Abstract
Larimichthys polyactis, a typically oceanodromous species found across the East China, Yellow, and Bohai Seas, is one of the most ecologically and commercially important species in East Asian countries. Moreover, over the past decades, L. polyactis has experienced significant changes in its biological characteristics under long-term intensive fishing pressure, suggesting a need for urgent protection. A robust understanding of connectivity at the spatiotemporal scale is critical for the effective and thorough management of L. polyactis. In the present study, the otolith stable carbon (δ13C) and oxygen (δ18O) isotope ratios of four adult L. polyactis groups (Y-1–4) sampled in the southern Yellow and East China Seas (SYS and ECS) were determined at multiple life stages, including the larval dispersal period (core), overwintering period (A1), and one whole life cycle except the post-spawning period (A2). Dunn’s multiple comparison test showed that there was no difference among the Y-1, Y-2, and Y-3 groups in the otolith core and A1 zones (p > 0.05); the otolith δ13C and δ18O of the Y-4 group were significantly higher than those of the Y-3 group (p < 0.05) in the three analysed zones. In the otolith A2 zone, δ13C and δ18O of the Y-1 group were significantly higher than those of the Y-3 group (p < 0.05). Combined with the biplot of otolith δ13C and δ18O, the quadratic discriminant analysis (QDA) of the otolith core, A1 and A2 zones showed that: (1) in the otolith core zone, two dominant larval aggregations occurred, likely distributed in the coastal waters of northern Lvsi and Haizhou Bay fishing grounds (Y-4 and part Y-1/2 groups) and Zhoushan and southern Yangtze Estuary fishing grounds (Y-3 and part Y-1/2); (2) in the otolith A1 zone, two clear aggregations were separated by Y-4 and Y-1/2/3, suggesting two dominant groups overwintering in the SYS and ECS, respectively; and (3) in the otolith A2 zone, two dominant aggregations were separated by Y-4/1 and Y-2/3. In addition to the long-term larval dispersal process, the migratory route between spawning and overwintering grounds may be diverse, explaining the non-significant genetic differentiation of L. polyactis from different groups. Combining these results with those of previous studies on the life history of L. polyactis, a schematic map of the migratory routes is depicted providing important references for effective resource management.
1. Introduction
A robust understanding of the connectivity or the exchange of individuals (e.g., eggs, larvae, juveniles, or adults) among marine populations is critical for developing the effective management of fish species in marine, coastal, and freshwater systems worldwide [1]. For most migratory fishes, especially diadromous fishes (e.g., Oncorhynchus mykiss) [2] or long-distance oceanodromous fishes (e.g., Thunnus thynnus) [3] with multiple life histories, the exchange or integration primarily occurs during the pelagic larval dispersal duration. The tiny and pelagic eggs and larvae, and the vast and intricate ocean currents they inhabit, pose great challenges for the quantification of dispersal processes and connectivity [4]. Moreover, connectivity among natal origins, nursery grounds, and overwintering grounds at the population level, contributes to recruitment, survival, reproduction, and population structure [5] catching the attention of fishery scientists and administrators. Comprehensive information on connectivity among life stages or populations is a basis for effective fishery management as certain regional populations can suffer from unexpected high pressure by fisheries, resulting in the over-fishing of some stock components [1,6].
Direct or indirect observation of the distribution and migration of fishes and their ambient environment has, to date, derived from diverse approaches, including fishery vessel research [7], the tagging-recapture method [8], and satellite electronic technologies [7,9], but with the challenges of a high economic cost, meagre chance of recapture, and impracticability in small fish at large spatiotemporal scales, respectively [10]. Fish migration can be tracked either directly by following individuals over space and time, using the methods mentioned above, or indirectly using natural chemical tags derived from the fish tissues (e.g., muscle, blood, liver, scale, and otolith) [4]. Remarkably, otoliths, which are biomineralised tissues, grow continuously with daily rhythms and are not decomposed and absorbed [11,12] suggesting an optimal case. Based on the relationship between fish growth rate and otolith increment, migratory patterns throughout a lifetime can be reconstructed retrospectively from a single individual [13]. Structural elements, such as C and H are mainly derived from ambient waters [14], and stable isotopes of oxygen (δ18O) are particularly precipitated at or close to equilibrium with ambient waters [15,16]. Carbon stable isotopes (δ13C) are derived from both dissolved inorganic carbonate (DIC) in ambient seawater and metabolic carbon in blood [17]. Higher metabolic rates and respiration can produce a rising proportion of metabolic carbon, which has a markedly depleted carbon signature (δ13C values are more negative) compared to the DIC proportion [18]. Changes in otolith δ13C values were thus considered to predominately reflect metabolic shifts. Indeed, discriminating natal origins [19], reconstructing migratory routes [20], and evaluating the contributions of larval aggregations to adult stocks [21] have been addressed using otolith δ13C and δ18O. In addition, otolith Sr/Ca and Ba/Ca, which display positive otolith–salinity correlations, have also been widely applied in fish species [22,23], and Larmichthys polyactis is no exception [24,25]. In contrast, L. polyactis, a temperate fish species, entirely inhabits oceans, and its spawning, feeding, and overwintering migrations are significantly driven by temperature [26,27]. Thus, δ13C and δ18O are suitable proxies for investigating migratory routes and population connectivity in L. polyactis. Previous studies have used δ13C and δ18O in otoliths to discriminate populations from different regions [28,29]. In contrast to previous studies that used the δ13C and δ18O of whole otoliths [28], we determined the otolith δ13C and δ18O of specific areas, such as the otolith core and annual rings. We focused on the population connectivity at the spatial scale, as well as temporal scale, based on the otolith δ13C and δ18O of multiple life stages.
Larmichthys polyactis, a typically oceanodromous species, is widely distributed across the north–west Pacific Ocean, including the East China Sea, the Yellow Sea, and the Bohai Sea [30,31]. Previous studies have divided the stock of L. polyactis into three populations, namely the East China Sea (ECS) population, the southern Yellow Sea (SYS) population, and the Bohai/northern Yellow Seas (BNYS) population, based on spatiotemporal distribution [28,32], biological characteristics [32], and population genetics [33]. L. polyactis, an iteroparous species, spawns many times during the spawning season with spawning peaks in ECS, SYS, and BNYS populations in March, April, and May, respectively, showing a chronological trend from south to north [34,35,36]. The entire migratory cycle of L. polyactis was one year. For example, the SYS population is born in coastal waters from the end of March to early May, drifts by ocean currents or tides for approximately one month, grows and matures in nearshore waters from June to November, migrates offshore to overwinter from December to January in the following year, and returns to coastal waters to spawn from February [26]. While progress has been made with the whole life history of L. polyactis [26,37], details of the dispersal process of eggs and larvae and the connectivity between nursery grounds and overwintering grounds among populations remained unclear. Recent studies using otolith Sr/Ca have revealed basic information on early life histories [27,38]. Understanding the drivers of larval dispersal is a biophysical problem [1]. Consequently, ocean currents must be considered for a complete understanding of population connectivity.
Being one of the most economically important species in the north–western Pacific Ocean, L. polyactis has suffered from intense exploitation by various fishing nets, including gillnets, canvas stow nets, and bottom trawls, contributing to local fisheries in East Asian countries (https://www.fao.org/home/en/, accessed on 1 May 2022). Notably, under intensive fishing pressure over several decades, it was naturally characterised by miniaturisation of the body, youth in population structure, and expansion of spawning grounds [39,40], suggesting drastic changes in survival strategy. However, the potential of L. polyactis for self-regulation may have reached its peak [30,41]. Moreover, the resource of Larimichthys crocea, the sister species of L. polyactis, has nearly collapsed under equivalent fishing pressure [42] despite the slight recovery of the current stock [43]. Thus, the effective and thorough management of L. polyactis is urgently needed and requires clear information on the connectivity among multiple life stages, especially the larval dispersal stage.
Previous information regarding the population division of L. polyactis indicated that the main spawning grounds of the BNYS, SYS, and ECS populations were in the Haizhou Bay (HZB), Lvsi and Yangtze Estuary (LS and YZ), and Zhoushan and Yushan (ZS and YS) fishing grounds, respectively (Figure 1). Four groups of adult L. polyactis born in the same year were sampled in East China and Yellow Seas, essentially covering the distribution of ECS, SYS, and BNYS populations. In the present study, δ13C and δ18O of the otolith core, A1, and A2 zones representing the larval dispersal, overwintering, and one-year (except the post-spawning period) periods were quantified to investigate population connectivity at the spatiotemporal scale. To better understand the larval dispersal process, the monthly average sea surface temperature (SST) of respective spawning peaks for different populations and nearshore currents was incorporated with otolith isotope data.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas
The Yellow and East China Seas cover all habitats across the complete life history of L. polyactis, including spawning, foraging, and overwintering periods [34,36]. Following traditional population division of L. polyactis, these study areas were divided into three regions (A, B, and C) (Figure 1). Regions A, B, and C represent the BNYS, SYS, and ECS populations, respectively [32]. Regions A/B and region B/C were separated by 34° N and 32° N lines, respectively [32].
To further elucidate the early dispersal process of L. polyactis, SST data were used to show the environmental differences among regions A, B, and C. NOAA OI SST V2 High-Resolution Dataset data were downloaded from the website at https://psl.noaa.gov/data/gridded/data.noaa.oisst.v2.highres.html, accessed on 1 March 2022. The time resolution of the OI SST datasets was one day, with a 0.25° × 0.25° spatial resolution. OI SST datasets covering the entire study area between 1 April and 31 June 2015 were all downloaded. A total of 91 days of OI SST data were combined by month. Based on the spawning peak of the different L. polyactis populations, the mean monthly SST of regions A, B, and C were June, May, and April, respectively.
With reference to Wu et al. [44,45], the main nearshore currents of the Yellow and East China Seas in summer were depicted (Figure 1), contributing to a better understanding of the larval dispersal process of L. polyactis. Notably, the transport direction of the Subei Coastal Current (SBCC) in the SYS has traditionally been considered southward for the past decades [46]. In contrast, a northward-flowing SBCC derived from the Yangtze plume was proposed, especially in the summer, and was further verified by recent mooring observations [45] and numerical experiments [44,47].
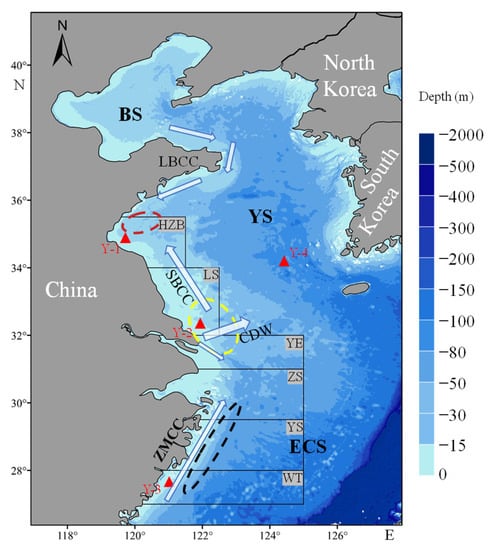
Figure 1.
Schematic map showing the sampling locations of Y-1~4 and main nearshore currents in China seas. The red triangles represent the sampling locations. The white arrows represent the major nearshore surface currents, including Subei Coastal Current (SBCC), Lubei Coastal Current (LBCC), Changjiang Diluted Water (CDW), and Zhemin Coastal Current (ZMCC) [44,45,47]. The incomplete black rectangular boxes represent the principal fishing grounds, including Haizhou Bay (HZB), Lusi (LS), Yangtze Estuary (YE), Zhoushan (ZS), Yushan (YS), Wentai (WT) fishing grounds. Regions A, B, and C represent the BNYS, SYS, and ECS population, respectively [28,32]. The red, yellow, and black ellipses represent the main spawning grounds of Larimichthys polyactis from the BNYS, SYS, and ECS populations, respectively [28,32].
2.2. Sampling and Ageing
Forty adult L. polyactis individuals were sampled from four sites covering the spawning grounds (Y-1–3) and overwintering ground (Y-4) in the East China and Yellow Seas (Table 1; Figure 1). All samples, except the Y-2 group, were captured from the fishery vessels using the gill nets (mesh size of 50 mm) in 2017. Samples of the Y-2 group were collected from anchored stow nets (mesh size of 25 mm in the cod end) in 2018. The captured samples were refrigerated immediately and remained frozen until external measurements, sex and gonad maturity determination, and otolith extraction were performed in the ground-based laboratory. Body weight (BW) and body length (BL) were measured to the nearest to 0.01 g and 1 mm, respectively. Following the characteristics described by Lim et al. [48], sex and the maturational stages of gonads were determined by experienced fishery researchers. The sagittal otoliths were then extracted, cleaned, measured, and stored in a 48-well plate. The left sagittal otoliths of the four groups were embedded in opaque epoxy resin, mounted on petrographic slides, ground with grit silicon carbide paper in the sagittal section on both planes to reveal the nucleus and daily growth increments, and then polished with lapping paper saturated with 0.3 μm Al2O3 solution on an automated polishing wheel (Labopol-35, Struers, Copenhagen, Denmark) to remove most scratches. After a final polish, the otolith slides were cleaned by ultrasonic treatment for 5 min, rinsed with ultrapure water six times, and dried in drying oven at 38 °C overnight for stable isotope analysis.

Table 1.
Detailed data of Larimichthys polyactis for otolith stable isotope analysis. N, BL, and SD represent the sample size, body length (mm), and standard deviation, respectively.
To ensure that the birth year of samples collected from the four sites was the same, the putative age of specimens was previously estimated by back-calculation based on the von Bertalanffy growth equation of Shui et al. [49], whose accuracy rate was validated by Kang et al. [50]. Two experienced readers further verified the age of the samples based on the counts of opaque zones in the otolith. Conflicting results between the ages estimated by the growth equation and those determined by visual examination were excluded. Detailed information about the samples used for the stable isotope analysis is shown in Table 1.
2.3. Selection of Different Developmental Stages
Otoliths, characterised by daily and annual rings affected by diurnal and seasonal rhythms have functioned as archival logs, exhibiting unrivalled time-keeping properties [51]. Notably, the relationship between daily increments/annual rings in L. polyactis otoliths and the growth rhythms of L. polyactis has been established [52,53,54,55], enabling us to match the drilling zones with corresponding growth stages. Consequently, three otolith zones, namely the core, A1, and A2 zones, were selected for δ13C and δ18O analyses (Figure 2). The core zone represents the larval dispersal period, covering egg to larvae stage. During this period, L. polyactis, which lacks swimming ability, is generally drifted by recurrent tides and nearshore currents, resulting in limited distribution. The external rims of zones A1 and A2 were tangential to the annual rings (Figure 2). The A1 zone is the translucent zone under the stereoscope formed during the winter season [19,55], and thus represents the overwintering period in the offshore waters of the ECS and YS. The overwintering periods for the different L. polyactis populations differed slightly. The ECS population, for example, overwintered from December to February of the following year. The A2 zone represents one whole life cycle, except for the post-spawning period, thus covering a more prolonged period from July to February in the following year for the East China Sea population.
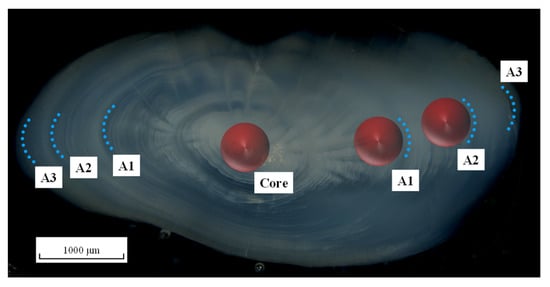
Figure 2.
Sagittal otolith section of a three-year-old Larimichthys polyactis under transmitted light showing the analysed regions for stable isotope δ13C and δ18O. The analysed regions include the core, A1, and A2 zones (red-filled spheres, diameter 500 μm). The blue dotted curves represent annual rings.
2.4. Stable Isotope Analysis
After determining the otolith zones for milling, stable isotope analysis was conducted at the Laboratory of Otolith Microchemistry, Freshwater Fisheries Research Institute, Wuxi, China. The micro-milling system (New Wave Research, Fremont, CA, USA) herein used incorporated an image analyser, a CMOS camera, a video monitor, and a micro-mill controlled by a computer. A portion of the otolith core, A1, and A2 zones (Figure 2) was extracted by drilling the otolith section with a round diamond drill equipped with a micro-milling micro-sampler. The depth and diameter in the central parts of the zones were set to 300 and 500 μm, respectively, for adequate signals. Milled otolith powder (approximately 100 μg per drilled zones) was collected. After each milling, an air duster was used to blow the otolith section to avoid cross contamination between the analysed zones. The stable isotope ratios of the otolith powder were determined using a Delta V Advantage stable isotope ratio mass spectrometer equipped with a Gas Bench II Gas generator (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Samples of otolith powder were placed at the bottom of glass test tubes (QSA00303, Thermo Fisher Scientific) prior to analysis. The natural abundance of the carbon/oxygen stable isotope is expressed as follows:
where X represents δ18O or δ13C and R represents the 18O/16O or 13C/12C ratio. The accuracy of δ13C and δ13O detection was monitored against an isotope standard (NBS 18, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, Austria) and expressed using Vienna Pee Dee Belemnite (VPDB) as an international standard unit [56]. The precision of the analyses based on measurements of this standard unit was within 0.03%.
δX (‰) = [(Rotolith − Rstandard)/Rstandard] × 1000
2.5. Data Analysis
Kruskal–Wallis tests were applied to test whether otolith δ13C and δ18O differed among sampling locations and life stages, as the data could not be transformed to satisfy both normality and homoscedasticity assumptions. Dunn’s multiple comparison test was used to identify pairwise differences in δ13C and δ18O between sampling groups and life stages using Origin 2022b (OriginLab, Northampton, MA, USA). Quadratic discriminant analysis (QDA) was conducted to test the ability of otolith δ13C and δ18O to accurately classify individuals into their actual groups at different life stages. QDA is robust to departures from normality and does not assume the homogeneity of variance–covariance matrices. Classification accuracy was assessed with jackknife (leave-one-out) cross-validation, using uniform priors for group membership.
3. Results
3.1. Monthly Averaged SST
In 2015, the nearshore waters of regions A, B, and C showed a downward trend in SST (Figure 3). The main spawning grounds of the BNYS, SYS, and ECS populations in the Yellow and East China Seas are depicted in incomplete black rectangular boxes (Figure 3), according to Dai et al. [29], Huang et al. [57], and Jiang et al. [35]. The SST ranges of spawning grounds for BNYS, SYS, and ECS populations were approximately 20–22, 16–18, and 14–16 °C, respectively (Figure 3).
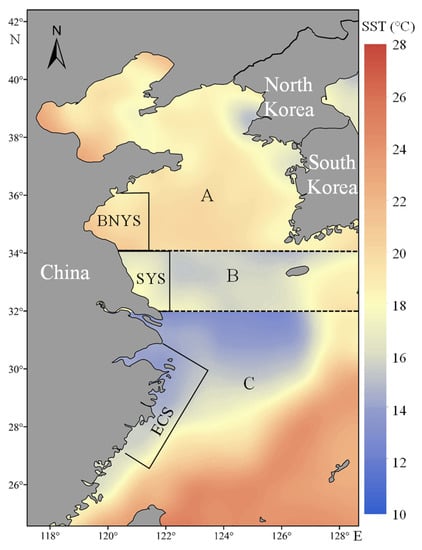
Figure 3.
Schematic map showing the spatial patterns of monthly averaged SST for main spawning grounds of regions A (June), B (May), and C (April) in 2015. The incomplete black rectangular box of regions A, B, and C represent the main spawning grounds of the BNYS, SYS, and ECS populations for Larimichthys polyactis.
3.2. Spatial Variation in Otolith δ13C and δ16O
At the otolith core zone of L. polyactis, the mean (±SD) values of δ13C and δ18O for Y-1 to Y-4 groups were −6.06 ± 3.28 and −13.38 ± 5.74; −7.69 ± 5.36 and −10.98 ± 6.47; −3.80 ± 1.03 and −6.07 ± 2.65; and −14.83 ± 3.42 and –21.83 ± 4.55, respectively. The differences in otolith δ13C and δ18O between the Y-3 and Y-4 groups were statistically significant (p < 0.01; Figure 4). The biplots of otolith δ13C and δ18O showed clear separation (Figure 5). Moreover, the value of otolith δ13C for the Y-4 group was significantly higher than that of Y-1, and the value of otolith δ18O for the Y-4 group was significantly higher than that for Y-2 (p < 0.01; Figure 4). There were no significant differences in otolith δ13C and δ18O among the Y-1, Y-2, and Y-3 groups (p > 0.01; Figure 4).
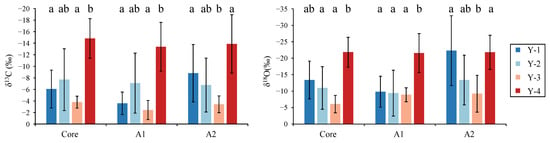
Figure 4.
Otolith δ13C and δ18O variation in different drilling zones for Larimichthys polyactis from Y-1, Y-2, Y-3, and Y-4 groups. Different letters indicate significant differences between growth zones (p < 0.05).
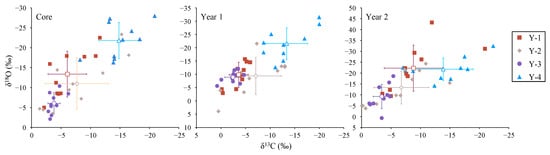
Figure 5.
Biplots of otolith δ13C and δ18O values in different sampling groups for otolith core, A1, and A2 zones. The hollow square, rhombus, circle, and triangle represent the mean value of corresponding groups, and the cross represents the plus or minus error bars.
At the otolith A1 zone of L. polyactis, the mean (±SD) values of δ13C and δ18O for Y-1 to Y-4 groups were −3.60 ± 1.94 and −9.83 ± 4.70; −7.09 ± 5.20 and −9.39 ± 6.96; −2.43 ± 1.66 and −8.90 ± 2.12; and −13.37 ± 4.24 and −21.57 ± 5.90, respectively. The values of otolith δ13C and δ18O for the Y-4 group were significantly higher than those of the other groups, except for the otolith δ13C for the Y2 group (p < 0.01; Figure 4). The biplots of otolith δ13C and δ18O for the Y-4 group showed a clear separation from the others (Figure 5). In line with the otolith core zone, there were no significant differences in otolith δ13C and δ18O among the Y-1, Y-2, and Y-3 groups (p > 0.01; Figure 4).
At the otolith A2 zone of L. polyactis, the mean (±SD) values of δ13C and δ18O for Y-1 to Y-4 groups were −8.81 ± 4.97 and −22.29 ± 10.59; −6.74 ± 4.66 and −8.90 ± 2.12; −3.42 ± 1.45 and −9.23 ± 5.59; and −13.87 ± 5.05 and −21.80 ± 5.19, respectively. The values of otolith δ13C and δ13O for the Y-1 and Y-4 groups were significantly higher than those for Y-3 (p < 0.01; Figure 4). The biplots of otolith δ13C and δ18O for the Y-3 group showed an obvious separation between Y-1 and Y-4 (Figure 3). In contrast to the otolith core and A2 zones, there were no significant differences in otolith δ13C and δ18O among Y-1, Y-2, and Y-4 groups (p > 0.01; Figure 4).
In summary, no significant difference was found between the Y-2 and Y-3 groups in otolith δ13C and δ18O at all life stages, and the values of otolith δ13C and δ18O for the Y-4 group were significantly higher than those of Y-3 at all life stages.
3.3. Temporal Variation in Otolith δ13C and δ18O
There was no significant difference in otolith δ13C and δ18O among the life stages for the Y-2, Y-3, and Y-4 groups (p > 0.01; Figure 6). The biplots of otolith δ13C and δ18O also showed a high overlap within life stages for the Y-2–4 groups (Figure 7). There was only one difference in the values of otolith δ13C and δ18O for the Y-1 group in the A2 zone, which was significantly higher than that of A1 (p < 0.01; Figure 6).
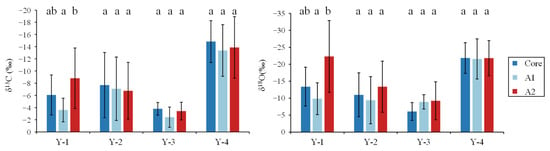
Figure 6.
Otolith δ13C and δ18O variation in different sampling groups for otolith core, A1, and A2 zones. Different letters indicate significant differences between growth zones (p < 0.05).
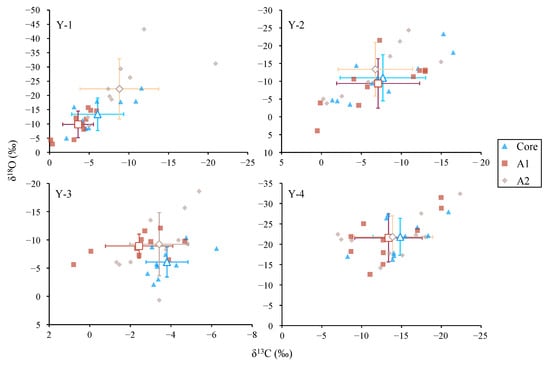
Figure 7.
Biplots of otolith δ13C and δ18O values in different drilling zones for Larimichthys polyactis from Y-1, Y-2, Y-3, and Y-4 groups. The hollow square, rhombus, and triangle represent the mean value of corresponding groups, and the cross represents the plus or minus error bars.
3.4. Quadratic Discriminant Analysis for Different Life Stages
At the core zone, the percentage of good assignment of these samples to their actual group by QDA with jackknife cross-validation was 90% and 70% for Y-4 and Y-3, respectively, showing a higher accuracy (Figure 8). In contrast, the Y-1 and Y-2 groups were largely misjudged as Y-3 or Y4 groups (Figure 8).
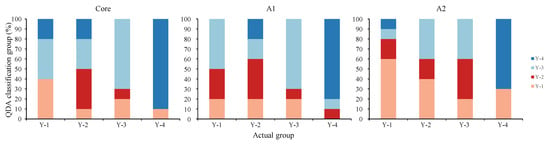
Figure 8.
Cross-validated classification accuracy by sampling group for quadratic discriminant analysis (QDA) conducted on core, A1, and A2 zones. Known sampling groups of Larimichthys polyactis are listed along the x-axis; the proportion of percentage assigned to each sampling group by QDA classification is indexed on the y-axis and represented by colours.
Similar to the core zone, based on QDA, Y-3 and Y-4 groups showed good assignment in the A1 zone with 70% and 80% accuracy, respectively (Figure 8). In contrast, 80% of the Y-1 group was misclassified as Y-2 or Y-3, showing an extremely low accuracy rate (Figure 8).
At A2 zone, the accuracy rate for Y-4 still remained at a high level with 70% accuracy (Figure 8). However, the percentage of good assignments for Y-3 decreased. In contrast, the Y-1 group showed good assignments with 60% accuracy (Figure 8). Similar to Y-1 in the otolith A1 zone, a high proportion of Y-2 groups were misjudged as Y-1/3 resulting in a lower accuracy rate.
Overall, spatial differences were reflected in the assignment of the individual groups. The overall discrimination accuracies were 60%, 62.5%, and 52.5% in the otolith core, A1, and A2, respectively.
4. Discussion
Larimichthys polyactis, a typical oceanodromous species, is originated in coastal waters, grows and matures in nearshore waters, overwinters in offshore waters, and reproduces in coastal waters showing a large-scale spatial connectivity (>350 km) throughout its entire life history [32,58]. While progress has been made over its entire life history, the larval dispersal component remains unsolved for L. polyactis. The long-term dispersal process of fish eggs and larvae can create a relatively unstable living environment, contributing to phenotypic plasticity and adaptive divergence [37,39]. Population differentiation has long been one of the main topics in evolutionary biology, including for L. polyactis. Studies on the population division of L. polyactis using various methods, including catching data analysis [32], geometry morphology [59,60,61], otolith microchemistry [27,28,29,58], and genetic makers [62,63,64,65,66,67,68], have had inconsistent results. Notably, there is a growing consensus that the genetic differentiation of L. polyactis in Chinese waters are not obvious, resulting from the passive dispersal of eggs and larvae or the random migration of adults. Overall, central to the issue of population differentiation for L. polyactis is the connectivity among multiple life stages, especially the larval dispersal period, which determines the targeted effective conservation and management of L. polyactis. Connectivity during the larval dispersal period is inherently driven by biophysical processes [1]. For a comprehensive and better understanding of the potential dispersive transport of L. polyactis eggs and larvae, the main nearshore currents in the SYS and ECS have been drawn [44,45,47].
In the otolith core zone representing the larval dispersal period of L. polyactis, δ13C and δ18O of the Y-4 groups were significantly higher than those of Y-3, suggesting that the ambient environments they inhabit were different. Moreover, there were no significant differences in otolith δ13C and δ18O among Y-1–3 groups. Based on the biplot of δ13C and δ18O for the core zone, there were two separated aggregations represented by the Y-1–3 and Y-4 groups and a few scattered individuals of Y-1 and Y-2 highly overlapping with Y-3 and Y-4. Based on the otolith core zone, QDA analysis also achieved better classification accuracy for the Y-3 and Y-4 groups, and most of the Y-1 and Y-2 groups were misjudged as Y-3/4. Otolith δ18O, as a proxy for temperature history, has been confirmed in many fish species [15,16,69] generally showing a negative relationship between otolith δ18O and ambient water temperature. From June to July 2006, a large-scale survey of the seawater δ18O profile across the China marginal seas, covering the SYS and ECS, showed that the δ18O range of coastal surface waters was −3.16 to 0.58, and no significant difference was found among coastal waters [70], suggesting that temperature is the most significant factor influencing the otolith δ18O of L. polyactis. Based on the monthly SST of regions A (June), B (May), and C (April) (Figure 3) a pronounced downtrend SST of coastal waters was observed from north to south, that is, from regions A to C. The mean SST of coastal waters in regions A, B, and C were estimated to be 20–22, 16–18, and 14–16 °C, respectively (Figure 3). According to the otolith δ18O of the Y-1–4 groups, the general distribution of the Y-1–4 groups was speculated to be in nearshore waters of regions A, B, B, and C, respectively (Figure 3).
Larimichthys. polyactis with a planktonic larval phase and connectivity between spawning and nursery grounds is one of the main drivers of recruitment [71,72]. Natal origin and dispersal pathways may affect the quality of the larval pool, thereby modulating juvenile survival [6,71]. Therefore, understanding connectivity at the dispersal scale is paramount to applying adapted management for population persistence. The first central finding was that there were two dominant aggregations of larval L. polyactis in the coastal waters in SYS and ECS. Notably, based on previous studies, there are three dominant spawning groups represented by the BNYS, SYS, and ECS populations, mainly distributed in the nearshore waters of the HZB, LS/YE, and ZS/YS fishing grounds, respectively [32]. Why are there two larval aggregations? Larval dispersal and connectivity may be gained from understanding the biological and hydrodynamic processes involved in the transport of eggs and larvae. The otolith core zone with a radius of 250 μm represents the larval stage from zero to 30 days post-hatching (DPH) [52,54,73]. Planktonic L. polyactis eggs and larvae, lacking sufficient swimming ability, are passively dispersed by surface currents, such as the Subei Coastal Current [38,53]. In the summer season, the Changjiang plume extends via two pathways: one pathway spreads offshore to the northeast, forming a front by salinity; the other pathway turns left and extends along the coast, ending at ~33.5° N, where it collides with the downward-stream Stokes drift resulting from the rotating tide in the YS [44]. L. polyactis eggs and larvae of the northern YE and LS fishing grounds are highly likely to be transported northward by the northern branch of the Yangtze River plume. This phenomenon of northern transport is supported by Huang et al. [57], who applied Lagrangian Particle Tracking to simulate transport routes. Huang et al. [57] found that at 30 days post-releasing, particles released in the LS fishing ground drifted northward along the coast to the HZB fishing ground. Coincidentally, the bloom originating from mariculture rafts on the coast of the LS fishing ground also drifted northward by hydrographic forcing [74]. Moreover, the otolith Sr/Ca ratio of larval L. polyactis captured in the LS and HZB fishing grounds showed a downward trend from the otolith core to the edge [25,38], suggesting that brackish waters were mainly derived from the northern branch of the Changjiang plume. This deduction of northern dispersal was also evidenced by the mixed subpopulation of L. polyactis in Haizhou Bay [35,60]. Similar to the northern YE/LS fishing grounds, L. polyactis eggs and larvae of the WT/YS fishing grounds are probably transported northward to the ZS and southern YZ fishing grounds hindered by the fresher CDW. The YZ fishing grounds served as common nursery grounds for mixed populations as reported by Lin et al. [75]. Consequently, from the biological and hydrodynamic points of view, there are two dominant aggregations of L. polyactis larvae in the SYS and ECS, that is, two nursery grounds. This argument is also supported by the finding that there are two main spawning/nursery grounds existing in SYS and ECS, respectively [76].
In the otolith A1 zone, representing the overwintering period of L. polyactis, δ13C and δ18O of the Y-4 group were significantly higher than those of Y-3 and Y-1. In contrast, there were no significant differences among the Y-1, Y-2, and Y-3 groups. Based on the biplot of δ13C and δ18O for the A1 zone, there are two clearly separated aggregations represented by the Y-1/2/3 and Y-4 groups, which is supported by the results of the QDA analysis. The Y-4 group achieved higher classification accuracy in the QDA analysis. However, the Y-1, Y-2, and Y-3 groups achieved lower classification accuracy, owing to greater misjudgements among them. The otolith A2 zone represents the one entire life cycle, except the post-spawning period. In contrast to A1 zone, the δ13C and δ18O values of the Y-1 and Y-4 groups were significantly higher than those of Y-3. There were no significant differences between the Y-3 and Y-1/2/4 groups. The Y-3 group achieved higher classification accuracy in the QDA analysis. Forty percent of the Y-4 group were misjudged by Y-1. Moreover, most of the Y-1 and Y-2 groups were misjudged by the other groups.
The second finding was that there were two overwintering populations of L. polyactis, inhabiting the offshore waters of the SYS and ECS. The biplot of δ13C and δ18O on the otolith A1 zone showed two obvious aggregations represented by the Y-4 and Y-1/2/3 groups. This result of two dominant overwintering populations is consistent with recent studies based on catch data [77], genome-wide sequence data [67], and microsatellite markers [78]. The difference between the two larval aggregations and the two overwintering aggregations is that most of the Y-1 and Y-2 groups were assigned to the Y-3 groups in the A1 zone. In the otolith core zone, the percentage of assignment for Y-3 was approximately 50%, indicating that the later migratory routes experienced by the other 50% are not consistent with the Y-4 group. The early dispersal of eggs and larvae, latter feeding routes, and overwintering routes may jointly promote intergroup communication. In addition, in the otolith A2 zone representing the complete migratory cycle, except the post-spawning period, the accuracy rate for the Y-2/3 groups decreased sharply in contrast to the trend for the Y-1 group. Overall, L. polyactis of the Y-4 group remained at a higher level of accuracy throughout the three zones, indicating that the Y-4 group may be a stable population. However, Y-1–3 groups born in the same year showed different accuracies with QDA at the otolith core, A1, and A2 zones, suggesting different migratory routes or habitats. Failure to detect the population structure of L. polyactis using various genetic markers further suggests L. polyactis has a high migration capability, enabling L. polyactis to overcome the effects of genetic drift [63,68]. The passive dispersal process of L. polyactis eggs and larvae has always been ignored in previous studies, and the migratory routes of different populations are considered to be unrelated [32,37]. Overall, the δ13C and δ18O values of the core, A1, and A2 zones were significantly different between the Y-1 and Y-4 groups, indicating that there may be two geographical populations in the SYS and ECS. Moreover, it is worth noting that there may be a mixed population in the adjacent water areas of the SYS and ECS, which is supported by a previous study [74]. Combined with the present results and previous studies, the potential migratory routes among spawning, nursery, and overwintering grounds are shown in Figure 9, contributing to further understanding of connectivity among multiple life stages of L. polyactis.
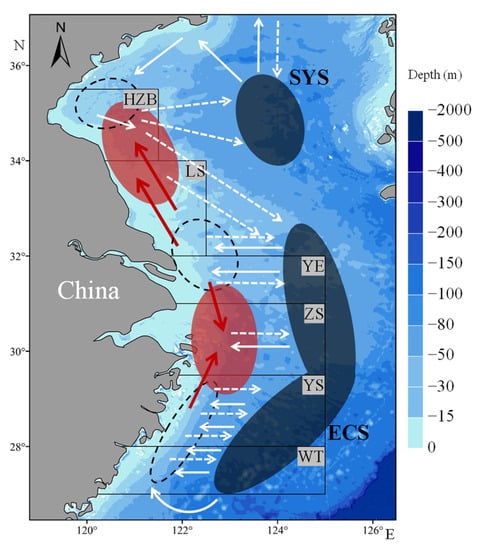
Figure 9.
Schematic map showing migratory routes of L. polyactis between spawning, nursery, and overwintering grounds. The black dashed ellipses represent the main spawning grounds in the southern Yellow and East China Seas [30]. The red and black solid ellipses represent the larvae and overwintering aggregations, respectively. The white concrete and dashed arrows represent the spawning and overwintering migratory routes, respectively. The solid red arrows represent the passive dispersal direction of L. polyactis eggs or larvae.
From 1980 to 2010, the global capture production of L. polyactis showed a steady increasing trend, and the catch reached record levels in 2011 (https://www.fao.org/home/en/, accessed on 1 May 2022). In December 2009, a marine protected area (MPA) of national germplasm resources for L. polyactis and Pampus argenteus was established in LS fishing grounds, greatly easing the pressure from resource restoration for L. polyactis up to a certain point [39]. In addition, 10 small-scale MPAs, widely distributed in the coastal waters of the ZS, YS, and WT fishing grounds, were established to protect spawning grounds for highly commercial fishes in June 2017 (https://www.zj.gov.cn, accessed on 1 May 2022). These MPAs were focused on the spawning stock. The larvae of fish species, the key drivers of resource restoration, are as crucial as the spawning stock [79,80] and have been ignored in MPAs. The results of the present study could provide valuable information for improving existing MPAs and designing new MPAs.
5. Conclusions
Larimichthys. polyactis, an important commercial and ecological species, has been exploited by intense fishing pressure over the past decades, resulting in drastic changes in its biological characteristics. Robust information on the connectivity and mechanism of pelagic dispersal within L. polyactis eggs and larvae is the central basis for proposing effective and thorough protection. In the present study, the otolith δ13C and δ18O of multiple life stages, including the larval dispersal period (core zone), overwintering period (A1 zone), and one whole life cycle, except the post-spawning period (A2 zone), were determined to investigate the population connectivity of L. polyactis at different life stages. The present results show that in the SYS and ECS there may be two dominating larval aggregations distributed in the northern LS/HZB fishing grounds (Y-4 and part of Y-1/2 groups) and southern YE/ZS (Y-3 and part of Y-1/2 groups) fishing grounds, indicating L. polyactis eggs and larvae of the YE and WT/YS fishing grounds were partly transported northward by the ZMCC and SBCC, respectively. The results of the otolith A1 zone showed that there were two dominating overwintering aggregations. In contrast, the otolith A2 zone showed no obvious aggregations, suggesting that the migratory routes among spawning, feeding, and overwintering grounds for L. polyactis are not stable and single. Overall, there may be two geographical populations in the SYS and ECS and a mixed population in the adjacent water area. These results may explain why population genetic variation among L. polyactis has not been detected in numerous studies based on various population genetic markers. Information on connectivity among multiple life stages, especially in the pelagic larval dispersal period, could contribute to further understanding the life history of L. polyactis and provide valuable references when developing marine protected areas for L. polyactis.
Author Contributions
D.S., D.L., and Y.X. conceived the ideas and designed the experiments. D.S. completed the experiments, analysed the data, and drafted the manuscript. D.L., T.J., J.Y., Z.K., X.Z., and Y.X. supervised the study and reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31802297).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal experiments complied with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. All Larimichthys polyactis samples were dead individuals from legal commercial fisheries. Therefore, there was no need for approval from the Animal Ethics Committee.
Data Availability Statement
The data applied in this study will be available upon request with permission from the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cowen, R.K.; Sponaugle, S. Larval dispersal and marine population connectivity. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009, 1, 443–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, C.E.; Reeves, G.H. Population structure of sympatric anadromous and nonanadromous Oncorhynchus mykiss: Evidence from spawning surveys and otolith microchemistry. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. 2000, 57, 2152–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooker, J.R.; Bremer, J.R.A.; Block, B.A.; Dewar, H.; de Metrio, G.; Corriero, A.; Kraus, R.T.; Prince, E.D.; Rodríguez-Marín, E.; Secor, D. Life history and stock structure of Atlantic bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus). Rev. Fish. Sci. 2007, 15, 265–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsdon, T.S.; Gillanders, B.M. Reconstructing migratory patterns of fish based on environmental influences on otolith chemistry. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2003, 13, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botsford, L.W.; Hasting, A.; Gaines, S.T. Dependence of sustainability on the configuration of marine reserves and larval dispersal distance. Ecol. Lett. 2001, 4, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, R.K.; Gawarkiewicz, G.; Pineda, J.; Thorrold, S.M.; Werner, F. Population connectivity in marine systems: An overview. Oceanography 2007, 20, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, B.A.; Teo, S.L.H.; Walli, A.; Boustany, A.; Stokesbury, M.J.W.; Farwell, C.J.; Weng, K.C.; Dewar, H.; Williams, T.D. Electronic tagging and population structure of Atlantic bluefin tuna. Nature 2005, 434, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M.C.; Baras, E. Methods for studying spatial behaviour of freshwater fishes in the natural environment. Fish Fish. 2000, 1, 283–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abascal, F.J.; Medina, A.; De La Serna, J.M.; Godoy, D.; Aranda, G. Tracking bluefin tuna reproductive migration into the Mediterranean Sea with electronic pop-up satellite archival tags using two tagging procedures. Fish. Oceanogr. 2016, 25, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.J.; Neat, F.C.; Gibb, F.M.; Gibb, I.M.; Thordarson, H. Evidence for metapopulation structuring in cod from the west of Scotland and North Sea. J. Fish Biol. 2006, 69, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.A.; Crowder, L.B.; Binkowski, F.P. Evaluating otolith analysis for bloater Coregonus hoyi: Do Otoliths Ring True? Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1985, 114, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halden, N.M.; Friedrich, L.A. Trace-element distributions in fish otoliths: Natural markers of life histories, environmental conditions and exposure to tailings effluence. Miner. Mag. 2008, 72, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturrock, A.M.; Trueman, C.N.; Darnaude, A.M.; Hunter, E. Can otolith elemental chemistry retrospectively track migrations in fully marine fishes? J. Fish Biol. 2012, 81, 766–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, B.D. The art of otolith chemistry: Interpreting patterns by integrating perspectives. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2019, 70, 1643–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.S.; Komatsu, K.; Yoneda, M.; Ishimura, T.; Higuchi, T.; Shirai, K.; Kamimura, Y.; Watanabe, C.; Kawabata, A. Temperature dependence of δ18O in otolith of juvenile Japanese sardine: Laboratory rearing experiment with micro-scale analysis. Fish. Res. 2017, 194, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Yoneda, M.; Ishimura, T.; Shirai, K.; Tamamura, M.; Nishida, K. Temperature dependency equation for chub mackerel (Scomber japonicus) identified by a laboratory rearing experiment and microscale analysis. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2020, 71, 1384–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawazu, M.; Tawa, A.; Ishihara, T.; Uematsu, Y.; Sakal, S. Discrimination of eastward trans-Pacific migration of the Pacific bluefin tuna Thunnus orientalis through otolith δ13C and δ18O analyses. Mar. Biol. 2020, 167, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.T.; Trueman, C.N.; Godiksen, J.A.; Grønkjær, P. Otolith δ13C values as a metabolic proxy: Approaches and mechanical underpinnings. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2019, 70, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artetxe-Arrate, I.; Fraile, I.; Clear, N.; Darnaude, A.M.; Dettman, D.L.; Pécheyran, C.; Farley, J.; Murua, H. Discrimination of yellowfin tuna Thunnus albacares between nursery areas in the Indian Ocean using otolith chemistry. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2021, 673, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hane, Y.; Kimura, S.; Yokoyama, Y.; Miyairi, Y.; Ushikubo, T.; Ishimura, T.; Ogawa, N.; Aono, T.; Nishida, K. Reconstruction of temperature experienced by Pacific bluefin tuna Thunnus orientalis larvae using SIMS and microvolume CF-IRMS otolith oxygen isotope analyses. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2020, 649, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brophy, D.; Rodríguez-Ezpeleta, N.; Fraile, I.; Arrizabalaga, H. Combining genetic markers with stable isotopes in otoliths reveals complexity in the stock structure of Atlantic bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.R.; Schmidt, D.J.; Crook, D.A.; Hughes, J.M. Non-diadromous life history and limited movement in northern lineages of Australian smelt: Evidence from otolith chemistry analysis. Ecol. Freshw. Fish. 2019, 28, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.T.; Labonne, M.; Hoang, H.D.; Panfili, J. Changes in environmental salinity during the life of Pangasius krempfi in the Mekong Delta (Vietnam) estimated from otolith Sr:Ca ratios. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2019, 70, 1734–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhong, X.M.; Tang, J.H.; Yang, J. Migration and population structure characteristics of the small yellow croaker Larimichthys polyactis in the southern Yellow Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2016, 35, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.D.; Xiong, Y.; Jiang, T.; Yang, J.; Zhong, X.M.; Tang, J.H. Early life migration and population discrimination of the small yellow croaker Larimichthys polyactis from the Yellow Sea: Inferences from otolith Sr/Ca ratios. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2022, 40, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Xu, Z.L.; Chen, X.Z. The spatial distribution pattern of fishing ground for small yellow croaker in China Seas. J. Fish. China 2010, 34, 236–244, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.B.; Tian, S.Q.; Peng, X.; Gao, C.X.; Ye, S.; Du, X.X.; Liu, P. Distribution of Larimichthys polyactis and its relationship with environmental factors in offshore water of southern Zhejiang. Chinese J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 1352–1358, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.K.; Huang, J.S.; Tang, X.X.; Jin, X.S.; Sun, Y. Stable isotopic composition of otoliths in identification of stock structure of small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) in China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2016, 35, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Wang, Y.K.; Zhang, T.T.; Jin, X.S.; Sun, Y. Investigating the population structure of Larmichthys polyactis from the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea using stable isotope mass spectrometry. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2019, 40, 11–18, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.Y.; Jiao, Y.; Ren, Y.P.; Xue, Y. Population dynamics modelling with spatial heterogeneity for yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) along the coast of China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2020, 39, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.P.; Shan, X.J.; Jin, X.S.; Corfine, H.; Chen, Y.L.; Su, C.C. Changes in Distribution Patterns for Larimichthys polyactis in Response to Multiple Pressures in the Bohai Sea Over the Past Four Decades. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 931015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.Z. Biological characteristics and resource status of three main commercial fishes in offshore waters of China. J. Fish. China 1987, 11, 187–194, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.S.; Ying, Y.P.; Han, Z.Q.; Xiao, Y.S.; Gao, T.X. AFLP analysis on genetic diversity and population structure of small yellow croaker Larimichthys polyactis. Afr. J. Biomed. Res. 2009, 8, 2700–2706. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, N.; Chen, Y.G.; Jin, Y.; Yuan, X.W.; Ling, J.Z.; Jiang, Y.Z. Distribution of the early life stages of small yellow croaker in the Yangtze River estuary and adjacent waters. Fish. Sci. 2018, 84, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.Q.; Zhang, C.; Ye, Z.J.; Tian, Y.J. Analyses of egg size, otolith shape, and growth revealed two components of small yellow croaker in Haizhou Bay spawning stock. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2019, 37, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, R.D.; Gao, C.X.; Tian, S.Q.; Ma, Q.Y.; Fan, Q.S. Heterogeneity of growth and maturity of Larimichthys polyactis in the offshore waters of southern Zhejiang, China. Chinese J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 333–341, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.L.; Chen, J.J. Analysis on migratory routine of Larimichthy polyactis. J. Fish. Sci. China 2009, 16, 931–940, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; Yang, J.; Jiang, T.; Liu, H.B.; Zhong, X.M.; Tang, J.H. Early life history of the small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) in sandy ridges of the South Yellow Sea. Mar. Biol. Res. 2017, 13, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.J.; Li, X.S.; Yang, T.; Sharifuzzaman, S.M.; Zhang, G.Z. Biological responses of small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) to multiple stressors: A case study in the Yellow Sea, China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2017, 36, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Q.; Lee, A.; Liu, Z.L.; Szuwalski, C.S. Life history changes and fisheries assessment performance: A case study for small yellow croaker. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2019, 77, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.P.; Liu, Z.L.; Zhang, H.; Ling, J.Z.; Yuan, X.W.; Li, S.F. On the evolution of biological characteristics and resources of small yellow croaker. Mar. Sci 2014, 36, 481–487, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; de Mitcheson, Y.S. Profile of a fishery collapse: Why mariculture failed to save the large yellow croaker. Fish Fish. 2008, 9, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Lu, G.Q.; Zhao, L.L.; Du, X.Q.; Gao, T.X. Assessment of fishery resources using environmental DNA: The large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) in the East China Sea. Fish. Res. 2021, 235, 105813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Shen, J.; Zhu, J.R.; Zhang, J.; Li, L. Characteristics of the Changjiang plume and its extension along the Jiangsu Coast. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 76, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Gu, J.; Zhu, P. Winter Counter-Wind Transport in the Inner Southwestern Yellow Sea. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 2018, 123, 411–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B. Characteristics of the East China Sea current system. In Essays on the East China Sea Shelf; Institute of Oceanology: Qingdao, China; Chinese Academy of Sciences: Qingdao, China, 1978; pp. 126–133, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.Z.; Yin, B.S.; Liu, Z.L.; Feng, X.R. Numerical study of the ocean circulation of the East China Sea shelf and a Kuroshio bottom branch northeast of Taiwan. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, C05015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.K.; Le, M.H.; An, C.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, M.S.; Chang, Y.J. Reproductive cycle of yellow croaker Larimichthys polyactis in southern waters off Korea. Fish. Sci. 2010, 76, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, B.N. Study on the age and growth of Pseudosciaena polyactis in the South of the Yellow Sea and north of the East China Sea. J. Zhejiang Ocean Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2003, 22, 16–20, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Z.J.; Song, D.D.; Li, G.; Yan, L.P.; Zhong, X.M.; Tang, J.H.; Wang, Y.P.; Wu, L.; Xiong, Y. Age identification for Larimichthys polyactis based on different sections of sagittal otolith and comparison with result of age backward inferring from growth equation. Mar. Sci. 2022, 44, 543–554, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Katayama, S. A description of four types of otolith opaque zone. Fish. Sci. 2018, 84, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Tang, J.H.; Xu, X.M.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.Y.; Xu, H.; Cheng, J.H. Comparison of otolith microstructures in small yellow croaker larvae and juveniles from Sanmen Bay and Lvsi. Mar. Fish. 2013, 35, 423–431, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, W.; Lou, B.; Chen, R.Y.; Mao, G.M.; Liu, F.; Xu, D.D.; Wang, L.G.; Ma, T.; Xu, Q.X. Observation of embryonic, larva and juvenile development of small yellow croaker, Larimichthys polyactis. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2016, 47, 1033–1039, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.T.; Wang, Y.K.; Yuan, W.; Jin, X.S.; Chen, C.; Sun, Y. Research on Sagitta Microstructure Characteristics of Young of the Year (YOY) Larimichthy polyactis in the Bohai Sea. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2019, 41, 35–40, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Ye, Z.J. Inter-annual otolith growth pattern of adult small yellow croaker in the East China Sea and its response to environmental changes. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2021, 104, 1643–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, J. Revealing Population Connectivity of the Estuarine Tapertail Anchovy Coilia nasus in the Changjiang River Estuary and Its Adjacent Waters Using Otolith Microchemistry. Fishes 2022, 7, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.K.; Ye, Z.J.; Yu, H.Q.; Tian, Y.J. Preliminary Study on Early Transport of Larvae of Larimichthys polyactis in the Central and Southern Yellow Sea Based on Lagrangian Particle Tracking. J. Zhejiang Ocean Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2020, 39, 538–543, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.D.; Xiong, Y.; Jiang, T.; Yang, J.; Zhong, X.M.; Tang, J.H.; Kang, Z.J. Evaluation of spawning- and natal-site fidelity of Larimichthys polyactis in the southern Yellow Sea using otolith microchemistry. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 820492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Guo, Z.M.; Xian, W.W.; Chen, M.R.; Yang, S.Y. The application of otolith morphology in life history and group recognition of small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) in the Yangtze River Estuary. Period. Ocean. Univ. China 2018, 48, 57–67, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Ye, Z.J.; Wan, R.; Ma, Q.Y.; Li, Z.G. Investigating the population structure of small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) using internal and external features of otoliths. Fish. Res. 2014, 153, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Ye, Z.J.; Li, G.Z.; Dou, S.Z. A morphometric investigation of the small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis Bleeker, 1877): Evidence for subpopulations on the Chinese coast. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2015, 32, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.S.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, T.X.; Yanagimoto, T.; Yabe, M.; Sakurai, Y. Genetic diversity in the mtDNA control region and population structure in the small yellow croaker Larimichthys polyactis. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2009, 85, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, M.J.; Park, J.Y. Genetic diversity, relationships and demographic history of the small yellow croaker, Larimichthys polyactis (Pisces: Sciaenidae) from Korea and China inferred from mitochondrial control region sequence data. Anim. Cells Syst. 2010, 14, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Min, G.S.; Yoon, M.; Kim, Y.; Choi, J.H.; Oh, T.Y.; Ni, Y. Genetic structure of Larimichthys polyactis (Pisces: Sciaenidae) in the Yellow and East China Seas inferred from microsatellite and mitochondrial DNA analyses. Anim. Cells Syst. 2012, 16, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, S.F.; Zhuang, Z.M.; Guo, L.; Meng, Z.N.; Lin, H.R. Population Genetic Studies Revealed Local Adaptation in a High Gene-Flow Marine Fish, the Small Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys polyactis). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Chen, W.M.; Ma, L. Genetic diversity and population structure of small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) in the Yellow and East China seas based on microsatellites. Aquat. Living Resour. 2019, 32, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.D.; Xue, D.X.; Li, Y.L.; Liu, J.X. RAD genotyping reveals fine-scale population structure and provides evidence for adaptive divergence in a commercially important fish from the northwestern Pacific Ocean. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.D.; Li, Y.L.; Xue, D.X.; Liu, J.X. Population genomic evidence for high genetic connectivity among populations of small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) in inshore waters of China. Fish. Res. 2020, 225, 105505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastelle, C.R.; Helser, T.E.; Laurel, B.J.; Copeman, L.A.; Stone, K.R.; McKay, J.L. Oxygen isotope fractionation in otoliths: Experimental results from four North Pacific and Arctic gadid species. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2022, 686, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.Q.; Chen, M.; Cao, J.P.; Qiu, Y.S.; Tong, J.L.; Ma, Q. Oxygen isotope in seawater and its hydrological implication in the southern Yellow Sea and the East China Sea. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2012, 43, 1057–1066, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shima, J.S.; Swearer, S.E. Larval quality is shaped by matrix effects: Implications for connectivity in a marine metapopulation. Ecology 2009, 90, 1255–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Ling, J.Z.; Hu, F. Temporal and spatial distribution and growth characteristics of Larimichthys polyactis larvae and juveniles in the coastal waters of the Yangtze River Estuary. Mar. Fish. 2018, 40, 404–412, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.Z.; Li, X.S.; Zhu, J.C.; Dai, F.Q.; Jin, X.S. The growth characteristics of larval small yellow croaker Larimichthys polyactis in the central and southern Yellow Sea. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2010, 31, 15–22, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.Y.; Kessing, J.K.; He, P.M.; Wang, Z.L.; Shi, Y.J. The world’s largest macroalgal bloom in the Yellow Sea, China: Formation and implications. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 129, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.S.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Liu, Z.L.; Dou, S.Z.; Gao, T.X. Analysis of the distribution difference of small yellow croaker between the southern Yellow Sea and the East China Sea. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2010, 40, 1–6, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.K.; Li, S.F.; Liu, Z.L.; Jin, Y.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y. Spatial connectivity in juvenile Larimichthys polyactis from otolith microchemistry in coastal areas of southern Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Mar. Fish. 2022, 44, 140–151, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.L.; Chen, J.J. Population division of Larimichthys polyactis in China Sea. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 21, 2856–2864, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.J.; Zhang, B.D.; Xue, D.X.; Gao, T.X.; Liu, J.X. Population Structure and Adaptive Divergence in a High Gene Flow Marine Fish: The Small Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys polyactis). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.R. Population maintenance among tropical reef fishes: Inferences from small-island endemics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5667–5670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strathmann, R.R.; Hughes, T.P.; Kuris, A.M.; Lindeman, K.C.; Morgan, S.G.; Pandolfi, M.J.; Warner, R.R. Evolution of local recruitment and its consequences for marine populations. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2002, 70, 377–396. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).