An Economic View on the Effects of Invasive Rabbitfishes Based on Fishers’ Perspectives: The Case of the Parrotfish Métier in the South Ionian Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Their perception regarding the parrotfish population, spatial distribution, and its evolution during the last decade;
- The main problems arising from the presence of rabbitfishes in the fishing grounds they used to fish, and their main impacts (e.g., degradation of fishing grounds, interaction with of commercial species);
- If/how they adapt their fishing habits based on the presence of rabbitfishes;
- How much additional workload is needed to disentangle rabbitfish from the nets, based on different catch shares (10%, 25%, 50%, 75%, or 100%);
- Identification of hot and cold spots of rabbitfishes using area maps;
- Fuel costs related to the parrotfish métier and whether they increase in case they try to avoid the rabbitfishes’ areas of distribution;
- Average wages in the area (hourly rate);
- Prices of parrotfish and other commercial species identified by the fishers operating the parrotfish métier considering also potential prices for rabbitfishes in local markets.
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frazão Santos, C.; Agardy, T.; Andrade, F.; Calado, H.; Crowder, L.B.; Ehler, C.N.; García-Morales, S.; Gissi, E.; Halpern, B.S.; Orbach, M.K.; et al. Integrating climate change in ocean planning. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rilov, G. Multi-species collapses at the warm edge of a warming sea. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenetos, A.; Galanidi, M. Mediterranean non indigenous species at the start of the 2020s: Recent changes. Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2020, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrabou, J.; Coma, R.; Bensoussan, N.; Bally, M.; Chevaldonné, P.; Cigliano, M.; Diaz, D.; Harmelin, J.G.; Gambi, M.C.; Kersting, D.K.; et al. Mass mortality in Northwestern Mediterranean rocky benthic communities: Effects of the 2003 heat wave. Glob. Change Biol. 2009, 15, 1090–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrabou, J.; Gómez-Gras, D.; Medrano, A.; Cerrano, C.; Ponti, M.; Schlegel, R.; Bensoussan, N.; Turicchia, E.; Sini, M.; Gerovasileiou, V.; et al. Marine heatwaves drive recurrent mass mortalities in the Mediterranean Sea. Glob. ChangeBiol. 2022, 28, 5708–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenetos, A.; Albano, P.G.; Garcia, E.L.; Stern, N.; Tsiamis, K.; Galanidi, M. Established non-indigenous species increased by 40% in 11 years in the Mediterranean Sea. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2022, 23, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzani, P.; Cuthbert, R.N.; Briski, E.; Galil, B.; Castellanos-Galindo, G.A.; Kouba, A.; Kourantidou, M.; Leung, B.; Soto, I.; Haubrock, P.J. Knowledge needs in economic costs of invasive species facilitated by canalisation. NeoBiota 2022, 78, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourantidou, M.; Cuthbert, R.N.; Haubrock, P.J.; Novoa, A.; Taylor, N.G.; Leroy, B.; Capinha, C.; Renault, D.; Angulo, E.; Diagne, C.; et al. Economic costs of invasive alien species in the mediterranean basin. NeoBiota 2021, 67, 427–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkan, A.S.; Yoğurtçuoğlu, B.; Karachle, P.K.; Kalogianni, E.; Top Karakuş, N.; Tricarico, E. Editorial: Understanding the Impact and Invasion Success of Aquatic Non-native Species: How They Interact with Novel Environments and Native Biota. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 790540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakoumi, S.; Pey, A.; Thiriet, P.; Francour, P.; Guidetti, P. Patterns of predation on native and invasive alien fish in Mediterranean protected and unprotected areas. Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 150, 104792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, M.; Scarcella, G. Mediterranean sea: A failure of the European fisheries management system. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint Research Centre; Scientific, Technical and Economic Committee for Fisheries. The 2021 Annual Economic Report on the EU Fishing Fleet; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2021; ISBN 978-92-76-40959-5. [Google Scholar]
- Tsiamis, K.; Palialexis, A.; Stefanova, K.; Gladan, Ž.N.; Skejić, S.; Despalatović, M.; Cvitković, I.; Dragičević, B.; Dulčić, J.; Vidjak, O.; et al. Non-indigenous species refined national baseline inventories: A synthesis in the context of the European Union’s Marine Strategy Framework Directive. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelist, D.; Rilov, G.; Golani, D.; Carlton, J.T.; Spanier, E. Restructuring the Sea: Profound shifts in the world’s most invaded marine ecosystem. Divers. Distrib. 2013, 19, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragkousis, M.; Sini, M.; Koukourouvli, N.; Zenetos, A.; Katsanevakis, S. Invading the Greek Seas: Spatiotemporal Patterns of Marine Impactful Alien and Cryptogenic Species. Diversity 2023, 15, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakoumi, S.; Cebrian, E.; Kokkoris, G.D.; Ballesteros, E.; Sala, E. Relationships between fish, sea urchins and macroalgae: The structure of shallow rocky sublittoral communities in the Cyclades, Eastern Mediterranean. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 109, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanevakis, S.; Tempera, F.; Teixeira, H. Mapping the impact of alien species on marine ecosystems: The Mediterranean Sea case study. Divers. Distrib. 2016, 22, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rijn, I.; Kiflawi, M.; Belmaker, J. Alien species stabilize local fisheries catch in a highly invaded ecosystem. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 77, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Aswatha, S.M. An analysis of the influence of growth periods on physical appearance, and acemannan and elemental distribution of Aloe vera L. gel. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 48, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirintanis, K.; Azzurro, E.; Crocetta, F.; Dimiza, M.; Froglia, C.; Gerovasileiou, V.; Langeneck, J.; Mancinelli, G.; Rosso, A.; Stern, N.; et al. Bioinvasion impacts on biodiversity, ecosystem services, and human health in the Mediterranean Sea. Aquat. Invasions 2022, 17, 308–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasidis, V.; Doumpas, N.; Giovos, I.; Kleitou, P.; Kaminas, A.; Moutopoulos, D.K. Assessing Consumer Attitude towards Marine Non-Indigenous Fish Species: A Case Study From Greece (Eastern Mediterranean Sea). Thalassas 2023, 39, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavraro, F.; Anelli Monti, M.; Matić-Skoko, S.; Caccin, A.; Pranovi, F. Vulnerability of the Small-Scale Fishery to Climate Changes in the Northern-Central Adriatic Sea (Mediterranean Sea). Fishes 2023, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanatos, E.; Georgiadis, M.; Peristeraki, P. Small-Scale Fisheries in Greece: Status, Problems, and Management. InSmall-Scale Fisheries in Europe: Status, Resilience and Governance; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 125–150. [Google Scholar]
- Liontakis, A.; Tzouramani, I.; Mantziaris, S.; Sintori, A. Unravelling the role of gender in fisheries’ socio-economic performance: The case of Greek small-scale fisheries. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanevakis, S.; Zenetos, A.; Belchior, C.; Cardoso, A.C. Invading European Seas: Assessing pathways of introduction of marine aliens. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 76, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenetos, A.; Gofas, S.; Verlaque, M.; Çinar, M.E.; García Raso, J.G.; Bianchi, C.N.; Morri, C.; Azzurro, E.; Bilecenoglu, M.; Froglia, C.; et al. Alien species in the Mediterranean Sea by 2010. A contribution to the application of European Union’s Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). Part I. Spatial distribution. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2010, 11, 381–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayram, Ö. Non-Indigenous Species in the Mediterranean and the Black Sea; General Fisheries Commission for the Mediterranean: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A.; Galil, B. Marine alien species as an aspect of global change. Adv. Oceanogr. Limnol. 2010, 1, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanidi, M.; Zenetos, A.; Bacher, S. Assessing the socio-economic impacts of priority marine invasive fishes in the Mediterranean with the newly proposed SEICAT methodology. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2018, 19, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peristeraki, P.; Skarvelis, K.; Giannakaki, A.; Tambakakis, K.; Tserpes, G. Preliminary results on the abundance of alien species in the coastal fisheries catches of Crete. In Proceedings of the 11th Panhellenic Symposium on Oceanography and Fisheries, Mytilene, Lesvos Island, Greece, 13–17 May 2015; pp. 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Kalogirou, S.; Mittermayer, F.; Pihl, L.; Wennhage, H. Feeding ecology of indigenous and non-indigenous fish species within the family Sphyraenidae. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 80, 2528–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogirou, S. Ecological characteristics of the invasive pufferfish Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) in Rhodes, Eastern Mediterranean Sea. A case study. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2013, 14, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogirou, S.; Wennhage, H.; Pihl, L. Non-indigenous species in Mediterranean fish assemblages: Contrasting feeding guilds of Posidonia oceanica meadows and sandy habitats. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 96, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bariche, M.; Letourneur, Y.; Harmelin-Vivien, M. Temporal fluctuations and settlement patterns of native and Lessepsian herbivorous fishes on the Lebanese coast (eastern Mediterranean). Environ. Biol. Fishes 2004, 70, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanou, M.; Valavanis, V.D.; Karachle, P.K.; Giannoulaki, M. Looking at the Expansion of Three Demersal Lessepsian Fish Immigrants in the Greek Seas: What Can We Get from Spatial Distribution Modeling? Diversity 2023, 15, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öndes, F.; Ünal, V. The dominance of non-indigenous species in the catch composition of small-scale fisheries: A case study from the Kaş–Kekova Special Environmental Protection Area, Türkiye, Eastern Mediterranean. Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 2023, 53, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, M.; Cebrian, E.; Francour, P.; Galil, B.; Savini, D. Monitoring Marine Invasive Species in Mediterranean Marine Protected Areas (MPAs): A Strategy and Practical Guide for Managers; IUCN: Malaga, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- GFCM-UNEP/MAP. Report of the Joint GFCM-UN Environment/MAP Subregional Pilot Study for the Eastern Mediterranean on Non-Indigenous Species in Relation to Fisheries UNEP(DEPI)/MED WG.445/4; UNEP: Geneva, Swotzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- WWF. Fishing in the Tine of Climate Change: The Economy and Biodiversity of the Mediterranean Are Being Threatened by New Invaders. Available online: https://wwf.exposure.co/fishing-at-the-time-of-climate-change (accessed on 7 August 2023).
- Giakoumi, S.; Katsanevakis, S.; Albano, P.G.; Azzurro, E.; Cardoso, A.C.; Cebrian, E.; Deidun, A.; Edelist, D.; Francour, P.; Jimenez, C.; et al. Management priorities for marine invasive species. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magneville, C.; Leréec Le Bricquir, M.L.; Dailianis, T.; Skouradakis, G.; Claverie, T.; Villéger, S. Long-duration remote underwater videos reveal that grazing by fishes is highly variable through time and dominated by non-indigenous species. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 9, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleitou, P.; Moutopoulos, D.K.; Giovos, I.; Kletou, D.; Savva, I.; Cai, L.L.; Hall-Spencer, J.M.; Charitou, A.; Elia, M.; Katselis, G.; et al. Conflicting interests and growing importance of non-indigenous species in commercial and recreational fisheries of the Mediterranean Sea. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2022, 29, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsini, M.; Stamatellos, S. Information collected at the Hydrobiological Station of Rhodes (Greece) on Lessepsian migrant fishes. In Proceedings of the 16th European Union of Aquarium Curators Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 25–29 September 1998; pp. 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Quintana, A.; Marcos, S.; Malpica-Cruz, L.; Tamayo, L.; CantoNoh, J.Á.; Fernández-RiveraMelo, F.; Fulton, S. Socioeconomic dilemmas of commercial markets for invasive species: Lessons from lionfish in Mexico. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2023, 80, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, M.A.; Kuebbing, S.; Dimarco, R.D.; Simberloff, D. Invasive Species: To eat or not to eat, that is the question. Conserv. Lett. 2012, 5, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, B.; Sims, C. Can We Love Invasive Species to Death? Creating Efficient Markets for Invasive Species Harvests. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2023, 85, 443–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arianoutsou, M.; Adamopoulou, C.; Andriopoulos, P.; Bazos, I.; Christopoulou, A.; Galanidis, A.; Kalogianni, E.; Karachle, P.K.; Kokkoris, Y.; Martinou, A.F. HELLAS-ALIENS. The invasive alien species of Greece: Time trends, origin and pathways. NeoBiota 2023, 86, 45–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagarakis, K.; Palialexis, A.; Vassilopoulou, V. Mediterranean fishery discards: Review of the existing knowledge. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 71, 1219–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, G.; Prearo, M.; Menconi, V.; Mugetti, D.; Meloni, D.; Tomasoni, M.; Pizzul, E.; Piras, P.; Renzi, M.; Gaspa, D.; et al. Northward spread of the parrotfish Sparisoma cretense (Teleostei: Scaridae) in the mediterranean sea: An update on current distribution with two new records from Sardinia. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoutsoglou, E.S.; Lyndon, A.R. Distribution of α-amylase along the alimentary tract of two Mediterranean fish species, the parrotfish Sparisoma cretense L. and the stargazer, Uranoscopus scaber L. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2003, 4, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Giakoumi, S. Distribution patterns of the invasive herbivore Siganus luridus (Rüppell, 1829) and its relation to native benthic communities in the central Aegean Sea, Northeastern Mediterranean. Mar. Ecol. 2014, 35, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavvadas, S.; Damalas, D.; Georgakarakos, S.; Maravelias, C.; Tserpes, G.; Papaconstantinou, C.; Bazigos, G. IMAS-Fish: Integrated MAnagement System to support the sustainability of Greek Fisheries resources. A multidisciplinary web-based database management system: Implementation, capabilities, utilization and future prospects for fisheries stakeholde. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2013, 14, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogirou, S.; Corsini-Foka, M.; Sioulas, A.; Wennhage, H.; Pihl, L. Diversity, structure and function of fish assemblages associated with Posidonia oceanica beds in an area of the eastern Mediterranean Sea and the role of non-indigenous species. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 77, 2338–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, J.W.; Feldman, P.; Schuemann, K. Simetar™; Department of Agricultural Economics, Texas A&M University: College Station, TX, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Concu, G.B.; Atzeni, G.; Meleddu, M.; Vannini, M. Policy design for climate change mitigation and adaptation in sheep farming: Insights from a study of the knowledge transfer chain. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 107, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scientific Technical and Economic Committee for Fisheries (STECF). Scientific, Technical and Economic Committee for Fisheries (STECF): The 2019 Annual Economic Report on the EU Fishing Fleet (STECF 19-06); Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2019; Volume JRC 97371, ISBN 9789276095170. [Google Scholar]
- Sgardeli, V.; Damalas, D.; Liontakis, A.; Maravelias, C.D.; Mantopoulou-Palouka, D.; Tserpes, G. The Aegean Sea demersal fishery under four climatic and socio-political futures. Mar. Policy 2022, 144, 105194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liontakis, A.; Vassilopoulou, V. Exploring fishing tourism sustainability in North-Eastern Mediterranean waters, through a stochastic modelling analysis: An opportunity for the few or a viable option for coastal communities? Ocean Coast. Manag. 2022, 221, 106118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liontakis, A.; Tzouramani, I. Economic sustainability of organic aloe vera farming in Greece under risk and uncertainty. Sustainability 2016, 8, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozakis, S.; Tsiboukas, K.; Petsakos, A. Greek Cotton Farmers’ Supply Response to Partial Decoupling of Subsidies. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Congress, Ghent, Belgium, 26–29 August 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintori, A.; Tsiboukas, K.; Zervas, G. Evaluating Socio-economic and Environmental Sustainability of the Sheep Farming Activity in Greece: A Whole-Farm Mathematical Programming Approach. In Methods and Procedures for Building Sustainable Farming Systems; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 219–235. [Google Scholar]
- Vallerand, F.; Dubeuf, J.P.; Tsiboukas, K. Le lait de brebis et de chèvre en méditerranée et dans les balkans: Diversité des situations locales et des perspectives sectorielles. Cah. Agric. 2007, 16, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergés, A.; Tomas, F.; Cebrian, E.; Ballesteros, E.; Kizilkaya, Z.; Dendrinos, P.; Karamanlidis, A.A.; Spiegel, D.; Sala, E. Tropical rabbitfish and the deforestation of a warming temperate sea. J. Ecol. 2014, 102, 1518–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonocore, E.; Grande, U.; Franzese, P.P.; Russo, G.F. Trends and evolution in the concept of marine ecosystem services: An overview. Water 2021, 13, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygu, İ.; Heymans, J.J.; Fox, C.J.; Özbilgin, H.; Eryaşar, A.R.; Gökçe, G. The importance of alien species to the food web and bottom trawl fisheries of the Northeastern Mediterranean, a modelling approach. J. Mar. Syst. 2020, 202, 103253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rilov, G.; Peleg, O.; Yeruham, E.; Garval, T.; Vichik, A.; Raveh, O. Alien turf: Overfishing, overgrazing and invader domination in south-eastern Levant reef ecosystems. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2018, 28, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rilov, G.; Mazaris, A.D.; Stelzenmüller, V.; Helmuth, B.; Wahl, M.; Guy-Haim, T.; Mieszkowska, N.; Ledoux, J.B.; Katsanevakis, S. Adaptive marine conservation planning in the face of climate change: What can we learn from physiological, ecological and genetic studies? Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 17, e00566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, E.A.; Kaiser, M.J.; Edwards-Jones, G. Variation in fishers’ attitudes within an inshore fishery: Implications for management. Environ. Conserv. 2005, 32, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schadeberg, A.; Kraan, M.; Hamon, K.G. Beyond métiers: Social factors influence fisher behaviour. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2021, 78, 1530–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijermans, N.; Boonstra, W.J.; Orach, K.; Hentati-Sundberg, J.; Schlüter, M. Behavioural diversity in fishing—Towards a next generation of fishery models. Fish Fish. 2020, 21, 872–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraan, M.; Bitetto, I.; Bellanger, M.; Brown, E.J.; Depestele, J.; Frangoudes, K.; Hamon, K.; Hegland, T.; Lehuta, S.; Letschert, J.; et al. SEAwise Report on Fisher Behaviour Submodels; Technical University of Denmark: Lyngby, Denmark, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, G.F.; Feiring, B.; Stidsen, S. Enhancing Accountability for Small-Scale Fishers—Using Human Rights Monitoring to Guide Effective Implementation of SDG Target 14.B; The Danish Institute for Human Rights: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2021. [Google Scholar]
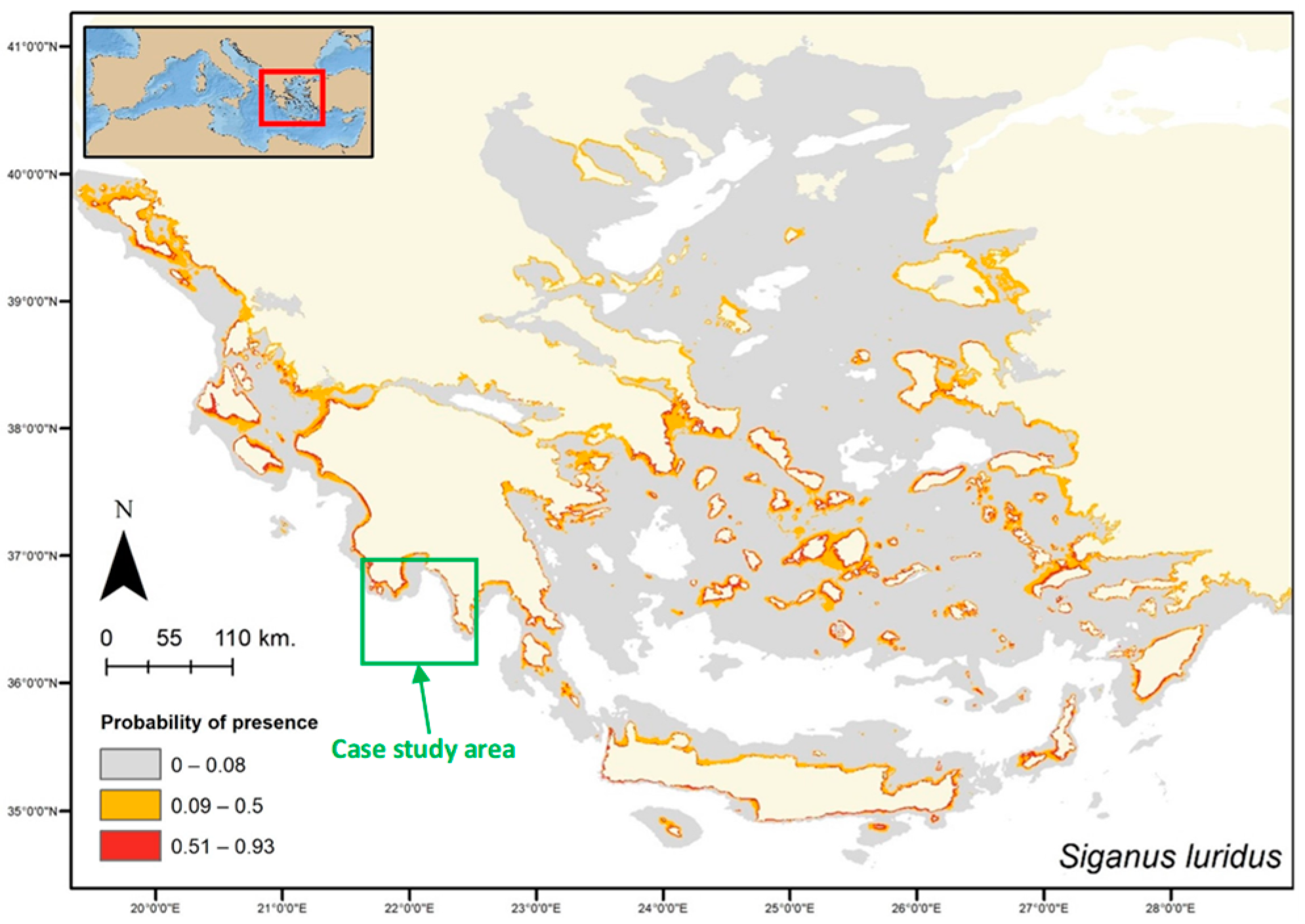
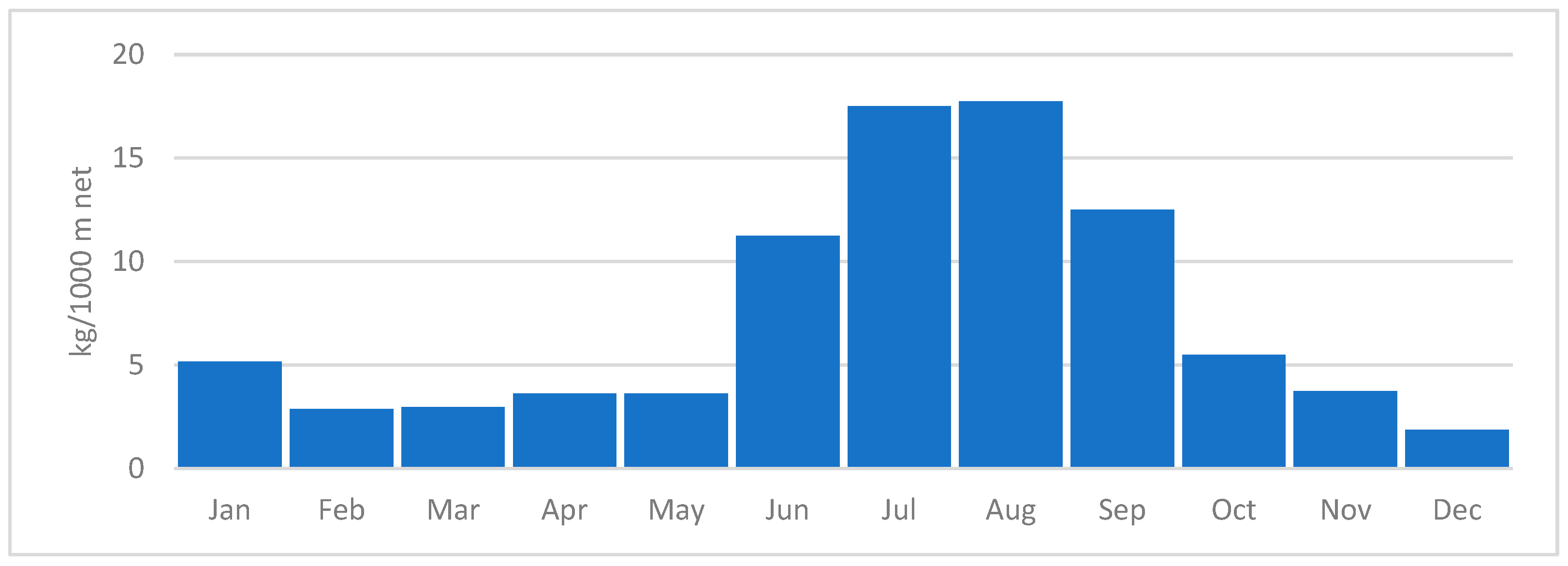

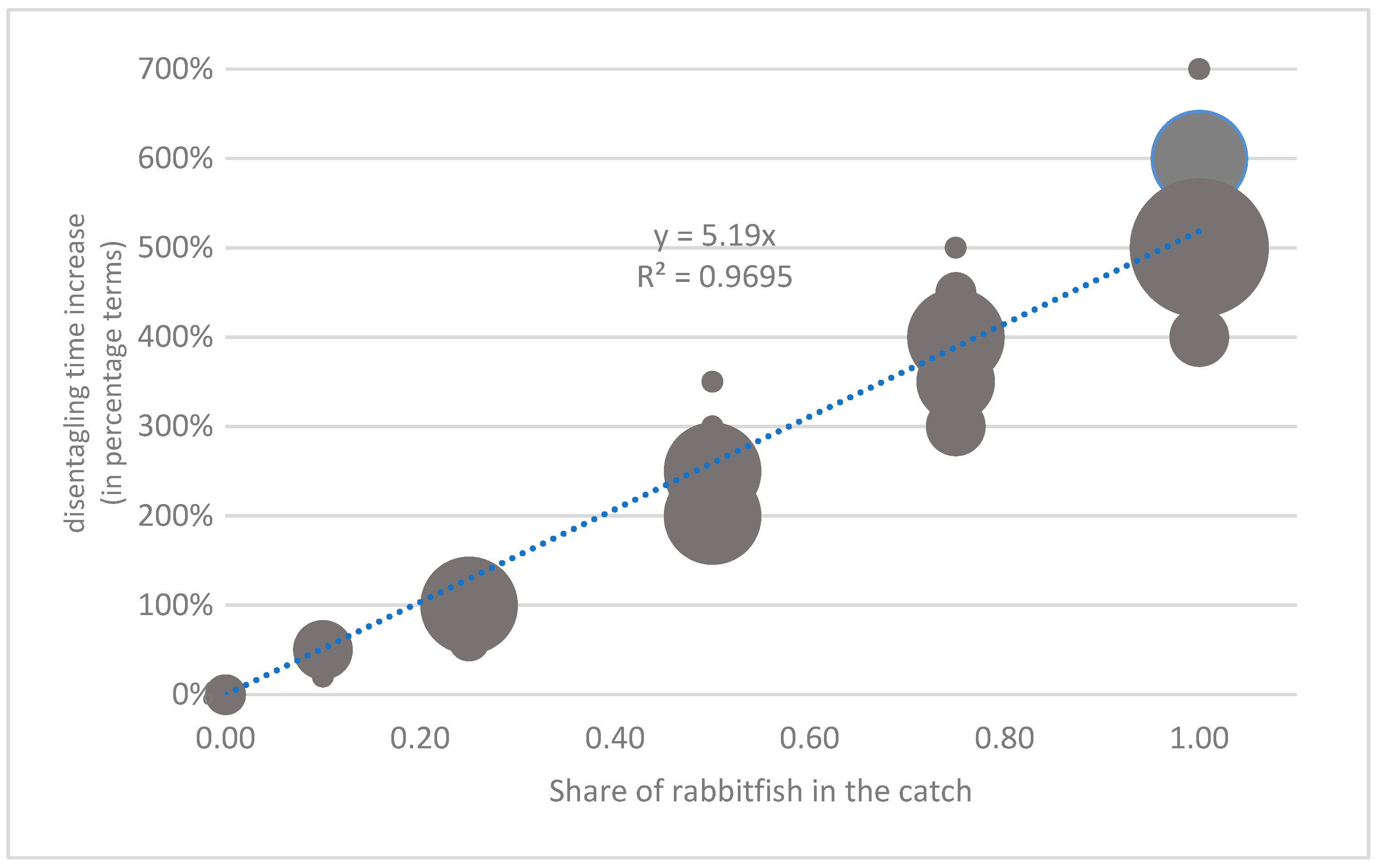
| Parrotfish | Rabbitfish | Siganus luridus | Siganus rivulatus | Other Commercial Species | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019–2021 | ||||||
| Catch (gr) | 1528 | 969 | 438 | 531 | 3125 | 5622 |
| Catch share (%) | 27 | 17 | 8 | 9 | 56 | |
| Share of hauls (%) that include the species * | 87 | 14 | 10 | 10 | 100 | |
| 2014–2016 | ||||||
| Catch (gr) | 2078 | 324 | 273 | 51 | 3503 | 5937 |
| Catch share (%) | 35 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 59 | |
| Share of hauls (%) that include the species * | 88 | 44 | 42 | 9 | 100 | |
| Share of Hauls, including Rabbitfishes | D | p-Value | Exact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2014–2016 | 0.0169 | 0.989 | 0.042 * |
| 2019–2021 | −0.3011 | 0.026 | |
| Combined K-S | 0.3011 | 0.052 | |
| % weight share of rabbitfishes in the catch (gr) | D | p-value | Exact |
| 2014–2016 | 0.0714 | 0.795 | 0.019 ** |
| 2019–2021 | −0.3117 | 0.013 | |
| Combined K-S | 0.3117 | 0.026 |
| Vessels Smaller than 6 Meters | Vessels Larger than 6 Meters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DFN0006 | Parrotfish Métier | DFN0612 | Parrotfish Métier | |
| Gross value of landings | 86.65 | 53.55 | 125.94 | 133.88 |
| Other sources of income and operating subsidies | 6.53 | 6.53 | 9.98 | 9.98 |
| Total Revenues | 93.18 | 60.08 | 135.92 | 143.85 |
| Cost structure | ||||
| Energy costs | 11.08 | 11.08 | 19.93 | 19.93 |
| Personnel costs * | 14.73 | 0 | 6.33 | 10.01 |
| Value of unpaid labor | 33.02 | 26.59 | 29.52 | 46.70 |
| Other cost categories ** | 23.79 | 23.79 | 63.69 | 63.69 |
| Family Fishing Income (FFI) | 43.58 | 25.21 | 45.97 | 50.22 |
| Status Quo | Optimistic | Expected | Pessimistic | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Share of parrotfish (%) | 27 | 24 | 22 | 20 |
| Share of rabbitfish (%) | 17 | 20 | 23 | 26 |
| Share of other species (%) | 56 | 56 | 55 | 54 |
| Vessels < 6 m | ||||
| Economic losses (in EUR) | 3.51 | 6.14 | 8.78 | |
| Fishing Family Income (in EUR) | 21.70 | 19.06 | 16.43 | |
| %Δ (Fishing Family Income) | −14 | −24 | −35 | |
| Vessels 6–12 m | ||||
| Economic losses (in EUR) | 13.57 | 18.82 | 24.08 | |
| Fishing Family Income (in EUR) | 36.66 | 31.41 | 26.15 | |
| % Δ (Fishing Family Income) | −27 | −37 | −48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liontakis, A.; Vassilopoulou, V. An Economic View on the Effects of Invasive Rabbitfishes Based on Fishers’ Perspectives: The Case of the Parrotfish Métier in the South Ionian Sea. Fishes 2023, 8, 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8090447
Liontakis A, Vassilopoulou V. An Economic View on the Effects of Invasive Rabbitfishes Based on Fishers’ Perspectives: The Case of the Parrotfish Métier in the South Ionian Sea. Fishes. 2023; 8(9):447. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8090447
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiontakis, Angelos, and Vassiliki Vassilopoulou. 2023. "An Economic View on the Effects of Invasive Rabbitfishes Based on Fishers’ Perspectives: The Case of the Parrotfish Métier in the South Ionian Sea" Fishes 8, no. 9: 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8090447
APA StyleLiontakis, A., & Vassilopoulou, V. (2023). An Economic View on the Effects of Invasive Rabbitfishes Based on Fishers’ Perspectives: The Case of the Parrotfish Métier in the South Ionian Sea. Fishes, 8(9), 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8090447







