Underwater Soundscape Monitoring and Fish Bioacoustics: A Review
Abstract
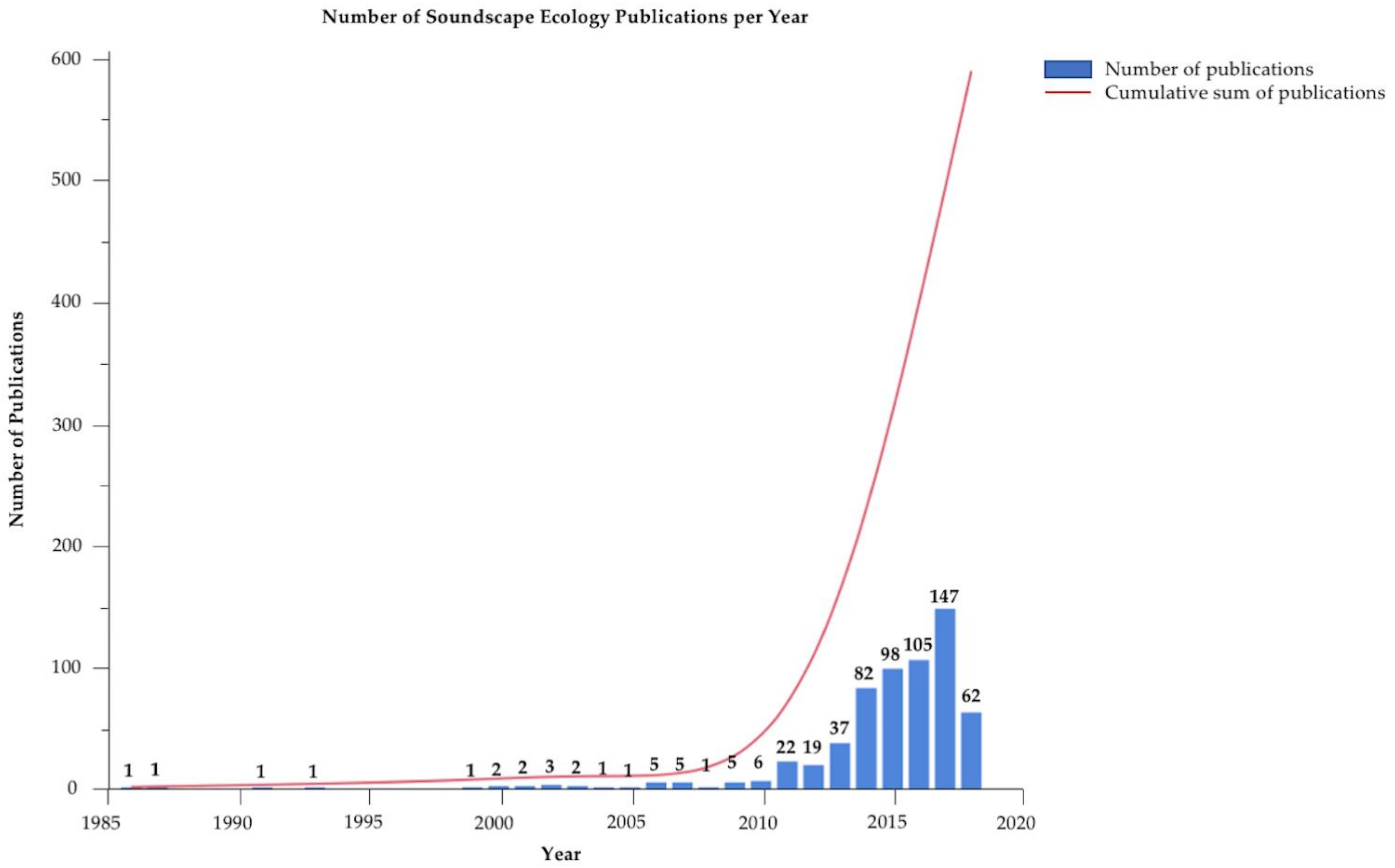
:1. Introduction
2. Fish Acoustic Monitoring
3. Ambient Sound
4. Long-Term Passive Acoustic Monitoring Methods
5. Data Analysis
5.1. Acoustic Parameters and Measurements
5.2. Acoustic Indices
5.3. Acoustic Statistical Software
6. Contrasting Soundscapes
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pijanowski, B.C.; Villanueva-Rivera, L.J.; Dumyahn, S.L.; Farina, A.; Krause, B.L.; Napoletano, B.M.; Gage, S.H.; Pieretti, N. Soundscape ecology: The science of sound in the landscape. BioScience 2011, 61, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, R.M. The Tuning of the World; Alfred A. Knopf: New York, NY, USA, 1977; ISBN 0-394-40966-3. [Google Scholar]
- Staaterman, E.; Rice, A.N.; Mann, D.A.; Paris, C.B. Soundscapes from a tropical Eastern Pacific reef and a Caribbean Sea reef. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobel, P.S. The “choral reef”: The ecology of underwater sounds. In Proceedings of the 2013 AAUS/ESDP Curaçao Joint International Scientific Diving Symposium, Dauphin Island, AL, USA, 24–27 October 2013; pp. 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Jolivet, A.; Tremblay, R.; Olivier, F.; Gervaise, C.; Sonier, R.; Genard, B.; Chauvaud, L. Validation of trophic and anthropic underwater noise as settlement trigger in blue mussels. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lillis, A.; Bohnenstiehl, D.; Peters, J.W.; Eggleston, D. Variation in habitat soundscape characteristics influences settlement of a reef-building coral. PeerJ 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lillis, A.; Eggleston, D.B.; Bohnenstiehl, D.R. Oyster larvae settle in response to habitat-associated underwater sounds. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 79337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillis, A.; Eggleston, D.B.; Bohnenstiehl, D.R. Soundscape variation from a larval perspective: The case for habitat-associated sound as a settlement cue for weakly swimming estuarine larvae. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 509, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobel, P.S. Scuba bubble noise and fish behavior: A rationale for silent diving technology. In Proceedings of the American Academy of Underwater Sciences; University of Connecticut: Storrs, CT, USA, 2005; pp. 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Lobel, P.S. Underwater acoustic ecology: Boat noises and fish behavior. In Proceedings of the American Academy of Underwater Sciences 28th Symposium, Atlanta, GA, USA, 13–14 March 2009; Pollock, N.W., Ed.; AAUS: Dauphin Island, AL, USA, 2009; pp. 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeij, M.J.A.; Marhaver, K.L.; Huijbers, C.M.; Nagelkerken, I.; Simpson, S.D. Coral larvae move toward reef sounds. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, 10660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fish, M.P.; Mowbray, W.H. Sounds of Western North Atlantic Fishes. A Reference File of Biological Underwater Sounds; Rhode Island Univ Kingston Narragansett Marine Lab: Kingston, RI, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Myrberg, A.; Spanier, E.; Ha, S.J. Temporal patterning in acoustical communication. In Contrasts in Behavior; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 137–179. [Google Scholar]
- Tavolga, W.N.; Lanyon, W.E. Animal Sounds and Communication; American Institute of Biological Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Winn, H. The biological significance of fish sounds. Mar. Bio-Acoust. 1964, 2, 213–231. [Google Scholar]
- Fine, M.L.; Winn, H.; Olla, B.L. Communication in fishes. In How Animals Communicate; Sebeok, T.A., Ed.; Indiana University Press: Bloomington, IN, USA, 1977; pp. 472–518. [Google Scholar]
- Au, W.W.L.; Richlen, M.; Lammers, M.O. Soundscape of a nearshore coral reef near an urban center. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 730, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertucci, F.; Parmentier, E.; Berten, L.; Brooker, R.M.; Lecchini, D. Temporal and spatial comparisons of underwater sound signatures of different reef habitats in Moorea Island, French Polynesia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 135733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, J.; Stanley, J.A.; Butler, M.J. Underwater soundscapes in near-shore tropical habitats and the effects of environmental degradation and habitat restoration. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2016, 479, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammers, M.O.; Brainard, R.E.; Au, W.W.L.; Mooney, T.A.; Wong, K.B. An ecological acoustic recorder (EAR) for long-term monitoring of biological and anthropogenic sounds on coral reefs and other marine habitats. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, T.; Connell, S.D.; Nagelkerken, I. The sounds of silence: Regime shifts impoverish marine soundscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staaterman, E.; Ogburn, M.B.; Altieri, A.H.; Brandl, S.J.; Whippo, R.; Seemann, J.; Goodison, M.; Duffy, J.E. Bioacoustic measurements complement visual biodiversity surveys: Preliminary evidence from four shallow marine habitats. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 575, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueur, J.; Pavoine, S.; Hamerlynck, O.; Duvail, S. Rapid acoustic survey for biodiversity appraisal. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, 4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobel, P.S. Fish bioacoustics and behavior: Passive acoustic detection and the application of a closed-circuit rebreather for field study. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 2001, 35, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobel, P.S. Sounds produced by spawning fishes. Environ. Biol. Fish. 1992, 33, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobel, P.S.; Mann, D.A. Spawning sounds of the damselfish, Dascyllus albisella (Pomacentridae), and relationship to male size. Bioacoustics 1995, 6, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, D.A.; Lobel, P.S. Passive acoustic detection of sounds produced by the Damselfish, Dascyllus albisella (Pomacentridae). Bioacoustics 1995, 6, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rountree, R.A.; Gilmore, R.G.; Goudey, C.A.; Hawkins, A.D.; Luczkovich, J.J.; Mann, D.A. Listening to fish: Applications of passive acoustics to fisheries science. Fisheries 2006, 31, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luczkovich, J.J.; Pullinger, R.C.; Johnson, S.E.; Sprague, M.W. Identifying sciaenid critical spawning habitats by the use of passive acoustics. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2008, 137, 576–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowell, T.J.; Demer, D.A.; Aburto-Oropeza, O.; Cota-Nieto, J.J.; Hyde, J.R.; Erisman, B.E. Estimating fish abundance at spawning aggregations from courtship sound levels. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lobel, P.S.; Rice, A.N.; Kaatz, I.M. Acoustic behavior of coral reef fishes. In Reproduction and Sexuality in Marine Fishes: Patterns and Processes; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 307–347. ISBN 978-0-520-26433-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bass, A.H.; McKibben, J.R. Neural mechanisms and behaviors for acoustic communication in teleost fish. Prog. Neurobiol. 2003, 69, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.N.; Kerridge, E.; Simpson, S.D. Acoustic communication in a noisy world: Can fish compete with anthropogenic noise? Behav. Ecol. 2014, 25, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, M.L.; Parmentier, E. Mechanisms of fish sound production. In Sound Communication in Fishes; Ladich, F., Ed.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; Vienna, Austria, 2015; Volume 4, pp. 77–126. ISBN 978-3-7091-1845-0. [Google Scholar]
- Lobel, P.S.; Lobel, L.K. Stalking spawning fishes. In Proceedings of the 2013 AAUS/ESDP Curaçao Joint International Scientific Diving Symposium, Dauphin Island, AL, USA, 24–27 October 2013; pp. 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Felisberto, P.; Rodríguez, O.; Santos, P.; Zabel, F.; Jesus, S.M. Using passive acoustics for monitoring seagrass beds. In Proceedings of the Oceans 2016 MTS/IEEE Monterey, Monterey, CA, USA, 19–23 September 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, C.A.; Jeffs, A.G.; Tindle, C.T.; Montgomery, J.C.; Montgomery, J.C. Temporal patterns in ambient noise of biological origin from a shallow water temperate reef. Oecologia 2008, 156, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staaterman, E.; Paris, C.B.; DeFerrari, H.A.; Mann, D.A.; Rice, A.N.; D’Alessandro, E.K. Celestial patterns in marine soundscapes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 508, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locascio, J.V.; Mann, D.A. Diel periodicity of fish sound production in Charlotte Harbor, Florida. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2008, 137, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenz, G.M. Acoustic Ambient Noise in the Ocean: Spectra and Sources. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1962, 34, 1936–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University of Rhode Island What Are Common Underwater Sounds? Available online: https://dosits.org/science/sounds-in-the-sea/what-are-common-underwater-sounds/ (accessed on 1 September 2018).
- Pieretti, N.; Farina, A.; Morri, D. A new methodology to infer the singing activity of an avian community: The Acoustic Complexity Index (ACI). Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieretti, N.; Lo Martire, M.; Farina, A.; Danovaro, R. Marine soundscape as an additional biodiversity monitoring tool: A case study from the Adriatic Sea (Mediterranean Sea). Ecol. Indic. 2017, 83, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piercy, J.J.B.; Codling, E.A.; Hill, A.J.; Smith, D.J.; Simpson, S.D. Habitat quality affects sound production and likely distance of detection on coral reefs. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 516, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parmentier, E.; Berten, L.; Rigo, P.; Aubrun, F.; Nedelec, S.L.; Simpson, S.D.; Lecchini, D. The influence of various reef sounds on coral-fish larvae behaviour. J. Fish. Biol. 2015, 86, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radford, C.A.; Stanley, J.A.; Simpson, S.D.; Jeffs, A.G. Juvenile coral reef fish use sound to locate habitats. Coral Reefs 2011, 30, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, P.; Berenshtein, I.; Besson, M.; Roux, N.; Parmentier, E.; Banaigs, B.; Lecchini, D. From the ocean to a reef habitat: How do the larvae of coral reef fishes find their way home? A state of art on the latest advances. Vie et Milieu 2015, 65, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, S.D.; Meekan, M.G.; Jeffs, A.; Montgomery, J.C.; McCauley, R.D. Settlement-stage coral reef fish prefer the higher-frequency invertebrate-generated audible component of reef noise. Anim. Behav. 2008, 75, 1861–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S.D.; Meekan, M.G.; Larsen, N.J.; McCauley, R.D.; Jeffs, A. Behavioral plasticity in larval reef fish: Orientation is influenced by recent acoustic experiences. Behav. Ecol. 2010, 21, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heenan, A.; Simpson, S.D.; Braithwaite, V.A. Testing the Generality of Acoustic Cue Use at Settlement in Larval Coral Reef Fish. 6. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Stephen_Simpson5/publication/266447888_Testing_the_generality_of_acoustic_cue_use_at_settlement_in_larval_coral_reef_fish/links/54b6494d0cf26833efd36db8/Testing-the-generality-of-acoustic-cue-use-at-settlement-in-larval-coral-reef-fish.pdf. (accessed on 1 September 2018).
- Lecchini, D.; Shima, J.; Banaigs, B.; Galzin, R. Larval sensory abilities and mechanisms of habitat selection of a coral reef fish during settlement. Oecologia 2005, 143, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, D.; Casper, B.; Boyle, K.; Tricas, T. On the attraction of larval fishes to reef sounds. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 338, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curtis, K.R.; Howe, B.M.; Mercer, J.A.; Curtis, K.R.; Howe, B.M.; Mercer, J.A. Low-frequency ambient sound in the North Pacific: Long time series observations. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 106, 3189–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haxel, J.H.; Dziak, R.P.; Matsumoto, H. Observations of shallow water marine ambient sound: The low frequency underwater soundscape of the central Oregon coast. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, 2586–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindseth, A.V. Determining temporal recording schemes for underwater acoustic monitoring studies. Master’s Thesis, Boston University, Boston, MA, USA, 2019; p. 42. [Google Scholar]
- Heenehan, H.L.; Van Parijs, S.M.; Bejder, L.; Tyne, J.A.; Southall, B.L.; Southall, H.; Johnston, D.W. Natural and anthropogenic events influence the soundscapes of four bays on Hawaii Island. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowell, T.J.; Schärer, M.T.; Appeldoorn, R.S.; Nemeth, M.I.; Mann, D.A.; Rivera, J.A. Sound production as an indicator of red hind density at a spawning aggregation. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 462, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wall, C.C.; Mann, D.A.; Lembke, C.; Taylor, C.; He, R.; Kellison, T. Mapping the soundscape off the southeastern USA by using passive acoustic glider technology. Mar. Coast. Fish. 2017, 9, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locascio, J.V.; Burton, M.L. A passive acoustic survey of fish sound production at Riley’s Hump within Tortugas South Ecological Reserve: Implications regarding spawning and habitat use. Fish. Bull. 2015, 114, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depraetere, M.; Pavoine, S.; Jiguet, F.; Gasc, A.; Duvail, S.; Sueur, J. Monitoring animal diversity using acoustic indices: Implementation in a temperate woodland. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 13, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, M.B.; Mooney, T.A.; Partan, J.; Solow, A.R. Coral reef species assemblages are associated with ambient soundscapes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 533, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benoit-Bird, K.J.; Au, W.W.L.; Brainard, R.E.; Lammers, M.O. Diel horizontal migration of the Hawaiian mesopelagic boundary community observed acoustically. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 217, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stanley, J.A.; Van Parijs, S.M.; Hatch, L.T. Underwater sound from vessel traffic reduces the effective communication range in Atlantic cod and haddock. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggins, S.M.; Hall, J.M.; Thayre, B.J.; Hildebrand, J.A. Gulf of Mexico low-frequency ocean soundscape impacted by airguns. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 140, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parks, S.E.; Miksis-Olds, J.L.; Denes, S.L. Assessing marine ecosystem acoustic diversity across ocean basins. Ecol. Inf. 2014, 21, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.G.; Godin, O.A.; Zang, X.; Ball, J.S.; Zabotin, N.A.; Zabotina, L.Y.; Williams, N.J. Ocean acoustic remote sensing using ambient noise: Results from the Florida Straits. Geophy. J. Int. 2016, 206, 574–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilov, A.N.; Parsons, M.J.G. A Matlab tool for the characterisation of recorded underwater sound (CHORUS). Acoust. Aust. 2014, 42, 190–196. [Google Scholar]
- Merchant, N.D.; Fristrup, K.M.; Johnson, M.P.; Tyack, P.L.; Witt, M.J.; Blondel, P.; Parks, S.E. Measuring acoustic habitats. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fisher-pool, P.I.; Lammers, M.O.; Gove, J.; Wong, K.B. Does primary productivity turn up the volume? Exploring the relationship between chlorophyll a and the soundscape of coral reefs in the Pacific. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 875, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisaka, T.; Shinohara, M.; Nakahara, F.; Akamatsu, T. Effects of ambient noise on the whistles of Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphin populations. J. Mammal. 2005, 86, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliam, J.N.; Hawkins, A.D. A comparison of inshore marine soundscapes. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 446, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Elson, J.; Girod, L.; Estrin, D.; Yao, K. Target classification and localization in habitat monitoring. ICASSP IEEE Int. Conf. Acoust. Speech Signal. Process. 2003, 4, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.; Henderson, L. Global ocean soundscapes. Proc. Meet. Acoust. 2013, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staaterman, E.; Paris, C.B.; Kough, A.S. First evidence of fish larvae producing sounds. Biol. Lett. 2014, 10, 20140643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueur, J.; Farina, A.; Gasc, A.; Pieretti, N.; Pavoine, S. Acoustic indices for biodiversity assessment and landscape investigation. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2014, 100, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolgan, M.; Amorim, M.C.P.; Fonseca, P.J.; Di Iorio, L.; Parmentier, E. Acoustic complexity of vocal fish communities: A field and controlled validation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, A.N.; Soldevilla, M.S.; Quinlan, J.A. Nocturnal patterns in fish chorusing off the coasts of Georgia and eastern Florida. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2017, 93, 455–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towsey, M.; Wimmer, J.; Williamson, I.; Roe, P. The use of acoustic indices to determine avian species richness in audio-recordings of the environment. Ecol. Inf. 2014, 21, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towsey, M.; Zhang, L.; Cottman-Fields, M.; Wimmer, J.; Zhang, J.; Roe, P. Visualization of long-duration acoustic recordings of the environment. Proced. Comput. Sci. 2014, 29, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.A.; Shears, N.T.; Radford, C.A. Ecoacoustic indices as proxies for biodiversity on temperate reefs. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Rivera, L.J.; Pijanowski, B.C.; Doucette, J.; Pekin, B. A primer of acoustic analysis for landscape ecologists. Landsc. Ecol. 2011, 26, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueur, J.; Aubin, T.; Simonis, C. Sound analysis and synthesis with the package Seewave. Bioacoustics 2008, 18, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertucci, F.; Parmentier, E.; Berthe, C.; Besson, M.; Hawkins, A.D.; Aubin, T.; Lecchini, D. Snapshot recordings provide a first description of the acoustic signatures of deeper habitats adjacent to coral reefs of Moorea. PeerJ 2017, 5, e4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erbe, C.; Verma, A.; McCauley, R.; Gavrilov, A.; Parnum, I. The marine soundscape of the Perth Canyon. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 137, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felisberto, P.; Rodriguez, O.; Santos, P.; Zabel, F.; Jesus, S. Variability of the ambient noise in a seagrass bed. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2014 Oceans, St. John’s, NL, USA, 14–19 September 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, C.; Stanley, J.; Tindle, C.; Montgomery, J.; Jeffs, A. Localised coastal habitats have distinct underwater sound signatures. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 401, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radford, C.; Stanley, J.; Jeffs, A. Adjacent coral reef habitats produce different underwater sound signatures. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 505, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, E.H.; Hildebrand, J.A.; Wiggins, S.M.; Ross, D. Underwater ambient noise on the Chukchi Sea continental slope from 2006–2009. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 131, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randall, J.E.; Lobel, P.S.; Kennedy, C.W. Comparative ecology of the gobies Nes longus and Ctenogobius saepepallens, both symbiotic with the snapping shrimp Alpheus floridanus. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2005, 74, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovitvongsa, K.E.; Lobel, P.S. Convenient fish acoustic data collection in the digital age. In Proceedings of the American Academy of Underwater Sciences 28th Symposium, Atlanta, GA, USA, 13–14 March 2009; Pollock, N.W., Ed.; AAUS: Dauphin Island, AL, USA, 2009; pp. 43–57. [Google Scholar]
- Erbe, C. Underwater passive acoustic monitoring & noise impacts on marine fauna-A workshop report. Acoust. Aust. 2013, 41, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Giard, J.L.; Vigness-Raposa, K.J.; Frankel, A.S.; Ellison, W.T. Visualization of spatially explicit acoustic layers in an underwater soundscape. In Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics; Acoustical Society of America: Dublin, Ireland, 2016; Volume 27. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, D.A.; Lobel, P.S. Propagation of damselfish (Pomacentridae) courtship sounds. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1997, 101, 3783–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosharo, K.K.; Lobel, P.S. Acoustic signals of two toadfishes from Belize: Sanopus astrifer and Batrachoides gilberti (Batrachoididae). Environ. Biol. Fish. 2012, 94, 623–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripley, J.L.; Lobel, P.S. Correlation of acoustic and visual signals in the cichlid fish, Tramitichromis intermedius. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2004, 71, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricas, T.; Boyle, K. Acoustic behaviors in Hawaiian coral reef fish communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 511, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tricas, T.C.; Webb, J.F. Acoustic communication in butterflyfishes: Anatomical novelties, physiology, evolution, and behavioral ecology. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 877, 57–92. [Google Scholar]
- Lobel, P. Diversity of fish courtship and spawning sounds and application for monitoring reproduction. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 112, 2201–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumstein, D.T.; Mennill, D.J.; Clemins, P.; Girod, L.; Yao, K.; Patricelli, G.; Deppe, J.L.; Krakauer, A.H.; Clark, C.; Cortopassi, K.A.; et al. Acoustic monitoring in terrestrial environments using microphone arrays: Applications, technological considerations and prospectus. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 48, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dushaw, B.; Au, W.W.L.; Beszczynska-Moller, A.; Brainard, R.E.; Cornuelle, B.D.; Duda, T.F.; Dzieciuch, M.A.; Fahrbach, E.; Forbes, A.; Freitag, L.; et al. A Global Ocean Acoustic Observing Network. 2009. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/263031402_A_Global_Ocean_Acoustic_Observing_Network (accessed on 1 September 2018).
- Frommolt, K.H.; Tauchert, K.H. Applying bioacoustic methods for long-term monitoring of a nocturnal wetland bird. Ecol. Inf. 2014, 21, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brainard, R.; Bainbridge, S.; Brinkman, R.; Eakin, C.M.; Field, M.; Gattuso, P.; Gledhill, D.; Gramer, L.; Green, A.; Hendee, J.; et al. An International Network of Coral Reef Ecosystem Observing Systems (I-CREOS). 2009. Available online: http://www.obs-vlfr.fr/~gattuso/publications_PDF/Brainard_etal_2009.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2018).
- Hatch, L.T.; Wahle, C.M.; Gedamke, J.; Harrison, J.; Laws, B.; Moore, S.E.; Stadler, J.H.; Van Parijs, S.M. Can you hear me here? Managing acoustic habitat in US waters. Endanger. Species Res. 2016, 30, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Og̃uz, H.N. A theoretical study of low-frequency oceanic ambient noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1994, 95, 1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieretti, N.; Duarte, M.H.L.; Sousa-Lima, R.S.; Rodrigues, M.; Young, R.J.; Farina, A. Determining temporal sampling schemes for passive acoustic studies in different tropical ecosystems. Trop. Conserv. Sci. 2015, 8, 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggleston, D.B.; Lillis, A.; Bohnenstiehl, D.R. Soundscapes and larval settlement: Larval bivalve responses to habitat-associated underwater sounds. In The Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life II; Popper, A.N., Hawkins, A., Eds.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; Volume 875, pp. 255–263. [Google Scholar]

| Recording Rate | Paper | Location |
|---|---|---|
| 30 s every 4 min | [56] | Hawaii, US |
| 12 s every 5 min | [38] | Florida Keys, US |
| 12 s every 5 min | [3] | Florida Keys, US; Panama |
| 20 s every 5 min | [57] | Puerto Rico; US Virgin Islands |
| 30 s every 5 min | [58] | Southeast USA waters |
| 10 s every 10 min | [59] | Florida Keys, US |
| 1 min every 10 min | [22] | Bocas del Toro, Panama |
| 2 min every 10 min | [6] | Curaçao |
| 30 s every 15 min | [20] | Oahu, Hawaii, US |
| 150 s every 15 min | [60] | France |
| 1 min every 20 min | [61] | St. John, US Virgin Islands |
| 10 min every 1 h | [46] | Lizard Island, GBR, Australia |
| 1 h every 3 h | [62] | Hawaii, US |
| Continuously for 24 h | [5] | Prince Edward Island, Canada |
| Continuously for 24 h | [22] | Bocas del Toro, Panama |
| Continuously for 48 h | [43] | Adriatic Sea, Italy |
| Recording Frequency Rate | Paper | Location |
|---|---|---|
| 2 kHz | [54] | Oregon, US |
| 2 kHz | [63] | Stellwagen Bank NMS, USA |
| 2 kHz | [64] | Gulf of Mexico |
| 20 kHz | [3] | Florida Keys, US; Panama |
| 44.1 kHz | [11] | Curaçao |
| 96 kHz | [6] | Curaçao |
| 96 kHz | [21] | Adelaide, South Australia, Australia |
| 250 kHz | [65] | Ascension Island; Diego Garcia Island; Wake Island |
| Index | Definition | Assumption/Limitation | Group | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acoustic Entropy (H) | Evenness/species richness of acoustic space | Combines spectral and temporal H | α | 1. [23] |
| 0 = pure tones; 1 = random noise; | 2. [22,60,61,65,78,79,80] | |||
| Geophony/anthrophony reduce reliability and produce false high values | ||||
| Acoustic Richness (AR) | Species richness of acoustic space | Combines temporal H and amplitude; | α | 1. [60] |
| = pure tones; 1 = random noise; | 2. [23,80] | |||
| More accurate than H in areas of lower diversity | ||||
| Acoustic Dissimilarity Index (D) | Dissimilarity between two communities | Compares two signals of same duration and frequency; | β | 1. [23] |
| 2. [60] | ||||
| 0 = similar sounds; 1 = distinct sounds | ||||
| increases with number of unshared chorus pairs | ||||
| Acoustic Complexity Index (ACI) | Degree of complexity | Sums absolute difference between two adjacent intensities; better for soundscapes of constant intensity; | α | 1. [42] |
| 2, [1,19,22,38,43,61,71,78,79,80] | ||||
| Reliability reduced if one dominant acoustic spp.; | ||||
| time-consuming calculations |
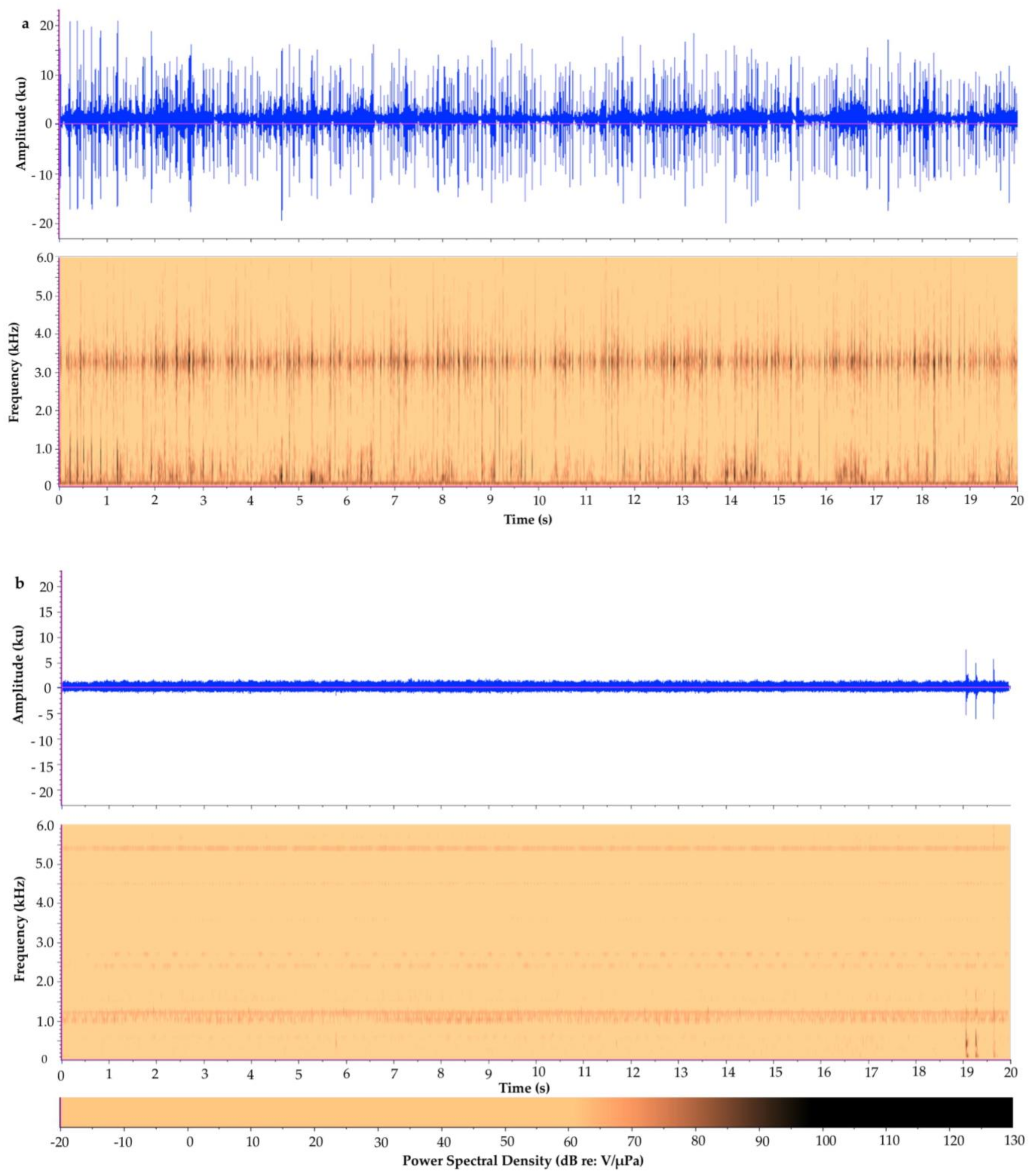
| Tunicate Cove | Glovers Atoll Mangrove | |
|---|---|---|
| Acoustic Metric | Mean ± S.D. (Range) n = 20 | Mean ± S.D. (Range) n = 20 |
| Aggregate Entropy (u) | 4.32 ± 0.17 (3.84–4.52) | 5.27 ± 0.17 (4.67–5.37) |
| Average Entropy (u) | 2.99 ± 0.22 (2.54–3.41) | 5.03 ± 0.08 (4.81–5.10) |
| Average PSD (dB) | 67.3 ± 1.2 (66.1–70.1) | 53.7 ± 1.2 (53.1–58.3) |
| Peak PSD (dB) | 100.5 ± 2.5 (96.9–106.4) | 76.4 ± 4.1 (72.1–92.1) |
| SPL (dB) | n/a 1 | n/a 1 |
| Peak Frequency (Hz) | 1364.0 ± 1435.2 (187.5–3281.2) | 1181.3 ± 167.7 (468.8–1218.8) |
| Energy (dB) | 111.1 ± 1.2 (109.0–113.9) | 97.4 ± 1.2 (96.3–102.1) |
| RMS Amplitude (u) | 1801.3 ± 228.1 (1466.9–2367.5) | 343.6 ± 59.6 (297.4–589.5) |
| ACI | n/a 2 | n/a 2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lindseth, A.V.; Lobel, P.S. Underwater Soundscape Monitoring and Fish Bioacoustics: A Review. Fishes 2018, 3, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3030036
Lindseth AV, Lobel PS. Underwater Soundscape Monitoring and Fish Bioacoustics: A Review. Fishes. 2018; 3(3):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3030036
Chicago/Turabian StyleLindseth, Adelaide V., and Phillip S. Lobel. 2018. "Underwater Soundscape Monitoring and Fish Bioacoustics: A Review" Fishes 3, no. 3: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3030036
APA StyleLindseth, A. V., & Lobel, P. S. (2018). Underwater Soundscape Monitoring and Fish Bioacoustics: A Review. Fishes, 3(3), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3030036





