Structural Analysis of Acidic Glycosphingolipids in the Adductor Muscle of the Japanese Giant Scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
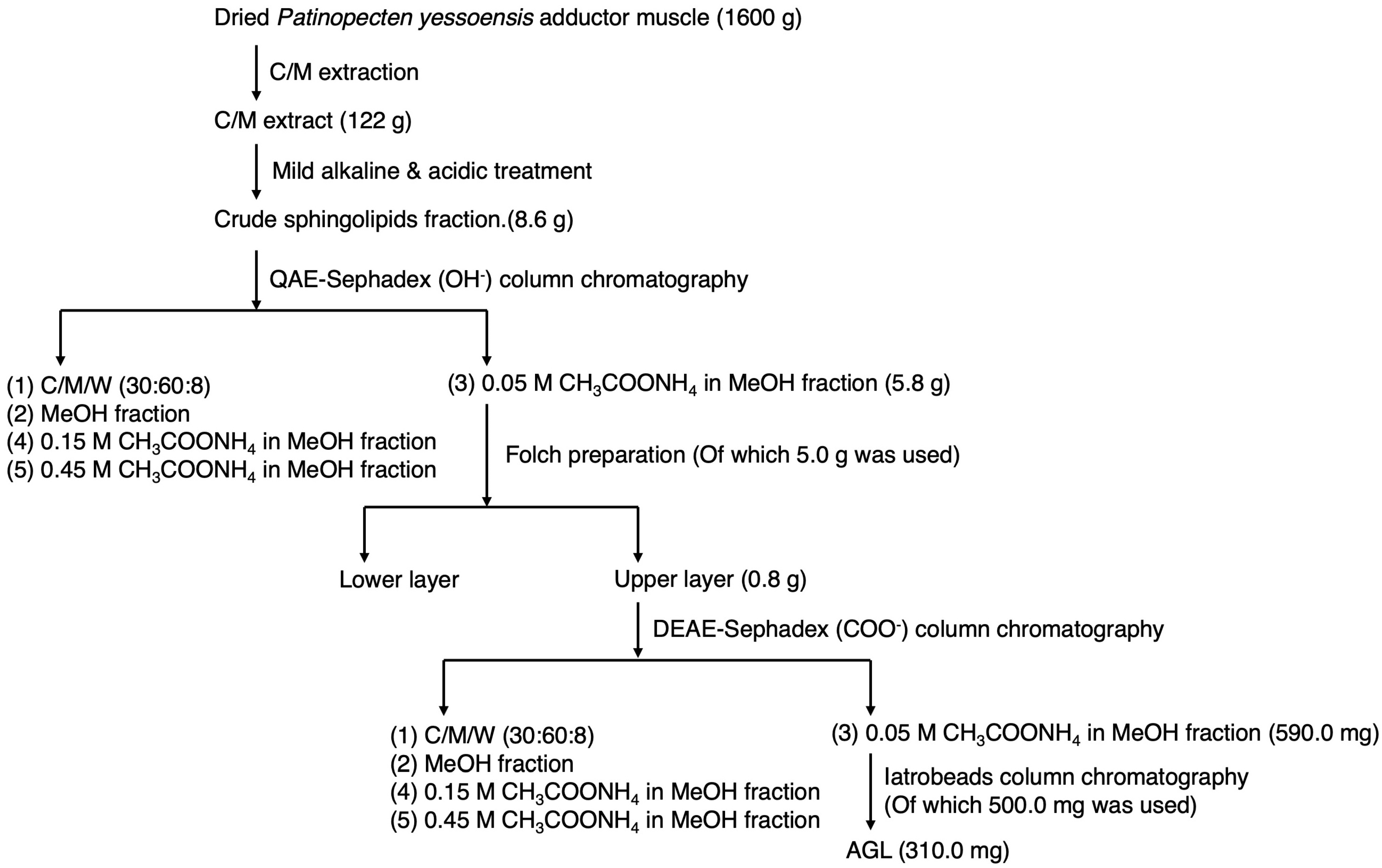
2.1. Preparation of Crude Sphingolipids
2.2. Fractionation of AGL
2.2.1. QAE-Sephadex Column Chromatography
2.2.2. Folch Partition
2.2.3. DEAE-Sephadex Column Chromatography
2.2.4. Iatrobeads Column Chromatography
2.2.5. Reduction of AGL
2.2.6. Partial Hydrolysis of Sugar Chain
2.3. Analysis of AGL
2.3.1. TLC Analysis
2.3.2. Analysis of Sugar Chain Composition
2.3.3. Analysis of Sugar Linkage
2.3.4. Analyses of Fatty Acids and Long-Chain Bases (LCBs)
2.3.5. Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (1H-NMR) Analysis
2.3.6. TLC-Immunostaining Assay
2.3.7. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) Analysis
3. Results
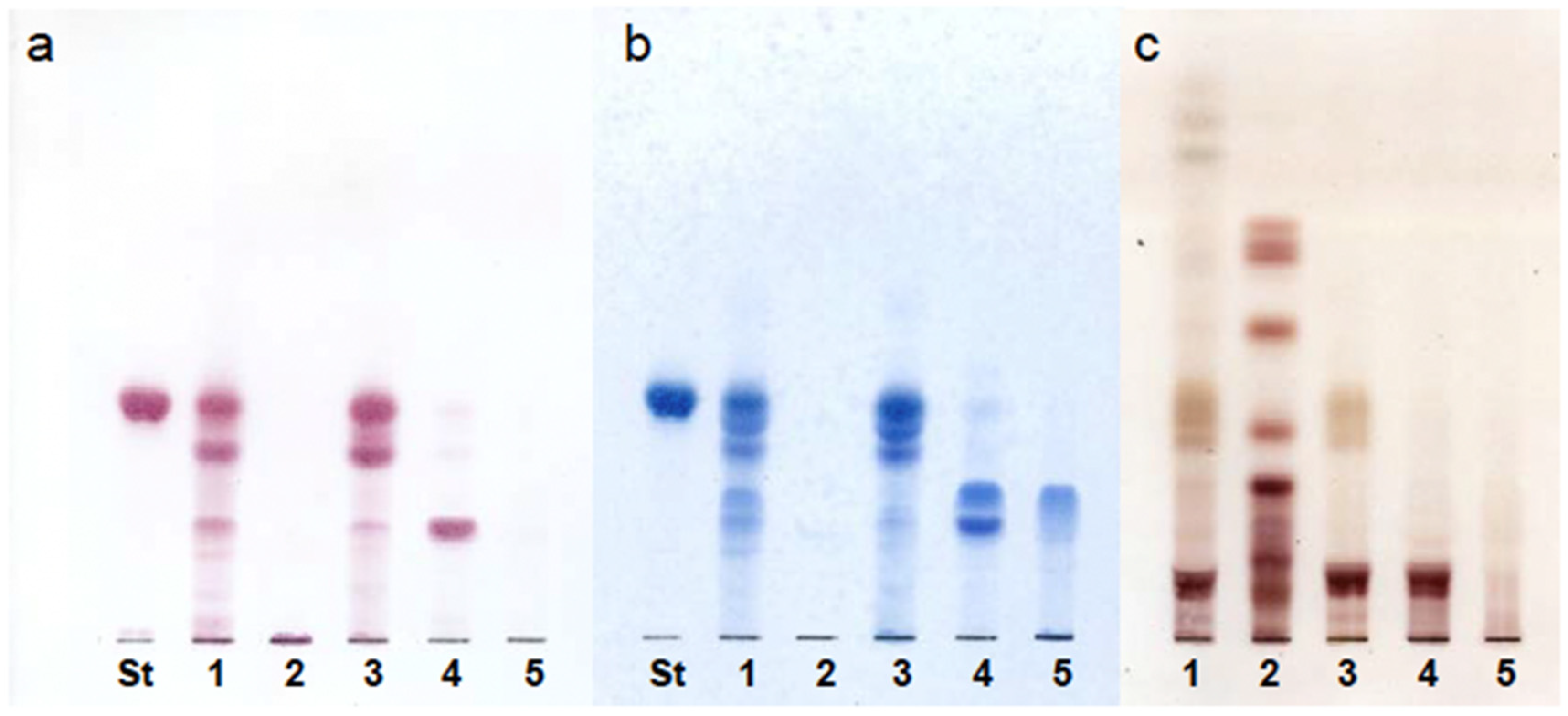
3.1. Fractionation of AGL
3.1.1. QAE-Sephadex Column Chromatography
3.1.2. Folch Partition
3.1.3. DEAE-Sephadex Column Chromatography
3.1.4. Iatrobeads Column Chromatography
3.1.5. Reduction of AGL
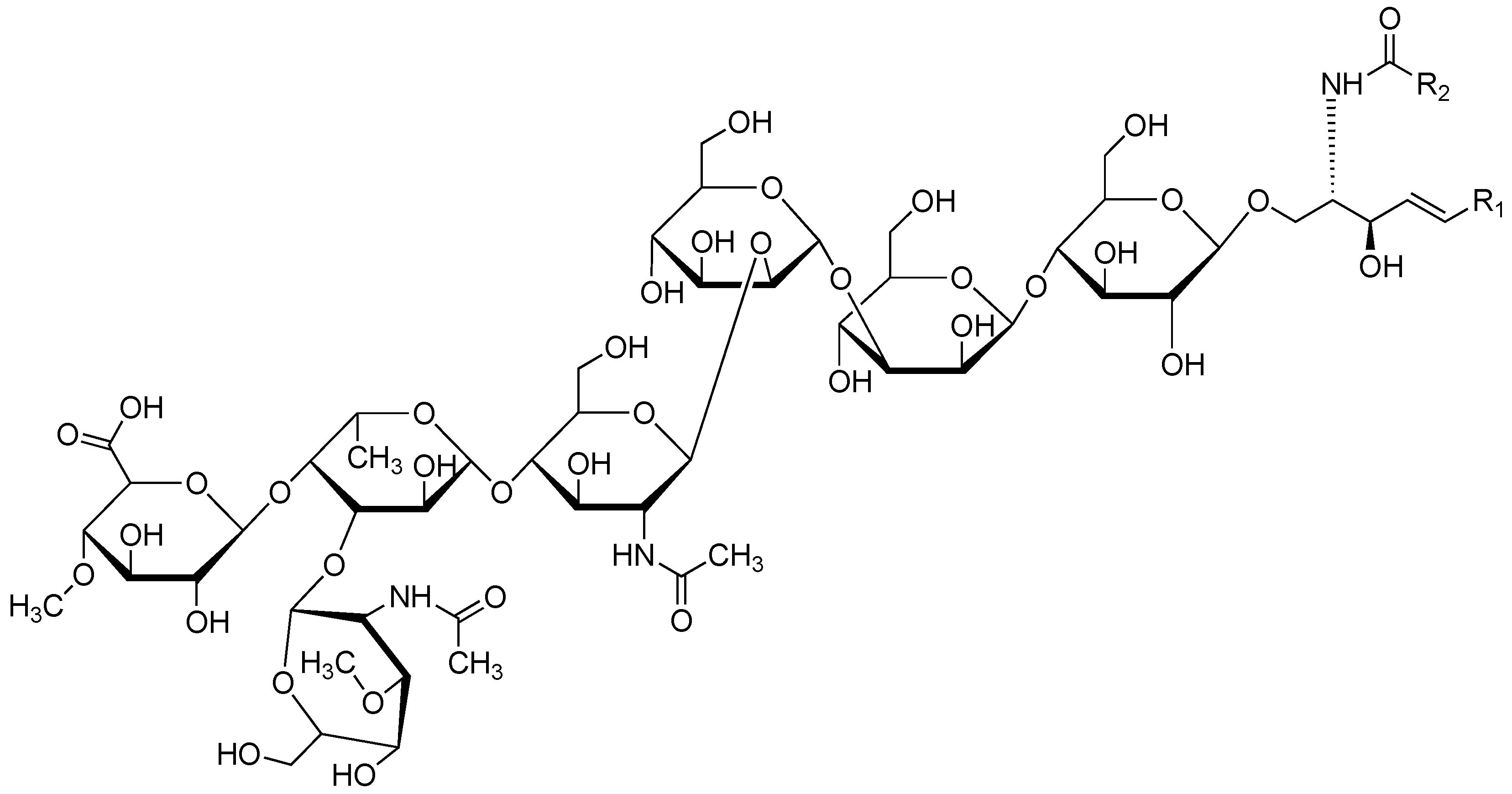
3.2. Structural Analysis of AGL
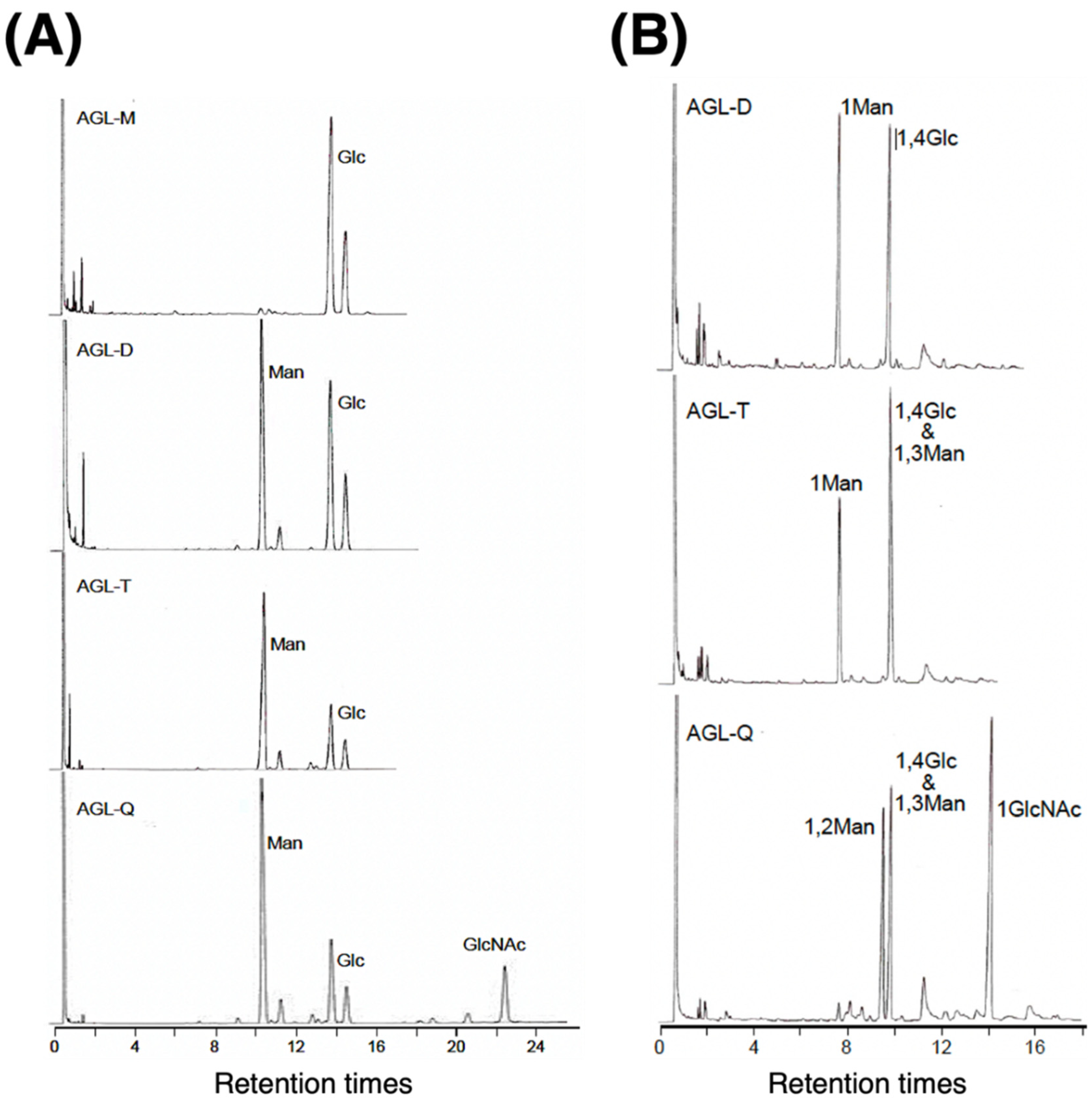
3.2.1. Sugar Composition of AGL
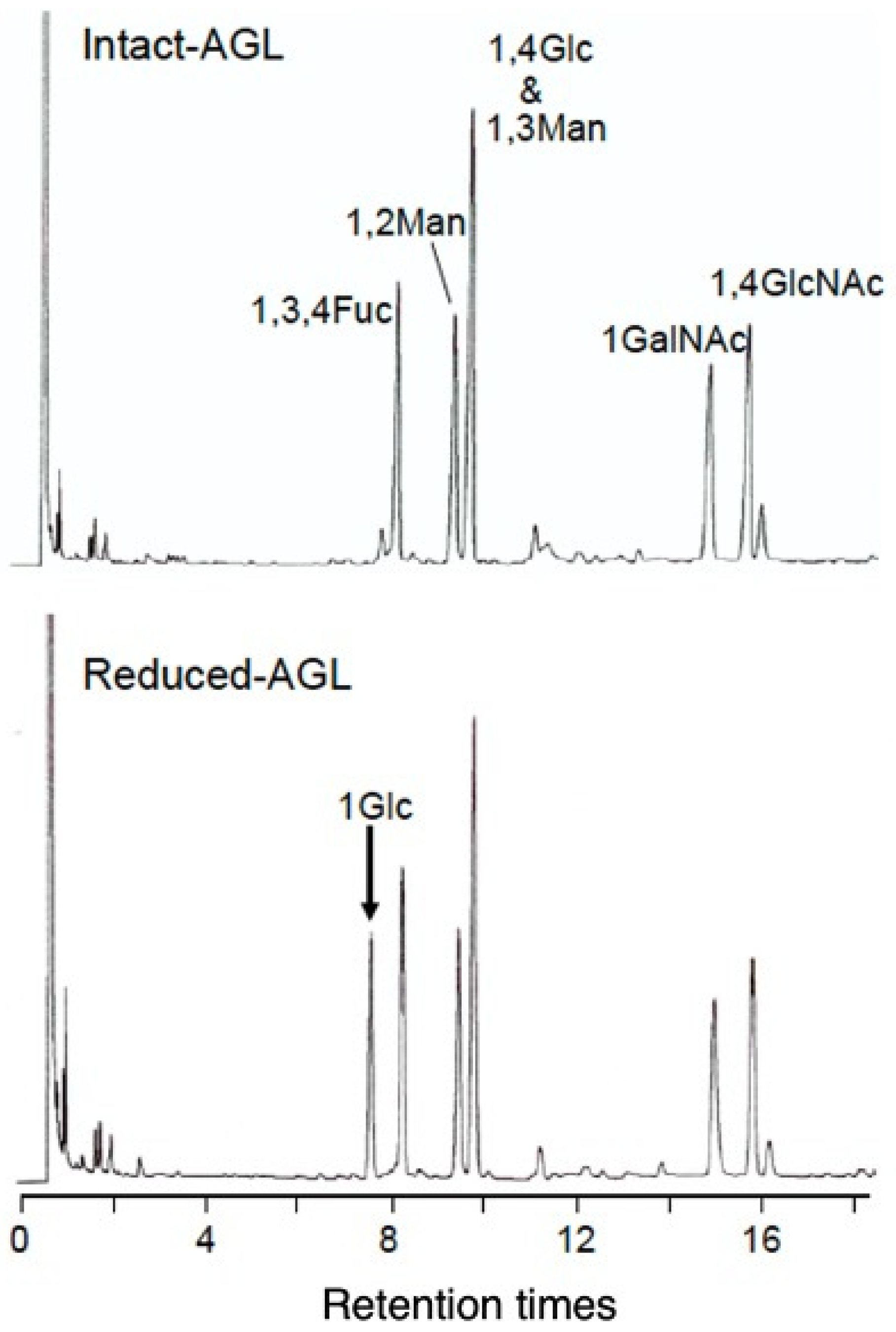
3.2.2. Sugar Linkage Analysis
3.2.3. 1H-NMR Analysis
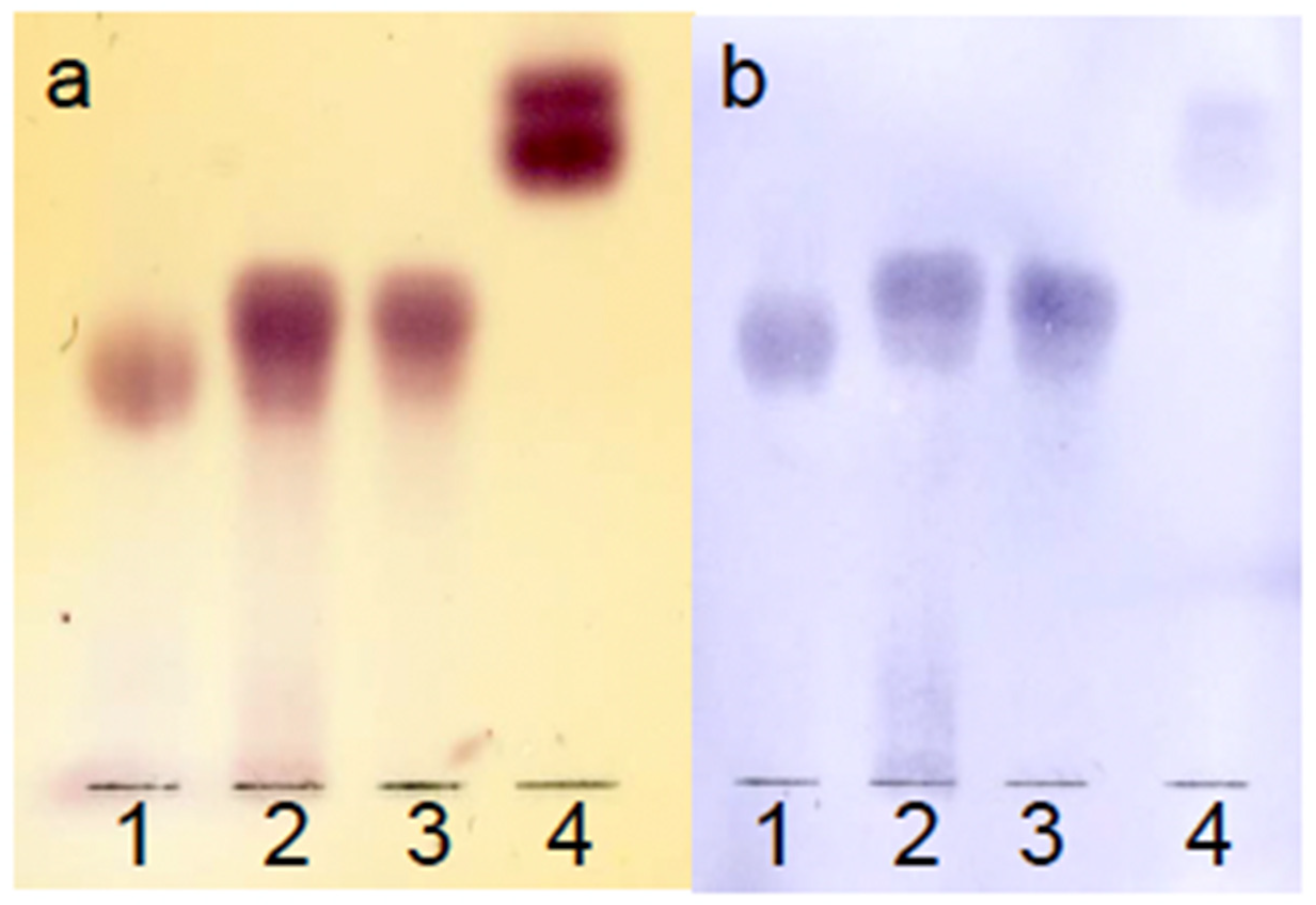
3.2.4. TLC-Immunostaining Assay
3.2.5. Ceramide Composition Analysis
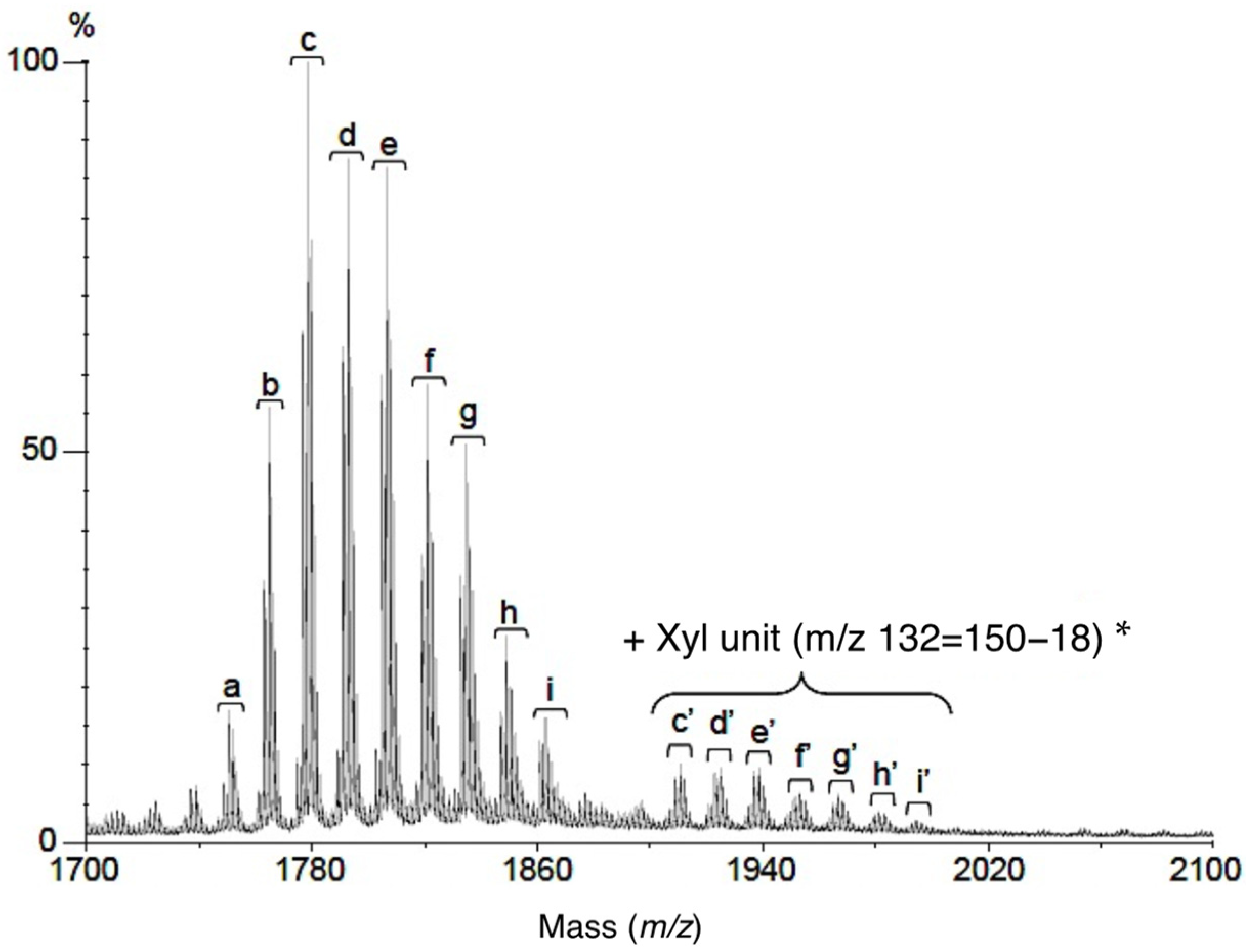
3.2.6. MALDI-TOF/MS Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 1,2Man | 1,2,5-tri-O-acetyl-3,4,6-tri-O-methylmannitol |
| 1,3,4Fuc | 1,3,4,5-tetra-O-acetyl-2-O-methylfucitol |
| 1,3Man | 1,3,5-tri-O-acetyl-2,4,6-tri-O-methylmannitol |
| 1,4Glc | 1,4,5-tri-O-acetyl-2,3,6-tri-O-methylglucitol |
| 1,4GlcNAc | 1,4,5-tri-O-acetyl-3,6-di-O-methyl-N-acetylglucosaminitol |
| 1GalNAc | 1,5-di-O-acetyl-3,4,6-tri-O-methyl-N-acetylgalactosaminitol |
| 1Glc | 1,5-di-O-acetyl-2,3,4,6-tetra-O-methylglucitol |
| 1H-NMR | proton nuclear magnetic resonance |
| 4-O-Me-GlcA | 4-O-methyl-glucuronic acid |
| 4-O-Me-Hexitol | 1,2,3,5,6-penta-O-acetyl-4-methylhexitol |
| AGLs | acidic glycosphingolipids |
| AGL-D | acidic glycosphingolipids-disaccharides |
| AGL-M | acidic glycosphingolipids-monosaccharide |
| AGL-Q | acidic glycosphingolipids-tetrasaccharides |
| AGL-T | acidic glycosphingolipids-trisaccharides |
| C/M | chloroform/methanol |
| C/M/W | chloroform/methanol/water |
| Cer | ceramide |
| Fuc | fucose |
| Gal | galactose |
| GalNAc | N-acetyl galactosamine |
| GalNAc3Me | 3-O-methyl-N-acetyl galactosamine |
| GC | gas chromatography |
| GC-MS | gas chromatograph-mass spectrometry |
| Glc | glucose |
| GlcA | glucuronic acid |
| GlcNAc | N-acetyl glucosamine |
| GSLs | glycosphingolipids |
| Hex | hexose |
| HexAMe | O-methyl hexuronic acid |
| HexNAc | N-acetyl hexosamine |
| HexNAcMe | O-methyl-N-acetyl hexosamine |
| LCB | long-chain bases |
| M/W | methanol/water |
| MALDI-TOF MS | matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry |
| PMAA | partially methylated alditol acetates |
| TLC | thin-layer chromatography |
| TMS | trimethylsilyl |
| Xyl | xylose |
References
- Enda, H.; Sagane, Y.; Nakazawa, Y.; Sato, H.; Yamazaki, M. Data on color and chemical composition of dried scallop (Mizuhopecten yessoensis) produced in different areas of Hokkaido, Japan. Data Brief 2018, 16, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, K.; Miyazono, A.; Matsuyama, K.; Kohno, S.; Kubota, S. Occurrence and detrimental effects of the bivalve-inhabiting hydroid Eutima japonica on juveniles of the Japanese scallop Mizuhopecten yessoensis in Funka Bay, Japan: Relationship to juvenile massive mortality in 2003. Mar. Biol. 2007, 151, 1977–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Yu, R.C.; Gao, Y.; Kong, F.Z.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhang, Q.C.; Kang, Z.J.; Yan, T.; Zhou, M.J. Tracing the origin of paralytic shellfish toxins in scallop Patinopecten yessoensis in the northern Yellow Sea. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2013, 30, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M. Studies on the quality control of the Japanese scallop adductor muscle. Sci. Rep. Hokkaido Fish. Exp. Stn. 2003, 65, 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, T. Anatomy of the Mollusca: Sepia esculenta (Cephalopoda: Sepiidae), Turbo cornutus (Gastropoda: Turbinidae) and Patinopecten yessoensis (Bivalvia: Pectinidae). Fossils 2008, 84, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, Z.; Wu, B.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Q.; Wu, W.; Yang, A. Differences between fast and slow muscles in scallops revealed through proteomics and transcriptomics. BMC Genomics 2018, 19, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutsell, S.J. Natural history of the bay scallop (Pecten irradians). U.S. Bur. Fish. 1930, 46, 569–632. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, M.A.; Hamilton, P.V. Factors influencing swimming in bay scallops, Argopectenirradians (Lamarck, 1819). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1985, 88, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murate, M.; Abe, M.; Kasahara, K.; Iwabuchi, K.; Umeda, M.; Kobayashi, T. Transbilayer distribution of lipids at nano scale. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 1627–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnino, S.; Prinetti, A.; Mauri, L.; Chigorno, V.; Tettamanti, G. Dynamic and structural properties of sphingolipids as driving forces for the formation of membrane domains. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 2111–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwabuchi, K.; Nakayama, H.; Masuda, H.; Kina, K.; Ogawa, H.; Takamori, K. Membrane microdomains in immunity: Glycosphingolipid-enriched domain-mediated innate immune responses. BioFactors 2012, 38, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakomori, S.; Handa, K.; Iwabuchi, K.; Yamamura, S.; Prinetti, A. New insights in glycosphingolipid function: “glycosignaling domain,” a cell surface assembly of glycosphingolipids with signal transducer molecules, involved in cell adhesion coupled with signaling. Glycobiology 1998, 8, xi–xix. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, K.; Seydel, U.; Matsuura, M.; Danbara, H.; Rietschel, E.T.; Zähringer, U. Chemical structure of glycosphingolipids isolated from Sphingomonas paucimobilis. FEBS Lett. 1991, 292, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wennekes, T.; van den Berg, R.J.; Boot, R.G.; van der Marel, G.A.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Aerts, J.M. Glycosphingolipids--nature, function, and pharmacological modulation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2009, 48, 8848–8869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingwood, C.A. Glycosphingolipid functions. Cold Spring Harb Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Go, S.; Takasaki, K.; Kakazu, Y.; Ohashi, M.; Nagafuku, M.; Kabayama, K.; Sekimoto, J.; Suzuki, S.; Takaiwa, K.; et al. Mice lacking ganglioside GM3 synthase exhibit complete hearing loss due to selective degeneration of the organ of Corti. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9483–9488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Hashiramoto, A.; Haluzik, M.; Mizukami, H.; Beck, S.; Norton, A.; Kono, M.; Tsuji, S.; Daniotti, J.L.; Werth, N.; et al. Enhanced insulin sensitivity in mice lacking ganglioside GM3. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3445–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, T.; Sugita, M.; Ando, S.; Tsukada, K.; Shiota, K.; Tsuzuki, M.; Itasaka, O. Isolation and characterization of a 4-O-methylglucuronic acid-containing glycosphingolipid from spermatozoa of a fresh water bivalve, Hyriopsis schlegelii. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 2239–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, M.; Nakano, Y.; Nose, T.; Itasaka, O.; Hori, T. Neutral glycosphingolipids of ova of the fresh-water bivalve, Hyriopsis schlegelii. J. Biochem. 1984, 95, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itasaka, O.; Kosuga, M.; Okayama, M.; Hori, T. Characterization of a novel ceramide octasaccharide isolated from whole tissue of a fresh-water bivalve, Corbicula sandai. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1983, 750, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, M.; Nakae, H.; Yamamura, T.; Takamiya, Y.; Itasaka, O.; Hori, T. The occurrence of glycosphingolipids containing mannose in the sea-water bivalve, Meretrix lusoria (Hamaguri). J. Biochem. 1985, 98, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Matsumuro, Y.; Yamada, S.; Kitamura, T.; Itonori, S.; Sugita, M. Isolation and characterization of a novel uronic acid-containing acidic glycosphingolipid from the ascidian Halocynthia roretzi. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, H.; Shinohara, R.; Itonori, S.; Ito, M. Characterization of a novel rhamnose-containing acidic glycosphingolipid from the ascidian Halocynthia aurantium. J. Oleo Sci. 2017, 66, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasawa, H.; Miyazaki, S.; Kyogashima, M. Simple separation of glycosphingolipids in the lower phase of a Folch’s partition from crude lipid fractions using zirconium dioxide. Glycoconj J. 2022, 39, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.L.; Conrad, H.E. Stoichiometric depolymerization of polyuronides and glycosaminoglycuronans to monosaccharides following reduction of their carbodiimide-activated carboxyl groups. Biochemistry 1972, 11, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itonori, S.; Takahashi, M.; Kitamura, T.; Aoki, K.; Dulaney, J.T.; Sugita, M. Microwave-mediated analysis for sugar, fatty acid, and sphingoid compositions of glycosphingolipids. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bajwa, B.; Xing, X.; Terry, S.A.; Gruninger, R.J.; Abbott, D.W. Methylation-GC-MS/FID-based glycosidic linkage analysis of unfractionated polysaccharides in red seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Itonori, S.; Kajiwara, C.; Hada, N.; Takeda, T.; Sugita, M. Structural Elucidation of the Neutral glycosphingolipids, Mono-, di-, tri- and tetraglycosylceramides from the Marine Crab Erimacrus isenbeckii. J. Oleo Sci. 2014, 63, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberacher, H.; Whitley, G.; Berger, B. Evaluation of the sensitivity of the ‘Wiley registry of tandem mass spectral data, MSforID’ with MS/MS data of the ‘NIST/NIH/EPA mass spectral library’. J. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 48, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, M.; Inoue, T.; Itasaka, O.; Hori, T. The localization of 4-O-methylglucuronic acid-containing glycosphingolipid on the cell surface of bivalve spermatozoa by use of an immunological method. J. Biochem. 1984, 95, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, K.; Sugiyama, S.; Dulaney, J.T.; Itonori, S.; Sugita, M. Classification into a Novel Mollu-Series of Neutral glycosphingolipids from the Lamp Shell, Lingula unguis. J. Oleo Sci. 2002, 51, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, M.; Itonori, S.; Inagaki, F.; Hori, T. Characterization of two glucuronic acid-containing glycosphingolipids in larvae of the green-bottle fly, Lucilia caesar. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 15028–15033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seppo, A.; Moreland, M.; Schweingruber, H.; Tiemeyer, M. Zwitterionic and acidic glycosphingolipids of the Drosophila melanogaster embryo. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 3549–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makita, A.; Sato, A.; Sugita, M.; Itonori, S.; Ito, M.; Arakawa, Y. Chemical characterization of two main sphingolipids of scallop. Bull. Tenshi Coll. 2010, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar]

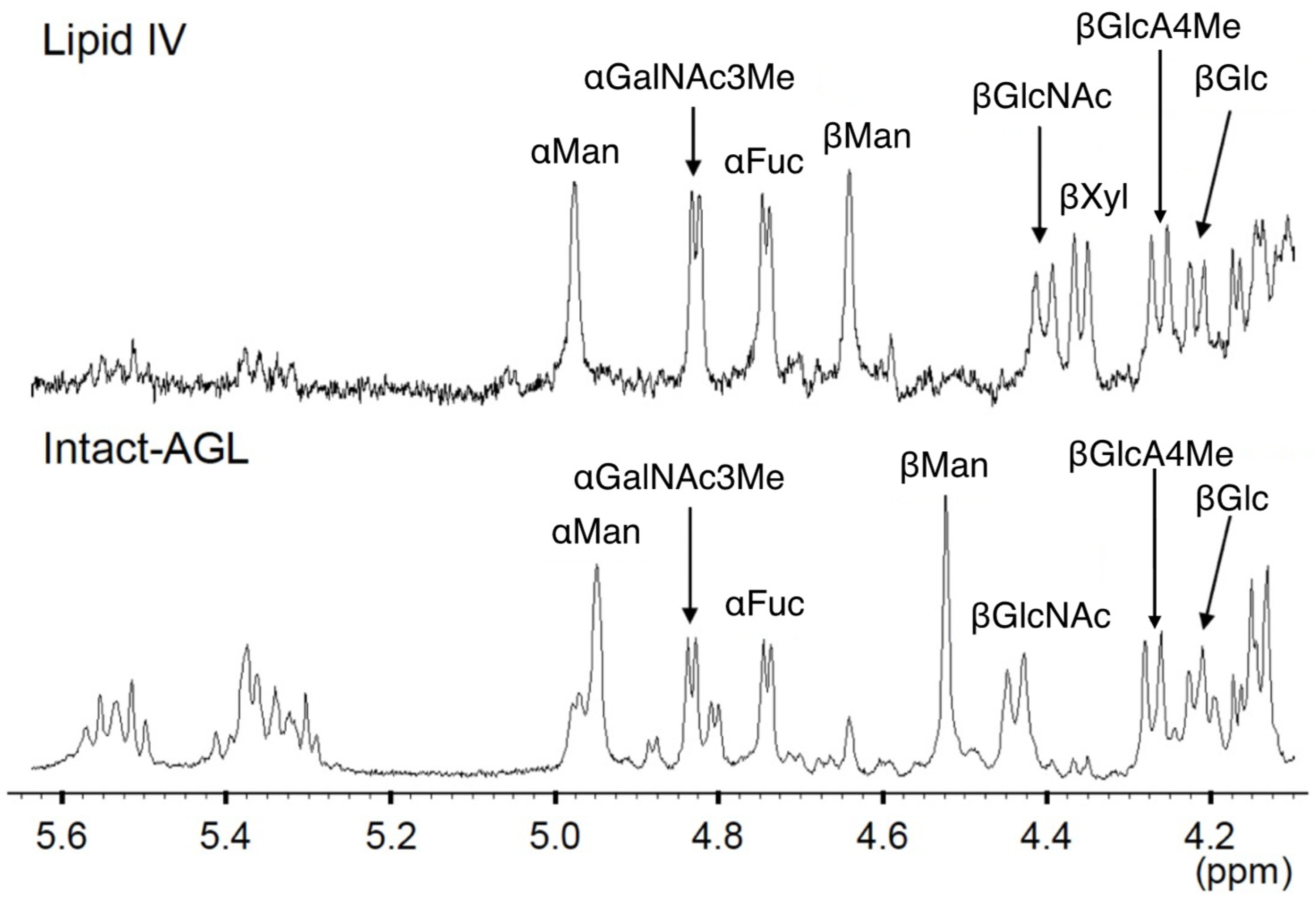
| Chemical Shifts [ppm] (Coupling Constants [Hz]) | |
|---|---|
| βGlc | 4.23 (6.63) |
| βMan | 4.53 (Singlet) |
| αMan | 4.96 (Singlet) |
| βGlcNAc | 4.45 (8.04) |
| αFuc | 4.75 (3.74) |
| αGalNAc3Me | 4.84 (3.74) |
| βGlcA4Me | 4.28 (7.82) |
| Names | Intact-AGL | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Fatty acid (wt%) | |||
| Saturated fatty acid | |||
| C16:0 | 25.0 | ||
| iso-C17:0 | 6.9 | ||
| C17:0 | 7.9 | ||
| C18:0 | 18.9 | ||
| C 20:0 | 10.6 | ||
| C 22:0 | 8.0 | ||
| Unsaturated fatty acid | |||
| C20:1 | 12.4 | ||
| C22:1 | 10.3 | ||
| Long-chain bases (wt%) | |||
| Sphingenine | |||
| d16:1 | 43.4 | ||
| d17:1 | 8.4 | ||
| d18:1 | 22.6 | ||
| Sphingadienine | |||
| d18:2 | 25.6 | ||
| Measured Value [m/z] | Calculated Value [M-H]− | Fatty Acid-LCB | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 1750.85 | 1750.91 | C16:0-d16:1 |
| b | 1764.87 | 1764.93 | C16:0-d17:1, C17:0-d16:1 |
| c | 1776.86 | 1776.93 | C16:0-d18:2 |
| 1778.88 | 1778.94 | C16:0-d18:1, C17:0-d17:1, C18:0-d16:1 | |
| d | 1790.88 | 1790.94 | C17:0-d18:2 |
| 1792.89 | 1792.96 | C17:0-d18:1, C18:0-d17:1 | |
| e | 1804.89 | 1804.96 | C18:0-d18:2, C20:1-d16:1 |
| 1806.90 | 1806.97 | C18:1-d18:1, C20:0-d16:1 | |
| f | 1818.90 | 1818.97 | C20:1-d17:1 |
| 1820.90 | 1820.99 | C20:0-d17:1 | |
| g | 1830.88 | 1830.97 | C20:1-d18:2 |
| 1832.91 | 1832.99 | C20:1-d18:1, C20:0-d18:2, C22:1-d16:1 | |
| 1834.92 | 1835.01 | C20:0-d18:1, C22:0-d16:1 | |
| h | 1846.93 | 1847.01 | C22:1-d17:1 |
| 1848.93 | 1849.02 | C22:0-d17:1 | |
| i | 1858.88 | 1859.01 | C22:1-d18:2 |
| 1860.95 | 1861.02 | C22:1-d18:1, C22:0-d18:2 | |
| 1862.95 | 1863.04 | C22:0-d18:1 | |
| c′ | 1908.91 | 1908.97 | C16:0-d18:2 |
| 1910.92 | 1910.96 | C16:0-d18:1, C17:0-d17:1, C18:0-d16:1 | |
| d′ | 1922.92 | 1922.99 | C17:0-d18:2 |
| 1924.92 | 1925.00 | C17:0-d18:1, C18:0-d17:1 | |
| e′ | 1936.93 | 1937.00 | C18:0-d18:2, C20:1-d16:1 |
| 1938.94 | 1939.02 | C18:0-d18:1, C20:0-d16:1 | |
| f′ | 1950.93 | 1951.02 | C20:1-d17:1 |
| 1952.94 | 1953.03 | C20:0-d17:1 | |
| g′ | 1964.96 | 1965.03 | C20:1-d18:1, C20:0-d18:2, C22:1-d16:1 |
| 1966.96 | 1967.05 | C20:0-d18:1, C22:0-d16:1 | |
| h′ | 1978.97 | 1979.05 | C22:1-d17:1 |
| 1980.97 | 1981.06 | C22:0-d17:1 | |
| i′ | 1990.93 | 1991.05 | C22:1-d18:2 |
| 1992.96 | 1993.06 | C22:1-d18:1, C22:0-d18:2 | |
| 1994.98 | 1995.08 | C22:0-d18:1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sonoda, S.; Itonori, S.; Sugita, M.; Higashino, A.; Sugimoto, K.; Hosomi, R.; Fukunaga, K. Structural Analysis of Acidic Glycosphingolipids in the Adductor Muscle of the Japanese Giant Scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis). Fishes 2025, 10, 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090460
Sonoda S, Itonori S, Sugita M, Higashino A, Sugimoto K, Hosomi R, Fukunaga K. Structural Analysis of Acidic Glycosphingolipids in the Adductor Muscle of the Japanese Giant Scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis). Fishes. 2025; 10(9):460. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090460
Chicago/Turabian StyleSonoda, Shunsuke, Saki Itonori, Mutsumi Sugita, Ayako Higashino, Koki Sugimoto, Ryota Hosomi, and Kenji Fukunaga. 2025. "Structural Analysis of Acidic Glycosphingolipids in the Adductor Muscle of the Japanese Giant Scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis)" Fishes 10, no. 9: 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090460
APA StyleSonoda, S., Itonori, S., Sugita, M., Higashino, A., Sugimoto, K., Hosomi, R., & Fukunaga, K. (2025). Structural Analysis of Acidic Glycosphingolipids in the Adductor Muscle of the Japanese Giant Scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis). Fishes, 10(9), 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090460







