Round Goby Detection in Lakes Huron and Michigan—An Evaluation of eDNA and Fish Catches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Activities
2.2. Sample Processing and DNA Extraction
2.3. qPCR
2.4. ddPCR
2.5. Quality Assurance
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparisons of qPCR and ddPCR
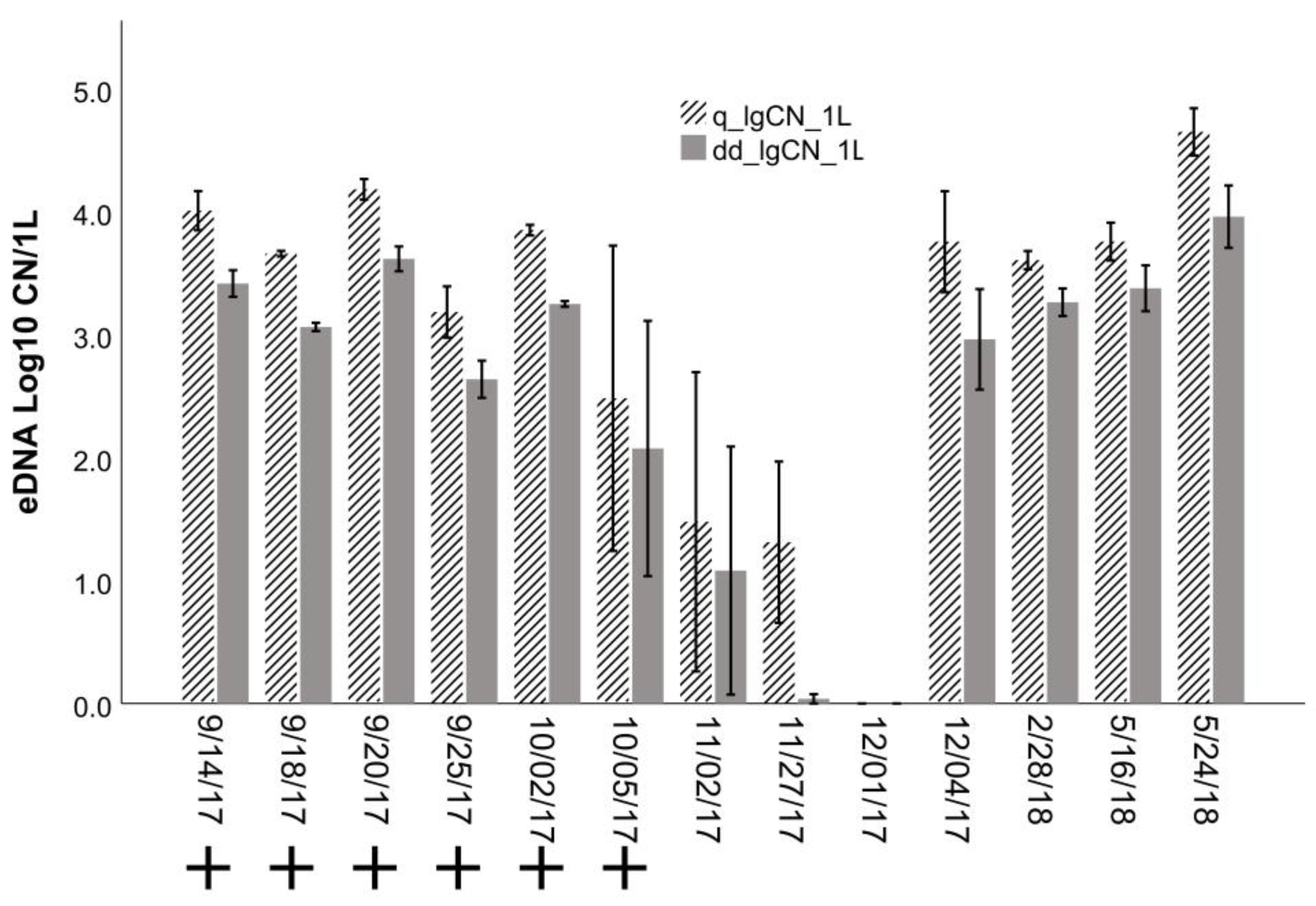
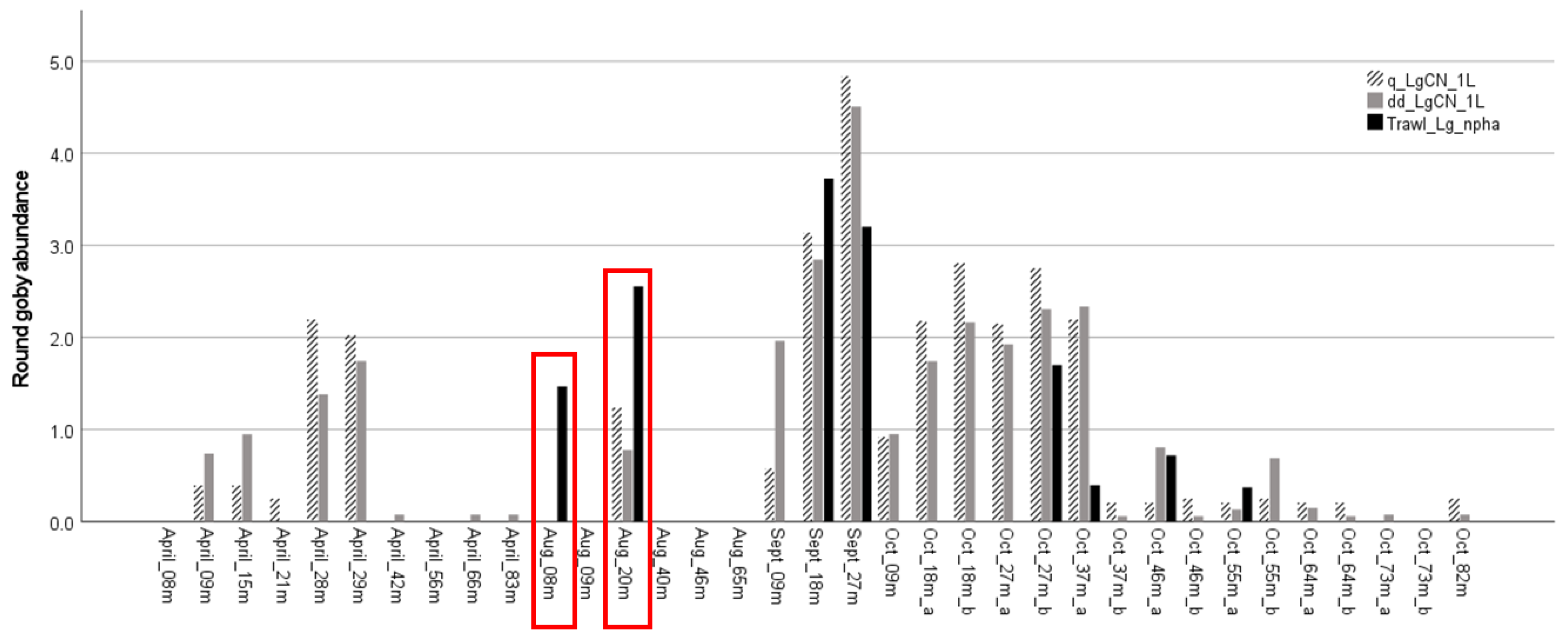
3.2. Detection Sensitivity: Comparison of eDNA vs. Traditional Surveys
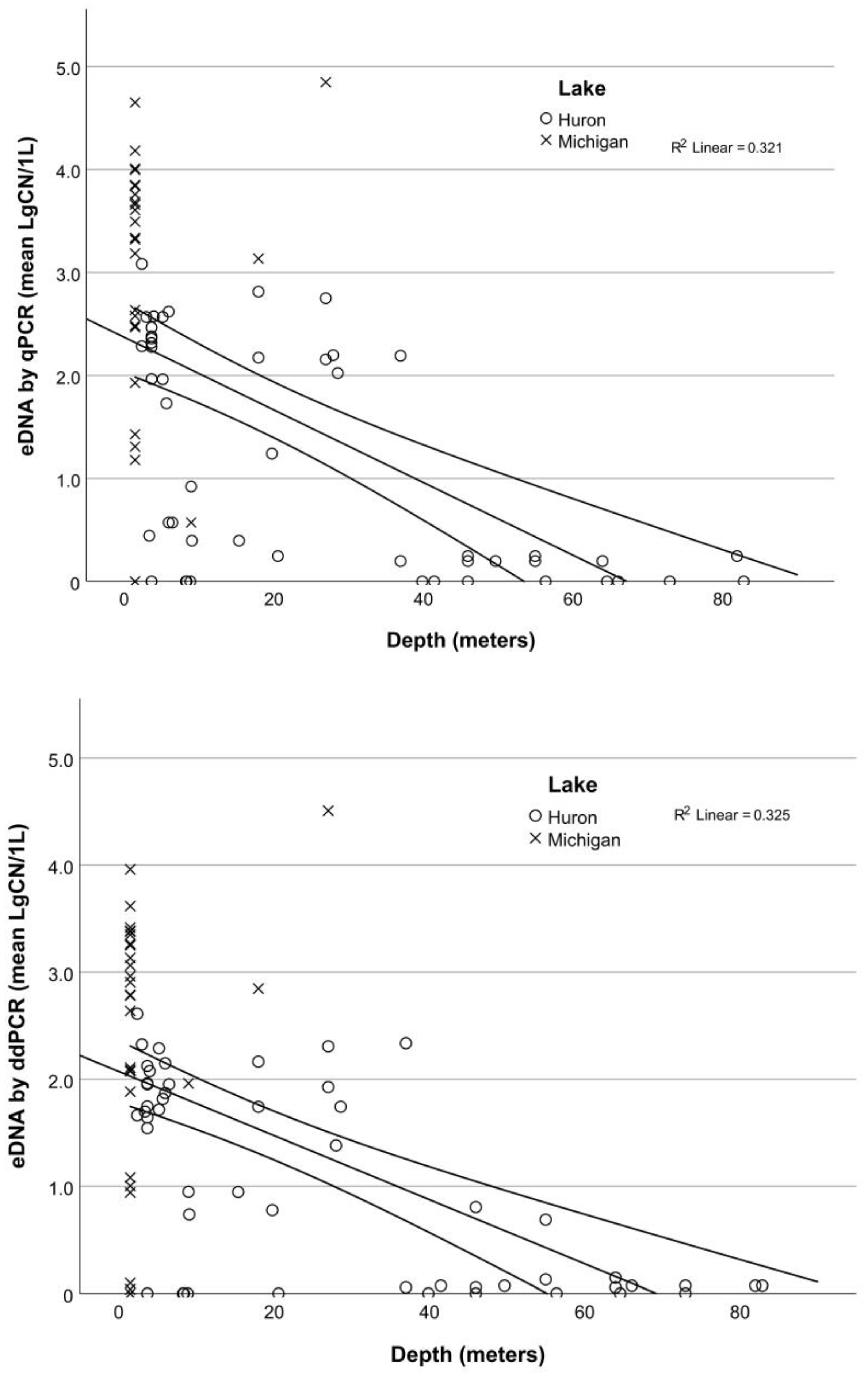
3.3. Application: Evaluating Seasonal and Depth Distribution of Round Goby
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Molecular Analyses: ddPCR and qPCR
4.2. Detection by eDNA and Traditional Surveys
4.3. Application
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jude, D.J.; Reider, R.H.; Smith, G.R. Establishment of Gobiidae in the Great Lakes Basin. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1992, 49, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, O.T. Prey fish communities of the Laurentian Great Lakes: A cross-basin overview of status and trends based on bottom trawl surveys, 1978–2016. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2019, 22, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapp, D.F.; Schneeberger, P.J.; Jude, D.J.; Madison, G.; Pistis, C. Monitoring round goby (Neogobius melanostomus) population expansion in eastern and northern Lake Michigan. J. Great Lakes Res. 2001, 27, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.B.; Allen, M.; Corkum, L.D.; Lee, V.A. Comparison of methods needed to estimate population size of round gobies (Neogobius melanostomus) in western Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2005, 31, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, M.A.; Evrard, L.M.; Mensinger, A.F. Distribution, abundance, and range of the round goby, Apollina melanostoma, in the Duluth-Superior Harbor and St. Louis River Estuary, 1998–2004. J. Great Lakes Res. 2008, 34, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornis, M.S.; Mercado-Silva, N.; Vander Zanden, M.J. Twenty years of invasion: A review of round goby Neogobius melanostomus biology, spread and ecological implications. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 80, 235–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rourke, M.L.; Fowler, A.M.; Hughes, J.M.; Broadhurst, M.K.; DiBattista, J.D.; Fielder, S.; Wilkes Walburn, J.; Furlan, E.M. Environmental DNA (eDNA) as a tool for assessing fish biomass: A review of approaches and future considerations for resource surveys. Environ. DNA 2022, 4, 9–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, G.S.; Hoffman, J.C.; Trebitz, A.S.; Hatzenbuhler, C.I.; Myers, J.T.; Ross, J.E.; Okum, S.L.; Pilgrim, E.M. Early detection monitoring for non-indigenous fishes; comparison of survey approaches during two species introductions in a Great Lakes port. Biol. Invasions 2022, 24, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, L.M.; Simmons, M.; Wegleitner, B.J.; Jerde, C.L.; Mahon, A.R. Quantifying environmental DNA signals for aquatic invasive species across multiple detection platforms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12800–12806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevers, M.B.; Byappanahalli, M.N.; Morris, C.C.; Shively, D.; Przybyla-Kelly, K.; Spoljaric, A.M.; Dickey, J.; Roseman, E.F. Environmental DNA (eDNA): A tool for quantifying the abundant but elusive round goby (Neogobius melanostomus). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, L.R.; Jerde, C.L.; Budny, M.L.; Mahon, A.R. The use of environmental DNA in invasive species surveillance of the Great Lakes commercial bait trade. Conserv. Biol. 2015, 29, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevers, M.B.; Przybyla-Kelly, K.; Shively, D.; Morris, C.C.; Dickey, J.; Byappanahalli, M.N. Influence of sediment and stream transport on detecting a source of environmental DNA. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, S.D.; Baldigo, B.P.; Rees, C.B.; Bartron, M.L.; Winterhalter, D. Eastward expansion of round goby in New York: Assessment of detection methods and current range. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2021, 150, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.W.; Ostrom, P.; Ostrom, N.E.; Klump, J.V.; Steinman, A.D.; Dreelin, E.A.; Vander Zanden, M.J.; Fisk, A.T. Grand challenges for research in the Laurentian Great Lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 2510–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Møller, P.R.; Sigsgaard, E.E.; Knudsen, S.W.; Jørgensen, O.A.; Willerslev, E. Environmental DNA from seawater samples correlate with trawl catches of subarctic, deepwater fishes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, S.W.; Ebert, R.B.; Hesselsøe, M.; Kuntke, F.; Hassingboe, J.; Mortensen, P.B.; Thomsen, P.F.; Sigsgaard, E.E.; Hansen, B.K.; Nielsen, E.E. Species-specific detection and quantification of environmental DNA from marine fishes in the Baltic Sea. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2019, 510, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter, I.; Joensen, M.; Kristiansen, R.; Steingrund, P.; Vestergaard, P. Environmental DNA concentrations are correlated with regional biomass of Atlantic cod in oceanic waters. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 461. [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckle, M.Y.; Adolf, J.; Charlop-Powers, Z.; Dunton, K.J.; Hinks, G.; VanMorter, S.M. Trawl and eDNA assessment of marine fish diversity, seasonality, and relative abundance in coastal New Jersey, USA. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2021, 78, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capo, E.; Spong, G.; Koizumi, S.; Puts, I.; Olajos, F.; Königsson, H.; Karlsson, J.; Byström, P. Droplet digital PCR applied to environmental DNA, a promising method to estimate fish population abundance from humic-rich aquatic ecosystems. Environ. DNA 2021, 3, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, T.; Halfmaerten, D.; Neyrinck, S.; De Regge, N.; Jacquemyn, H.; Brys, R. Accurate detection and quantification of seasonal abundance of American bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus) using ddPCR eDNA assays. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Uchii, K.; Takahara, T.; Matsuhashi, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Minamoto, T. Use of droplet digital PCR for estimation of fish abundance and biomass in environmental DNA surveys. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, M.E.; Meigs-Friend, G.; Ferrante, J.A.; Kamla, A.T.; Dorazio, R.M.; Diagne, L.K.; Luna, F.; Lanyon, J.M.; Reid, J.P. Surveys of environmental DNA (eDNA): A new approach to estimate occurrence in vulnerable manatee populations. Endanger. Species Res. 2018, 35, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majaneva, M.; Diserud, O.H.; Eagle, S.H.C.; Boström, E.; Hajibabaei, M.; Ekrem, T. Environmental DNA filtration techniques affect recovered biodiversity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyla-Kelly, K.J.; Spoljaric, A.M. Round Goby Detection by Environmental DNA, Trawl, and Angling in Lakes Huron and Michigan: U.S. Geological Survey Data Release; USGS Bureau: Reston, VA, USA, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Klymus, K.E.; Merkes, C.M.; Allison, M.J.; Goldberg, C.S.; Helbing, C.C.; Hunter, M.E.; Jackson, C.A.; Lance, R.F.; Mangan, A.M.; Monroe, E.M. Reporting the limits of detection and quantification for environmental DNA assays. Environ. DNA 2020, 2, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klymus, K.E.; Richter, C.A.; Chapman, D.C.; Paukert, C. Quantification of eDNA shedding rates from invasive bighead carp Hypophthalmichthys nobilis and silver carp Hypophthalmichthys molitrix. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, C.S.; Sepulveda, A.; Ray, A.; Baumgardt, J.; Waits, L.P. Environmental DNA as a new method for early detection of New Zealand mudsnails (Potamopyrgus antipodarum). Freshw. Sci. 2013, 32, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, M.E.; Meigs-Friend, G.; Ferrante, J.A.; Smith, B.J.; Hart, K.M. Efficacy of eDNA as an early detection indicator for Burmese pythons in the ARM Loxahatchee National Wildlife Refuge in the greater Everglades ecosystem. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, E.; Paddock, R.W.; Janssen, J. Seasonal offshore/inshore migration of round gobies. J. Great Lakes Res. 2021, 47, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlebois, P.M.; Marsden, J.E.; Goettel, R.G.; Wolfe, R.K.; Jude, D.J.; Rudnika, S. The Round Goby, Neogobius Melanostomus (Pallas): A Review of European and North American Literature; Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant Program: Urbana, IL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Brys, R.; Halfmaerten, D.; Neyrinck, S.; Mauvisseau, Q.; Auwerx, J.; Sweet, M.; Mergeay, J. Reliable eDNA detection and quantification of the European weather loach (Misgurnus fossilis). J. Fish Biol. 2021, 98, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Pochon, X.; Laroche, O.; von Ammon, U.; Adamson, J.; Zaiko, A. A comparison of droplet digital polymerase chain reaction (PCR), quantitative PCR and metabarcoding for species-specific detection in environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 19, 1407–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bleijswijk, J.D.L.; Engelmann, J.C.; Klunder, L.; Witte, H.J.; Witte, J.I.J.; van der Veer, H.W. Analysis of a coastal North Sea fish community: Comparison of aquatic environmental DNA concentrations to fish catches. Environ. DNA 2020, 2, 429–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penaluna, B.E.; Allen, J.M.; Arismendi, I.; Levi, T.; Garcia, T.S.; Walter, J.K. Better boundaries: Identifying the upper extent of fish distributions in forested streams using eDNA and electrofishing. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, L.S.; Godwin, J.C.; Renshaw, M.A.; Larson, E. Environmental DNA (eDNA) detection probability is influenced by seasonal activity of organisms. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.K.; Meyer, M.J.; McPhee, C.; Gaston, J.R.; Venesky, M.D.; Case, B.F. Seasonal and diel signature of eastern hellbender environmental DNA. J. Wildl. Manag. 2018, 82, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedwell, M.E.; Goldberg, C.S. Spatial and temporal patterns of environmental DNA detection to inform sampling protocols in lentic and lotic systems. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 1602–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxton, A.S.; Groombridge, J.J.; Zakaria, N.B.; Griffiths, R.A. Seasonal variation in environmental DNA in relation to population size and environmental factors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laramie, M.B.; Pilliod, D.S.; Goldberg, C.S. Characterizing the distribution of an endangered salmonid using environmental DNA analysis. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, R.A.; Merkes, C.M.; Jackson, C.A.; Goforth, R.R.; Amberg, J.J. Seasonal trends in eDNA detection and occupancy of bigheaded carps. J. Great Lakes Res. 2017, 43, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, S.; Shibata, N. Identifying spawning events in fish by observing a spike in environmental DNA concentration after spawning. Environ. DNA 2021, 3, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
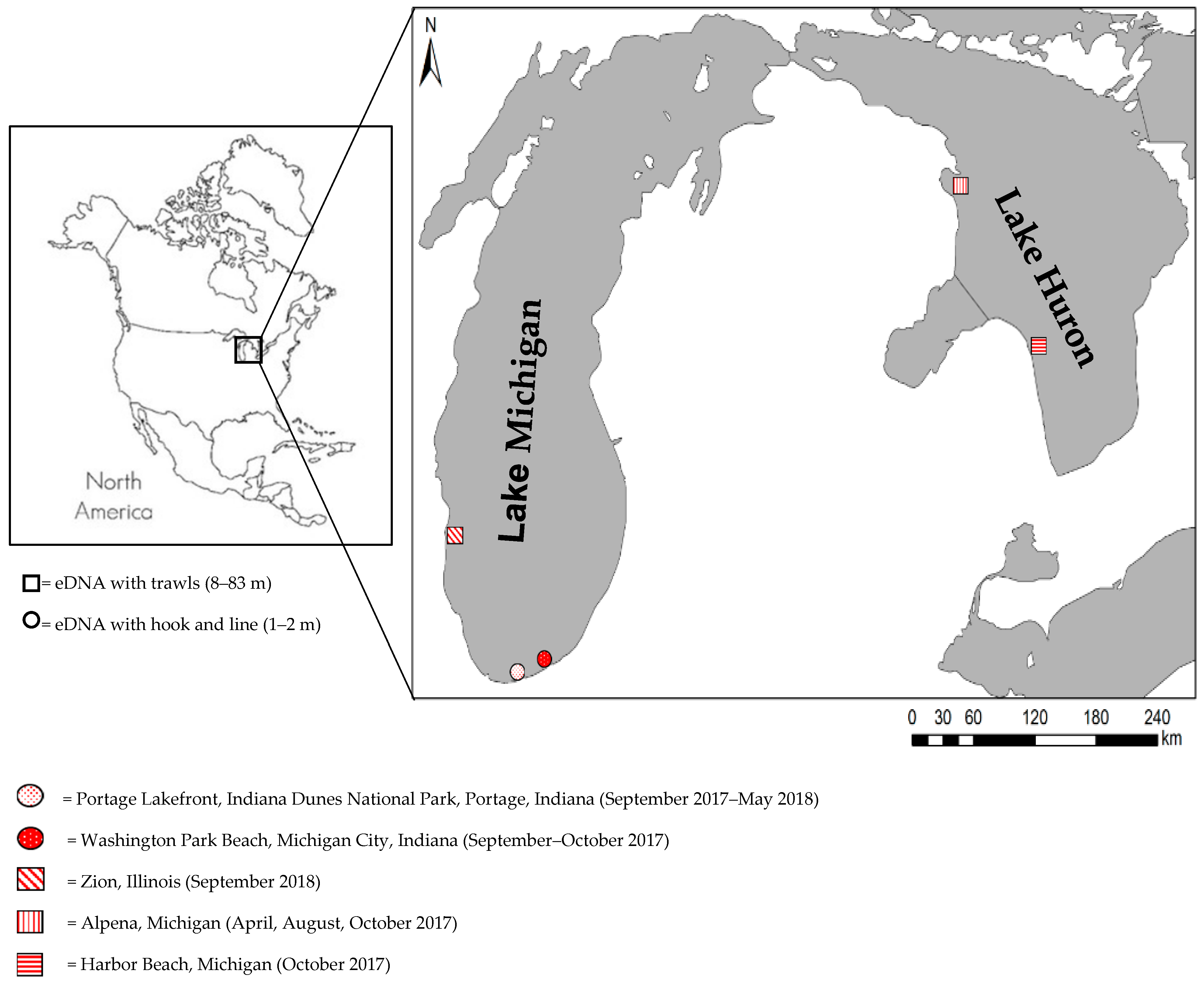

| Lake | Port/Site * | Month, Year | Traditional Monitoring and eDNA Sampling | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth (Meters) | Trawl/Angling N | eDNA N | |||
| Trawling | |||||
| Huron | Alpena, MI | April, 2017 | 8, 9, 15, 21, 28, 29, 42, 56, 66, 83 | 10 | 20 |
| Alpena, MI | April, 2017 | 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 50 | 0 | 15 | |
| Alpena, MI | August, 2017 | 8, 9, 20, 40, 46, 65 | 6 | 12 | |
| Alpena, MI | August, 2017 | 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 | 0 | 16 | |
| Good Harbor, MI | October, 2017 | 18, 27, 37, 46, 55, 64, 73 | 7 | 14 | |
| Michigan | Zion, IL | September, 2018 | 9, 18, 27 | 3 | 6 |
| Angling | |||||
| Michigan | Portage Lakefront, IN | September, 2017 | 1.5–2 | 2 | 6 |
| October, 2017 | 1.5–2 | 2 | 6 | ||
| September–December (2017), February, May (2018) | 1.5–2 | 0 | 60 | ||
| Washington Park, IN | September, 2017 | 1.5–2 | 2 | 6 | |
| September, 2017 | 1.5–2 | 0 | 10 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
At least a portion of this work is authored by Kasia Przybyla-Kelly and Meredith Nevers on behalf of the U.S Government and as regards, Kasia Przybyla-Kelly and Meredith Nevers and the U.S Government, is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign and other copyrights may apply.
Share and Cite
Przybyla-Kelly, K.J.; Spoljaric, A.M.; Nevers, M.B. Round Goby Detection in Lakes Huron and Michigan—An Evaluation of eDNA and Fish Catches. Fishes 2023, 8, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8010041
Przybyla-Kelly KJ, Spoljaric AM, Nevers MB. Round Goby Detection in Lakes Huron and Michigan—An Evaluation of eDNA and Fish Catches. Fishes. 2023; 8(1):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8010041
Chicago/Turabian StylePrzybyla-Kelly, Kasia J., Ashley M. Spoljaric, and Meredith B. Nevers. 2023. "Round Goby Detection in Lakes Huron and Michigan—An Evaluation of eDNA and Fish Catches" Fishes 8, no. 1: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8010041
APA StylePrzybyla-Kelly, K. J., Spoljaric, A. M., & Nevers, M. B. (2023). Round Goby Detection in Lakes Huron and Michigan—An Evaluation of eDNA and Fish Catches. Fishes, 8(1), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8010041






