Diversity Analysis of Microbial Communities in Shrimp Polyculture Ponds in Coastal Saline–Alkali Regions of Hebei, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Basic Aquaculture Details
2.2. Sample Collection and Processing
2.3. DNA Extraction and Illumina Sequencing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
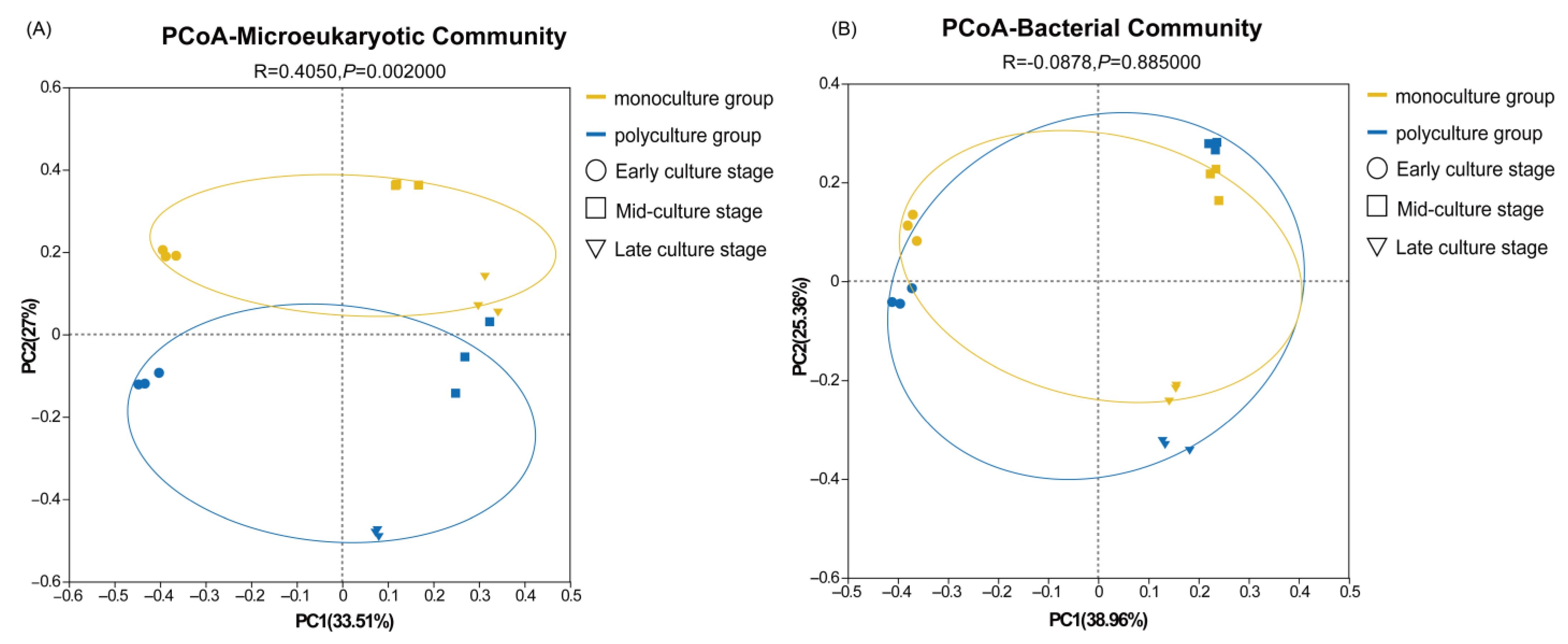
3.1. Diversity Analysis of Microeukaryotic and Bacterial Communities in Aquatic Environments
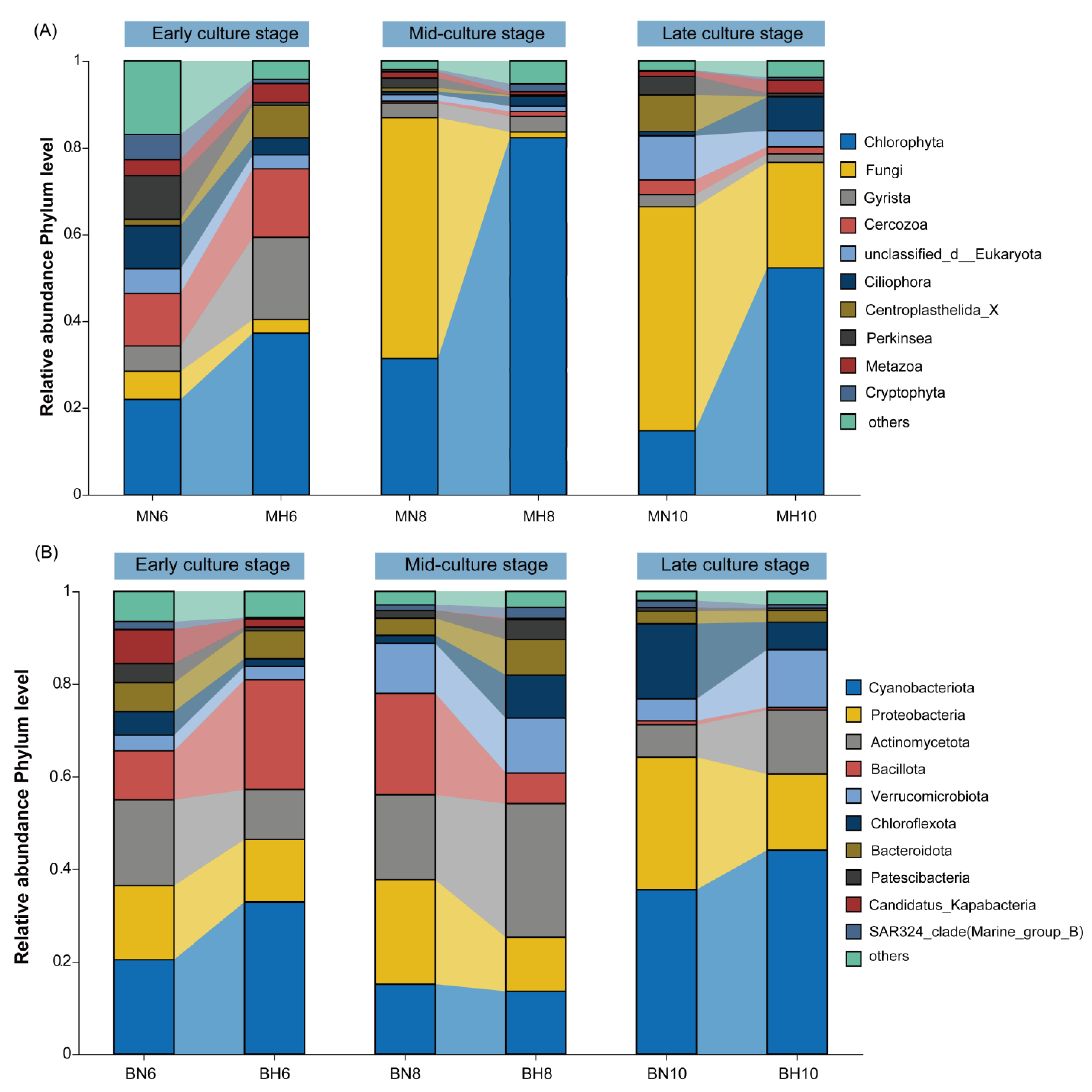
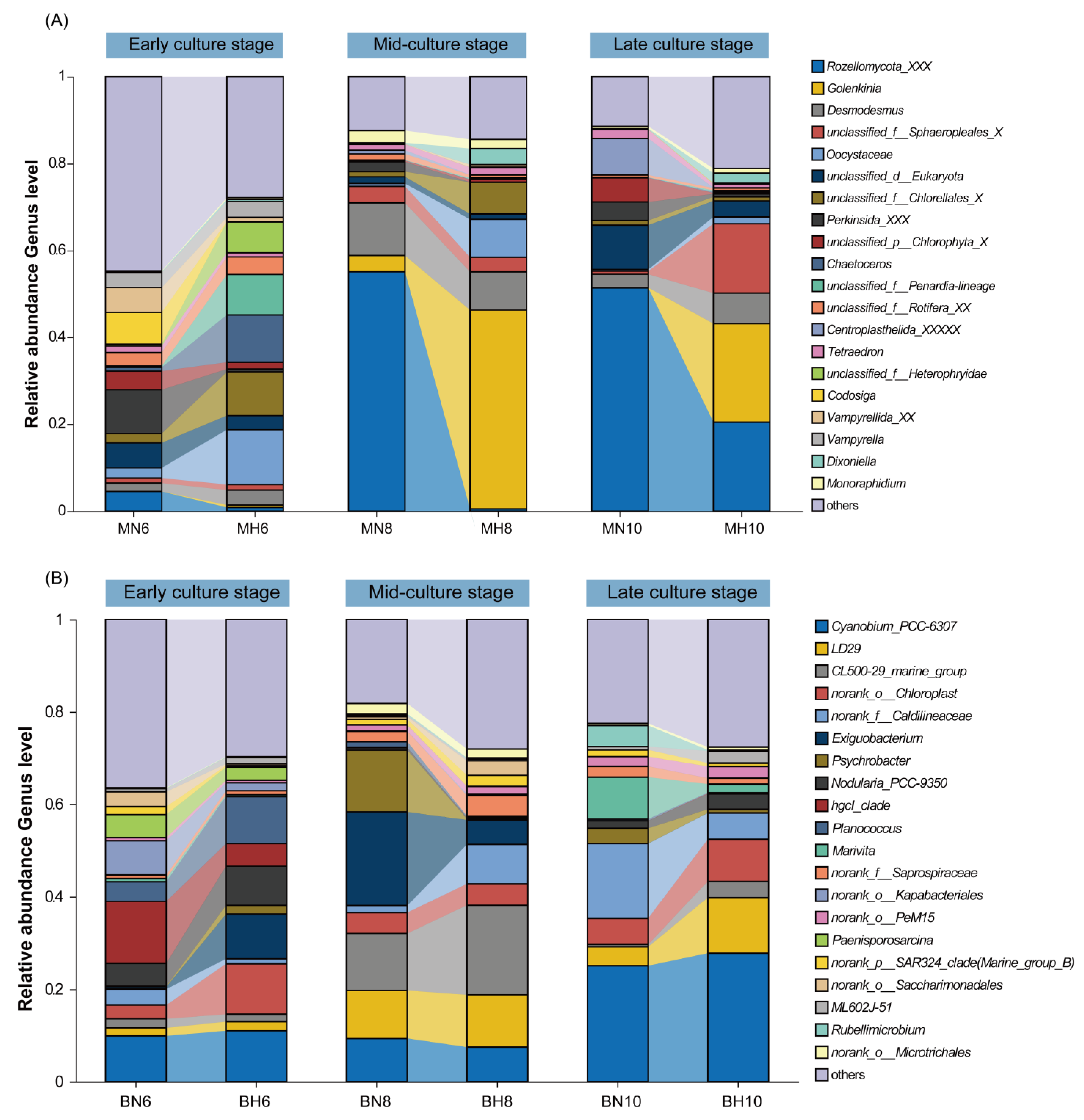
3.2. Composition Analysis of Microeukaryotic and Bacterial Communities in Aquatic Environments
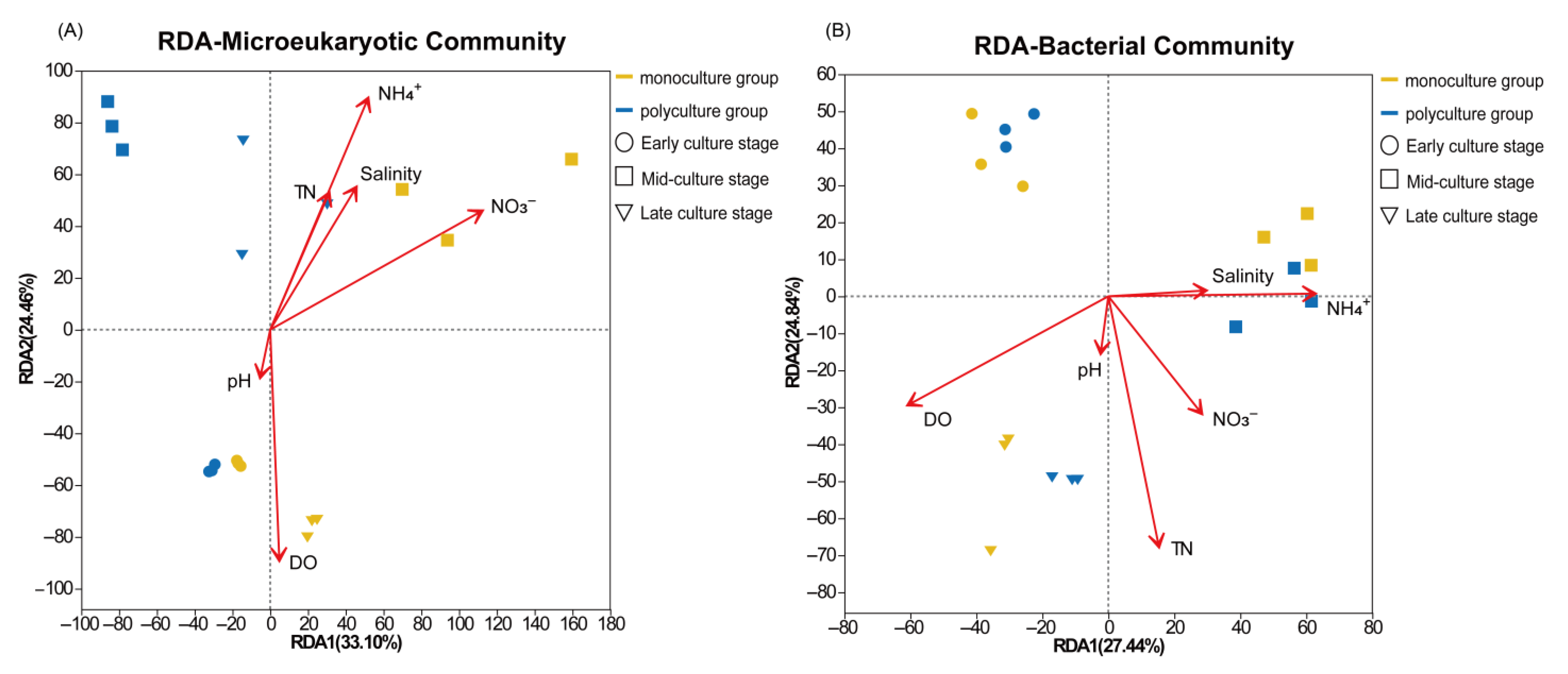
3.3. Correlation Analysis Between Environmental Factors and Microbial Communities
3.4. Co-Occurrence Network Analysis Between Monoculture and Polyculture Systems
4. Discussion
4.1. Diversity Characteristics of Microeukaryotic and Bacterial Communities in the Water Column
4.2. Composition Characteristics of Microeukaryotic and Bacterial Communities in the Water Column
4.3. Correlation Analysis of Environmental Factors
4.4. Co-Occurrence Network Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J. Development and prospect of the research on salt-affected soils in China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2008, 45, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fang, W.; Liu, L.; Fu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, D.; Huang, X.; Mu, C.; Wang, C. Molecular characterization and DNA methylation analysis of carbonic anhydrase (Sp-CA) in the mud crab Scylla paramamosain: Its potential osmoregulation role under carbonate alkalinity stress. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 30, 101591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Yang, M.; Chen, S.; Su, J.; Lü, H.; Jia, H.; Liu, Z. Saline-alkali land management in China: Current situation, problems and prospects. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2025, 48, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishery Administration Bureau of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs. 2024 China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2024.
- Wyban, J.; Sweeney, J.N.; Institute, O. Intensive Shrimp Production Technology: The Oceanic Institute Shrimp Manual; Argent Chemical Laboratories: Redmond, WA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, W.; Lawrence, A.; Leung-Trujillo, J. The effect of salinity on growth and survival of Penaeus vannamei, with observations on the interaction of IHHN virus and salinity. Aquaculture 1994, 122, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.; Thunjai, T. Concentrations of Major Ions in Waters of Inland Shrimp Farms in China, Ecuador, Thailand, and the United States. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2007, 34, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, M. Freshwater prawn farming: Global status, recent research and a glance at the future. Aquac. Res. 2005, 36, 210–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Luo, D.; Zhao, Z.; Tu, Z.; Dai, C.; Li, X.; Chen, W. Ecological mixed culture technology of Macrobrachium rosenbergii and Litopenaeus vannamei in ponds. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2022, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Dong, Q.; Wu, C. Experimental study on efficient culture of Litopenaeus vannamei and Macrobrachium rosenbergii. J. Anhui Agric. 2015, 43, 118–119+141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Sui, C.; Hu, B.; Zheng, B. Experiment on mixed culture of Macrobrachium rosenbergii in the main pond of Litopenaeus vannamei. North. Chin. Fish. 2025, 44, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, M.; Chen, X.-f.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, L.-m.; Yuan, J.-l.; Gu, Z.-m.; Zhou, Z.-m. Feasibility and compatibility of polyculture of Litopenaeus vannamei and Macrobrachium rosenbergii in the intertidal ponds. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 4205–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Jia, R.; Li, B.; Zhu, J.; Ge, X. Alterations in Soil Bacterial Community and Its Assembly Process within Paddy Field Induced by Integrated Rice–Giant River Prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) Farming. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, S. Effects of Different Densities of Macrobrachium rosenbergii on Water Quality, Growth Performance, Nutritional Flavor, Intestinal Microflora of Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis) Ponds. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Pan, L.; Huang, F.; Gao, S.; Su, C.; Zhang, M.; He, Z. Metagenomic analysis of composition, function and cycling processes of microbial community in water, sediment and effluent of Litopenaeus vannamei farming environments under different culture modes. Aquaculture 2019, 506, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhou, J.; Du, C.; Yang, Q.; Huang, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, M. Relationship between Nitrogen Dynamics and Key Microbial Nitrogen-Cycling Genes in an Intensive Freshwater Aquaculture Pond. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; He, H.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Z.; Leng, Y.; Liao, M.; Xiong, W. Effects of Three Antibiotics on Nitrogen-Cycling Bacteria in Sediment of Aquaculture Water. Water 2024, 16, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, H.; Zheng, P.; Li, G.; He, C.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; Gong, J. The habitat differentiation, dynamics and functional potentials of bacterial and micro-eukaryotic communities in shrimp aquaculture systems with limited water exchange. Aquaculture 2023, 566, 739156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wu, T.; Wang, H.; Yan, H.; Han, J.; Guan, W. Dynamic changes of bacterioplankton communities in Litopenaeus vannamei farming pond using saline-alkaline water. J. Fish. Sci. China 2024, 31, 940–953. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Masoudi, A.; Wang, M.; Yang, J.; Yu, Z.; Liu, J. Land-use types shape soil microbial compositions under rapid urbanization in the Xiong’an New Area, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 145976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. Study on the Structure of Phytoplankton-Microbial Community in Several Aquaculture Systems in Ningxia. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Romo, S.; Villena, M. Phytoplankton strategies and diversity under different nutrient levels and planktivorous fish densities in a shallow Mediterranean lake. J. Plankton Res. 2005, 27, 1273–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Li, G.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, L. Profiling sediment bacterial communities and the response to pattern-driven variations of total nitrogen and phosphorus in long-term polyculture ponds. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1403909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraza-Guardado, R.; Arreola-Lizárraga, J.; López-Torres, M.; Casillas-Hernández, R.; Miranda-Baeza, A.; Magallón-Barrajas, F.; Ibarra-Gámez, C. Effluents of Shrimp Farms and Its Influence on the Coastal Ecosystems of Bahía de Kino, Mexico. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 306370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.T.; Nguyen, K.L.P.; Le, H.A.; Eppe, G. The Integrating Impacts of Extreme Weather Events and Shrimp Farming Practices on Coastal Water Resource Quality in Ninh Thuan Province, Vietnam. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, C.; Lukwambe, B.; Nicholaus, R.; Lu, K.; Zheng, Z. Succession of phytoplankton community during intensive shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) cultivation and its effects on cultivation systems. Aquaculture 2020, 520, 734733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Xu, K.; Naoum, J.; Lian, Y.; Wu, B.; He, Z.; Yan, Q. Deciphering microeukaryotic–bacterial co-occurrence networks in coastal aquaculture ponds. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2023, 5, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossart, H.; Wurzbacher, C.; James, T.; Kagami, M. Discovery of dark matter fungi in aquatic ecosystems demands a reappraisal of the phylogeny and ecology of zoosporic fungi. Fungal Ecol. 2016, 19, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letcher, P.; Longcore, J.; James, T.; Leite, D.; Simmons, D.; Powell, M. Morphology, Ultrastructure, and Molecular Phylogeny of Rozella multimorpha, a New Species in Cryptomycota. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2017, 65, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Xing, B.; Zhang, Q. Researching progress of Cryptomycota (Eukaryota, Fungi). J. Ocean. Univ. China 2013, 43, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, A. Development of Rozella in Allomyces: A single zoospore produces numerous zoosporangia and resistant sporangia. Can. J. Bot. 1980, 58, 959–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, F.; Carney, L.; Lilje, O.; Glockling, S. Ecological potentials of species of Rozella (Cryptomycota). Fungal Ecol. 2012, 5, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letcher, P.; Longcore, J.; Quandt, C.; Leite, D.; James, T.; Powell, M. Morphological, molecular, and ultrastructural characterization of Rozella rhizoclosmatii, a new species in Cryptomycota. Fungal Biol. 2017, 121, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laverock, B.; Smith, C.; Tait, K.; Osborn, A.; Widdicombe, S.; Gilbert, J. Bioturbating shrimp alter the structure and diversity of bacterial communities in coastal marine sediments. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1531–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y. To farm fish and shrimp is to manage water. Prim. Agric. Technol. Ext. 2013, 1, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Ran, Z.; Xie, H.; Kong, F.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Liao, K.; Yan, X.; Xu, J.-L. A systematic analysis and evaluation of nutritional composition of 23 strains of marine microalgae commonly used in aquaculture. Algal Res. 2023, 72, 103122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewangan, N.; Gopalakrishnan, A.; Malaroli, R.; Roy, S.; Murugesan, P.; Somasundaram, S.; Kannan, D.; Singh, R. Occurrence of microsporidian in white faeces syndrome (WFS)-diseased Litopenaeus vannamei of intensive grow-out ponds of India. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Verdejo, A.; Montero, F.E.; de la Gándara, F.; Gallego, M.; Ortega, A.; Raga, J.; Palacios-Abella, J. A severe microsporidian disease in cultured Atlantic Bluefin Tuna (Thunnus thynnus). IMA Fungus 2022, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoïz, S.; Metz, S.; Derelle, E.; Reñé, A.; Garcés, E.; Bass, D.; Soudant, P.; Chambouvet, A. Emerging Parasitic Protists: The Case of Perkinsea. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 735815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Jiang, Y.; Qian, D.; Chen, C.; Li, A.; Huang, J.; Yang, B. Infection with Perkinsus Olseni. China Fish. 2012, 436, 49–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, Y.; Hamano, K.; Tsutsui, I.; Aue-umneoy, D.; Ban, M.; Satomi, M. Occurrence, molecular characterization, and antimicrobial susceptibility of Aeromonas spp. in marine species of shrimps cultured at inland low salinity ponds. Food Microbiol. 2015, 47, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruprecht, J.; Birrer, S.; Dafforn, K.; Mitrovic, S.; Crane, S.L.; Johnston, E.; Wemheuer, F.; Navarro, A.; Harrison, A.; Turner, I.L.; et al. Wastewater effluents cause microbial community shifts and change trophic status. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergen, B.; Herlemann, D.R.; Labrenz, M.; Jürgens, K. Distribution of the verrucomicrobial clade Spartobacteria along a salinity gradient in the Baltic Sea. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2014, 6, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Gao, Z. The diversity and distribution pattern of bacterial community in the water of Yellow River estuary. Biotechnol. Bull. 2017, 33, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Fu, Z. Shifts of bacterial community and predictive functional profiling of denitrifying phosphorus removal—Partial nitrification—Anammox three-stage nitrogen and phosphorus removal before and after coupling for treating simulated wastewater with low C/N. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yin, J.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Yin, F.; Yang, B.; Zhang, W. High nitrite–nitrogen stress intensity drives nitrite anaerobic oxidation to nitrate and inhibits methanogenesis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Tan, L.; Shen, Z.; Zhou, Y.; He, X.; Chen, X. Enhanced denitrification of dispersed swine wastewater using Ca(OH)2-pretreated rice straw as a solid carbon source. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xv, K.; Zhang, S.; Pang, A.; Wang, T.; Dong, S.; Xv, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liang, J.; Fang, Y.; Tan, B.; et al. White feces syndrome is closely related with hypoimmunity and dysbiosis in Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 38, 102329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Feng, C.; Hu, J.; Lin, H.; Luo, H.; Zhang, Q.; He, H. Impact of tidal fluctuations on bacterial community structure in Wuyuan Bay: A comparative analysis of waters inside and outside the tidal barrage. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0312283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Weng, S.; Lu, X.; Zhong, L.; Fan, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; He, J. Multiple bacteria species were involved in hepatopancreas necrosis syndrome (HPNS) of Litopenaeus vannamei. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2016, 55, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Cao, Y.; Wen, G.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Xu, W.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z. Effect of combined use of Bacillus and molasses on microbial communities in shrimp cultural enclosure systems. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 2691–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Ding, Z.; Li, F.; Wan, C.; Guan, W. Microbial composition in water of recirculating aquaculture ponds of red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Fish. Sci. 2025, 44, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ji, J.; Li, P.; Peng, X.; Wang, J.; Fu, C.; Zong, Y. Characterization of microbial communities in the upstream water body of Linzhi City section of Yarlung Tsangpo River and changes in nitrogen cycle-related microbiota. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2025, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Dong, D.; Li, C.; Wang, F.; Shan, H. Relationship between concentrations of ammonia and nitrite in water, microbial community structure and abundance of nitrogen cycling function genes. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2025, 46, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Xiong, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, H.; Guo, A.; Wu, J.; Dai, H. Bacterioplankton assemblages as biological indicators of shrimp health status. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 38, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Tu, K.; Zheng, Z. Insights into the intestinal microbiota of several aquatic organisms and association with the surrounding environment. Aquaculture 2019, 507, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.; Pace, M.; Carpenter, S.; Kitchell, J. Persistence of net heterotrophy in lakes during nutrient addition and food web manipulations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 1718–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, D.; Yallop, M.; Memmott, J. Functional group diversity increases with modularity in complex food webs. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barranca, V.; Zhou, D.; Cai, D. Low-rank network decomposition reveals structural characteristics of small-world networks. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 92, 062822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Fu, Y.; Peng, X.; Ma, S.; Liu, Y.-R.; Chen, W.; Huang, Q.; Hao, X. Microplastics Trigger Soil Dissolved Organic Carbon and Nutrient Turnover by Strengthening Microbial Network Connectivity and Cross-Trophic Interactions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 5596–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Bajić, D.; Vila, J.C.; Estrela, S.; Sanchez, A. Emergent coexistence in multispecies microbial communities. Science 2023, 381, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Qin, Y.; Tu, Q.; Yang, Y.; He, Z.; Schadt, C.; Zhou, J. Network succession reveals the importance of competition in response to emulsified vegetable oil amendment for uranium bioremediation. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 18, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artime, O.; Grassia, M.; De Domenico, M.; Gleeson, J.; Makse, H.; Mangioni, G.; Perc, M.; Radicchi, F. Robustness and resilience of complex networks. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2024, 6, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Neori, A.; He, Y.; Li, J.; Qiao, L.; Preston, S.; Liu, P.; Li, J. Development and current state of seawater shrimp farming, with an emphasis on integrated multi-trophic pond aquaculture farms, in China—A review. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 2544–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Culture Stage | Group | ACE | Chao1 | Shannon | Simpson | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| microeukaryotes | Early culture stage | N | 554.11 ± 25.91 a | 554.46 ± 33.80 a | 4.34 ± 0.02 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 a |
| H | 478.92 ± 7.62 b | 489.18 ± 14.16 b | 4.02 ± 0.14 b | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | ||
| Mid-culture stage | N | 290.46 ± 47.89 a | 301.36 ± 50.97 a | 2.06 ± 0.56 a | 0.34 ± 0.19 a | |
| H | 287.09 ± 3.41 a | 288.40 ± 7.51 a | 2.62 ± 0.15 a | 0.23 ± 0.03 a | ||
| Late culture stage | N | 204.61 ± 51.77 a | 215.31 ± 57.63 a | 2.40 ± 0.05 b | 0.20 ± 0.02 a | |
| H | 231.83 ± 128.41 a | 227.32 ± 117.92 a | 2.76 ± 0.19 a | 0.14 ± 0.04 b | ||
| Bacteria | Early culture stage | N | 1347.4 ± 157.44 a | 1241.2 ± 86.70 a | 4.46 ± 0.37 a | 0.04 ± 0.02 a |
| H | 1252 ± 168.72 a | 1194.1 ± 90.10 a | 4.48 ± 0.08 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | ||
| Mid-culture stage | N | 946.52 ± 111.55 b | 906.55 ± 110.78 b | 3.79 ± 0.21 b | 0.07 ± 0.01 a | |
| H | 1198.4 ± 86.52 a | 1159 ± 102.47 a | 4.29 ± 0.13 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | ||
| Late culture stage | N | 749.63 ± 125.77 a | 680.56 ± 48.816 a | 3.79 ± 0.28 a | 0.06 ± 0.02 a | |
| H | 681.2 ± 283.39 a | 674.75 ± 260.36 a | 4.03 ± 0.01 a | 0.06 ± 0.00 a |
| Topological Parameters | Bacterial Communities | Microeukaryotic Communities | Microeukaryote–Bacteria Communities | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | H | N | H | N | H | |
| Number of nodes | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Number of edges | 197 | 287 | 226 | 185 | 209 | 254 |
| Number of positive edges | 135 (68.5%) | 138 (48.1%) | 139 (61.5%) | 94 (50.8%) | 112 (53.6%) | 129 (50.8%) |
| Number of negative edges | 62 (31.5%) | 149 (51.9%) | 87 (38.5%) | 91 (49.2%) | 97 (46.4%) | 125 (49.2%) |
| Average degree | 7.88 | 11.36 | 9.04 | 7.4 | 8.36 | 10.16 |
| Average weighted degree | 13.90 | 20.12 | 15.73 | 12.81 | 14.70 | 17.97 |
| Diameter | 7 | 8 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 5 |
| Density | 0.161 | 0.232 | 0.184 | 0.151 | 0.171 | 0.207 |
| Modularity | 0.512 | 0.527 | 0.399 | 0.52 | 0.516 | 0.569 |
| Average clustering coefficient | 0.64 | 0.818 | 0.642 | 0.582 | 0.786 | 0.797 |
| Average path length | 2.897 | 3.346 | 1.887 | 2.697 | 2.231 | 2.313 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suo, E.; Chen, Z.; Gao, H.; Yuan, S.; Chang, Z. Diversity Analysis of Microbial Communities in Shrimp Polyculture Ponds in Coastal Saline–Alkali Regions of Hebei, China. Fishes 2025, 10, 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090433
Suo E, Chen Z, Gao H, Yuan S, Chang Z. Diversity Analysis of Microbial Communities in Shrimp Polyculture Ponds in Coastal Saline–Alkali Regions of Hebei, China. Fishes. 2025; 10(9):433. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090433
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuo, Enhui, Zhao Chen, Huan Gao, Shijia Yuan, and Zhiqiang Chang. 2025. "Diversity Analysis of Microbial Communities in Shrimp Polyculture Ponds in Coastal Saline–Alkali Regions of Hebei, China" Fishes 10, no. 9: 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090433
APA StyleSuo, E., Chen, Z., Gao, H., Yuan, S., & Chang, Z. (2025). Diversity Analysis of Microbial Communities in Shrimp Polyculture Ponds in Coastal Saline–Alkali Regions of Hebei, China. Fishes, 10(9), 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10090433






