Abstract
This study aimed to evaluate and compare the effects of biofloc technology (BFT) and clear water (CW) on water quality physiological and productive performance of juvenile freshwater Northern River shrimp, Cryphiops caementarius under three stocking densities (100, 200, and 400 shrimp m−2). Shrimp with an initial body weight of 0.44 ± 0.07 g were stocked in 18 rectangular fiberglass tanks with a water volume 150 L for 290 days. During the experiment, water quality parameters stayed within acceptable ranges for shrimp growth. The highest survival rate was recorded in BFT treatments; however, the growth performance of shrimp in the treatments with the lowest stocking density was higher than that with the highest stocking density, regardless of whether BFT or CW was used. Transcriptional levels of heat shock protein (Hsp70) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) showed significant differences (p < 0.05) between treatments, particularly in BFT. These results indicate that an initial stocking density of 200 shrimp m−2 appears to be appropriate for shrimp juveniles cultured in a BFT system. Thus, this technology emerges as an effective tool for river shrimp farmers looking to increase their stocking densities and improve the efficiency of their production systems in arid zones.
Key Contribution:
The results revealed BFT allows for higher stocking (to an intensive level) density than the traditional CW system.
1. Introduction
The shrimp farming model has undergone drastic changes over the past decade, shifting from extensive systems with low production and large ponds to intensive systems with smaller ponds that offer greater control and biosecurity [1]. In shrimp production intensification, the density of the shrimp population remains the most important parameter [2,3,4]. The ideal stocking density can vary depending on factors such as species, life stage, culture system, management practices, and environmental parameters [5,6]. High density is often employed in commercial farming systems to optimize the use of available space, achieve maximum production rates, and minimize rearing expenses [7]. However, while increasing stocking densities can enhance productivity, excessively high densities can create a stressful environment for the shrimp, affecting their performance due to reduced space, limited food availability, cannibalism, increased susceptibility to pathogen outbreaks, water quality degradation, and accumulation of organic matter in the tanks [8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. Conversely, densities below optimal levels can reduce overall productivity by not utilizing all available space [15]. Increasing stocking density in an intensive aquaculture system necessitates the use of advanced aquaculture techniques and technologies to address these challenges [16]. In recent years, special attention has been given to the biofloc culture system, also known as biofloc technology (BFT), as a promising tool for sustainable shrimp aquaculture [17,18]. BFT has been widely applied worldwide to reduce environmental impact and production cost through a well-managed heterogeneous mixture of heterotrophic bacteria, microalgae, food, fecal remnants, exoskeletons, zooplankton into grown flocs and its ability to maintain good water quality [19,20]. The fundamental principle of BFT is to recycle waste nutrients, particularly inorganic nitrogen resulting from uneaten feed and feces, into microbial biomass by steering high the Carbon:Nitrogen ratio of the water through the modification of carbohydrate content in feed or by adding a carbon source to the water [21,22,23]. This process improves water quality and enhances water use efficiency by minimizing water turnover, among other benefits such as complementary feeds to the formulated diet, increased biosecurity, growth and survival [24,25,26,27,28]. BFT is considered one of the best aquaculture systems for intensive shrimp culture [29,30]. Additionally, BFT provides several immunological enhancements in penaeid shrimp due to its probiotic effects improving the non-specific immune system and resistance against infections and stress [31,32,33,34]. In BFT systems, shrimp stocking density can be increased beyond that of clear water systems [35,36,37,38]; thus, under higher stocking density conditions compared to clear water, shrimp welfare is not adversely affected, and they can still grow well [39,40,41].
Growing interest in sustainable production emphasizes the need to develop native species for aquaculture [42]. The native palaemonid species Cryphiops caementarius, known as the “Northern River shrimp”, is a subtropical freshwater species [43,44]. The geographical distribution of this South American caridean spans the rivers along west coast of Peru and Chile from the Taymi River in Peru (6 °S) to the Maipo River in Chile (33 °S) [45,46]. C. caementarius has market recognition due to its consistent exploitation through artisanal fishing in Chile and Peru [44,47,48]. However, its populations have significantly declined due to pollution, destruction of natural ecosystems, and anthropogenic activities such as mining and fishing pressure [49,50]. C. caementarius has been listed as vulnerable by the Ministerio de Medio Ambiente of Chile [51] and has been included in the red list of threatened species (https://www.iucnredlist.org, accessed on 12 May 2024). The rearing of C. caementarius is an alternative not only for conservation purposes but also for production purposes, making it a candidate for aquaculture diversification in semi-desert regions of northern Chile. In addition, BFT is relevant for implementing land-based aquaculture systems for C. caementarius that are more environmentally friendly and reduce water use [52,53].
In BFT, optimizing stocking density is a crucial factor that should be carefully studied. The appropriate stocking density varies for each species based on its feeding patterns, growth rate, management practices, and stress tolerance [6,54,55]. Moreover, maintaining an appropriate stocking density is essential for biofloc dynamics, as it ensures an adequate nutrient supply to support the formation of bioflocs and the microbial community responsible for water quality management and nutrient cycling [28,37]. Stocking density significantly affects the metabolism, immune function, growth, hematology, and stress levels of aquatic organisms [56,57,58,59]. Hence, the objectives of this study were to investigate the effects of stocking density on water quality, physiological responses, and production performance of C. caementarius cultured at different densities and to determine the optimal stocking density for shrimp culture.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Conditions
The experiment was carried out from January to November 2020 (290 days) at the Crustacean laboratory at the Universidad Católica del Norte, Coquimbo, Chile (29°57′ S 71″57′ S–71°21′ W). The experiment was applied in a 2 × 3 factorial design consisting of two treatment systems, Biofloc (B) and clear water (CW), and three stocking densities (100, 200, and 400 shrimp m−2). Three replicate tanks were randomly assigned to each treatment. The juveniles used in this research came from naturally spawned domesticated shrimp broodstock in the laboratory. The shrimp were acclimatized to local rearing conditions for one week prior to the start of the experiment. The shrimp were stocked at an initial mean weight of 0.44 ± 0.07 g. and randomly distributed into eighteen fiberglass rectangular tanks (107 × 63 × 45 cm) with a water effective volume of 150 L. A hydraulic aeration pipe was connected to a Sweetwater brand 2.5 HP blower, and two rubber/polyethylene (Aero-tube™ Colorite Aero-Tube, Ridgefield, CT, USA) air diffuser hoses were placed in each of the rearing tanks. The culture water temperature was controlled with submersible 200-watt heaters (Whale VK-1000, Zhongshan Enjoyroyal Appliance Co., Ltd., Guangdong, China) set to maintain the temperature at 23 ± 1 °C. The BFT culture system was composed of 3 experimental units that independently interconnected to a 250 L reserve circular tank (90 diameter × 80 cm) and fiberglass rectangular settling tanks (90 × 55 × 47 cm), equipped with one aquarium pump (Submersible Pump, Atman model AT-105, Guangzhou Ample Technology Co., Ltd., Zhongshan, China) to circulate the water (Qmax. 3000 L h−1) with the objective of maintaining both the water quality and the quali-quantitative profile of the planktonic community equally in all experimental units, avoiding the negative influence of these factors in the experiment [60,61]. Each experimental unit BFT was inoculated with 150 L of a biofloc solution taken from another BFT tank, which was already mature. The organic carbon source (liquid molasses, 30% carbon) was added daily to maintain a 15:1 C:N ratio [21,62]. The carbon source was mixed with tank water in a beaker and evenly distributed throughout each of the selected tanks. In clear water groups, a regular water exchange at a level of 80% of the total volume was performed once a week, whereas in BFT groups, clean freshwater was only added to replace loss due to evaporation. The water used was collected from the municipal water supply network, remaining for 24 h with continuous aeration to complete the dechlorination process. In both systems, six to ten PVC pipe shelters (10 cm × 32 inches) were placed in each tank.
The shrimp were fed with a commercial rainbow trout feed (BioMar, Puerto Montt, Chile) twice a day (09:00 and 16:00 h) at 5% biomass. The nutritional composition of the commercial diet consisted of 48.5% crude protein, 18.5% crude lipid, 1.9% crude fiber, 12% ash, and 10% moisture.
2.2. Water Quality Parameters
The dissolved oxygen concentration, temperature, and pH were monitored daily using a HACH multiparameter model HQ40d. Total ammonia as nitrogen (TAN), nitrate as nitrogen, nitrite as nitrogen, phosphorus, total suspended solids (TSS), biofloc volumes (FV), and total alkalinity were monitored once a week. TAN measurements were carried out by method 8155(salicylate method, 0.01 to 0.50 mg L−1 NH3−N), nitrite as nitrogen by method 8507 (Diazotization method, 0 to 0.300 mg L−1 NO2−N), nitrate as nitrogen by method 8039 (Cadmium Reduction Method, 0 to 30.0 mg L−1 NO3−N) and phosphorus (Ascorbic Acid Method 0.02 to 3.00 mg L−1 PO4−3) with reagents purchased from Hach Company. Water samples were quantified for TAN, nitrite-N, nitrate-N, and phosphorus on a Hach DR 3900 Spectrophotometer using the Hach program: 385 (wavelength 655 Nm), 355 (Wavelength 500 Nm), 371 (Wavelength 507 Nm) and 485 (Wavelength 530 Nm) respectively [63]. Concerning the solids analyses, the method 2540-D described by the American Public Health Association [64] was used for TSS, and for the biofloc volume (FV), a sample of 1 L of water with bioflocs was taken directly from the rearing tanks and poured into Imhoff cones (1000-0010 Vitlab, Grossostheim, Germany). Then, it was left to stand still for 20–30 min, and after this period, the volume of the settled plug was read [65]. Total alkalinity was determined using the titration method Bromophenol blue, with the HI3811 alkalinity kit (Hanna Instruments, Smithfield, RI, USA). Solids control was done weekly, always maintaining the ranges described as suitable for shrimp culture.
2.3. Shrimp Performance
Biometrics were performed every two months to monitor the growth of the shrimp under each density treatment throughout the study (n = 30 shrimp per tank), using a digital scale with two decimal places (Mettler PJ3600 DeltaRange). Excess moisture was removed from each organism with paper before weighing. The average weight of the shrimp was calculated, and the amount of feed supplied was adjusted. At the end of the experiment, the following performance parameters were evaluated: Specific growth rate (SGR) = (lnTW2 — lnTW1) × 100/(T2 —T1); were TW1 and TW2 are total weight at days T1 (start of the experiment) and T2 (after 290 days); survival rate (SR%) = final shrimp number/initial shrimp number) × 100; feed conversion ratio (FCR) = offered feed (g)/(final biomass (g)—initial biomass (g)); Final mean weight (g): ∑ final weight of live animals (g)/total number of animals; total biomass (g): ∑ final weight of all live animals (g).
2.4. Total RNA Extraction and Gene Expression Analysis by qPCR
Twelve shrimp were randomly collected from each density at the end of the experiment, and gill tissue collected from each animal was placed in 2 mL eppendorf tubes and stored at −80 °C. Total RNA was separately extracted using a Trizol® reagent kit (Ambion, Austin, TX, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Obtained RNA concentration and purity were verified by measuring absorbances at 260 and 280 nm by spectrophotometry using an Epoch microplate spectrophotometer (Biotek, Winooski, VT, USA), and the integrity was assessed by agarose gel electrophoresis. cDNA was obtained using 0.8 μg of total RNA and PrimeScript™ RT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (Takara, San Jose, CA, USA), following the manufacturer’s indications. The obtained cDNA was stored at −20 °C until further use.
The expression levels of genes, including heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and elongation factor (ELF1), were measured by RT-qPCR using the Real-Time PCR System Agilent Technologies (Stratagene MX3000P, La Jolla, CA, USA). The primers used for qPCR are shown in Table 1. RT-qPCR was performed using 20 μL of reaction volume containing 2 μL of cDNA, 0.6 μL of each primer (10 mM), and 10 μL of Takyon Low ROX SYBR 2× (Nalgene, Rochester, NY, USA). Samples were tested in triplicate. Initial denaturing time was 3 min at 95 °C, 40 cycles at 95 °C (15 s) and 60 °C (30 s), and an extension of 15 s at 95 °C, 15 s at 55 °C, and 15 s at 95 °C. The elongation factor (ELF1) was used as a housekeeping gene [66]. The analysis of gene expression was performed by comparative threshold cycle method 2ΔΔct [67].

Table 1.
List of primers sequences used to study mRNA expression of the gene in river shrimp (Criphiops caementarius) by RT-qPCR.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The results of water quality, survival, and gene expression were analyzed using a two-way ANOVA, followed by a Tukey’s test. Before analyses, data were assessed for normality and homogeneity of variance with the Shapiro-Wilk test and Fligner-Killeen test, respectively [68]. For growth, a non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test was performed, followed by the Wilcoxon test. For the analysis of Hsp70 and SOD gene expression, the data were transformed to square root and log base 10, respectively. Survival data were arcsine transformed. The level of significance was (p < 0.05). The data was expressed as means ± standard error (X ± SE). The free computer package RStudio, Inc. (Version 1.1.442) was used for the analyses [69].
3. Results
3.1. Water Quality
The results of the water quality of the physicochemical parameters in the culture systems with their respective densities are shown in Table 2. Temperature, oxygen, pH, TAN, and nitrite did not present significant differences between technologies and their different densities (p > 0.05). The temperature was kept at 22.49 ± 0.06 °C, and oxygen was maintained higher than 6.62 mg L−1 pH ranged between 8.44 ± 0.02, TAN kept around 0.07 ± 0.01 mg L−1 and nitrite 0.03 ± 0.01 mg L−1. Nitrate, phosphorus, alkalinity, FV, SST, and SSV showed significant differences between the culture technologies (p < 0.05). A higher concentration of nitrate was observed in the BFT in all their densities, but there were no significant differences between them (p > 0.05). Phosphorus, VF, SST, and SSV, the highest levels, were found at the density of 400 shrimp m−2 with BFT and the lowest at the density of 100 shrimp m−2 of CW.

Table 2.
Water quality parameters of river shrimp (Criphiops caementarius) in biofloc system (B) and clear wáter (CW) with different densities during the experimental period.
3.2. Zootechnical Performance Responses
At the start of the experiment, there was no difference in shrimp performance between juveniles from different treatments (p > 0.05). Table 3 shows the improvements in mean growth performance resulting from various treatments. However, significant differences in survival, weight gain, specific growth rate, and feed conversion rate were noted between culture technologies and shrimp densities at the experiment’s end (p < 0.05). Survival was a crucial factor influencing the determination of productive indices, reducing the power to establish final values and determine significant differences between treatments. Nonetheless, results suggest that BFT technology positively affects growth, specific growth rate, and feed conversion factor of juvenile C. caementarius. In general, survival was significantly higher in shrimp from biofloc treatments across all stocking densities compared to CW groups (p < 0.05). The survival rate of B200 was (p < 0.05) higher (37.67%) than other groups 28.00%, (B400); 25.67% (B100) compared to the CW groups (16.66–15.33%). The mean weight of shrimp in the treatments with the lowest stocking density was higher than that with the highest stocking density, independently from BFT and CW in the system. Values SGR were reduced significantly (p < 0.05) in shrimp reared at a high stocking rate (400 shrimp m−2) when compared with other groups.

Table 3.
Performance parameters of river shrimp (Criphiops caementarius) in biofloc system (B) and clear water (CW) with different densities during the experimental period.
3.3. Expression of Genes
The heat shock protein 70 KDa (Hsp70) exhibited similar patterns across the 100, 200, and 400 shrimp m−2 BFT-treated tanks. Notably, gene expression in the high-density CW group (400 shrimp m−2) was significantly higher than in the low (100 shrimp m−2) and medium (200 shrimp m−2) density group in both culture systems (p < 0.05) (Figure 1A). Conversely, superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels decreased with increasing CW culture density, reaching the lowest levels in the high-density group. Specifically, the SOD gene showed higher expression in the 100 m−2 shrimp treatment in CW (0.89 ± 0.26), significantly differing from other culture densities (p < 0.05) (Figure 1B).
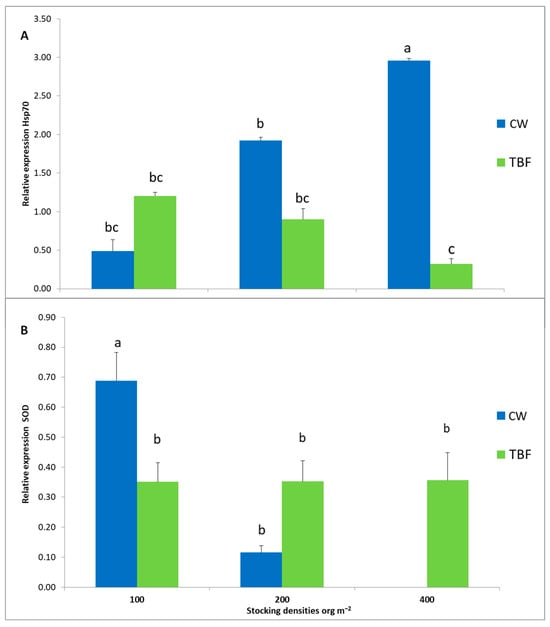
Figure 1.
Relative expression of genes in juveniles of Criphiops caementarius cultured at different initial stocking densities for 290 days. Effect of stocking density on (A) heat shock protein (Hsp70) and (B) superoxide dismutase (SOD). Data are presented as mean ± standard error. Different letters indicated significant differences between experimental groups (p < 0.05, ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test).
4. Discussion
It is well known that while increasing population density can negatively affect water quality [12,70,71,72]. In our study, the water quality parameters did not affect the zootechnical performance of the shrimp during the experiment. Water quality parameters remained stable and within the optimal values for the development of C. caementarius in both culture conditions [48,73,74,75,76]. Regarding the biofloc system, the ammonia levels were kept under control in the system, both through assimilation by heterotrophic bacteria and by oxidation of this compound by nitrifying bacteria, as indicated by the accumulation of nitrate [77,78,79]. In addition, nitrate is relatively non-toxic to aquatic organisms, unlike nitrite or ammonia [80]. In the present study, nitrite levels were lower than the recommended levels of less than 0.5 mg L−1 in shrimp farms [81]. Nitrate was below the levels of 75 mg L−1, which is considered to affect the welfare and growth of the farmed animal [82]. The mean dissolved oxygen (DO) content in all the treatments was above 5 mg L−1, which is the optimum recommended for shrimp culture and required for bacteria for the nitrification process [83,84]. It also plays a dominant role in the growth of heterotrophic bacteria [62]. The pH present in the BFT culture systems with different densities was in the range of 7.0 to 9.0, which favors the growth of heterotrophic and nitrifying bacteria [85]. In addition, pH values lower than 6.0 or higher than 10 could be harmful to shrimp gills [86]. Alkalinity was above 150 mg CaCO3 L−1 which is a recommended value in closed systems because the process of ammonium oxidation to nitrate consumes alkalinity [62]. These high alkalinity levels prevented pH fluctuations, and favored biofloc formation and the development of nitrifying bacteria [87,88]. Phosphorus concentration was at higher levels in the BFT than in the CW; this is because it tends to accumulate in these systems [89]. Within the BFT culture, an increase of this compound is observed in the systems that have a higher density, probably because a greater amount of food was added to these systems, which is the main source of this compound, and to the decomposition of the excreta of the animals [90,91].
In the BFT systems, the FV was around 15 mL L−1 which is the recommended value for shrimp by Hargreaves [78]. Higher levels of bioflocs might lead to clogging gills and result in the death of the organisms [92]. Regarding TSS, the optimal range for shrimp should be between 200–500 mg L−1 [93,94]; values exceeding 500 mg L−1 can interfere with water quality parameters and shrimp production rates [77], while values below 200 mg L−1 result in decreased ammonia removal due to slow nitrification by autotrophic bacteria [95]. The difference in TSS and SSV in BFTs is probably due to a higher number of heterotrophic bacteria, which assimilate ammonia nitrogen and utilize molasses as an energy source to build cell biomass and protein [77,96], leading to an accumulation of solids in the water column [97]. In contrast, the water parameters in the clear water ponds were kept low mainly by a constant water replacement strategy [98].
It has been widely documented that the stocking density in shrimp farming affects the productive indices of the animals [92,99,100,101,102,103]. Since this is a potential source of chronic stress that can affect the health and behavior of farmed organisms, it is a critical factor in intensive aquaculture management [8,9]. In general, it has been described that shrimp farming in BFT conditions improves productivity, average body weight, survival, and low FCR compared to CW. However, as stocking density increases, growth would decrease even under BFT [89,104]. Results from the current study reconfirmed the growth was affected significantly only by the stocking density (p < 0.05). The highest growth values were observed in shrimp reared in treatments with the lowest density, indicating that as stocking density increases, the growth and welfare of juvenile shrimp are negatively affected [4,105,106]. Regarding culture density, it has been suggested that higher population densities generally result in a lower survival rate [25,106,107,108]. In our case, this trend is not very marked, but significant differences are observed in the density of 200 shrimp m−2 in BFT. Our results showed lower SR compared with other shrimp species, and this may be attributed to the fact that C. camentarius exhibits territorialism and cannibal behavior [109,110], similar to other territorial species such as M. rosenbergii [111,112,113], Cherax quadricarinatus and P. semisulcatus [114,115]. This demonstrates that high stocking densities affect survival due to competition and cannibalism. In addition, the fact of sharing the same space, different social mechanisms could have regulated growth, causing a combination of the following effects: Aggressiveness and social hierarchy; aggressive interactions and established hierarchies; hyperactivity of subordinate individuals: mechanisms of social control; molt loss: molt deprivation and early sexual maturation: non-dominant males stop their somatic growth [116,117,118,119,120,121,122].
In the present study, differences in survival were observed between the BFT and CW treatments throughout the culture period. Organisms in the BFT treatment showed the highest SR (25–37%), while the CW treatments showed the lowest survival rates (15–16%) at the end of the experiment. The positive effect of BFT on survival compared to CW has also been described in other shrimp species, including L. vannamei (BFT: 87.1%, CW: 74.2%), L. stylirostris (BFT: 93.5%, CW: 64.2%), M. rosembergii (BFT: 86.52%, CW: 78.22%), Penaeus indicus (BFT: 92%, CW: 81%), P. monodon (BFT: 81.87%, CW: 65.73%), P. semisulcatus (BFT: 87.78%, CW: 76.67%) and Marsupenaeus japonicus (BFT: 65.7%, CW: 52.3%) [33,123,124,125,126,127,128]. The possible explanation for the higher SR in BFT may be that the flocs create a turbid condition in the water, which may help to decrease the physical interaction between the shrimp and possibly the perception of the density stressor stimulus [129]. Additionally, flocs represent a food source that is available in situ 24 h a day, offering a rich source of proteins and lipids [130].
The conversion factor parameters are called “apparent” efficiency and are more of practical information than of biological significance, as the actual consumption of diets could not be monitored in biofloc-based tanks, nor could the impact of cannibalism and biofloc consumption be directly evaluated [131]. It has been reported that the FCR for the BFT was significantly lower than the CW culture [132]. An FCR of 1.61 is considered good for shrimp [133,134]. Additionally, FCR is strongly linked to survival, as the calculation of the daily food ration is estimated based on the biomass measured at each sampling, potentially leading to an underestimation of this parameter [135]. In this study, the FCR could not be determined in the three densities of clear water and in the density of B400 because the final biomass was lower than the initial biomass, all due to low survival. The high FCR values (8.94 ± 0.27, 10.06 ± 0.24 recorded may be attributed to the type of feed supplied, which was not specifically formulated for shrimp, potentially leading to inadequate digestibility of the ration [136].
Previous studies indicate that the Hsp70 heat shock protein can be used as a biomarker because it plays an important role in protecting fish, shrimp, and mollusks against abiotic and biotic stress [137,138,139,140,141,142]. When the organism is exposed to environmental stress, the Hsp expression level increases significantly [143,144]. Hsp70 expression in our experiment increased with increasing stocking density in CW conditions compared to BFT, highlighting that it was stressful for shrimp under high stocking density conditions in CW [145]. Our results coincide with those reported by Nath and Haldar [146], who found that increasing stocking density induced the expression of stress-related protein Hsp70 in shrimps. In prawns, Macrobrachium nipponense, and crayfish Astacus leptodactylus found increasing stocking density elevated Hsp70 [147,148], and in fish, such as rainbow trout and tilapia, an increase in density, increases the expression level of Hsp70 [149,150,151,152].
The stress response can increase reactive oxygen species (ROS), and the first line of defense against ROS is antioxidant enzymes, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), which converts the superoxide radical (O2•−) to peroxide (H2O2) [153,154]. SOD has been described as an important biomarker of oxidative stress and antioxidant capacity in aquatic organisms [155]. In the present study, SOD expression was similar at all densities under BTF conditions of C. camentarius juveniles. These similarities can suggest that the oxidant/antioxidant balance in shrimp was not altered despite the stress condition [156]. This effect on the antioxidant activity of BFT could be related to the contribution of bioactive compounds that have antioxidant effects, such as carotenoids, polysaccharides, phytosterols, taurine, chlorophylls, vitamin C, and essential fatty acids [157,158,159]. Furthermore, it has been shown that some microbial communities present in biofloc can influence the redox state of shrimp [160,161]. All these compounds can be absorbed by shrimp through biofloc consumption, contributing to a healthy state, increasing stress tolerance, and helping activate antioxidant activity in farmed shrimp [90,162,163,164]. It is possible that with this background, the molecules contained in biofloc are antioxidants and that they act directly on the oxygen free radicals (which are a substrate for SOD) produced in metabolic processes; therefore, the expression of SOD is greater with respect to shrimp that are in clear water. Therefore, using exogenous antioxidants can help preserve energy reserves and endogenous antioxidant responses by improving resistance against pro-oxidant situations [165].
Another important factor is the reduction of water needed compared to CW systems. In BFT, it is only necessary to compensate for water loss due to evaporation [166]. However, the recovery and reuse of fresh water must be studied. In our study, we managed to conserve around 90% of the water resource, a figure close to the values found in the study by Huang et al. [167], which reports a conservation of 93.6% of the water resource. This is particularly beneficial in areas with limited water resources, like northern Chile, where the endemic river shrimp C. caementarius is being cultivated.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrated that BFT positively impacts both water quality and the metabolic response of C. caementarius. Water quality remained within suitable ranges for the species, with no significant treatment effects, suggesting that productivity differences were due to technology and stocking density. The BFT system supports higher stocking densities compared to traditional CW systems and has proven to improve the resilience and survival of shrimp. Based on these results, an optimal stocking density of 200 shrimp/m2 is recommended for biofloc systems to enhance survival, growth, physiological responses, and feed efficiency. Therefore, BFT is an effective tool for river shrimp farmers to increase stocking density and production efficiency, especially in arid regions.
Author Contributions
C.A.M.: Execution of test; generation of database; Formal analysis; writing and original draft. K.B.: conceptualization; design, and supervision of the project; review & editing original draft. M.C.M.: Resources; project administration and review & editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Agency for Research and Development (ANID), FONDEF (grant number ID15I20353) and FONDECYT (grant number 1211055).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The authors followed all applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals. Studies on animals were reviewed and approved by the scientific ethics committee of the Universidad Católica del Norte (UCN) (CEC-UCN-45), Coquimbo, Chile. In addition, the number of animals was kept to the minimum necessary to obtain scientific results, considering that the gain in knowledge and long-term benefit to the subject species is high. The animals were kept and slaughtered under production conditions; after being immersed in ice, they were subjected to analysis. They were not subjected to any procedures during the experimental period, and all analyses were conducted post mortem.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We express our sincere gratitude to the research staff of the Laboratorio de Crustaceos from UCN and Laboratorio de Fisiología y Genética Marina (FIGEMA). The authors would like to express our gratitude and appreciation to those who have taken time to critically review this manuscript. This research was conducted within the framework of the Programa Cooperativo de Doctorado involving Universidad de Chile, Universidad Católica del Norte, and Universidad Católica de Valparaíso, Chile. It is part of the degree thesis of Carlos Andrés Méndez.
Conflicts of Interest
All the authors declare that there were no conflicts of interest or personal relationships that interfered with this study.
References
- McIntosh, R. Modelling shrimp industry towards sustainability. INFOFISH 2019. In Proceedings of the World Shrimp Conference and Exposition “Modelling for Sustainability”, Bangkok, Thailand, 12–14 November 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Olague, D.; Ponce-Palafox, J.T.; Castillo-Vargasmachuca, S.G.; Arámbul-Muñoz, E.; de los Santos, R.C.; Esparza-Leal, H.M. Effect of nursery system and stocking density to produce juveniles of whiteleg shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquacult. Rep. 2021, 20, 100709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, D.; Genç, E.; Güroy, D.; Dinçer, S.; Yılmaz, B.H.; Yıldız, H.Y. Evaluation of biofloc technology for Astacus leptodactylus: Effect of different stocking densities on production performance and physiological responses. Acta Aquat. Turc. 2021, 17, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galkanda-Arachchige, H.S.C.; Hussain, A.S.; Davis, D.A. Improvement in laboratory research: Effects of stocking density, variation and sample size on outcomes of growth studies with shrimp. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fróes, C.; Fóes, G.; Krummenauer, D.; Poersch, L.H.; Wasielesky, W. Densidade de estocagem na engorda de camarão-branco cultivado em sistema de biofloco. Pesq. Agropec. Bras. 2013, 48, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Battisti, E.K.; Rabaioli, A.; Uczay, J.; Sutili, F.J.; Lazzari, R. Effect of stocking density on growth, hematological and biochemical parameters and antioxidant status of silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) cultured in a biofloc system. Aquaculture 2020, 524, 735213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falahatkar, B.; Bagheri, M.; Efatpanah, I. The effect of stocking densities on growth performance and biochemical indices in new hybrid of Leuciscus aspius ♀ × Rutilus frisii ♂. Aquacult. Rep. 2019, 15, 100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, T.; North, B.; Scott, A.P.; Bromage, N.R.; Porter, M.; Gadd, D. The relationships between stocking density and welfare in farmed rainbow trout. J. Fish Biol. 2002, 61, 493–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, S.J.; Sellars, M.J.; Crocos, P.J.; Coman, G.J. Intensive production of juvenile tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon: An evaluation of stocking density and artificial substrates. Aquaculture 2006, 261, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sookying, D.; Silva, F.S.D.; Davis, D.A.; Hanson, T.R. Effects of stocking density on the performance of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei cultured under pond and outdoor tank conditions using a high soybean meal diet. Aquaculture 2011, 319, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chen, J.C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yeh, S.T.; Chen, L.L.; Huang, C.L.; Hsieh, J.F.; Li, C.C. Crowding of white shrimp Litopenaeus vananmei depresses their immunity to and resistance against Vibrio alginolyticus and white spot syndrome virus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 45, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silveira, L.G.P.; Krummenauer, D.; Poersch, L.H.; Rosas, V.T.; Wasielesky, W. Hyperintensive stocking densities for Litopenaeus vannamei grow-out in biofloc technology culture system. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2020, 51, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, N.T.N.; Shayo, F.A.; Nevejan, N.; Van Hoa, N. Effects of stocking densities and feeding rates on water quality, feed efficiency, and performance of white leg shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei in an integrated system with sea grape Caulerpa lentillifera. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 3331–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preto, A.L.; Pisseti, T.L.; Wasielesky, W.J.; Poersch, L.H.; Cavalli, R.O. Production of live bait-shrimp (Farfantepenaeus paulensis) in cages at varying stoking densities. Bol. Inst. Pesca 2009, 35, 39–45. Available online: https://institutodepesca.org/index.php/bip/article/view/836/820 (accessed on 14 May 2024).
- Li, J.; Xu, S.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, H.; Lin, L.; Lv, X. The effects of net-chasing training on survival and growth are related to stocking density in the freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Aquaculture 2022, 561, 738621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nageswari, P.; Verma, A.K.; Gupta, S.; Jeyakumari, A.; Hittinahalli, C.M. Effects of different stocking densities on haematological, non-specific immune, and antioxidant defence parameters of striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) fingerlings reared in finger millet-based biofloc system. Aquacult. Int. 2022, 30, 3229–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanjani, M.H.; Sharifinia, M. Biofloc technology as a promising tool to improve aquaculture production. Rev. Aquacult. 2020, 12, 1836–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.F.M. Use of biofloc technology in shrimp aquaculture: A comprehensive review, with emphasis on the last decade. Rev. Aquacult. 2021, 13, 676–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerenciano, M.; Cuzon, G.; Paredes, A.; Gaxiola, G. Evaluation of biofloc technology in pink shrimp Farfantepenaeus duorarum culture: Growth performance, water quality, microorganisms profile and proximate analysis of biofloc. Aquacult. Int. 2013, 21, 1381–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatobá, A.; da Silva, B.C.; da Silva, J.S.; Vieira, F.; Mouriño, J.L.P.; Seiffert, W.Q.; Toledo, T.M. Protein levels for Litopenaeus vannamei in semi-intensive and biofloc systems. Aquaculture 2014, 432, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnimelech, Y. Carbon/nitrogen ratio as a control element in aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 1999, 176, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crab, R.; Defoirdt, T.; Bossier, P.; Verstraete, W. Biofloc technology in aquaculture: Beneficial effects and future challenges. Aquaculture 2012, 356–357, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekasari, J.; Angela, D.; Waluyo, S.H.; Bachtiar, T.; Surawidjaja, E.H.; Bossier, P.; De Schryver, P. The size of biofloc determines the nutritional composition and the nitrogen recovery by aquaculture animals. Aquaculture 2014, 426–427, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crab, R.; Kochva, M.; Verstraete, W.; Avnimelech, Y. Bio-flocs technology application in over-wintering of tilapia. Aquacult. Eng. 2009, 40, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krummenauer, D.; Peixoto, S.; Cavalli, R.O.; Poersch, L.H.; Wasielesky, W., Jr. Superintensive Culture of White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, in a Biofloc Technology System in Southern Brazil at Different Stocking Densities. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 2011, 42, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekasari, J.; Hanif Azhar, M.; Surawidjaja, E.H.; Nuryati, S.; De Schryver, P.; Bossier, P. Immune response and disease resistance of shrimp fed biofloc grown on different carbon sources. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2014, 41, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekasari, J.; Rivandi, D.R.; Firdausi, A.P.; Surawidjaja, E.H.; Zairin, M., Jr.; Bossier, P.; De Schryver, P. Biofloc technology positively affects Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) larvae performance. Aquaculture 2015, 441, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanjani, M.H.; Mohammadi, M.G.C.; Emerenciano, A. Microorganisms in biofloc aquaculture system. Aquacult. Rep. 2022, 26, 101300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossier, P.; Ekasari, J. Biofloc technology application in aquaculture to support sustainable development goals. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerenciano, M.G.C.; Miranda-Baeza, A.; Martínez-Porchas, M.; Poli, M.A.; Vieira, F.N. Biofloc Technology (BFT) in Shrimp Farming: Past and Present Shaping the Future. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 813091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerenciano, M.; Ballester, E.L.C.; Cavalli, R.O.; Wasielesky, W. Effect of Biofloc technology (BFT) on the early postlarval stage of pink shrimp Farfantepenaeus paulensis: Growth performance, floc composition and salinity stress tolerance. Aquacult. Int. 2011, 19, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslun, J.; Correia, E.; Strychar, K.; Morris, T.; Samocha, T. Characterization of bioflocs in a no water exchange super-intensive system for the production of food size pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Int. J. Aquacult. 2012, 2, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.H.; Song, X.L.; Yang, C.H.; Zhang, X.G.; Wang, G.C. The application of bioflocs technology in high-intensive, zero exchange farming systems of Marsupenaeus japonicus. Aquaculture 2012, 354–355, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanjani, M.H.; Alizadeh, M.; Sharifinia, M. Rearing of the Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei in a biofloc system: The effects of different food sources and salinity levels. Aquacult. Nutr. 2020, 26, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poersch, L.H.; Foes, G.; Krummenauer, D.; Romano, L.A.; Wasielesky, W. Biofloco: Uma Alternativa Para Camarões Saudáveis, 130th ed.; Panorama da Aquicultura: Laranjeiras, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Taw, N.; Saleh, U. Malaysia Shrimp Project Scales up for Production in Biosecure Biofloc Modules. Global Aquaculture Advocate January/February 2013. Available online: www.globalseafood.org/advocate/malaysia-shrimp-project-scales-up-for-production-in-biosecure-biofloc-modules/ (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- De Lorenzo, M.A.; Poli, M.A.; Candia, E.W.S.; Schleder, D.D.; Rodrigues, M.S.; Guimarães, A.M.; Seiffert, W.Q.; do Nascimento Vieira, F. Hatchery performance of the pacific white shrimp in biofloc system using different stocking densities. Aquacult. Eng. 2016, 75, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holanda, M.; Santana, G.; Furtado, P.; Rodrigues, R.V.; Cerqueira, V.R.; Sampaio, L.A.; Wasielesky, W., Jr.; Poersch, L.H. Evidence of total suspended solids control by Mugil liza reared in an integrated system with pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei using biofloc technology. Aquacult. Rep. 2020, 18, 100479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.J.; Pan, L.Q. Enhancement of immune response and antioxidant status of Litopenaeus vannamei juvenile in biofloc-based culture tanks manipulating high C/N ratio of feed input. Aquaculture 2013, 412–413, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-Jiménez, M.; Aguilera-Rivera, D.; Wasielesky, W., Jr.; Hernández-López, I.; Rodríguez-Fuentes, G.; Durruty-Lagunes, C.; Cuzon, G.; Gaxiola, G. The effect of biofloc and clear water at low and high salinity concentration on growth performance and antioxidant response of wild juveniles of Atlantic white shrimp Penaeus setiferus. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2021, 49, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrini, C.; Castro, C.; Bittencourt-Guimarães, A.; Frozza, A.; Ortiz-Kracizy, R.; Cupertino-Ballester, E. Stocking density for freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii (Decapoda, Palaemonidae) in biofloc system. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2017, 45, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, P.V.; Melo, F.P.; Ferreira, M.G.P.; Flickinger, D.L.; Correia, E.S. Larviculture of the painted river prawn Macrobrachium carcinus in different culture systems. Aquacult. Eng. 2021, 92, 102139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meruane, J.A.; Morales, M.C.; Galleguillos, C.A.; Rivera, M.A.; Hosokawa, H. Experiencias y resultados de investigaciones sobre el camarón de rio del norte Cryphiops caementarius (Molina, 1782) (Decapoda: Palaemonidae): Historia natural y cultivo. Gayana 2006, 70, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, C. Camarones Dulceacuícolas en Chile; Informe técnico-científico; Instituto de Zoología, Universidad Austral de Chile: Valdivia, Chile, 1994; 15p. [Google Scholar]
- Moscoso, V. Catálogo de crustáceos decápodos y estomatópodos del Perú. Bol. Inst. Mar. Perú 2012, 27, 209. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12958/2190 (accessed on 14 May 2024).
- Meruane, J.; Rivera, M.; Morales, C.; Galleguillos, C.; Hosokawa, H. Juvenile production of the freshwater prawn Cryphiops caementarius (Decapoda: Palaemonidae) under laboratory conditions in Coquimbo, Chile. Gayana 2006, 70, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacarías, S.; Yépez, V. Camarón de río Cryphiops caementarius (Molina, 1782) en la costa centro-sur del Perú, 2007. Inf. Inst. Mar. Perú 2015, 42, 398–415. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12958/2989 (accessed on 14 May 2024).
- Moreno-Reyes, J.E.; Morales, M.C.; Meruane, J. A feasible path towards year-round production: Effects of temperature and photoperiod on ovarian maturity of subtropical palaemonid, the river shrimp, Cryphiops caementarius. Aquacult. Rep. 2021, 21, 100809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, C.; Wilson, A.E.; Torres-Avilés, D.; Alanís, Y.; Cárcamo, F.; Morales, M.C.; Tapia, C. Propuesta de Plan de Manejo Integrado Para el Camarón de río del Norte (Cryphiops caementarius) en la Cuenca del río Choapa; Instituto de Fomento Pesquero: Valparaíso, Chile, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio Del Medio Ambiente (MMA). Decreto Supremo N°52 Aprueba y Oficializa Clasificación de Especies Según su Estado de Conservación, Décimo Proceso. Diario Oficial de la República de Chile, N°40.945, Cuerpo I-5. 2014. Available online: https://www.bcn.cl/leychile/navegar?idNorma=1065895&idParte=0http://bcn.cl/2rhef (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Ulloa, D.A.; Morales, M.C.; Emerenciano, M.G. Biofloc technology: Principles focused on potential species and the case study of Chilean river shrimp Cryphiops caementarius. Rev. Aquacult. 2020, 12, 1759–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, C.A.; Morales, M.C.; Merino, G.E. Settling velocity distribution of bioflocules generated with different carbon sources during the rearing of the river shrimp Cryphiops caementarius with biofloc technology. Aquacult. Eng. 2021, 93, 102157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulloa, D. Efectos de la Tecnología Biofloc, Utilizando dos Fuentes de Carbono, Sobre Parámetros Zootécnicos, Enzimas Digestivas y Respuesta Inmune en Cryphiops caementarius (Molina, 1782). Ph.D. Thesis, Programa Cooperativo, Universidad de Chile, Universidad Católica del Norte, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Valparaíso, Valparaiso, Chile, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Mao, Y.; Su, Y.; Wang, J. Effects of stocking density on the survival, growth and physical injury of Marsupenaeus japonicus juveniles in a flowing water aquaculture system. Aquacult. Res. 2020, 51, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nageswari, P.; Verma, A.K.; Gupta, S.; Jeyakumari, A.; Chandrakant, M.H. Optimization of stocking density and its impact on growth and physiological responses of Pangasianodon hypophthalmus (Sauvage, 1878) fingerlings reared in finger millet based biofloc system. Aquaculture 2022, 551, 737909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhu, S.; Liu, D.; Guo, X.; Ye, Z. Effects of stocking density of the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) on immunities, antioxidant status, and resistance against Vibrio harveyi in a biofloc system. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 67, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Xu, X.; Yin, X.; Lu, H.; Chen, G.; Yu, J.; Ruan, Y. Effect of stock density on the microbial community in biofloc water and Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) gut microbiota. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 4241–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, M.A.; Legarda, E.C.; de Lorenzo, M.A.; Martins, M.A.; do Nascimento Vieira, F. Pacific White shrimp and Nile tilapia integrated in a biofloc system under different fish-stocking densities. Aquaculture 2019, 498, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, M.; Islami, H.R.; Nafisi Bahabadi, M.; Hosseini Shekarabi, S.P. Production of Pacific white shrimp under different stocking density in a zero-water exchange biofloc system: Effects on water quality, zootechnical performance, and body composition. Aquacult. Eng. 2023, 100, 102313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasielesky, W., Jr.; Atwood, H.; Stokes, A.; Browdy, C.L. Effect of natural production in a zero-exchange suspended microbial floc based super-intensive culture system for white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2006, 258, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerenciano, M.G.C.; Wasielesky, W., Jr.; Soares, R.B.; Ballester, E.C.; Izeppi, E.M.; Cavalli, R.O. Crescimento e sobrevivência do camarão-rosa (Farfantepenaeus paulensis) na fase de berçário em meio heterotrófico. Acta Sci. Biol. Sci. 2007, 29, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling, J.M.; Timmons, M.B.; Bisogni, J.J. Engineering analysis of the stoichiometry of photoautotrophic, autotrophic, and heterotrophic removal of ammonia-nitrogen in aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 2006, 257, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HACH. DR/2500 Spectrophotometer Procedure Manual; HACH Company: Loveland, CO, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 19th ed.; American Public Health Association Inc.: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Avnimelech, Y.; Kochba, M. Evaluation of nitrogen uptake and excretion by tilapia in biofloc tanks, using 15N tracing. Aquaculture 2009, 287, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.K.; Bowers, R.M.; Licon, K.S.; Veazey, G.; Read, B. Validation of reference genes for quantitative measurement of immune gene expression in shrimp. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 1688–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokal, R.R.; Rohlf, F.J. Biometry: The Principles and Practices of Statistics in Biological Research, 3rd ed.; W. H. Freeman & Company: New York, NY, USA, 1995; p. 887. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Manduca, L.G.; da Silva, M.A.; de Alvarenga, É.R.; Alves, G.F.O.; Fernandes, A.F.A.; Assumpcao, A.F.; Cardoso, C.C.; de Sales, S.C.M.; Teixeira, E.A.; Silva, M.A.; et al. Effects of a zero exchange biofloc system on the growth performance and health of Nile tilapia at different stocking densities. Aquaculture 2020, 521, 735064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardera, G.; Owen, M.A.G.; Façanha, F.N.; Alcaraz-Calero, J.M.; Alexander, M.E.; Sloman, K.A. The influence of density and dominance on Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) feeding behavior. Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hawarry, W.N.; Shourbela, R.M.; Haraz, Y.G.; Khatab, S.A.; Dawood, M.A.O. The influence of carbon source on growth, feed efficiency, and growth-related genes in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) reared under biofloc conditions and high stocking density. Aquaculture 2021, 542, 736919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Avalos, W. Efecto del recipiente de cultivo sobre la supervivencia y el crecimiento de machos de Cryphiops caementarius en sistemas individualizados. Rev. Bio Ciencias 2016, 3, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, C.; Pachamoro, M.; Reyes Avalos, W. Supervivencia y crecimiento de machos adultos del camarón de río Cryphiops caementarius Molina, 1782 (Crustacea, Palaemonidae) Expuestos a salinidades. Ecol. Apl. 2017, 16, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Terrones, S.; Reyes, W. Effect of diets with biological silage of mollusk residues on the growth of shrimp Cryphiops caementarius and tilapia Oreochromis niloticus in intensive co-culture. Sci. Agropecu. 2018, 9, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Chujutalli, K.; Sernaqué-Jacinto, J.; Reyes-Avalos, W. Optimal temperature and thermal tolerance of postlarvae of the freshwater prawn Cryphiops (Cryphiops) caementarius acclimated to different temperatures. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avnimelech, Y. Biofloc Technology: A Practical Guidebook, 2nd ed.; The World Aquaculture Society: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2012; 272p. [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves, J.A. Biofloc Production Systems for Aquaculture; Southern Regional Aquaculture Center National Institute of Food and Agriculture, US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; SRAC Publication No. 4503; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, I.; Babitha Rani, A.M.; Verma, A.K.; Maqsood, M. Biofloc technology: An emerging avenue in aquatic animal healthcare and nutrition. Aquacult. Int. 2017, 25, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijn, J.; Tal, Y.; Schreier, H.J. Denitrification in recirculating systems: Theory and applications. Aquacult. Eng. 2006, 34, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.; Abutbul, S.; Zilberg, D. Acute and Chronic Effects of nitrite on White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, Cultured in Low-Salinity Brackish Water. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 2004, 35, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtado, P.S.; Valenzuela, M.A.; Rodriguez-Fuentes, G.; Campos, B.R.; Wasielesky, W., Jr.; Gaxiola, G. Chronic effect of nitrite on the rearing of the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei in two salinities. Mar. Freshwater Behav. Physiol. 2016, 49, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Liu, C.H.; Kuo, C.M. Effects of dissolved oxygen on hemolymph parameters of freshwater giant prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii (de Man). Aquaculture 2003, 220, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeling, J.M.; Timmons, M.B. Recirculating Aquaculture Systems, 2nd ed.; Cayuga Aqua Ventures: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2010; 939p. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Ling, J.; Blancheton, J.P. Nitrification kinetics of biofilm as affected by water quality factors. Aquacult. Eng. 2006, 34, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wyk, P.; Scarpa, J. Water quality requirements and management. In Farming Marine Shrimp in Recirculating Freshwater Systems; Van Wyk, P., Davis-Hodgkins, M., Laramore, R., Main, K.L., Mountain, J., Scarpa, J., Eds.; Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1999; pp. 141–162. [Google Scholar]
- Furtado, P.S.; Poersch, L.H.; Wasielesky, W. The effect of different alkalinity levels on Litopenaeus vannamei reared with biofloc technology (BFT). Aquacult. Int. 2015, 23, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, E.S.; Wilkenfeld, J.S.; Morris, T.C.; Wei, L.; Prangnell, D.I.; Samocha, T.M. Intensive nursery production of the Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei using two commercial feeds with high and low protein content in a biofloc-dominated system. Aquacult. Eng. 2014, 59, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.R.; Sarkar, S.; Saranya, C.; Esakkiraj, P.; Aravind, R.; Saraswathy, R.; Rekha, P.N.; Muralidhar, M.; Panigrahi, A. Co-culture of Indian white shrimp, Penaeus indicus and seaweed, Gracilaria tenuistipitata in amended biofloc and recirculating aquaculture system (RAS). Aquaculture 2022, 548, 737432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, A.; Saranya, C.; Sundaram, M.; Vinoth Kannan, S.R.; Das, R.R.; Satish Kumar, R.; Rajesh, P.; Otta, S.K. Carbon: Nitrogen (C:N) ratio level variation influences microbial community of the system and growth as well as immunity of shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) in biofloc based culture system. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 81, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Abakari, G.; Luo, G.; Tan, H.; Wu, X. Comparative analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus budgets in a bioflocs aquaculture system and recirculation aquaculture system during over-wintering of tilapia (GIFT, Oreochromis niloticus). Aquacult. Eng. 2020, 89, 102026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaona, C.P.A.; de Almeida, M.S.; Viau, V.; Poersch, L.H.; Wasielesky, W., Jr. Effect of different total suspended solids levels on a Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) BFT culture system during biofloc formation. Aquacult. Res. 2017, 48, 1070–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schveitzer, R.; Arantes, R.; Custódio, P.F.S.; do Espírito Santo, C.M.; Arana, L.V.; Seiffert, W.Q.; Andreatta, E.R. Effect of different biofloc levels on microbial activity, water quality and performance of Litopenaeus vannamei in a tank system operated with no water exchange. Aquacult. Eng. 2013, 56, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samocha, T.M.; Patnaik, S.; Speed, M.; Ali, A.M.; Burger, J.M.; Almeida, R.V.; Ayub, Z.; Harisanto, M.; Horowitz, A.; Brock, D.L. Use of molasses as carbon source in limited discharge nursery and grow-out systems for Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquacult. Eng. 2007, 36, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fróes, C.N.; Fóes, G.; Krummenauer, D.; Ballester, E.; Poersch, L.H.; Wasielesky, W., Jr. Fertilização orgânica com carbono no cultivo intensivo em viveiros com sistema de bioflocos do camarão branco Litopenaeus Vannamei. Atlântica 2012, 34, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schryver, P.; Verstraete, W. Nitrogen removal from aquaculture pond water by heterotrophic nitrogen assimilation in lab-scale sequencing batch reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, A.J.; Lotz, J.M. Comparing a chemoautotrophic-based biofloc system and three heterotrophic-based systems receiving different carbohydrate sources. Aquacult. Eng. 2014, 63, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Fuentes, J.A.; Pérez-Rostro, C.I.; Hernández-Vergara, M.P. Pond-reared Malaysian prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii with the biofloc system. Aquaculture 2013, 400–401, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araneda, M.; Pérez, E.P.; Gasca-Leyva, E. White shrimp Penaeus vannamei culture in freshwater at three densities: Condition state based on length and weight. Aquaculture 2008, 283, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, S.J.; Coman, F.E.; Jackson, C.J.; Groves, S.A. High-intensity, zero water-exchange production of juvenile tiger shrimp, Penaeus monodon: An evaluation of artificial substrates and stocking density. Aquaculture 2009, 293, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, G.; Peyail, S.; Ramachandran, K.; Theivasigamani, A.; Savji, K.A.; Chokkaiah, M.; Nataraj, P. Growth of Cultured White Leg Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone 1931) In Different Stocking Density. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2011, 2, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Carvajal-Valdes, R.; Arjona, E.; Bueno, G. Feeding rate and stocking density in semi-intensive Litopenaeus vannamei culture with moderate periodic fertilization. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2012, 7, 899–904. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, E.; Silva, J.; Ferreira, F.; Soares, M.; Soares, R.; Peixoto, S. Influence of stocking density on the zootechnical performance of Litopenaeus vannamei during the nursery phase in a biofloc system. Bol. Inst. Pesca 2015, 41, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, A.; Sundaram, M.; Saranya, C.; Satish Kumar, R.; Syama Dayal, J.; Saraswathy, R.; Otta, S.K.; Shyne Anand, P.S.; Nila Rekha, P.; Gopal, C. Influence of differential protein levels of feed on production performance and immune response of pacific white leg shrimp in a biofloc–based system. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasielesky, W., Jr.; Froes, C.; Fóes, G.; Krummenauer, D.; Lara, G.; Poersch, L. Nursery of Litopenaeus vannamei reared in a biofloc system: The effect of stocking densities and compensatory growth. J. Shellfish Res. 2013, 32, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza-Leal, H.M.; Ponce-Palafox, J.T.; Álvarez-Ruiz, P.; López-Álvarez, E.S.; Vázquez-Montoya, N.; López-Espinoza, M.; Montoya, M.; Gómez-Peraza, R.L.; Nava-Perez, E. Effect of stocking density and water exchange on performance and stress tolerance to low and high salinity by Litopenaeus vannamei postlarvae reared with biofloc in intensive nursery phase. Aquacult. Int. 2020, 28, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.S.; Davis, D.A.; Arnold, C.R. Density-Dependent Growth and Survival of Penaeus setiferus and Penaeus vannamei in a Semi-Closed Recirculating System. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 1996, 27, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, W.C.; New, M.B. Grow-out Systems—Monoculture. In Freshwater Prawn Culture: The Farming of Macrobrachium rosenbergii; New, M.B., Valenti, W.C., Eds.; Blackwell Science Ltd.: London, UK, 2000; pp. 157–176. [Google Scholar]
- Ponce, J.E. Importancia del flujo de agua en los estanques-criaderos de camarón. In Proceedings of the Actas del Simposio sobre Acuicultura en América Latina, Montevideo, Uruguay, 26 November–2 December 1974; Documentos de Investigación. FAO, Informes de Pesca. FAO: Rome, Italy, 1977; Volume 159, pp. 240–248. Available online: https://www.fao.org/4/AC866S/AC866S00.htm#TOC (accessed on 14 May 2024).
- Cano, F.; Carrion, S.; Reyes, W. Efecto de altas densidades de siembra en el crecimiento y supervivencia de postlarvas de Cryphiops caementarius (Crustacea: Palaemonidae) en agua salobre. Rev. Citecsa 2014, 5, 62–78. [Google Scholar]
- Alston, D.E.; Sampaio, C.M.S. Nursery systems and management. In Freshwater Prawn Culture: The Farming of Macrobrachium rosenbergii; New, M.B., Valenti, W.C., Eds.; Blackwell Science Ltd.: London, UK, 2000; pp. 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- Tidwell, J.H.; D’Abramo, L.R.; Coyle, S.D.; Yasharian, D. Overview of recent research and development in temperate culture of the freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii De Man) in the South Central United States. Aquacult. Res. 2005, 36, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boock, M.V.; de Almeida Marques, H.L.; Mallasen, M.; Barros, H.P.; Moraes-Valenti, P.; Valenti, W.C. Effects of prawn stocking density and feeding management on rice-prawn culture. Aquaculture 2016, 451, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.M.; Ruscoe, I.M. Assessment of stocking size and density in the production of redclaw crayfish, Cherax quadricarinatus (von Martens) (Decapoda: Parastacidae), cultured under earthen pond condition. Aquaculture 2000, 189, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, D.; Genc, E.; Genc, M.A.; Aktas, M.; Eroldogan, O.T.; Guroy, D. Biofloc technology in recirculating aquaculture system as a culture model for green tiger shrimp, Penaeus semisulcatus: Effects of different feeding rates and stocking densities. Aquaculture 2020, 528, 735526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, B.J.; McCloud, P.I. Effects of stocking and feeding rates on experimental pond production of the crayfish Cherax destructor Clark (Decapoda: Parastacidae). Aquaculture 1983, 34, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karplus, I.; Hulata, G.; Wohlfarth, G.W.; Halevy, A. The effect of size-grading juvenile Macrobrachium rosenbergii prior to stocking on their population structure and production in polyculture: I. Dividing the population into two fractions. Aquaculture 1986, 56, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barki, A.; Karplus, I.; Goren, M. Effects of size and morphotype on dominance hierarchies and resource competition in the freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Anim. Behav. 1992, 44, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClain, W.R. Investigations of crayfish density and supplemental feeding as factors influencing growth and production of Procambarus clarkii. Freshw. Crayfish 1995, 10, 512–520. [Google Scholar]
- Ahvenharju, T. Food Intake, Growth and Social Interactions of Signal Crayfish, Pacifastacus leniusculus (Dana). Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland, 2007; 60p. [Google Scholar]
- Moraes-Valenti, P.; de Morais, P.A.; de Lima Preto, B.; Valenti, W.C. Effect of density on population development in the Amazon River prawn Macrobrachium amazonicum. Aquat. Biol. 2010, 9, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, N.; Zeng, C. Cannibalism of Decapod Crustaceans and Implications for Their Aquaculture: A Review of its Prevalence, Influencing Factors, and Mitigating Methods. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquacult. 2016, 25, 42–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, E.; Lorgeoux, B.; Chim, L.; Goguenheim, J.; Le Delliou, H.; Cahu, C. Biofloc contribution to antioxidant defense status, lipid nutrition and reproductive performance of broodstock of the shrimp Litopenaeus stylirostris: Consequences for the quality of eggs and larvae. Aquaculture 2016, 452, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.S.; Mohammad, D.A.; Ali, E.M.; Sallam, W.S. Growth Performance of the Green Tiger Shrimp Penaeus semisulcatus Raised in Biofloc Systems. J. Aquac. Mar. Biol. 2015, 2, 00038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, C.; Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G. Effects of C/N ratio control combined with probiotics on the immune response, disease resistance, intestinal microbiota and morphology of giant fresh-water prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii). Aquaculture 2017, 476, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan-Vivas, E.; Magaña, E.; Maldonado, C.; Escalante, K.; Gaxiola, G.; Cuzon, G. Does Biofloc Improve the Energy Distribution and Final Muscle Quality of Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1883)? J. World Aquacult. Soc. 2019, 50, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AftabUddin, S.; Siddique, M.A.M.; Sein, A.; Dey, P.K.; Rashed-Un-Nabi, M.; Haque, M.A. First use of biofloc technology for Penaeus monodon culture in Bangladesh: Effects of stocking density on growth performance of shrimp, water quality and bacterial growth. Aquacult. Rep. 2020, 18, 100518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, A.; Das, R.R.; Sivakumar, M.R.; Saravanan, A.; Saranya, C.; Sudheer, N.S.; Kumaraguru Vasagam, K.P.; Mahalakshmi, P.; Kannappan, S.; Gopikrishna, G. Bio-augmentation of heterotrophic bacteria in biofloc system improves growth, survival, and immunity of Indian white shrimp Penaeus indicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silveira, L.G.P.; Rosas, V.T.; Krummenauer, D.; Fróes, C.; da Silva, A.; Poersch, L.H.; Fóes, G.; Wasielesky, W. Establishing the most productive stocking densities for each stage of a multi-phase shrimp culture in BFT system. Aquacult. Int. 2022, 30, 1889–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerenciano, M.G.C.; Martínez- Córdova, L.R.; Martínez-Porchas, M.; Miranda-Baeza, A. Biofloc Technology (BFT): A Tool for Water Quality Management in Aquaculture. In Water Quality; Tutu, H., Ed.; Intech.: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2017; pp. 91–109. [Google Scholar]
- Tacon, A.G.J.; Cody, J.J.; Conquest, L.D.; Divakaran, S.; Forster, I.P.; Decamp, O.E. Effect of culture system on the nutrition and growth performance of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) fed different diets. Aquacult. Nutr. 2002, 8, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.S.; Mohammad, D.A.; Sallam, W.S.; Shoukry, N.M.; Davis, D.A. Effects of culturing the Pacific white shrimp Penaeus vannamei in “biofloc” vs “synbiotic” systems on the growth and immune system. Aquaculture 2021, 542, 736905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wyk, P. Nutrition and Feeding of Litopenaeus vannamei in Intensive Culture Systems. In Farming Marine Shrimp in Recirculating Freshwater Systems; Van Wyk, P., Davis-Hodgkins, M., Laramore, R., Main, J.K., Mountain, L., Scarpa, J., Eds.; Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1999; pp. 125–139. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, D.D.; Lawrence, A.L.; Crockett, J.; Taylor, D. Evaluation of bioflocs derived from confectionary food effluent water as a replacement feed ingredient for fishmeal or soy meal for shrimp. Aquaculture 2016, 454, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silveira, L.G.P.; Krummenauer, D.; Poersch, L.H.; Fóes, G.K.; Rosas, V.T.; Wasielesky, W., Jr. The effect of partial harvest on production and growth performance of Litopenaeus Vannamei reared in biofloc technologic system. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marqués, H.L.A.; Lombardi, J.V.; Mallasen, M.; Barros, H.P.; Boock, M.V. Stocking densities in cage rearing of Amazon River prawn (Macrobrachium amazonicum) during nursery phases. Aquaculture 2010, 307, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.Y. Heat Shock Proteins: An Alternative to Control Disease in Aquatic Organism. J. Marine Sci. Res. Dev. 2014, 4, e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.Y.; Roberts, R.J.; Bossier, P. Enhancement of Hsp70 synthesis protects common carp, Cyprinus carpio L., against lethal ammonia toxicity. J. Fish Dis. 2012, 35, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celi, M.; Filiciotto, F.; Vazzana, M.; Arizza, V.; Maccarrone, V.; Ceraulo, M.; Mazzola, S.; Buscaino, G. Shipping noise affecting immune responses of European spiny lobster Palinurus elephas (Fabricius, 1787). Can. J. Zool. 2015, 93, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.Y.; Pineda, C.; MacRae, T.H.; Sorgeloos, P.; Bossier, P. Exposure of gnotobiotic Artemia franciscana larvae to abiotic stress promotes heat shock protein 70 synthesis and enhances resistance to pathogenic Vibrio campbellii. Cell Stress Chaperones 2008, 13, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishi, K.; Sinnasamy, S.; MacRae, T.H.; Tengku-Muhammad, T.S.; Lv, A.; Sun, J.; Chen, S.; Shi, H.; Pau, T.M.; Abdullah, M.D.D.; et al. Hsp70 knockdown reduced the tolerance of Litopenaeus vannamei post larvae to low pH and salinity. Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, V.; Brokordt, K.; Romero, A.; Farías, A.; Uriarte, I. Evaluation of physiological stress and nutritional deficiency related to cannibalism in early paralarvae of Patagonian red octopus Enteroctopus megalocyathus. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder, M.E.; Hofmann, G.E. Heat-shock proteins, molecular chaperones, and the stress response: Evolutionary and ecological physiology. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1999, 61, 243–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, S.S.; Giri, S.S. Physiological Role of Heat Shock Proteins, Molecular Function and Stress Removal in Fishes. In Heat Shock Proteins in Veterinary Medicine and Sciences; Asea, A., Kaur, P., Eds.; Heat Shock Proteins; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 12, pp. 215–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; He, Z.; Vector, H.; Zhao, B.; Li, Z.; He, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Chu, Z. Effect of Stocking density on Growth, Oxidative Stress and HSP 70 of Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Turk. J. Fish Aquat. Sci. 2017, 17, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, S.; Haldar, C. Effects of Stress among Shrimp Post-Larvae stocked at High Stocking Density in Nursery Culture System: A Review. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2020, 9, 2987–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Y.; Feng, J.; Lu, W.; Liu, D.; Wu, T.; Zhu, H.; Liu, P.; Li, W.; Ren, Q.; Gu, W.; et al. Identification of a novel cognate cytosolic Hsp70 gene (MnHsc70-2) from oriental river prawn Macrobrachium nipponense and comparison of its expressions with the first cognate Hsc70 (MnHsc70-1) under different stresses. Cell Stress Chaperones 2014, 19, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksu, Ö.; Kutluyer, F.; Can, E.; Erişir, M.; Benzer, F. Influence of stock density on digestive enzyme activity (trypsin), heat shock protein 70 (HSP70), and oxidative stress biomarkers of narrow clawed crayfish, Astacus leptodactylus Eschscholtz, 1823 (Decapoda, Astacidae). Crustaceana 2016, 89, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.H.; Petersen, N.S.; Young, P.A.; Stansbury, M.A.; Farag, A.M.; Bergman, H.L. Accumulation of hsp70 in juvenile and adult rainbow trout gill exposed to metal-contaminated water and/or diet. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1996, 15, 1324–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridha, M.T. Comparative study of growth performance of three strains of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, L. at two stocking densities. Aquacult. Res. 2006, 37, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksakal, E.; Ekinci, D.; Erdogan, O.; Beydemir, S.; Alım, Z.; Ceyhun, S.B. Increasing stocking density causes inhibition of metabolic–antioxidant enzymes and elevates mRNA levels of heat shock protein 70 in rainbow trout. Lives. Sci. 2011, 141, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanein, H.M.; Banhawy, M.A.; Soliman, F.M.; Abdel-Rehim, S.A.; Müller, W.E.; Schröder, H.C. Induction of HSP70 by the herbicide oxyfluorfen (Goal) in the Egyptian Nile fish, Oreochromis niloticus. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Vaseeharan, B.; Chen, J.C. Identification of the extracellular copper–zinc superoxide dismutase (ecCuZnSOD) gene of the mud crab Scylla serrata and its ex-pression following β-glucan and peptidoglycan injections. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 1346–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, B. The role of Cu/Zn-SOD and Mn-SOD in the immune response to oxidative stress and pathogen challenge in the clam Meretrix meretrix. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 42, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, M.A.; Alabssawy, A.N.; Nour, A.A.M.; El Basuini, M.F.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Alkahtani, S.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. The impact of stocking density and dietary carbon sources on the growth, oxidative status and stress markers of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) reared under biofloc conditions. Aquacult. Rep. 2020, 16, 100282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, L.S.; Palacios, E.; Campa-Córdova, Á.; Tovar-Ramírez, D.; Hernández- Herrera, R.; Racotta, I.S. Metabolic and immune responses in Pacific whiteleg shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei exposed to a repeated handling stress. Aquaculture 2006, 258, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.J.; Pan, L.Q. Evaluation of dietary protein level on selected parameters of immune and antioxidant systems, and growth performance of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei reared in zero-water exchange biofloc-based culture tanks. Aquaculture 2014, 426–427, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, L.; Zhu, R.; Li, M.; Wu, L.F. Effects of bioflocs with different C/N ratios on growth, immunological parameters, antioxidants and culture water quality in Opsariichthys kaopingensis Dybowski. Aquacul. Res. 2020, 51, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Quan, Y.N.; Huang, Z.Q.; Wang, H.H.; Wu, L.F. Monitoring oxidative stress, immune response, Nrf2/NF-κB signaling molecules of Rhynchocypris lagowski living in BFT system and exposed to waterborne ammonia. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 205, 11116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Z.Y.; Forster, I.; Conquest, L.; Dominy, W. Enhanced growth effects on shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) from inclusion of whole shrimp floc or floc fractions to a formulated diet. Aquacult. Nutr. 2008, 14, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Martins, Á.C.; Artigas-Flores, J.; Porto, C.; Wasielesky, W., Jr.; Monserrat, J.M. Antioxidant and oxidative damage responses in different organs of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) reared in a biofloc technology system. Mar. Freshwater Behav. Physiol. 2015, 48, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, D.C.; Wasiliesky, W., Jr.; Monserrat, J.M. Quercetin influence in water quality and biochemical responses of shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei reared in Biofloc Technology System. Aquacult. Res. 2018, 49, 3569–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krummenauer, D.; Abreu, P.C.; Poersch, L.; Reis, P.A.C.P.; Suita, S.M.; dos Reis, W.G.; Wasielesky, W., Jr. The relationship between shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) size and biofloc consumption determined by the stable isotope technique. Aquaculture 2020, 529, 735635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, A.; Das, R.R.; Sundaram, M.; Sivakumar, M.R.; Jannathulla, R.; Lalramchhani, C.; Antony, J.; Shyne Anand, P.S.; Vinay Kumar, K.; Jayanthi, M.; et al. Cellular and molecular immune response and production performance of Indian white shrimp Penaeus indicus (H. Milne-Edwards, 1837), reared in a biofloc-based system with different protein levels of feed. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 119, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brol, J.; Müller, L.; Cordeiro Andrade Prates, E.; Silva de Farias, B.; Fonseca Pedrosa, V.; de Almeida Pinto, L.A.; Sant’anna Cadaval, T.R., Jr.; Borges Tesser, M.; Wasielesky, W.; Ventura-Lima, J. Dietary chitosan supplementation in Litopenaeus vannamei reared in a biofloc system: Effect on antioxidant status facing saline stress. Aquaculture 2021, 544, 737034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, F.P.D.; Ferreira, M.G.P.; Lima, J.P.V.D.; Correia, E.D.S. Marine shrimp culture with bioflocs under different protein levels with and without probiotic. Rev. Caatinga 2015, 28, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, H.H.; Li, C.Y.; Song, Y.; Lei, Y.J.; Yang, P.H. Growth performance of shrimp and water quality in a freshwater biofloc system with a salinity of 5.0‰: Effects on inputs, costs and wastes discharge during grow-out culture of Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquacult. Eng. 2022, 98, 102265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).