An Assessment of Seasonal Differences in Fish Populations in Laizhou Bay Using Environmental DNA and Conventional Resource Survey Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Sites
2.2. Sampling
2.2.1. eDNA Sampling
2.2.2. Conventional Sampling Techniques
2.3. eDNA Analysis Methods
2.3.1. eDNA Extraction, Library Construction, and Sequencing
2.3.2. Pre-Processing and Information Quality Control
2.3.3. Identification of Fish Species
2.3.4. Structure Division in the Community
2.3.5. Seasonal Variation of Fish
2.4. Conventional Analysis Method
3. Results
3.1. Fish Species
3.1.1. eDNA Outcomes
3.1.2. Conventional Resource Survey Outcomes
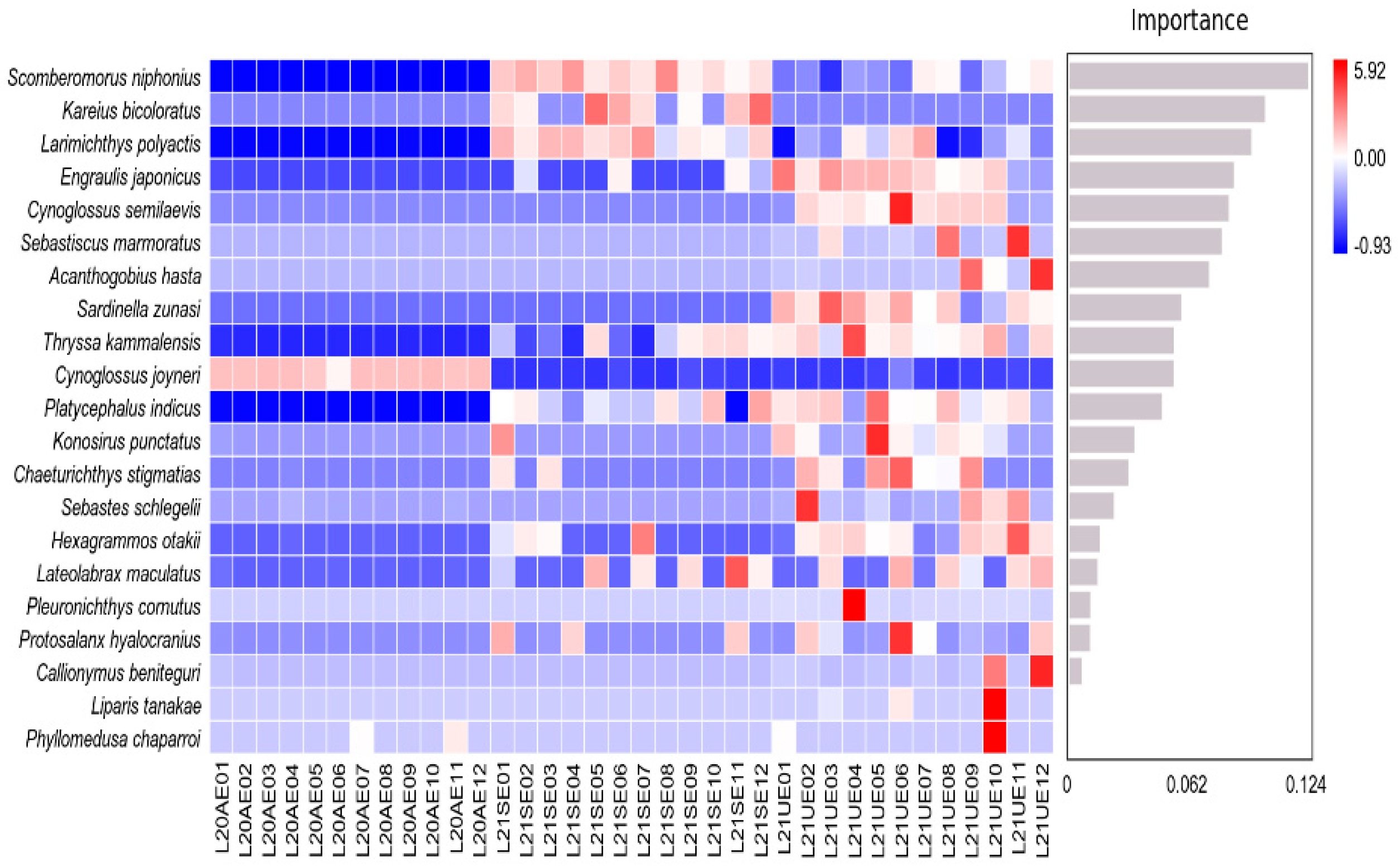
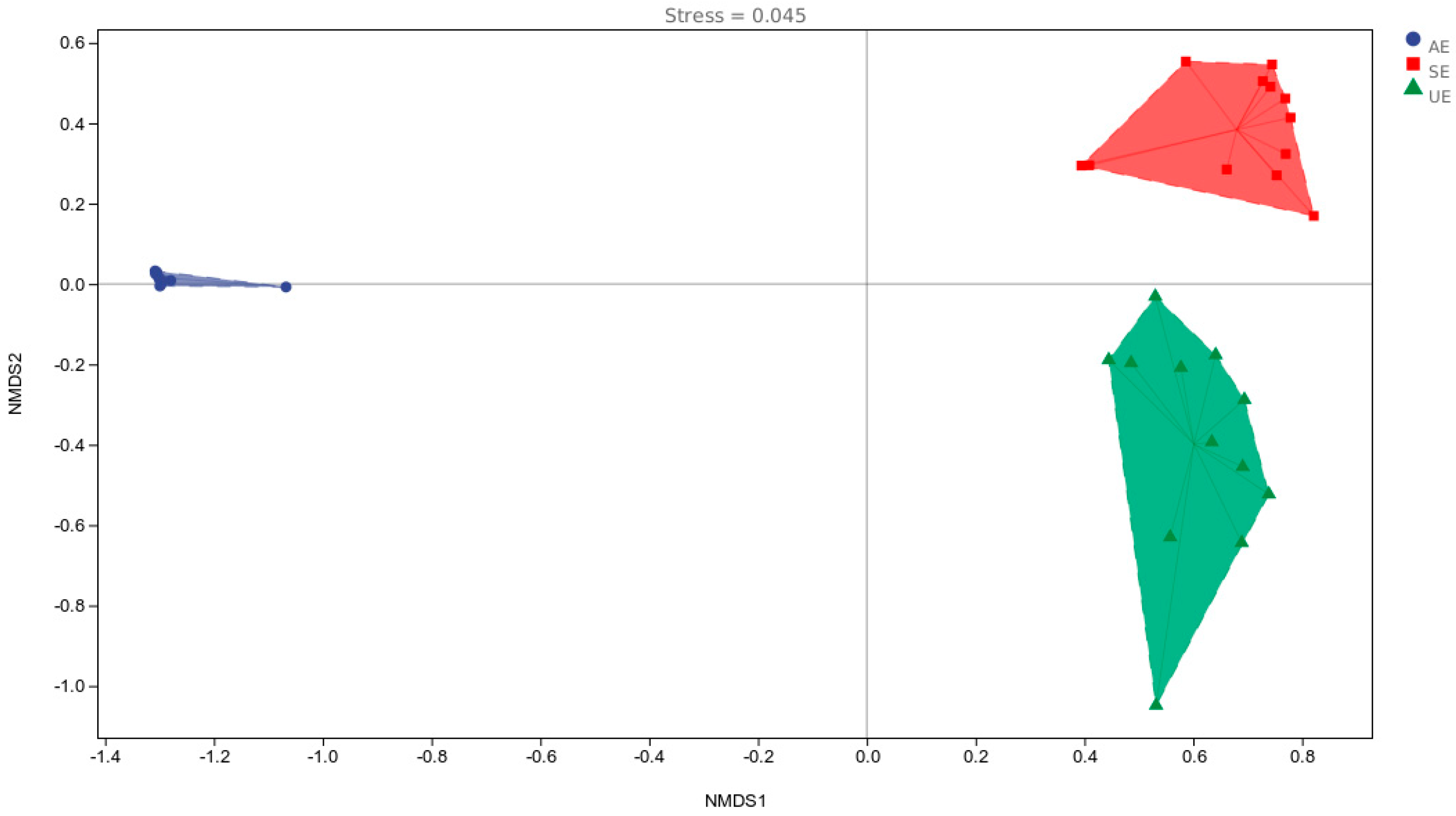
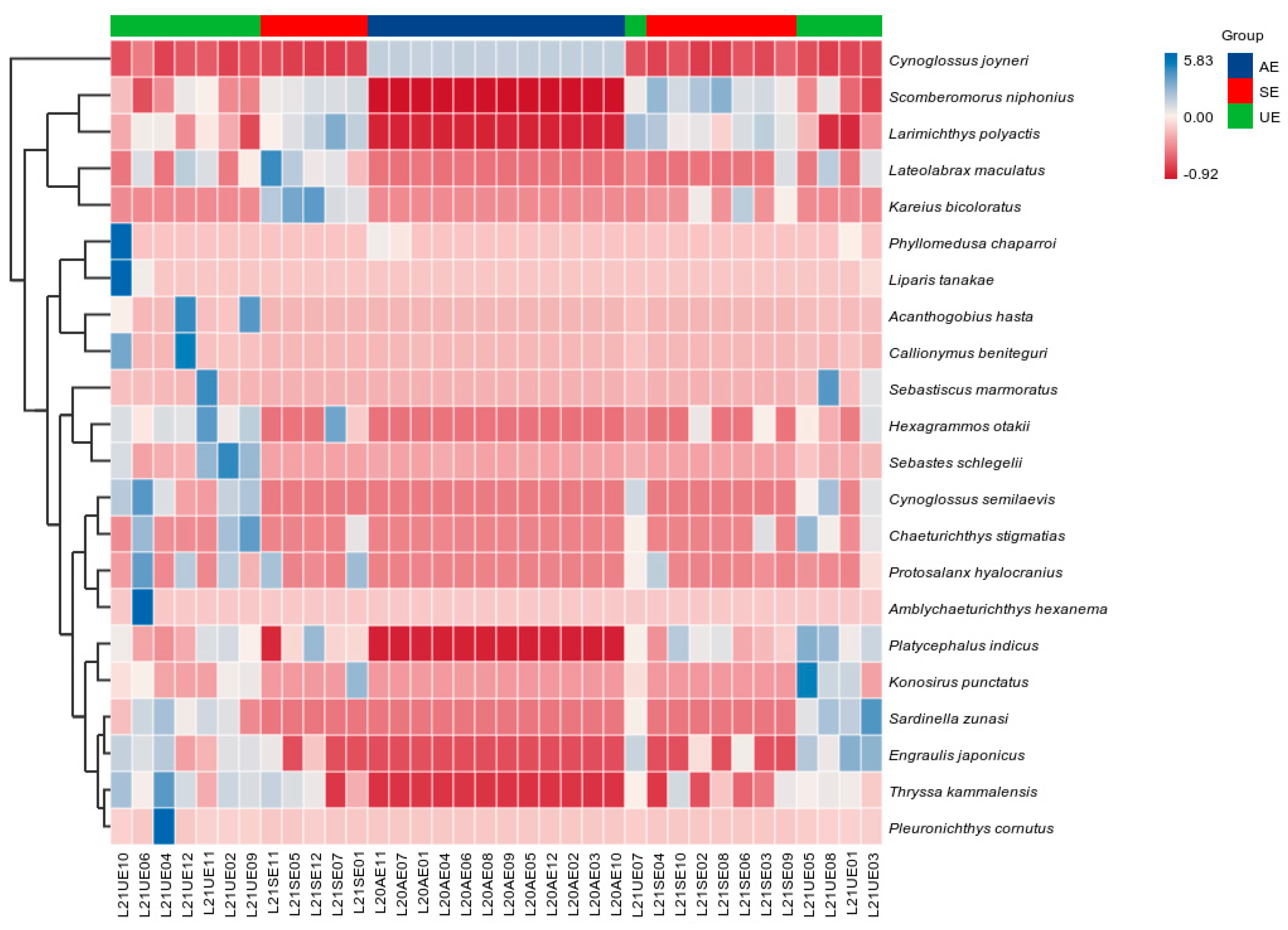
3.2. Fish Community Diversity
3.3. Seasonal Variation
4. Discussion
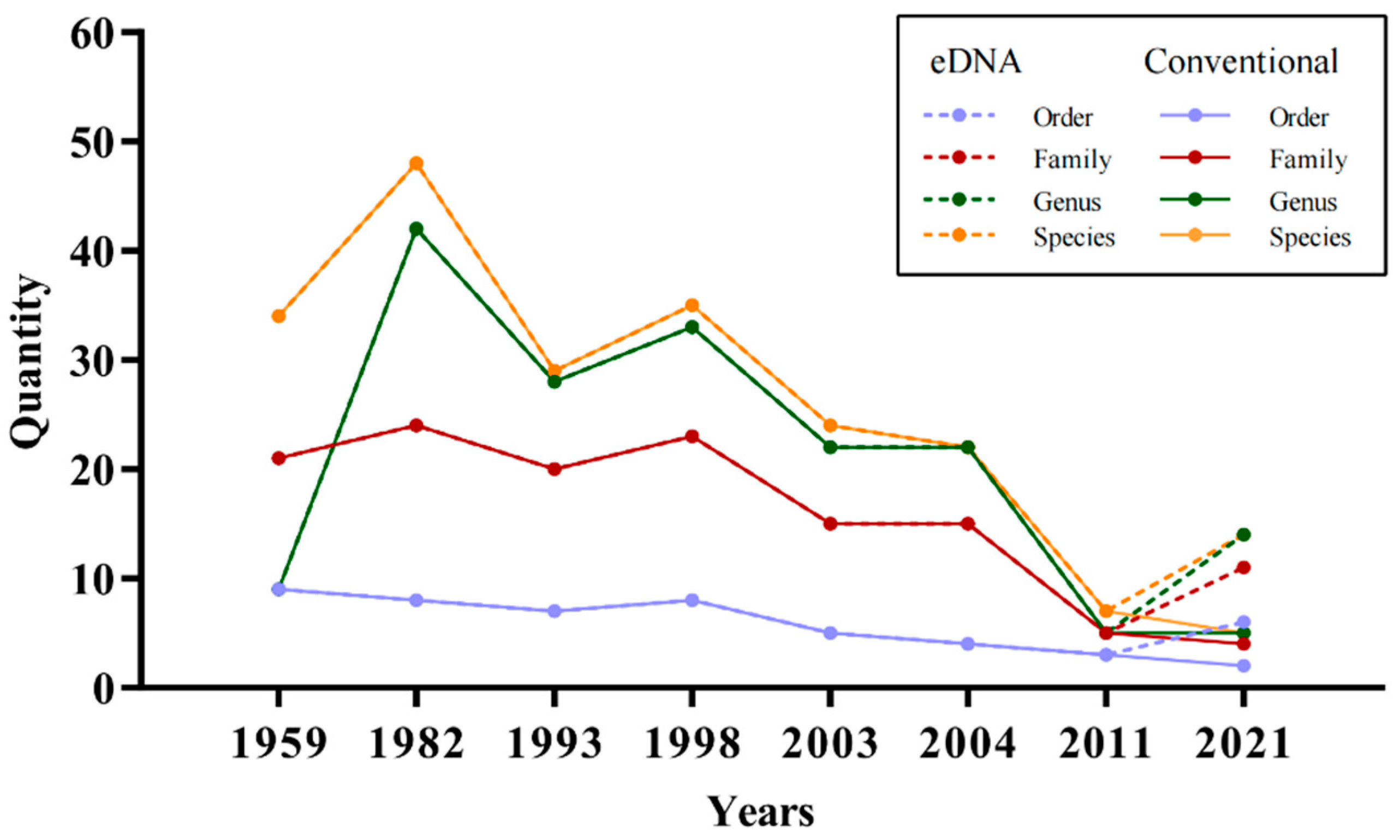
4.1. Fish Diversity and Annual Variation in Laizhou Bay
| Year | Species Number | Technique |
|---|---|---|
| 1959 [41] | Trichiurus lepturus, Larimichthys polyactis, Cynoglossus semilaevis, Pennahia argentata | Conventional investigation technique |
| 1982 [46] | Setipinna tenuifilis, Engraulis japonicus, Nibeaalbiflora, Larimichthys polyactis, Lateolabraxjaponicus; | Conventional investigation technique |
| 1993 [47] | Engraulis japonicus, Thryssa kammalensis, Setipinna tenuifilis, Konosirus punctatus | Conventional investigation technique |
| 1998 [48] | Thryssa kammalensis, Eneraulisiaponicus, Setipinna tenuifilis, Konosirus punctatus: | Conventional investigation technique |
| 2003 [49] | Thryssa kammalensis, Setipinna tenuifilis, Larimichthys polyactis, Pampus argenteus | Conventional investigation technique |
| 2004 [49] | Setipinna tenuifilis, Liparis tanakae, Enedriasfangi, Thryssa kammalensis | Conventional investigation technique |
| 2011 [50] | Symechogobius hasta, callionymus beniteguri, Cynoglossus joyneri, Chaeturichthys stigmatias, Enedriasfangi | Conventional investigation technique |
| 2021 | Scomberomorus niphonius, Larimichthys polyactis, Platycephalus indicus, Thryssa kammalensis, Kareius bicoloratus, Cynoglossus joyneri, Lateolabrax maculatus, Hexagrammos otakii, Engraulis japonicus | eDNA (outcome of this research) |
| 2021 | Sebastes schlegelii, Hexagrammos otakii, Acanthogobiushasta and Ctenogobiusgiurinus | Conventional investigation technique (outcome of this research) |
4.2. Seasonal Variation of Fish in Laizhou Bay
4.3. eDNA vs. Conventional Resource Survey Methodologies
4.4. eDNA as a Revolutionary Method for Analyzing Fish Divergence
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, X.; Shan, X.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Cui, Y.; Zuo, T. Long-Term Changes in the Fishery Ecosystem Structure of Laizhou Bay, China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, F.; Zheng, X.; Ai, J.; Hu, X.; Huang, G.; Zhang, H. GIS-Based Health Assessment of the Marine Ecosystem in Laizhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 125, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Han, M.; Hui, H.; Li, Y. Effects of Human Activities in the Coastal Zone of Laizhou Bay. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2021, 28, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón-Díaz, M.P.; Bovcon, N.D.; Cochia, P.D.; Góngora, M.E.; Galván, D.E. Fish Functional Diversity as an Indicator of Resilience to Industrial Fishing in Patagonia Argentina. J. Fish Biol. 2021, 99, 1650–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänfling, B.; Handley, L.L.; Read, D.S.; Hahn, C.; Li, J.; Nichols, P.; Blackman, R.C.; Oliver, A.; Winfield, I.J. Environmental DNA Metabarcoding of Lake Fish Communities Reflects Long-Term Data from Established Survey Methods. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 3101–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberlet, P.; Coissac, E.; Hajibabaei, M.; Rieseberg, L.H. Environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1789–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogram, A.; Sayler, G.S.; Barkay, T. The Extraction and Purification of Microbial DNA from Sediments. J. Microbiol. Methods 1987, 7, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Fuhrman, J.A. DNA Hybridization to Compare Species Compositions of Natural Bacterioplankton Assemblages. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Miaud, C.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P. Species Detection Using Environmental DNA from Water Samples. Biol. Lett. 2008, 4, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamoto, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Takahara, T.; Honjo, M.N.; Kawabata, Z. Surveillance of Fish Species Composition Using Environmental DNA. Limnology 2011, 13, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, N.T.; Shirey, P.D.; Wieringa, J.G.; Mahon, A.R.; Lamberti, G.A. Comparative Cost and Effort of Fish Distribution Detection via Environmental DNA Analysis and Electrofishing. Fisheries 2017, 42, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigsgaard, E.E.; Carl, H.; Møller, P.R.; Thomsen, P.F. Monitoring the Near-Extinct European Weather Loach in Denmark Based on Environmental DNA from Water Samples. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigsgaard, E.E.; Nielsen, I.B.; Carl, H.; Krag, M.A.; Knudsen, S.W.; Xing, Y.; Holm-Hansen, T.H.; Møller, P.R.; Thomsen, P.F. Seawater Environmental DNA Reflects Seasonality of a Coastal Fish Community. Mar. Biol. 2017, 164, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stat, M.; John, J.; DiBattista, J.D.; Newman, S.J.; Bunce, M.; Harvey, E.S. Combined Use of EDNA Metabarcoding and Video Surveillance for the Assessment of Fish Biodiversity. Conserv. Biol. 2018, 33, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClenaghan, B.; Fahner, N.; Cote, D.; Chawarski, J.; McCarthy, A.; Rajabi, H.; Singer, G.; Hajibabaei, M. Harnessing the Power of EDNA Metabarcoding for the Detection of Deep-Sea Fishes. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, C.; Jia, H.; Guo, S.; Hou, G.; Xian, W.; Zhang, H. Biodiversity Exploration in Autumn Using Environmental DNA in the South China Sea. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yoshizawa, S.; Iwasaki, W.; Xian, W. Seasonal Fish Assemblage Structure Using Environmental DNA in the Yangtze Estuary and Its Adjacent Waters. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Han, M.; Han, G.; Wang, M.; Tian, L.; Zhu, J.; Kong, X. Reclamation-Oriented Spatiotemporal Evolution of Coastal Wetland along Bohai Rim, China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2022, 41, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miya, M.; Sato, Y.; Fukunaga, T.; Sado, T.; Poulsen, J.Y.; Sato, K.; Minamoto, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Araki, H.; et al. MiFish, a Set of Universal PCR Primers for Metabarcoding Environmental DNA from Fishes: Detection of More than 230 Subtropical Marine Species. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 150088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boivin-Delisle, D.; Laporte, M.; Burton, F.; Dion, R.; Normandeau, E.; Bernatchez, L. Using Environmental DNA for Biomonitoring of Freshwater Fish Communities: Comparison with Established Gillnet Surveys in a Boreal Hydroelectric Impoundment. Environ. DNA 2020, 3, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Yoshizawa, S.; Iwasaki, W.; Li, Y.; Xian, W.; Zhang, H. Seasonal Variation and Assessment of Fish Resources in the Yangtze Estuary Based on Environmental DNA. Water 2020, 12, 2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-Filtering Vastly Improves Diversity Estimates from Illumina Amplicon Sequencing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Fu, Z.; Zhao, C.L.; Liu, H.J.; Li, C.S. Fishes of Bo Hai; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker, R.H. Evolution and Measurement of Species Diversity. Taxon 1972, 21, 213–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, R.H. Vegetation of the Siskiyou Mountains, Oregon and California. Ecol. Monogr. 1960, 30, 279–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A. Nonparametric Estimation of the Number of Classes in a Population. Scand. J. Stat. 1984, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of Diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faith, D.P. Conservation Evaluation and Phylogenetic Diversity. Biol. Conserv. 1992, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielou, E.C. The Measurement of Diversity in Different Types of Biological Collections. J. Theor. Biol. 1966, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, I.J. The Population Frequencies of Species and the Estimation of Population Parameters. Biometrika 1953, 40, 237–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Interpretation of Ecological Structures. In Numerical Ecology; Developments in Environmental Modelling; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 24, pp. 521–624. ISBN 978-0-444-53868-0. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An Ordination of the Upland Forest Communities of Southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, K.L.; van Belle, G.; Simberloff, D. Explicit Calculation of the Rarefaction Diversity Measurement and the Determination of Sufficient Sample Size. Ecology 1975, 56, 1459–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, P.F.; Aller, J.Y. Bacterial Diversity in Aquatic and Other Environments: What 16S RDNA Libraries Can Tell Us. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 47, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.C.; Sun, B.L.; Yang, J.M. Analysis of the fish fauna of the Bohai Sea. Stud. Mar. Sin. 1993, 34, 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Jin, X. Dynamic Characteristics of Abundance and Community Structure of Fishery Species in the Overwintering Ground of the Bohai Sea. J. Nat. Resour. 2001, 16, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Pinkas, L.; Oliphant, M.S.; Iverson, I.L.K. Food Habits of Albacore, Bluefin Tuna, and Bonito in California Waters. Available online: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/7t5868rd (accessed on 16 September 2022).
- Liao, H.; Pierce, C.L.; Larscheid, J.G. Empirical Assessment of Indices of Prey Importance in the Diets of Predacious Fish. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2001, 130, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.-S.; Deng, J.-Y. Variations in Community Structure of Fishery Resources and Biodiversity in the Laizhou Bay, Shandong. Biodivers. Sci. 2000, 08, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, G.; Zhao, L.; Du, X.; Gao, T. Assessment of Fishery Resources Using Environmental DNA: The Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) in the East China Sea. Fish. Res. 2021, 235, 105813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, R.A.; Kerr, S.R.; Taylor, W.W.; Larkin, P.A. Community Consequences of Fish Stock Diversity. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1981, 38, 1856–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.F.; Song, C.; Sun, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, S.G. Spatiotemporal Distribution, Source Apportionment and Combined Pollution of Antibiotics in Natural Waters Adjacent to Mariculture Areas in the Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Han, H.; Li, X.; Song, D.; Shi, W.; Zhang, S.; Lv, X. Inversion of the Degradation Coefficient of Petroleum Hydrocarbon Pollutants in Laizhou Bay. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Tang, Q. The structure, distribution and variation of the fishery resources in the Bohai Sea. J. Fish. Sci. China 1998, 5, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X. The dynamics of major fishery resources in the Bohai Sea. J. Fish. Sci. China 2000, 7, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.Y.; Jin, X.S. Study on Fishery Biodiversity and Its Conservation in Laizhou Bay and Yellow River Estuary. Zool. Res. 2000, 21, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Niu, M.; Dai, F. The characteristics of structure and distribution of spawning stock of fishery species in the Bohai Sea. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2008, 4, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Yuan, W.; Dan, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Evaluation on Biological Integrity of Fish in Laizhou Bay. J. Hydroecology 2021, 42, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.S.; Qiu, S.Y.; Li, P.J.; Cui, Y. Ecological Environment and Biotic Community in the Coastal Waters of the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea; China Ocean University Press: Qingdao, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Meng, T.; Ren, S.; Qiu, X.; Zhu, J. Species Composition and Quantity Distribution of Fishes in the Bohai Sea. Mar. Fish. Res. 1988, 9, 11–89. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.L.; Chen, J.J. Analysis on Migratory Routine of Larimichthy polyactis. J. Fish. Sci. China 2009, 16, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, P.; Chícharo, M.A.; Chícharo, L. Changes in a Temperate Estuary during the Filling of the Biggest European Dam. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2245–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.T.; Mendoza, R.L.; Covarrubias, L.T.; Hernandez, M.C. Ichthyofauna Catch Composition in a Small-Scale Fishery from Isabel Island (Southeastern Gulf of California). Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2016, 44, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Huang, L.; Xu, Q.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Feng, W. Analysis and comparison of catch performance of cage net with different mesh sizes in Laizhou Bay in spring. Fish. Mod. 2021, 48, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wineland, S.M.; Welch, S.M.; Pauley, T.K.; Apodaca, J.J.; Olszack, M.; Mosher, J.J.; Holmes, J.N.; Waldron, J.L. Using Environmental DNA and Occupancy Modelling to Identify Drivers of Eastern Hellbender (Cryptobranchus alleganiensis alleganiensis) Extirpation. Freshw. Biol. 2019, 64, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.A.; Turner, C.R. The Ecology of Environmental DNA and Implications for Conservation Genetics. Conserv. Genet. 2015, 17, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bálint, M.; Pfenninger, M.; Grossart, H.-P.; Taberlet, P.; Vellend, M.; Leibold, M.A.; Englund, G.; Bowler, D. Environmental DNA Time Series in Ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2018, 33, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.J.; Cheng, J.H.; Shen, W.; Liu, Z.L. Feeding Ecology of Lophius Litulon in the South of Yellow Sea. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 3117–3125. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, K.; Chen, J.; Ruan, H.; Li, Z.; Guo, W.; Li, M.; Liu, L. EDNA Metabarcoding as a Promising Conservation Tool for Monitoring Fish Diversity in a Coastal Wetland of the Pearl River Estuary Compared to Bottom Trawling. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.; Clarke, P.M.; O’Connor, R.V. A Mechanism to Explore Proactive Knowledge Retention in Open Source Software Communities. J. Softw. Evol. Process 2019, 32, e2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, N.T.; Olds, B.P.; Renshaw, M.A.; Turner, C.R.; Li, Y.; Jerde, C.L.; Mahon, A.R.; Pfrender, M.E.; Lamberti, G.A.; Lodge, D.M. Quantification of Mesocosm Fish and Amphibian Species Diversity via Environmental DNA Metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, S.; Baillie, C.; Colosimo, G.; Riesgo, A. Sponges as Natural Environmental DNA Samplers. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, R401–R402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sub-Area | Station | Longitude | Latitude |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area for the integration of wind power in pastures | 1 | 119°39.850 | 37°14.963 |
| 2 | 119°41.092 | 37°15.071 | |
| 3 | 119°42.169 | 37°15.031 | |
| Reef area | 4 | 119°41.050 | 37°16.623 |
| 5 | 119°40.853 | 37°18.382 | |
| 6 | 119°40.154 | 37°20.442 | |
| Surrounding reef area | 7 | 119°42.300 | 37°18.300 |
| 8 | 119°37.889 | 37°20.683 | |
| 9 | 119°42.441 | 37°20.974 | |
| Control area | 10 | 119°34.897 | 37°16.623 |
| 11 | 119°34.398 | 37°18.224 | |
| 12 | 119°34.103 | 37°20.153 |
| Species | Common Name | Autumn | Spring | Summer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acanthogobius hasta | Asian fresh water goby | + | ||
| Acanthopagrus schlegelii | + | |||
| Amblychaeturichthys hexanema | Blackhead Seabream | + | ||
| callionymus beniteguri | Pinkgray goby | + | + | |
| Chaeturichthys stigmatias | + | + | + | |
| Coilia mystus | + | + | ||
| Collichthys lucidus | Tapertail anchovy | + | ||
| Cryptocentrus filifer | + | + | ||
| Ctenotrypauchen chinensis Steindachner | light maigre | + | ||
| Cynoglossus joyneri | + | |||
| Cynoglossus robustus | + | |||
| Cynoglossus semilaevis | + | + | ||
| Enedriasfangi | robust tonguefish | + | ||
| Engraulis japonicus | + | + | + | |
| Harpadon nehereus | Tongue Sole | + | + | + |
| Hexagrammos otakii | Fang’s gunnel | + | ||
| Ilisha elongata | + | + | ||
| Jaydia lineata | Japanese anchovy | + | + | + |
| Johnius belangerii | + | |||
| Johnius grypotus | Bombay duck | + | ||
| Kareius bicoloratus | The Otaki six-liner | + | + | + |
| Konosirus punctatus | Ilisha elongata | + | + | |
| Larimichthys crocea | Verticalstriped Cardinalfish | + | + | + |
| Larimichthys polyactis | + | + | ||
| Lateolabrax japonicus | Belanger’s croaker | + | ||
| Lateolabrax maculatus | + | + | + | |
| Liparis tanakae | + | |||
| Miichthys miiuy | Stone flounder | + | + | |
| Mugil cephalus | + | + | ||
| Muraenesox bagio | Dotted Gizzard Shad | + | ||
| Muraenesox cinereus | + | |||
| Pennahia argentata | Large yellow croaker | + | + | |
| Platycephalus indicus | + | + | + | |
| Pleuronichthys cornutus | Little Yellow Croaker | + | + | |
| Protosalanx hyalocranius | + | + | + | |
| Rhinogobius similis | Japaneseseaperch | + | ||
| Sardinella zunasi | Spotted Seabass | + | + | + |
| Scomber japonicus | + | + | ||
| Scomberomorus niphonius | + | + | + | |
| Sebastes schlegelii | Brown Croaker | + | + | |
| Sebastiscus marmoratus | + | + | ||
| Setipinna taty | Sea Mullet | + | + | |
| Strongylura anastomella | + | |||
| Synechogobius hasta | Common pike conger | + | + | |
| Terapon jarbua | + | |||
| Thryssa kammalensis | daggertooth pike conger | + | + | |
| Zoarces gillii | + |
| Season | Dominant Species |
|---|---|
| Autumn 2020 | Cynoglossus joyneri |
| Spring 2021 | Scomberomorus niphonius, Ctenogobius giurinus, Larimichthys polyactis, Platycephalus indicus, Thryssa kammalensis, Kareius bicoloratus, Cynoglossus joyneri, Lateolabrax maculatus, Hexagrammos otakii, and Engraulis japonicus |
| Summer 2021 | Sardinella zunasi, Scomberomorus niphonius, Thryssa kammalensis, Engraulis japonicus, Platycephalus indicus, Larimichthys polyactis, Cynoglossus semilaevis, Hexagrammos otakii, Cynoglossus joyneri, Chaeturichthys stigmatias, Lateolabrax maculatus, Protosalanx hyalocranius, Konosirus punctatus, and Acanthogobius hasta |
| Species | Autumn 2020 | Number | Spring 2021 | Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sebastes schlegelii | + | 53 | + | 3 |
| Lateolabrax japonicus | + | 10 | ||
| Hexagrammos otakii | + | 3 | + | 6 |
| Synechogobius ommaturus | + | 16 | ||
| Chaemrichthys stigmatias Richardson | + | 1 | + | 20 |
| Sebastiscus marmoratus | + | 1 | ||
| Ctenogobiusgiurinus | + | 11 | ||
| EnedrasfangiWangetWang | + | 3 | ||
| Cynoglossus semilaevis | + | 23 | ||
| Pleuronichthys cornutus | + | 6 | ||
| Platichthys bicoloratus | + | 3 |
| Season | Species | W/% | N/% | IRI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autumn 2020 | Sebastes schlegelii | 78 | 45.7 | 5715 |
| Lateolabrax japonicus | 5.4 | 8.6 | 322 | |
| Hexagrammos otakii | 0.8 | 2.6 | 78 | |
| Synechogobius ommaturus | 6.7 | 13.8 | 1261 | |
| Acanthogobiushasta | 0.04 | 0.86 | 7 | |
| Sebastiscus marmoratus | 0.04 | 0.86 | 7 | |
| Cynoglossus semilaevis | 6 | 19.8 | 459 | |
| Pleuronichthys cornutus | 1.8 | 5.2 | 108 | |
| Platichthys bicoloratus | 1.1 | 2.6 | 57 | |
| Spring 2021 | Sebastes schlegelii | 53 | 7 | 3426 |
| Hexagrammos otakii | 30 | 14 | 2512 | |
| Acanthogobiushasta | 8.4 | 46.5 | 1175 | |
| Ctenogobiusgiurinus | 8 | 25.6 | 1441 | |
| Enedrasfangi | 0.54 | 7 | 108 |
| Technique | Number of Species | Dominant Species in Autumn 2020 | Dominant Species in Spring 2021 |
|---|---|---|---|
| eDNA | 47 | Cynoglossus joyneri | Scomberomorus niphonius, Ctenogobius giurinus, Larimichthys polyactis, Platycephalus indicus, Thryssa kammalensis, Kareius bicoloratus, Cynoglossus joyneri, Lateolabrax maculatus, Hexagrammos otakii, and Engraulis japonicus |
| Conventional investigation technique | 11 | Sebastes schlegelii and Synechogobius ommaturus | Sebastes schlegelii, Hexagrammos otakii, Acanthogobius hasta, and Ctenogobius giurinus |
| 10 | / | Sebastes schlegelii, Hexagrammos otakii |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, S.; Bai, M.; Jia, H.; Xian, W.; Zhang, H. An Assessment of Seasonal Differences in Fish Populations in Laizhou Bay Using Environmental DNA and Conventional Resource Survey Techniques. Fishes 2022, 7, 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050250
Dai S, Bai M, Jia H, Xian W, Zhang H. An Assessment of Seasonal Differences in Fish Populations in Laizhou Bay Using Environmental DNA and Conventional Resource Survey Techniques. Fishes. 2022; 7(5):250. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050250
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Shuqin, Maojuan Bai, Hui Jia, Weiwei Xian, and Hui Zhang. 2022. "An Assessment of Seasonal Differences in Fish Populations in Laizhou Bay Using Environmental DNA and Conventional Resource Survey Techniques" Fishes 7, no. 5: 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050250
APA StyleDai, S., Bai, M., Jia, H., Xian, W., & Zhang, H. (2022). An Assessment of Seasonal Differences in Fish Populations in Laizhou Bay Using Environmental DNA and Conventional Resource Survey Techniques. Fishes, 7(5), 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050250







