Differences in Recreational Fishers’ Motivations for Utilising Two Estuarine Fisheries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
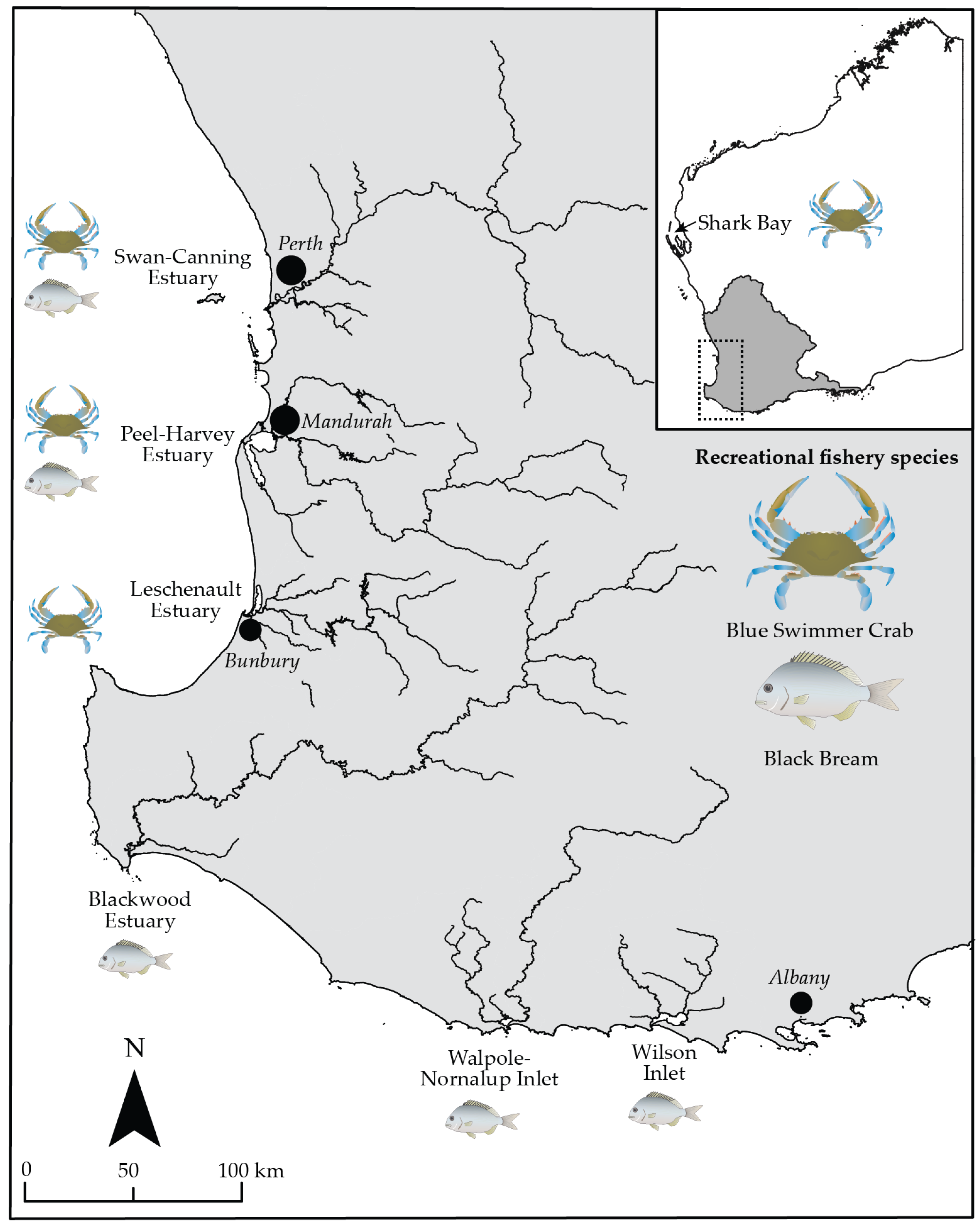
2.1. Study Area and Fisheries
2.1.1. Blue Swimmer Crab
2.1.2. Black Bream
2.2. Social Surveys
2.3. Quantitative Identification of Fisher Groups
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
3.2. Fisher Groups
3.3. Motivations for Fishing
3.4. Comparisons to Other Types of Fishing and Outdoor Activities
4. Discussion
4.1. Identification of Recreational Fisher Groups
4.2. Motivation for Fishing Recreationally
4.2.1. Blue Swimmer Crab
4.2.2. Black Bream
4.3. Management Implications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Charles, A.T. Sustainable Fishery Systems; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Salas, S.; Gaertner, D. The behavioural dynamics of fishers: Management implications. Fish Fish. 2004, 5, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, I.C.; Warwick, R.M.; Hall, N.G.; Tweedley, J.R. The physico-chemical characteristics, biota and fisheries of estuaries. In Freshwater Fisheries Ecology; Craig, J., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2015; pp. 48–79. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, M.; Houde, E.D.; Lamberth, S.J.; Lonsdale, J.-A.; Tweedley, J.R. Management of fishes and fisheries in estuaries. In Fish and Fisheries in Estuaries: A Global Perspective; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 706–797. Available online: https://www.wiley.com/en-au/Fish+and+Fisheries+in+Estuaries:+A+Global+Perspective,+2+Volume+Set-p-9781119705352 (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Maitland, P.S. Conservation of fish species. In The Management of Temperate Communities for Conservation; Spellerberg, I.F., Goldsmith, F.B., Morris, M.G., Eds.; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 1990; p. 566. [Google Scholar]
- Urquhart, J.; Acott, T.G.; Symes, D.; Zhao, M. Introduction: Social issues in sustainable fisheries management. In Social Issues in Sustainable Fisheries Management; Urquhart, J., Acott, T.G., Symes, D., Zhao, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, K.; Schirmer, J.; Pascoe, S.; Triantafillos, L.; Jebreen, E.; Cannard, T.; Dichmont, C.M. Selecting and assessing social objectives for Australian fisheries management. Mar. Policy 2015, 53, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, K.; Voyer, M.; Mazur, N.; Payne, A.M.; Mauli, S.; Kinch, J.; Fabinyi, M.; Smith, G. The importance of qualitative social research for effective fisheries management. Fish. Res. 2017, 186, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Recreational Fisheries; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2012; p. 176. [Google Scholar]
- Arlinghaus, R.; Tillner, R.; Bork, M. Explaining participation rates in recreational fishing across industrialised countries. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2015, 22, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, G.W.; Lyle, J.M. The National Recreational and Indigenous Fishing Survey; Fisheries Research and Development Corporation: Canberra, Austrilia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Young, M.A.L.; Foale, S.; Bellwood, D.R. Why do fishers fish? A cross-cultural examination of the motivations for fishing. Mar. Policy 2016, 66, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DPIRD. Annual Report 2018; Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development: Perth, WA, Australia, 2019; p. 248.
- Ryan, K.L.; Hall, N.G.; Lai, E.K.; Smallwood, C.B.; Taylor, S.M.; Wise, B.S. State-Wide Survey of Boat-Based Recreational Fishing in Western Australia 2013/14; Department of Fisheries: Perth, WA, Australia, 2015; p. 208.
- Kyle, G.; Norman, W.; Jodice, L.; Graefe, A.; Marsinko, A. Segmenting anglers using their consumptive orientation profiles. Hum. Dimens. Wildl. 2007, 12, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, M.F.; Nicholas, L.; Lee, I.; Lee, J.-H.; Scott, D. Social stratification in recreational fishing participation: Research and policy implications. Leis. Sci. 2006, 28, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, C.; Voyer, M.; McIlgorm, A.; Li, O. Chasing the thrill or just passing the time? Trialing a new mixed methods approach to understanding heterogeneity amongst recreational fishers based on motivations. Fish. Res. 2018, 199, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, L.M.; Sutton, S.G.; Arlinghaus, R. Illustrating the critical role of human dimensions research for understanding and managing recreational fisheries within a social-ecological system framework. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2013, 20, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlinghaus, R.; Cooke, S.J.; Potts, W. Towards resilient recreational fisheries on a global scale through improved understanding of fish and fisher behaviour. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2013, 20, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homans, F.R.; Ruliffson, J.A. The effects of minimum size limits on recreational fishing. Mar. Resour. Econ. 1999, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radomski, P.J.; Grant, G.C.; Jacobson, P.C.; Cook, M.F. Visions for recreational fishing regulations. Fisheries 2001, 26, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, P.D.; Tweedley, J.R.; Whitfield, A.K. Conservation of estuarine fishes. In Fish and Fisheries in Estuaries; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 617–683. Available online: https://www.wiley.com/en-au/Fish+and+Fisheries+in+Estuaries:+A+Global+Perspective,+2+Volume+Set-p-9781119705352 (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Leisher, C.; Mangubhai, S.; Hess, S.; Widodo, H.; Soekirman, T.; Tjoe, S.; Wawiyai, S.; Neil Larsen, S.; Rumetna, L.; Halim, A.; et al. Measuring the benefits and costs of community education and outreach in marine protected areas. Mar. Policy 2012, 36, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorrilla-Pujana, J.; Rossi, S. Integrating environmental education in marine protected areas management in Colombia. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2014, 93, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poh, B.; Tweedley, J.R.; Chaplin, J.A.; Trayler, K.M.; Crisp, J.A.; Loneragan, N.R. Influence of physico-chemical and biotic factors on the distribution of a penaeid in a temperate estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 218, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, D.J.; Yeoh, D.E. Carapace width-weight relationships of blue swimmer crab Portunus armatus (A. Milne-Edwards, 1861) (Crustacea: Brachyura: Portunidae) in southwestern Australia: Influences of sex, decadal change, environment, and season. J. Crustacean Biol. 2020, 40, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.L.; Hall, N.G.; Lai, E.K.; Smallwood, C.B.; Tate, A.; Taylor, S.M.; Wise, B.S. Statewide Survey of Boat-Based Recreational Fishing in Western Australia 2017/18; Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development: Perth, WA, Australia, 2019.
- Johnston, D.; Yeoh, D.; Harris, D.; Denham, A.; Fisher, E. Blue Swimmer Crab (Portunus armatus) Resource in the West Coast Bioregion, Western Australia. Part 1: Peel-Harvey Estuary, Cockburn Sound and Swan-Canning Estuary; Department of Primary Indistrues and Regional Development: Perth, WA, Australia, 2020.
- Smallwood, C.B.; Hesp, S.A.; Beckley, L.E. Biology, Stock Status and Management Summaries for Selected fish Species in South-Western Australia; Department of Fisheries: Perth, WA, Australia, 2013; p. 180.
- Sarre, G.A.; Potter, I.C. Comparisons between the reproductive biology of black bream Acanthopagrus butcheri (Teleostei: Sparidae) in four estuaries with widely differing characteristics. Int. J. Salt Lake Res. 1999, 8, 179–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valesini, F.J.; Cottingham, A.; Hallett, C.S.; Clarke, K.R. Interdecadal changes in the community, population and individual levels of the fish fauna of an extensively modified estuary. J. Fish Biol. 2017, 90, 1734–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.A. Review of Fishery Resources and Status of Key Fishery Stocks in the Swan-Canning Estuary; Department of Fisheries: Perth, WA, Australia, 2006; p. 86.
- DPIRD. Recreational Fishing Guide 2022; Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development: Perth, WA, Australia, 2022; p. 64.
- Heck, N.; Stedman, R.C.; Gaden, M. Human dimensions information needs of fishery managers in the Laurentian Great Lakes. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malseed, B.E.; Sumner, N.R. A 12-Month Survey of Recreational Fishing in the Swan-Canning Estuary Basin of Western Australia during 1998–1999; Department of Fisheries: Perth, WA, Australia, 2001; p. 44.
- Tweedley, J.R.; Warwick, R.M.; Hallett, C.S.; Potter, I.C. Fish-based indicators of estuarine condition that do not require reference data. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 191, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweedley, J.R.; Krispyn, K.N.; Cottingham, A. Swan Canning Estuary Condition Assessment Based on Fish Communities—2021; Final report to the Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions; Murdoch University: Perth, WA, Australia, 2022; p. 47. [Google Scholar]
- Lenanton, R.C.J. The Commercial Fisheries of Temperate Western Australian Estuaries: Early Settlement to 1975; Department of Fisheries and Wildlife: Perth, Australia, 1984; p. 82.
- Malseed, B.E.; Sumner, N.R. A 12-Month Survey of Recreational Fishing in the Peel-Harvey Estuary of Western Australia during 1998–1999; Department of Fisheries: Perth, WA, Australia, 2001; p. 52.
- Morison, A.; Daume, S.; Gardner, C.; Lack, M. Western Australia Peel Harvey Estuarine Fishery MSC Full Assessment Public Certification Report; SCS Global Services, Sustainable Seafood Program: Melbourne, Australia, 2016; p. 416. [Google Scholar]
- DPIRD. Protecting Breeding Stock Levels of the Blue Swimmer Crab Resource in the South West; Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development: Perth, Australia, 2018; p. 39.
- Veale, L.; Tweedley, J.R.; Clarke, K.R.; Hallett, C.S.; Potter, I.C. Characteristics of the ichthyofauna of a temperate microtidal estuary with a reverse salinity gradient, including inter-decadal comparisons. J. Fish Biol. 2014, 85, 1320–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, B.S.; Telfer, C.F.; Lai, E.K.M.; Hall, N.G.; Jackson, G. Long-term monitoring of boat-based recreational fishing in Shark Bay, Western Australia: Providing scientific advice for sustainable management in a World Heritage Area. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2012, 63, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brearley, A. Ernest Hodgkin’s Swanland, 1st ed.; University of Western Australia Press: Crawley, UK, 2005; p. 550. [Google Scholar]
- Prior, S.; Beckley, L.E. Characteristics of recreational anglers in the Blackwood Estuary, a popular tourist destination in southwestern Australia. Tour. Mar. Environ. 2007, 4, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DEC. Walpole and Nornalup Inlets Marine Park Management Plan 2009–2019; Department of Environment and Conservation: Perth, Australia, 2009; p. 85.
- Tweedley, J.R.; Warwick, R.M.; Valesini, F.J.; Platell, M.E.; Potter, I.C. The use of benthic macroinvertebrates to establish a benchmark for evaluating the environmental quality of microtidal, temperate southern hemisphere estuaries. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1210–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obregón, C.; Hughes, M.; Loneragan, N.R.; Poulton, S.J.; Tweedley, J.R. A two-phase approach to elicit and measure beliefs on management strategies: Fishers supportive and aware of trade-offs associated with stock enhancement. Ambio 2020, 49, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, W. Strategies of research design. In Social Research Methods: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches, 5th ed.; Neuman, W., Ed.; Pearson Education Limited: Essex, UK, 2003; pp. 165–200. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, M.; Ham, S.; Brown, T. Influencing park visitor behaviour, a belief based approach. J. Park Recreat. Adm. 2009, 27, 38–53. [Google Scholar]
- Vanwindekens, F.M.; Stilmant, D.; Baret, P.V. Development of a broadened cognitive mapping approach for analysing systems of practices in social–ecological systems. Ecol. Model. 2013, 250, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daw, T.M. Shifting baselines and memory illusions: What should we worry about when inferring trends from resource user interviews? Anim. Conserv. 2010, 13, 534–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunce, M.; Rodwell, L.D.; Gibb, R.; Mee, L. Shifting baselines in fishers’ perceptions of island reef fishery degradation. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2008, 51, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER v7: User Manual/Tutorial; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2015; p. 296. [Google Scholar]
- Valesini, F.J.; Coen, N.J.; Wildsmith, M.D.; Hourston, M.; Tweedley, J.R.; Hallett, C.S.; Linke, T.E.; Potter, I.C. Relationships between Fish Faunas and Habitat Type in South-Western Australian Estuaries. Project 2004/045. Draft Final Report for Fisheries Research and Development Corporation; Murdoch University: Perth, WA, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tweedley, J.R.; Bird, D.J.; Potter, I.C.; Gill, H.S.; Miller, P.J.; O’Donovan, G.; Tjakrawidjaja, A.H. Species compositions and ecology of the riverine ichthyofaunas on two Sulawesian islands in the biodiversity hotspot of Wallacea. J. Fish Biol. 2013, 82, 1916–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust. J. Ecol. 1993, 18, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlinghaus, R.; Beardmore, B.; Riepe, C.; Meyerhoff, J.; Pagel, T. Species-specific preferences of German recreational anglers for freshwater fishing experiences, with emphasis on the intrinsic utilities of fish stocking and wild fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2014, 85, 1843–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, H. Leisure value systems and recreational specialization: The case of Trout fishermen. J. Leis. Res. 1977, 9, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlinghaus, R. On the apparently striking disconnect between motivation and satisfaction in recreational fishing: The case of catch orientation of German anglers. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2006, 26, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salz, R.J.; Loomis, D.K.; Finn, K.L. Development and validation of a specialization index and testing of specialization theory. Hum. Dimens. Wildl. 2001, 6, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unruh, D.R. Characteristics and types of participation in social worlds. Symb. Interact. 1979, 2, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, C.; Loomis, D.K.; Salz, R.J. A replication of the internal validity and reliability of a multivariable index to measure recreation specialization. Hum. Dimens. Wildl. 2009, 14, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthén, B.; Muthén, L.K. Integrating person-centered and variable-centered analyses: Growth mixture modeling with latent trajectory classes. Alcohol: Clin. Exp. Res. 2000, 24, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditton, R.B.; Loomis, D.K.; Choi, S. Recreation specialization: Re-conceptualization from a social worlds perspective. J. Leis. Res. 1992, 24, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly, N.A.; Knuth, B.A.; Brown, T.L. An angler typology based on angler fishing preferences. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2001, 130, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokki, H.; Pellikka, J.; Eskelinen, P.; Moilanen, P. Regional fishing site preferences of subgroups of Finnish recreational fishers. Scand. J. Hosp. Tour. 2021, 21, 442–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valesini, F.J.; Hourston, M.; Wildsmith, M.D.; Coen, N.J.; Potter, I.C. New quantitative approaches for classifying and predicting local-scale habitats in estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 86, 645–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, B.; Clarke, K.R.; Platell, M.E.; Potter, I.C. An innovative statistical approach to constructing a readily comprehensible food web for a demersal fish community. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 125, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudreau, A.H.; Levin, P.S.; Norman, K.C. Using folk taxonomies to understand stakeholder perceptions for species conservation. Conserv. Lett. 2011, 4, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedler, A.J.; Ditton, R.B. Understanding angler motivations in fisheries management. Fisheries 1994, 19, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obregón, C.; Christensen, J.; Zeller, D.; Hughes, M.; Tweedley, J.R.; Gaynor, A.; Loneragan, N.R. Local fisher knowledge reveals changes in size of blue swimmer crabs in small-scale fisheries. Mar. Policy 2022, 143, 105144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithwick, W.; Reid, K.; Ensor, R. Black Water Prawning: Drag Netting in the Swan River; Arts Naked Publications: Perth, WA, Australia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tweedley, J.R.; Loneragan, N.R.; Crisp, J.A.; Poh, B.; Broadley, A.D.; Bennett, A.L.; Hodson, K.P.; Trayler, K.M.; Jenkins, G.I.; Chaplin, J.A. Stock Enhancement of the Western School Prawn (Metapenaeus dalli) in the Swan-Canning Estuary; Evaluating Recruitment Limitation, Environment and Release Strategies; Murdoch University: Perth, Australia, 2017; Available online: https://www.frdc.com.au/project/2013-221 (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Schroeder, S.A.; Fulton, D.C.; Currie, L.; Goeman, T. He said, she said: Gender and angling specialization, motivations, ethics, and behaviors. Hum. Dimens. Wildl. 2006, 11, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindley, J.; Quinn, L. Perceptions of compliance in recreational fisheries: Case study of the Peel-Harvey blue swimmer crab fishery. Front. Conserv. Sci. 2022, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindley, J.; Quinn, L. Compliance in recreational fisheries: Case study of two blue swimmer crab fisheries. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0279600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeldner, C.R.; Ritchie, J.R.B. Tourism: Principles, Practices, Philosophies, 12th ed.; Wiley: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Johns, N.; Gyimothy, S. Market segmentation and the prediction of tourist behaviour: The case of Bornholm, Denmark. J. Travel Res. 2002, 40, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvache-Franco, M.; Segarra-Oña, M.; Carrascosa-López, C. Segmentation and motivations in eco-tourism: The case of a coastal national park. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2019, 178, 104812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obregón, C.; Admiraal, R.; van Putten, I.; Hughes, M.; Tweedley, J.R.; Loneragan, N.R. Who you speak to matters: Information sharing and the management of a small-scale fishery. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 578014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, A.S.; Free, C.M.; Jensen, O.P. Angler preferences and satisfaction in a high-threshold bucket-list recreational fishery. Fish. Res. 2019, 220, 105364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlock, G.C.; Saul, G.E.; Bryan, C.E. Importance of fish consumption to sport fishermen. Fisheries 1988, 13, 25–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, R.P.; Lyle, J.M.; Lennox, R.J.; Cooke, S.J.; Semmens, J.M. Motivation and harvesting behaviour of fishers in a specialized fishery targeting a top predator species at risk. People Nat. 2019, 1, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweedley, J.R.; Obregón, C.; Hughes, M.; Loneragan, N.R.; Cottingham, A.; Abagna, D.; Tull, M.; Beukes, S.J.; Garnett, A.M. Golden Fish: Evaluating and Optimising the Biological, Social and Economic Returns of Small-Scale Fisheries; Murdoch University: Perth, WA, Australia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Vecchio, J.L.; Wenner, C.A. Catch-and-release mortality in subadult and adult red drum captured with popular fishing hook types. North Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2007, 27, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, S.G.; Ditton, R.B. Understanding catch-and-release behavior among U.S. Atlantic bluefin tuna anglers. Hum. Dimens. Wildl. 2001, 6, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottingham, A.; Hesp, S.A.; Hall, N.G.; Hipsey, M.R.; Potter, I.C. Marked deleterious changes in the condition, growth and maturity schedules of Acanthopagrus butcheri (Sparidae) in an estuary reflect environmental degradation. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 149, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuwen, B.M.; Hoeksema, S.D.; Potter, I.C. Factors influencing the characteristics of the fish faunas in offshore, deeper waters of permanently-open, seasonally-open and normally-closed estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 81, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottingham, A.; Huang, P.; Hipsey, M.R.; Hall, N.G.; Ashworth, E.; Williams, J.; Potter, I.C. Growth, condition, and maturity schedules of an estuarine fish species change in estuaries following increased hypoxia due to climate change. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 7111–7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweedley, J.R.; Hallett, C.S.; Warwick, R.M.; Clarke, K.R.; Potter, I.C. The hypoxia that developed in a microtidal estuary following an extreme storm produced dramatic changes in the benthos. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2016, 67, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, C.S.; Valesini, F.J.; Clarke, K.R.; Hoeksema, S.D. Effects of a harmful algal bloom on the community ecology, movements and spatial distributions of fishes in a microtidal estuary. Hydrobiologia 2016, 763, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottingham, A.; Cronin-O’Reilly, S.; Beatty, S.J.; Tweedley, J.R. Report Card for Assessing Black Bream Heath in the Vasse-Wonnerup and Estimation of the Impact of a Fish Kill; Report for the Department of Water and Environmental Regulation; Murdoch University: Perth, WA, Australia, 2022; p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Boys, C.A.; Rowland, S.J.; Gabor, M.; Gabor, L.; Marsh, I.B.; Hum, S.; Callinan, R.B. Emergence of epizootic ulcerative syndrome in native fish of the Murray-Darling River System, Australia: Hosts, distribution and possible vectors. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindley, J. Fishing non-compliance and culture. Mar. Policy 2023, 152, 105581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koemle, D.; Beardmore, B.; Dorow, M.; Arlinghaus, R. The human dimensions of recreational anglers targeting freshwater species in coastal ecosystems, with implications for management. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2021, 41, 1572–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Gil, M.D.; Amigo-Dobaño, L.; Surís-Regueiro, J.C.; Varela-Lafuente, M. Perceptions on incentives for compliance with regulation. The case of Spanish fishermen in the Atlantic. Fish. Res. 2015, 170, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

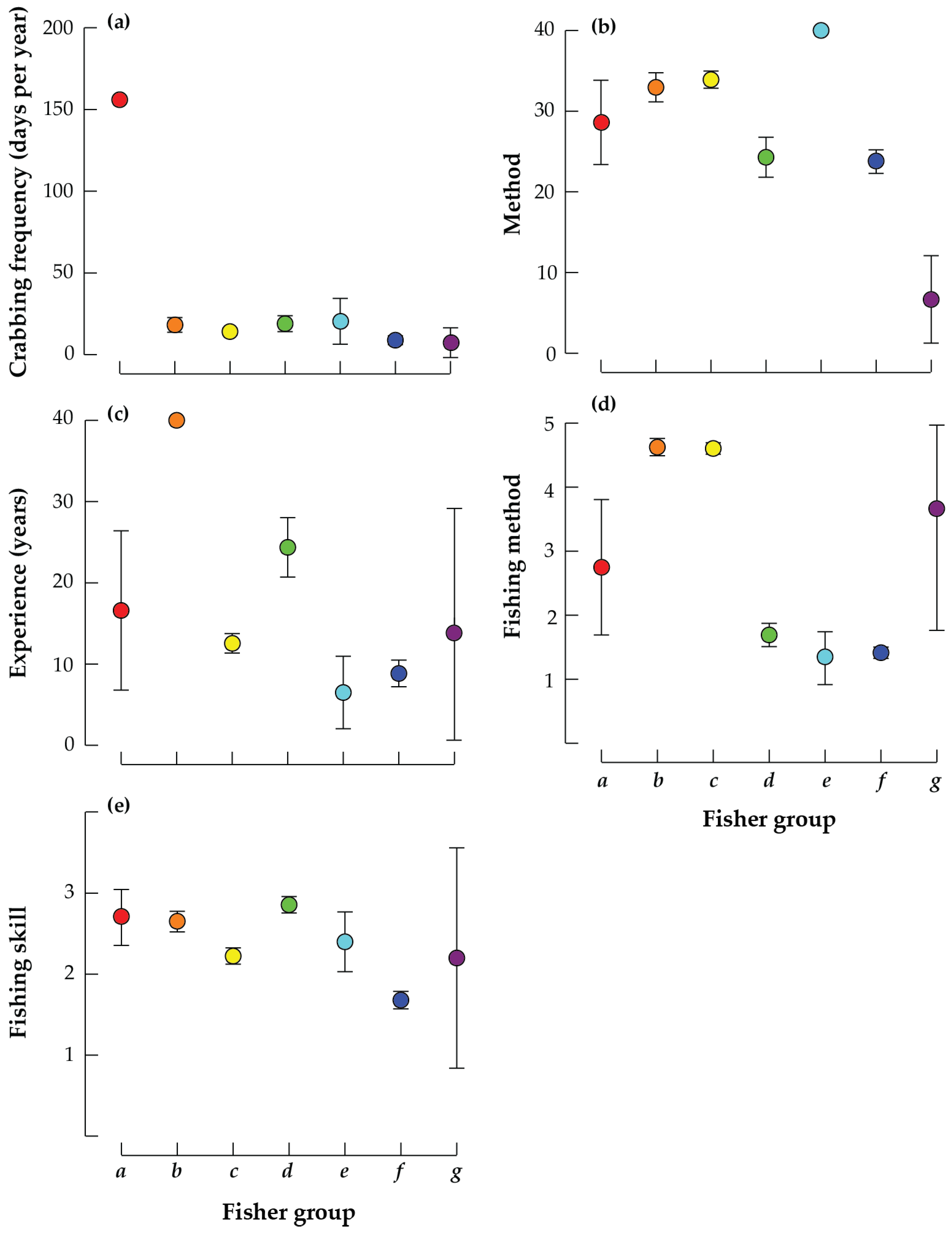





| Fisher Group | Name | Description | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) blue swimmer crab | |||
| a | Very frequent fishers | Fishers that fish >150 times per year and of intermediate/expert skill level | 2.85 |
| b | Experienced boat-based fishers | Fishers that have fished for >40 years, primarily from a boat using drop nets | 16.24 |
| c | Inexperienced boat-based fishers | Fishers that have fished for ~10 years, primarily from a boat using drop nets | 40.74 |
| d | Relatively experienced, expert shore-based fishers | Expert fishers that have fished for ~25 years, primarily from the shore using a range of methods | 13.96 |
| e | Inexperienced shore-based drop net fishers | Fishers that have fished for ~7 years, primarily from a shore using drop nets | 2.85 |
| f | Inexperienced, shore-based novice fishers | Novice fishers that have fished for <10 years, primarily from a shore using a range of methods | 21.65 |
| g | Bi-monthly, hand fishers | Fishers that fish every two months and catch their crabs by hand | 1.71 |
| (b) black bream | |||
| a | Very frequent fishers | Fishers that fish >150 times per year and of intermediate skill level | 0.96 |
| b | Very frequent, expert lure fishers | Fishers that fish >150 times per year are of expert skill level, use expensive fishing gear and lures and fish in competitions | 2.88 |
| c | Experienced fishers | Fishers that have fished for ~40 years, primarily from a kayak/boat and of intermediate/expert skill, some of whom fish in competitions | 5.77 |
| d | Inexperienced intermediate skilled fishers | Intermediate skills fishers that have fished for <10 years, primarily from a kayak using relatively cheap gear and who do not enter competitions | 56.73 |
| e | Inexperienced but keen fishers | Intermediate/expert fishers that have fished for <10 years using expensive gear and who fish in competitions | 33.65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tweedley, J.R.; Obregón, C.; Beukes, S.J.; Loneragan, N.R.; Hughes, M. Differences in Recreational Fishers’ Motivations for Utilising Two Estuarine Fisheries. Fishes 2023, 8, 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8060292
Tweedley JR, Obregón C, Beukes SJ, Loneragan NR, Hughes M. Differences in Recreational Fishers’ Motivations for Utilising Two Estuarine Fisheries. Fishes. 2023; 8(6):292. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8060292
Chicago/Turabian StyleTweedley, James R., Clara Obregón, Sarah J. Beukes, Neil R. Loneragan, and Michael Hughes. 2023. "Differences in Recreational Fishers’ Motivations for Utilising Two Estuarine Fisheries" Fishes 8, no. 6: 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8060292
APA StyleTweedley, J. R., Obregón, C., Beukes, S. J., Loneragan, N. R., & Hughes, M. (2023). Differences in Recreational Fishers’ Motivations for Utilising Two Estuarine Fisheries. Fishes, 8(6), 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8060292









