index, suggesting that the combination of light and seaweed provides a more complex and diverse habitat, which helps to maintain high species diversity. Although one diversity index is slightly higher, combining light traps and seaweed rafts does not significantly enhance the aggregative effect compared to using each method independently. The light trap alone resulted in the highest abundance of juvenile fish, indicating a lack of synergistic effect when combining light and seaweed for fish attraction. This finding is consistent with previous studies that have shown that artificial light significantly increases fish abundance and diversity at night [32].
The juvenile fish from the seaweed raft had the lowest diversity indices and abundance, potentially due to the strong species-specific attraction of S. fuscescens, which may lead to the competitive exclusion of other species. This effect reduces the overall diversity as the habitat becomes dominated by a single species that monopolizes the available resources [33]. This pattern suggests that floating seaweed acts as a miniature ecosystem where competition for resources can drive changes in community structure, consistent with Gause’s principle of competitive exclusion [34]. While floating seaweed and debris play critical roles in attracting juvenile fish, their effectiveness is closely tied to their structural complexity and the abundance of associated resources [19,35]. The benefits provided by the structural complexity of the seaweed, such as shelter and food resources [30], may also contribute to the survival and growth of juvenile fish [16,36]. However, this benefit can be offset by reduced diversity when a dominant species monopolizes the habitat. This creates an ecological trade-off where the advantages of shelter and food availability may be outweighed by the competitive exclusion effect, particularly in habitats where one species, like S. fuscescens, can dominate.
Our findings reveal distinct diel patterns in the aggregation of juvenile fish around floating seaweeds, which were consistent with the nocturnal aggregation and daytime dispersal behaviors observed in Seriola spp. juveniles [19,37]. Significant fish aggregations were sustained during peak periods, particularly at noon and late night, while dispersal mainly occurred at dawn and dusk (Figure 3 and Figure 5). These patterns suggested an adaptive strategy among juvenile fish aimed at seeking refuge from predators and mitigating exposure to harsh environmental conditions such as the intense midday sun. The observed aggregation beneath floating seaweeds, potentially a response to negative phototropism and shade provided, underscores a natural behavior aimed at vulnerability [35,38]. The nocturnal gathering of juvenile fish around seaweeds likely serves as a deterrent against night-time predators, enhancing survival rates [39]. Similarly, the observed daytime aggregation under the floating seaweed rafts might reflect a similar survival strategy, offering shelter against daytime threats [19]. The variances in fish group sizes during dawn and dusk could be associated with changing light conditions, affecting fish visibility and predator susceptibility. Moreover, the variations of juvenile fish abundance could be linked to the diel patterns of plankton, thereby influencing food availability [40]. Considering the principles of foraging and predator avoidance, our results suggested that the observed diel shift in juvenile fish assemblage patterns within seaweed rafts was primarily driven by survival strategies. Seaweed rafts provide vital cover and protection during both night-time and midday, while during the periods of dawn and dusk, juvenile fish may leave these shelters to exploit feeding opportunities under reduced predation risk [13]. Specifically, the aggregation observed at noon underscores the importance of shade provided by seaweed rafts as a significant attractant and protective habitat in tropical coastal ecosystems.
The tide also affects the distribution of juvenile fish [41]. Our study found that the abundance of juvenile fish is higher during the ebb tide (noon and late night) compared to the flood tide (early night, dawn, and dusk). The ebb tide may expose more food resources or make them more accessible to juvenile fish, as suggested by the “concentration of food supply” hypothesis [11]. This hypothesis posits that floating seaweeds directly or indirectly provide more food sources for fish. The reduced water volume during ebb tide could limit the movement of larger predators, providing a safer environment for juvenile fish [42]. Additionally, juvenile fish might be using the ebb tide to move from deeper to shallower areas, increasing their concentration around floating seaweeds, which serve as refuges [19]. This adaptive strategy highlights the critical ecological role of floating seaweeds within coastal ecosystems as indispensable habitats that offer juvenile fish refuge from predators and reprieve from the rigors of their environment [43]. Additionally, we collected some crustaceans, such as Brachyura, from the floating seaweed rafts. The presence of these organisms could affect the aggregation of fish, either positively by providing additional food sources or negatively by increasing competition or predation [12]. Floating seaweed directly or indirectly provides more food sources for fish [11]. The ecological benefits of floating seaweed may lead to the aggregation of juvenile fish [9].
5. Conclusions
This study highlights the effectiveness of three sampling methods (i.e., light trap, seaweed rafts, and light trap–seaweed rafts) in evaluating juvenile fish assemblages within tropical coastal ecosystems. Variations in species diversity and abundance were observed depending on the time of day and night, emphasizing the importance of diel patterns in fish behavior. Among these methods, light traps proved particularly effective for nocturnal sampling, attracting a broad range of species and yielding the highest indices of richness and evenness. Light traps are highly recommended for ecological studies and fisheries assessments focused on nocturnal juvenile fish assemblages. The combination of light traps with seaweed rafts did not produce a synergistic effect beyond what each method achieved independently, indicating that while both methods are effective, their concurrent use does not provide additional benefits for fish aggregation. Seaweed rafts, especially during nocturnal and midday periods, served as critical habitats for juvenile fish, providing shelter and resources that are essential for their survival and growth. The study also emphasizes the role of diel and tidal patterns in shaping juvenile fish behavior and aggregation. Our findings inform future research and management practices, emphasizing the importance of selecting the most appropriate sampling method based on specific research goals and the target species. Our study provides valuable insights for future research and management practices aimed at conserving and enhancing juvenile fish populations in tropical coastal water.
Author Contributions
C.F. and S.X. considered the experimental design. C.F., W.X. and Y.L. (Yongxiang Li), and Y.L. (Ying Lu) collected the juvenile fish sample. Z.M. identified fish species. C.F. and Y.S. performed the statistical analysis and C.F. wrote the original manuscript. Y.S. and S.X. reviewed and edited the original manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by National Key R&D Program of China (Nos. 2022YFD2401302 and 2022YFC3106303), National Science Foundation of China (Nos. 42376114, 42166004, and 32360917), Hainan Province Science and Technology Special Fund (Nos. ZDYF2023SHFZ101 and ZDYF2024SHFZ070), and Hainan University Start-up Funding for Scientific Research (Nos. KYQD (ZR)-21130, KYQD[ZR]-22058, and KYQD[ZR]-21033).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted using juvenile fish obtained directly from the usual professional fishing process. As no procedures were carried out on the fish while they were alive, and they were analyzed post-mortem, current regulations do not require permits.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lefcheck, J.S.; Hughes, B.B.; Johnson, A.J.; Pfirrmann, B.W.; Rasher, D.B.; Smyth, A.R.; Williams, B.L.; Beck, M.W.; Orth, R.J. Are coastal habitats important nurseries? A meta-analysis. Conserv. Lett. 2019, 12, e12645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.; Kendall, A.W. Early Life History of Marine Fishes; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 23–56. [Google Scholar]
- Nagelkerken, I.; Roberts, C.v.; Van Der Velde, G.; Dorenbosch, M.; Van Riel, M.; De La Moriniere, E.C.; Nienhuis, P. How important are mangroves and seagrass beds for coral-reef fish? The nursery hypothesis tested on an island scale. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 244, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorenbosch, M.; Verberk, W.; Nagelkerken, I.; Van der Velde, G. Influence of habitat configuration on connectivity between fish assemblages of Caribbean seagrass beds, mangroves and coral reefs. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 334, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.J.; Thrush, S.; Hewitt, J.; Cummings, V.; Funnell, G. Fishing impacts and the degradation or loss of habitat structure. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 1999, 6, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, K. Sustainability, biomass yields, and health of coastal ecosystems: An ecological perspective. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. Oldendorf 1994, 112, 277–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, A.; Bricker, S.B.; Dauer, D.M.; Demetriades, N.T.; Ferreira, J.G.; Forbes, A.T.; Hutchings, P.; Jia, X.; Kenchington, R.; Marques, J.C. Overview of integrative tools and methods in assessing ecological integrity in estuarine and coastal systems worldwide. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 1519–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R.; Winker, H.; Coro, G.; Demirel, N.; Tsikliras, A.C.; Dimarchopoulou, D.; Scarcella, G.; Palomares, M.L.D.; Dureuil, M.; Pauly, D. Estimating stock status from relative abundance and resilience. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2020, 77, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothäusler, E.; Gutow, L.; Thiel, M. Floating seaweeds and their communities. In Seaweed Biology: Novel Insights into Ecophysiology, Ecology and Utilization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 359–380. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, J.; Santiago, J.; Hernández-García, V. Fish associated with fish aggregation devices off the Canary Islands (Central-East Atlantic). Sci. Mar. 1999, 63, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.J.; Santiago, J.A.; Santana-Ortega, A.T. A general theory on fish aggregation to floating objects: An alternative to the meeting point hypothesis. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2002, 11, 255–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsford, M.; Choat, J. The fauna associated with drift algae captured with a plankton-mesh purse seine net 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1985, 30, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safran, P.; Omori, M. Some ecological observations on fishes associated with drifting seaweed off Tohoku coast, Japan. Mar. Biol. 1990, 105, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutow, L.; Beermann, J.; Buschbaum, C.; Rivadeneira, M.M.; Thiel, M. Castaways can’t be choosers—Homogenization of rafting assemblages on floating seaweeds. J. Sea Res. 2015, 95, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsford, M.J. Drift algae: A contribution to near-shore habitat complexity in the pelagic environment and an attractant for fish. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. Oldendorf 1995, 116, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandendriessche, S.; Messiaen, M.; O’Flynn, S.; Vincx, M.; Degraer, S. Hiding and feeding in floating seaweed: Floating seaweed clumps as possible refuges or feeding grounds for fishes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 71, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, S.; Ajisaka, T.; Lahbib, S.; Kokubu, Y.; Alabsi, M.; Komatsu, T. Spatial distributions of floating seaweeds in the East China Sea from late winter to early spring. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, T.; Manda, A.; Takatsuki, N.; Kawabata, Y.; Nishihara, G.N.; Fujita, S.; Kawabe, R.; Yamada, M.; Kinoshita, T.; Yamawaki, N. Feeding habit of juvenile fishes associated with drifting seaweeds in the East China Sea with reference to oceanographic parameters. Aquac. Sci. 2016, 64, 157–171. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, T.; Takatsuki, N.; Kawabata, Y.; Kawabe, R.; Nishihara, G.N.; Ishimatsu, A.; Soyano, K.; Okamura, K.; Furukawa, S.; Yamada, M. Continuous behavioral observation reveals the function of drifting seaweeds for Seriola spp. juveniles. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 573, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, S.; Li, C.; Wang, T.; Du, F.; Sun, D.; Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Y. Thirty years of change: Assessing the dynamics of fish communities in Daya Bay, a semi-enclosed coastal ecosystem of the South China sea. Water Biol. Secur. 2024, 3, 100268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Miao, Z.; Wang, S.; Chen, K.; Liu, Y.; Xie, S. Influence of tidal and diurnal rhythms on fish assemblages in the surf zone of sandy beaches. Fish. Oceanogr. 2023, 32, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Meng, T.; Yao, D.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, J.; Mu, D.; Bao, S. Benthic Sargassum composition and community characteristics in the intertidal zone of Hainan Island, China. Mar. Biol. Res. 2022, 18, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, M.L.; Auster, P.J.; Bichy, J.B. Effects of mat morphology on large Sargassum-associated fishes: Observations from a remotely operated vehicle (ROV) and free-floating video camcorders. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1998, 51, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cheng, F.; Ren, P.; Wang, Z.; Xie, S. Longitudinal recovery gradients of drifting larval fish assemblages in the middle reach of the Yangtze River: Impact of the Three Gorges Dam and conservation implementation. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 76, 2256–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cheng, F.; Murphy, B.R.; Xie, S. Downstream effects of the Three Gorges Dam on larval dispersal, spatial distribution, and growth of the four major Chinese carps call for reprioritizing conservation measures. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 75, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, L.E.; Costello, M.J. Light traps for sampling marine biodiversity. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2017, 71, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strydom, N.A. An assessment of habitat use by larval fishes in a warm temperate estuarine creek using light traps. Estuaries 2003, 26, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendrick, A.; Hyndes, G. Patterns in the abundance and size-distribution of syngnathid fishes among habitats in a seagrass-dominated marine environment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 57, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooper, C.N.; Williams, K.; De Robertis, A.; Tuttle, V. Effect of underwater lighting on observations of density and behavior of rockfish during camera surveys. Fish. Res. 2015, 172, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsford, M.J. Drift algae and small fish in coastal waters of northeastern New Zealand. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1992, 80, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesan, M.; Spoto, M.; Verginella, L.; Ferrero, E.A. Behavioural effects of artificial light on fish species of commercial interest. Fish. Res. 2005, 73, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, M.P.; Esteban, E.; Limm, M.; Kurth, R. Evaluating aspects of larval light trap bias and specificity in the northern Sacramento River system: Do size and color matter? Am. Fish. Soc. Symp. 2003, 39, 269–280. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, C.H. Predation, competitive exclusion, and diversity in the soft-sediment benthic communities of estuaries and lagoons. In Ecological Processes in Coastal and Marine Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1979; pp. 233–264. [Google Scholar]
- Gause, G.F. The Struggle for Existence: A Classic of Mathematical Biology and Ecology; Courier Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, J.R.; Mitchell, C. Association of fishes with flotsam in offshore waters of Central America. Fish. Bull. Fish Wildl. Serv. 1967, 66, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, M.A.; Kelaher, B.P. Connectivity among fragmented populations of a habitat-forming alga, Phyllospora comosa (Phaeophyceae, Fucales) on an urbanised coast. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 381, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillans, R.; Franklin, C.; Tibbetts, I. Food choice in Siganus fuscescens: Influence of macrophyte nutrient content and availability. J. Fish Biol. 2004, 64, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooding, R.M.; Magnuson, J.J. Ecological Significance of a Drifting Object to Pelagic Fishes. Pac. Sci. 1967, 21, 486–497. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner, L.; Stuart, I.; Zampatti, B. Determining diel variation in fish assemblages downstream of three weirs in a regulated lowland river. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 72, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorke, A.; Weber, A.; Hofmann, H.; Peeters, F. Opposing diel migration of fish and zooplankton in the littoral zone of a large lake. Hydrobiologia 2008, 600, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reis-Filho, J.A.; Barros, F.; Da Costa, J.D.A.C.; Sampaio, C.L.S.; De Souza, G.B.G. Moon and tide effects on fish capture in a tropical tidal flat. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2011, 91, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rypel, A.L.; Layman, C.A.; Arrington, D.A. Water depth modifies relative predation risk for a motile fish taxon in Bahamian tidal creeks. Estuaries Coasts 2007, 30, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, T.J. Functions of shoaling behaviour in teleosts. In The Behaviour of Teleost Fishes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 294–337. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).