Knockdown of klotho Leads to Cell Movement Impairment during Zebrafish Gastrulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Care, Embryo Collection, and Whole-Mount In Situ Hybridization
2.2. Morpholino (MO) Preparation, Microinjection, Phenotypes Recording, and Images
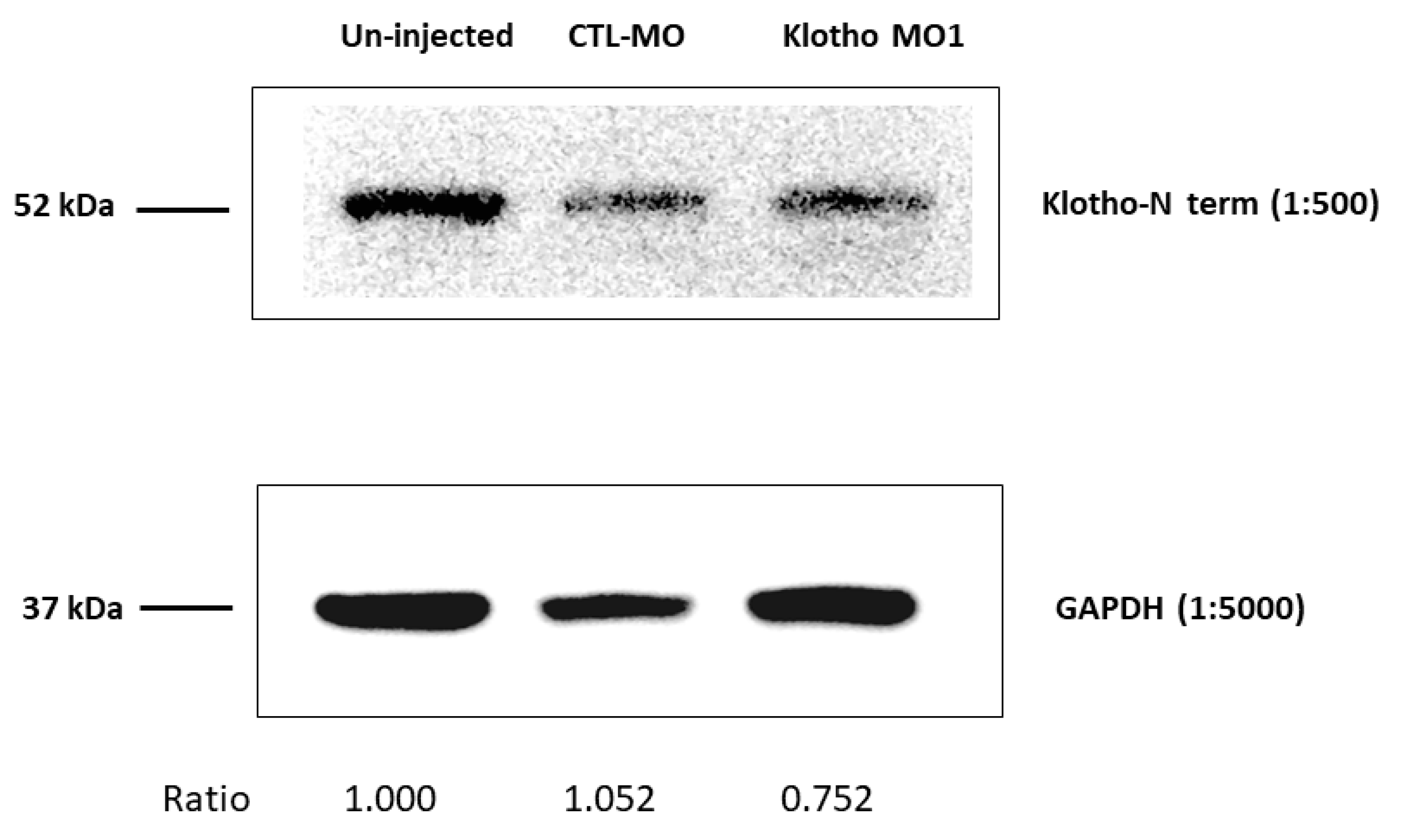
2.3. Embryonic Protein Extraction and Western Blotting
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
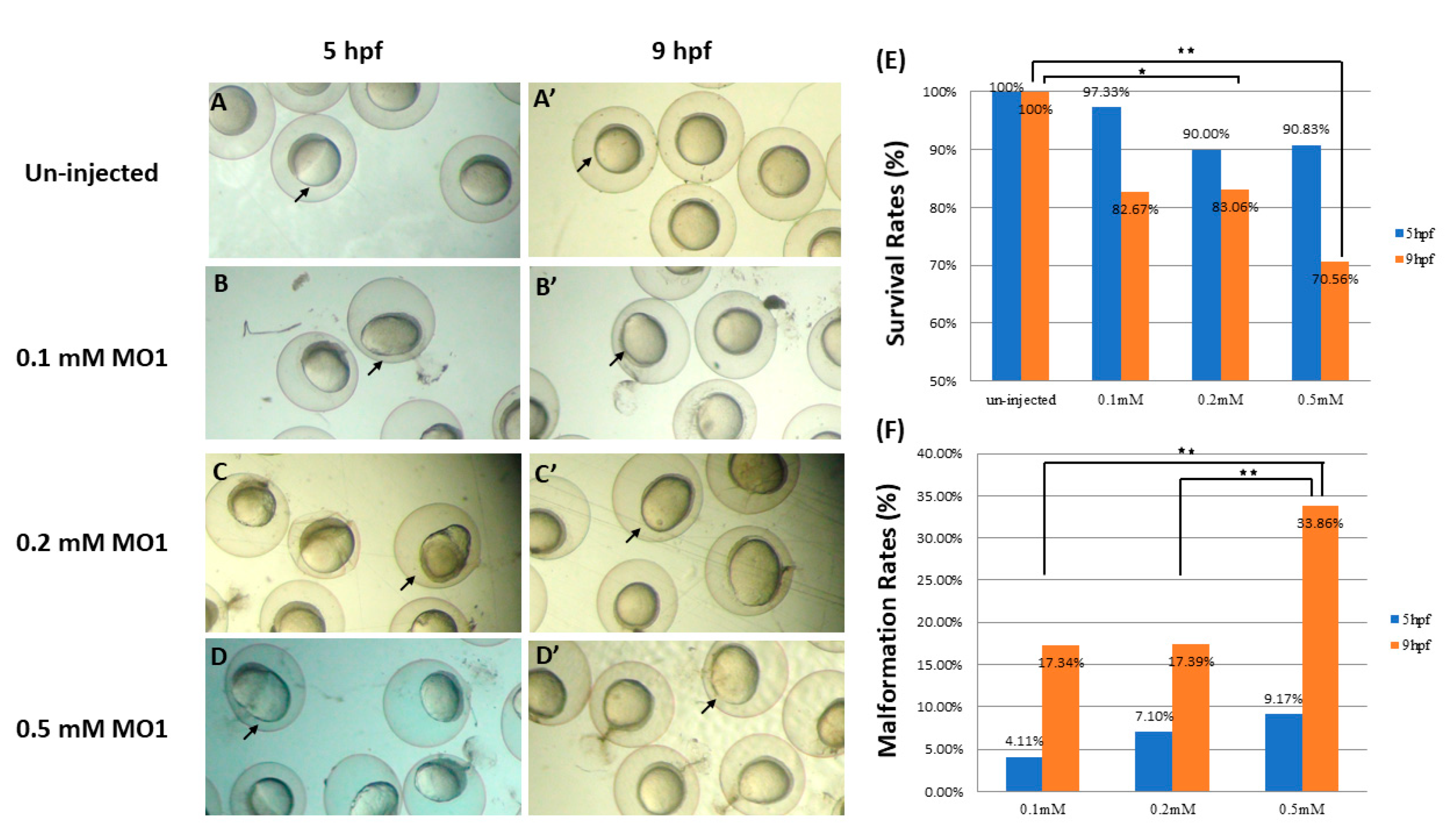
3.1. Knockdown of Zebrafish klotho Expression Led to Abnormal Embryonic Shapes
3.2. Knockdown of klotho Led to Longitudinal Shapes in a Dose-Dependent Manner
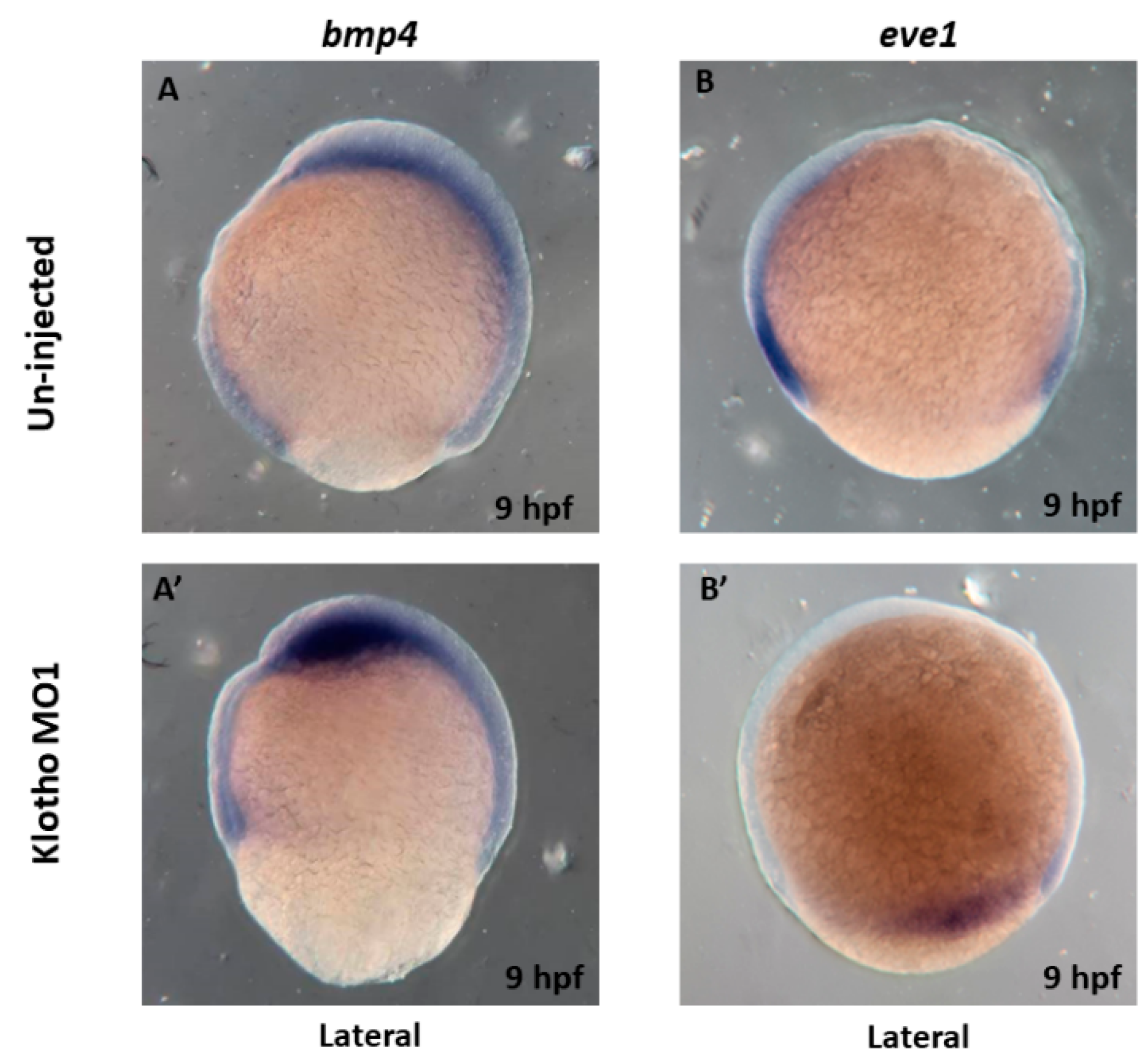
3.3. Longitudinal Shapes Embryos Might Be Due to Abnormal Cell Movement
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurosu, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Clark, J.D.; Pastor, J.V.; Nandi, A.; Gurnani, P.; McGuinness, O.P.; Chikuda, H.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kawaguchi, H.; et al. Suppression of aging in mice by the hormone Klotho. Science 2005, 309, 1829–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, Z. Molecular basis of klotho: From gene to function in aging. Endocr. Rev. 2015, 36, 174–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuro-o, M. Klotho and aging. Biochim. Biophy. Acta 2009, 1790, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donate-Correa, J.; Martín-Núñez, E.; Mora-Fernández, C.; Muros-de-Fuentes, M.; Pérez-Delgado, N.; Navarro-González, J.F. Klotho in cardiovascular disease: Current and future perspectives. World J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 6, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, F.; Wu, D.; Du, H.; Yang, X.; Yang, M.; Pang, X.; Xu, Y. Serum Klotho protein levels and their correlations with the progression of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Compl. 2017, 31, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewicz, M.; Panneerselvam, K.; Marks, N. Role of Klotho in migration and proliferation of human dermal microvascular endothelial cells. Microvasc. Res. 2016, 107, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Ye, N.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y. Klotho inhibits proliferation and migration of angiotensin II-induced vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) by modulating NF-kB p65, Akt, and extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) signaling activities. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 4851–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.Y.; Chou, C.Y.; Hsieh, Y.T.; Lo, K.C.; Liou, Y.L.; Chen, Y.H. Klotho exerts an emerging role in cytokinesis. Genes 2020, 11, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Typiak, M.; Piwkowska, A. Antiinflammatory actions of Klotho: Implications for therapy of diabetic nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugano, Y.; Lardelli, M. Identification and expression analysis of the zebrafish orthologue of Klotho. Dev. Genes Evol. 2011, 221, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zupkovitz, G.; Kabiljo, J.; Martin, D.; Laffer, S.; Schöfer, C.; Pusch, O. Phylogenetic analysis and expression profiling of the Klotho gene familyin the short-lived African killifish Nothobranchius furzeri. Dev. Genes Evol. 2018, 228, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogura, Y.; Kaneko, R.; Ujibe, K.; Wakamatsu, Y.; Hirata, H. Loss of αklotho causes reduced motor ability and short life span in zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.P.; Sosa, M.X.; Fang, J.; Shanmukhappa, S.K.; Hubaud, A.; Fawcett, C.H.; Molind, G.J.; Tsai, T.; Capodieci, P.; Wetzel, K.; et al. αKlotho regulates age-associated vascular calcification and lifespan in zebrafish. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 2767–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, B.; Kim, J.; Jeong, D.; Jeon, S.; Jung, S.I.; Yang, Y.; Kim, K.I.; Lim, J.S.; Kim, C.; Lee, M.S. Klotho inhibits the capacity of cell migration and invasion in cervical cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghani, M.; Brobey, R.; Wang, Y.; Souza, G.; Amato, R.J.; Rosenblatt, K.P. Klotho inhibits EGF-induced cell migration in Caki-1 cells through inactivation of EGFR and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Oncotargets 2018, 9, 26737–26750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shen, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wu, S.; Xu, W.; Zhao, W.; Lin, M.; Wu, J. Klotho antagonizes pulmonary fibrosis through suppressing pulmonary fibroblasts activation, migration, and extracellular matrix production: A therapeutic implication for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Aging 2020, 12, 5812–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, S.F. Developmental Biology, 6th ed.; Sinauer Associates, Inc. Press: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rohde, L.A.; Heisenberg, C.-P. Zebrafish gastrulation: Cell movements, signals and mechanisms. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2007, 261, 159–192. [Google Scholar]
- Marlow, F. Setting up for gastrulation in zebrafish. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2020, 136, 33–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.J.; Fong, T.H.; Chen, S.L.; Wei, J.C.; Wang, I.J.; Wen, C.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Chen, X.G.; Chen, W.Y.; Chen, H.M.; et al. Perturbation of cytosolic calcium by 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate and caffeine affects zebrafish myofibril alignment. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.N.; Sun, C.Y.; Ding, Y.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Lo, K.C.; Weng, C.C.; Lin, J.W.; Chang, C.F.; Hsu, L.S.; Chen, H.M.; et al. Embryonic exposure to 4-methylimidazole leads to zebrafish myofibril misalignment. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyama, R.; O’Connell, M.L.; Wright, C.V.; Kuehn, M.R.; Dawid, I.B. Nodal induces ectopic goosecoid and lim1 expression and axis duplication in zebrafish. Development 1995, 121, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerschmidt, M.; Serbedzija, G.N.; McMahon, A.P. Genetic analysis of dorsoventral pattern formation in the zebrafish: Requirement of a BMP-like ventralizing activity and its dorsal repressor. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 2452–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, K.; Patient, R.; Holder, N. Analysis of FGF function in normal and no tail zebrafish embryos reveals separate mechanisms for formation of the trunk and the tail. Development 1995, 121, 2983–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.H.; Chang, M.Y.; Hsu, C.H.; Chen, Y.H. Essential roles of basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors, Capsulin and Musculin, during craniofacial myogenesis of zebrafish. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 4065–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book: A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio), 5th ed.; University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schulte-Merker, S.; Hammerschmidt, M.; Beuchle, D.; Cho, K.W.; De Robertis, E.M.; Nüsslein-Volhard, C. Expression of zebrafish goosecoid and no tail gene products in wild-type and mutant no tail embryos. Development 1994, 120, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stickney, H.L.; Imai, Y.; Draper, E.; Moens, C.; Talbot, W.S. Zebrafish bmp4 functions during late gastrulation to specify ventroposterior cell fates. Dev. Biol. 2007, 310, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgani, S.M.; Hadjantonakis, A.-K. Signaling regulation during gastrulation: Insights from mouse embryos and in vitro system. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2020, 137, 391–431. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, H.A.; Hyodo-Miura, J.; Nagamune, T.; Ueno, N. FGF signal regulates gastrulation cell movements and morphology through its target NRH. Dev. Biol. 2005, 282, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urakawa, I.; Yamazaki, Y.; Shimada, T.; Iijima, K.; Hasegawa, H.; Okawa, K.; Fujita, T.; Fukumoto, S.; Yamashita, T. Klotho converts canonical FGF receptor into a specific receptor for FGF23. Nature 2006, 444, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Sun, Z. Klotho-deficiency-induced arterial calcification involves osteoblastic transition of VSMCs and activation of BMP signaling. J. Cell. Physiol. 2022, 237, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, D.A.; Kimmel, C. The zebrafish midblastula transition. Development 1993, 119, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, H.-C.; Lo, K.-C.; Wang, Y.-H.; Huang, H.-T.; Cheng, S.-C.; Sun, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-H. Knockdown of klotho Leads to Cell Movement Impairment during Zebrafish Gastrulation. Fishes 2023, 8, 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8090440
Pan H-C, Lo K-C, Wang Y-H, Huang H-T, Cheng S-C, Sun C-Y, Chen Y-H. Knockdown of klotho Leads to Cell Movement Impairment during Zebrafish Gastrulation. Fishes. 2023; 8(9):440. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8090440
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Heng-Chih, Kang-Chieh Lo, Yun-Hsin Wang, Han-Ting Huang, Shu-Chun Cheng, Chiao-Yin Sun, and Yau-Hung Chen. 2023. "Knockdown of klotho Leads to Cell Movement Impairment during Zebrafish Gastrulation" Fishes 8, no. 9: 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8090440
APA StylePan, H.-C., Lo, K.-C., Wang, Y.-H., Huang, H.-T., Cheng, S.-C., Sun, C.-Y., & Chen, Y.-H. (2023). Knockdown of klotho Leads to Cell Movement Impairment during Zebrafish Gastrulation. Fishes, 8(9), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8090440




