Predicting Sex-Related Transcripts in the Chinese Giant Salamander (Andrias davidianus): A Transcriptomics Study, Selection Gender for Preservation, Breeding and Reintroduction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Sample Collection
2.2. RNA Extraction, Transcriptome Library Preparation and Illumina Sequencing
2.3. Transcriptome Assembly and Quality Evaluation
2.4. Identification and Annotation of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
2.5. qPCR Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Quality of Sequencing, Transcriptome Assembly and Matching
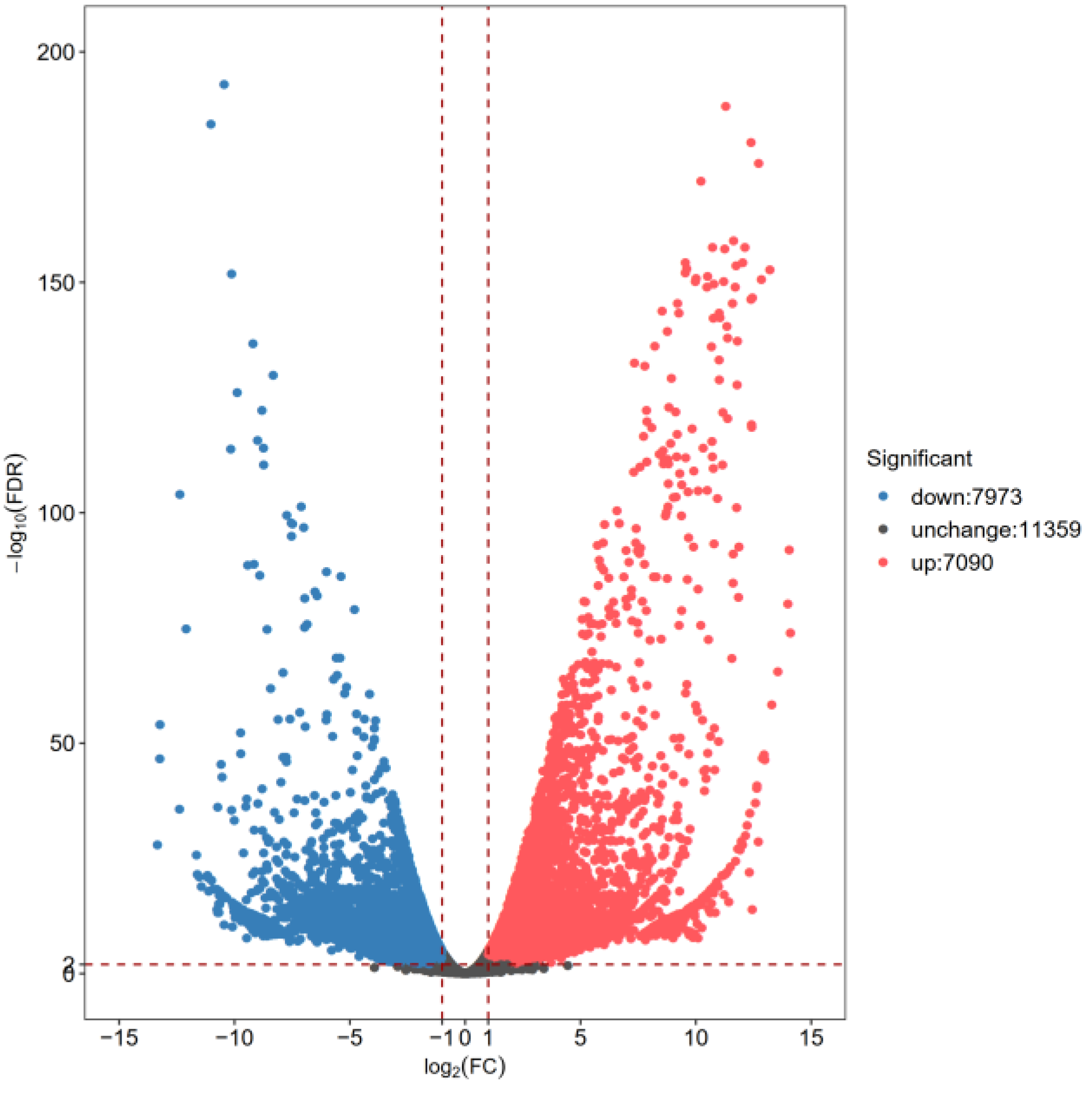
3.2. Identification of DEGs
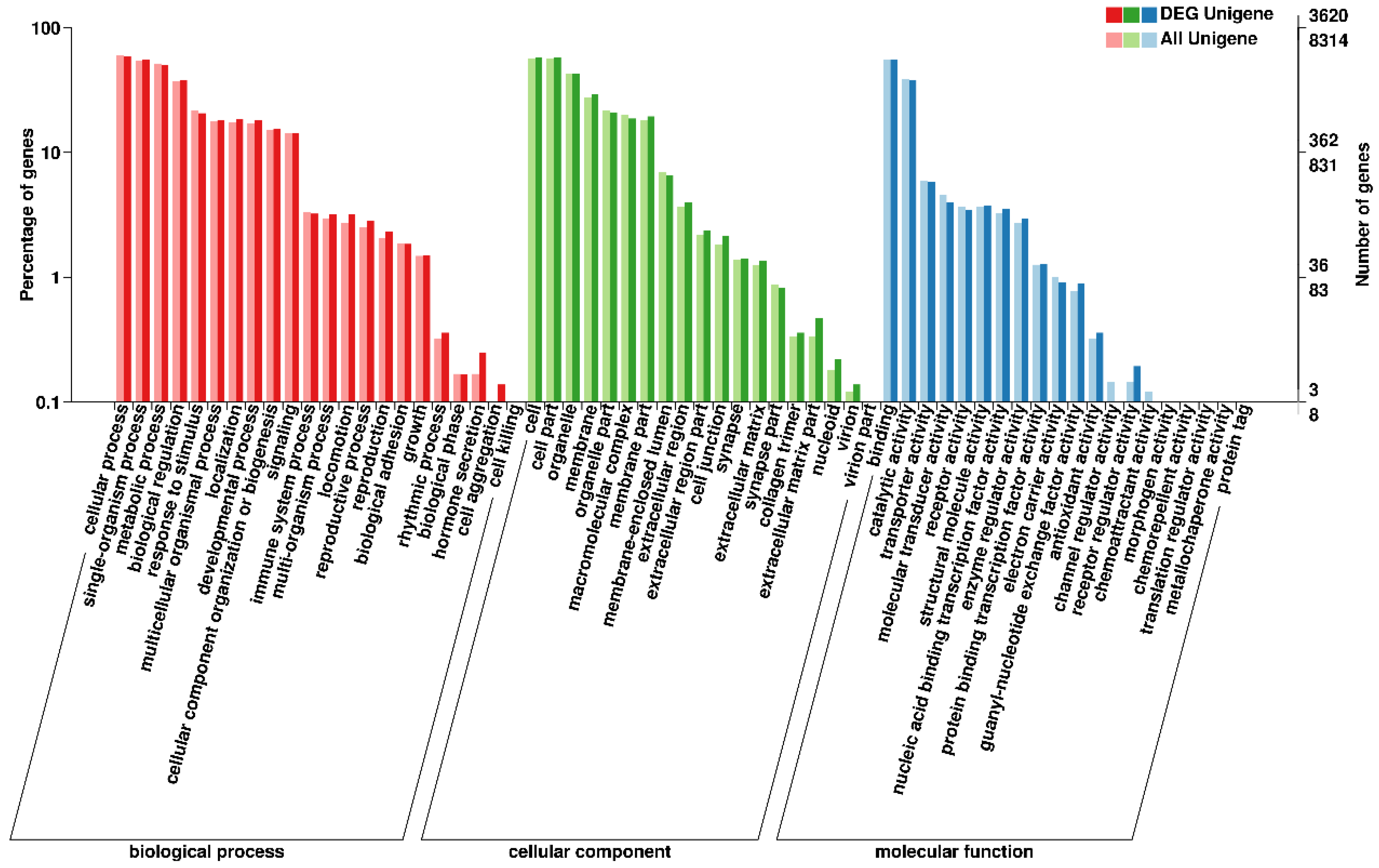
3.3. GO Annotation of DEGs
3.4. KEGG Annotation of DEGs
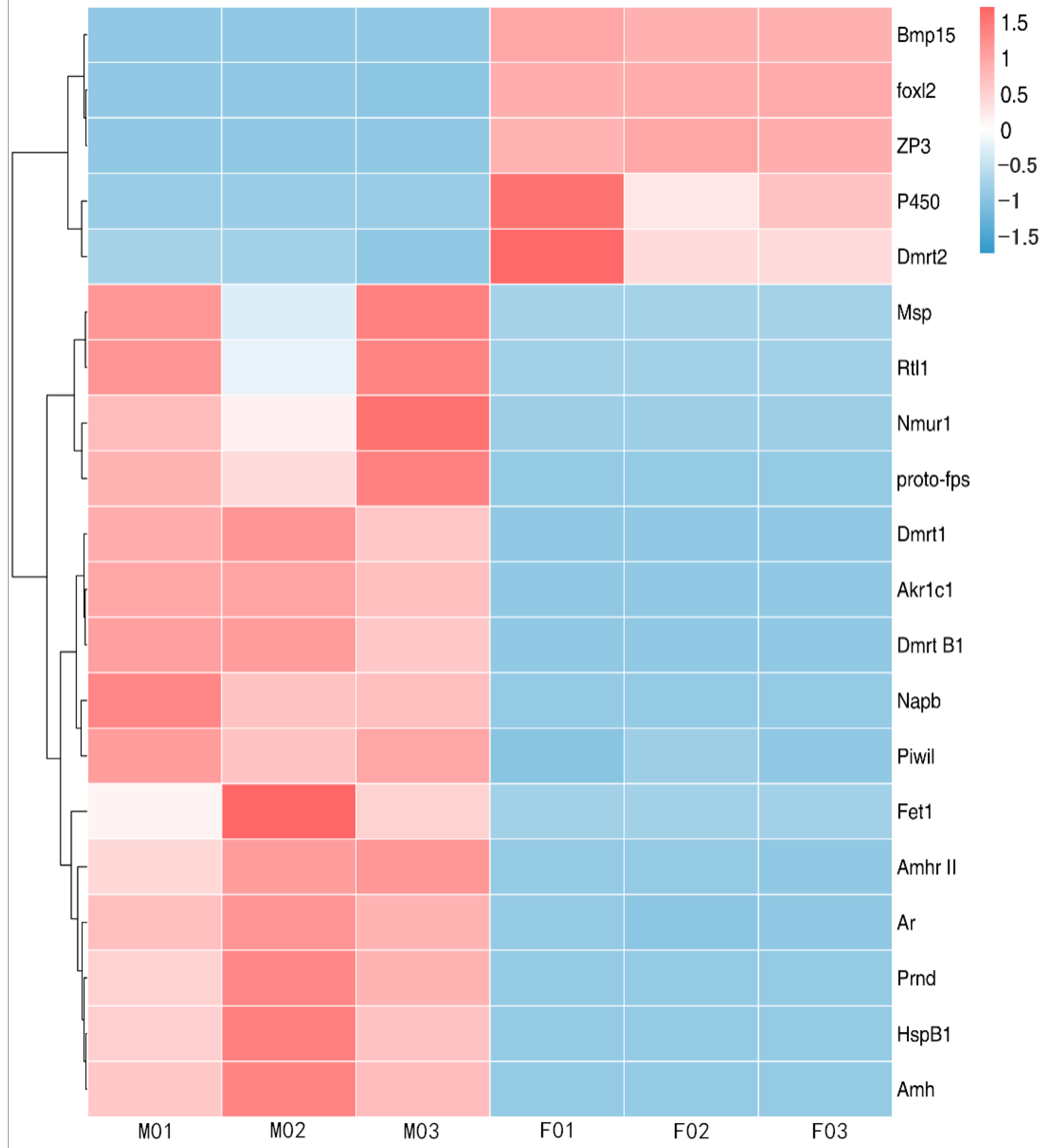
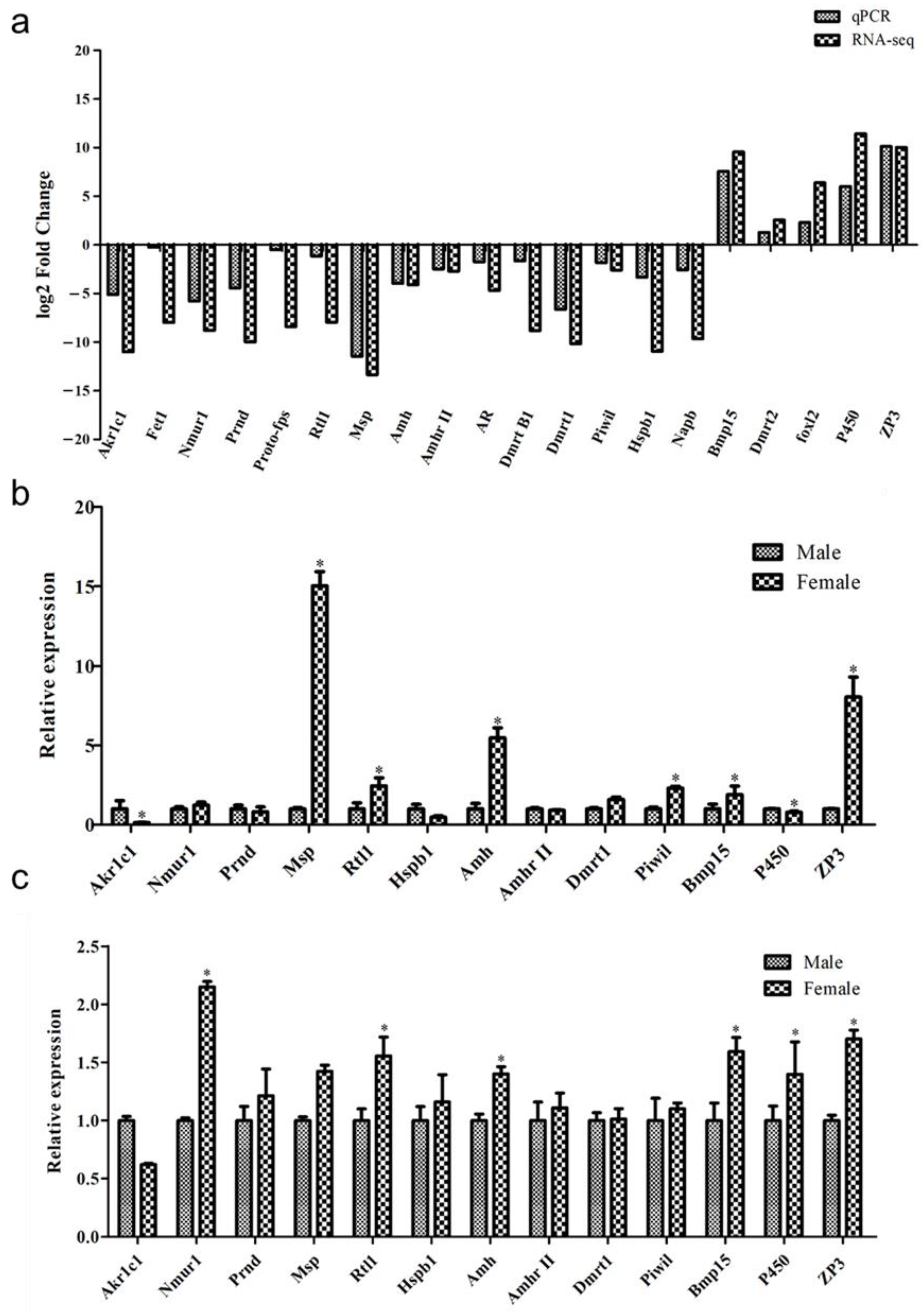
3.5. Validation of DEGs with qPCR
3.6. Relative Expression of the mRNA Expression of the Identified DGEs in the Skin and Muscle
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huo, Z.; Guo, J.; Li, X.; Yu, X. Post-fledging dispersal and habitat use of a reintroduced population of the Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon). Avian Res. 2014, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, M.; Kuemmerlen, M.; Wittwer, C.; Cocchiararo, B.; Khaliq, I.; Pfenninger, M.; Nowak, C. Combining environmental DNA and species distribution modeling to evaluate reintroduction success of a freshwater fish. Ecol. Appl. 2020, 30, e02034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, M.L.; Tonkin, Z.; Yen, J.D.L.; Johnson, G.; Ingram, B.A.; Sharley, J.; Lyon, J.; Chapple, D.G.; Sunnucks, P.; Pavlova, A. Using multiple sources during reintroduction of a locally extinct population benefits survival and reproduction of an endangered freshwater fish. Evol. Appl. 2021, 14, 950–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, X.; Wei, H.; Shang, H.; Zhou, M.; Chen, B.; Zhang, F.; Zang, X.; Li, P.; Sun, J.; Che, J.; et al. Data from proteomic analysis of the skin of Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus). Data Br. 2015, 3, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Jin, W.; Chen, D.; Dong, M.; Xin, X.; Li, C.; Xu, Z. Collagens made from giant salamander (Andrias davidianus) skin and their odorants. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.Q.; Shubin, N.H. Earliest known crown-group salamanders. Nature 2003, 422, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turvey, S.T.; Chen, S.; Tapley, B.; Wei, G.; Xie, F.; Yan, F.; Yang, J.; Liang, Z.; Tian, H.; Wu, M.; et al. Imminent extinction in the wild of the world’s largest amphibian. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R592–R594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittwoch, U. Sex determination and sex reversal: Genotype, phenotype, dogma and semantics. Hum. Genet. 1992, 89, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandra, G.E.; Norma, M.M. Sexual determination and differentiation in teleost fish. Rev. Fish Biol. Fisher. 2010, 20, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, T.B. Sex determination and primary sex differentiation in amphibians: Genetic and developmental mechanisms. J. Exp. Zool. 1998, 281, 373–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, R.H.; Nagahama, Y. Sex determination and sex differentiation in fish: An overview of genetic, physiological, and environmental influences. Aquaculture 2002, 208, 191–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: A revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, W.; Fu, C.; Zhang, W.; Han, F.; Wu, H. Genomic and transcriptomic insights into the molecular basis of sexually dimorphic nuptial spines in Leptobrachium leishanense. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, J.; Anboukaria, H.; Luo, Z.; Zhao, M.; Wu, H. Comparative transcriptome analyses of seven anurans reveal functions and adaptations of amphibian skin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Shen, W.; Veizades, S.; Liang, G.; Sayed, N.; Nguyen, P.K. Single-cell transcriptional profiling reveals sex and age diversity of gene expression in mouse endothelial cells. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.J.; Zheng, L.P.; Duan, X.P. Application of PCR for sex determination from bovine muscle tissue. J. Tianjin Agric. Coll. 2001, 8, 22–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yang, G.; Zhou, K.; Wei, F.; Yan, J. PCR amplification of the Sry gene for cetacean sex identification. J. Vet. Sci. 2005, 25, 20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Tian, H.; Li, W.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, H. Identification of critical sex-biased genes in Andrias davidianus by de novo transcriptome. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2019, 294, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yang, C.; Gao, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, C.; Ji, H.; Dong, W. Molecular characterisation of oestrogen receptor ERα and the effects of bisphenol A on its expression during sexual development in the Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus). Reprod. Fert. Develop. 2019, 31, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Xiao, H.; Wang, Q.; Tian, H.; Meng, Y. Identification and expression of forkhead box genes in the Chinese giant salamander Andrias davidianus. Reprod. Fert. Develop. 2018, 30, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Hong, X.; Zhu, X.; Xu, H. Identification and analysis of lncRNAs and mRNAs involved in sex regulation in Asian yellow pond turtle (Mauremys mutica). J. Fish. China 2020, 44, 1960–1975. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bowles, J.; Knight, D.; Smith, C.; Wilhelm, D.; Richman, J.; Mamiya, S.; Yashiro, K.; Chawengsaksophak, K.; Wilson, M.J.; Rossant, J. Retinoid signaling determines germ cell fate in mice. Science 2006, 312, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.Y.; Miao, Y.L.; Schatten, H. Towards a new understanding on the regulation of mammalian oocyte meiosis resumption. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 2741–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.G.; Su, Y.Q.; Fan, H.Y.; Schatten, H.; Sun, Q.Y. Mechanisms regulating oocyte meiotic resumption: Roles of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 2037–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herpin, A.; Schartl, M. Dmrt1 genes at the crossroads: A widespread and central class of sexual development factors in fish. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, J.C.; Fitzgibbon, Q.P.; Smith, G.; Elizur, A.; Ventura, T. Y-linked iDmrt1 paralogue (iDMY) in the Eastern spiny lobster, Sagmariasus verreauxi: The first invertebrate sex-linked Dmrt. Dev. Biol. 2017, 430, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirst, C.E.; Major, A.T.; Ayers, K.L.; Brown, R.J.; Mariette, M.; Sackton, T.B.; Smith, C.A. Sex reversal and comparative data undermine the W chromosome and support Z-linked DMRT1 as the regulator of gonadal sex differentiation in birds. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 2970–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Zhou, L.; Yao, B.; Li, C.J.; Gui, J.F. Differential and spermatogenic cell-specific expression of DMRT1 during sex reversal in protogynous hermaphroditic groupers. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007, 263, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, P.N.; Lovell-Badge, R. SRY and sex determination in mammals. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1993, 27, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilmann, C.; Capel, B. Cellular and molecular pathways regulating mammalian sex determination. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 2002, 57, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpert-De Meyts, E.; Jørgensen, N.; Græm, N.; Müller, J.; Cate, R.L.; Skakkebæk, N.E. Expression of anti-Mullerian hormone during normal and pathological gonadal development: Association with differentiation of Sertoli and granulosa cells. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 1999, 84, 3836–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Mei, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, L.; Gui, J.F. Distinct and cooperative roles of amh and dmrt1 in self-renewal and differentiation of male germ cells in zebrafish. Genetics 2017, 207, 1007–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, M. Sex determination in amphibians. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2009, 20, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Watakabe, I.; Nishimura, T.; Picard, J.-Y.; Toyoda, A.; Taniguchi, Y.; di Clemente, N.; Tanaka, M. Hyperproliferation of mitotically active germ cells due to defective anti-Müllerian hormone signaling mediates sex reversal in medaka. Development 2012, 139, 2283–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Guo, W.; Gao, Y.; Tang, R.; Li, D.P. Molecular cloning and characterization of amh and dax1 genes and their expression during sex inversion in rice-field eel Monopterus albus. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhu, H.J.; Tao, Y.F.; Xu, P.; Qiang, J. Research progress on the effect of AMH gene on sex determination in fish. Heilongjiang Anim. Hus. Vet. Med. 2022, 2, 26–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Ma, H.; Liu, X.; Shi, H.; Li, M.; Wang, D. Mutation of foxl2 or cyp19a1a results in female to male sex reversal in XX Nile tilapia. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 2634–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Mu, X.; Gui, L.; Su, M.; Li, H.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J. Characterization and gonadal expression of FOXL2 relative to Cyp19a genes in spotted scat Scatophagus argus. Gene 2015, 561, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; You, F.; Liu, M.; Wu, Z.; Wen, A.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, P. Steroid sex hormone dynamics during estradiol-17β induced gonadal differentiation in Paralichthys olivaceus (Teleostei). Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2010, 28, 254–259. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.D.M.; Castro, E.A.; Souza, C.J.H.; Paiva, S.R.; Sartori, R.; Franco, M.M.; Azevedo, H.C.; Silva, T.A.S.N.; Vieira, A.M.C.; Neves, J.P.; et al. A new polymorphism in the growth and differentiation factor 9 (GDF9) gene is associated with increased ovulation rate and prolificacy in homozygous. Anim. Genet. 2011, 42, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dranow, D.B.; Hu, K.; Bird, A.M.; Lawry, S.T.; Adams, M.T.; Sanchez, A.; Amatruda, J.F.; Draper, B.W. Bmp15 is an oocyte-produced signal required for maintenance of the adult female sexual phenotype in zebrafish. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, N.K. On the food of the air-breathing catfish, Clarias batrachus (Linn.) occurring in wild waters. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. Hydrogr. 1978, 63, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulvsbäck, M.; Lindström, C.; Weiber, H.; Abrahamsson, P.A.; Lilja, H.; Lundwall, Å. Molecular cloning of a small prostate protein, known as β-microsemenoprotein, PSP94 or β-inhibin, and demonstration of transcripts in non-genital tissues. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989, 164, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.P.; Su, Y.J.; Rao, D.Q.; Zhang, Z.W.; Xia, D.Q.; Wu, T.T. Isolation and purification of β-microseminoprotein-like proteins from the skin of the mountain salamander, Salmo salamander, and their cDNA cloning. J. Nanjing Agricult. Univ. 2007, 30, 94–99. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]

| Gene | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) Forward | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| Akr1c1 | CAATACCAACGAGTACCCAGAA | GGAGAGCAGTCATCATAAATAAGG |
| Fet1 | GGCTGAATCTCAACCGACTC | CCTGCTTGGAAACTATATGTATGC |
| Nmur1 | ACCATCGTTACTGTCCTCTACC | GTCTCCTTCTTCCTGTCTCCAA |
| Prnd | CTGGCGGTTCTCCTTCTCAT | AGTTGCTTGCGTAGTAGATGTC |
| Proto-fps | TGGTGGACAGTGGTGAAGTT | GCTCTCAATTACGGCAGATATACA |
| Rtl1 | GAATGAGAGGAAGAGGATAACGATT | TGGACATACATAGACGACAACCT |
| Msp | TCAGTGTTGGTCTAAGCGGG | AGGCGTGTGTGGACATTTTC |
| Amh | TCCGCTCAACAGTCTCTTCC | GGCAACAACTCGCACCAAT |
| Amhr II | CAGGCAGTGAACAAGAGATAGAG | AGTTCTCCTTCTGGTGTCAGG |
| AR | GTAACTATACCTCCTTCCAACACTC | ATGCTGCCACATAAGACTGATG |
| Bmp15 | GCGAGTGACTTCAGATGAGATG | CAGCACCAAGACCAGCATTC |
| Dmrt B1 | ACAGCCAGTCACCTTCTCAG | TTGGTTGCCTTGTGGATTGC |
| Dmrt1 | CTGCTGCTGCCTCCTACAT | ATCTTGACTACTCGGTGGTGAA |
| Dmrt2 | AGGCTGGAAGACATCATACACT | GCAAGGCACTGAGGTCATATC |
| Foxl2 | GGTCCACGGTCCAGTAGTTG | CCAGTACATCATCGGCAAGTTC |
| P450 | GGATGCTGTGCGATGAGTATC | TGACTGAGGAGAATGTGAACCA |
| Piwil | TGCGGTATGTGCGGTTGT | CTGATGGCGGTCTCTTCCTAT |
| HspB1 | GGCAAACACGAGGAGAAG | GGGCAGTGTGTATTTCCT |
| ZP3 | CCACGTCCCTTAATGCT | ATCTGGTGTCACCTGTAAG |
| Napb | CCACTGATCCAAACGAGATAC | TTCTTCAAAGCAGCCCTATG |
| β-actin | TGAACCCAAAAGCCAACCGAGAAAAGAT | TACGACCAGAGGCATACAGGGACAGGAC |
| Pathway | ko_id | Significant Genes | Annotated Genes | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inositol phosphate metabolism | ko00562 | 40 | 70 | 0.003642 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | ko04010 | 125 | 256 | 0.003936 |
| Mucin-type O-glycan biosynthesis | ko00512 | 19 | 29 | 0.005815 |
| Endocytosis | ko04144 | 119 | 245 | 0.006011 |
| Glycosaminoglycan degradation | ko00531 | 14 | 20 | 0.007509 |
| Phosphatidylinositol signaling system | ko04070 | 45 | 83 | 0.008032 |
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | ko04920 | 41 | 77 | 0.01627 |
| Insulin signaling pathway | ko04910 | 75 | 152 | 0.016859 |
| Osteoclast differentiation | ko04380 | 10 | 14 | 0.019613 |
| Starch and sucrose metabolism | ko00500 | 24 | 42 | 0.022051 |
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | ko04722 | 14 | 22 | 0.024577 |
| Oocyte meiosis | ko04114 | 57 | 115 | 0.030965 |
| Prolactin signaling pathway | ko04917 | 9 | 13 | 0.035474 |
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | ko04810 | 102 | 219 | 0.039699 |
| Histidine metabolism | ko00340 | 13 | 21 | 0.039838 |
| GnRH signaling pathway | ko04912 | 42 | 83 | 0.040708 |
| Type II diabetes mellitus | ko04930 | 5 | 6 | 0.04383 |
| TGF-beta signaling pathway | ko04350 | 40 | 79 | 0.044602 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H.; Huang, J.; Fang, C.; Ma, H.; Zhang, H.; Deng, J.; Jiang, W.; Kong, F.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; et al. Predicting Sex-Related Transcripts in the Chinese Giant Salamander (Andrias davidianus): A Transcriptomics Study, Selection Gender for Preservation, Breeding and Reintroduction. Fishes 2022, 7, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060399
Zhao H, Huang J, Fang C, Ma H, Zhang H, Deng J, Jiang W, Kong F, Zhang H, Liu H, et al. Predicting Sex-Related Transcripts in the Chinese Giant Salamander (Andrias davidianus): A Transcriptomics Study, Selection Gender for Preservation, Breeding and Reintroduction. Fishes. 2022; 7(6):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060399
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Hu, Jiqin Huang, Cheng Fang, Hongying Ma, Han Zhang, Jie Deng, Wei Jiang, Fei Kong, Hongxing Zhang, Hong Liu, and et al. 2022. "Predicting Sex-Related Transcripts in the Chinese Giant Salamander (Andrias davidianus): A Transcriptomics Study, Selection Gender for Preservation, Breeding and Reintroduction" Fishes 7, no. 6: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060399
APA StyleZhao, H., Huang, J., Fang, C., Ma, H., Zhang, H., Deng, J., Jiang, W., Kong, F., Zhang, H., Liu, H., & Wang, Q. (2022). Predicting Sex-Related Transcripts in the Chinese Giant Salamander (Andrias davidianus): A Transcriptomics Study, Selection Gender for Preservation, Breeding and Reintroduction. Fishes, 7(6), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060399






