Commercial Quality, Biological Indices and Biochemical Composition of Queen Scallop Aequipecten opercularis in Culture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Shellfish Sampling and Ex Situ Culture
2.2. Morphological Measurements
2.3. Measurements of Biochemical Components
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
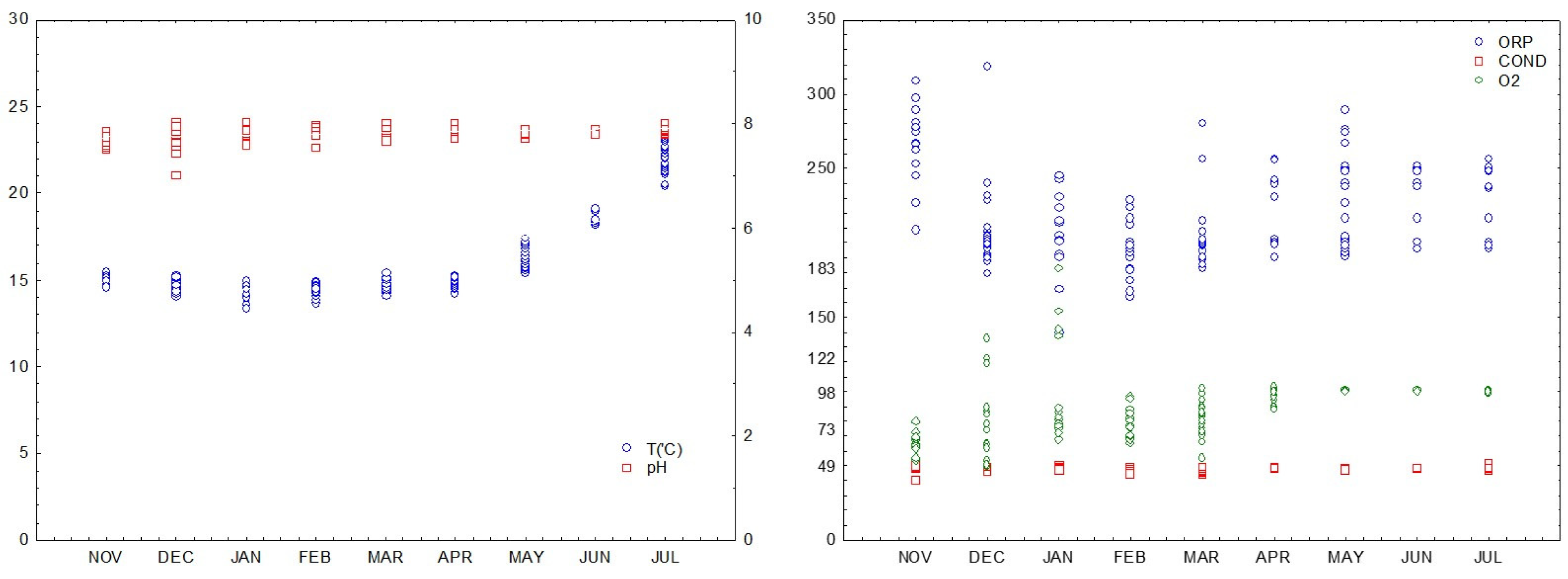
3.1. Seawater Conditions
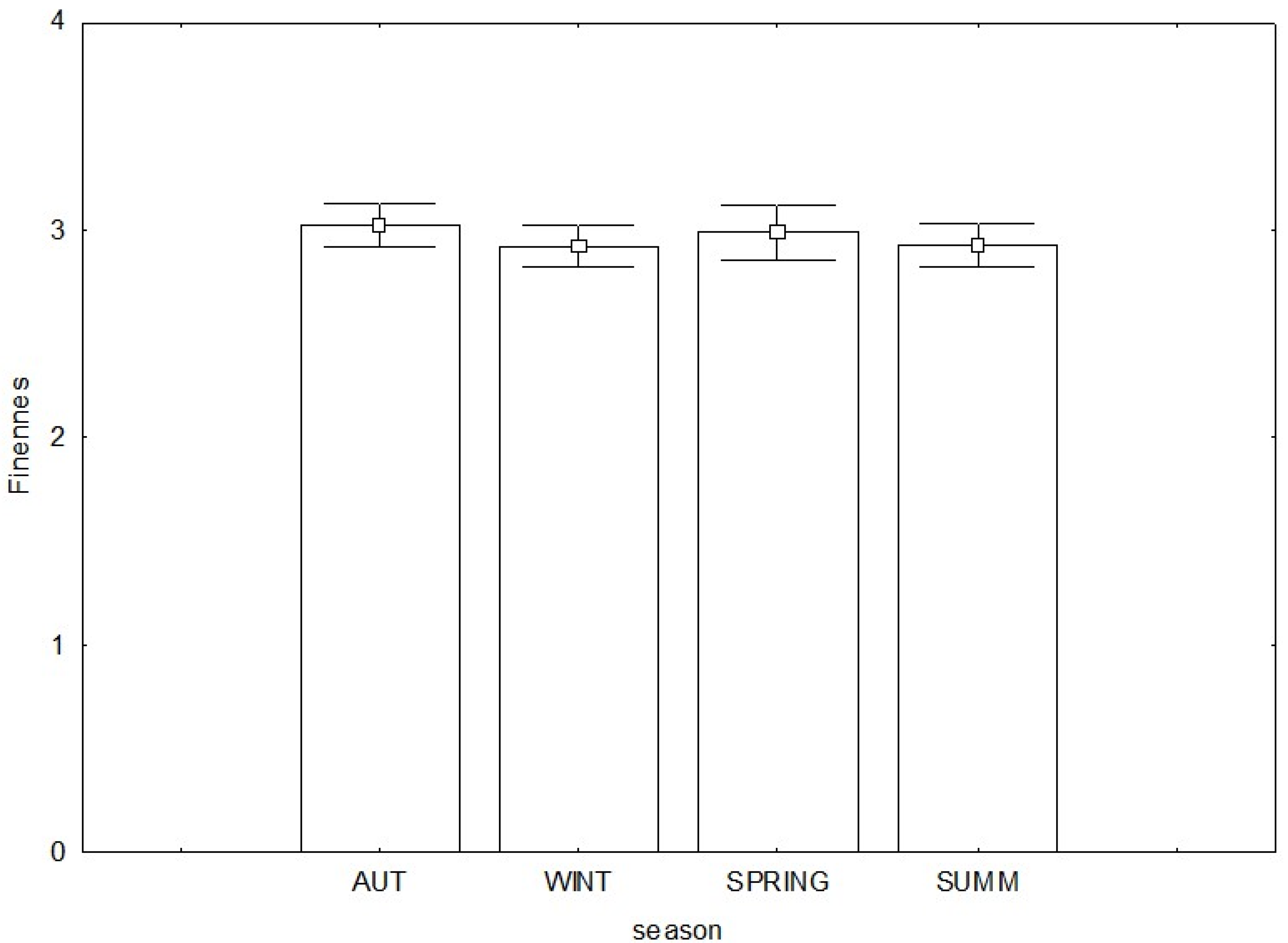
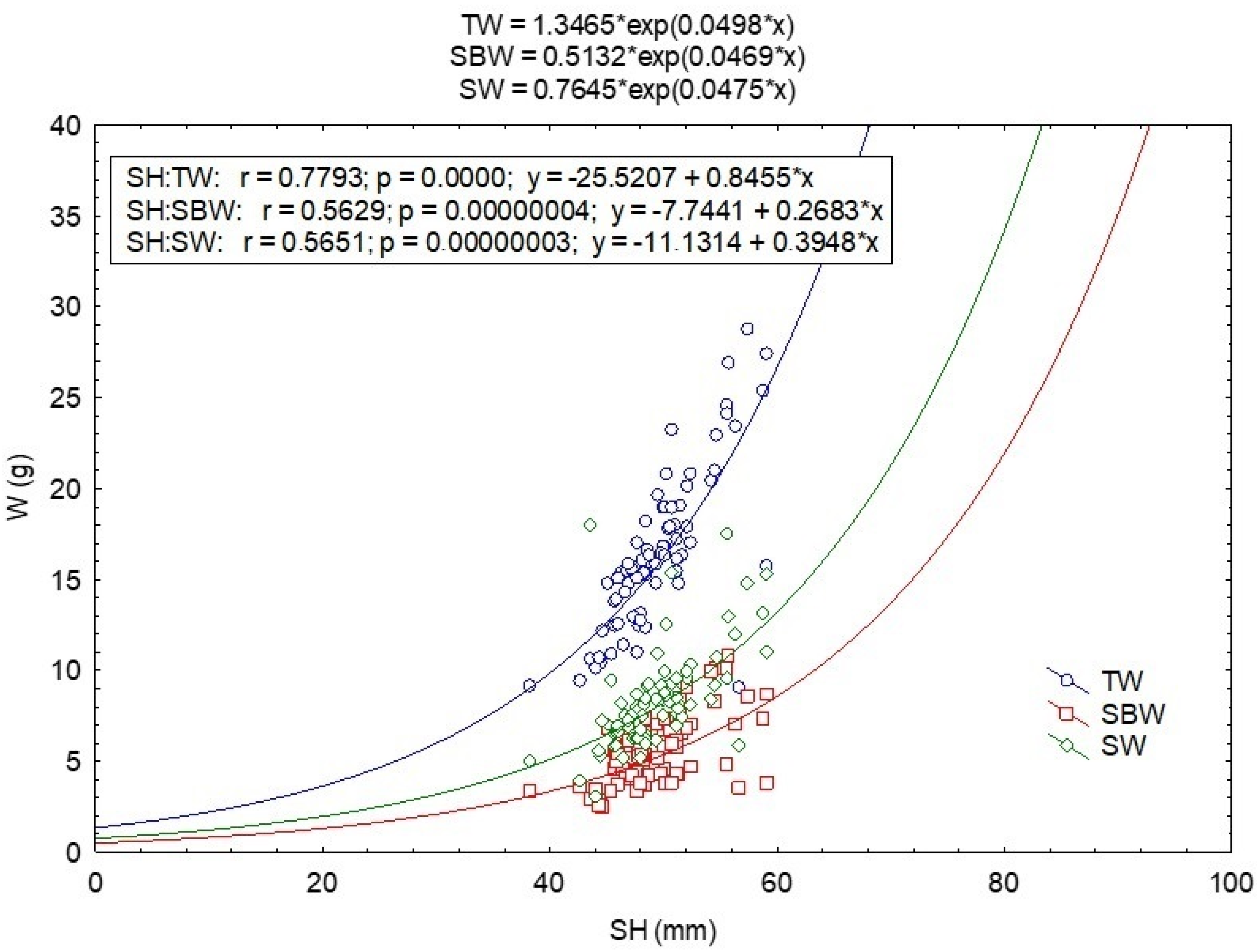
3.2. Morphology
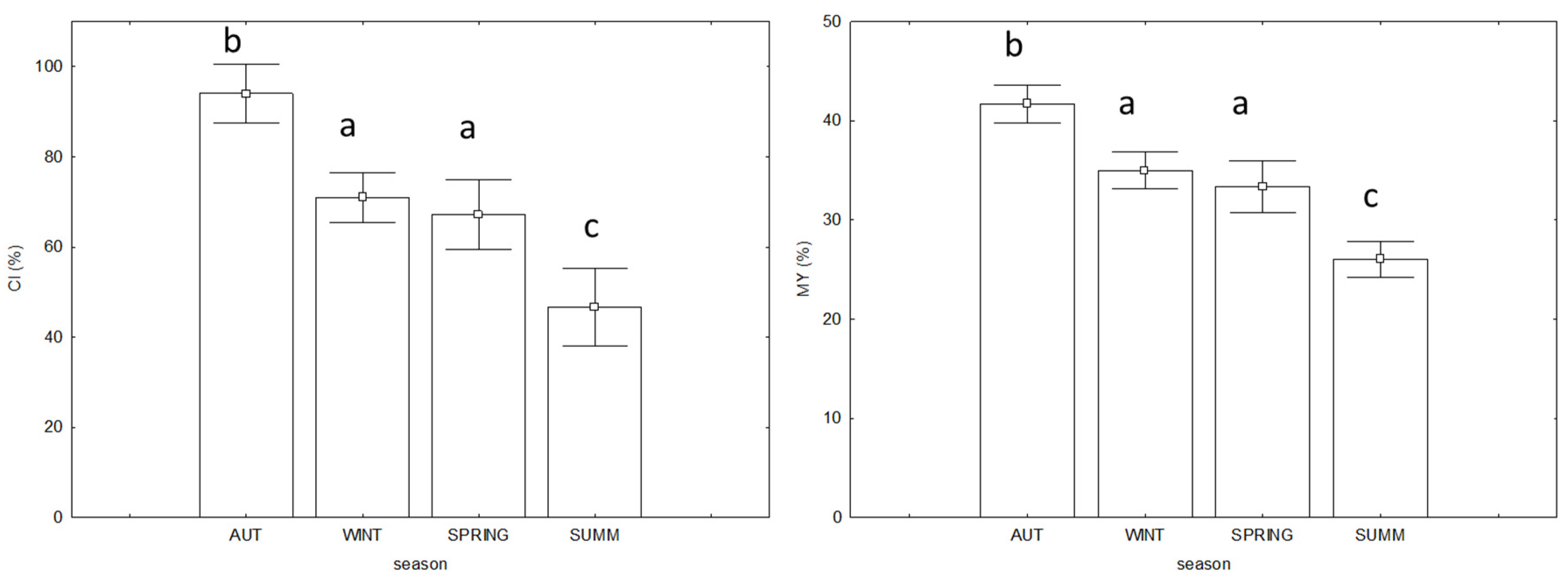
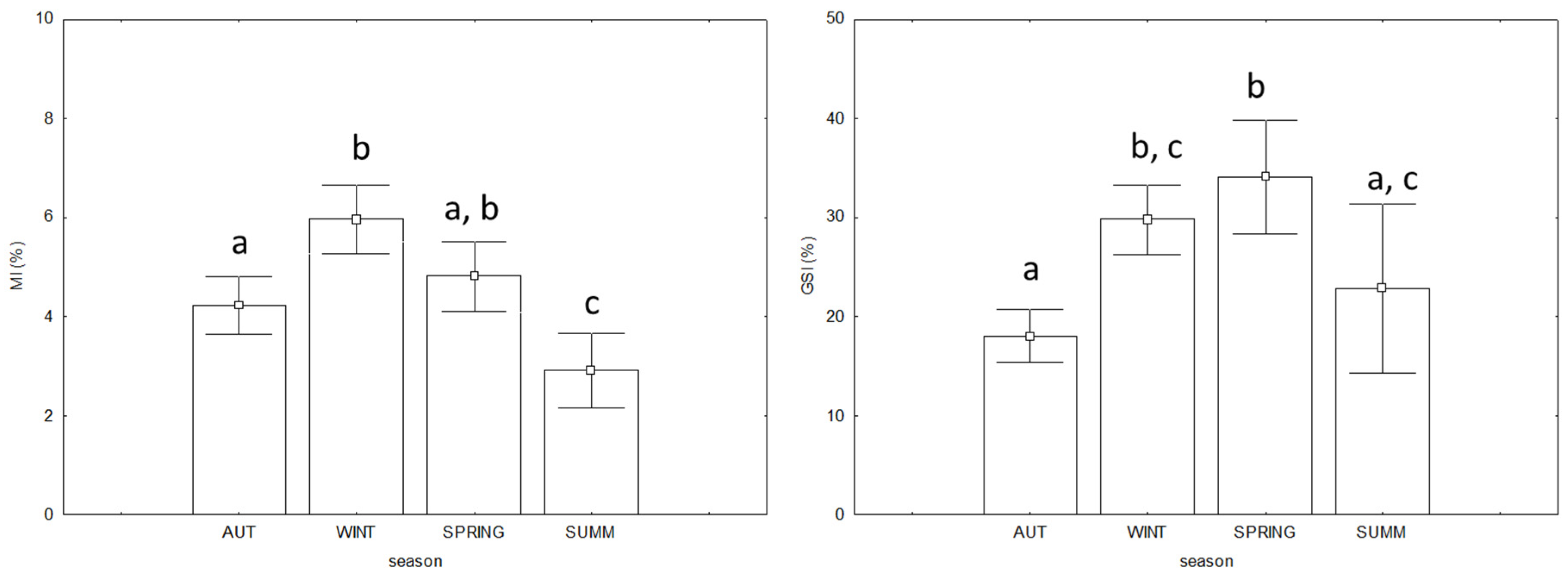
3.3. Commercial Quality and Biological Indices
3.4. Biochemical Composition
3.5. Correlation of Morphological, Biological, Biochemical and Environmental Parameters
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mizuta, D.D.; Froehlich, H.E.; Wilson, J.R. The changing role and definitions of aquaculture for environmental purposes. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 15, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meulenberg, C.J.; Hawke, S.M.; Cavaion, I.; Kumer, P.; Lenarčič, B. Understanding interdisciplinarity through Adriatic maricultures and climate change adaptation. Vis. Sustain. 2022, 18, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Y.; Tu, C.; Jiang, H.; Benjakul, S.; Ni, J.; Dong, K.; Zhang, B. Effects of Sous Vide Cooking on the Physicochemical and Volatile Flavor Properties of Half-Shell Scallop (Chlamys farreri) during Chilled Storage. Foods 2022, 11, 3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallina, V.; Torresan, S.; Zabeo, A.; Critto, A.; Glade, T.; Marcomini, A. A Multi-Risk Methodology for the Assessment of Climate Change Impacts in Coastal Zones. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakit, J.; Álvarez, G.; Díaz, P.A.; Uribe, E.; Sfeir, R.; Villasante, S.; Bas, T.G.; Lira, G.; Pérez, H.; Hurtado, A.; et al. Disentangling Environmental, Economic, and Technological Factors Driving Scallop (Argopecten purpuratus) Aquaculture in Chile. Fishes 2022, 7, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.A.; Choi, C.Y. Temporal Changes in Physiological Responses of Bay Scallop: Performance of Antioxidant Mechanism in Argopecten irradians in Response to Sudden Changes in Habitat Salinity. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, R.; Henríquez-Castillo, C.; Lohrmann, K.B.; Romero, M.S.; Ramajo, L.; Schmitt, P.; Brokordt, K. The Gill Microbiota of Argopecten purpuratus Scallop Is Dominated by Symbiotic Campylobacterota and Upwelling Intensification Differentially Affects Their Abundance. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orban, E.; Di Lena, G.; Nevigato, T.; Casini, I.; Marzetti, A.; Caproni, R. Seasonal changes in meat content, condition index and chemical composition of mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) cultured in two different Italian sites. Food Chem. 2002, 77, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, S.; Kiffney, T.; Tanaka, K.R.; Morse, D.; Brady, D.C. Meta-analysis of growth and mortality rates of net cultured sea scallops across the North Atlantic. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, P.F.; Brand, A.R.; Srand, Ø.; Foucher, E. The European Scallop Fisheries for Pecten maximus, Aequipecten opercularis, Chlamys islandica, and Mimachlamys varia. In Developments in Aquaculture and Fisheries, Scallops: Biology, Ecology, 3rd, ed.; Shumway, S.E., Parsons, G.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 40, p. 1216. [Google Scholar]
- Topić Popović, N.; Beer Ljubić, B.; Strunjak-Perović, I.; Babić, S.; Lorencin, V.; Jadan, M.; Čižmek, L.; Matulić, D.; Bojanić, K.; Čož-Rakovac, R. Seasonal antioxidant and biochemical properties of the Northern Adriatic Pecten jacobaeus. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolović, M.; Antolović, N. Biological and ecological characteristics of variegated scallop (Chlamys varia L.)—Basis for farming. Croat. J. Fish 2012, 70, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Nerlović, V. Exploitation of scallop Pecten jacobaeus (Linneaus, 1758) in the north western coastal region of Istria. In Proceedings of the 39th Croatian Symposium on Agriculture with International Participation; Zagreb, Croatia, 17–20 February 2004, Žimbrek, T., Ed.; Faculty of Agriculture, University of Zagreb: Zagreb, Croatia, 2004; pp. 606–608. [Google Scholar]
- Marčeta, T.; Da Ros, L.; Marin, M.G.; Codognotto, V.F.; Bressan, M. Overview of the biology of Flexopecten glaber in the North Western Adriatic Sea (Italy): A good candidate for future shellfish farming aims? Aquaculture 2016, 462, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veske, E.; Çankırılıgil, E.C.; Yavuzcan, H. Seasonal Proximate Composition, Amino Acid and Trace Metal Contents of the Great Mediterranean scallop (Pecten jacobaeus) Collected from the Gulf of Antalya. J. Anat. Env. Anim. Sci. 2016, 7, 358–366. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Yang, H. Review of molluscan bivalve condition index calculations and application in Northern Quahogs Mercenaria mercenaria. Aquac. Res. 2020, 52, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orban, E.; Di Lena, G.; Nevigato, T.; Casini, I.; Caproni, R.; Santaroni, G.; Giulini, G. Nutritional and commercial quality of the striped venus clam, Chamelea gallina, from the Adriatic Sea. Food Chem. 2006, 101, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biandolino, F.; Parlapiano, I.; Grattagliano, A.; Fanelli, G.; Prato, E. Comparative Characteristics of Percentage Edibility, Condition Index, Biochemical Constituents and Lipids Nutritional Quality Indices of Wild and Farmed Scallops (Flexopecten glaber). Water 2020, 12, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthey-Karl, M.; Lehmann, I.; Ostermeyer, U.; Rehbein, H.; Schröder, U. Meat composition and quality assessment of king scallops (Pecten maximus) and frozen Atlantic sea scallops (Placopecten magellanicus) on a retail level. Foods 2015, 4, 524–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbott, P.A. Developmental and seasonal metabolic activities in marine molluscs. In The Mollusca; Hochachka, P.W., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1983; Volume 2, pp. 165–217. [Google Scholar]
- Dadswell, M.J.; Weihs, D. Size-related hydrodynamic characteristics of the giant scallop, Placopecten magellanicus (Bivalvia: Pectinidae). Can. J. Zool. 1990, 68, 77885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumus, I.; Stirling, H.P. Seasonal variations in the weight, condition index and biochemical composition of mussels (Mytilus edulis L.) in suspended culture in two Scottish sea lochs. Aquaculture 1998, 159, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, S.R.; Lart, W.; Vause, B.J.; Brand, A.R. Seasonal swimming behaviour in the queen scallop (Aequipecten opercularis) and its effect on dredge fisheries. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 289, 16379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang Yong, L. Laboratory Manual on Analytical Methods and Procedures for Fish and Fish Products. In Measurement of Free and Expressible Drips; Marine Fisheries Research Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center: Singapore, 1987; Chapter B-1.1–B-1.2, p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Stanley, G.H.S. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric methods for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supić, N.; Grbec, B.; Vilibić, I.; Ivančić, I. Long-term changes in hydrographic conditions in northern Adriatic and its relationship to hydrological and atmospheric processes. Ann. Geophys. 2014, 22, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, L.; Blancheton, J.; Liu, Y.; Triplet, S.; Michaud, L. Effect of oxidation–reduction potential on performance of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) in recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquac. Int. 2014, 22, 1263–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, R.; Tan, E.; Puah, A. Oxidation-reduction potential in saline water reverse osmosis membrane desalination and its potential use for system control. Desalin. Wat. Treat. 2009, 3, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Laranjeira, A.; Serradeiro, R.; Santos, M.A.; Pacheco, M. Ozonated seawater induces genotoxicity and hematological alterations in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus)—Implications for management of recirculation aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 2011, 318, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Philipp, E.E.R.; Abele, D. Size and age-dependent changes of escape response to predator attack in the Queen scallop Aequipecten opercularis. Mar. Biol. Res. 2008, 4, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buban, I.C.R.; Cabiles, C.D.; Bobiles, R.U.; Camaya, A.P.; Soliman, V.S. Sinusoidal growth, recruitment, mortality, yield-per-recruit analysis of Buried fan scallop Mimachlamys funebris (Reeve, 1853) and their implications for mariculture. J. Fish. 2020, 8, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophersen, G.; Strand, Ø. Effect of reduced salinity on the great scallop (Pecten maximus) spat at two rearing temperatures. Aquaculture 2003, 215, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Henderson, S.; Miller-Ezzy, P.A.; Li, X.X.; Qin, J.G. Analysis of the seasonal impact of three marine bivalves on seston particles in water column. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2020, 522, 151251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodeiros, C.; Himmelman, J. Identification of factors affecting growth and survival of the tropical scallop Euvola (Pecten ziczac) in the Golfo de Cariaco, Venezuela. Aquaculture 2000, 182, 91–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvaud, L.; Patry, Y.; Jolivet, A.; Cam, E.; Clement, L.; Strand, Ø.; Charrier, G.; Thebault, J.; Lazure, P.; Gotthard, K.; et al. Variation in Size and Growth of the Great Scallop Pecten maximus along a Latitudinal Gradient. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 0037717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, B.; Stokesbury, K. Shell growth of sea scallops (Placopecten magellanicus) in the southern and northern Great South Channel, USA. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 63, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.; Hickson, A.; Swan, J.; Brown, M.; Heaton, T.; Chenery, S.; Balson, P. The Queen Scallop Aequipecten opercularis: A new source of information on late Cenozoic marine environments in Europe. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2015, 177, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prato, E.; Biandolino, F.; Parlapiano, I.; Papa, L.; Denti, G.; Fanelli, G. Seasonal changes of commercial traits, proximate and fatty acid compositions of the scallop Flexopecten glaber from the Mediterranean Sea (Southern Italy). PeerJ 2019, 7, 5810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, B.A.; Bricelj, V.M.; Shumway, S.E. Physiology: Energy Acquisition and Utilisation. In Developments in Aquaculture and Fisheries; Scallops: Biology, Ecology; Shumway, S.E., Parsons, G.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 301–353. [Google Scholar]
- Pichaud, N.; Briatte, S.; Desrosiers, V.; Pellerin, J.; Fournier, M.; Blier, P. Metabolic Capacities and Immunocompetence of Sea Scallops (Placopecten magellanicus, Gmelin) at Different Ages and Life Stages. J. Shellfish Res. 2009, 28, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Li, W.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Shu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Xing, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. Sexual Development of the Hermaphroditic Scallop Argopecten irradians Revealed by Morphological, Endocrine and Molecular Analysis. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2021, 16, 646754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiorno, T.; Iacumin, L.; Tubaro, F.; Marcuzzo, E.; Sensidoni, A.; Tulli, F. Seasonal changes in technological and nutritional quality of Mytilus galloprovincialis from suspended culture in the Gulf of Trieste (North Adriatic Sea). Food. Chem. 2015, 173, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, J.B.; Blake, N.J. Reproductive physiology. In Scallops: Biology, Ecology and Aquaculture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991; p. 377428. [Google Scholar]
- Berik, N.; Çankırılıgil, E.C.; Gül, G. Meat Yield and Shell Dimension of Smooth Scallop (Flexopecten glaber) Caught from Çardak Lagoon in Canakkale, Turkey. Aquac. Mar. Biol. 2017, 5, 00122. [Google Scholar]
- Ansell, A.D. Seasonal changes in biochemical composition of the bivalve Chlamys septemradiata from the Clyde Sea area. Mar. Biol. 1974, 25, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.C.; Venn, T.J. Seasonal variation in weight and biochemical composition of the tissues of the queen scallop, Chlamys opercularis, from the Clyde Sea area. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. 1979, 59, 605–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liao, Y.-L.; Jiang, L.-L.; Chen, M.-M.; Yang, S.-B. Effects of Ultrasound-Assisted Immersion Freezing on the Protein Structure, Physicochemical Properties and Muscle Quality of the Bay Scallop (Argopecten irradians) during Frozen Storage. Foods 2022, 11, 3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleadin, J.; Kvrgić, K.; Zrncić, S.; Lešić, T.; Vulić, A.; Džafić, N.; Oraić, D.; Krešić, G.; Koprivnjak, O. Variations in nutritive composition of three shellfish species. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2019, 31, 716–730. [Google Scholar]
- Karnjanapratum, S.; Benjaku, S.; Soottawat, K.; Hideki, T.; Tassi, Y.H. Chemical compositions and nutritional value of Asian hard clam (Meretrix lusoria) from the coast of Andaman Sea. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 4138–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prato, E.; Biandolino, F.; Parlapiano, I.; Gianguzza, P.; Fanelli, G. The recruitment of scallops (and beyond) by two different artificial collectors (Gulf of Taranto, Mediterranean Sea). Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 3319–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laming, S.R.; Jenkins, S.R.; McCarthy, I.D. Repeatability of escape response performance in the queen scallop, Aequipecten opercularis. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 3264–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aberoumad, A.; Pourshafi, K. Chemical and proximate composition properties of different fish species obtained from Iran. World J. Fish. Mar. Sci. 2010, 2, 237–239. [Google Scholar]
- Telahigue, K.; Chetoui, I.; Rabeh, I.; Romdhane, S.M.; Cafsi, M.E. Comparative fatty acid profiles in edible parts of wild scallops from the Tunisian coast. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 744–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.; Venkatesan, V.; Rajagopal, S. Biochemical composition of different body parts of Gafrarium tumidum (Roding, 1798) from Mandapam, Southeast coast of India. Afr. J. Biotech. 2012, 11, 1700–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, N.; Murugan, S.; Bharadhirajan, P. Biochemical composition of marine bivalve Donax incarnatus (Gmelin, 1791) from Cuddalore southeast coast of India. Int. J. Adv. Phar. Biol. Chem. 2014, 3, 575–582. [Google Scholar]

| Parameter | AUT | WINT | SPRING | SUMM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture (g/100 g) | 87.18 ± 0.07 | 86.08 ± 0.38 | 88.63 ± 0.37 | 88.81 ± 0.18 |
| Ash (g/100 g) | 2.58 ± 0.03 | 2.68 ± 0.01 | 2.79 ± 0.03 | 2.64 ± 0.06 |
| Protein (g/100 g) | 8.23 ± 0.16 | 9.56 ± 0.29 | 8.59 ± 0.19 | 6.89 ± 0.16 |
| Lipid (g/100 g) | 0.45 ± 0.03 | 0.40 ± 0.06 | 0.33 ± 0.01 | 0.32 ± 0.03 |
| Carbohydrate (g/100 g) | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.33 ± 0.01 |
| Parameters | H | df | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | 9.35 | 3 | 0.02 |
| Ash | 8.31 | 3 | 0.04 |
| Protein | 10.38 | 3 | 0.01 |
| Lipid | 6.75 | 3 | 0.08 |
| Carbohydrate | 10.76 | 3 | 0.01 |
| Parameters | T | pH | ORP | COND | O2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fineness | 0.10 | −0.24 | −0.03 | −0.24 | −0.21 |
| Condition index | −0.51 | −0.61 | 0.18 | 0.15 | −0.37 |
| Meat yield | −0.60 | −0.53 | 0.15 | 0.12, | −0.39 |
| Muscle index | −0.38 | −0.20 | 0.05 | −0.22 | −0.12 |
| Gonadosomatic index | −0.03 | 0.15 | −0.14 | −0.20 | 0.12 |
| Parameters | T | pH | ORP | COND | O2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | 0.69 | 0.65 | 0.45 | 0.74 | 0.16 |
| Ash | −0.27 | 0.66 | −0.20 | 0.11 | 0.42 |
| Protein | −0.93 | 0.16 | −0.46 | −0.75 | −0.45 |
| Lipid | −0.45 | −0.58 | 0.16 | −0.19 | −0.41 |
| Carbohydrate | 0.97 | −0.20 | 0.29 | 0.55 | 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kovačić, I.; Žunec, A.; Matešković, M.; Burić, P.; Iveša, N.; Štifanić, M.; Frece, J. Commercial Quality, Biological Indices and Biochemical Composition of Queen Scallop Aequipecten opercularis in Culture. Fishes 2023, 8, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8010048
Kovačić I, Žunec A, Matešković M, Burić P, Iveša N, Štifanić M, Frece J. Commercial Quality, Biological Indices and Biochemical Composition of Queen Scallop Aequipecten opercularis in Culture. Fishes. 2023; 8(1):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8010048
Chicago/Turabian StyleKovačić, Ines, Ante Žunec, Mauro Matešković, Petra Burić, Neven Iveša, Mauro Štifanić, and Jadranka Frece. 2023. "Commercial Quality, Biological Indices and Biochemical Composition of Queen Scallop Aequipecten opercularis in Culture" Fishes 8, no. 1: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8010048
APA StyleKovačić, I., Žunec, A., Matešković, M., Burić, P., Iveša, N., Štifanić, M., & Frece, J. (2023). Commercial Quality, Biological Indices and Biochemical Composition of Queen Scallop Aequipecten opercularis in Culture. Fishes, 8(1), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8010048










