Modeling Skipjack Tuna Purse Seine Fishery Distribution in the Western and Central Pacific Ocean Under ENSO Scenarios: An Integrated MGWR-BME Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Period
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. Fisheries Data
2.2.2. Environmental Data
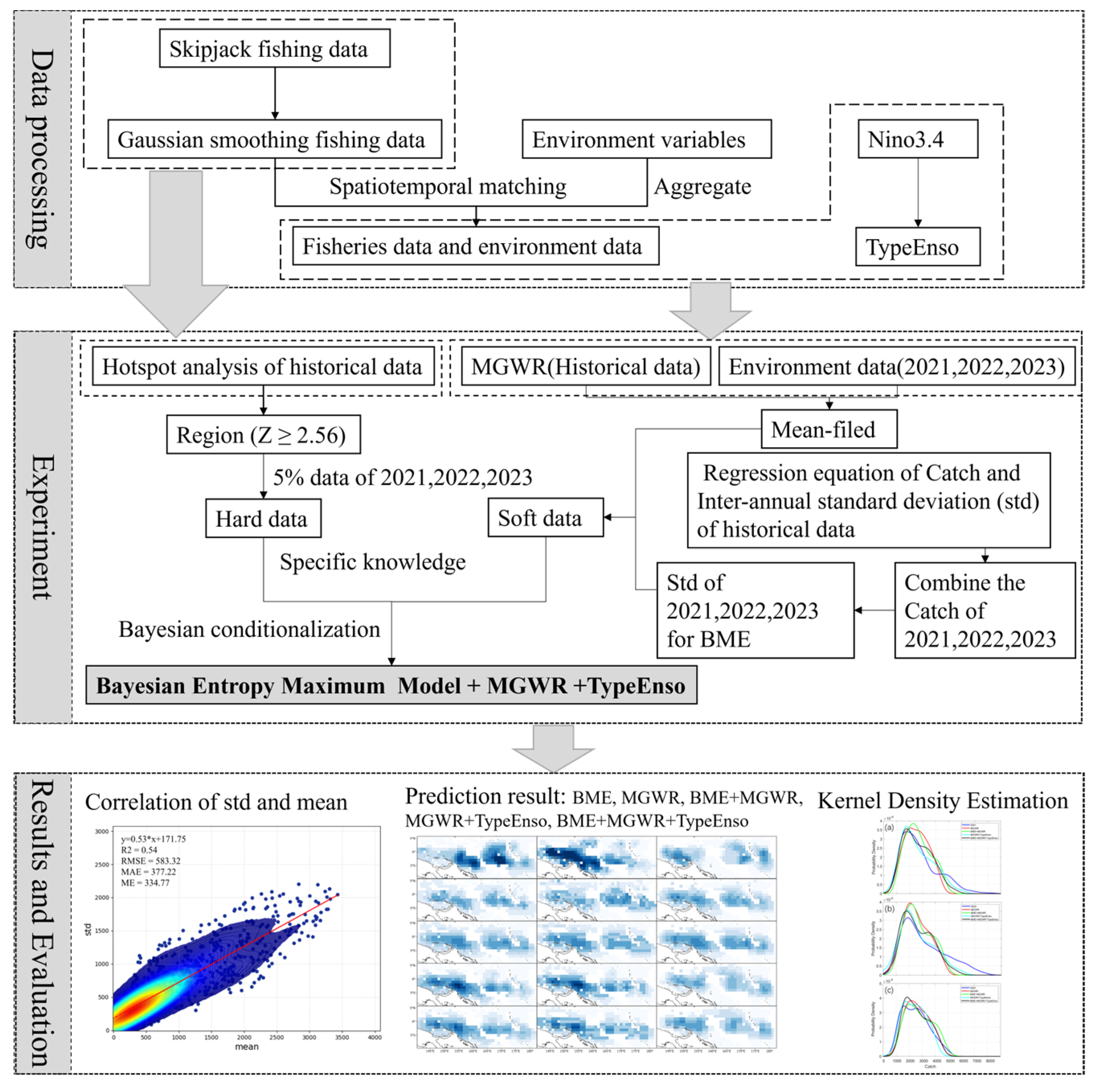
2.3. Data Preprocessing
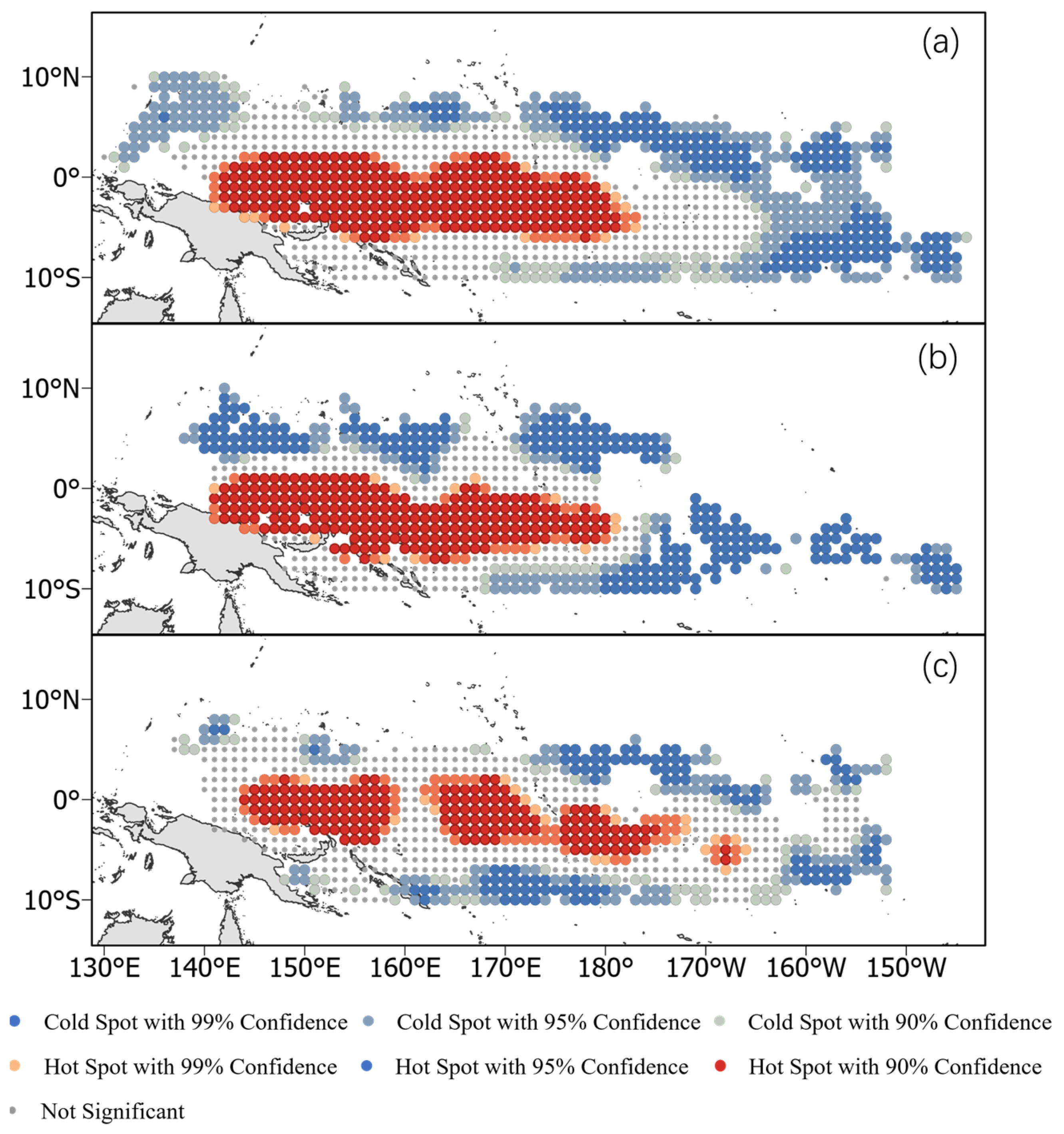
2.4. Hotspot Analysis
2.5. Multi-Scale Geographically Weighted Regression
2.6. Bayesian Maximum Entropy (BME)
2.6.1. Spatiotemporal Random Field Model
2.6.2. Hard Data and Soft Data
2.6.3. Basic Framework of BME
2.7. Model Evaluation Metrics
2.7.1. Common Evaluation Metrics
2.7.2. KDE Curve
3. Results
3.1. Hotspot Characteristics of Purse Seine Skipjack Tuna Catches
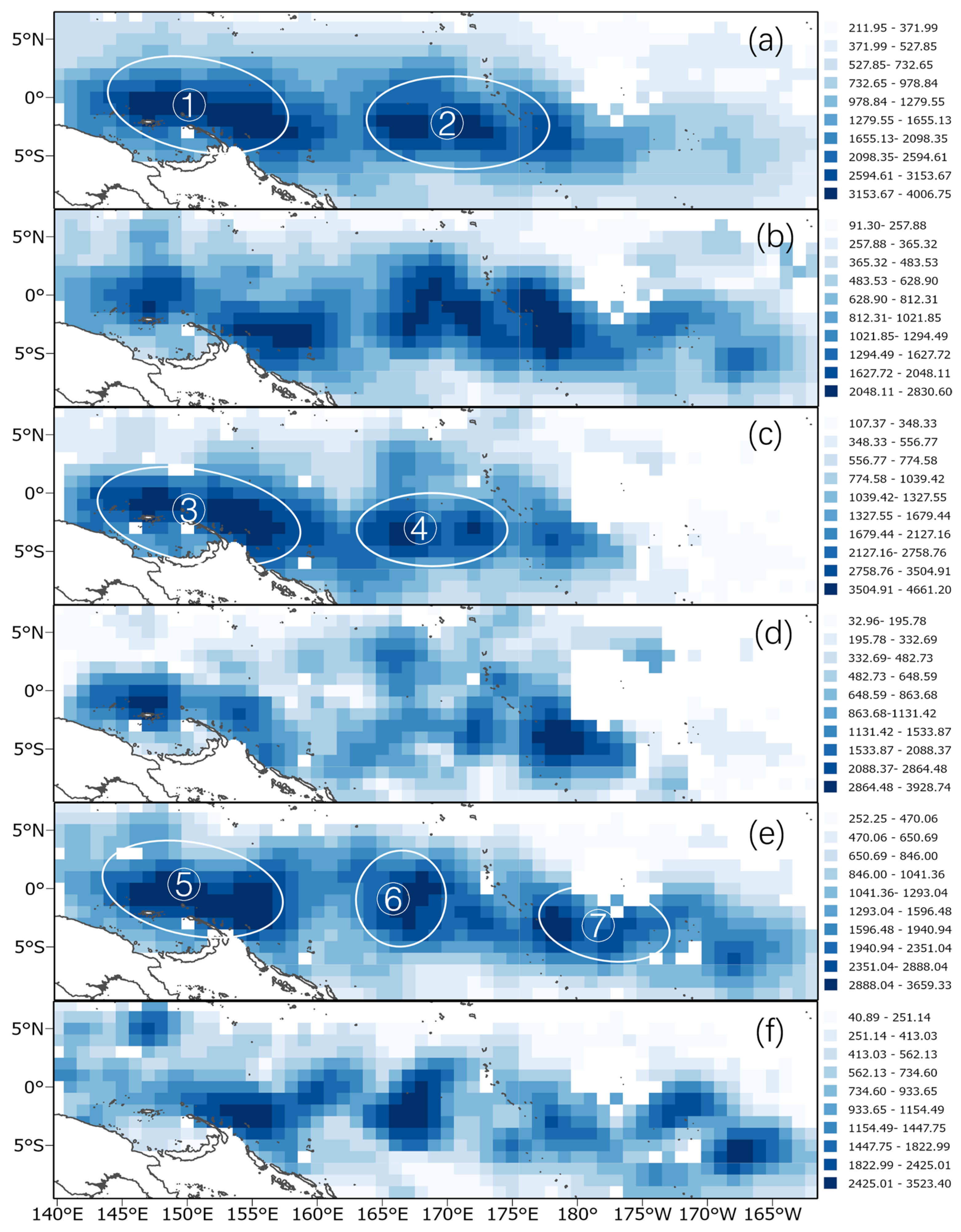
3.2. Construction of Soft Data Based on the MGWR Model
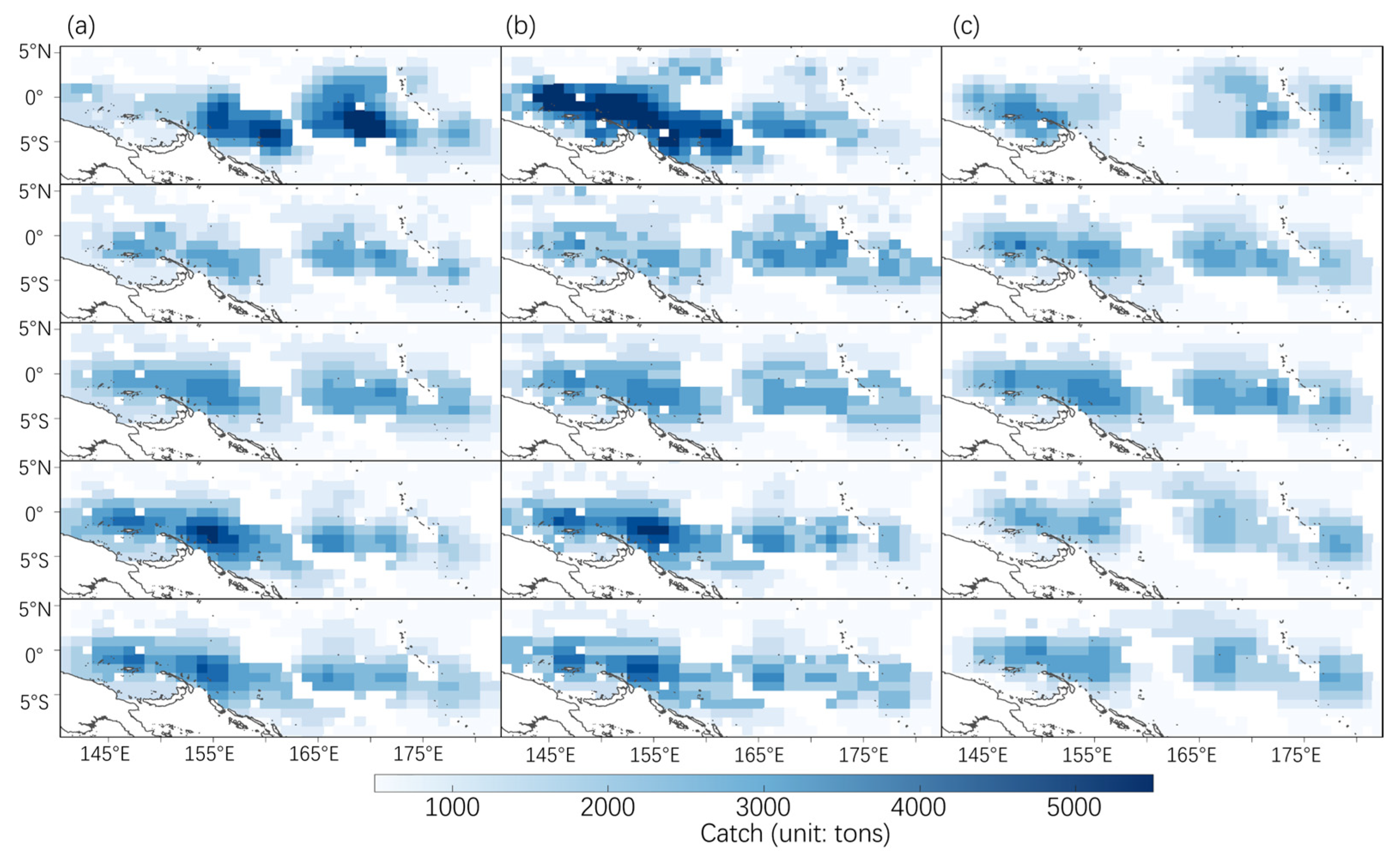
3.3. Comparison of Spatial Predictions from Different Models with Actual Distributions
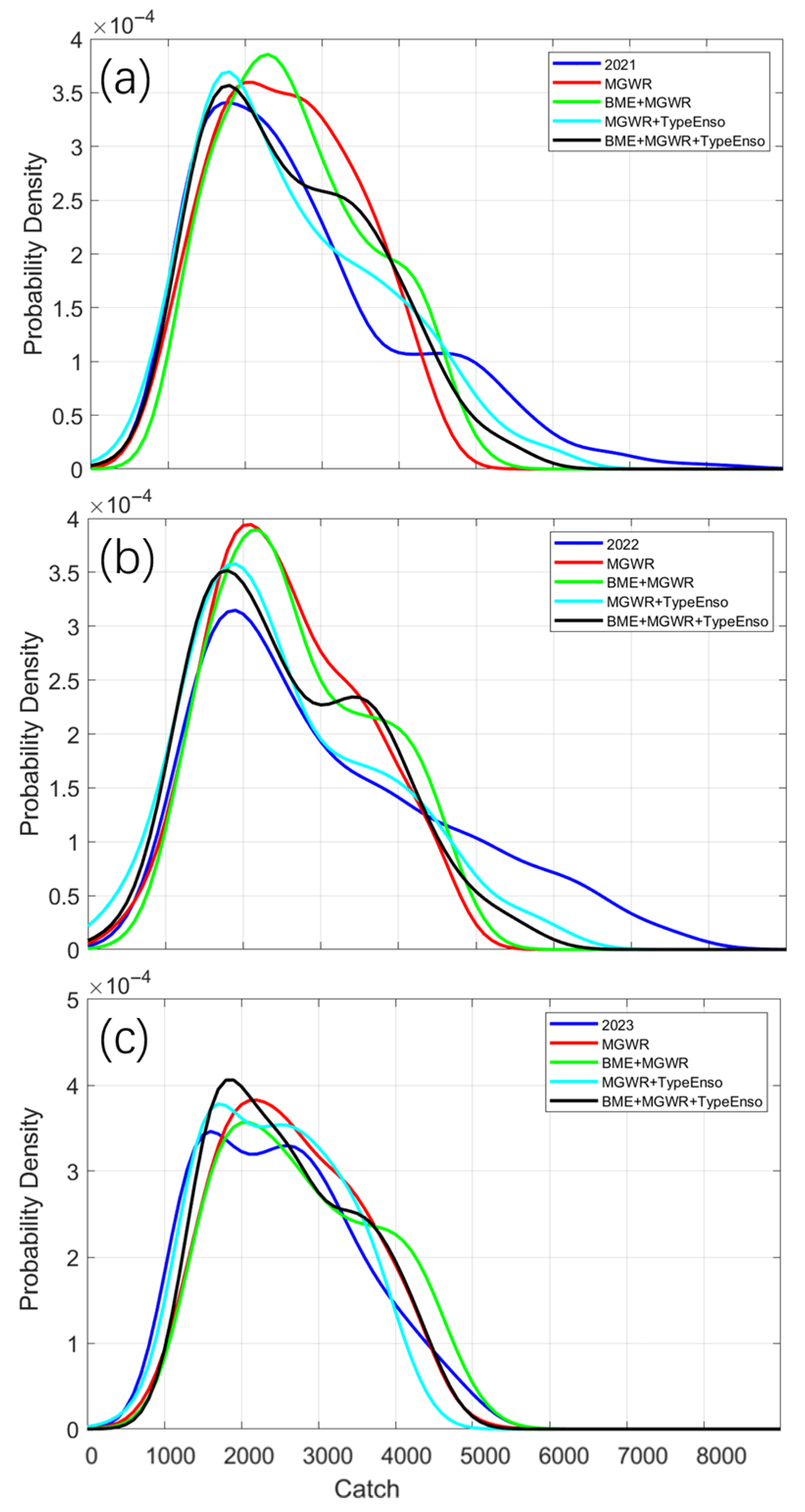
3.4. Model Performance Comparison
4. Discussion
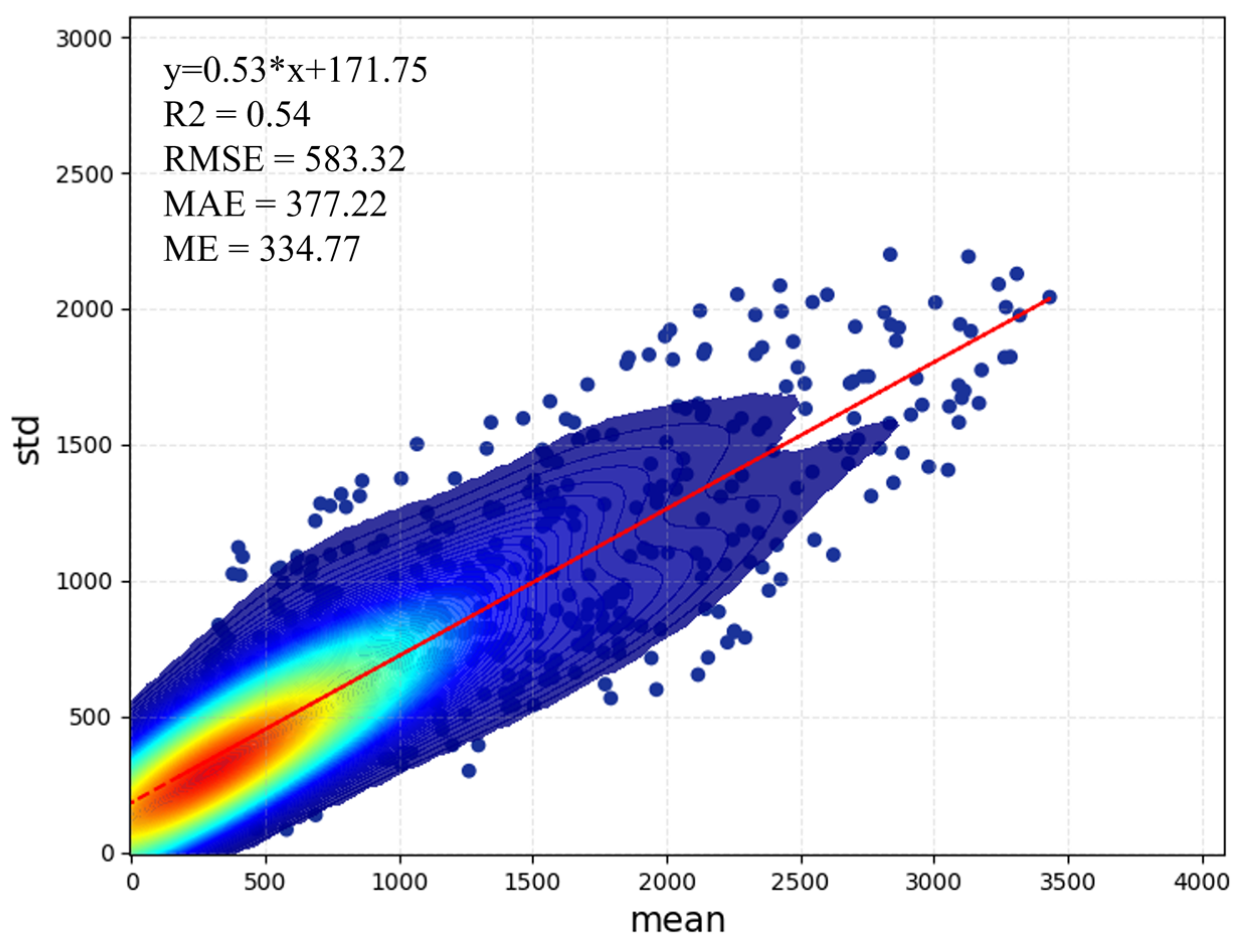
4.1. Uncertainty Characterization Under Different Climatic Conditions
4.2. Analysis of Spatial Variability in Skipjack Tuna Catch Under Different Climate Types
4.3. Application of the Integrated MGWR-BME Method in Skipjack Tuna Prediction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collette, B.N. FAO Species Catalogue; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1983; Volume 2, Scombrids of the world. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of tunas, mackerels, bonitos and related species known to date.
- Sarkka, S.; Hartikainen, J. On Gaussian optimal smoothing of non-linear state space models. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2010, 18, 1938–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilborn, R. Modeling the Stability of Fish Schools: Exchange of Individual Fish between Schools of Skipjack Tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1991, 48, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehodey, P.; Bertignac, M.; Hampton, J.; Lewis, A.; Picaut, J. El Nino Southern Oscillation and tuna in the western Pacific. Nature 1997, 389, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picaut, J.; Ioualalen, M.; Menkes, C.; Delcroix, T.; McPhaden, M.J. Mechanism of the zonal displacements of the Pacific warm pool: Implications for ENSO. Science 1996, 274, 1486–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugo, R.; Saitoh, S.-I.; Nihira, A.; Kuroyama, T. Habitat characteristics of skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) in the western North Pacific: A remote sensing perspective. Fish. Oceanogr. 2010, 19, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, X.M.; Zhu, J.F. Oscillation mode analysis on time series of the abundance of unassociated school Katsuwonus pelamis in the Western and Central Pacific Ocean. Mar. Fish. 2024, 46, 266–274. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfatinah, A.; Chu, H.-J.; Tatas, S.R.; Patra, S.R. Fishing Area Prediction Using Scene-Based Ensemble Models. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puspita, A.R.; Syamsuddin, M.L.; Subiyanto; Syamsudin, F.; Purba, P.N. Predictive Modeling of Eastern Little Tuna (Euthynnus affinis) Catches in the Makassar Strait Using the Generalized Additive Model. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, R.; Zainuddin, M.; Mallawa, A.; Mustapha, M.A.; Putri, A.R.S. Estimating potential fishing zones for Skipjack Tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) Abundance in Southern Makassar Strait. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 564, 012082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, K.-W.; Wang, G.; Lu, H.-J. Evaluating habitat suitability and relative abundance of skipjack (Katsuwonus pelamis) in the Western and Central Pacific during various El Nino events. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2017, 139, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.; Leiva, F.; Lastra, J. Predicting the current and future suitable habitat distributions of the anchovy (Engraulis ringens) using the Maxent model in the coastal areas off central-northern Chile. Fish. Oceanogr. 2019, 28, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W. Quantifying the spatial nonstationary response of environmental factors on purse seine tuna vessel fishing. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L. An integrative machine learning approach to understanding South Pacific Ocean albacore tuna habitat features. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2025, 82, fsaf003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H. Improving XCO2 retrieval under high aerosol loads with fused satellite aerosol Data: Advancing understanding of anthropogenic emissions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2025, 223, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Christakos, G.; Wu, J.; Li, M.; Leng, J. Spatiotemporal BME characterization and mapping of sea surface chlorophyll in Chesapeake Bay (USA) using auxiliary sea surface temperature data. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, Y. Can the spatial prediction of soil organic matter be improved by incorporating multiple regression confidence intervals as soft data into BME method? CATENA 2019, 178, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, X.; Bergquist, R.; Lv, X.; Liu, Y.; Gao, F.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z. Bayesian maximum entropy-based prediction of the spatiotemporal risk of schistosomiasis in Anhui Province, China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazipour, F.; Mahjouri, N. A multi-model data fusion methodology for seasonal drought forecasting under uncertainty: Application of Bayesian maximum entropy. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 304, 114245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrizabalaga, H.; Dufour, F.; Kell, L. Global habitat preferences of commercially valuable tuna. Elsevier 2015, 113, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, A.; Hampton, J.; Ogura, M. Stock assessment of skipjack tuna in the western and central Pacific Ocean. In Proceedings of the First Meeting of the Scientific Committee of the Western and Central Pacific Fisheries Commission, Working Paper, New Caledonia, France, 8–19 August 2005; Volume 4, p. 68. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, G.; Lal, M.; Stockwell, B.; Hampton, J.; Smith, N.; Nicol, S.; Rico, C. No Population Genetic Structure of Skipjack Tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) in the Tropical Western and Central Pacific Assessed Using Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 7, 570760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Deng, H.; Wang, Y.M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Kernel Density Estimation Based Gaussian and Non-Gaussian Random Vibration Data Induction for High-Speed Train Equipment. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 90914–90923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souris, M.; Demoraes, F. Improvement of Spatial Autocorrelation, Kernel Estimation, and Modeling Methods by Spatial Standardization on Distance. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2019, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.P.; Sabnani, C.S.; Kapse, V.S. Hotspot Analysis of Structure Fires in Urban Agglomeration: A Case of Nagpur City, India. Fire 2021, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinming, Z.; Xiaoning, S.; Pei, L.; Ronghai, H.U. Spatial downscaling of land surface temperature with the multi-scale geographically weighted regression. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2021, 25, 1749–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christakos, G. Spatiotemporal information systems in soil and environmental sciences. Geoderma 1998, 85, 141–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.T. Research on Key Issues and Applications of Spatiotemporal Prediction Using Bayesian Maximum Entropy Method. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2017. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Farooq, N.; Patterson, A.J.; Walsh, S.R.; Prytherch, D.R.; Justin, T.A.; Tang, T.Y. R2: A useful measure of model performance when predicting a dichotomous outcome. Stat. Med. 1999, 18, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, C.P.A.; Fantinato, D.G.; Neves, A. Epanechnikov kernel for PDF estimation applied to equalization and blind source separation. Signal Process. 2021, 189, 108251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streiner, D.L. Maintaining standards: Differences between the standard deviation and standard error, and when to use each. Can. J. Psychiatry 1996, 41, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, X. Fast feature selection for interval-valued data through kernel density estimation entropy. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2020, 11, 2607–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartoko, A.; Suradi, W.S.; Ghofar, A. Impact of climate variability on skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) catches in the Indonesian Fisheries Management Area (FMA) 715. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: London, UK, 2021; Volume 800, p. 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartoko, A.; Saputra, S.W.; Ghofar, A.; Nugraha, E. Impact of El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), variability on skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) catches in the fisheries management area (FMA) 715, Indonesia. AACL Bioflux 2021, 14, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.W.; Zhu, G.P.; Wang, X.F.; Xu, L.X. Spatio-temporal distribution of skipjack tuna(Katsuwonus pelamis) abundance and its relationship with sea surface temperature in Western and Central Pacific Ocean. Mar. Fish. 2022, 33, 417–422. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druon, J.-N.; Chassot, E.; Murua, H.; Lopez, J. Skipjack Tuna Availability for Purse Seine Fisheries Is Driven by Suitable Feeding Habitat Dynamics in the Atlantic and Indian Oceans. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Chen, X.J.; Guo, L.X.; Fang, Z. Fishing ground forecasting on Katsuwonus pelamis based on different climatic conditions in western and central Pacific Ocean. J. Shanghai Ocean. Univ. 2019, 28, 145–153. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.T.; Chen, X.J. Changes and Prediction of the Fishing Ground Gravity of Skipjack (Katsuwonus pelamis) in Western-Central Pacific. Period. Ocean. Univ. China 2013, 43, 44–48. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.C. Influence of environmental factors on CPUE of three different fishing methods in skipjack tuna fisheries. South China Fish. Sci. 2023, 19, 11–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lehodey, P. Climate variability, fish, and fisheries. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 5009–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.-T.; Sun, C.-L.; Yeh, S.-Z.; Chen, S.-C.; Su, W.-C. Spatio-temporal distributions of tuna species and potential habitats in the Western and Central Pacific Ocean derived from multi-satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 4543–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, T.; Jia, F.; Cai, W.; Wu, L.; Gan, B.; Jing, Z.; Li, S.; McPhaden, M.J. Increased occurrences of consecutive La Nina events under global warming. Nature 2023, 619, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Donat, M.G.; England, M.H.; Alexander, L.V.; Hirsch, A.L.; Delgado-Torres, C. Enhanced multi-year predictability after El Nino and La Nina events. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Na, H.; Park, Y.-G.; Kim, Y.H. Potential predictability of skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) catches in the Western Central Pacific. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Or, D.; Bogaert, P. Spatial prediction of categorical variables with the Bayesian Maximum Entropy approach: The Ooypolder case study. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2004, 55, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.H.; Yang, X.M.; Zhu, J.F. Environmental impact mechanism of skipjack tuna fishery in Western and Central Pacific Ocean based on Multi-scale Geographical Weighted Regression Model (MGWR). South China Fish. Sci. 2023, 19, 1–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hanigan, I.C.; Yu, W.; Yuen, C.; Gopi, K.; Knibbs, L.D.; Cowie, C.T.; Jalaludin, B.; Cope, H.M.; Riley, M.L. Heyworth Deep ensemble machine learning with Bayesian blending improved accuracy and precision of modelled ground-level ozone for region with sparse monitoring: Australia, 2005–2018. Environ. Model. Softw. 2025, 187, 106378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, K. Climate Variability and Fish Community Dynamics: Impacts of La Niña Events on the Continental Shelf of the Northern South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Unit | Source |
|---|---|---|
| SLA | m | http://marine.copernicus.eu/ accessed on 1 March 2023 |
| MLD | m | http://www.science.oregonstate.edu/ |
| CHL | Mg/m2/day | |
| T5, T55, T105 | °C | http://www.argo.org.cn/ |
| SSS | PSS-78 | |
| V55, U55 | m/s | https://cfs.ncep.noaa.gov/ |
| Variable | VIF |
|---|---|
| SLA | 1.12 |
| MLD | 4.00 |
| CHL | 1.70 |
| SSS | 4.01 |
| T5 | 6.97 |
| T55 | 5.18 |
| T105 | 3.65 |
| V55 | 1.24 |
| U55 | 1.37 |
| Model | R2 | RMSE | MAE | ME | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | BME | 0.09 | 1627.46 | 1104.43 | 983.29 |
| MGWR | 0.53 | 946.83 | 687.49 | 240.95 | |
| MGWR + TypeEnso | 0.44 | 1037.98 | 786.54 | 157.48 | |
| BME + MGWR | 0.60 | 870.75 | 577.61 | 300.51 | |
| BME + MGWR + TypeEnso | 0.67 | 796.69 | 557.44 | 216.84 | |
| 2022 | BME | 0.06 | 1895.52 | 1319.4 | 1256.32 |
| MGWR | 0.23 | 1404.94 | 1070.65 | 534.37 | |
| MGWR + TypeEnso | 0.61 | 988.82 | 753.82 | 552.3 | |
| BME + MGWR | 0.34 | 1297.51 | 857.42 | 717.34 | |
| BME + MGWR + TypeEnso | 0.62 | 960.35 | 753.39 | 525.07 | |
| 2023 | BME | 0.03 | 1169.36 | 874.85 | 686.49 |
| MGWR | 0.26 | 835.46 | 667.97 | −126.97 | |
| MGWR + TypeEnso | 0.37 | 784.74 | 616.98 | 92.81 | |
| BME + MGWR | 0.30 | 804.77 | 622.56 | 124.11 | |
| BME + MGWR + TypeEnso | 0.40 | 777.99 | 591.11 | 146.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, M.; Zhu, J. Modeling Skipjack Tuna Purse Seine Fishery Distribution in the Western and Central Pacific Ocean Under ENSO Scenarios: An Integrated MGWR-BME Framework. Fishes 2025, 10, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090450
Wang Y, Yang X, Li M, Zhu J. Modeling Skipjack Tuna Purse Seine Fishery Distribution in the Western and Central Pacific Ocean Under ENSO Scenarios: An Integrated MGWR-BME Framework. Fishes. 2025; 10(9):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090450
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuhan, Xiaoming Yang, Menghao Li, and Jiangfeng Zhu. 2025. "Modeling Skipjack Tuna Purse Seine Fishery Distribution in the Western and Central Pacific Ocean Under ENSO Scenarios: An Integrated MGWR-BME Framework" Fishes 10, no. 9: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090450
APA StyleWang, Y., Yang, X., Li, M., & Zhu, J. (2025). Modeling Skipjack Tuna Purse Seine Fishery Distribution in the Western and Central Pacific Ocean Under ENSO Scenarios: An Integrated MGWR-BME Framework. Fishes, 10(9), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090450






